人教版(2019)选择性必修 第二册Unit 5 First Aid Reading and Thinking 2 + Build up your vocabulary课件(共28张)
文档属性
| 名称 | 人教版(2019)选择性必修 第二册Unit 5 First Aid Reading and Thinking 2 + Build up your vocabulary课件(共28张) |  | |
| 格式 | pptx | ||
| 文件大小 | 3.5MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 人教版(2019) | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2025-03-02 14:48:01 | ||
图片预览








文档简介
(共28张PPT)
Unit 5 FIRST AID
Lesson 2: Reading and Thinking(2)+ Build up your vocabulary
At the end of the lesson, you will be able to
learn to prevent getting burnt
summarize the writing style and language features of expository writing
build up your vocabulary on the first-aid for burns
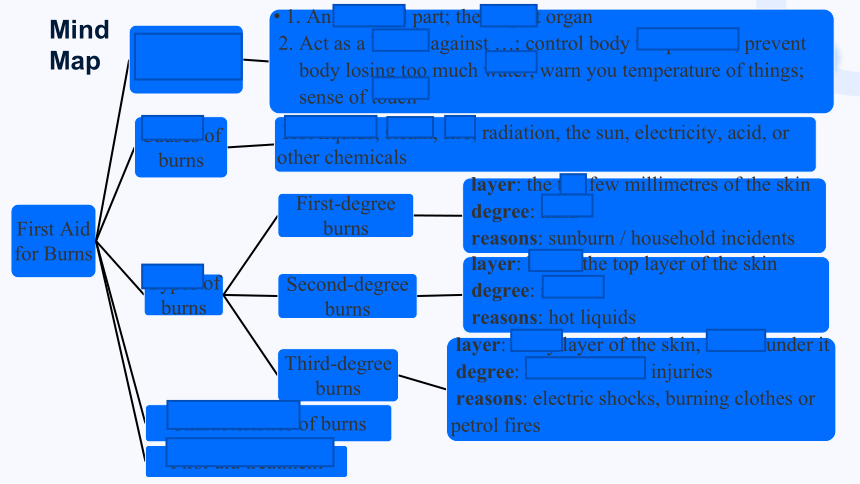
Please take out the mind map of the reading passage you have done after the first reading lesson;
Let's work out the missing words in this mind map.
Mind
Map
Mind
Map
When we cook in the kitchen, we are likely to get burnt. When using fire, we should be careful. When taking things out from the oven or off the fire, we should wear oven gloves.
What are the possible occasions when students are likely to get burnt at school How to prevent them
When getting hot water after class or doing experiments in the lab.
Not all burnt victims need to see a doctor.
It is effective to use cold water or ice on a burn to reduce the pain.
break the blisters
Not all burnt victims need to see a doctor.
It is effective to use cold water or ice on a burn to reduce the pain.
break the blisters
Good advice. First-degree burns and minor second-degree burns do not require medical attention. However, if the wound becomes painful or smelly or a high temperature is developed, it is necessary to see a doctor.
Bad advice. Cold water or ice will damage the skin.
Bad advice. Blisters should remain intact(完整的) for as long as possible as they form a natural barrier and prevent the burn from getting infected.
√
explore writing style and language features
What is the genre of this text
In narration(记叙文), the writer is a storyteller; in description, the writer is a painter of the picture; in argumentation(议论文), the writer is trying to convince(说服) the reader that he is right and in expository writing(说明文), the writer only states(陈述) the fact.
explore writing style and language features
2. What kinds of things are mentioned in the text
functions of the skin, causes of burns, different types of burns, characteristics of each type of burns and treatment for burns
The purpose of an expository writing is to provide the reader with as much useful information as possible. The reader should feel as if he or she has learned something after reading. This can be accomplished through classification(分类法), example, comparison and contrast(作比较), numbers, definition, process, the analysis of cause and effect(因果分析), etc.
explore writing style and language features
the analysis of cause and effect
classification(分类法)
example
process
explore writing style and language features
3. Is this text mainly written in first, second or third person
4. What tense is used
5. Are there any passive voice How do they make you feel
In second and third person.
The simple present tense.
explore writing style and language features
5. Are there any passive voice How do they make you feel
explore writing style and language features
5. Are there any passive voice How do they make you feel
Yes. They make the text sound objective.
explore style of writing and language features
6. What adjectives can you think of to describe this text
Objective(客观的), scientific(科学的), professional(专业的), specific, clear, concise(简明的), etc.
summary
Expository writing, as its name implies(暗示), is writing that exposes(呈现) facts. In other words, it’s writing that explains and educates its readers, rather than entertaining or attempting to persuade them. When you read a scholarly(学术的) article, a textbook page, a news report, or an instructional(指导的) guide, you’re reading expository writing.
Learning About Language
Build up your vocabulary
organ
acid
millimetre
radiation/rays
fabric
victim
Building up your vocabulary through learning synonyms
context (语境)
relation
content
slight: small in size, degree, or amount; not serious
a slight breeze; It has only made a slight difference.
minor: less, or little, in importance, size etc.
She has to go into hospital for a minor operation.
tiny: extremely small
Though she was tiny, she had a very loud voice.
reduce: to make less, smaller etc.
The shop reduced its prices; The train reduced speed.
relax: to make or become less tight or less worried etc.
Relax your shoulders.
ease: to free from pain, trouble or anxiety减轻;缓解(痛苦等)
A hot bath eased his tired limbs.
victim: a person or thing that suffers harm, death, etc.
Food is being sent to the victims of the disaster.
patient: a person who is being treated by a doctor, dentist etc.
The hospital had too many patients.
sufferer: a person suffering from an illness
accident: an unexpected event, especially one resulting in damage or harm
car accidents on icy roads.
incident: an event or happening
There was a strange incident in the supermarket today.
occasion: a particular time or a special event
I've heard him speak on several occasions. The wedding was a great occasion.
urgency: importance needing immediate attention 紧迫性
She stressed the urgency of an early solution.
emergency: an unexpected, especially dangerous happening or situation 紧急情况;突发事件
Call the doctor – it's an emergency.
seriousness: importance, significance or danger 严重性
the seriousness of the crisis
Building up your vocabulary through completing a short passage
acid
incidents
urgent
organs
loosely
victim
What we have learned today
how to prevent getting burnt
the writing style and language features of expository writing
how to build up your vocabulary
Unit 5 FIRST AID
Lesson 2: Reading and Thinking(2)+ Build up your vocabulary
At the end of the lesson, you will be able to
learn to prevent getting burnt
summarize the writing style and language features of expository writing
build up your vocabulary on the first-aid for burns
Please take out the mind map of the reading passage you have done after the first reading lesson;
Let's work out the missing words in this mind map.
Mind
Map
Mind
Map
When we cook in the kitchen, we are likely to get burnt. When using fire, we should be careful. When taking things out from the oven or off the fire, we should wear oven gloves.
What are the possible occasions when students are likely to get burnt at school How to prevent them
When getting hot water after class or doing experiments in the lab.
Not all burnt victims need to see a doctor.
It is effective to use cold water or ice on a burn to reduce the pain.
break the blisters
Not all burnt victims need to see a doctor.
It is effective to use cold water or ice on a burn to reduce the pain.
break the blisters
Good advice. First-degree burns and minor second-degree burns do not require medical attention. However, if the wound becomes painful or smelly or a high temperature is developed, it is necessary to see a doctor.
Bad advice. Cold water or ice will damage the skin.
Bad advice. Blisters should remain intact(完整的) for as long as possible as they form a natural barrier and prevent the burn from getting infected.
√
explore writing style and language features
What is the genre of this text
In narration(记叙文), the writer is a storyteller; in description, the writer is a painter of the picture; in argumentation(议论文), the writer is trying to convince(说服) the reader that he is right and in expository writing(说明文), the writer only states(陈述) the fact.
explore writing style and language features
2. What kinds of things are mentioned in the text
functions of the skin, causes of burns, different types of burns, characteristics of each type of burns and treatment for burns
The purpose of an expository writing is to provide the reader with as much useful information as possible. The reader should feel as if he or she has learned something after reading. This can be accomplished through classification(分类法), example, comparison and contrast(作比较), numbers, definition, process, the analysis of cause and effect(因果分析), etc.
explore writing style and language features
the analysis of cause and effect
classification(分类法)
example
process
explore writing style and language features
3. Is this text mainly written in first, second or third person
4. What tense is used
5. Are there any passive voice How do they make you feel
In second and third person.
The simple present tense.
explore writing style and language features
5. Are there any passive voice How do they make you feel
explore writing style and language features
5. Are there any passive voice How do they make you feel
Yes. They make the text sound objective.
explore style of writing and language features
6. What adjectives can you think of to describe this text
Objective(客观的), scientific(科学的), professional(专业的), specific, clear, concise(简明的), etc.
summary
Expository writing, as its name implies(暗示), is writing that exposes(呈现) facts. In other words, it’s writing that explains and educates its readers, rather than entertaining or attempting to persuade them. When you read a scholarly(学术的) article, a textbook page, a news report, or an instructional(指导的) guide, you’re reading expository writing.
Learning About Language
Build up your vocabulary
organ
acid
millimetre
radiation/rays
fabric
victim
Building up your vocabulary through learning synonyms
context (语境)
relation
content
slight: small in size, degree, or amount; not serious
a slight breeze; It has only made a slight difference.
minor: less, or little, in importance, size etc.
She has to go into hospital for a minor operation.
tiny: extremely small
Though she was tiny, she had a very loud voice.
reduce: to make less, smaller etc.
The shop reduced its prices; The train reduced speed.
relax: to make or become less tight or less worried etc.
Relax your shoulders.
ease: to free from pain, trouble or anxiety减轻;缓解(痛苦等)
A hot bath eased his tired limbs.
victim: a person or thing that suffers harm, death, etc.
Food is being sent to the victims of the disaster.
patient: a person who is being treated by a doctor, dentist etc.
The hospital had too many patients.
sufferer: a person suffering from an illness
accident: an unexpected event, especially one resulting in damage or harm
car accidents on icy roads.
incident: an event or happening
There was a strange incident in the supermarket today.
occasion: a particular time or a special event
I've heard him speak on several occasions. The wedding was a great occasion.
urgency: importance needing immediate attention 紧迫性
She stressed the urgency of an early solution.
emergency: an unexpected, especially dangerous happening or situation 紧急情况;突发事件
Call the doctor – it's an emergency.
seriousness: importance, significance or danger 严重性
the seriousness of the crisis
Building up your vocabulary through completing a short passage
acid
incidents
urgent
organs
loosely
victim
What we have learned today
how to prevent getting burnt
the writing style and language features of expository writing
how to build up your vocabulary
