高一英语初升高衔接复习 词性 课件(共46张PPT)
文档属性
| 名称 | 高一英语初升高衔接复习 词性 课件(共46张PPT) |  | |
| 格式 | pptx | ||
| 文件大小 | 17.0MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 通用版 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2025-08-04 11:04:29 | ||
图片预览









文档简介
(共46张PPT)
词性
名词(Noun)
01
1. 定义:名词是表示人、事物、地点、概念或抽象实体的词汇,在句子中可充当主语、宾语、表语等多种成分。
2. 核心特征:
具有单复数形态变化(如:cat → cats)
可被冠词(a/an/the)、数量词(some/many)或形容词修饰(如:a red apple)
部分名词可通过所有格形式('s或of)表示所属关系(如:Tom's book)双重所有格:a friend of my father's(我父亲的朋友之一)
3.分类:
(1)普通名词 vs 专有名词:
类型 定义 例子
普通名词 泛指一类事物 book, teacher, happiness
专有名词 特指具体名称(首字母大写) China,London, Coca-Cola
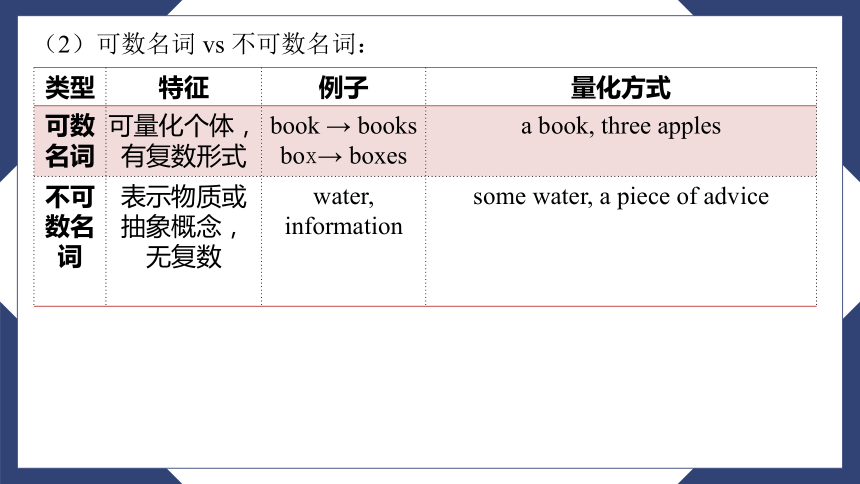
(2)可数名词 vs 不可数名词:
类型 特征 例子 量化方式
可数名词 可量化个体,有复数形式 book → books
box → boxes a book, three apples
不可数名词 表示物质或抽象概念,无复数 water, information some water,
a piece of advice
(2)可数名词 vs 不可数名词:
类型 特征 例子 量化方式
可数名词 可量化个体,有复数形式 book → books box→ boxes a book, three apples
不可数名词 表示物质或抽象概念,无复数 water, information some water, a piece of advice
(3)复合名词:由两个及以上词汇构成新含义
l 按书写形式分类
类型 示例 备注
连写式 notebook, sunflower, fireworks 现代英语中逐渐合并(如:website早期写作web site)
连字符式 mother-in-law, editor-in-chief 多用于避免歧义(如:man-eating shark vs. man eating shark)
分体式 post office, traffic light 常保留原词独立性(如:living room≠“活着的房间”)
(3)复合名词:由两个及以上词汇构成新含义
l 按构成成分分类
类型 构成方式 示例
名词+名词 主体+功能/属性 bookshelf(书架),raincoat(雨衣),airplane(飞机)
动词+名词 动作+受事/工具 swimming pool(游泳池),breakfast(早餐)
形容词+名词 特征+实体 blackboard(黑板),highway(公路),software(软件)
动名词+名词 动态过程+相关事物 dining table(餐桌),waiting room(候车室),reading list(书单)
介词/副词+动词 方向/状态+动作 outlook(观点),income(收入),upgrade(升级)
4.功能:
(1)主语(Subject)
例:Knowledge is power.
(2)宾语(Object)
直接宾语:She bought a necklace.
间接宾语:He gave his sister a gift.
(3)表语(Predicative)
例:His dream is to become a scientist.
(4)定语(Attributive)
例:a stone bridge(名词作定语修饰bridge)
(5)同位语(Appositive)
例:Mr. Zhu, our principal, will give a speech.
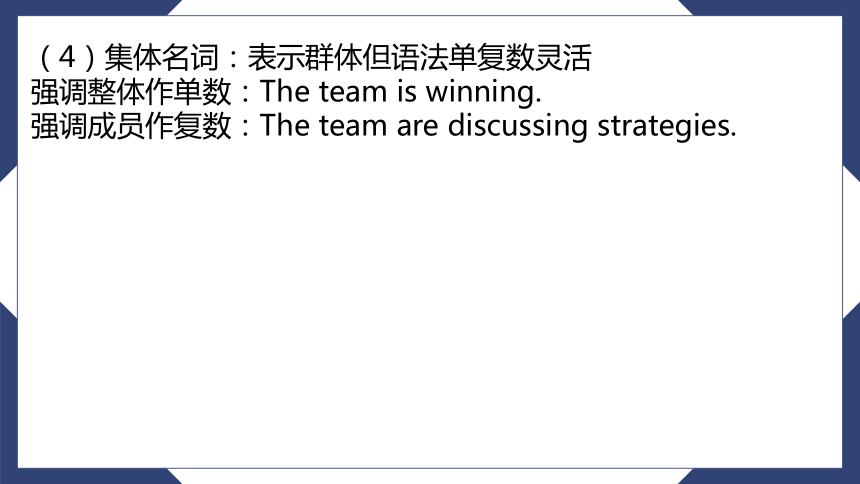
(4)集体名词:表示群体但语法单复数灵活
强调整体作单数:The team is winning.
强调成员作复数:The team are discussing strategies.
4.功能:
(1)主语(Subject)
例:Knowledge is power.
(2)宾语(Object)
直接宾语:She bought a necklace.
间接宾语:He gave his sister a gift.
(3)表语(Predicative)
例:His dream is to become a scientist.
(4)定语(Attributive)
例:a stone bridge(名词作定语修饰bridge)
(5)同位语(Appositive)
例:Mr. Zhu, our principal, will give a speech.
(2)不可数名词量化表达:
容器量词:a bottle of water → three bottles of water
形状量词:a piece of paper
抽象量词:an item of news
5.名词形态变化规则
(1)复数形式:
常规加-s:cat → cats
-s/-x/-ch/-sh后加-es:box → boxes
辅音+y结尾变i加-es:baby → babies
-f/-fe结尾变-ves :knife → knives
不规则变化:child → children
单复数同形:sheep → sheep
(2)不可数名词量化表达:
容器量词:a bottle of water → three bottles of water
形状量词:a piece of paper
抽象量词:an item of news
(2)不可数名词量化表达:
容器量词:a bottle of water → three bottles of water
形状量词:a piece of paper
抽象量词:an item of news
(3)名词所有格结构:
生命体 名词+'s the student's notebook
非生命体 of+名词 the roof of the house
双重所有格 of+名词所有格 a friend of my father's
(2)不可数名词量化表达:
容器量词:a bottle of water → three bottles of water
形状量词:a piece of paper
抽象量词:an item of news
6.特殊用法与易错点:
(1)专有名词普通化:
例:He is the Shakespeare of our time.(指"文学巨匠")
(2)不可数名词可数化:
例:Two coffees, please.(指"两杯咖啡")
(3)复数形式改变含义:
例:custom(习俗)→ customs(海关)
(4)集体名词主谓一致:
例:The family is large.(强调整体)
The family are all doctors.(强调个体成员)
动词(Verb)
02
1. 定义:动词用来表示动作或状态,是句子的核心成分,决定时态、语态和语气。
2.核心功能:
(1)构成句子主干:She writes books.
(2)传递时间信息:通过时态变化,如wrote表过去
(3)表达逻辑关系:通过语态和语气,如被动语态is written
3.分类:
(1)实义动词 vs 助动词:
类型 功能 示例
实义动词 独立表达完整含义 eat, drink, read, write
助动词 辅助构成时态或语态、否定或疑问 be(进行时,被动语态), have(完成时), do(否定/疑问)
(2)及物动词 vs 不及物动词:
类型 特征 示例
及物动词 必须接宾语(直接作用于对象) buy(buy a car), solve(solve a problem)
不及物动词 无需宾语即可完整表意 sleep, arrive, disappear
部分动词兼具及物与不及物性 The bell rings. / She rings the bell.
(3)系动词: 连接主语与表语,描述状态或特征。
常见的系动词有:
① “状态”类:be(am,is,are,was,were)
② “持续”类:keep,stay,remain,lie等
③ “表象”类:seem,appear等
④ “感官”类:look,sound,smell,taste,feel
⑤ “变化”类:grow,turn,get,go,become,come,fall
⑥ “证明”类:prove
情态动词 核心含义 示例
can/could 能力/可能性 She can speak 8 languages.
must 必须/强烈推测 You must finish your homework tomorrow.
should 建议/义务 Students should study hard.
(4)情态动词:表达可能性、必要性或许可(无时态与人称变化)
4.动词语法形态与变化规则:
(1)动词五大基本形态
形态 功能 示例
原形 一般现在时(非第三人称) speak, run
第三人称单数 主语为he/she/it时加-s/-es speaks, runs
过去式 一般过去时 spoke, ran
过去分词 完成时/被动语态 spoken, run
现在分词(-ing) 进行时/动名词 speaking, running
4.动词语法形态与变化规则:
(2)规则与不规则变化
类型 规则 示例
规则动词 过去式/过去分词加-ed play → played, watch → watched
不规则动词 无固定规则(需单独记忆) sing sang → sung,
break → broke → broken,
run →ran →run
5.动词时态与语态:
(1)12大时态
时间轴 一般时 进行时 完成时 完成进行时
现在 She writes a book. She is writing a book. She has written a book. She has been writing a book.
过去 She wrote a book. She was writing a book. She had written a book. She had been writing a book.
将来 She will write a book. She will be writinga book. She will have written a book. She will have been writing a book.
结构:be + done(过去分词),强调动作承受者而非执行者。
例:
主动:The team completed the project.
被动:The project was completed (by the team).
适用场景:
① 执行者未知或不重要(例:The novel was published in 2020.)
② 客观陈述(例:Mistakes were made during the process.)
5.动词时态与语态:
(2)被动语态
结构:be + done(过去分词),强调动作承受者而非执行者。
例:
主动:The team completed the project.
被动:The project was completed (by the team).
适用场景:
① 执行者未知或不重要(例:The novel was published in 2020.)
② 客观陈述(例:Mistakes were made during the process.)
6.动词特殊用法
(1)非谓语动词
类型 功能 示例
不定式to do 表目的或潜在动作 She studies hard to get good grades.
动名词-ing 作主语或宾语 Swimming improves flexibility.
分词(现在分词-ing、过去分词done) 作定语或状语 China is a developing country now.(现在分词)The fallen leaves will be removed by cleaners.(过去分词)
结构:be + done(过去分词),强调动作承受者而非执行者。
例:
主动:The team completed the project.
被动:The project was completed (by the team).
适用场景:
① 执行者未知或不重要(例:The novel was published in 2020.)
② 客观陈述(例:Mistakes were made during the process.)
5.动词时态与语态:
(2)主谓一致
① 核心规则:
1)单数主语+单数动词(例:The list of items is on the desk.)
2)复数主语+复数动词(例:The strategies are being revised.)
② 特殊处理:
1)集体名词(family, team等)可单可复(例:The team has/ have different opinions.)
2)“Either...or”等结构就近原则(例:Either the manager or the employees
are responsible.)
形容词(Adjective)
03
1.定义:修饰名词,描述性质或状态。
2.位置:
名词前: a happy child.
连系动词后: The cake tastes delicious.
3.形容词常用后缀:
-al、-able (有能力的)、 -(a)n(某国人的)、 -ese(某国人的)、-en (多用于表示材料的名词后)、 -ern (方向的)、 -ful、 -(ic)al、 -ish、 -ive、 -less (表示否定)、 -like (像……的)、 -ly、 -ed、 -ing、 -ous、 -some、 -y (表示天气)等。
4.比较级与最高级:
(1)规则变化:
① 直接加-er/-est:long→longer→longest
② 加-r/-st:wide→wider→widest
③ 辅音字母加y结尾,变y为i再加er/est: happy→happier→happiest
④ 双写末尾字母再加er/est: big→bigger→biggest
⑤ 多音节前加more/most: important→more important→most important
(2)不规则变化:good→better→best, bad→worse→worst
副词(Adverb)
04
1.定义:修饰动词、形容词、其他副词或整个句子。
2.常见类型:
方式副词(quickly, carefully)
频率副词(always, rarely)
程度副词(very, extremely)
3.副词位置规则:
频度副词:I often read books.(实义动词前)
程度副词:She is extremely happy.(修饰形容词)
3.去e加-ly
true-truly whole-wholly
形容词与副词转换——副词构成规律:
1.直接加-ly:
real-really、quick-quickly 、quiet-quietly
2.以辅音字母加y结尾,变y为i再加-ly:
lucky-luckily、happy-happily、busy-busily
3.去e加-ly:
true-truly、whole-wholly
4.以le结尾,去e再加y:
simple-simply、possible-possibly、gentle-gently
5.以ic结尾,加al再加ly:
energetic-energetically、basic-basically
6.直接加y:
full-fully、dull-dully
3.去e加-ly
true-truly whole-wholly
形容词与副词转换——副词构成规律:
7.形容词与副词同形:
fast early late far straight right
high adj,高的——high adv.在高处——highly adv.很,非常
hard adj.硬的——hard adv.努力地——hardly adv.几乎不
near adj.近的——near adv.在附近——nearly adv. 几乎
8.形容词与副词异形:
good-well
代词(Pronoun)
05
1.定义:替代名词以避免重复。
2.分类:
人称代词(主格):I, we, you, you, he, she, they, it
人称代词(宾格):me, us, you, him, her, them, it
形容词性物主代词:my, our, your, his, her, their, its
名词性物主代词:mine, ours, yours, his, hers, theirs
反身代词:myself, ourselves, yourself, yourselves, himself, herself, themselves, itself
指示代词:this, that, these, those
不定代词:some/any, each other/one another。
介词(Preposition)
06
1.定义:表示名词与其他词的关系。
2.常见介词:in, on, at, with, by, from, to, of
时间介词对比:
in:月份/季节(in June,in the morning/afternoon)
on:具体的某一天(on Monday)
at:钟点(at 7:00)
“动词+介词”固定搭配:
agree with(同意某人)、apply for(申请)
介词短语作后置定语:
The book on the desk is mine.(桌子上那本书)
连词(Conjunction)
07
2.分类:
(1)并列连词(and, but, or)
1.定义:连接单词、短语或句子。
连词 逻辑关系 典型例句
and 并列/递进 Teachers are our guides and friends.
but 转折 She wants to go out, but her parents doesn’t allow.
or 选择/假设 Come on or we will be late.
(2)从属连词
类型 常用连词 例句 易错点
时间 when, before, until When you finish the homework, you can go to play. While表时间需接进行时
因果 because, since,for He was punished because he was late again. 避免与so连用
条件 if, unless If you finish your homework, you can go to play. Unless=if not
让步 although, even if/though Although he failed to pass the exam, he was praised by teachers. 不与but连用
(3)关联连词
连词 功能 例句
either…or 二选一(要么...要么...) Either you or he will be the monitor.
neither…nor 两者都不(既不...也不...) Neither you nor he will be punished.
not only…but also 强调递进(不但...而且...) The teacher not only teaches us knowledge but also teaches us how to be a person.
whether…or 多条件选择(是否...) The system checks whether the user is human or a robot.
冠词(Article)
08
1.定义:限定名词。
2.分类:
(1)不定冠词: a/an表泛指
注意:辅音音标前用a, 元音音标前用an。
(2)定冠词: the表特指
零冠词场景:
抽象概念:Love is important.
固定搭配:go to school, by bus
数词
09
2.分类:
(1)基数词
1. 定义:表示数量(基数词)或顺序(序数词)的词汇,可在句子中作主语、表语、定语、表语等。
范围 构成规则
1-12 独立单词(one, twelve)
13-19 基数词+teen(thirteen, fifteen)
20-90整十 基数词+ty(twenty, ninety)
复合数(21-99) 整十数+连字符+个位数(twenty-one)
百/千/百万 千位逗号分隔(5,000 → five thousand)
(2)序数词:
形式 构成规则
第一至第三 独立词形(first, second, third)
第四及以上 基数词+th(fourth, tenth)
以y结尾的数 y变i+eth(twenty → twentieth)
复合序数词 仅最后部分变序数(twenty-first → 21st)
(3)特殊数词(分数/小数/倍数)
类型 构成规则 例子
分数 分子(基数)+分母(序数+s) 2/3 → two-thirds(需加连字符)
小数 小数点读作“point” 0.5 → zero point five / 3.14 → three point one four
倍数 基数词+times(double/triple为特例)
感 谢 观 看
T H A N K S
词性
名词(Noun)
01
1. 定义:名词是表示人、事物、地点、概念或抽象实体的词汇,在句子中可充当主语、宾语、表语等多种成分。
2. 核心特征:
具有单复数形态变化(如:cat → cats)
可被冠词(a/an/the)、数量词(some/many)或形容词修饰(如:a red apple)
部分名词可通过所有格形式('s或of)表示所属关系(如:Tom's book)双重所有格:a friend of my father's(我父亲的朋友之一)
3.分类:
(1)普通名词 vs 专有名词:
类型 定义 例子
普通名词 泛指一类事物 book, teacher, happiness
专有名词 特指具体名称(首字母大写) China,London, Coca-Cola
(2)可数名词 vs 不可数名词:
类型 特征 例子 量化方式
可数名词 可量化个体,有复数形式 book → books
box → boxes a book, three apples
不可数名词 表示物质或抽象概念,无复数 water, information some water,
a piece of advice
(2)可数名词 vs 不可数名词:
类型 特征 例子 量化方式
可数名词 可量化个体,有复数形式 book → books box→ boxes a book, three apples
不可数名词 表示物质或抽象概念,无复数 water, information some water, a piece of advice
(3)复合名词:由两个及以上词汇构成新含义
l 按书写形式分类
类型 示例 备注
连写式 notebook, sunflower, fireworks 现代英语中逐渐合并(如:website早期写作web site)
连字符式 mother-in-law, editor-in-chief 多用于避免歧义(如:man-eating shark vs. man eating shark)
分体式 post office, traffic light 常保留原词独立性(如:living room≠“活着的房间”)
(3)复合名词:由两个及以上词汇构成新含义
l 按构成成分分类
类型 构成方式 示例
名词+名词 主体+功能/属性 bookshelf(书架),raincoat(雨衣),airplane(飞机)
动词+名词 动作+受事/工具 swimming pool(游泳池),breakfast(早餐)
形容词+名词 特征+实体 blackboard(黑板),highway(公路),software(软件)
动名词+名词 动态过程+相关事物 dining table(餐桌),waiting room(候车室),reading list(书单)
介词/副词+动词 方向/状态+动作 outlook(观点),income(收入),upgrade(升级)
4.功能:
(1)主语(Subject)
例:Knowledge is power.
(2)宾语(Object)
直接宾语:She bought a necklace.
间接宾语:He gave his sister a gift.
(3)表语(Predicative)
例:His dream is to become a scientist.
(4)定语(Attributive)
例:a stone bridge(名词作定语修饰bridge)
(5)同位语(Appositive)
例:Mr. Zhu, our principal, will give a speech.
(4)集体名词:表示群体但语法单复数灵活
强调整体作单数:The team is winning.
强调成员作复数:The team are discussing strategies.
4.功能:
(1)主语(Subject)
例:Knowledge is power.
(2)宾语(Object)
直接宾语:She bought a necklace.
间接宾语:He gave his sister a gift.
(3)表语(Predicative)
例:His dream is to become a scientist.
(4)定语(Attributive)
例:a stone bridge(名词作定语修饰bridge)
(5)同位语(Appositive)
例:Mr. Zhu, our principal, will give a speech.
(2)不可数名词量化表达:
容器量词:a bottle of water → three bottles of water
形状量词:a piece of paper
抽象量词:an item of news
5.名词形态变化规则
(1)复数形式:
常规加-s:cat → cats
-s/-x/-ch/-sh后加-es:box → boxes
辅音+y结尾变i加-es:baby → babies
-f/-fe结尾变-ves :knife → knives
不规则变化:child → children
单复数同形:sheep → sheep
(2)不可数名词量化表达:
容器量词:a bottle of water → three bottles of water
形状量词:a piece of paper
抽象量词:an item of news
(2)不可数名词量化表达:
容器量词:a bottle of water → three bottles of water
形状量词:a piece of paper
抽象量词:an item of news
(3)名词所有格结构:
生命体 名词+'s the student's notebook
非生命体 of+名词 the roof of the house
双重所有格 of+名词所有格 a friend of my father's
(2)不可数名词量化表达:
容器量词:a bottle of water → three bottles of water
形状量词:a piece of paper
抽象量词:an item of news
6.特殊用法与易错点:
(1)专有名词普通化:
例:He is the Shakespeare of our time.(指"文学巨匠")
(2)不可数名词可数化:
例:Two coffees, please.(指"两杯咖啡")
(3)复数形式改变含义:
例:custom(习俗)→ customs(海关)
(4)集体名词主谓一致:
例:The family is large.(强调整体)
The family are all doctors.(强调个体成员)
动词(Verb)
02
1. 定义:动词用来表示动作或状态,是句子的核心成分,决定时态、语态和语气。
2.核心功能:
(1)构成句子主干:She writes books.
(2)传递时间信息:通过时态变化,如wrote表过去
(3)表达逻辑关系:通过语态和语气,如被动语态is written
3.分类:
(1)实义动词 vs 助动词:
类型 功能 示例
实义动词 独立表达完整含义 eat, drink, read, write
助动词 辅助构成时态或语态、否定或疑问 be(进行时,被动语态), have(完成时), do(否定/疑问)
(2)及物动词 vs 不及物动词:
类型 特征 示例
及物动词 必须接宾语(直接作用于对象) buy(buy a car), solve(solve a problem)
不及物动词 无需宾语即可完整表意 sleep, arrive, disappear
部分动词兼具及物与不及物性 The bell rings. / She rings the bell.
(3)系动词: 连接主语与表语,描述状态或特征。
常见的系动词有:
① “状态”类:be(am,is,are,was,were)
② “持续”类:keep,stay,remain,lie等
③ “表象”类:seem,appear等
④ “感官”类:look,sound,smell,taste,feel
⑤ “变化”类:grow,turn,get,go,become,come,fall
⑥ “证明”类:prove
情态动词 核心含义 示例
can/could 能力/可能性 She can speak 8 languages.
must 必须/强烈推测 You must finish your homework tomorrow.
should 建议/义务 Students should study hard.
(4)情态动词:表达可能性、必要性或许可(无时态与人称变化)
4.动词语法形态与变化规则:
(1)动词五大基本形态
形态 功能 示例
原形 一般现在时(非第三人称) speak, run
第三人称单数 主语为he/she/it时加-s/-es speaks, runs
过去式 一般过去时 spoke, ran
过去分词 完成时/被动语态 spoken, run
现在分词(-ing) 进行时/动名词 speaking, running
4.动词语法形态与变化规则:
(2)规则与不规则变化
类型 规则 示例
规则动词 过去式/过去分词加-ed play → played, watch → watched
不规则动词 无固定规则(需单独记忆) sing sang → sung,
break → broke → broken,
run →ran →run
5.动词时态与语态:
(1)12大时态
时间轴 一般时 进行时 完成时 完成进行时
现在 She writes a book. She is writing a book. She has written a book. She has been writing a book.
过去 She wrote a book. She was writing a book. She had written a book. She had been writing a book.
将来 She will write a book. She will be writinga book. She will have written a book. She will have been writing a book.
结构:be + done(过去分词),强调动作承受者而非执行者。
例:
主动:The team completed the project.
被动:The project was completed (by the team).
适用场景:
① 执行者未知或不重要(例:The novel was published in 2020.)
② 客观陈述(例:Mistakes were made during the process.)
5.动词时态与语态:
(2)被动语态
结构:be + done(过去分词),强调动作承受者而非执行者。
例:
主动:The team completed the project.
被动:The project was completed (by the team).
适用场景:
① 执行者未知或不重要(例:The novel was published in 2020.)
② 客观陈述(例:Mistakes were made during the process.)
6.动词特殊用法
(1)非谓语动词
类型 功能 示例
不定式to do 表目的或潜在动作 She studies hard to get good grades.
动名词-ing 作主语或宾语 Swimming improves flexibility.
分词(现在分词-ing、过去分词done) 作定语或状语 China is a developing country now.(现在分词)The fallen leaves will be removed by cleaners.(过去分词)
结构:be + done(过去分词),强调动作承受者而非执行者。
例:
主动:The team completed the project.
被动:The project was completed (by the team).
适用场景:
① 执行者未知或不重要(例:The novel was published in 2020.)
② 客观陈述(例:Mistakes were made during the process.)
5.动词时态与语态:
(2)主谓一致
① 核心规则:
1)单数主语+单数动词(例:The list of items is on the desk.)
2)复数主语+复数动词(例:The strategies are being revised.)
② 特殊处理:
1)集体名词(family, team等)可单可复(例:The team has/ have different opinions.)
2)“Either...or”等结构就近原则(例:Either the manager or the employees
are responsible.)
形容词(Adjective)
03
1.定义:修饰名词,描述性质或状态。
2.位置:
名词前: a happy child.
连系动词后: The cake tastes delicious.
3.形容词常用后缀:
-al、-able (有能力的)、 -(a)n(某国人的)、 -ese(某国人的)、-en (多用于表示材料的名词后)、 -ern (方向的)、 -ful、 -(ic)al、 -ish、 -ive、 -less (表示否定)、 -like (像……的)、 -ly、 -ed、 -ing、 -ous、 -some、 -y (表示天气)等。
4.比较级与最高级:
(1)规则变化:
① 直接加-er/-est:long→longer→longest
② 加-r/-st:wide→wider→widest
③ 辅音字母加y结尾,变y为i再加er/est: happy→happier→happiest
④ 双写末尾字母再加er/est: big→bigger→biggest
⑤ 多音节前加more/most: important→more important→most important
(2)不规则变化:good→better→best, bad→worse→worst
副词(Adverb)
04
1.定义:修饰动词、形容词、其他副词或整个句子。
2.常见类型:
方式副词(quickly, carefully)
频率副词(always, rarely)
程度副词(very, extremely)
3.副词位置规则:
频度副词:I often read books.(实义动词前)
程度副词:She is extremely happy.(修饰形容词)
3.去e加-ly
true-truly whole-wholly
形容词与副词转换——副词构成规律:
1.直接加-ly:
real-really、quick-quickly 、quiet-quietly
2.以辅音字母加y结尾,变y为i再加-ly:
lucky-luckily、happy-happily、busy-busily
3.去e加-ly:
true-truly、whole-wholly
4.以le结尾,去e再加y:
simple-simply、possible-possibly、gentle-gently
5.以ic结尾,加al再加ly:
energetic-energetically、basic-basically
6.直接加y:
full-fully、dull-dully
3.去e加-ly
true-truly whole-wholly
形容词与副词转换——副词构成规律:
7.形容词与副词同形:
fast early late far straight right
high adj,高的——high adv.在高处——highly adv.很,非常
hard adj.硬的——hard adv.努力地——hardly adv.几乎不
near adj.近的——near adv.在附近——nearly adv. 几乎
8.形容词与副词异形:
good-well
代词(Pronoun)
05
1.定义:替代名词以避免重复。
2.分类:
人称代词(主格):I, we, you, you, he, she, they, it
人称代词(宾格):me, us, you, him, her, them, it
形容词性物主代词:my, our, your, his, her, their, its
名词性物主代词:mine, ours, yours, his, hers, theirs
反身代词:myself, ourselves, yourself, yourselves, himself, herself, themselves, itself
指示代词:this, that, these, those
不定代词:some/any, each other/one another。
介词(Preposition)
06
1.定义:表示名词与其他词的关系。
2.常见介词:in, on, at, with, by, from, to, of
时间介词对比:
in:月份/季节(in June,in the morning/afternoon)
on:具体的某一天(on Monday)
at:钟点(at 7:00)
“动词+介词”固定搭配:
agree with(同意某人)、apply for(申请)
介词短语作后置定语:
The book on the desk is mine.(桌子上那本书)
连词(Conjunction)
07
2.分类:
(1)并列连词(and, but, or)
1.定义:连接单词、短语或句子。
连词 逻辑关系 典型例句
and 并列/递进 Teachers are our guides and friends.
but 转折 She wants to go out, but her parents doesn’t allow.
or 选择/假设 Come on or we will be late.
(2)从属连词
类型 常用连词 例句 易错点
时间 when, before, until When you finish the homework, you can go to play. While表时间需接进行时
因果 because, since,for He was punished because he was late again. 避免与so连用
条件 if, unless If you finish your homework, you can go to play. Unless=if not
让步 although, even if/though Although he failed to pass the exam, he was praised by teachers. 不与but连用
(3)关联连词
连词 功能 例句
either…or 二选一(要么...要么...) Either you or he will be the monitor.
neither…nor 两者都不(既不...也不...) Neither you nor he will be punished.
not only…but also 强调递进(不但...而且...) The teacher not only teaches us knowledge but also teaches us how to be a person.
whether…or 多条件选择(是否...) The system checks whether the user is human or a robot.
冠词(Article)
08
1.定义:限定名词。
2.分类:
(1)不定冠词: a/an表泛指
注意:辅音音标前用a, 元音音标前用an。
(2)定冠词: the表特指
零冠词场景:
抽象概念:Love is important.
固定搭配:go to school, by bus
数词
09
2.分类:
(1)基数词
1. 定义:表示数量(基数词)或顺序(序数词)的词汇,可在句子中作主语、表语、定语、表语等。
范围 构成规则
1-12 独立单词(one, twelve)
13-19 基数词+teen(thirteen, fifteen)
20-90整十 基数词+ty(twenty, ninety)
复合数(21-99) 整十数+连字符+个位数(twenty-one)
百/千/百万 千位逗号分隔(5,000 → five thousand)
(2)序数词:
形式 构成规则
第一至第三 独立词形(first, second, third)
第四及以上 基数词+th(fourth, tenth)
以y结尾的数 y变i+eth(twenty → twentieth)
复合序数词 仅最后部分变序数(twenty-first → 21st)
(3)特殊数词(分数/小数/倍数)
类型 构成规则 例子
分数 分子(基数)+分母(序数+s) 2/3 → two-thirds(需加连字符)
小数 小数点读作“point” 0.5 → zero point five / 3.14 → three point one four
倍数 基数词+times(double/triple为特例)
感 谢 观 看
T H A N K S
同课章节目录
