Unit 5 Poems Learning About Language 课件 (共33张)-高中英语人教版(2019)选择性必修第三册
文档属性
| 名称 | Unit 5 Poems Learning About Language 课件 (共33张)-高中英语人教版(2019)选择性必修第三册 |  | |
| 格式 | pptx | ||
| 文件大小 | 7.1MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 人教版(2019) | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2025-04-02 20:35:23 | ||
图片预览










文档简介
(共33张PPT)
Learning About Language
Unit 5 Poems
Teaching Objectives:
1. Identify and analyse the usages of direct speech and indirect speech.
2. Use indirect speech to express your ideas.
3. Raise the awareness of environmental protection.
Key and difficult points:
Key point:Find out and summarize the rules for changing direct speech into indirect speech and learn to use indirect speech in the context.
Difficult point:How to use indirect speech in real situations.
Part 1 Build up your vocabulary
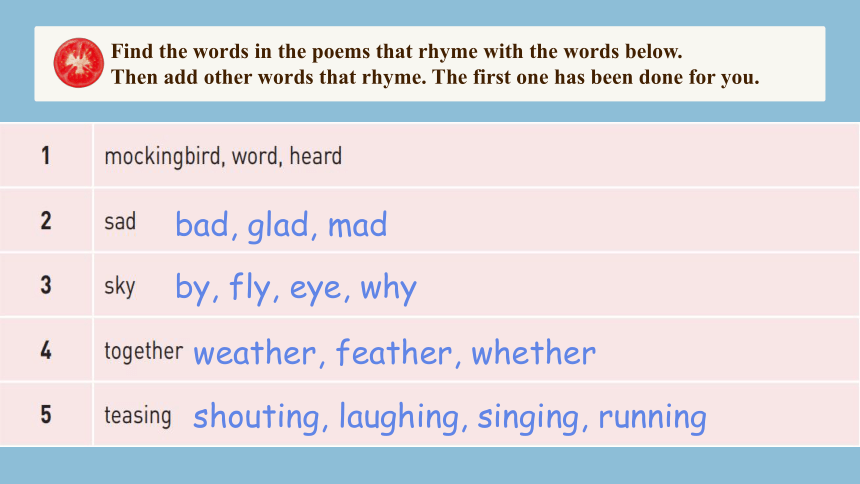
Find the words in the poems that rhyme with the words below.
Then add other words that rhyme. The first one has been done for you.
bad, glad, mad
by, fly, eye, why
weather, feather, whether
shouting, laughing, singing, running
Complete the sentences using the correct forms of the words in the box.
1. It seems incredible to me that the question of how best to __________ books on shelves could cause a lively online discussion.
2. The purpose of __________ criticism is to get to the core of the text and discover what message the author is attempting to convey.
3. If you need to handle a __________ situation, you should behave wisely.
4. The poet __________ quite a few poems featuring the image of cherry blossoms, and describing the joys and __________ of life.
5. Blank verse is probably one of the most common and influential forms of English __________. It is so close to the natural __________ of English speech and it has no rhyming. In Shakespeare’s __________, characters from civilians to kings all speak in blank verse, but still in distinctive voices.
arrange
literary
delicate
composed
sorrows
poetry
rhythm
dramas
Complete each sentence using the correct word.
1. Could you __________ what you just said
2. Students are required to __________ over 60 ancient poems or works of prose they have learnt from their Chinese course.
3. If you have finished reading the story, please try to __________ it in your own words.
repeat
recite
recite / repeat / retell
1. Could you __________ what you just said
2. Students are required to __________ over 60 ancient poems or works of prose they have learnt from their Chinese course.
3. If you have finished reading the story, please try to __________ it in your own words.
emotion / mood / spirit
retell
spirits
emotion
mood
Part 2
复习定语从句
定义:用来修饰名词或代词的从句叫定语从句。被定语从句所修饰的名词或代词叫先行词(antecedent)。定语从句一般是由关系代词或关系副词来引导的。相当于名词和形容词的作用。
定语从句
The book that I bought yesterday is very interesting.
结构:先行词 + 关系词 + 定语从句。关系词在定语从句中起着连接主句和从句的作用,同时还在从句中充当一定的句子成分。
“The book” 是先行词,“that I bought yesterday” 是定语从句,用来修饰 “book”,说明是我昨天买的那本书
用法:
关系代词除了指代主句中的先行词外,同时还在定语从句中作主语、宾语、表语等。作宾语时可以省略;但关系代词作介词宾语,而且介词提到它的前面时,关系代词不能省略。
关系代词 修饰的先行词 在从句中所作的成分
who 人 主语、宾语
whom 人 宾语
whose 人或物 定语
that 人或物 主语、宾语、表语
which 物或事 主语、宾语、定语、表语
as 人、物或事 主语、宾语、表语
关系代词
that的用法
The boy that is standing there is my brother.
“that” 指代 “the boy”,在从句中作主语
指人或物,在从句中作主语、宾语或表语。
作主语:
I love the movie that I watched last night.
"that"指代"the movie",在从句中作"watched"的宾语,可省略
作宾语:
She is no longer the girl that she used to be.
“that” 指代 “the girl”,在从句中作表语
作表语:
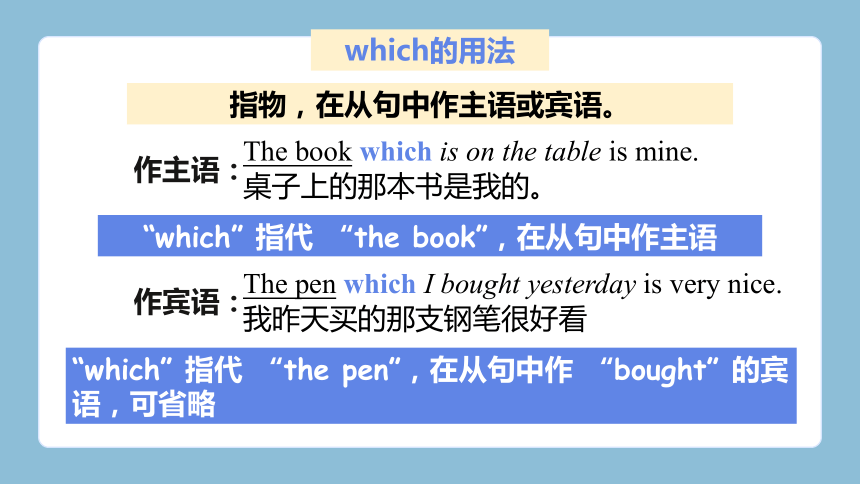
which的用法
The book which is on the table is mine.
桌子上的那本书是我的。
“which” 指代 “the book”,在从句中作主语
指物,在从句中作主语或宾语。
作主语:
The pen which I bought yesterday is very nice.
我昨天买的那支钢笔很好看
“which” 指代 “the pen”,在从句中作 “bought” 的宾语,可省略
作宾语:
who的用法
The man who is talking to my father is a teacher.
正在和我父亲说话的那个人是一位老师。
“who” 指代 “the man”,在从句中作主语
指人,在从句中作主语或宾语。
作主语:
The girl who I met at the party is very friendly.
我在聚会上遇到的那个女孩很友好。
“who” 指代 “the girl”,在从句中作 “met” 的宾语,可省略
作宾语:
whom的用法
The person whom you talked to just now is my boss.
你刚才和他说话的那个人是我的老板。
“whom” 指代 “the person”,作 “talked to” 的宾语。
可省略为:The person you talked to just now is my boss.
指人,在从句中作宾语
作宾语:
whose的用法
The boy whose father is a doctor is my classmate.
那个父亲是医生的男孩是我的同学。
“whose” 指代 “the boy's”,在从句中作 “father” 的定语
既可以指人,也可以指物,在从句中作定语,表示所属关系。
指人时:
I like the house whose windows are big.
我喜欢那座窗户很大的房子。
“whose”指代“the house's”,在从句中作“windows” 的定语
指物时:
Look at these sentences and underline the restrictive relative clauses. What kind of information does each clause communicate
1. It was a time when people were divided geographically.
2. Emperor Qinshihuang united the seven major states into one unified country where the Chinese writing system began to develop in one direction.
3. There are many reasons why people learn a foreign language.
4. These were animal bones and shells on which symbols were carved by ancient Chinese people.
修饰 a time, when 在从句中作时间状语
修饰one unified country, where在从句中作地点状语
修饰reasons, why在从句中作原因状语
修饰 animal bones and shells, on which =on the animal bones and shells。
关系副词的用法
I still remember the day when I first came to this school.
我仍然记得我第一次来到这所学校的那一天。
“when”在从句中作时间状语,相当于“on which”,即“on the day”
when:在定语从句中作时间状语,其先行词通常是表示时间的名词,如 day, month, year 等。
She came to the city in 2008, when the Olympic Games were held in Beijing.
她在 2008 年来到这个城市,那年北京举办了奥运会。
“when”指代“in 2008”,在从句中作时间状语
关系副词的用法
This is the place where we played football last Sunday.
这是我们上周日踢足球的地方。
“where”在从句中作地点状语,相当于“in which”,即“in the place”
where:在定语从句中作地点状语,其先行词通常是表示地点的名词,如place, city, school等。
The hotel where we stayed during our holiday is very nice.
我们度假时住的酒店非常好。
“where” 指代 “in the hotel”,在从句中作地点状语
关系副词的用法
Do you know the reason why he was late for school
你知道他上学迟到的原因吗?
“why” 在从句中作原因状语,相当于“for which”,即“for the reason”
why:在定语从句中作原因状语,其先行词通常是reason。
I don't believe the reason why he gave for his absence.
我不相信他为自己缺席给出的理由。
“why” 引导的定语从句修饰“reason”,“why”在从句中作原因状语
限制性定语从句
The book that I bought yesterday is very useful.
我昨天买的那本书很有用。
如果去掉定语从句"that I bought yesterday",句子"The book is very useful."的意思就不明确是哪本书有用了
是先行词不可缺少的部分,去掉它主句意思往往不明确。
Any student who breaks the rules will be punished.
任何违反规则的学生都将受到惩罚。
“who breaks the rules” 是对 “student” 的限定,去掉后就不知道是哪些学生要受惩罚了
非限制性定语从句
My mother, who is 50 years old, is a teacher.
即使去掉定语从句"who is 50 years old",句子"My mother is a teacher."的意思仍然完整,"who is 50 years old"只是对"my mother"的补充说明
是对先行词的补充说明,去掉它不影响主句的意思。它与主句之间通常用逗号隔开,关系代词不能用 that。
The sun, which is one of millions of stars in the universe, gives us light and heat.
太阳,它是宇宙中数百万颗恒星之一,给我们提供光和热。
"which is one of millions of stars in the universe"是对"the sun"的补充说明
“介词 + 关系代词”引导的定语从句
I'll never forget the day on which (= when) my son was born.
我永远忘不了我儿子出生的那一天。
I'd like you to explain the reason for which (=why) you refused my offer.
我想让你解释一下你拒绝我帮助的原因。(for 依据 for the reason 确定)
关系副词when, where, why引导定语从句时,关系副词可用“介词 +关系代词”代替。在“介词 +关系代词”引导的定语从句中,关系代词只能用which或whom,不可用that或who。
替代when
替代where
This is the farm on which (=where) I used to work.
这就是我过去工作过的农场。 (on 依据 on the farm 确定)
替代why
“介词 +which”可以替代关系副词 when, where, why
“介词 + 关系代词”引导的定语从句
依据与先行词的固定搭配确定使用什么介词
I'll never forget the time during which I was with my friends in the country.
我永远不会忘记和朋友们一起在乡村度过的时光。
依据定语从句中动词或形容词的搭配来确定介词
She bought several books, on which she spent all her money.
她买了几本书,这些书花光了她所有的钱。
根据定语从句所表达的具体意思来确定介词
Can you see the river across which there is a bridge
你能看见上面有座桥的那条河吗
(during依据during the time确定)
(on依据spend...on确定)
“介词 + 关系代词”引导的定语从句
如果在whom和which 之前用of 表示所属关系(即of whom, of which表示所属关系),这时名词需要特指,应加定冠词该名词放在of whom, of which之前或之后均可。
I'd like a room the window of which looks out over the sea.
I'd like a room of which the window looks out over the sea.
因为whose也表示所属关系,所以可以转换为:
I'd like a room whose window looks out over the sea.
“介词 + 关系代词”引导的定语从句
在whom和which之前用of,还可以表示部分与整体的关系。这时,表示“部分”的数词或代词,放在 of whom, of which 之前或之后均可。
She has three daughters, one of whom is a doctor.
She has three daughters, all of whom are beautiful.
She has three daughters, the oldest of whom is called Mary.
She has three daughters, of whom one is a doctor.
She has three daughters, of whom all are beautiful.
还可以说:
定语从句与同位语从句
The news that you told me yesterday is true.
“that”在从句中作“told” 的宾语,“you told me yesterday”是对“news” 的修饰,说明是你告诉我的那个消息
定语从句:是对先行词的修饰和限定,关系词在从句中充当成分。
“that” 引导的从句 “our team won the game” 是对 “news” 内容的说明,“that” 不充当任何成分
同位语从句:是对名词的内容进行解释和说明,连接词在从句中不充当成分。
The news that our team won the game is exciting.
Part 3 Vocabulary
Vocabulary
blank
go blank (脑子里)突然一片空白
a blank look/expression 木然的表情
adj.空白的;无图画(或韵律、装饰)的;没表情的
练习: The exciting news was being broad-cast when the television _____________ (出现空白).
went blank
n. (记忆中的)空白;(文件等的)空白处,空格
fill in the blanks 填空
Vocabulary
sympathetic
be sympathetic towards/to
对……同情;赞同;支持
a sympathetic ear
乐于倾听别人的困难
adj. 同情的;有同情心的;赞同的
练习: The railway workers came out in sympathy ____________ the miners.
with
I am sympathetic towards Jane, for she has undergone a lot of sufferings. 我同情简,因为她经历了很多痛苦的事。
Vocabulary
correspondence
enter into correspondence with sb. 与某人通信
personal/private correspondence 私人来往信件
the correspondence column/page 读者来信专栏/版面
n. 来往信件;通信联系
练习: We have corresponded ___________ each other since we first met in Paris.
with
The editor welcomes correspondence from readers on any subject.
编辑欢迎读者有关任何问题的来信。
Part 4 Practice
语法填空
Most children love being told about nursery rhymes. The most popular rhymes ___________ (list) here. Even elders love to hear these rhymes ___________ are sweet to our ears forever. These rhymes speak volumes about the interest ___________ (show) by the education department to ensure the children to speak out.
The list is clearly not exhaustive but ___________ is believed that a good cross section of famous poems for children has been included. We have selected the most famous nursery rhymes for children. We have done our best ___________ (collect) all the nursery rhymes from all sources and add them here for your ___________ (refer). The addition of more and more rhymes is going on every day.
are listed
that/which
shown
it
to collect
reference
语法填空
These nursery rhymes for children ________________ (pass) over the years and because ___________ the short nature of the verse, they can ___________ (easy) be remembered by most children from a very early age. Analysis of these nursery rhymes will reflect the ___________ (history) background where these nursery rhymes were written.
have been passed
of
easily
historical
SEE YOU NEXT TIME
Learning About Language
Unit 5 Poems
Teaching Objectives:
1. Identify and analyse the usages of direct speech and indirect speech.
2. Use indirect speech to express your ideas.
3. Raise the awareness of environmental protection.
Key and difficult points:
Key point:Find out and summarize the rules for changing direct speech into indirect speech and learn to use indirect speech in the context.
Difficult point:How to use indirect speech in real situations.
Part 1 Build up your vocabulary
Find the words in the poems that rhyme with the words below.
Then add other words that rhyme. The first one has been done for you.
bad, glad, mad
by, fly, eye, why
weather, feather, whether
shouting, laughing, singing, running
Complete the sentences using the correct forms of the words in the box.
1. It seems incredible to me that the question of how best to __________ books on shelves could cause a lively online discussion.
2. The purpose of __________ criticism is to get to the core of the text and discover what message the author is attempting to convey.
3. If you need to handle a __________ situation, you should behave wisely.
4. The poet __________ quite a few poems featuring the image of cherry blossoms, and describing the joys and __________ of life.
5. Blank verse is probably one of the most common and influential forms of English __________. It is so close to the natural __________ of English speech and it has no rhyming. In Shakespeare’s __________, characters from civilians to kings all speak in blank verse, but still in distinctive voices.
arrange
literary
delicate
composed
sorrows
poetry
rhythm
dramas
Complete each sentence using the correct word.
1. Could you __________ what you just said
2. Students are required to __________ over 60 ancient poems or works of prose they have learnt from their Chinese course.
3. If you have finished reading the story, please try to __________ it in your own words.
repeat
recite
recite / repeat / retell
1. Could you __________ what you just said
2. Students are required to __________ over 60 ancient poems or works of prose they have learnt from their Chinese course.
3. If you have finished reading the story, please try to __________ it in your own words.
emotion / mood / spirit
retell
spirits
emotion
mood
Part 2
复习定语从句
定义:用来修饰名词或代词的从句叫定语从句。被定语从句所修饰的名词或代词叫先行词(antecedent)。定语从句一般是由关系代词或关系副词来引导的。相当于名词和形容词的作用。
定语从句
The book that I bought yesterday is very interesting.
结构:先行词 + 关系词 + 定语从句。关系词在定语从句中起着连接主句和从句的作用,同时还在从句中充当一定的句子成分。
“The book” 是先行词,“that I bought yesterday” 是定语从句,用来修饰 “book”,说明是我昨天买的那本书
用法:
关系代词除了指代主句中的先行词外,同时还在定语从句中作主语、宾语、表语等。作宾语时可以省略;但关系代词作介词宾语,而且介词提到它的前面时,关系代词不能省略。
关系代词 修饰的先行词 在从句中所作的成分
who 人 主语、宾语
whom 人 宾语
whose 人或物 定语
that 人或物 主语、宾语、表语
which 物或事 主语、宾语、定语、表语
as 人、物或事 主语、宾语、表语
关系代词
that的用法
The boy that is standing there is my brother.
“that” 指代 “the boy”,在从句中作主语
指人或物,在从句中作主语、宾语或表语。
作主语:
I love the movie that I watched last night.
"that"指代"the movie",在从句中作"watched"的宾语,可省略
作宾语:
She is no longer the girl that she used to be.
“that” 指代 “the girl”,在从句中作表语
作表语:
which的用法
The book which is on the table is mine.
桌子上的那本书是我的。
“which” 指代 “the book”,在从句中作主语
指物,在从句中作主语或宾语。
作主语:
The pen which I bought yesterday is very nice.
我昨天买的那支钢笔很好看
“which” 指代 “the pen”,在从句中作 “bought” 的宾语,可省略
作宾语:
who的用法
The man who is talking to my father is a teacher.
正在和我父亲说话的那个人是一位老师。
“who” 指代 “the man”,在从句中作主语
指人,在从句中作主语或宾语。
作主语:
The girl who I met at the party is very friendly.
我在聚会上遇到的那个女孩很友好。
“who” 指代 “the girl”,在从句中作 “met” 的宾语,可省略
作宾语:
whom的用法
The person whom you talked to just now is my boss.
你刚才和他说话的那个人是我的老板。
“whom” 指代 “the person”,作 “talked to” 的宾语。
可省略为:The person you talked to just now is my boss.
指人,在从句中作宾语
作宾语:
whose的用法
The boy whose father is a doctor is my classmate.
那个父亲是医生的男孩是我的同学。
“whose” 指代 “the boy's”,在从句中作 “father” 的定语
既可以指人,也可以指物,在从句中作定语,表示所属关系。
指人时:
I like the house whose windows are big.
我喜欢那座窗户很大的房子。
“whose”指代“the house's”,在从句中作“windows” 的定语
指物时:
Look at these sentences and underline the restrictive relative clauses. What kind of information does each clause communicate
1. It was a time when people were divided geographically.
2. Emperor Qinshihuang united the seven major states into one unified country where the Chinese writing system began to develop in one direction.
3. There are many reasons why people learn a foreign language.
4. These were animal bones and shells on which symbols were carved by ancient Chinese people.
修饰 a time, when 在从句中作时间状语
修饰one unified country, where在从句中作地点状语
修饰reasons, why在从句中作原因状语
修饰 animal bones and shells, on which =on the animal bones and shells。
关系副词的用法
I still remember the day when I first came to this school.
我仍然记得我第一次来到这所学校的那一天。
“when”在从句中作时间状语,相当于“on which”,即“on the day”
when:在定语从句中作时间状语,其先行词通常是表示时间的名词,如 day, month, year 等。
She came to the city in 2008, when the Olympic Games were held in Beijing.
她在 2008 年来到这个城市,那年北京举办了奥运会。
“when”指代“in 2008”,在从句中作时间状语
关系副词的用法
This is the place where we played football last Sunday.
这是我们上周日踢足球的地方。
“where”在从句中作地点状语,相当于“in which”,即“in the place”
where:在定语从句中作地点状语,其先行词通常是表示地点的名词,如place, city, school等。
The hotel where we stayed during our holiday is very nice.
我们度假时住的酒店非常好。
“where” 指代 “in the hotel”,在从句中作地点状语
关系副词的用法
Do you know the reason why he was late for school
你知道他上学迟到的原因吗?
“why” 在从句中作原因状语,相当于“for which”,即“for the reason”
why:在定语从句中作原因状语,其先行词通常是reason。
I don't believe the reason why he gave for his absence.
我不相信他为自己缺席给出的理由。
“why” 引导的定语从句修饰“reason”,“why”在从句中作原因状语
限制性定语从句
The book that I bought yesterday is very useful.
我昨天买的那本书很有用。
如果去掉定语从句"that I bought yesterday",句子"The book is very useful."的意思就不明确是哪本书有用了
是先行词不可缺少的部分,去掉它主句意思往往不明确。
Any student who breaks the rules will be punished.
任何违反规则的学生都将受到惩罚。
“who breaks the rules” 是对 “student” 的限定,去掉后就不知道是哪些学生要受惩罚了
非限制性定语从句
My mother, who is 50 years old, is a teacher.
即使去掉定语从句"who is 50 years old",句子"My mother is a teacher."的意思仍然完整,"who is 50 years old"只是对"my mother"的补充说明
是对先行词的补充说明,去掉它不影响主句的意思。它与主句之间通常用逗号隔开,关系代词不能用 that。
The sun, which is one of millions of stars in the universe, gives us light and heat.
太阳,它是宇宙中数百万颗恒星之一,给我们提供光和热。
"which is one of millions of stars in the universe"是对"the sun"的补充说明
“介词 + 关系代词”引导的定语从句
I'll never forget the day on which (= when) my son was born.
我永远忘不了我儿子出生的那一天。
I'd like you to explain the reason for which (=why) you refused my offer.
我想让你解释一下你拒绝我帮助的原因。(for 依据 for the reason 确定)
关系副词when, where, why引导定语从句时,关系副词可用“介词 +关系代词”代替。在“介词 +关系代词”引导的定语从句中,关系代词只能用which或whom,不可用that或who。
替代when
替代where
This is the farm on which (=where) I used to work.
这就是我过去工作过的农场。 (on 依据 on the farm 确定)
替代why
“介词 +which”可以替代关系副词 when, where, why
“介词 + 关系代词”引导的定语从句
依据与先行词的固定搭配确定使用什么介词
I'll never forget the time during which I was with my friends in the country.
我永远不会忘记和朋友们一起在乡村度过的时光。
依据定语从句中动词或形容词的搭配来确定介词
She bought several books, on which she spent all her money.
她买了几本书,这些书花光了她所有的钱。
根据定语从句所表达的具体意思来确定介词
Can you see the river across which there is a bridge
你能看见上面有座桥的那条河吗
(during依据during the time确定)
(on依据spend...on确定)
“介词 + 关系代词”引导的定语从句
如果在whom和which 之前用of 表示所属关系(即of whom, of which表示所属关系),这时名词需要特指,应加定冠词该名词放在of whom, of which之前或之后均可。
I'd like a room the window of which looks out over the sea.
I'd like a room of which the window looks out over the sea.
因为whose也表示所属关系,所以可以转换为:
I'd like a room whose window looks out over the sea.
“介词 + 关系代词”引导的定语从句
在whom和which之前用of,还可以表示部分与整体的关系。这时,表示“部分”的数词或代词,放在 of whom, of which 之前或之后均可。
She has three daughters, one of whom is a doctor.
She has three daughters, all of whom are beautiful.
She has three daughters, the oldest of whom is called Mary.
She has three daughters, of whom one is a doctor.
She has three daughters, of whom all are beautiful.
还可以说:
定语从句与同位语从句
The news that you told me yesterday is true.
“that”在从句中作“told” 的宾语,“you told me yesterday”是对“news” 的修饰,说明是你告诉我的那个消息
定语从句:是对先行词的修饰和限定,关系词在从句中充当成分。
“that” 引导的从句 “our team won the game” 是对 “news” 内容的说明,“that” 不充当任何成分
同位语从句:是对名词的内容进行解释和说明,连接词在从句中不充当成分。
The news that our team won the game is exciting.
Part 3 Vocabulary
Vocabulary
blank
go blank (脑子里)突然一片空白
a blank look/expression 木然的表情
adj.空白的;无图画(或韵律、装饰)的;没表情的
练习: The exciting news was being broad-cast when the television _____________ (出现空白).
went blank
n. (记忆中的)空白;(文件等的)空白处,空格
fill in the blanks 填空
Vocabulary
sympathetic
be sympathetic towards/to
对……同情;赞同;支持
a sympathetic ear
乐于倾听别人的困难
adj. 同情的;有同情心的;赞同的
练习: The railway workers came out in sympathy ____________ the miners.
with
I am sympathetic towards Jane, for she has undergone a lot of sufferings. 我同情简,因为她经历了很多痛苦的事。
Vocabulary
correspondence
enter into correspondence with sb. 与某人通信
personal/private correspondence 私人来往信件
the correspondence column/page 读者来信专栏/版面
n. 来往信件;通信联系
练习: We have corresponded ___________ each other since we first met in Paris.
with
The editor welcomes correspondence from readers on any subject.
编辑欢迎读者有关任何问题的来信。
Part 4 Practice
语法填空
Most children love being told about nursery rhymes. The most popular rhymes ___________ (list) here. Even elders love to hear these rhymes ___________ are sweet to our ears forever. These rhymes speak volumes about the interest ___________ (show) by the education department to ensure the children to speak out.
The list is clearly not exhaustive but ___________ is believed that a good cross section of famous poems for children has been included. We have selected the most famous nursery rhymes for children. We have done our best ___________ (collect) all the nursery rhymes from all sources and add them here for your ___________ (refer). The addition of more and more rhymes is going on every day.
are listed
that/which
shown
it
to collect
reference
语法填空
These nursery rhymes for children ________________ (pass) over the years and because ___________ the short nature of the verse, they can ___________ (easy) be remembered by most children from a very early age. Analysis of these nursery rhymes will reflect the ___________ (history) background where these nursery rhymes were written.
have been passed
of
easily
historical
SEE YOU NEXT TIME
