八下英语 Unit 1 What's the Matter A 1a - 2d教案
文档属性
| 名称 | 八下英语 Unit 1 What's the Matter A 1a - 2d教案 |

|
|
| 格式 | docx | ||
| 文件大小 | 17.2KB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 人教新目标(Go for it)版 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2025-03-24 00:00:00 | ||
图片预览

文档简介
Unit 1 What's the Matter A 1a - 2d 教案
I. Teaching Aims
1. Knowledge Aims
Students can master the following words and phrases: matter, sore, have a cold, stomachache, have a stomachache, foot, neck, stomach, throat, fever, lie, lie down, rest, cough, X - ray, toothache, take one's temperature, headache, have a fever, break.
Students can use the target language to talk about health problems and accidents, such as "What's the matter I have a stomachache." "What should I do You should lie down and rest."
2. Ability Aims
Students can improve their listening, speaking, reading and writing skills by talking about health problems and giving advice.
Students can learn to analyze and solve problems by themselves or with their partners.
3. Emotional Aims
Students can care about their own health and others' health.
Students can be brave when facing problems and learn to help others.
4. Cultural Aims
Students can know some common health problems and ways to deal with them in Western countries.
II. Teaching Key and Difficult Points
1. Teaching Key Points
Key words and phrases about health problems.
The target language for talking about health problems and giving advice.
2. Teaching Difficult Points
How to use the target language to communicate freely and fluently.
How to guide students to give proper advice according to different health problems.
III. Teaching Methods
Communicative teaching method
Task - based teaching method
Audio - visual teaching method
IV. Teaching Aids
Multimedia, pictures, cards
V. Teaching Procedures
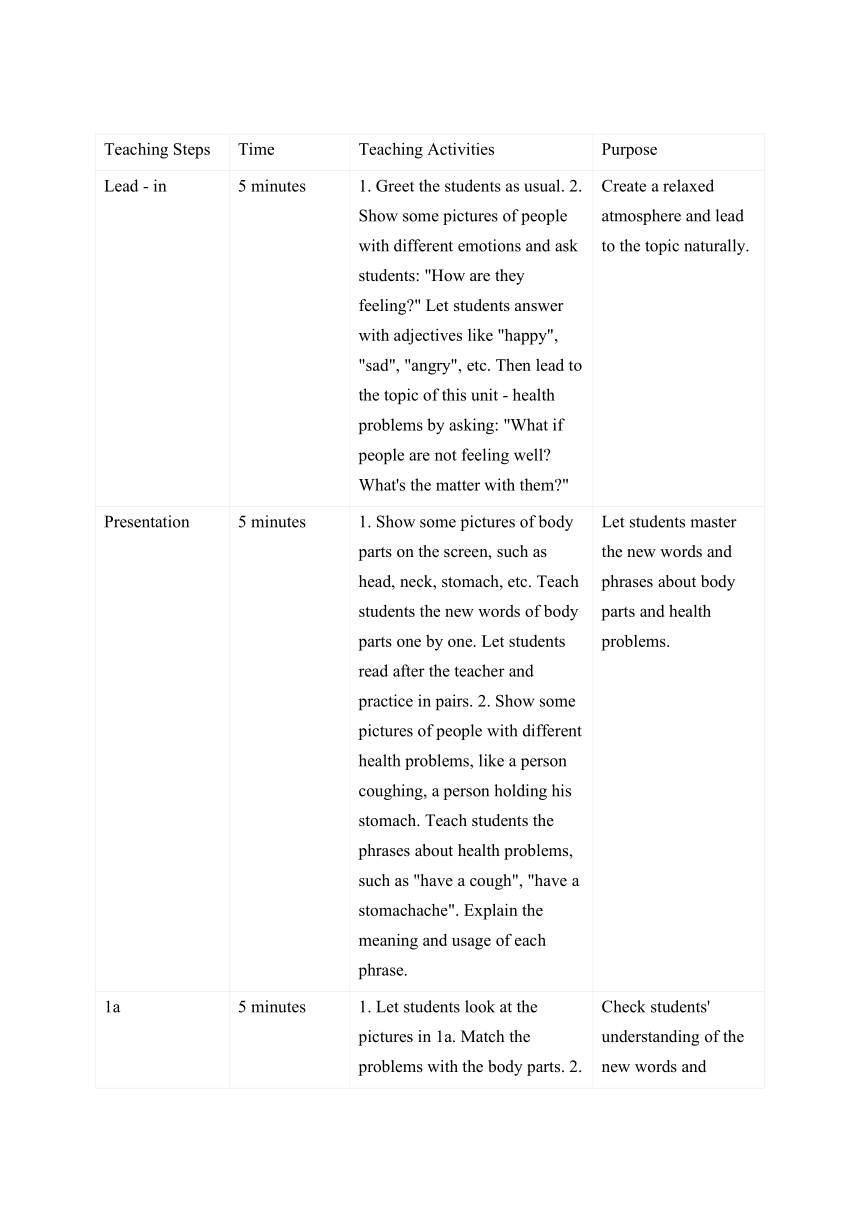
Teaching Steps Time Teaching Activities Purpose
Lead - in 5 minutes 1. Greet the students as usual. 2. Show some pictures of people with different emotions and ask students: "How are they feeling " Let students answer with adjectives like "happy", "sad", "angry", etc. Then lead to the topic of this unit - health problems by asking: "What if people are not feeling well What's the matter with them " Create a relaxed atmosphere and lead to the topic naturally.
Presentation 5 minutes 1. Show some pictures of body parts on the screen, such as head, neck, stomach, etc. Teach students the new words of body parts one by one. Let students read after the teacher and practice in pairs. 2. Show some pictures of people with different health problems, like a person coughing, a person holding his stomach. Teach students the phrases about health problems, such as "have a cough", "have a stomachache". Explain the meaning and usage of each phrase. Let students master the new words and phrases about body parts and health problems.
1a 5 minutes 1. Let students look at the pictures in 1a. Match the problems with the body parts. 2. Check the answers with the whole class. Check students' understanding of the new words and phrases.
1b 5 minutes 1. Play the recording for 1b. Let students listen and number the problems in the order they hear. 2. Play the recording again. Check the answers. Train students' listening skills.
Pair Work 5 minutes 1. Let students work in pairs. One student points to a body part and the other says a problem. Then change roles. 2. Walk around the classroom and offer help if necessary. Let students practice using the target language in pairs.
2a 5 minutes 1. Tell students they will hear some advice. First, let them look at the pictures in 2a and guess what advice they might hear. 2. Play the recording for 2a. Let students listen and circle the advice they hear. 3. Check the answers. Train students' listening skills and prediction ability.
2b 5 minutes 1. Play the recording for 2b. Let students listen again and match the problems with the advice. 2. Check the answers. Further train students' listening skills.
Group Work 3 minutes 1. Divide students into groups of four. Give each group some cards with different health problems written on them. 2. Each group discusses and writes down as much advice as possible for each problem. 3. Each group presents their advice to the class. The other groups can add more advice if they have different ideas. Let students work together to give advice for different health problems, improving their speaking and cooperative abilities.
2d 5 minutes 1. Let students read the conversation in 2d silently first. Then answer some questions on the screen, like "What's the matter with Lisa " "What should she do " 2. Explain the key sentences and language points in the conversation, such as "I think I sat in the same way for too long without moving." 3. Let students practice reading the conversation in pairs. Pay attention to the intonation and pronunciation. 4. Invite some pairs to come to the front and act out the conversation. Improve students' reading, understanding and speaking abilities.
Summary 1 minute 1. Summarize the key words, phrases and sentences of this class with the students. 2. Ask students to remember them. Help students review what they have learned in this class.
Homework 1 minute 1. Ask students to make a list of common health problems and the advice for each problem. 2. Let students write a short passage about their own health problems and how they dealt with them. Consolidate what students have learned in class and improve their writing skills.
VI. Teaching Reflection
In this class, through various teaching methods such as pictures, recordings and group work, students showed great interest in learning. They actively participated in different activities, which improved their language skills to a certain extent. For example, in the group work of giving advice, students could communicate with each other in English and come up with many creative ideas. However, there were also some problems. Some students were still a little shy to speak English in front of the class during the pair work and group presentation. In the future teaching, more encouragement and more chances should be given to these students. Also, when explaining some difficult language points, the examples might not be vivid enough for some students to fully understand. It is necessary to find more interesting and practical examples to help students master the knowledge better.
I. Teaching Aims
1. Knowledge Aims
Students can master the following words and phrases: matter, sore, have a cold, stomachache, have a stomachache, foot, neck, stomach, throat, fever, lie, lie down, rest, cough, X - ray, toothache, take one's temperature, headache, have a fever, break.
Students can use the target language to talk about health problems and accidents, such as "What's the matter I have a stomachache." "What should I do You should lie down and rest."
2. Ability Aims
Students can improve their listening, speaking, reading and writing skills by talking about health problems and giving advice.
Students can learn to analyze and solve problems by themselves or with their partners.
3. Emotional Aims
Students can care about their own health and others' health.
Students can be brave when facing problems and learn to help others.
4. Cultural Aims
Students can know some common health problems and ways to deal with them in Western countries.
II. Teaching Key and Difficult Points
1. Teaching Key Points
Key words and phrases about health problems.
The target language for talking about health problems and giving advice.
2. Teaching Difficult Points
How to use the target language to communicate freely and fluently.
How to guide students to give proper advice according to different health problems.
III. Teaching Methods
Communicative teaching method
Task - based teaching method
Audio - visual teaching method
IV. Teaching Aids
Multimedia, pictures, cards
V. Teaching Procedures
Teaching Steps Time Teaching Activities Purpose
Lead - in 5 minutes 1. Greet the students as usual. 2. Show some pictures of people with different emotions and ask students: "How are they feeling " Let students answer with adjectives like "happy", "sad", "angry", etc. Then lead to the topic of this unit - health problems by asking: "What if people are not feeling well What's the matter with them " Create a relaxed atmosphere and lead to the topic naturally.
Presentation 5 minutes 1. Show some pictures of body parts on the screen, such as head, neck, stomach, etc. Teach students the new words of body parts one by one. Let students read after the teacher and practice in pairs. 2. Show some pictures of people with different health problems, like a person coughing, a person holding his stomach. Teach students the phrases about health problems, such as "have a cough", "have a stomachache". Explain the meaning and usage of each phrase. Let students master the new words and phrases about body parts and health problems.
1a 5 minutes 1. Let students look at the pictures in 1a. Match the problems with the body parts. 2. Check the answers with the whole class. Check students' understanding of the new words and phrases.
1b 5 minutes 1. Play the recording for 1b. Let students listen and number the problems in the order they hear. 2. Play the recording again. Check the answers. Train students' listening skills.
Pair Work 5 minutes 1. Let students work in pairs. One student points to a body part and the other says a problem. Then change roles. 2. Walk around the classroom and offer help if necessary. Let students practice using the target language in pairs.
2a 5 minutes 1. Tell students they will hear some advice. First, let them look at the pictures in 2a and guess what advice they might hear. 2. Play the recording for 2a. Let students listen and circle the advice they hear. 3. Check the answers. Train students' listening skills and prediction ability.
2b 5 minutes 1. Play the recording for 2b. Let students listen again and match the problems with the advice. 2. Check the answers. Further train students' listening skills.
Group Work 3 minutes 1. Divide students into groups of four. Give each group some cards with different health problems written on them. 2. Each group discusses and writes down as much advice as possible for each problem. 3. Each group presents their advice to the class. The other groups can add more advice if they have different ideas. Let students work together to give advice for different health problems, improving their speaking and cooperative abilities.
2d 5 minutes 1. Let students read the conversation in 2d silently first. Then answer some questions on the screen, like "What's the matter with Lisa " "What should she do " 2. Explain the key sentences and language points in the conversation, such as "I think I sat in the same way for too long without moving." 3. Let students practice reading the conversation in pairs. Pay attention to the intonation and pronunciation. 4. Invite some pairs to come to the front and act out the conversation. Improve students' reading, understanding and speaking abilities.
Summary 1 minute 1. Summarize the key words, phrases and sentences of this class with the students. 2. Ask students to remember them. Help students review what they have learned in this class.
Homework 1 minute 1. Ask students to make a list of common health problems and the advice for each problem. 2. Let students write a short passage about their own health problems and how they dealt with them. Consolidate what students have learned in class and improve their writing skills.
VI. Teaching Reflection
In this class, through various teaching methods such as pictures, recordings and group work, students showed great interest in learning. They actively participated in different activities, which improved their language skills to a certain extent. For example, in the group work of giving advice, students could communicate with each other in English and come up with many creative ideas. However, there were also some problems. Some students were still a little shy to speak English in front of the class during the pair work and group presentation. In the future teaching, more encouragement and more chances should be given to these students. Also, when explaining some difficult language points, the examples might not be vivid enough for some students to fully understand. It is necessary to find more interesting and practical examples to help students master the knowledge better.
同课章节目录
- Unit 1 What's the matter?
- Section A
- Section B
- Unit 2 I'll help to clean up the city parks.
- Section A
- Section B
- Unit 3 Could you please clean your room?
- Section A
- Section B
- Unit 4 Why don't you talk to your parents?
- Section A
- Section B
- Unit 5 What were you doing when the rainstorm came
- Section A
- Section B
- Review of Units 1-5
- Unit 6 An old man tried to move the mountains.
- Section A
- Section B
- Unit 7 What's the highest mountain in the world?
- Section A
- Section B
- Unit 8 Have you read Treasure Island yet?
- Section A
- Section B
- Unit 9 Have you ever been to a museum?
- Section A
- Section B
- Unit 10 I've had this bike for three years.
- Section A
- Section B
