Unit 3 Conservation Lesson 1 The Sixth Extinction(Grammar)课件(共33张)-高中英语北师大版(2019)选择性必修第一册(共34页PPT)
文档属性
| 名称 | Unit 3 Conservation Lesson 1 The Sixth Extinction(Grammar)课件(共33张)-高中英语北师大版(2019)选择性必修第一册(共34页PPT) |  | |
| 格式 | pptx | ||
| 文件大小 | 24.5MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 北师大版(2019) | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2025-08-01 10:13:13 | ||
图片预览









文档简介
(共33张PPT)
Lesson 1 (Grammar)
Unit 3
Conservation
Learning Objectives
PART. 01
Understand the daily study and life of British middle school students by watching videos. Based on your own daily study and life, compare the study and life in Chinese and British schools, and find out the similarities and differences between the two. Talk about your first impression of high school life, and have a preliminary perception of the study and life in the senior high school stage.
Learning Objectives
Identify and use defining and non-defining relative clauses correctly, and apply them accurately in discussions about environmental problems. Expand environmental-themed vocabulary and practice integrating relative clauses into sentences to explain human-caused environmental issues and solutions.
Explore cultural values of environmental protection, understanding how human activity drives environmental problems. Recognize shared cultural responsibility for finding solutions, reflecting on how different societies address ecological challenges.
Analyze sentences to distinguish defining/non-defining clauses, interpreting their impact on meaning. Break down environmental issues into components, using relative clauses to structure logical explanations.
Use “grammar-in-context” strategies to master relative clauses. By independently analyzing clauses, completing translation tasks, and reflecting on environmental solutions, students take ownership of learning.
Understand the daily study and life of British middle school students by watching videos. Based on your own daily study and life, compare the study and life in Chinese and British schools, and find out the similarities and differences between the two. Talk about your first impression of high school life, and have a preliminary perception of the study and life in the senior high school stage.
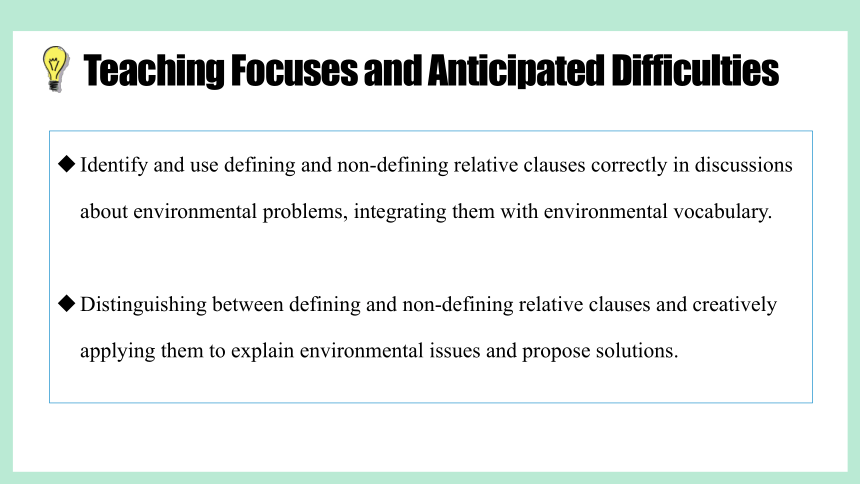
Teaching Focuses and Anticipated Difficulties
Identify and use defining and non-defining relative clauses correctly in discussions about environmental problems, integrating them with environmental vocabulary.
Distinguishing between defining and non-defining relative clauses and creatively applying them to explain environmental issues and propose solutions.
Lead-in
PART. 02
Compare what the differences are between the following two sentences.
①The student who won the first prize in the English contest is my deskmate.
②My deskmate, who won the first prize in the English contest, is very hard-working.
①句无逗号,从句是“识别同桌的关键”;②句有逗号,从句是“额外信息”。由此引出“限制性定语从句(必要信息)” 和“非限制性定语从句(补充信息)”的概念。
Grammar
PART. 03
Relative Clauses-Defining and non-defining Relative Clauses
(定语从句——限制性与非限制性定语从句)
定语从句:在复合句中用来限制、描绘或说明主句中某一名词或代词而起定语作用的从句。
先行词:定语从句所修饰的名词或代词叫作先行词。先行词可以是人、物,也可以是整个句子或者句子的一部分,先行词一般位于定语从句之前。
She is a kind teacher who often helps students with their problems.
Tom decided to start his own business, which amazed his parents.
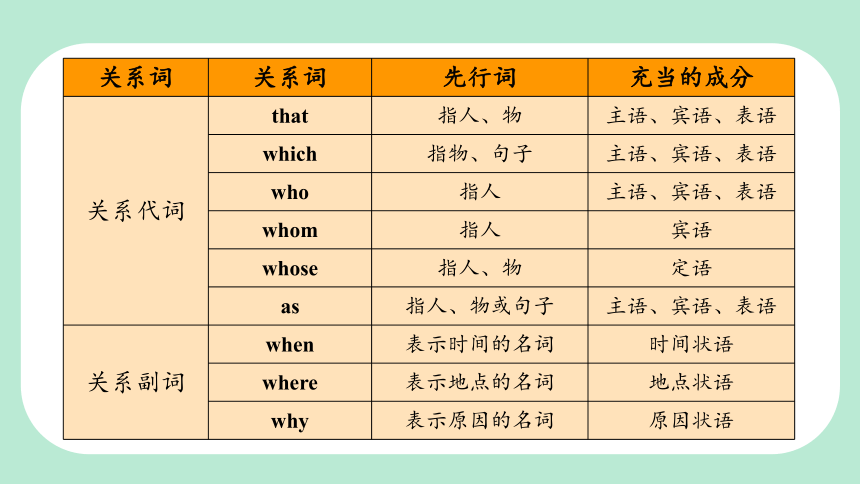
关系词:引导定语从句的词叫作关系词。按照关系词在定语从句中所作的成分,可将关系词分为关系代词和关系副词。
The beautiful city which/that we visited last summer is Hangzhou.
This is the place where I met my best friend.
关系词 关系词 先行词 充当的成分
关系代词 that 指人、物 主语、宾语、表语
which 指物、句子 主语、宾语、表语
who 指人 主语、宾语、表语
whom 指人 宾语
whose 指人、物 定语
as 指人、物或句子 主语、宾语、表语
关系副词 when 表示时间的名词 时间状语
where 表示地点的名词 地点状语
why 表示原因的名词 原因状语
一、定语从句的分类
1. 限制性定语从句
限制性定语从句对先行词起修饰、限制作用,是句中不可缺少的部分,主句和从句关系非常紧密,不能用逗号分开。
He bought the book that/which is recommended by the teacher.
2. 非限制性定语从句
非限制性定语从句往往是对先行词或整个主句进行附加说明,主从句的关系并不十分密切,若将其去掉,主句的意义仍然完整清楚。从句和主句之间往往用逗号隔开。除了that和why不能引导之外,所有其他关系词如 who, whom, which, whose, as, when,where 等均可引导。
Beijing, which is the capital of China, has a long history.
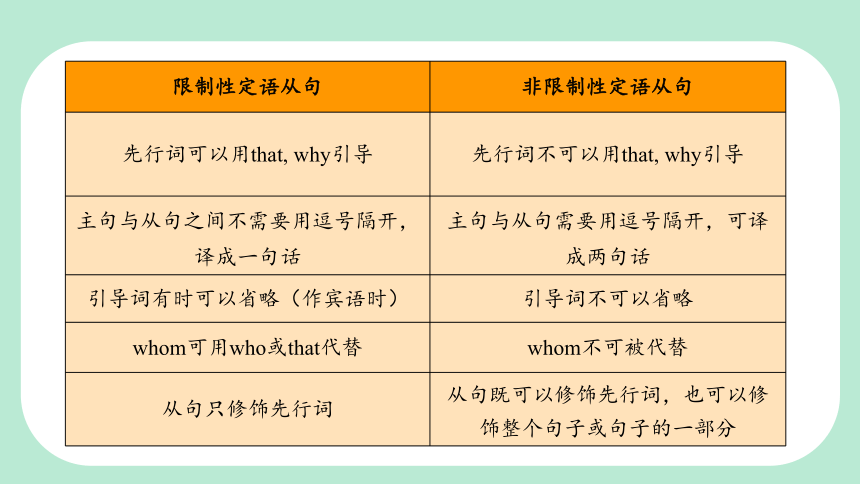
限制性定语从句 非限制性定语从句
先行词可以用that, why引导 先行词不可以用that, why引导
主句与从句之间不需要用逗号隔开,译成一句话 主句与从句需要用逗号隔开,可译成两句话
引导词有时可以省略(作宾语时) 引导词不可以省略
whom可用who或that代替 whom不可被代替
从句只修饰先行词 从句既可以修饰先行词,也可以修饰整个句子或句子的一部分
二、非限制性定语从句的使用情况
1. 当关系代词指代整个主句内容时,用非限制性定语从句(用which或as引导)。
She won the first prize in the competition, which made her classmates really proud.
她在比赛中得了一等奖,这让她的同学们特别骄傲。
2. 当先行词指的是世界上独一无二的事物或专有名词时,用非限制性定语从句。
The Great Wall, which stands as a symbol of Chinese history, attracts millions of tourists yearly.
长城作为中国历史的象征,每年吸引数百万游客。
Mount Qomolangma, which is the highest peak on Earth, has inspired adventurers.
珠穆朗玛峰是地球最高峰,激励了探险者 。
3. 先行词指某人的亲属关系,具有唯一性和确认性时,例如son, daughter, father, mother, wife 等,用非限制性定语从句。
Her mother, who runs a popular bakery downtown, often shares homemade pastries with neighbors.
她妈妈在市中心经营一家很火的面包店,经常给邻居分享自制糕点。
4. 当引导定语从句的关系代词中,含有some/many/few/a few/little/a little/none/ much/most/half of which (whom)等时,多用非限制性定语从句。
The library has hundreds of old books, few of which have been digitized so far.
图书馆藏有数百本古籍,目前很少有被数字化的。
三、as与which引导的非限制性定语从句的区别
1. as引导定语从句时,仍具有“正如,像,由……可知”等意思,这些字眼翻译时可 不必译出。as定语从句中常含有这些动词:see, know, hear, watch, remember, say, tell, show, expect, guess等。这类动词与as连用几乎成了一种固定搭配。as引导的定语从句可以置于句首、句中或向尾。
She is always working hard, as everyone can see.
正如大家所看到的那样,她一直工作很努力。
2. 在从句中作定语或介词的宾语时,要用 which。
My cousins might visit this weekend, in which situation we’ll prepare a big dinner.
我的表兄妹们这周末可能来,要是那样的话,我们就准备一顿丰盛的晚餐。
3. which引导的从句对主句所叙述的事情进行补充说明表明事物的状态或结果。
which此时指前面主句所提到的这件事,常译为“这一点,这件事”等。这时它所引导的从句与主句之间常表示并列意义或状语意义。注意它引导的从句不像as那样位置灵活,它只能位于主句的后面。
The school canceled the outdoor activity, which disappointed all the students.
学校取消了户外活动,这让所有学生都很失望。
4. 当从句的谓语是否定形式或含着一个复合宾语时,一般用which而不用as。
He avoided joining the football team, which his coach couldn’t figure out.
他回避加入足球队,教练一直搞不懂这事。
四、“介词+关系代词”引导的定语从句
关系副词when, where, why引导定语从句时可被“介词+关系代词”代替。在“介词+关系代词”引导的定语从句中,关系代词只能用which或whom,不可用that或who。先行词指物时用which,先行词指人时用whom。
1. “介词 +which”可以替代关系副词 when, where, why
(1)替代when
I still remember the moment at which (= when) I received my diploma and felt a rush of pride. (at 依据 at the moment 确定)
The era during which (= when) the Industrial Revolution took place was full of dramatic changes. (during 依据 during the era 确定)
(2)替代why
I’m curious about the reason for which (= why) he decided to pursue a career in acting. (for 依据 for the reason 确定)
2. 依据与先行词的固定搭配确定使用什么介词
I’ll always cherish the vacation during which I explored the ancient ruins in Greece. (during 依据 during the vacation 确定)
3. 依据定语从句中动词或形容词的搭配来确定介词
He bought a new guitar, on which he spent nearly half of his monthly salary. (on 依据 spend...on 确定)
These are the scientific theories of which she is most skeptical. (of 依据 be skeptical of 确定)
4. 根据定语从句所表达的具体意思来确定介词
Can you see the mountain behind which lies a small village
除了“介词+which”以外,如果定语从句的先行词是“人”,那么也可以用“介词+whom”引导定语从句。
5. “介词 + 关系代词”的其他表达法
(1)如果在whom和which 之前用of 表示所属关系(即of whom, of which表示所属关系),这时名词需要特指,应加定冠词该名词放在of whom, of which 之前或之后均可。
The book, the cover of which is very attractive, is a best-seller.
The book, of which the cover is very attractive, is a best-seller.
(2)在whom和which之前用of还可以表示部分与整体的关系。这时表示“部分”的数词或代词,放在of whom, of which之前或之后均可。
The class has 30 students, one of whom won the national math competition.
The class has 30 students, of whom one won the national math competition.
The team has ten players, all of whom are highly skilled.
The team has ten players, of whom all are highly skilled.
The club has five founders, the youngest of whom is just 25 years old.
The club has five founders, of whom the youngest is just 25 years old.
五、定语从句的简化
如果含有定语从句的复合句很复杂,为了表意清晰,可以把定语从句进行简化。
1. 关系代词的省略
关系代词 who、whom、that、which 在限制性定语从句中作宾语时,可以省略。
The man (that/who/whom) I met on the street is my old friend.
我在街上遇见的那个人是我的老朋友。
注意:关系代词作介词的宾语时,介词位于句尾时,关系代词可以省略,但关系代词紧跟在介词后面作宾语时,不能省略。
This is the girl (whom) he worked with./ This is the girl with whom he worked.
这是曾与他一起工作过的女孩。
2. 将定语从句变为非谓语动词
①定语从句转换成不定式短语
He is a good comrade with whom you can work.
→ He is a good comrade to work with. 他是个可以与之一起工作的好伙伴。
②定语从句转换成现在分词短语
The people who are living in the village have moved to other places.
→ The people living in the village have moved to other places.
住在村子里的人已经搬到别的地方去了。
③定语从句转换成过去分词短语
I have heard the report which was made by Professor Wang.
→ I have heard the report made by Professor Wang. 我听了王教授作的报告。
Read the sentences and discuss which word(s) the clauses (in italics) refer to.
1. Extinctions, where entire species are wiped out, are not unusual in our Earth’s history.
Refers to extinctions
2. These include the third mass extinction, known as the “Great Dying”, which killed 90% to 96% of all species.
Refers to the “Great Dying”
3. A 2015 study by scientists who were based at Brown University and Duke University in the US, looked at how quickly species die out due to natural causes ...
Refers to scientists
Read the sentences and discuss which word(s) the clauses (in italics) refer to.
4. If a sixth mass extinction occurs, scientists who have studied the issue believe that up to three quarters of all species on Earth could die out.
Refers to scientists
5. We need to take steps to save endangered species, including setting up special areas where plants and animals can be protected.
Refers to special areas
Which of the clauses above:
(1) give information to identify the persons/objects. (_______________)
(2) give extra information about a person or a thing, which can be left out. (__________________)
defining clause
non-defining clause
Underline the relative clauses in the sentences and decide if they are defining (D) or non-defining (ND). Translate them into Chinese. Discuss the difference in meaning between the two types of relative clauses.
( ) 1 He went to a city where iron was produced in huge quantities.
( ) 2 The bus which was full of tourists stopped near the Leaning Tower of Pisa.
( ) 3 Melissa lent me some money, which was very generous of her.
( ) 4 The ground is covered with snow and ice, which makes driving very dangerous.
( ) 5 I met the famous professor in the hotel, where the meeting was held.
D
D
ND
ND
ND
Group Work Choose two or three environmental problems that are caused by human activity. Offer solutions. Try to use relative clauses where appropriate.
Exercise
PART. 04
His latest novel, _______ was published last month, has become a bestseller.
We visited the museum _______ collection includes 10,000 ancient coins.
The reason _____________ he was late for class was that his bike broke down.
My favorite writer, ______ books are full of humor, will attend the festival.
He bought a new camera, _________ he spent all his savings.
The professor __________ we invited to give a speech is from Peking University.
This is the laboratory ______________ the important experiment was carried out.
Our monitor, ______ is always ready to help others, was praised by the teacher.
Exercise: 用合适的关系词填空
which
on which
whose
why/for which
whom/that
whose
where/in which
who
The project _________ they are working hard will be completed next year.
I still remember the day _____________ we first traveled abroad together.
He missed the train, ______ made him late for work.
Her car, ______ color is bright red, stands out in the parking lot.
The summer holiday, ______ we plan to travel abroad, is coming soon.
Mr. Smith, ______ son is in my class, often volunteers at the community center.
_______ is known to all, environmental protection is crucial for human survival.
______ can be seen from the data, the number of endangered species is increasing.
on which
when/on which
Exercise: 用合适的关系词填空
which
whose
when
whose
As
As
Summary
PART. 05
添加标题
ADD THE TITLE HERE
Lesson 1 (Grammar)
非限制性定语从句的使用情况
定语从句——限制性与非限制性定语从句
as与which引导的非限制性定语从句的区别
“介词+关系代词”引导的定语从句
定语从句的简化
定语从句的分类
Homework
PART. 06
Summarise what we have learnt in this lesson;
Prepare for the next lesson.
Homework
See you next class!
Lesson 1 (Grammar)
Unit 3
Conservation
Learning Objectives
PART. 01
Understand the daily study and life of British middle school students by watching videos. Based on your own daily study and life, compare the study and life in Chinese and British schools, and find out the similarities and differences between the two. Talk about your first impression of high school life, and have a preliminary perception of the study and life in the senior high school stage.
Learning Objectives
Identify and use defining and non-defining relative clauses correctly, and apply them accurately in discussions about environmental problems. Expand environmental-themed vocabulary and practice integrating relative clauses into sentences to explain human-caused environmental issues and solutions.
Explore cultural values of environmental protection, understanding how human activity drives environmental problems. Recognize shared cultural responsibility for finding solutions, reflecting on how different societies address ecological challenges.
Analyze sentences to distinguish defining/non-defining clauses, interpreting their impact on meaning. Break down environmental issues into components, using relative clauses to structure logical explanations.
Use “grammar-in-context” strategies to master relative clauses. By independently analyzing clauses, completing translation tasks, and reflecting on environmental solutions, students take ownership of learning.
Understand the daily study and life of British middle school students by watching videos. Based on your own daily study and life, compare the study and life in Chinese and British schools, and find out the similarities and differences between the two. Talk about your first impression of high school life, and have a preliminary perception of the study and life in the senior high school stage.
Teaching Focuses and Anticipated Difficulties
Identify and use defining and non-defining relative clauses correctly in discussions about environmental problems, integrating them with environmental vocabulary.
Distinguishing between defining and non-defining relative clauses and creatively applying them to explain environmental issues and propose solutions.
Lead-in
PART. 02
Compare what the differences are between the following two sentences.
①The student who won the first prize in the English contest is my deskmate.
②My deskmate, who won the first prize in the English contest, is very hard-working.
①句无逗号,从句是“识别同桌的关键”;②句有逗号,从句是“额外信息”。由此引出“限制性定语从句(必要信息)” 和“非限制性定语从句(补充信息)”的概念。
Grammar
PART. 03
Relative Clauses-Defining and non-defining Relative Clauses
(定语从句——限制性与非限制性定语从句)
定语从句:在复合句中用来限制、描绘或说明主句中某一名词或代词而起定语作用的从句。
先行词:定语从句所修饰的名词或代词叫作先行词。先行词可以是人、物,也可以是整个句子或者句子的一部分,先行词一般位于定语从句之前。
She is a kind teacher who often helps students with their problems.
Tom decided to start his own business, which amazed his parents.
关系词:引导定语从句的词叫作关系词。按照关系词在定语从句中所作的成分,可将关系词分为关系代词和关系副词。
The beautiful city which/that we visited last summer is Hangzhou.
This is the place where I met my best friend.
关系词 关系词 先行词 充当的成分
关系代词 that 指人、物 主语、宾语、表语
which 指物、句子 主语、宾语、表语
who 指人 主语、宾语、表语
whom 指人 宾语
whose 指人、物 定语
as 指人、物或句子 主语、宾语、表语
关系副词 when 表示时间的名词 时间状语
where 表示地点的名词 地点状语
why 表示原因的名词 原因状语
一、定语从句的分类
1. 限制性定语从句
限制性定语从句对先行词起修饰、限制作用,是句中不可缺少的部分,主句和从句关系非常紧密,不能用逗号分开。
He bought the book that/which is recommended by the teacher.
2. 非限制性定语从句
非限制性定语从句往往是对先行词或整个主句进行附加说明,主从句的关系并不十分密切,若将其去掉,主句的意义仍然完整清楚。从句和主句之间往往用逗号隔开。除了that和why不能引导之外,所有其他关系词如 who, whom, which, whose, as, when,where 等均可引导。
Beijing, which is the capital of China, has a long history.
限制性定语从句 非限制性定语从句
先行词可以用that, why引导 先行词不可以用that, why引导
主句与从句之间不需要用逗号隔开,译成一句话 主句与从句需要用逗号隔开,可译成两句话
引导词有时可以省略(作宾语时) 引导词不可以省略
whom可用who或that代替 whom不可被代替
从句只修饰先行词 从句既可以修饰先行词,也可以修饰整个句子或句子的一部分
二、非限制性定语从句的使用情况
1. 当关系代词指代整个主句内容时,用非限制性定语从句(用which或as引导)。
She won the first prize in the competition, which made her classmates really proud.
她在比赛中得了一等奖,这让她的同学们特别骄傲。
2. 当先行词指的是世界上独一无二的事物或专有名词时,用非限制性定语从句。
The Great Wall, which stands as a symbol of Chinese history, attracts millions of tourists yearly.
长城作为中国历史的象征,每年吸引数百万游客。
Mount Qomolangma, which is the highest peak on Earth, has inspired adventurers.
珠穆朗玛峰是地球最高峰,激励了探险者 。
3. 先行词指某人的亲属关系,具有唯一性和确认性时,例如son, daughter, father, mother, wife 等,用非限制性定语从句。
Her mother, who runs a popular bakery downtown, often shares homemade pastries with neighbors.
她妈妈在市中心经营一家很火的面包店,经常给邻居分享自制糕点。
4. 当引导定语从句的关系代词中,含有some/many/few/a few/little/a little/none/ much/most/half of which (whom)等时,多用非限制性定语从句。
The library has hundreds of old books, few of which have been digitized so far.
图书馆藏有数百本古籍,目前很少有被数字化的。
三、as与which引导的非限制性定语从句的区别
1. as引导定语从句时,仍具有“正如,像,由……可知”等意思,这些字眼翻译时可 不必译出。as定语从句中常含有这些动词:see, know, hear, watch, remember, say, tell, show, expect, guess等。这类动词与as连用几乎成了一种固定搭配。as引导的定语从句可以置于句首、句中或向尾。
She is always working hard, as everyone can see.
正如大家所看到的那样,她一直工作很努力。
2. 在从句中作定语或介词的宾语时,要用 which。
My cousins might visit this weekend, in which situation we’ll prepare a big dinner.
我的表兄妹们这周末可能来,要是那样的话,我们就准备一顿丰盛的晚餐。
3. which引导的从句对主句所叙述的事情进行补充说明表明事物的状态或结果。
which此时指前面主句所提到的这件事,常译为“这一点,这件事”等。这时它所引导的从句与主句之间常表示并列意义或状语意义。注意它引导的从句不像as那样位置灵活,它只能位于主句的后面。
The school canceled the outdoor activity, which disappointed all the students.
学校取消了户外活动,这让所有学生都很失望。
4. 当从句的谓语是否定形式或含着一个复合宾语时,一般用which而不用as。
He avoided joining the football team, which his coach couldn’t figure out.
他回避加入足球队,教练一直搞不懂这事。
四、“介词+关系代词”引导的定语从句
关系副词when, where, why引导定语从句时可被“介词+关系代词”代替。在“介词+关系代词”引导的定语从句中,关系代词只能用which或whom,不可用that或who。先行词指物时用which,先行词指人时用whom。
1. “介词 +which”可以替代关系副词 when, where, why
(1)替代when
I still remember the moment at which (= when) I received my diploma and felt a rush of pride. (at 依据 at the moment 确定)
The era during which (= when) the Industrial Revolution took place was full of dramatic changes. (during 依据 during the era 确定)
(2)替代why
I’m curious about the reason for which (= why) he decided to pursue a career in acting. (for 依据 for the reason 确定)
2. 依据与先行词的固定搭配确定使用什么介词
I’ll always cherish the vacation during which I explored the ancient ruins in Greece. (during 依据 during the vacation 确定)
3. 依据定语从句中动词或形容词的搭配来确定介词
He bought a new guitar, on which he spent nearly half of his monthly salary. (on 依据 spend...on 确定)
These are the scientific theories of which she is most skeptical. (of 依据 be skeptical of 确定)
4. 根据定语从句所表达的具体意思来确定介词
Can you see the mountain behind which lies a small village
除了“介词+which”以外,如果定语从句的先行词是“人”,那么也可以用“介词+whom”引导定语从句。
5. “介词 + 关系代词”的其他表达法
(1)如果在whom和which 之前用of 表示所属关系(即of whom, of which表示所属关系),这时名词需要特指,应加定冠词该名词放在of whom, of which 之前或之后均可。
The book, the cover of which is very attractive, is a best-seller.
The book, of which the cover is very attractive, is a best-seller.
(2)在whom和which之前用of还可以表示部分与整体的关系。这时表示“部分”的数词或代词,放在of whom, of which之前或之后均可。
The class has 30 students, one of whom won the national math competition.
The class has 30 students, of whom one won the national math competition.
The team has ten players, all of whom are highly skilled.
The team has ten players, of whom all are highly skilled.
The club has five founders, the youngest of whom is just 25 years old.
The club has five founders, of whom the youngest is just 25 years old.
五、定语从句的简化
如果含有定语从句的复合句很复杂,为了表意清晰,可以把定语从句进行简化。
1. 关系代词的省略
关系代词 who、whom、that、which 在限制性定语从句中作宾语时,可以省略。
The man (that/who/whom) I met on the street is my old friend.
我在街上遇见的那个人是我的老朋友。
注意:关系代词作介词的宾语时,介词位于句尾时,关系代词可以省略,但关系代词紧跟在介词后面作宾语时,不能省略。
This is the girl (whom) he worked with./ This is the girl with whom he worked.
这是曾与他一起工作过的女孩。
2. 将定语从句变为非谓语动词
①定语从句转换成不定式短语
He is a good comrade with whom you can work.
→ He is a good comrade to work with. 他是个可以与之一起工作的好伙伴。
②定语从句转换成现在分词短语
The people who are living in the village have moved to other places.
→ The people living in the village have moved to other places.
住在村子里的人已经搬到别的地方去了。
③定语从句转换成过去分词短语
I have heard the report which was made by Professor Wang.
→ I have heard the report made by Professor Wang. 我听了王教授作的报告。
Read the sentences and discuss which word(s) the clauses (in italics) refer to.
1. Extinctions, where entire species are wiped out, are not unusual in our Earth’s history.
Refers to extinctions
2. These include the third mass extinction, known as the “Great Dying”, which killed 90% to 96% of all species.
Refers to the “Great Dying”
3. A 2015 study by scientists who were based at Brown University and Duke University in the US, looked at how quickly species die out due to natural causes ...
Refers to scientists
Read the sentences and discuss which word(s) the clauses (in italics) refer to.
4. If a sixth mass extinction occurs, scientists who have studied the issue believe that up to three quarters of all species on Earth could die out.
Refers to scientists
5. We need to take steps to save endangered species, including setting up special areas where plants and animals can be protected.
Refers to special areas
Which of the clauses above:
(1) give information to identify the persons/objects. (_______________)
(2) give extra information about a person or a thing, which can be left out. (__________________)
defining clause
non-defining clause
Underline the relative clauses in the sentences and decide if they are defining (D) or non-defining (ND). Translate them into Chinese. Discuss the difference in meaning between the two types of relative clauses.
( ) 1 He went to a city where iron was produced in huge quantities.
( ) 2 The bus which was full of tourists stopped near the Leaning Tower of Pisa.
( ) 3 Melissa lent me some money, which was very generous of her.
( ) 4 The ground is covered with snow and ice, which makes driving very dangerous.
( ) 5 I met the famous professor in the hotel, where the meeting was held.
D
D
ND
ND
ND
Group Work Choose two or three environmental problems that are caused by human activity. Offer solutions. Try to use relative clauses where appropriate.
Exercise
PART. 04
His latest novel, _______ was published last month, has become a bestseller.
We visited the museum _______ collection includes 10,000 ancient coins.
The reason _____________ he was late for class was that his bike broke down.
My favorite writer, ______ books are full of humor, will attend the festival.
He bought a new camera, _________ he spent all his savings.
The professor __________ we invited to give a speech is from Peking University.
This is the laboratory ______________ the important experiment was carried out.
Our monitor, ______ is always ready to help others, was praised by the teacher.
Exercise: 用合适的关系词填空
which
on which
whose
why/for which
whom/that
whose
where/in which
who
The project _________ they are working hard will be completed next year.
I still remember the day _____________ we first traveled abroad together.
He missed the train, ______ made him late for work.
Her car, ______ color is bright red, stands out in the parking lot.
The summer holiday, ______ we plan to travel abroad, is coming soon.
Mr. Smith, ______ son is in my class, often volunteers at the community center.
_______ is known to all, environmental protection is crucial for human survival.
______ can be seen from the data, the number of endangered species is increasing.
on which
when/on which
Exercise: 用合适的关系词填空
which
whose
when
whose
As
As
Summary
PART. 05
添加标题
ADD THE TITLE HERE
Lesson 1 (Grammar)
非限制性定语从句的使用情况
定语从句——限制性与非限制性定语从句
as与which引导的非限制性定语从句的区别
“介词+关系代词”引导的定语从句
定语从句的简化
定语从句的分类
Homework
PART. 06
Summarise what we have learnt in this lesson;
Prepare for the next lesson.
Homework
See you next class!
同课章节目录
- Unit 1 Relationshis
- Lesson 1 Teachers
- Lesson 2 How Do We Like Teachers’ Feedback?
- Lesson 3 So Close,Yet So Fa
- Unit 2 Success
- Lesson 1 Money vs Success
- Lesson 2 Top Five Secrets of Success
- Lesson 3 Getting to the Top
- Unit 3 Conservation
- Lesson 1 The Sixth Extinction
- Lesson 2 War on Plastic Packets
- Lesson 3 The Road to Destruction
