UNIT 8 LITERATURE LESSON 1 The Last Leaf课件(共53张PPT,内镶嵌视频)-高中英语北师大版(2019)选择性必修第三册
文档属性
| 名称 | UNIT 8 LITERATURE LESSON 1 The Last Leaf课件(共53张PPT,内镶嵌视频)-高中英语北师大版(2019)选择性必修第三册 |

|
|
| 格式 | pptx | ||
| 文件大小 | 9.2MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 北师大版(2019) | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2025-04-03 22:17:00 | ||
图片预览








文档简介
(共53张PPT)
UNIT 8 LITERATURE
LESSON 1
THE LAST LEAF
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
To read and talk about the main character and plot of the story;
To recognize the point of view of multiple characters in a piece of literature;
To compare personal opinions with the ideas of others;
To read for specific information to understand words in context;
To recall and summarise information;
To learn and practise using state verbs and activity verbs.
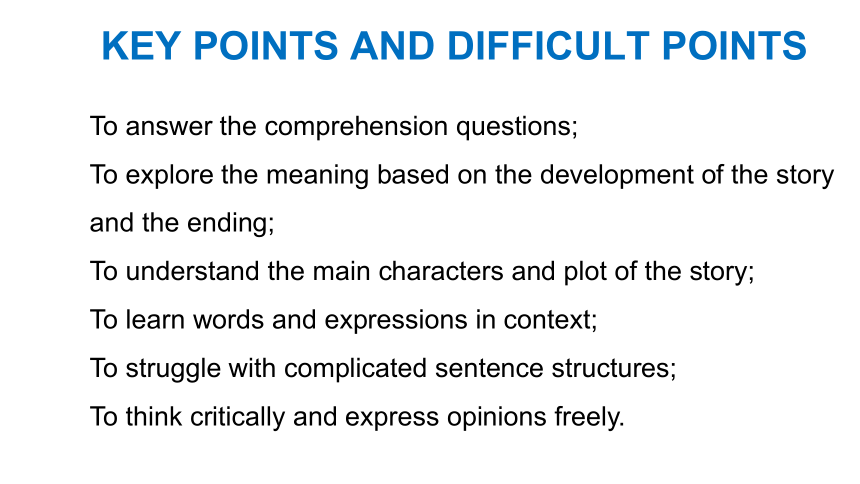
KEY POINTS AND DIFFICULT POINTS
To answer the comprehension questions;
To explore the meaning based on the development of the story and the ending;
To understand the main characters and plot of the story;
To learn words and expressions in context;
To struggle with complicated sentence structures;
To think critically and express opinions freely.
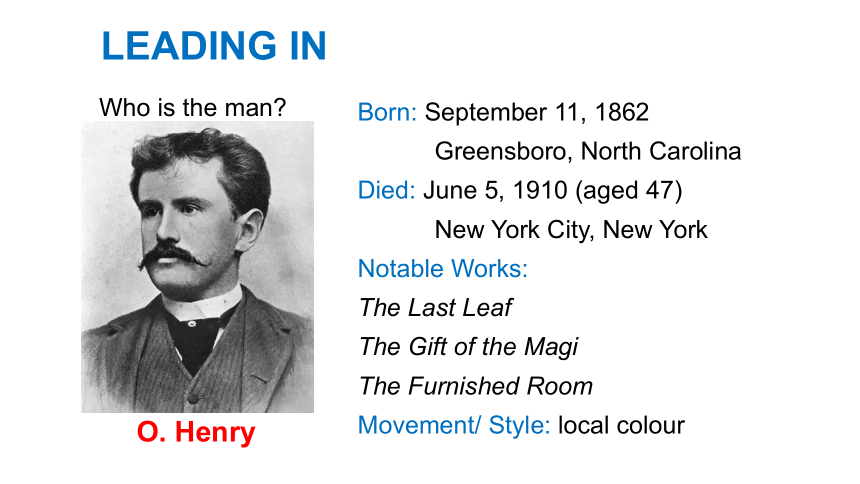
LEADING IN
Born: September 11, 1862
Greensboro, North Carolina
Died: June 5, 1910 (aged 47)
New York City, New York
Notable Works:
The Last Leaf
The Gift of the Magi
The Furnished Room
Movement/ Style: local colour
Who is the man
O. Henry
LEADING IN
O. Henry was an American short story writer, the founder of the American modern short story, whose stories are set in his own time, the early 20th century. Many take place in New York City and frequently feature characters with blue-collar jobs, such as policemen and waitresses. Among them, The Gift of the Magi, The Cop and The Anthem and The Last Leaf enjoy huge popularity.
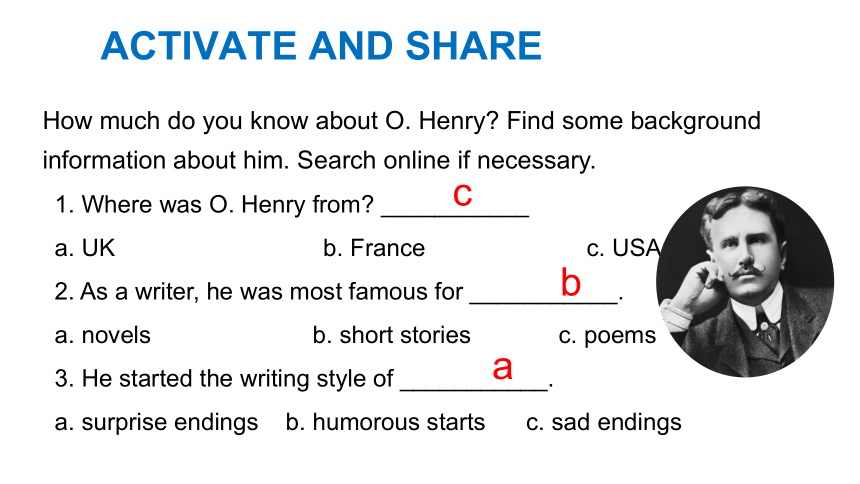
ACTIVATE AND SHARE
How much do you know about O. Henry Find some background information about him. Search online if necessary.
1. Where was O. Henry from ___________
a. UK b. France c. USA
2. As a writer, he was most famous for ___________.
a. novels b. short stories c. poems
3. He started the writing style of ___________.
a. surprise endings b. humorous starts c. sad endings
c
b
a
"The Last Leaf" is one of O. Henry's most famous short stories.
Read the story quickly and answer the questions.
1. Who are the main characters
Sue, Johnsy, Mr Pneumonia, the doctor, and Mr Behrman.
3. What happened at the end
READ AND EXPLORE
2. When and where did the story take place
The story took place in November in Greenwich Village, New York City.
Mr Behrman dies of pneumonia because he painted an ivy leaf for Johnsy in the rain.
READ AND EXPLORE
(Paras.1-2)
(Paras.3-7)
(Paras.8-9)
What is the plot of the story
Scene 1
Scene 2
Scene 3
Johnsy caught pneumonia.
Johnsy decided that she would die when the last ivy leaf fell.
Sue told Behrman about Johnsy’s situation.
(Paras.10-11)
Scene 4
As Johnsy was encouraged by the last leaf, her will to live returned.
(Paras.12-13)
Scene 5
The doctor told Sue that Johnsy would recover, but Behrman caught pneumonia himself and had died.
Pair Work Read the story more carefully. Complete the timeline with what happened in the story. Then tell the story.
READ AND EXPLORE
READ AND EXPLORE
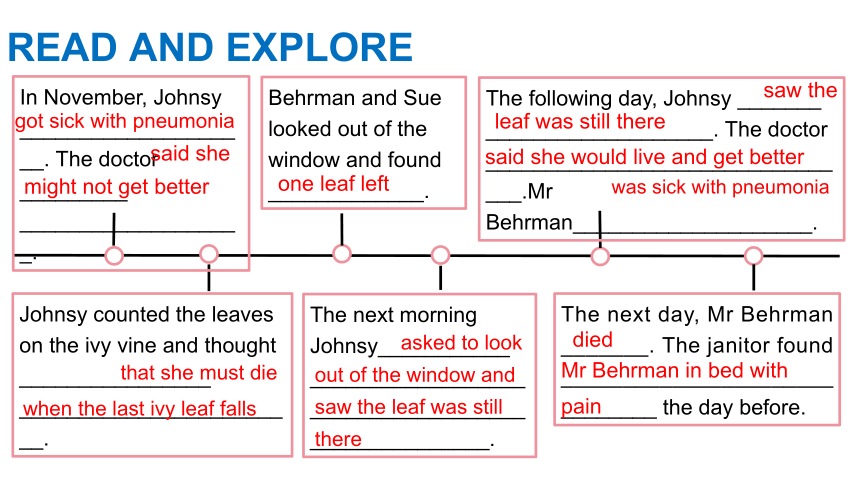
In November, Johnsy ____________________. The doctor _________
___________________.
Johnsy counted the leaves on the ivy vine and thought ________________
________________________.
Behrman and Sue looked out of the window and found _____________.
The next morning Johnsy___________
___________________________________________________.
The next day, Mr Behrman _______. The janitor found ______________________________ the day before.
The following day, Johnsy _______
___________________. The doctor ________________________________.Mr Behrman____________________.
said she
might not get better
one leaf left
that she must die when the last ivy leaf falls
asked to look out of the window and saw the leaf was still there
saw the
said she would live and get better
was sick with pneumonia
died
Mr Behrman in bed with pain
got sick with pneumonia
leaf was still there
Answer the questions.
READ AND EXPLORE
1. When Sue began a pen drawing in Johnsy's room, what did Johnsy do
Johnsy started to count the ivy leaves when Sue began a pen drawing in Johnsy's room.
2. When Sue told Mr Behrman about Johnsy's belief, what was Mr Behrman's response
Mr Behrman cried with disbelief and thought that Johnsy's belief was foolish.
Answer the questions.
READ AND EXPLORE
3. Behrman said, "This is not a place in which Miss Johnsy shall lie sick. Someday I will paint a masterpiece, and we shall all go away." What did he mean
Mr Behrman realised that Johnsy would become better, and that he would paint his masterpiece before they all died.
4. How did Johnsy change her attitude
She saw that the last leaf remained brave and realised that she was wrong to want to die.
Answer the questions.
READ AND EXPLORE
5. What did the janitor find
The janitor found Mr Berhman in bed wearing wet clothes and in terrible pain.
6. Why did Mr Behrman get pneumonia
Mr Berhman got pneumonia because he was outside in the cold rain painting the leaf on the wall.
7. Are there any descriptions that you find impressive Underline them and explain why.
READ AND EXPLORE
Group Work Tell the story from Johnsy's or Sue's point of view.
Example:
In November, I suddenly got sick with pnenmonia. My friend Sue encouraged me, but I felt desperate at that time...
Expressions about feelings:
embarrassed, ashamed, guilty, sensitive, heartbroken, miserable, depressed, discouraged, melancholy, anxious ...
Climax
Falling Action
Rising Action
Johnsy was ill.
Johnsy counted the leaves outside.
The following day, the last leaf was still there. Johnsy survived.
Mr Behrman died.
READ AND EXPLORE
There was only one leaf outside the window.
READ AND EXPLORE
Read paragraph 2 of the story. Answer the questions.
1. How did the writer describe pneumonia
O. Henry described pneumonia as if it were a character. He personified the sickness by saying it placed its finger on Johnsy.
2. Why did he describe pneumonia in this way
He described it in this way in order to make pneumonia scary.
3. How do you feel about the description
READ AND EXPLORE
Pair Work In the story, the writer uses different words to express similar meanings. Read the story and write them down. Then work in pairs and use each word to describe a scene.
say: ______________________________________
see: ______________________________________
die: _______________________________________
claim, ask, reply, cry, tell
look, watch, stare, notice
go, go sailing down, go away, slip away
READ AND EXPLORE
1. What do you think Sue's comment "it's Behrman's masterpiece" means
Group Work Think and share
It was painted true to life that Johnsy didn't even find it was a picture. It is the best art he ever painted because it kept Johnsy hopeful and alive.
2. What do you think the story is trying to express
The story is trying to express how people love and take care of each other. It also invites readers to think about attitudes towards life.
READ AND EXPLORE
3. Does the ending of the story surprise you If yes, how What do you think of such an ending
Group Work Think and share
It is surprising because the reader expects Johnsy to either die or recover, but the reader does not think that Mr Berhman would be affected by Johnsy's sickness.
FOCUS ON LANGUAGE: STATE VERBS AND ACTIVITY VERBS
Look at the following verbs from the text. Which verbs can be used in both simple and continuous tenses Which can be used only in simple tenses
lie have hear find watch
stare notice count fall sail drop
open remain visit wonder encourage
FOCUS ON LANGUAGE: STATE VERBS AND ACTIVITY VERBS
Look at the following verbs from the text. Which verbs can be used in both simple and continuous tenses Which can be used only in simple tenses
Only in simple tenses In both simple and continuous tenses
is arrive
hear, find, notice, remain
lie, have, watch, stare, count, fall, sail, drop, open, visit, wonder, encourage
Can you add other verbs to each column
FOCUS ON LANGUAGE: STATE VERBS AND ACTIVITY VERBS
2. Which sentences cannot be changed into the present continous tense
a. The coffee tastes awful.
b. We have breakfast very early.
c. They feel they need more time.
d. I have a serious headache.
e. She thinks about her mother a lot.
√
√
FOCUS ON LANGUAGE: STATE VERBS AND ACTIVITY VERBS
3. Which of the following sentences are wrong Correct the wrong ones.
1. I'm loving the painting you bought yesterday.
2. Dad is lying on the bed now.
3. We are noticing the changes in the experiment.
1. I love the painting you bought yesterday.
3. We noticed the changes in the experiment.
FOCUS ON LANGUAGE: STATE VERBS AND ACTIVITY VERBS
3. Which of the following sentences are wrong Correct the wrong ones.
4. He's having a bath.
5. Why is he staring at me
6. Where did he drop his suitcase
EXPRESS YOURSELF
1. What typical writing features have you noticed in "The Last Leaf" Give examples.
2. Find more information about O. Henry's stories and his writing style online. Share the information you found with the class.
GRAMMAR
状态动词和动作动词
一、状态动词
状态动词 是表示相对静止状态的动词,通常用于描述人或事物所处的状态,而不是动作。这类动词通常不用于进行时态,因为它们描述的是一种静态的状态或特征。 以下是最常见的状态动词:
GRAMMAR
状态动词和动作动词
1. 表示思维活动的动词:admit, agree, believe, know, mean, prefer, realise, remember, think, understand, want...
He admitted taking the money, but promised never to do it again.
他承认拿了钱,但他保证再也不会做这样的事了。
GRAMMAR
状态动词和动作动词
2. 表示情感的动词:adore, care, like, dislike, love, hate, hope…
Cultural note: we adore potatoes in the UK. They are a comfort food.
文化便签:在英国,我们非常喜欢土豆。土豆是一种非常适宜的食物。
GRAMMAR
状态动词和动作动词
3. 表示拥有和存在的动词:appear, be, belong, contain, have, include, need, seem, possess, stand, lie…
That dictionary belongs to me.
那本字典是属于我的。
We've bought the house, but we can't possess it before July.
我们买下了这栋房子,但要到7月份才能拥有它。
GRAMMAR
状态动词和动作动词
4. 感官动词:feel, hear, look ,see, smell, sound, taste…
This kind of cloth feels very soft.
这种布摸上去很软。
This flower smells very sweet.
这朵花闻起来很香。
GRAMMAR
状态动词和动作动词
注意:
1. 有些状态动词也可以表示动作。在这种语境下,这些动词可以用于进行时态。
2. 感官连系动词feel, smell, sound, taste, look等,其后要使用形容词,而不用副词。
GRAMMAR
状态动词和动作动词
二、动作动词
动作动词一般指实义动词,即行为动词,表示动作的动词。它是意义完整,能独立用作谓语的动词,包括及物动词、不及物动词。动作动词描述动作,可用于一般时态和进行时态。动作动词分为持续性动词和终止性动词。
GRAMMAR
状态动词和动作动词
1. 持续性动词
持续性动词又称延续性动词,表示一种可以持续的行为过程或状态。常见的持续性动词:burn, drink, eat, fly, have, keep, know, lie, live, play, rain, read, run, sing, sleep, smoke, snow, stand, study, talk, wait, walk, wear, work...
GRAMMAR
状态动词和动作动词
2. 终止性动词
终止性动词又称非延续性动词,表示行为或过程是瞬间完成的。常见的终止性动词:admit, arrive, begin, borrow, buy, break, close, come, die, fall, go, hit, join, jump, leave, lose, move , marry, open, put , return, reach, start, stop…
GRAMMAR
状态动词和动作动词
3. 持续性动词与终止性动词的用法
(1)持续性动词可用表示一段时间的状语修饰,而终止性动词则不可。
They will work here till next Friday.
他们要在这里工作到下周五。
He was a French traveller who lived in Italy for some time.
他是一位法国旅行家,在意大利生活过一段时间。
GRAMMAR
状态动词和动作动词
(2)有时,终止性动词也可同表示一段时间的时间状语搭配。但这种表示一段时间的状语,实质上是表示一段时间内的某个时间“点”。
The play will start in half an hour.
戏剧将在半个小时内开始。
The fire broke out during the night.
火灾是夜间发生的。
GRAMMAR
状态动词和动作动词
(3)终止性动词一般不用于while引起的时间状语从句。
While I came home she was cooking dinner. (×)
When I came home she was cooking dinner. (√)
我到家时,她正在做饭。
GRAMMAR
状态动词和动作动词
(4)持续性动词前加 get/ begin/ come to等可表示短暂性动作。
When did you get to know him
你什么时候认识他的?
They began to see that they had made a serious mistake.
他们开始认识到自己犯了一个严重的错误。
GRAMMAR
状态动词和动作动词
(5)常用的持续性动词与终止性动词的对照:
词义 终止性动词 持续性动词
爱上 fall in love with be in love with
联系 get in touch with keep in touch with
穿 put on wear
结婚 marry be married
GRAMMAR
状态动词和动作动词
(5)常用的持续性动词与终止性动词的对照:
词义 终止性动词 持续性动词
认识 get to know know
回来 come back be back
离开 leave be away
死亡 die be dead
VOCABULARY
1. absorbing
absorb vt. 吸收;吸引;使专心
absorb one's attention 吸引某人的注意
absorb…from… 从……中吸收……
be absorbed in 全神贯注于
练习:Children will find other exhibits equally ______________.
absorbing
VOCABULARY
2. contradictory
be contradictory to 与……矛盾/ 对立
contradict v. 反驳;相矛盾
contradiction n. 不一致,矛盾
in contradiction to 与……相矛盾;反之
练习:Customs officials have made a series of _______________ statements about the problem.
contradictory
VOCABULARY
3. significant
It is significant that... ……很重要
a significant difference between…and… ……和……有明显差别
significance n. 重要性,意义
attach (great/ little) importance/ significance to...
认为……(很/ 几乎不) 重要
the significance of… ……的重要性
significantly adv. 有重大意义地;显著地;明显地
练习:There remained one _______________ problem.
significant
VOCABULARY
4. claim
claim to do sth. 声称要做某事
claim sth. back 要回某物
claim sb.'s life 要了某人的命;夺去某人的生命
It is claimed that… 据称……
make a claim for sth. 提出对某事物的赔偿要求
练习:The situation remains confused as both sides _________ success.
claim
VOCABULARY
5. attempt
attempt to do sth. 尝试/ 努力做某事
make an attempt to do/ at doing sth. 试图/ 努力做某事
at the first attempt 第一次尝试时
in an attempt to do… 试图做……
attempted adj. 未遂的 attempted murder 谋杀未遂
练习:He dived into his pocket in an _________ to find the key.
attempt
VOCABULARY
6. disbelief
in disbelief 难以置信地,怀疑地 with disbelief 难以置信地
belief n. 信仰;信念;相信,信心
beyond belief 令人难以置信 hold the belief that... 相信……
It's one's belief that... = One's belief is that… 某人相信……
练习:Liz stared at us in _____________ as we told her what had happened.
disbelief
LANGUAGE POINTS
1. ...where the art people came together, hunting for apartments with north-facing windows and low rents.
hunt for 寻找;搜寻
He is hunting for a proper shelf to keep all the books he has collected these years.
他正在寻找一个合适的书架来存放他这些年收集的所有的书。
hunt after 追猎(某动物);追逐(某物)
Many people hunt after fame in their lives but never find it.
很多人一生追逐名望,但总是不能成功。
LANGUAGE POINTS
2. ...she lay, barely moving, in her bed staring at a blank wall under her blanket.
blank
(1)空白的
When asked to recite the poem he hadn’t prepared, the boy went blank.
当被要求背诵没有准备好的诗时,那个男孩脑子一片空白。
(2)没表情的;不理解的
There was a blank look on his face.
他面无表情。
LANGUAGE POINTS
3. I’m tired of waiting.
be tired of 厌倦;厌烦
be tired of 表厌倦的状态;get/become tired of 表厌倦的动作。
I don’t know about you,but I am sick and tired of this weather.
我不知道你怎么样,不过我对这样的天气厌烦透了。(状态)
I get tired of(playing)this game. Let’s play something else.
我厌倦了(玩)这个游戏。我们玩别的吧。(动作)
be/get tired from... 因……而疲倦
be/feel/get tired out 疲惫不堪,筋疲力尽
PRACTICE
1. He _____________ (has joined/ has been) in the army for three years.
2. There _____________ (stands/ is standing) an old temple on the top of the hill.
3. Look, she _____________ (has/ is having) some tea in the bar.
4. She _____________________ (has been married/ has married) for seven years and has two sons.
has been
stands
is having
has been married
SUMMARY
Read and talk about the main character and plot of the story;
Recognize the point of view of multiple characters in a piece of literature;
Explore the meaning based on the development of the story and the ending;
Compare personal opinions with the ideas of others;
Read for general understanding and specific information;
Understand and learn words and expressions in context;
Learn and practice using state verbs and activity verbs.
Thank you
UNIT 8 LITERATURE
LESSON 1
THE LAST LEAF
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
To read and talk about the main character and plot of the story;
To recognize the point of view of multiple characters in a piece of literature;
To compare personal opinions with the ideas of others;
To read for specific information to understand words in context;
To recall and summarise information;
To learn and practise using state verbs and activity verbs.
KEY POINTS AND DIFFICULT POINTS
To answer the comprehension questions;
To explore the meaning based on the development of the story and the ending;
To understand the main characters and plot of the story;
To learn words and expressions in context;
To struggle with complicated sentence structures;
To think critically and express opinions freely.
LEADING IN
Born: September 11, 1862
Greensboro, North Carolina
Died: June 5, 1910 (aged 47)
New York City, New York
Notable Works:
The Last Leaf
The Gift of the Magi
The Furnished Room
Movement/ Style: local colour
Who is the man
O. Henry
LEADING IN
O. Henry was an American short story writer, the founder of the American modern short story, whose stories are set in his own time, the early 20th century. Many take place in New York City and frequently feature characters with blue-collar jobs, such as policemen and waitresses. Among them, The Gift of the Magi, The Cop and The Anthem and The Last Leaf enjoy huge popularity.
ACTIVATE AND SHARE
How much do you know about O. Henry Find some background information about him. Search online if necessary.
1. Where was O. Henry from ___________
a. UK b. France c. USA
2. As a writer, he was most famous for ___________.
a. novels b. short stories c. poems
3. He started the writing style of ___________.
a. surprise endings b. humorous starts c. sad endings
c
b
a
"The Last Leaf" is one of O. Henry's most famous short stories.
Read the story quickly and answer the questions.
1. Who are the main characters
Sue, Johnsy, Mr Pneumonia, the doctor, and Mr Behrman.
3. What happened at the end
READ AND EXPLORE
2. When and where did the story take place
The story took place in November in Greenwich Village, New York City.
Mr Behrman dies of pneumonia because he painted an ivy leaf for Johnsy in the rain.
READ AND EXPLORE
(Paras.1-2)
(Paras.3-7)
(Paras.8-9)
What is the plot of the story
Scene 1
Scene 2
Scene 3
Johnsy caught pneumonia.
Johnsy decided that she would die when the last ivy leaf fell.
Sue told Behrman about Johnsy’s situation.
(Paras.10-11)
Scene 4
As Johnsy was encouraged by the last leaf, her will to live returned.
(Paras.12-13)
Scene 5
The doctor told Sue that Johnsy would recover, but Behrman caught pneumonia himself and had died.
Pair Work Read the story more carefully. Complete the timeline with what happened in the story. Then tell the story.
READ AND EXPLORE
READ AND EXPLORE
In November, Johnsy ____________________. The doctor _________
___________________.
Johnsy counted the leaves on the ivy vine and thought ________________
________________________.
Behrman and Sue looked out of the window and found _____________.
The next morning Johnsy___________
___________________________________________________.
The next day, Mr Behrman _______. The janitor found ______________________________ the day before.
The following day, Johnsy _______
___________________. The doctor ________________________________.Mr Behrman____________________.
said she
might not get better
one leaf left
that she must die when the last ivy leaf falls
asked to look out of the window and saw the leaf was still there
saw the
said she would live and get better
was sick with pneumonia
died
Mr Behrman in bed with pain
got sick with pneumonia
leaf was still there
Answer the questions.
READ AND EXPLORE
1. When Sue began a pen drawing in Johnsy's room, what did Johnsy do
Johnsy started to count the ivy leaves when Sue began a pen drawing in Johnsy's room.
2. When Sue told Mr Behrman about Johnsy's belief, what was Mr Behrman's response
Mr Behrman cried with disbelief and thought that Johnsy's belief was foolish.
Answer the questions.
READ AND EXPLORE
3. Behrman said, "This is not a place in which Miss Johnsy shall lie sick. Someday I will paint a masterpiece, and we shall all go away." What did he mean
Mr Behrman realised that Johnsy would become better, and that he would paint his masterpiece before they all died.
4. How did Johnsy change her attitude
She saw that the last leaf remained brave and realised that she was wrong to want to die.
Answer the questions.
READ AND EXPLORE
5. What did the janitor find
The janitor found Mr Berhman in bed wearing wet clothes and in terrible pain.
6. Why did Mr Behrman get pneumonia
Mr Berhman got pneumonia because he was outside in the cold rain painting the leaf on the wall.
7. Are there any descriptions that you find impressive Underline them and explain why.
READ AND EXPLORE
Group Work Tell the story from Johnsy's or Sue's point of view.
Example:
In November, I suddenly got sick with pnenmonia. My friend Sue encouraged me, but I felt desperate at that time...
Expressions about feelings:
embarrassed, ashamed, guilty, sensitive, heartbroken, miserable, depressed, discouraged, melancholy, anxious ...
Climax
Falling Action
Rising Action
Johnsy was ill.
Johnsy counted the leaves outside.
The following day, the last leaf was still there. Johnsy survived.
Mr Behrman died.
READ AND EXPLORE
There was only one leaf outside the window.
READ AND EXPLORE
Read paragraph 2 of the story. Answer the questions.
1. How did the writer describe pneumonia
O. Henry described pneumonia as if it were a character. He personified the sickness by saying it placed its finger on Johnsy.
2. Why did he describe pneumonia in this way
He described it in this way in order to make pneumonia scary.
3. How do you feel about the description
READ AND EXPLORE
Pair Work In the story, the writer uses different words to express similar meanings. Read the story and write them down. Then work in pairs and use each word to describe a scene.
say: ______________________________________
see: ______________________________________
die: _______________________________________
claim, ask, reply, cry, tell
look, watch, stare, notice
go, go sailing down, go away, slip away
READ AND EXPLORE
1. What do you think Sue's comment "it's Behrman's masterpiece" means
Group Work Think and share
It was painted true to life that Johnsy didn't even find it was a picture. It is the best art he ever painted because it kept Johnsy hopeful and alive.
2. What do you think the story is trying to express
The story is trying to express how people love and take care of each other. It also invites readers to think about attitudes towards life.
READ AND EXPLORE
3. Does the ending of the story surprise you If yes, how What do you think of such an ending
Group Work Think and share
It is surprising because the reader expects Johnsy to either die or recover, but the reader does not think that Mr Berhman would be affected by Johnsy's sickness.
FOCUS ON LANGUAGE: STATE VERBS AND ACTIVITY VERBS
Look at the following verbs from the text. Which verbs can be used in both simple and continuous tenses Which can be used only in simple tenses
lie have hear find watch
stare notice count fall sail drop
open remain visit wonder encourage
FOCUS ON LANGUAGE: STATE VERBS AND ACTIVITY VERBS
Look at the following verbs from the text. Which verbs can be used in both simple and continuous tenses Which can be used only in simple tenses
Only in simple tenses In both simple and continuous tenses
is arrive
hear, find, notice, remain
lie, have, watch, stare, count, fall, sail, drop, open, visit, wonder, encourage
Can you add other verbs to each column
FOCUS ON LANGUAGE: STATE VERBS AND ACTIVITY VERBS
2. Which sentences cannot be changed into the present continous tense
a. The coffee tastes awful.
b. We have breakfast very early.
c. They feel they need more time.
d. I have a serious headache.
e. She thinks about her mother a lot.
√
√
FOCUS ON LANGUAGE: STATE VERBS AND ACTIVITY VERBS
3. Which of the following sentences are wrong Correct the wrong ones.
1. I'm loving the painting you bought yesterday.
2. Dad is lying on the bed now.
3. We are noticing the changes in the experiment.
1. I love the painting you bought yesterday.
3. We noticed the changes in the experiment.
FOCUS ON LANGUAGE: STATE VERBS AND ACTIVITY VERBS
3. Which of the following sentences are wrong Correct the wrong ones.
4. He's having a bath.
5. Why is he staring at me
6. Where did he drop his suitcase
EXPRESS YOURSELF
1. What typical writing features have you noticed in "The Last Leaf" Give examples.
2. Find more information about O. Henry's stories and his writing style online. Share the information you found with the class.
GRAMMAR
状态动词和动作动词
一、状态动词
状态动词 是表示相对静止状态的动词,通常用于描述人或事物所处的状态,而不是动作。这类动词通常不用于进行时态,因为它们描述的是一种静态的状态或特征。 以下是最常见的状态动词:
GRAMMAR
状态动词和动作动词
1. 表示思维活动的动词:admit, agree, believe, know, mean, prefer, realise, remember, think, understand, want...
He admitted taking the money, but promised never to do it again.
他承认拿了钱,但他保证再也不会做这样的事了。
GRAMMAR
状态动词和动作动词
2. 表示情感的动词:adore, care, like, dislike, love, hate, hope…
Cultural note: we adore potatoes in the UK. They are a comfort food.
文化便签:在英国,我们非常喜欢土豆。土豆是一种非常适宜的食物。
GRAMMAR
状态动词和动作动词
3. 表示拥有和存在的动词:appear, be, belong, contain, have, include, need, seem, possess, stand, lie…
That dictionary belongs to me.
那本字典是属于我的。
We've bought the house, but we can't possess it before July.
我们买下了这栋房子,但要到7月份才能拥有它。
GRAMMAR
状态动词和动作动词
4. 感官动词:feel, hear, look ,see, smell, sound, taste…
This kind of cloth feels very soft.
这种布摸上去很软。
This flower smells very sweet.
这朵花闻起来很香。
GRAMMAR
状态动词和动作动词
注意:
1. 有些状态动词也可以表示动作。在这种语境下,这些动词可以用于进行时态。
2. 感官连系动词feel, smell, sound, taste, look等,其后要使用形容词,而不用副词。
GRAMMAR
状态动词和动作动词
二、动作动词
动作动词一般指实义动词,即行为动词,表示动作的动词。它是意义完整,能独立用作谓语的动词,包括及物动词、不及物动词。动作动词描述动作,可用于一般时态和进行时态。动作动词分为持续性动词和终止性动词。
GRAMMAR
状态动词和动作动词
1. 持续性动词
持续性动词又称延续性动词,表示一种可以持续的行为过程或状态。常见的持续性动词:burn, drink, eat, fly, have, keep, know, lie, live, play, rain, read, run, sing, sleep, smoke, snow, stand, study, talk, wait, walk, wear, work...
GRAMMAR
状态动词和动作动词
2. 终止性动词
终止性动词又称非延续性动词,表示行为或过程是瞬间完成的。常见的终止性动词:admit, arrive, begin, borrow, buy, break, close, come, die, fall, go, hit, join, jump, leave, lose, move , marry, open, put , return, reach, start, stop…
GRAMMAR
状态动词和动作动词
3. 持续性动词与终止性动词的用法
(1)持续性动词可用表示一段时间的状语修饰,而终止性动词则不可。
They will work here till next Friday.
他们要在这里工作到下周五。
He was a French traveller who lived in Italy for some time.
他是一位法国旅行家,在意大利生活过一段时间。
GRAMMAR
状态动词和动作动词
(2)有时,终止性动词也可同表示一段时间的时间状语搭配。但这种表示一段时间的状语,实质上是表示一段时间内的某个时间“点”。
The play will start in half an hour.
戏剧将在半个小时内开始。
The fire broke out during the night.
火灾是夜间发生的。
GRAMMAR
状态动词和动作动词
(3)终止性动词一般不用于while引起的时间状语从句。
While I came home she was cooking dinner. (×)
When I came home she was cooking dinner. (√)
我到家时,她正在做饭。
GRAMMAR
状态动词和动作动词
(4)持续性动词前加 get/ begin/ come to等可表示短暂性动作。
When did you get to know him
你什么时候认识他的?
They began to see that they had made a serious mistake.
他们开始认识到自己犯了一个严重的错误。
GRAMMAR
状态动词和动作动词
(5)常用的持续性动词与终止性动词的对照:
词义 终止性动词 持续性动词
爱上 fall in love with be in love with
联系 get in touch with keep in touch with
穿 put on wear
结婚 marry be married
GRAMMAR
状态动词和动作动词
(5)常用的持续性动词与终止性动词的对照:
词义 终止性动词 持续性动词
认识 get to know know
回来 come back be back
离开 leave be away
死亡 die be dead
VOCABULARY
1. absorbing
absorb vt. 吸收;吸引;使专心
absorb one's attention 吸引某人的注意
absorb…from… 从……中吸收……
be absorbed in 全神贯注于
练习:Children will find other exhibits equally ______________.
absorbing
VOCABULARY
2. contradictory
be contradictory to 与……矛盾/ 对立
contradict v. 反驳;相矛盾
contradiction n. 不一致,矛盾
in contradiction to 与……相矛盾;反之
练习:Customs officials have made a series of _______________ statements about the problem.
contradictory
VOCABULARY
3. significant
It is significant that... ……很重要
a significant difference between…and… ……和……有明显差别
significance n. 重要性,意义
attach (great/ little) importance/ significance to...
认为……(很/ 几乎不) 重要
the significance of… ……的重要性
significantly adv. 有重大意义地;显著地;明显地
练习:There remained one _______________ problem.
significant
VOCABULARY
4. claim
claim to do sth. 声称要做某事
claim sth. back 要回某物
claim sb.'s life 要了某人的命;夺去某人的生命
It is claimed that… 据称……
make a claim for sth. 提出对某事物的赔偿要求
练习:The situation remains confused as both sides _________ success.
claim
VOCABULARY
5. attempt
attempt to do sth. 尝试/ 努力做某事
make an attempt to do/ at doing sth. 试图/ 努力做某事
at the first attempt 第一次尝试时
in an attempt to do… 试图做……
attempted adj. 未遂的 attempted murder 谋杀未遂
练习:He dived into his pocket in an _________ to find the key.
attempt
VOCABULARY
6. disbelief
in disbelief 难以置信地,怀疑地 with disbelief 难以置信地
belief n. 信仰;信念;相信,信心
beyond belief 令人难以置信 hold the belief that... 相信……
It's one's belief that... = One's belief is that… 某人相信……
练习:Liz stared at us in _____________ as we told her what had happened.
disbelief
LANGUAGE POINTS
1. ...where the art people came together, hunting for apartments with north-facing windows and low rents.
hunt for 寻找;搜寻
He is hunting for a proper shelf to keep all the books he has collected these years.
他正在寻找一个合适的书架来存放他这些年收集的所有的书。
hunt after 追猎(某动物);追逐(某物)
Many people hunt after fame in their lives but never find it.
很多人一生追逐名望,但总是不能成功。
LANGUAGE POINTS
2. ...she lay, barely moving, in her bed staring at a blank wall under her blanket.
blank
(1)空白的
When asked to recite the poem he hadn’t prepared, the boy went blank.
当被要求背诵没有准备好的诗时,那个男孩脑子一片空白。
(2)没表情的;不理解的
There was a blank look on his face.
他面无表情。
LANGUAGE POINTS
3. I’m tired of waiting.
be tired of 厌倦;厌烦
be tired of 表厌倦的状态;get/become tired of 表厌倦的动作。
I don’t know about you,but I am sick and tired of this weather.
我不知道你怎么样,不过我对这样的天气厌烦透了。(状态)
I get tired of(playing)this game. Let’s play something else.
我厌倦了(玩)这个游戏。我们玩别的吧。(动作)
be/get tired from... 因……而疲倦
be/feel/get tired out 疲惫不堪,筋疲力尽
PRACTICE
1. He _____________ (has joined/ has been) in the army for three years.
2. There _____________ (stands/ is standing) an old temple on the top of the hill.
3. Look, she _____________ (has/ is having) some tea in the bar.
4. She _____________________ (has been married/ has married) for seven years and has two sons.
has been
stands
is having
has been married
SUMMARY
Read and talk about the main character and plot of the story;
Recognize the point of view of multiple characters in a piece of literature;
Explore the meaning based on the development of the story and the ending;
Compare personal opinions with the ideas of others;
Read for general understanding and specific information;
Understand and learn words and expressions in context;
Learn and practice using state verbs and activity verbs.
Thank you
