Unit 4 History and Traditions Reading and Thinking 课件(共31张PPT)-人教版(2019)必修第二册
文档属性
| 名称 | Unit 4 History and Traditions Reading and Thinking 课件(共31张PPT)-人教版(2019)必修第二册 |  | |
| 格式 | pptx | ||
| 文件大小 | 5.9MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 人教版(2019) | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2025-07-29 16:47:13 | ||
图片预览






文档简介
(共31张PPT)
Unit 4
History and Traditions
Reading and Thinking
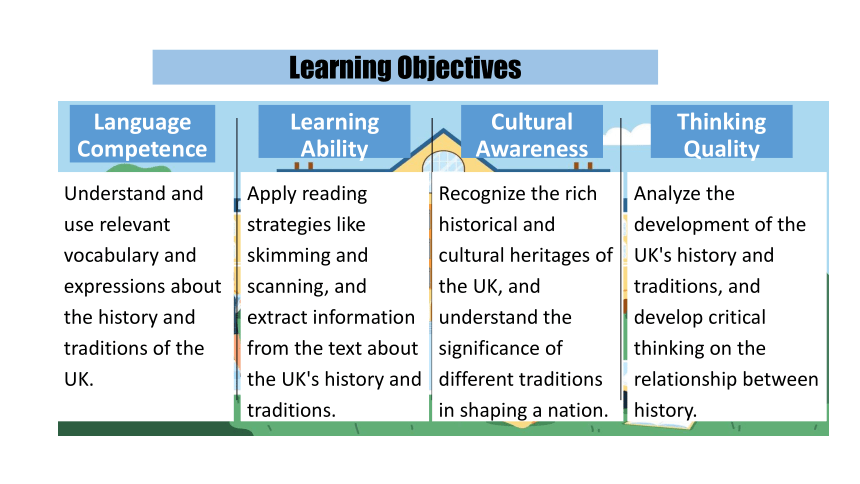
Language Competence
Understand and use relevant vocabulary and expressions about the history and traditions of the UK.
Learning Ability
Apply reading strategies like skimming and scanning, and extract information from the text about the UK's history and traditions.
Cultural Awareness
Recognize the rich historical and cultural heritages of the UK, and understand the significance of different traditions in shaping a nation.
Thinking Quality
Analyze the development of the UK's history and traditions, and develop critical thinking on the relationship between history.
Learning Objectives
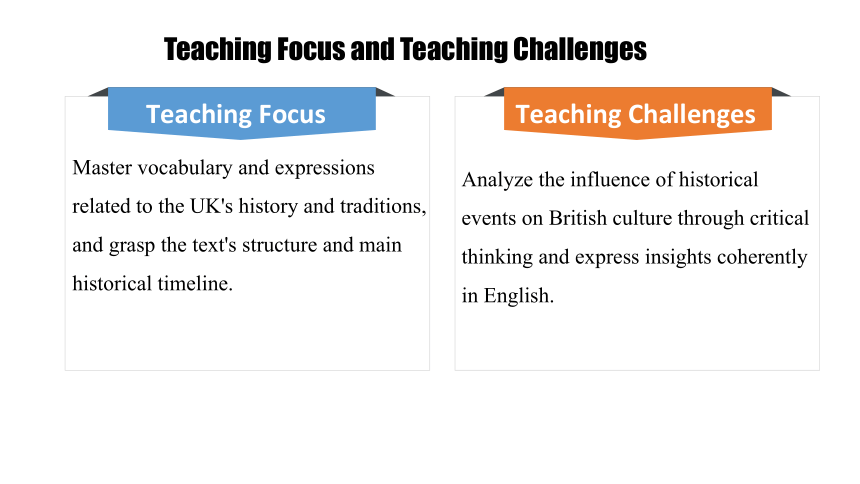
Teaching Focus
Master vocabulary and expressions related to the UK's history and traditions, and grasp the text's structure and main historical timeline.
Teaching Challenges
Analyze the influence of historical events on British culture through critical thinking and express insights coherently in English.
Teaching Focus and Teaching Challenges
Part 1
Listening & Speaking
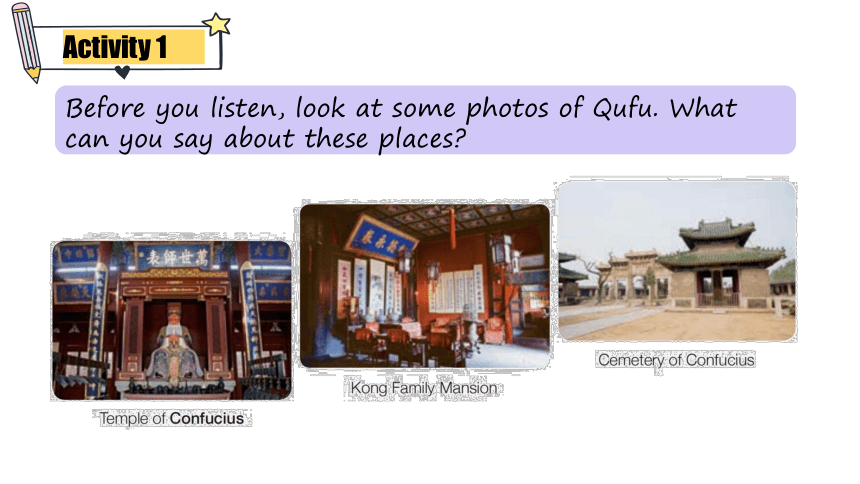
Activity 1
Before you listen, look at some photos of Qufu. What can you say about these places
Activity 1
Temple of Confucius
The most famous and largest temple honouring the great sage, it is also a UNESCO (联合国教科文组织) WorldHeritage Site.
It covers 16,000 square metres and has 460 rooms. The main part consists of nine courtyards with several gates. Dacheng Hall stands at the centre and is the principal place for offering sacrifices to Confucius.
Activity 1
Kong Family Mansion
Located to the east of the Temple of Confucius, this was the historical home of the descendants of Confucius from where theymanaged sites and ceremonies in Qufu.
Today it is a museum.
Activity 1
Cemetery of Confucius
This is where Confucius and his descendants are buried.
There are more than 10,000 of them, buried here over 2,000 years.
The cemetery has had many renovations (翻修) and extensions in its history.
Activity 2
Listen to a conversation between a British tourist and a Chinese student in Qufu, and then write down what they say about Confucius.
Name Fact/Opinion about Confucius
William 1. Confucius is one of his favourite philosophers.
2.
3.
1.
2.
3.
Xiao Kong
He was a wise man
He lived over 2500 years ago.
Confucius has over 3 million descendants.
He was a great educator and had many ideas about education.
He was one of the greatest minds in history.
Activity 3
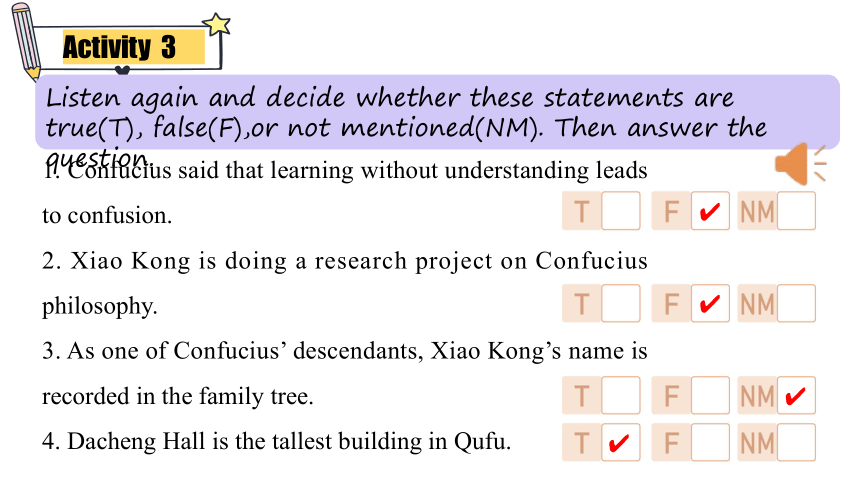
Listen again and decide whether these statements are true(T), false(F),or not mentioned(NM). Then answer the question.
1. Confucius said that learning without understanding leads to confusion.
2. Xiao Kong is doing a research project on Confucius philosophy.
3. As one of Confucius’ descendants, Xiao Kong’s name is recorded in the family tree.
4. Dacheng Hall is the tallest building in Qufu.
A There are famous halls in his hometown.
B There are not tall buildings in his hometown.
C Both places have a famous person who was born there.
D His hometown doesn't allow other buildings to be more noticeable than the historic buildings.
Activity 3
Why do you think William said his hometown was similar to Qufu
Activity 4
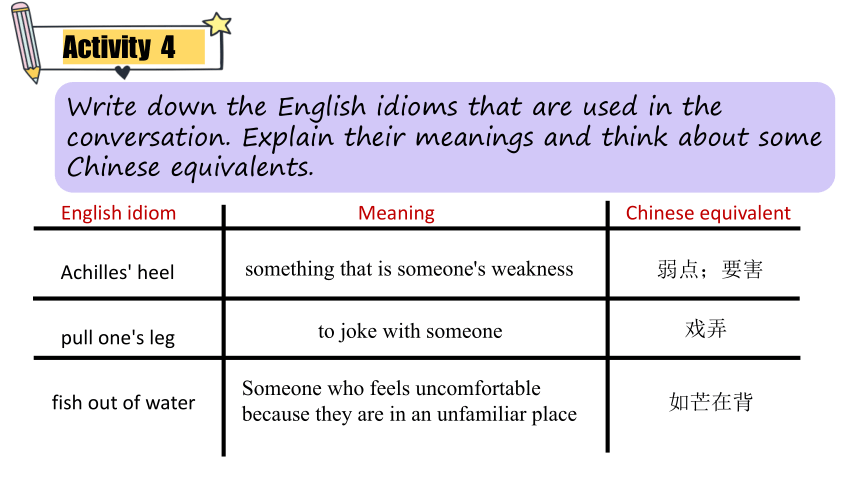
Write down the English idioms that are used in the conversation. Explain their meanings and think about some Chinese equivalents.
English idiom
Meaning
Chinese equivalent
Achilles' heel
pull one's leg
fish out of water
something that is someone's weakness
to joke with someone
Someone who feels uncomfortable because they are in an unfamiliar place
弱点;要害
戏弄
如芒在背
Activity 5
Discuss the questions in groups.
What do you know about Confucius' ideas on education Think of two or three examples. What else do you know about Confucius and his philosophy
Learning without reflection leads to confusion.
Teach students in accordance with their aptitude.
Think about a historic site that you have visited and give an introduction to its history and importance.
Location
Visiting experience
Feature
Historical event
Feeling/reflection
Part 2
Reading
Lead-in
Guess which city it is.
It's a country in Europe.
The flag consists of different crosses.
people there drive on the left - hand side of the road.
What do the different symbols (e.g. circles, spots) and colours stand for in the map?
the small circles stand for cities. The size of the circle often differentiates the scale of the town.
the red spot stands for the capital
different colours stand for different regions or countries
Skimming for the main idea of the each paragraph.
Paragraph 1
Paragraph 2
Paragraph 3
Paragraph 4
Paragraph 5
The people influencing the history and traditions of the UK.
The significance of studying the British history and culture.
People’s confusion about the different names of the UK.
How the UK came into being.
The similarities and differences of the four countries that
make up the UK.
Read para.1 and answer the question.
The United Kingdom, Great Britain, Britain, England—many people are confused by what these different names mean. So what is the difference between them, if any Getting to know a little bit about British history will help you solve this puzzle.
To introduce the topic. The last sentence leads the following paragraph.
What is the function of paragraph 1
What these different names mean: the United Kingdom, Great Britain,
Britain, England.
1. What makes people confused
Read para.2 and find the information.
name changed to “United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland
16th
Wales was joined to Kingdom of England.
18th
19th
“United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland”
20th
Scotland was joined to England and Wales.
Ireland was added.
The southern part of Ireland broke away.
How did the country’s name come into being What happened in the process
“the Kingdom of Great Britain”
“the Kingdom of England”
Read para.3 and find the information.
The four countries that belong to the United Kingdom work together in some areas. They use the same flag, known as the Union Jack, as well as share the same currency and military defence. However, they also have some differences. For example, England, Wales, Scotland, and Northern Ireland all have different education systems and legal systems. They also have their own traditions, like their own national days and national dishes. And they even have their own football teams for competitions like the World Cup!
Similarities
Differences
flag currency military defence
educational and legal systems their own traditions and even football teams for competitions
the Romans
the Anglo-Saxons
the beginning of the
the Vikings
the Normans
towns and roads
vocabulary and
castles, legal system,
and new words
from French
English language; the way names of locations
to build houses
Read para.4 & 5 and find the information.
Read again and sort out the information according to the timeline.
When What happened What changed
Romans arrived
Ango-Saxons came
Vikings came
11th century
1st century
5th century
8th century
Normans conquered England after the Battle of Hastings
towns and roads
language and way houses were built
vocabulary and names of locations across the UK
castles built, legal system changed, and new words from French introduced
A: Oh, I remember now! The southern part ____________from Northern Ireland, right
B: Yes, you got it well remembered! But __________________in history class next time.
Complete the passage about Wuzhen with the correct forms of the words in the box.
as well as belong to add to join to break away keep your eyes open
A: I can never remember what the UK means! There's England, Britain, ____________ Great Britain!
as well as
B: Well, it helps if you remember that there are four countries that __________ the UK.
That's why it's called the United Kingdom.
A: Four countries I must have been asleep in that part of our history class! So the first
B: Yes, right. First England, then Wales, then Scotland. The last country was Ireland, but
later the southern half didn't want to be ______________ the United Kingdom.
broke away
country was England, and the others were _____________ that
belong to
added to
join to
keep your eyes open
Part 3
Language Points
belong vi. 应在(某处);适应
belong to 属于;归…… 所有
belong together 应在一起;彼此适合
where one belongs 某人应在的地方;归宿
make sth. belong 使某物适合 / 融入
belonging n.归属;所有物(常用复数 )
练习:A sense of _________ is important for mental health.
belonging
surround vt.围绕;包围
in a...surrounding 在…… 的环境中
be surrounded by/with... 被……包围/环绕
surround oneself with sb./sth.
使自己身边常有(某类人 / 物);与…… 为伍
surrounding adj. 周围的;附近的
surroundings n. 环境(常用复数)
练习:The village is __________ by mountains and forests.
surrounded
break away(from sb./sth.) 脱离;背叛;逃脱;摆脱
break down (机器)出故障;(谈判)失败;(身体)垮掉;分解
break in 打断;插嘴说;闯入
break into 闯入…;爆发
break out (战争)爆发;(火灾)突然发生
break up 分解;解散;击碎;(关系等)破裂
break up with sb 与某人绝交
练习:The prisoner _______________ his guards and ran into the woods.
broke away from
Part 4
Exercise
Sample
1. ____________ (surround) by rows of trees, our school stands out from all the other buildings.
2.There is no ________ (证据) to support this theory.
3.Later in the next century, people from England made voyages to _________ (征服) other parts of the world.
4.Though they all live ________ (在附近), I lost contact with them really quickly.
5.She knew the exact ________ (位置) of the college.
6. Men and women, young and old, were fighting against the flood in _______ (defend) of their own homes.
conquer
evidence
location
nearby
Surrounded
defence
Homework
1. Summarise what we have learnt in this lesson;
2. Prepare for the next lesson
See you next time!
Unit 4
History and Traditions
Reading and Thinking
Language Competence
Understand and use relevant vocabulary and expressions about the history and traditions of the UK.
Learning Ability
Apply reading strategies like skimming and scanning, and extract information from the text about the UK's history and traditions.
Cultural Awareness
Recognize the rich historical and cultural heritages of the UK, and understand the significance of different traditions in shaping a nation.
Thinking Quality
Analyze the development of the UK's history and traditions, and develop critical thinking on the relationship between history.
Learning Objectives
Teaching Focus
Master vocabulary and expressions related to the UK's history and traditions, and grasp the text's structure and main historical timeline.
Teaching Challenges
Analyze the influence of historical events on British culture through critical thinking and express insights coherently in English.
Teaching Focus and Teaching Challenges
Part 1
Listening & Speaking
Activity 1
Before you listen, look at some photos of Qufu. What can you say about these places
Activity 1
Temple of Confucius
The most famous and largest temple honouring the great sage, it is also a UNESCO (联合国教科文组织) WorldHeritage Site.
It covers 16,000 square metres and has 460 rooms. The main part consists of nine courtyards with several gates. Dacheng Hall stands at the centre and is the principal place for offering sacrifices to Confucius.
Activity 1
Kong Family Mansion
Located to the east of the Temple of Confucius, this was the historical home of the descendants of Confucius from where theymanaged sites and ceremonies in Qufu.
Today it is a museum.
Activity 1
Cemetery of Confucius
This is where Confucius and his descendants are buried.
There are more than 10,000 of them, buried here over 2,000 years.
The cemetery has had many renovations (翻修) and extensions in its history.
Activity 2
Listen to a conversation between a British tourist and a Chinese student in Qufu, and then write down what they say about Confucius.
Name Fact/Opinion about Confucius
William 1. Confucius is one of his favourite philosophers.
2.
3.
1.
2.
3.
Xiao Kong
He was a wise man
He lived over 2500 years ago.
Confucius has over 3 million descendants.
He was a great educator and had many ideas about education.
He was one of the greatest minds in history.
Activity 3
Listen again and decide whether these statements are true(T), false(F),or not mentioned(NM). Then answer the question.
1. Confucius said that learning without understanding leads to confusion.
2. Xiao Kong is doing a research project on Confucius philosophy.
3. As one of Confucius’ descendants, Xiao Kong’s name is recorded in the family tree.
4. Dacheng Hall is the tallest building in Qufu.
A There are famous halls in his hometown.
B There are not tall buildings in his hometown.
C Both places have a famous person who was born there.
D His hometown doesn't allow other buildings to be more noticeable than the historic buildings.
Activity 3
Why do you think William said his hometown was similar to Qufu
Activity 4
Write down the English idioms that are used in the conversation. Explain their meanings and think about some Chinese equivalents.
English idiom
Meaning
Chinese equivalent
Achilles' heel
pull one's leg
fish out of water
something that is someone's weakness
to joke with someone
Someone who feels uncomfortable because they are in an unfamiliar place
弱点;要害
戏弄
如芒在背
Activity 5
Discuss the questions in groups.
What do you know about Confucius' ideas on education Think of two or three examples. What else do you know about Confucius and his philosophy
Learning without reflection leads to confusion.
Teach students in accordance with their aptitude.
Think about a historic site that you have visited and give an introduction to its history and importance.
Location
Visiting experience
Feature
Historical event
Feeling/reflection
Part 2
Reading
Lead-in
Guess which city it is.
It's a country in Europe.
The flag consists of different crosses.
people there drive on the left - hand side of the road.
What do the different symbols (e.g. circles, spots) and colours stand for in the map?
the small circles stand for cities. The size of the circle often differentiates the scale of the town.
the red spot stands for the capital
different colours stand for different regions or countries
Skimming for the main idea of the each paragraph.
Paragraph 1
Paragraph 2
Paragraph 3
Paragraph 4
Paragraph 5
The people influencing the history and traditions of the UK.
The significance of studying the British history and culture.
People’s confusion about the different names of the UK.
How the UK came into being.
The similarities and differences of the four countries that
make up the UK.
Read para.1 and answer the question.
The United Kingdom, Great Britain, Britain, England—many people are confused by what these different names mean. So what is the difference between them, if any Getting to know a little bit about British history will help you solve this puzzle.
To introduce the topic. The last sentence leads the following paragraph.
What is the function of paragraph 1
What these different names mean: the United Kingdom, Great Britain,
Britain, England.
1. What makes people confused
Read para.2 and find the information.
name changed to “United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland
16th
Wales was joined to Kingdom of England.
18th
19th
“United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland”
20th
Scotland was joined to England and Wales.
Ireland was added.
The southern part of Ireland broke away.
How did the country’s name come into being What happened in the process
“the Kingdom of Great Britain”
“the Kingdom of England”
Read para.3 and find the information.
The four countries that belong to the United Kingdom work together in some areas. They use the same flag, known as the Union Jack, as well as share the same currency and military defence. However, they also have some differences. For example, England, Wales, Scotland, and Northern Ireland all have different education systems and legal systems. They also have their own traditions, like their own national days and national dishes. And they even have their own football teams for competitions like the World Cup!
Similarities
Differences
flag currency military defence
educational and legal systems their own traditions and even football teams for competitions
the Romans
the Anglo-Saxons
the beginning of the
the Vikings
the Normans
towns and roads
vocabulary and
castles, legal system,
and new words
from French
English language; the way names of locations
to build houses
Read para.4 & 5 and find the information.
Read again and sort out the information according to the timeline.
When What happened What changed
Romans arrived
Ango-Saxons came
Vikings came
11th century
1st century
5th century
8th century
Normans conquered England after the Battle of Hastings
towns and roads
language and way houses were built
vocabulary and names of locations across the UK
castles built, legal system changed, and new words from French introduced
A: Oh, I remember now! The southern part ____________from Northern Ireland, right
B: Yes, you got it well remembered! But __________________in history class next time.
Complete the passage about Wuzhen with the correct forms of the words in the box.
as well as belong to add to join to break away keep your eyes open
A: I can never remember what the UK means! There's England, Britain, ____________ Great Britain!
as well as
B: Well, it helps if you remember that there are four countries that __________ the UK.
That's why it's called the United Kingdom.
A: Four countries I must have been asleep in that part of our history class! So the first
B: Yes, right. First England, then Wales, then Scotland. The last country was Ireland, but
later the southern half didn't want to be ______________ the United Kingdom.
broke away
country was England, and the others were _____________ that
belong to
added to
join to
keep your eyes open
Part 3
Language Points
belong vi. 应在(某处);适应
belong to 属于;归…… 所有
belong together 应在一起;彼此适合
where one belongs 某人应在的地方;归宿
make sth. belong 使某物适合 / 融入
belonging n.归属;所有物(常用复数 )
练习:A sense of _________ is important for mental health.
belonging
surround vt.围绕;包围
in a...surrounding 在…… 的环境中
be surrounded by/with... 被……包围/环绕
surround oneself with sb./sth.
使自己身边常有(某类人 / 物);与…… 为伍
surrounding adj. 周围的;附近的
surroundings n. 环境(常用复数)
练习:The village is __________ by mountains and forests.
surrounded
break away(from sb./sth.) 脱离;背叛;逃脱;摆脱
break down (机器)出故障;(谈判)失败;(身体)垮掉;分解
break in 打断;插嘴说;闯入
break into 闯入…;爆发
break out (战争)爆发;(火灾)突然发生
break up 分解;解散;击碎;(关系等)破裂
break up with sb 与某人绝交
练习:The prisoner _______________ his guards and ran into the woods.
broke away from
Part 4
Exercise
Sample
1. ____________ (surround) by rows of trees, our school stands out from all the other buildings.
2.There is no ________ (证据) to support this theory.
3.Later in the next century, people from England made voyages to _________ (征服) other parts of the world.
4.Though they all live ________ (在附近), I lost contact with them really quickly.
5.She knew the exact ________ (位置) of the college.
6. Men and women, young and old, were fighting against the flood in _______ (defend) of their own homes.
conquer
evidence
location
nearby
Surrounded
defence
Homework
1. Summarise what we have learnt in this lesson;
2. Prepare for the next lesson
See you next time!
