Unit 1 Laugh out loud! Using ideas课件(共40张PPT)-高中英语外研版(2019)选择性必修第一册(共41页PPT)
文档属性
| 名称 | Unit 1 Laugh out loud! Using ideas课件(共40张PPT)-高中英语外研版(2019)选择性必修第一册(共41页PPT) |  | |
| 格式 | pptx | ||
| 文件大小 | 29.3MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 外研版(2019) | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2025-06-13 18:23:17 | ||
图片预览







文档简介
(共40张PPT)
Using language
Unit 1
Laugh
out loud!
Learning Objectives
PART. 01
Understand the daily study and life of British middle school students by watching videos. Based on your own daily study and life, compare the study and life in Chinese and British schools, and find out the similarities and differences between the two. Talk about your first impression of high school life, and have a preliminary perception of the study and life in the senior high school stage.
Learning Objectives
Be able to distinguish between defining and non-defining attributive clauses, and accurately use non-defining attributive clauses in writing. Master English idioms related to “laughs”, expand their vocabulary of idiomatic expressions.
Perceive the positive attitude towards life, and understand the cultural emphasis on optimism and humor in dealing with difficulties.
Stimulate creative thinking when exploring similar English idioms, and the ability to make logical comments on humorous stories.
Actively apply learned language points in real-life situations, cultivating the habit of using English for practical communication and continuous language practice.
Understand the daily study and life of British middle school students by watching videos. Based on your own daily study and life, compare the study and life in Chinese and British schools, and find out the similarities and differences between the two. Talk about your first impression of high school life, and have a preliminary perception of the study and life in the senior high school stage.
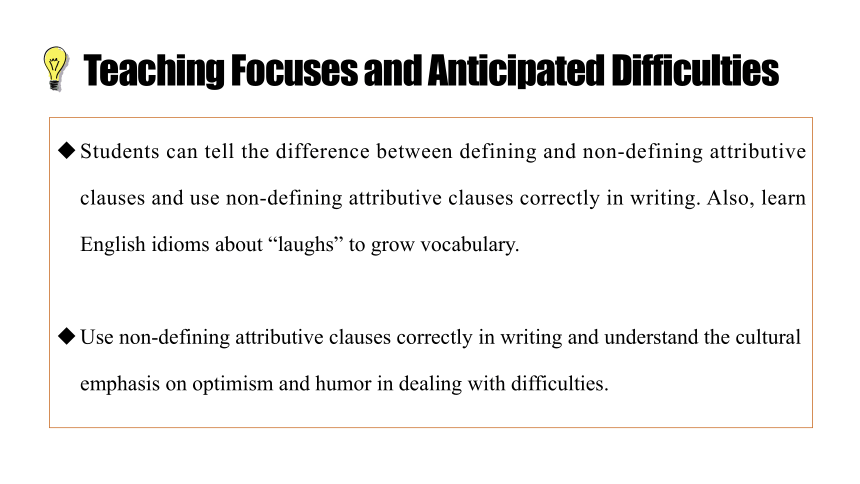
Teaching Focuses and Anticipated Difficulties
Students can tell the difference between defining and non-defining attributive clauses and use non-defining attributive clauses correctly in writing. Also, learn English idioms about “laughs” to grow vocabulary.
Use non-defining attributive clauses correctly in writing and understand the cultural emphasis on optimism and humor in dealing with difficulties.
Grammar
PART. 02
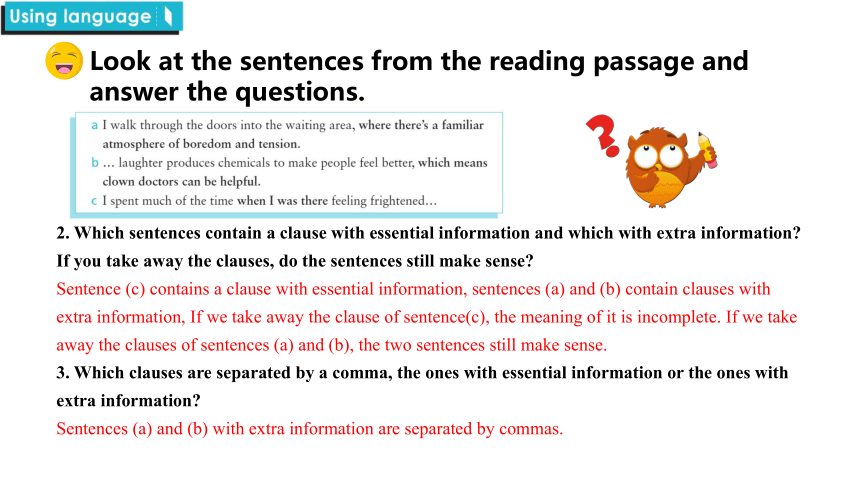
Look at the sentences from the reading passage and answer the questions.
1. What do “where”, “which” and “when” refer to in each sentence
In sentence (a) “where” refers to “the waiting area”; in sentence (b) “which” refers to ”... laughter produces chemicals to make people feel better”; in sentence (c) “when” refers to “the time”.
Look at the sentences from the reading passage and answer the questions.
2. Which sentences contain a clause with essential information and which with extra information If you take away the clauses, do the sentences still make sense
Sentence (c) contains a clause with essential information, sentences (a) and (b) contain clauses with extra information, If we take away the clause of sentence(c), the meaning of it is incomplete. If we take away the clauses of sentences (a) and (b), the two sentences still make sense.
3. Which clauses are separated by a comma, the ones with essential information or the ones with extra information
Sentences (a) and (b) with extra information are separated by commas.
Non-defining attributive clauses (非限制性定语从句)
定语从句:在复合句中用来限制、描绘或说明主句中某一名词或代词而起定语作用的从句。
先行词:定语从句所修饰的名词或代词叫作先行词。先行词可以是人、物,也可以是整个句子或者句子的一部分,先行词一般位于定语从句之前。
She is a kind teacher who often helps students with their problems.
Tom decided to start his own business, which amazed his parents.
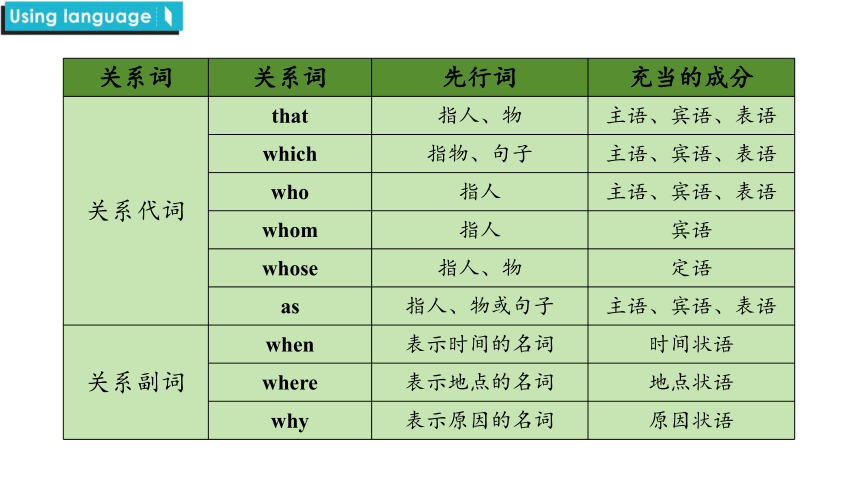
关系词:引导定语从句的词叫作关系词。按照关系词在定语从句中所作的成分,可将关系词分为关系代词和关系副词。
The beautiful city which/that we visited last summer is Hangzhou.
This is the place where I met my best friend.
关系词 关系词 先行词 充当的成分
关系代词 that 指人、物 主语、宾语、表语
which 指物、句子 主语、宾语、表语
who 指人 主语、宾语、表语
whom 指人 宾语
whose 指人、物 定语
as 指人、物或句子 主语、宾语、表语
关系副词 when 表示时间的名词 时间状语
where 表示地点的名词 地点状语
why 表示原因的名词 原因状语
一、定语从句的分类
1. 限制性定语从句
限制性定语从句对先行词起修饰、限制作用,是句中不可缺少的部分,主句和从句关系非常紧密,不能用逗号分开。
He bought the book that/which is recommended by the teacher.
2. 非限制性定语从句
非限制性定语从句往往是对先行词或整个主句进行附加说明,主从句的关系并不十分密切,若将其去掉,主句的意义仍然完整清楚。从句和主句之间往往用逗号隔开。除了that和why不能引导之外,所有其他关系词如 who, whom, which, whose, as, when,where 等均可引导。
Beijing, which is the capital of China, has a long history.
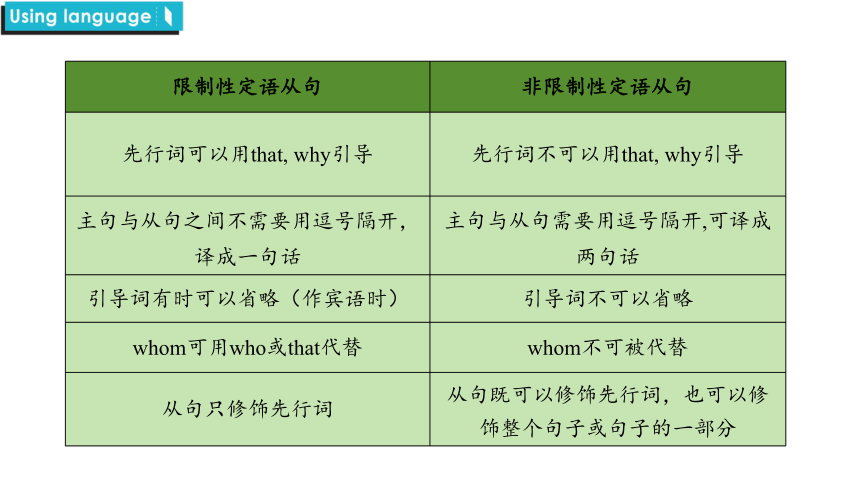
限制性定语从句 非限制性定语从句
先行词可以用that, why引导 先行词不可以用that, why引导
主句与从句之间不需要用逗号隔开,译成一句话 主句与从句需要用逗号隔开,可译成两句话
引导词有时可以省略(作宾语时) 引导词不可以省略
whom可用who或that代替 whom不可被代替
从句只修饰先行词 从句既可以修饰先行词,也可以修饰整个句子或句子的一部分
二、非限制性定语从句的使用情况
1. 当关系代词指代整个主句内容时,用非限制性定语从句(用which或as引导)。
She won the first prize in the competition, which made her classmates really proud.
她在比赛中得了一等奖,这让她的同学们特别骄傲。
2. 当先行词指的是世界上独一无二的事物或专有名词时,用非限制性定语从句。
The Great Wall, which stands as a symbol of Chinese history, attracts millions of tourists yearly.
长城作为中国历史的象征,每年吸引数百万游客。
Mount Qomolangma, which is the highest peak on Earth, has inspired adventurers.
珠穆朗玛峰是地球最高峰,激励了探险者 。
3. 先行词指某人的亲属关系,具有唯一性和确认性时,例如son, daughter, father, mother, wife 等,用非限制性定语从句。
Her mother, who runs a popular bakery downtown, often shares homemade pastries with neighbors.
她妈妈在市中心经营一家很火的面包店,经常给邻居分享自制糕点。
4. 当引导定语从句的关系代词中,含有some/many/few/a few/little/a little/none/ much/most/half of which (whom)等时,多用非限制性定语从句。
The library has hundreds of old books, few of which have been digitized so far.
图书馆藏有数百本古籍,目前很少有被数字化的。
三、关系代词引导的非限制性定语从句
1. which 指物,在定语从句中作主语或宾语。
I bought a hand-made vase yesterday, which was crafted by a local artisan.
我昨天买了一个手工花瓶,是当地一位工匠制作的。
2. who 指人,在定语从句中作主语或宾语。
Anna, who is an environmental volunteer, often organizes beach-cleaning activities.
安娜是一名环保志愿者,经常组织海滩清理活动。
3. whom 指人,在非限制性定语从句中作宾语,一般不能省略。
Peter, whom you met in London, is going to Paris next week.
你在伦敦见过的那个彼得,下周将要去巴黎。
4. whose 既可指人,也可指物,在定语从句中作定语。
The girl, whose grandmother is a famous folk artist, loves traditional handicrafts.
这个女孩热爱传统手工艺品,她的奶奶是知名民间艺人 。
The old house, whose roof was damaged in the storm, needs urgent repairs.
这座老房子的屋顶在暴风雨中受损了,急需修缮。
5. as 既可指人,也可指物,在定语从句中可以作主语或宾语。
He forgot to bring his pen with him, as was often the case.
他忘了带笔,这是常有的事。
As we all recognize, protecting wildlife is key to ecological balance.
众所周知,保护野生动物对生态平衡至关重要 。
四、as与which引导的非限制性定语从句的区别
1. as引导定语从句时,仍具有“正如,像,由……可知”等意思,这些字眼翻译时可 不必译出。as定语从句中常含有这些动词:see, know, hear, watch, remember, say, tell, show, expect, guess等。这类动词与as连用几乎成了一种固定搭配。as引导的定语从句可以置于句首、句中或向尾。
She is always working hard, as everyone can see.
正如大家所看到的那样,她一直工作很努力。
2. 在从句中作定语或介词的宾语时,要用 which。
My cousins might visit this weekend, in which situation we’ll prepare a big dinner.
我的表兄妹们这周末可能来,要是那样的话,我们就准备一顿丰盛的晚餐。
3. which引导的从句对主句所叙述的事情进行补充说明表明事物的状态或结果。
which此时指前面主句所提到的这件事,常译为“这一点,这件事”等。这时它所引导的从句与主句之间常表示并列意义或状语意义。注意它引导的从句不像as那样位置灵活,它只能位于主句的后面。
The school canceled the outdoor activity, which disappointed all the students.
学校取消了户外活动,这让所有学生都很失望。
4. 当从句的谓语是否定形式或含着一个复合宾语时,一般用which而不用as。
He avoided joining the football team, which his coach couldn’t figure out.
他回避加入足球队,教练一直搞不懂这事。
五、关系副词引导的非限制性定语从句
1. 关系副词when在非限制性定语从句中作时间状语,指代主句中表示时间的词语。
We moved the family gathering to Sunday, when all relatives can attend.
我们把家庭聚会改到周日,那时所有亲戚都能参加。
2. 副词where在非限制性定语从句中作地点状语,指代主句中表示地点的词语。
The volunteers went to the countryside, where they helped build a new library.
志愿者们去了乡村,在那儿帮忙建了一座新图书馆。
They toured the historical district, where ancient buildings are well-preserved.
他们游览了历史街区,那儿的古建筑保存得很好。
Read the passage and rewrite the tips using non-defining attributive clauses. Add more tips to the list if you can.
Go for a walk in the countryside, where you can enjoy the beautiful views and a peaceful atmosphere.
Spend time with your family and friends, which will activate chemicals in your brain to make you feel happier.
Try to accept your mistakes, where/through which you can learn a lot.
Close your eyes and picture the future, where you’ve made your dreams come true.
Complete the joke with the sentence parts in the box using who/which and put commas in the correct position.
One day, Sherlock Holmes and Dr Watson go camping. They put up their tent under the stars and go to sleep. Suddenly, in the middle of the night, Watson is woken up by Holmes 1______________________. “Watson,” Holmes says, “look up at the stars, and tell me what they tell you. ” Not quite sure what he means, Watson thinks Holmes is joking 2_______________________ at this time of night. Even so, he replies, “I see millions of stars and it’s quite likely there are some planets like Earth. And if so, this means that there might also be life on other planets. ” Watson is pleased with his answer 3___________________________________. But Holmes 4_____________________________ shouts, “Watson, look around you! Use your eyes! Somebody’s stolen our tent!”
, who is lying next to him
, which he finds annoying
, which he thinks will impress Holmes
, who has lost his patience by now,
has lost his patience by now he thinks will impress Holmes
is lying next to him he finds annoying
Listen and complete the conversations.
a smile
ear to ear
head off
smiles
laughing
Match the expressions you have completed in Activity 5 to their meanings.
laughing stock
be all smiles
grin from ear to ear
crack a smile
laugh one’s head off
Now work in groups and think of more expressions about laughter.
Work in pairs. Discuss other situations in which you could use these expressions.
You may start like this:
A: Tom must have passed that really hard test.
B: Why do you think so
A: Because he was grinning from ear to ear yesterday when I met him.
Listening
PART. 03
April Fool’s Day is on 1 April. It’s the one day of the year when people in many parts of the world play practical jokes on each other. Even newspapers, radio and TV stations play tricks on their readers and audiences. The jokes traditionally last until noon in the UK. But in some other countries, such as the US, they can last all day!
Did You Know
Listen to the radio programme and choose the pictures mentioned.
a
b
c
d
Listen again and complete the notes.
Now work in pairs. Discuss which of the practical jokes you think is funny.
“the washing of the lions”
18th and 19th centuries
1965
BBC News Channel
smells to be carried
1957
a really good harvest
a
c
d
Complete the boxes with expressions from the radio programme.
Let’s start with...
Now, my favourite one...
It’s a good one!
I don’t get it.
That’s so funny!
I can imagine!
Work in pairs. Tell each other a funny story and make comments using the expressions in this section.
Now give feedback on each other’s stories and help your partner to improve theirs.
Vocabulary
1. essential
essentially adv. 本质上,根本上
be essential to/for… 对……极其重要
It is essential that... (should ) do... ……极其重要
essential conditions 必要条件
It is essential (for sb.) to do sth (对某人来说)做某事是极其重要的/必不可少的
例题:
The debate over artificial intelligence is __________(essential) a discussion about how technology will reshape human society, ethics, and the future of work.
essentially
Vocabulary
2. impress
impression n. 印象 impressive adj. 令人钦佩的,给人深刻印象的
impress sb. with sth. 某事/ 物给某人留下深刻印象
be impressed with/by 对……印象深刻
impress sth. on sb. 使某人了解某事的重要性
impress sth. on one's mind/memory 使某人把……铭记在心
It impresses sb. that 令某人钦佩的是
leave/make a (n) impression on sb. 给某人留下……印象
例题:
Traveling abroad can change your ___________(impress) of the world.
impression
Vocabulary
3. deserve
deserve to do sth. 值得做某事,应该做某事
deserve all/everything sb. get 罪有应得
deserve consideration/attention 值得考虑/ 注意
例题:
Those who spread false information and harm others’ reputations deserve ______(face) legal consequences for their actions.
to face
Exercise
PART. 04
1. Reducing single-use plastics and promoting recycling are e________(极其重要的) steps toward creating a more sustainable and eco-friendly planet.
2. Children living in poverty d_________(应得) equal access to quality education and healthcare to build a brighter future.
3. The student’s comprehensive understanding of the subject matter i_________(使留下深刻印象) the professor, who praised her ability to analyze complex theories critically.
ssential
Exercise: 单词拼写
eserve
mpressed
Li Hua, ______ is my deskmate, won the English speech contest.
The new library, ______ was built last year, has a large collection of books.
My father, ______ you met at the party, is a doctor.
The town, ______ I grew up, holds many sweet memories.
He missed the train, ______ made him late for work.
Her car, ______ color is bright red, stands out in the parking lot.
The summer holiday, ______ we plan to travel abroad, is coming soon.
Mr. Smith, ______ son is in my class, often volunteers at the community center.
who
Exercise: 用合适的关系词填空
which
whom
where
which
whose
when
whose
Summary
PART. 05
Using language
Grammar
Vocabulary
Listening
非限制性定语从句
定语从句的分类
非限制性定语从句的使用情况
关系代词引导的非限制性定语从句
as与which引导的非限制性定语从句的区别
关系副词引导的非限制性定语从句
Homework
PART. 06
Review what you have learnt in this class;
Think of a joke you find funny and write it down using non-defining attributive clauses where appropriate.
Homework
See you next class!
Using language
Unit 1
Laugh
out loud!
Learning Objectives
PART. 01
Understand the daily study and life of British middle school students by watching videos. Based on your own daily study and life, compare the study and life in Chinese and British schools, and find out the similarities and differences between the two. Talk about your first impression of high school life, and have a preliminary perception of the study and life in the senior high school stage.
Learning Objectives
Be able to distinguish between defining and non-defining attributive clauses, and accurately use non-defining attributive clauses in writing. Master English idioms related to “laughs”, expand their vocabulary of idiomatic expressions.
Perceive the positive attitude towards life, and understand the cultural emphasis on optimism and humor in dealing with difficulties.
Stimulate creative thinking when exploring similar English idioms, and the ability to make logical comments on humorous stories.
Actively apply learned language points in real-life situations, cultivating the habit of using English for practical communication and continuous language practice.
Understand the daily study and life of British middle school students by watching videos. Based on your own daily study and life, compare the study and life in Chinese and British schools, and find out the similarities and differences between the two. Talk about your first impression of high school life, and have a preliminary perception of the study and life in the senior high school stage.
Teaching Focuses and Anticipated Difficulties
Students can tell the difference between defining and non-defining attributive clauses and use non-defining attributive clauses correctly in writing. Also, learn English idioms about “laughs” to grow vocabulary.
Use non-defining attributive clauses correctly in writing and understand the cultural emphasis on optimism and humor in dealing with difficulties.
Grammar
PART. 02
Look at the sentences from the reading passage and answer the questions.
1. What do “where”, “which” and “when” refer to in each sentence
In sentence (a) “where” refers to “the waiting area”; in sentence (b) “which” refers to ”... laughter produces chemicals to make people feel better”; in sentence (c) “when” refers to “the time”.
Look at the sentences from the reading passage and answer the questions.
2. Which sentences contain a clause with essential information and which with extra information If you take away the clauses, do the sentences still make sense
Sentence (c) contains a clause with essential information, sentences (a) and (b) contain clauses with extra information, If we take away the clause of sentence(c), the meaning of it is incomplete. If we take away the clauses of sentences (a) and (b), the two sentences still make sense.
3. Which clauses are separated by a comma, the ones with essential information or the ones with extra information
Sentences (a) and (b) with extra information are separated by commas.
Non-defining attributive clauses (非限制性定语从句)
定语从句:在复合句中用来限制、描绘或说明主句中某一名词或代词而起定语作用的从句。
先行词:定语从句所修饰的名词或代词叫作先行词。先行词可以是人、物,也可以是整个句子或者句子的一部分,先行词一般位于定语从句之前。
She is a kind teacher who often helps students with their problems.
Tom decided to start his own business, which amazed his parents.
关系词:引导定语从句的词叫作关系词。按照关系词在定语从句中所作的成分,可将关系词分为关系代词和关系副词。
The beautiful city which/that we visited last summer is Hangzhou.
This is the place where I met my best friend.
关系词 关系词 先行词 充当的成分
关系代词 that 指人、物 主语、宾语、表语
which 指物、句子 主语、宾语、表语
who 指人 主语、宾语、表语
whom 指人 宾语
whose 指人、物 定语
as 指人、物或句子 主语、宾语、表语
关系副词 when 表示时间的名词 时间状语
where 表示地点的名词 地点状语
why 表示原因的名词 原因状语
一、定语从句的分类
1. 限制性定语从句
限制性定语从句对先行词起修饰、限制作用,是句中不可缺少的部分,主句和从句关系非常紧密,不能用逗号分开。
He bought the book that/which is recommended by the teacher.
2. 非限制性定语从句
非限制性定语从句往往是对先行词或整个主句进行附加说明,主从句的关系并不十分密切,若将其去掉,主句的意义仍然完整清楚。从句和主句之间往往用逗号隔开。除了that和why不能引导之外,所有其他关系词如 who, whom, which, whose, as, when,where 等均可引导。
Beijing, which is the capital of China, has a long history.
限制性定语从句 非限制性定语从句
先行词可以用that, why引导 先行词不可以用that, why引导
主句与从句之间不需要用逗号隔开,译成一句话 主句与从句需要用逗号隔开,可译成两句话
引导词有时可以省略(作宾语时) 引导词不可以省略
whom可用who或that代替 whom不可被代替
从句只修饰先行词 从句既可以修饰先行词,也可以修饰整个句子或句子的一部分
二、非限制性定语从句的使用情况
1. 当关系代词指代整个主句内容时,用非限制性定语从句(用which或as引导)。
She won the first prize in the competition, which made her classmates really proud.
她在比赛中得了一等奖,这让她的同学们特别骄傲。
2. 当先行词指的是世界上独一无二的事物或专有名词时,用非限制性定语从句。
The Great Wall, which stands as a symbol of Chinese history, attracts millions of tourists yearly.
长城作为中国历史的象征,每年吸引数百万游客。
Mount Qomolangma, which is the highest peak on Earth, has inspired adventurers.
珠穆朗玛峰是地球最高峰,激励了探险者 。
3. 先行词指某人的亲属关系,具有唯一性和确认性时,例如son, daughter, father, mother, wife 等,用非限制性定语从句。
Her mother, who runs a popular bakery downtown, often shares homemade pastries with neighbors.
她妈妈在市中心经营一家很火的面包店,经常给邻居分享自制糕点。
4. 当引导定语从句的关系代词中,含有some/many/few/a few/little/a little/none/ much/most/half of which (whom)等时,多用非限制性定语从句。
The library has hundreds of old books, few of which have been digitized so far.
图书馆藏有数百本古籍,目前很少有被数字化的。
三、关系代词引导的非限制性定语从句
1. which 指物,在定语从句中作主语或宾语。
I bought a hand-made vase yesterday, which was crafted by a local artisan.
我昨天买了一个手工花瓶,是当地一位工匠制作的。
2. who 指人,在定语从句中作主语或宾语。
Anna, who is an environmental volunteer, often organizes beach-cleaning activities.
安娜是一名环保志愿者,经常组织海滩清理活动。
3. whom 指人,在非限制性定语从句中作宾语,一般不能省略。
Peter, whom you met in London, is going to Paris next week.
你在伦敦见过的那个彼得,下周将要去巴黎。
4. whose 既可指人,也可指物,在定语从句中作定语。
The girl, whose grandmother is a famous folk artist, loves traditional handicrafts.
这个女孩热爱传统手工艺品,她的奶奶是知名民间艺人 。
The old house, whose roof was damaged in the storm, needs urgent repairs.
这座老房子的屋顶在暴风雨中受损了,急需修缮。
5. as 既可指人,也可指物,在定语从句中可以作主语或宾语。
He forgot to bring his pen with him, as was often the case.
他忘了带笔,这是常有的事。
As we all recognize, protecting wildlife is key to ecological balance.
众所周知,保护野生动物对生态平衡至关重要 。
四、as与which引导的非限制性定语从句的区别
1. as引导定语从句时,仍具有“正如,像,由……可知”等意思,这些字眼翻译时可 不必译出。as定语从句中常含有这些动词:see, know, hear, watch, remember, say, tell, show, expect, guess等。这类动词与as连用几乎成了一种固定搭配。as引导的定语从句可以置于句首、句中或向尾。
She is always working hard, as everyone can see.
正如大家所看到的那样,她一直工作很努力。
2. 在从句中作定语或介词的宾语时,要用 which。
My cousins might visit this weekend, in which situation we’ll prepare a big dinner.
我的表兄妹们这周末可能来,要是那样的话,我们就准备一顿丰盛的晚餐。
3. which引导的从句对主句所叙述的事情进行补充说明表明事物的状态或结果。
which此时指前面主句所提到的这件事,常译为“这一点,这件事”等。这时它所引导的从句与主句之间常表示并列意义或状语意义。注意它引导的从句不像as那样位置灵活,它只能位于主句的后面。
The school canceled the outdoor activity, which disappointed all the students.
学校取消了户外活动,这让所有学生都很失望。
4. 当从句的谓语是否定形式或含着一个复合宾语时,一般用which而不用as。
He avoided joining the football team, which his coach couldn’t figure out.
他回避加入足球队,教练一直搞不懂这事。
五、关系副词引导的非限制性定语从句
1. 关系副词when在非限制性定语从句中作时间状语,指代主句中表示时间的词语。
We moved the family gathering to Sunday, when all relatives can attend.
我们把家庭聚会改到周日,那时所有亲戚都能参加。
2. 副词where在非限制性定语从句中作地点状语,指代主句中表示地点的词语。
The volunteers went to the countryside, where they helped build a new library.
志愿者们去了乡村,在那儿帮忙建了一座新图书馆。
They toured the historical district, where ancient buildings are well-preserved.
他们游览了历史街区,那儿的古建筑保存得很好。
Read the passage and rewrite the tips using non-defining attributive clauses. Add more tips to the list if you can.
Go for a walk in the countryside, where you can enjoy the beautiful views and a peaceful atmosphere.
Spend time with your family and friends, which will activate chemicals in your brain to make you feel happier.
Try to accept your mistakes, where/through which you can learn a lot.
Close your eyes and picture the future, where you’ve made your dreams come true.
Complete the joke with the sentence parts in the box using who/which and put commas in the correct position.
One day, Sherlock Holmes and Dr Watson go camping. They put up their tent under the stars and go to sleep. Suddenly, in the middle of the night, Watson is woken up by Holmes 1______________________. “Watson,” Holmes says, “look up at the stars, and tell me what they tell you. ” Not quite sure what he means, Watson thinks Holmes is joking 2_______________________ at this time of night. Even so, he replies, “I see millions of stars and it’s quite likely there are some planets like Earth. And if so, this means that there might also be life on other planets. ” Watson is pleased with his answer 3___________________________________. But Holmes 4_____________________________ shouts, “Watson, look around you! Use your eyes! Somebody’s stolen our tent!”
, who is lying next to him
, which he finds annoying
, which he thinks will impress Holmes
, who has lost his patience by now,
has lost his patience by now he thinks will impress Holmes
is lying next to him he finds annoying
Listen and complete the conversations.
a smile
ear to ear
head off
smiles
laughing
Match the expressions you have completed in Activity 5 to their meanings.
laughing stock
be all smiles
grin from ear to ear
crack a smile
laugh one’s head off
Now work in groups and think of more expressions about laughter.
Work in pairs. Discuss other situations in which you could use these expressions.
You may start like this:
A: Tom must have passed that really hard test.
B: Why do you think so
A: Because he was grinning from ear to ear yesterday when I met him.
Listening
PART. 03
April Fool’s Day is on 1 April. It’s the one day of the year when people in many parts of the world play practical jokes on each other. Even newspapers, radio and TV stations play tricks on their readers and audiences. The jokes traditionally last until noon in the UK. But in some other countries, such as the US, they can last all day!
Did You Know
Listen to the radio programme and choose the pictures mentioned.
a
b
c
d
Listen again and complete the notes.
Now work in pairs. Discuss which of the practical jokes you think is funny.
“the washing of the lions”
18th and 19th centuries
1965
BBC News Channel
smells to be carried
1957
a really good harvest
a
c
d
Complete the boxes with expressions from the radio programme.
Let’s start with...
Now, my favourite one...
It’s a good one!
I don’t get it.
That’s so funny!
I can imagine!
Work in pairs. Tell each other a funny story and make comments using the expressions in this section.
Now give feedback on each other’s stories and help your partner to improve theirs.
Vocabulary
1. essential
essentially adv. 本质上,根本上
be essential to/for… 对……极其重要
It is essential that... (should ) do... ……极其重要
essential conditions 必要条件
It is essential (for sb.) to do sth (对某人来说)做某事是极其重要的/必不可少的
例题:
The debate over artificial intelligence is __________(essential) a discussion about how technology will reshape human society, ethics, and the future of work.
essentially
Vocabulary
2. impress
impression n. 印象 impressive adj. 令人钦佩的,给人深刻印象的
impress sb. with sth. 某事/ 物给某人留下深刻印象
be impressed with/by 对……印象深刻
impress sth. on sb. 使某人了解某事的重要性
impress sth. on one's mind/memory 使某人把……铭记在心
It impresses sb. that 令某人钦佩的是
leave/make a (n) impression on sb. 给某人留下……印象
例题:
Traveling abroad can change your ___________(impress) of the world.
impression
Vocabulary
3. deserve
deserve to do sth. 值得做某事,应该做某事
deserve all/everything sb. get 罪有应得
deserve consideration/attention 值得考虑/ 注意
例题:
Those who spread false information and harm others’ reputations deserve ______(face) legal consequences for their actions.
to face
Exercise
PART. 04
1. Reducing single-use plastics and promoting recycling are e________(极其重要的) steps toward creating a more sustainable and eco-friendly planet.
2. Children living in poverty d_________(应得) equal access to quality education and healthcare to build a brighter future.
3. The student’s comprehensive understanding of the subject matter i_________(使留下深刻印象) the professor, who praised her ability to analyze complex theories critically.
ssential
Exercise: 单词拼写
eserve
mpressed
Li Hua, ______ is my deskmate, won the English speech contest.
The new library, ______ was built last year, has a large collection of books.
My father, ______ you met at the party, is a doctor.
The town, ______ I grew up, holds many sweet memories.
He missed the train, ______ made him late for work.
Her car, ______ color is bright red, stands out in the parking lot.
The summer holiday, ______ we plan to travel abroad, is coming soon.
Mr. Smith, ______ son is in my class, often volunteers at the community center.
who
Exercise: 用合适的关系词填空
which
whom
where
which
whose
when
whose
Summary
PART. 05
Using language
Grammar
Vocabulary
Listening
非限制性定语从句
定语从句的分类
非限制性定语从句的使用情况
关系代词引导的非限制性定语从句
as与which引导的非限制性定语从句的区别
关系副词引导的非限制性定语从句
Homework
PART. 06
Review what you have learnt in this class;
Think of a joke you find funny and write it down using non-defining attributive clauses where appropriate.
Homework
See you next class!
