人教版(PEP)小学英语小升初必考句型课件(共57张PPT)-2025-2026学年人教PEP版
文档属性
| 名称 | 人教版(PEP)小学英语小升初必考句型课件(共57张PPT)-2025-2026学年人教PEP版 |  | |
| 格式 | pptx | ||
| 文件大小 | 3.6MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 试卷 | ||
| 版本资源 | 人教版(PEP) | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2025-08-04 12:13:03 | ||
图片预览










文档简介
(共57张PPT)
英语小升初必考句型
目录
Part One.
There be 句型
Part Two.
一般现在时
Part Three.
现在进行时
Part Four.
一般过去时
Part Five.
形容词比较级 / 最高级
Part Six.
疑问句
Part Seven.
祈使句
Part Eight.
情态动词
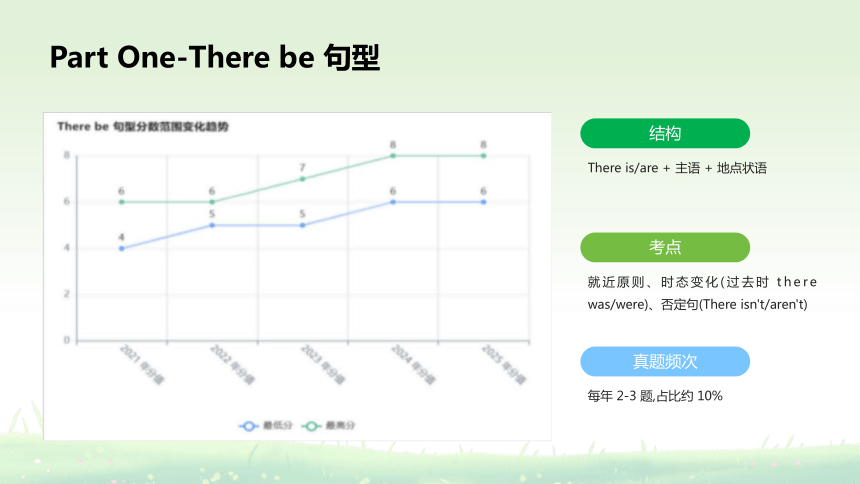
Part One-There be 句型
There is/are + 主语 + 地点状语
结构
就近原则、时态变化(过去时 there was/were)、否定句(There isn't/aren't)
考点
每年 2-3 题,占比约 10%
真题频次
一、基本结构与 be 动词的选择
01
There is a cat under the chair.(现在时,主语 “a cat” 为单数)
There was some milk in the glass yesterday.(过去时,主语 “milk” 为不可数名词)
单数主语 / 不可数名词 → 用 is(现在时)、was(过去时)
02
There are three books on the desk.(现在时,主语 “three books” 为复数)
There were many students in the hall last week.(过去时,主语 “students” 为复数)
复数主语 → 用 are(现在时)、were(过去时)
03
There is a pen and two pencils in the box.(最近的主语 “a pen” 为单数,用 is)
There are two pencils and a pen in the box.(最近的主语 “two pencils” 为复数,用 are)
就近原则:当主语是由 “and” 连接的多个名词时,be 动词的形式与最近的主语保持一致
二、时态变化
表示将来存在的状态,用 There will be 或 There is/are going to be
There will be a party tomorrow evening.
There is going to be a football match next week.
一般将来时:
表示过去存在的状态,用 was/were
There were no cars in this street 50 years ago.
一般过去时:
表示现在存在的状态,用 is/are
There is a park near my home.
一般现在时:
三、否定句
There won't be a meeting tomorrow.
将来时
There isn't a library here.(单数 / 不可数);There aren't any apples.(复数)
现在时
There wasn't a hospital in the village.;There weren't enough chairs.
过去时
02
01
03
在 be 动词后加 not(注意缩写形式)
四、疑问句
Is there a bank near here (肯定回答:Yes, there is. 否定回答:No, there isn't.)Were there any birds in the tree yesterday (肯定回答:Yes, there were. 否定回答:No, there weren't.)
一般疑问句
01
对数量提问(主语为可数名词):How many + 复数名词 + are there + 地点?
How many students are there in your class
对数量提问(主语为不可数名词):How much + 不可数名词 + is there + 地点?
How much water is there in the bottle
对地点提问:Where + be 动词 + there? Where is there a good restaurant
特殊疑问句
02
将 be 动词提到 there 之前,句末加问号:
五、易错点提醒
01
正确:There is a book on the desk.(桌上有一本书。)
正确:I have a book.(我有一本书。)
避免与 “have” 混淆:There be 表示 “存在”,have 表示 “拥有”。
02
正确:There is some rice in the bowl.(碗里有一些米饭。)
错误:There are some rice in the bowl.
不可数名词作主语时,be 动词用单数(is/was),即使有 “some” 修饰。
03
In the room, there are three people.(房间里有三个人。)
时间 / 地点状语可位于句末或句首(强调地点时)。
1. There ______ a big tree and some flowers in the garden.
A. is B. are
答案:A
解析:There be句型遵循"就近原则",靠近be动词的主语"a big tree"是单数,因此用is。
2. ______ there any milk in the fridge
A. Is B. Are
答案:A
解析:"milk"是不可数名词,视为单数,因此be动词用is。
小试牛刀
3.There ______ two libraries in our school five years ago.
A. was B. were
答案:B
解析:主语"two libraries"是复数,且时间状语"five years ago"表示过去,因此用were。
4. There ______ not any books on the shelf.
A. isn't B. aren't
答案:B
解析:主语"books"是复数,否定句中be动词用aren't。
小试牛刀
5. How many students ______ in your class
A. is there B. are there
答案:B
解析:"students"是复数,特殊疑问句中be动词用are,因此选are there。
6. There ______ a football match in our school tomorrow afternoon.
A. will be B. is
答案:A
解析:时间状语"tomorrow afternoon"表示将来,因此用There will be结构。
小试牛刀
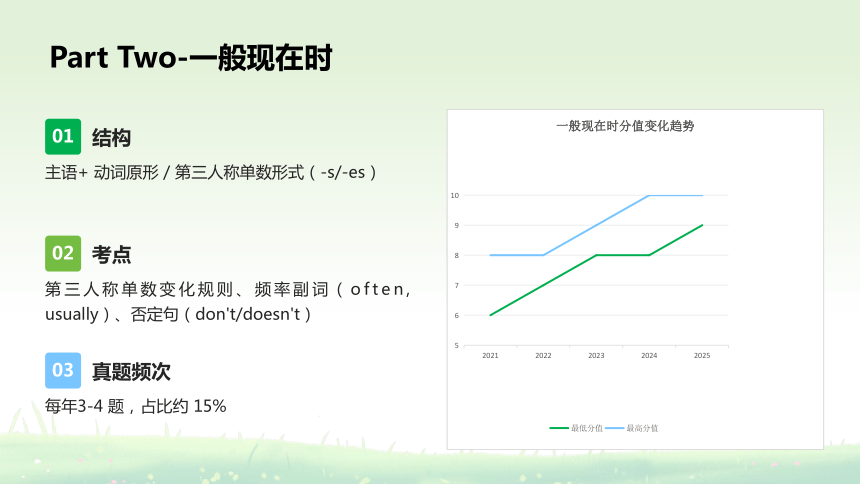
Part Two-一般现在时
主语+ 动词原形 / 第三人称单数形式(-s/-es)
结构
01
第三人称单数变化规则、频率副词(often, usually)、否定句(don't/doesn't)
考点
02
每年3-4 题,占比约 15%
真题频次
03
一、基本用法
表示经常性或习惯性的动作(常与时间状语如 always, usually, often, sometimes, every day 等连用)
I get up at 7:00 every morning.(我每天早上 7 点起床。)
She often goes to the park on weekends.(她经常周末去公园。)
表示客观事实、真理或永恒不变的状态
The sun rises in the east.(太阳从东方升起。)
Water boils at 100℃.(水在 100 摄氏度沸腾。)
表示现阶段的状态或特征
He likes playing basketball.(他喜欢打篮球。)
My brother is a teacher.(我哥哥是一名教师。)
用于时间、条件、让步状语从句中,代替一般将来时
I will call you when she arrives.(她到的时候我会打电话给你。)
If it rains tomorrow, we will stay at home.(如果明天下雨,我们就待在家里。)
二、动词形式变化
01
be 动词的变化
第一人称单数(I)→ am
第三人称单数(he/she/it/ 单数名词)→ is
其他人称(you/we/they/ 复数名词)→ are
例:
I am a student.
He is a doctor.
They are good friends.
02
实义动词的变化
主语是第三人称单数(he/she/it/ 单数名词)时,动词需加 -s/-es(规则变化):
一般动词加 -s:work → works;play → plays
以 s, x, ch, sh, o 结尾的动词加 -es:pass → passes;fix → fixes;teach → teaches;wash → washes;go → goes
以辅音字母 + y 结尾的动词,变 y 为 i 加 - es:study → studies;carry → carries
其他人称(I/you/we/they/ 复数名词)用动词原形:
例:I study English. / They play football.
三、句式结构
主语 + be 动词 + 其他.
例:She is happy. / They are in the classroom.
主语 + 实义动词 + 其他.
例:He plays tennis. / We eat breakfast at 7:00.
肯定句
Be 动词 + 主语 + 其他?
例:Is he a teacher → Yes, he is. / No, he isn’t.
Do/Does + 主语 + 实义动词原形 + 其他?(第三人称单数用 Does,其他人称用 Do)
例:Do you speak French → Yes, I do. / No, I don’t.
一般疑问句
主语 + be 动词 + not + 其他.
例:It is not cold. / You are not late.
主语 + don’t/doesn’t + 实义动词原形 + 其他.
(第三人称单数用 doesn’t,其他人称用 don’t)
例:She doesn’t like coffee. / They don’t live here.
否定句
疑问词 + be 动词 + 主语 + 其他?
例:Where is your bag → It’s on the desk.
疑问词 + do/does + 主语 + 实义动词原形 + 其他?
例:What do you do → I am a student.
特殊疑问句
四、常见易错点提示
01
第三人称单数动词的变化:易漏加 -s/-es,如误写 "He play football"(正确:He plays football)。
否定句和疑问句中实义动词的形式:需用原形,如误写 "She doesn’t plays tennis"(正确:She doesn’t play tennis)。
02
与 "be 动词" 和 "实义动词" 的连用:一般现在时中,be 动词和实义动词不能同时出现,如误写 "They are play basketball"(正确:They play basketball)。
03
1. My mother ______ (cook) dinner every evening.
小试牛刀
答案:cooks
解析:主语 “my mother” 是第三人称单数,根据一般现在时规则,实义动词需用第三人称单数形式,cook 的第三人称单数为 cooks。
2. ______ your father ______ (read) newspapers in the morning
A. Do; read B. Does; read
答案:B
解析:主语 “your father” 是第三人称单数,一般疑问句需用助动词 does 开头,后面接动词原形 read,故选 B。
3. Tom ______ (not like) playing basketball. He likes football.
小试牛刀
答案:doesn’t like
解析:主语 “Tom” 是第三人称单数,否定句需用助动词 doesn’t,后面接动词原形 like,故填 doesn’t like。
4. The earth ______ (go) around the sun.
答案:goes
解析:此句描述客观真理,用一般现在时;主语 “the earth” 是第三人称单数,go 的第三人称单数为 goes(以 o 结尾加 es)。
Part Three-现在进行时
主语+ am/is/are + 动词 - ing
结构
动词- ing 形式变化规则、时间状语(now, look)、疑问句(Is/Are...doing )
考点
每年2-3 题,占比约 10%
真题频次
一、基本结构
主语 + am/is/are + 动词 - ing 形式
第一人称单数(I)→ am + 动词 - ing
第三人称单数(he/she/it/ 单数名词)→ is + 动词 - ing
其他人称(you/we/they/ 复数名词)→ are + 动词 - ing
例:
I am reading a book.(我正在看书。)
She is singing.(她正在唱歌。)
They are playing football.(他们正在踢足球。)
二、动词 - ing 形式变化规则
一般动词:直接加 - ing
work → working;play → playing;look → looking
1
以不发音的 e 结尾:去 e 加 - ing
take → taking;dance → dancing;write → writing
2
以重读闭音节结尾(辅 + 元 + 辅):双写最后一个辅音字母加 - ing
run → running;swim → swimming;sit → sitting
3
以 ie 结尾:变 ie 为 y 加 - ing
lie → lying;die → dying
4
三、句式结构
主语 + am/is/are + 动词 - ing + 其他
He is watching TV now.(他现在正在看电视。)
We are having a class.(我们正在上课。)
肯定句
主语 + am/is/are + not + 动词 - ing + 其他
She is not (isn’t) dancing.(她没在跳舞。)
They are not (aren’t) playing basketball.(他们没在打篮球。)
否定句
疑问词 + am/is/are + 主语 + 动词 - ing + 其他?
What is she doing (她正在做什么?)
→ She is drawing a picture.
Where are they playing (他们正在哪里玩?)
→ They are playing in the park.
特殊疑问句
Am/Is/Are + 主语 + 动词 - ing + 其他?
Is he reading a newspaper (他正在看报纸吗?)
→ Yes, he is. / No, he isn’t.
Are they talking (他们在说话吗?)
→ Yes, they are. / No, they aren’t.
一般疑问句
1. Listen! Someone ______ (sing) in the next room.
答案:is singing
解析:“Listen!” 是现在进行时标志,主语 “someone” 视为单数,用 is + singing。
2.My parents ______ (watch) TV now.
答案:are watching
解析:“now” 提示现在进行时,主语 “my parents” 是复数,用 are + watching。
小试牛刀
3.We ______ (not play) football. We’re reading.
答案:aren’t playing
解析:后句用现在进行时,前句也用现在进行时否定形式 aren’t + playing。
Part Four-一般过去时
主语+ 动词过去式(规则 + ed / 不规则变化)
结构
不规则动词表、时间状语(yesterday, last week)、否定句(didn't + 动词原形)
考点
每年2-3 题,占比约 10%
真题频次
一、基本结构
一般过去时表示过去某个时间发生的动作或存在的状态,常与表示过去的时间状语连用,
如 yesterday, last week, two years ago, in 2020 等。
01
含实义动词:主语 + 动词过去式 + 其他
02
含 be 动词:主语 + was/were + 其他
第一人称单数(I)/ 第三人称单数(he/she/it/ 单数名词)→ was
其他人称(you/we/they/ 复数名词)→ were
二、动词过去式变化规则
01
规则动词:
一般加 - ed:work → worked;play → played
以不发音的 e 结尾加 - d:live → lived;like → liked
以辅音字母 + y 结尾:变 y 为 i 加 - ed:study → studied;carry → carried
以重读闭音节结尾(辅 + 元 + 辅):双写最后一个辅音字母加 - ed:stop → stopped;plan → planned
02
不规则动词:需特殊记忆(常见例词)
go → went;come → came;see → saw;eat → ate;do → did;is/am → was;are → were
三、句式结构
实义动词:主语 + didn’t + 动词原形 + 其他
例:He didn’t play basketball yesterday.(他昨天没打篮球。)
be 动词:主语 + wasn’t/weren’t + 其他
例:She wasn’t a teacher.(她以前不是老师。)
否定句:
实义动词:Did + 主语 + 动词原形 + 其他?
例:Did he play basketball yesterday (他昨天打篮球了吗?)
→ Yes, he did. / No, he didn’t.
be 动词:Was/Were + 主语 + 其他?
例:Were you at home last night (你昨晚在家吗?)
→ Yes, I was. / No, I wasn’t.
一般疑问句
实义动词:He played basketball yesterday.(他昨天打篮球了。)
be 动词:She was a student in 2018.(2018 年她是一名学生。)
肯定句:
疑问词 + did + 主语 + 动词原形 + 其他?(实义动词)
例:What did you do yesterday (你昨天做什么了?)
疑问词 + was/were + 主语 + 其他?(be 动词)
特殊疑问句:
1.He ______ (go) to the park with his friends yesterday.
答案:went
解析:“yesterday” 提示用一般过去时,go 的过去式是不规则变化 went。
2.______ you ______ (watch) TV last night
A. Do; watch B. Did; watch
答案:B
解析:“last night” 提示用一般过去时,一般疑问句用助动词 did 开头,后接动词原形 watch,故选 B。
小试牛刀
3.My parents ______ (not be) at home last weekend.
答案:weren’t
解析:“last weekend” 提示用一般过去时,主语 “parents” 是复数,be 动词用 were,否定形式为 weren’t。
4.She ______ (study) English in 2019.
答案:studied
解析:“in 2019” 提示用一般过去时,study 以 “辅音字母 + y” 结尾,过去式变 y 为 i 加 - ed,即 studied。
5.She ______ (not eat) breakfast this morning.
答案:didn’t eat
解析:“this morning”(今天早上,已过去)提示用一般过去时,否定句用 didn’t + 动词原形 eat。
小试牛刀
6.— ______ your brother ______ (be) in Shanghai last year
— No, he ______.
A. Was; wasn’t B. Were; weren’t
答案:A
解析:“last year” 提示用一般过去时,主语 “your brother” 是单数,be 动词用 was,否定回答用 wasn’t,故选 A。
Part Five-形容词比较级/最高级
比较级(-er/more)、最高级(-est/most)
结构
单音节 / 多音节词变化规则、than 和 the的使用、特殊变化(good→better→best)
考点
每年2-3 题,占比约 10%
真题频次
一、变化规则
形容词比较级用于两者之间的比较,表示 “更……”;最高级用于三者及以上的比较,表示 “最……”。两者均有规则变化和不规则变化,且句式结构有明确区别。
规则变化 情况 比较级(+er) 最高级(+est) 例词
单音节词(一般) 直接加 er 直接加 est tall → taller → tallest
以不发音 e 结尾 加 r 加 st nice → nicer → nicest
以 “辅音 + y” 结尾 变 y 为 i 加 er 变 y 为 i 加 est happy → happier → happiest
以 “辅 + 元 + 辅” 结尾(重读闭音节) 双写尾字母加 er 双写尾字母加 est big → bigger → biggest
多音节词(3 个及以上) 在词前加 more 在词前加 most beautiful → more beautiful → most beautiful
不规则变化(需特殊记忆) 原级 比较级 最高级
good/well better best
bad/ill worse worst
many/much more most
little less least
far farther/further farthest/furthest
二、句式结构
比较级(两者比较)
基本结构:A + be + 比较级 + than + B
例:Tom is taller than John.(汤姆比约翰高。)
修饰比较级:可用 much, a little, even 等
例:This book is much more interesting than that one.(这本书比那本有趣得多。)
01
最高级(三者及以上比较)
基本结构:A + be + the + 最高级 + 范围(of/in 短语)
例:She is the youngest in her family.(她是家里最小的。)
注意:最高级前必须加定冠词the,且需明确比较范围(如 of the three, in the class)。
02
三、常用易错点提示
01
比较级后漏用 than
错误:She is taller her sister.
正确:She is taller than her sister.(比较级需用 than 连接比较对象)
最高级前漏用 the
错误:He is tallest in the team.
正确:He is the tallest in the team.(最高级前必须加 the)
02
多音节词误用 - er/-est
错误:This story is interestinger than that one.
正确:This story is more interesting than that one.(多音节词用 more/most,不用 - er/-est)
03
比较对象不一致
错误:The population of China is larger than Japan.(中国人口与日本比较,对象不一致)
正确:The population of China is larger than that of Japan.(用 that 代替前面的 population,确保比较对象一致)
04
误用 “比较级 + and + 比较级” 表示 “越来越……” 时的结构
错误:It’s getting more and more cold.
正确:It’s getting colder and colder.(单音节词用 “比较级 + and + 比较级”,多音节词用 “more and more + 原级”)
05
1.This box is ______ (heavy) than that one.
答案:heavier
解析:两者比较用比较级,heavy 是 “辅 + 元 + 辅” 结尾,双写尾字母加 - er。
2.Which is ______ (big), the sun or the moon
答案:bigger
解析:两者比较用比较级,big 的比较级是 bigger。
小试牛刀
3.She is ______ (good) at English than her brother.
答案:better
解析:good 的比较级是不规则变化 better。
4.This is ______ (interesting) book I have ever read.
答案:the most interesting
解析:“I have ever read” 表示范围(三者及以上),用最高级,多音节词前加 most,且加 the。
5.— Who runs ______, Tom or Jack
— Tom does.
A. fast B. faster C. fastest
答案:B
解析:两者比较用比较级,fast 的比较级是 faster,故选 B。
小试牛刀
6.The weather is getting ______ (bad) these days.
答案:worse
解析:“these days” 暗示变化,bad 的比较级是不规则变化 worse,此处表示 “越来越糟”。
Part Six-疑问句
一般疑问句:Do/Does/Did + 主语 + 动词原形?
特殊疑问句:疑问词(what, where, how) + 一般疑问句?
结构
疑问词选择、助动词正确形式、回答完整性
考点
每年 3-4 题,占比约 15%
真题频次
一、分类及句式结构(1)
疑问句是用来提出问题的句子,通常以问号 “ ” 结尾。根据提问方式和功能,英语中疑问句可分为四类:一般疑问句、特殊疑问句、选择疑问句和反意疑问句。
一般疑问句(General Questions)
功能:询问一件事是否属实,通常用 “是 / 否”(Yes/No)回答。
结构:
含 be 动词(am/is/are/was/were):be 动词 + 主语 + 其他?
例:Is she a student (她是学生吗?)→ Yes, she is./No, she isn’t.
含情态动词(can/may/must/should 等):情态动词 + 主语 + 动词原形 + 其他?
例:Can you swim (你会游泳吗?)→ Yes, I can./No, I can’t.
含实义动词:助动词(do/does/did) + 主语 + 动词原形 + 其他?
例:Do you like apples (你喜欢苹果吗?)→ Yes, I do./No, I don’t.
01
特殊疑问句(Special Questions)
功能:对句子中的某一具体成分(如人、物、时间、地点等)提问,需用特殊疑问词引导。
常用特殊疑问词:
问人:who(主格)/whom(宾格)
问物 / 事情:what
问时间:when/what time
问地点:where
问原因:why
问方式:how
问数量:how many(可数名词)/how much(不可数名词)
问年龄:how old
问频率:how often
What is your name (你叫什么名字?)→ My name is Lily.
Where do you live (你住在哪里?)→ I live in Beijing.
How did you go to school yesterday (你昨天怎么去学校的?)→ By bike.
02
二、分类及句式结构(2)
选择疑问句(Alternative Questions)
功能:提出两个或多个选项,让对方选择其中一个回答,不能用 Yes/No 回答。
结构:
一般疑问句 + or + 选项?
例:Do you like tea or coffee (你喜欢茶还是咖啡?)→ Coffee, please.
特殊疑问句 + A + or + B?
例:Which is bigger, the earth or the moon (地球和月球哪个更大?)→ The earth.
03
反意疑问句(Tag Questions)
功能:对自己提出的观点或事实进行反问,希望得到对方的确认。
结构:陈述句 + 简短疑问句?(前肯后否,前否后肯)
前句为肯定:简短疑问句用否定(be 动词 / 助动词 / 情态动词的否定形式 + 主语代词)
例:He is a teacher, isn’t he (他是老师,不是吗?)→ Yes, he is./No, he isn’t.
前句为否定:简短疑问句用肯定(be 动词 / 助动词 / 情态动词 + 主语代词)
例:She doesn’t like sports, does she (她不喜欢运动,是吗?)→ Yes, she does./No, she doesn’t.
04
三、常用易错点提示
01
一般疑问句中实义动词的形式
错误:He likes music, does he like
正确:Does he like music (助动词 does 提前后,实义动词用原形 like)
特殊疑问句中 “主谓倒装” 的遗漏
错误:What you are doing
正确:What are you doing (特殊疑问词后需用一般疑问句语序,即 be 动词提前)
02
反意疑问句的 “前否后肯” 判断
错误:She never late for school, isn’t she
正确:She is never late for school, is she (never 表否定,前句视为否定,后句用肯定)
03
选择疑问句的回答误区
错误:— Do you want red or blue — Yes, I want red.
正确:— Do you want red or blue — Red.(选择疑问句不能用 Yes/No 回答,直接选选项)
04
特殊疑问词的混淆
错误:How is your name (how 问方式,问名字需用 what)
正确:What is your name
05
1.______ you speak French
A. Do B. Does C. Are
答案:A
解析:句中 “speak” 是实义动词,主语是 “you”,一般疑问句需用助动词 do,故选 A。
2.— ______ is the post office
— It’s next to the bank.
A. What B. Where C. How
答案:B
解析:答语 “next to the bank” 表示地点,用 where 提问,故选 B。
小试牛刀
3.______ he ______ to school by bus every day
A. Do; go B. Does; go C. Does; goes
答案:B
解析:主语 “he” 是第三人称单数,助动词用 does,后接动词原形 go,故选 B。
4.— ______ apples do you need
— Five, please.
A. How much B. How many C. How old
答案:B
解析:“apples” 是可数名词复数,用 how many 提问数量,故选 B。
小试牛刀
Part Seven-祈使句
动词原形+ 其他成分(否定句:Don't + 动词原形)
结构
礼貌用语(Please)、否定形式、情境应用(如警告、建议)
考点
每年1-2 题,占比约 5%
真题频次
一、基本结构及用法(1)
谓语动词用原形,句末用感叹号 “!” 或句号 “.”,语气强烈时用感叹号。
1. 肯定形式
结构:动词原形 + 其他成分(宾语 / 状语等)
表命令:Stand up!(站起来!)
表请求:Pass me the pen, please.(请递给我那支笔。)
表劝告:Eat more vegetables.(多吃点蔬菜。)
表邀请:Come to my party this weekend.(这周末来参加我的派对吧。)
注意:为使语气委婉,可在句首或句末加 “please”(句末加时,前面通常用逗号隔开)。
例:Please close the window. = Close the window, please.(请关窗。)
2. 第三人称祈使句
有时祈使句会以 “Let + 第三人称代词 / 名词 + 动词原形” 开头,表 “让某人做某事”。
例:Let him try again.(让他再试一次。)
Let the children play outside.(让孩子们在外面玩。)
一、基本结构及用法(2)
3. 否定形式
结构:Don’t + 动词原形 + 其他成分
表禁止:Don’t smoke here.(禁止吸烟。)
表劝阻:Don’t play with fire.(别玩火。)
表提醒:Don’t forget to lock the door.(别忘了锁门。)
特殊否定:对于以 let 开头的祈使句,否定形式有两种:
Let’s(包括说话者和听话者)的否定:Let’s not + 动词原形
例:Let’s not go out in the rain.(咱们别在雨天出去了。)
Let sb.(不包括说话者)的否定:Don’t let sb. + 动词原形
例:Don’t let him go alone.(别让他一个人走。)
4. 强调形式
为加强语气,可在肯定祈使句前加 “Do”(重读),意为 “务必、一定”。
例:Do come early!(一定要早点来!)
二、常见句式及场景应用
句式类型 结构示例 适用场景
基础肯定句 Open the door. 日常指令、操作提示
委婉请求句 Could you pass the salt (虽含情态动词,但本质是祈使语气) 礼貌请求
禁止警告句 No parking!(省略动词的简洁形式) 公共标识、安全警告
建议劝告句 Let’s go for a walk. 提议、邀请
三、常用易错点提示
01
谓语动词形式错误
错误:He closes the window!(祈使句省略主语 you,不能用第三人称单数形式 closes)
正确:Close the window!(用动词原形 close)
否定形式遗漏 “Don’t”
错误:Not run in the hallways!
正确:Don’t run in the hallways!(否定祈使句必须用 Don’t 开头)
02
“Let’s” 与 “Let us” 混淆
Let’s go(包括听话者:“咱们一起去”),Let us go(不包括听话者,需对方允许:“让我们去”)
例:Let’s play football.(邀请对方一起踢球)。Let us play football, mom.(请求妈妈允许 “我们” 踢球)
03
语气词 “please” 的位置不当
错误:Close please the door.
正确:Please close the door. 或 Close the door, please.(please 可放句首或句末,句末需加逗号)
04
误用主语
错误:You be quiet!(祈使句通常省略主语 you,加主语会使语气生硬,多用于训斥)
正确:Be quiet!(自然表达)
05
1.______ the lights when you leave the room.
A. Turn off B. Turns off C. Turning off
答案:A
解析:祈使句用动词原形开头,“turn off” 表示 “关掉”,故选 A。
2.______ late for class again.
A. Don’t be B. Not be C. Don’t are
答案:A
解析:否定祈使句用 “Don’t + 动词原形”,“be late” 是固定搭配,故选 A。
小试牛刀
3.______ quiet in the library, please.
A. Be B. Are C. Is
答案:the most interesting
解析:“I have ever read” 表示范围(三者及以上),用最高级,多音节词前加 most,且加 the。
4.— ______ me your phone number
— Sure, it’s 138xxxx5678.
A. Give B. To give C. Giving
答案:A
解析:此处是委婉请求的祈使句,用动词原形开头,故选 A。
小试牛刀
Part Eight-情态动词
can/can't, must/mustn't, should/shouldn't
结构
情态动词后接动词原形、否定句(直接加 not)、情境应用(能力、义务)
考点
每年 2-3 题,占比约 10%
真题频次
一、常用情态动词的基本用法(1)
情态动词是表示说话人对动作或状态的语气、态度(如能力、可能性、许可、义务、推测等)的动词,本身有一定意义,但不能单独作谓语,需与动词原形连用构成谓语。常见情态动词包括:can, could, may, might, must, shall, should, will, would, need, dare 等。
注意:could 表请求时,回答仍用 can(不用 could):
— Could I use your phone — Yes, you can.(√) / Yes, you could.(×)
can(现在时):表示 “能力、许可、可能性(用于否定 / 疑问句)”。
能力:She can speak three languages.(她会说三种语言。)
许可(口语,较随意):Can I borrow your pen (我能借你的笔吗?)
否定可能性:He can’t be at home.(他不可能在家。)
1
could(过去时 / 委婉语气):
过去的能力:I could swim when I was five.(我五岁时会游泳。)
委婉请求(比 can 更礼貌):Could you help me (你能帮我吗?)
推测(可能性比 may/might 小):This could be his book.(这可能是他的书。)
2
一、常用情态动词的基本用法(2)
must / have to
must:表示 “必须、肯定推测(语气最强)”,否定形式为 mustn’t(禁止)。
义务:You must wear a seatbelt.(你必须系安全带。)
肯定推测:This must be Tom’s bag.(这一定是汤姆的包。)
禁止:You mustn’t park here.(禁止在此停车。)
have to:强调 “客观需要、不得不”,有人称 / 时态变化(has to, had to)。
客观要求:I have to work overtime today.(我今天不得不加班。)
过去时:She had to walk home yesterday.(她昨天不得不步行回家。)
区别:must 强调主观意愿,have to 强调客观压力。
may / might
may:表示 “许可、可能性(用于肯定 / 否定句)”。
许可(较正式):May I come in (我可以进来吗?)
肯定推测:He may be late.(他可能会迟到。)
might:过去时 / 更委婉的推测(可能性比 may 小)。
过去的许可:She said I might leave early.(她说我可以早点走。)
推测(更不确定):It might rain tomorrow.(明天可能会下雨。)
注意:may 的否定回答用 mustn’t(禁止)或 can’t(不允许):
— May I smoke here — No, you mustn’t.(不,禁止吸烟。)
一、常用情态动词的基本用法(3)
shall / should
shall:用于第一人称(I/we),表示 “建议、征求意见”。
Shall we go to the park (我们去公园好吗?)
should:表示 “应该、建议、推测(按道理)”。
建议:You should exercise more.(你应该多锻炼。)
推测:They should be here by now.(他们现在应该到了。)
will:表示 “意愿、将来、请求(用于第二人称)”。
意愿:I will help you.(我会帮你。)
请求(口语):Will you pass the salt (能把盐递给我吗?)
would:过去的意愿 / 将来、委婉请求(比 will 礼貌)。
过去习惯:He would walk to school.(他过去常步行上学。)
委婉请求:Would you mind opening the window (你介意开窗吗?)
will / would
need:表示 “需要”,可作情态动词(多用于否定 / 疑问句,后接原形)或实义动词(有人称 / 时态变化,后接 to do)。
情态动词:You needn’t hurry.(你不必着急。)
实义动词:She needs to finish the work.(她需要完成工作。)
dare:表示 “敢于”,用法同 need。
情态动词:Dare he speak in public (他敢在公共场合讲话吗?)
实义动词:She dares to argue with him.(她敢和他争论。)
need / dare
二、情态动词表 “推测” 的用法对比
情态动词 推测语气 适用句式 例句
must 肯定(100%) 肯定句 He must be tired.(他一定累了。)
may 可能(50%) 肯定句 / 否定句(may not) She may come tomorrow.(她可能明天来。)
might 或许(30%) 肯定句 / 否定句(might not) It might rain.(可能会下雨。)
can 可能(否定 / 疑问) 否定句 / 疑问句 He can’t be a doctor.(他不可能是医生。)
should 按道理应该 肯定句 They should arrive soon.(他们应该很快到。
三、常用易错点提示
01
must 的否定混淆
错误:You mustn’t go(禁止去)≠ You needn’t go(不必去)。
例:Must I finish it today — No, you needn’t.(不必)/ Yes, you must.(必须)
03
may 与 might 表推测的时态误区
might 不只是 may 的过去时,还可表示 “可能性更小”,与时态无关。
例:She might come tomorrow.(明天可能来,可能性比 may 小)
05
need 作情态动词与实义动词的区别
情态动词:Need he go (他需要去吗?)→ 否定:He needn’t go.
实义动词:Does he need to go (他需要去吗?)→ 否定:He doesn’t need to go.
02
can 与 be able to 混淆
can 只有现在时(can)和过去时(could),其他时态需用 be able to。
错误:He will can swim next year.
正确:He will be able to swim next year.(他明年将学会游泳。)
04
should 与 ought to 混淆
should 后接动词原形,ought to 后接 to do,意义相近(“应该”)。
错误:You should to apologize.
正确:You should apologize. = You ought to apologize.(你应该道歉。)
06
推测时的时态错误
对过去的推测需用 “情态动词 + have done”。
错误:He must be late yesterday.
正确:He must have been late yesterday.(他昨天一定迟到了。)
1.— ______ I use your dictionary
— Sure, here you are.
A. Must B. May C. Need
答案:B
解析:表示请求许可,用 may(较正式),故选 B。
小试牛刀
2.You ______ play with fire. It’s dangerous.
A. mustn ’t B. needn’t C. wouldn’t
答案:A
解析:表示 “禁止”,用 mustn’t,故选 A。
3.They ______ have finished the work. I saw them resting just now.
A. must B. can C. need
答案:A
解析:对过去的肯定推测,用 must have done,故选 A。
小试牛刀
4.— ______ we go out for dinner
— Good idea!
A. Shall B. Will C. Would
答案:A
解析:第一人称征求意见,用 shall,故选 A。
谢 谢!
THANK YOU
英语小升初必考句型
目录
Part One.
There be 句型
Part Two.
一般现在时
Part Three.
现在进行时
Part Four.
一般过去时
Part Five.
形容词比较级 / 最高级
Part Six.
疑问句
Part Seven.
祈使句
Part Eight.
情态动词
Part One-There be 句型
There is/are + 主语 + 地点状语
结构
就近原则、时态变化(过去时 there was/were)、否定句(There isn't/aren't)
考点
每年 2-3 题,占比约 10%
真题频次
一、基本结构与 be 动词的选择
01
There is a cat under the chair.(现在时,主语 “a cat” 为单数)
There was some milk in the glass yesterday.(过去时,主语 “milk” 为不可数名词)
单数主语 / 不可数名词 → 用 is(现在时)、was(过去时)
02
There are three books on the desk.(现在时,主语 “three books” 为复数)
There were many students in the hall last week.(过去时,主语 “students” 为复数)
复数主语 → 用 are(现在时)、were(过去时)
03
There is a pen and two pencils in the box.(最近的主语 “a pen” 为单数,用 is)
There are two pencils and a pen in the box.(最近的主语 “two pencils” 为复数,用 are)
就近原则:当主语是由 “and” 连接的多个名词时,be 动词的形式与最近的主语保持一致
二、时态变化
表示将来存在的状态,用 There will be 或 There is/are going to be
There will be a party tomorrow evening.
There is going to be a football match next week.
一般将来时:
表示过去存在的状态,用 was/were
There were no cars in this street 50 years ago.
一般过去时:
表示现在存在的状态,用 is/are
There is a park near my home.
一般现在时:
三、否定句
There won't be a meeting tomorrow.
将来时
There isn't a library here.(单数 / 不可数);There aren't any apples.(复数)
现在时
There wasn't a hospital in the village.;There weren't enough chairs.
过去时
02
01
03
在 be 动词后加 not(注意缩写形式)
四、疑问句
Is there a bank near here (肯定回答:Yes, there is. 否定回答:No, there isn't.)Were there any birds in the tree yesterday (肯定回答:Yes, there were. 否定回答:No, there weren't.)
一般疑问句
01
对数量提问(主语为可数名词):How many + 复数名词 + are there + 地点?
How many students are there in your class
对数量提问(主语为不可数名词):How much + 不可数名词 + is there + 地点?
How much water is there in the bottle
对地点提问:Where + be 动词 + there? Where is there a good restaurant
特殊疑问句
02
将 be 动词提到 there 之前,句末加问号:
五、易错点提醒
01
正确:There is a book on the desk.(桌上有一本书。)
正确:I have a book.(我有一本书。)
避免与 “have” 混淆:There be 表示 “存在”,have 表示 “拥有”。
02
正确:There is some rice in the bowl.(碗里有一些米饭。)
错误:There are some rice in the bowl.
不可数名词作主语时,be 动词用单数(is/was),即使有 “some” 修饰。
03
In the room, there are three people.(房间里有三个人。)
时间 / 地点状语可位于句末或句首(强调地点时)。
1. There ______ a big tree and some flowers in the garden.
A. is B. are
答案:A
解析:There be句型遵循"就近原则",靠近be动词的主语"a big tree"是单数,因此用is。
2. ______ there any milk in the fridge
A. Is B. Are
答案:A
解析:"milk"是不可数名词,视为单数,因此be动词用is。
小试牛刀
3.There ______ two libraries in our school five years ago.
A. was B. were
答案:B
解析:主语"two libraries"是复数,且时间状语"five years ago"表示过去,因此用were。
4. There ______ not any books on the shelf.
A. isn't B. aren't
答案:B
解析:主语"books"是复数,否定句中be动词用aren't。
小试牛刀
5. How many students ______ in your class
A. is there B. are there
答案:B
解析:"students"是复数,特殊疑问句中be动词用are,因此选are there。
6. There ______ a football match in our school tomorrow afternoon.
A. will be B. is
答案:A
解析:时间状语"tomorrow afternoon"表示将来,因此用There will be结构。
小试牛刀
Part Two-一般现在时
主语+ 动词原形 / 第三人称单数形式(-s/-es)
结构
01
第三人称单数变化规则、频率副词(often, usually)、否定句(don't/doesn't)
考点
02
每年3-4 题,占比约 15%
真题频次
03
一、基本用法
表示经常性或习惯性的动作(常与时间状语如 always, usually, often, sometimes, every day 等连用)
I get up at 7:00 every morning.(我每天早上 7 点起床。)
She often goes to the park on weekends.(她经常周末去公园。)
表示客观事实、真理或永恒不变的状态
The sun rises in the east.(太阳从东方升起。)
Water boils at 100℃.(水在 100 摄氏度沸腾。)
表示现阶段的状态或特征
He likes playing basketball.(他喜欢打篮球。)
My brother is a teacher.(我哥哥是一名教师。)
用于时间、条件、让步状语从句中,代替一般将来时
I will call you when she arrives.(她到的时候我会打电话给你。)
If it rains tomorrow, we will stay at home.(如果明天下雨,我们就待在家里。)
二、动词形式变化
01
be 动词的变化
第一人称单数(I)→ am
第三人称单数(he/she/it/ 单数名词)→ is
其他人称(you/we/they/ 复数名词)→ are
例:
I am a student.
He is a doctor.
They are good friends.
02
实义动词的变化
主语是第三人称单数(he/she/it/ 单数名词)时,动词需加 -s/-es(规则变化):
一般动词加 -s:work → works;play → plays
以 s, x, ch, sh, o 结尾的动词加 -es:pass → passes;fix → fixes;teach → teaches;wash → washes;go → goes
以辅音字母 + y 结尾的动词,变 y 为 i 加 - es:study → studies;carry → carries
其他人称(I/you/we/they/ 复数名词)用动词原形:
例:I study English. / They play football.
三、句式结构
主语 + be 动词 + 其他.
例:She is happy. / They are in the classroom.
主语 + 实义动词 + 其他.
例:He plays tennis. / We eat breakfast at 7:00.
肯定句
Be 动词 + 主语 + 其他?
例:Is he a teacher → Yes, he is. / No, he isn’t.
Do/Does + 主语 + 实义动词原形 + 其他?(第三人称单数用 Does,其他人称用 Do)
例:Do you speak French → Yes, I do. / No, I don’t.
一般疑问句
主语 + be 动词 + not + 其他.
例:It is not cold. / You are not late.
主语 + don’t/doesn’t + 实义动词原形 + 其他.
(第三人称单数用 doesn’t,其他人称用 don’t)
例:She doesn’t like coffee. / They don’t live here.
否定句
疑问词 + be 动词 + 主语 + 其他?
例:Where is your bag → It’s on the desk.
疑问词 + do/does + 主语 + 实义动词原形 + 其他?
例:What do you do → I am a student.
特殊疑问句
四、常见易错点提示
01
第三人称单数动词的变化:易漏加 -s/-es,如误写 "He play football"(正确:He plays football)。
否定句和疑问句中实义动词的形式:需用原形,如误写 "She doesn’t plays tennis"(正确:She doesn’t play tennis)。
02
与 "be 动词" 和 "实义动词" 的连用:一般现在时中,be 动词和实义动词不能同时出现,如误写 "They are play basketball"(正确:They play basketball)。
03
1. My mother ______ (cook) dinner every evening.
小试牛刀
答案:cooks
解析:主语 “my mother” 是第三人称单数,根据一般现在时规则,实义动词需用第三人称单数形式,cook 的第三人称单数为 cooks。
2. ______ your father ______ (read) newspapers in the morning
A. Do; read B. Does; read
答案:B
解析:主语 “your father” 是第三人称单数,一般疑问句需用助动词 does 开头,后面接动词原形 read,故选 B。
3. Tom ______ (not like) playing basketball. He likes football.
小试牛刀
答案:doesn’t like
解析:主语 “Tom” 是第三人称单数,否定句需用助动词 doesn’t,后面接动词原形 like,故填 doesn’t like。
4. The earth ______ (go) around the sun.
答案:goes
解析:此句描述客观真理,用一般现在时;主语 “the earth” 是第三人称单数,go 的第三人称单数为 goes(以 o 结尾加 es)。
Part Three-现在进行时
主语+ am/is/are + 动词 - ing
结构
动词- ing 形式变化规则、时间状语(now, look)、疑问句(Is/Are...doing )
考点
每年2-3 题,占比约 10%
真题频次
一、基本结构
主语 + am/is/are + 动词 - ing 形式
第一人称单数(I)→ am + 动词 - ing
第三人称单数(he/she/it/ 单数名词)→ is + 动词 - ing
其他人称(you/we/they/ 复数名词)→ are + 动词 - ing
例:
I am reading a book.(我正在看书。)
She is singing.(她正在唱歌。)
They are playing football.(他们正在踢足球。)
二、动词 - ing 形式变化规则
一般动词:直接加 - ing
work → working;play → playing;look → looking
1
以不发音的 e 结尾:去 e 加 - ing
take → taking;dance → dancing;write → writing
2
以重读闭音节结尾(辅 + 元 + 辅):双写最后一个辅音字母加 - ing
run → running;swim → swimming;sit → sitting
3
以 ie 结尾:变 ie 为 y 加 - ing
lie → lying;die → dying
4
三、句式结构
主语 + am/is/are + 动词 - ing + 其他
He is watching TV now.(他现在正在看电视。)
We are having a class.(我们正在上课。)
肯定句
主语 + am/is/are + not + 动词 - ing + 其他
She is not (isn’t) dancing.(她没在跳舞。)
They are not (aren’t) playing basketball.(他们没在打篮球。)
否定句
疑问词 + am/is/are + 主语 + 动词 - ing + 其他?
What is she doing (她正在做什么?)
→ She is drawing a picture.
Where are they playing (他们正在哪里玩?)
→ They are playing in the park.
特殊疑问句
Am/Is/Are + 主语 + 动词 - ing + 其他?
Is he reading a newspaper (他正在看报纸吗?)
→ Yes, he is. / No, he isn’t.
Are they talking (他们在说话吗?)
→ Yes, they are. / No, they aren’t.
一般疑问句
1. Listen! Someone ______ (sing) in the next room.
答案:is singing
解析:“Listen!” 是现在进行时标志,主语 “someone” 视为单数,用 is + singing。
2.My parents ______ (watch) TV now.
答案:are watching
解析:“now” 提示现在进行时,主语 “my parents” 是复数,用 are + watching。
小试牛刀
3.We ______ (not play) football. We’re reading.
答案:aren’t playing
解析:后句用现在进行时,前句也用现在进行时否定形式 aren’t + playing。
Part Four-一般过去时
主语+ 动词过去式(规则 + ed / 不规则变化)
结构
不规则动词表、时间状语(yesterday, last week)、否定句(didn't + 动词原形)
考点
每年2-3 题,占比约 10%
真题频次
一、基本结构
一般过去时表示过去某个时间发生的动作或存在的状态,常与表示过去的时间状语连用,
如 yesterday, last week, two years ago, in 2020 等。
01
含实义动词:主语 + 动词过去式 + 其他
02
含 be 动词:主语 + was/were + 其他
第一人称单数(I)/ 第三人称单数(he/she/it/ 单数名词)→ was
其他人称(you/we/they/ 复数名词)→ were
二、动词过去式变化规则
01
规则动词:
一般加 - ed:work → worked;play → played
以不发音的 e 结尾加 - d:live → lived;like → liked
以辅音字母 + y 结尾:变 y 为 i 加 - ed:study → studied;carry → carried
以重读闭音节结尾(辅 + 元 + 辅):双写最后一个辅音字母加 - ed:stop → stopped;plan → planned
02
不规则动词:需特殊记忆(常见例词)
go → went;come → came;see → saw;eat → ate;do → did;is/am → was;are → were
三、句式结构
实义动词:主语 + didn’t + 动词原形 + 其他
例:He didn’t play basketball yesterday.(他昨天没打篮球。)
be 动词:主语 + wasn’t/weren’t + 其他
例:She wasn’t a teacher.(她以前不是老师。)
否定句:
实义动词:Did + 主语 + 动词原形 + 其他?
例:Did he play basketball yesterday (他昨天打篮球了吗?)
→ Yes, he did. / No, he didn’t.
be 动词:Was/Were + 主语 + 其他?
例:Were you at home last night (你昨晚在家吗?)
→ Yes, I was. / No, I wasn’t.
一般疑问句
实义动词:He played basketball yesterday.(他昨天打篮球了。)
be 动词:She was a student in 2018.(2018 年她是一名学生。)
肯定句:
疑问词 + did + 主语 + 动词原形 + 其他?(实义动词)
例:What did you do yesterday (你昨天做什么了?)
疑问词 + was/were + 主语 + 其他?(be 动词)
特殊疑问句:
1.He ______ (go) to the park with his friends yesterday.
答案:went
解析:“yesterday” 提示用一般过去时,go 的过去式是不规则变化 went。
2.______ you ______ (watch) TV last night
A. Do; watch B. Did; watch
答案:B
解析:“last night” 提示用一般过去时,一般疑问句用助动词 did 开头,后接动词原形 watch,故选 B。
小试牛刀
3.My parents ______ (not be) at home last weekend.
答案:weren’t
解析:“last weekend” 提示用一般过去时,主语 “parents” 是复数,be 动词用 were,否定形式为 weren’t。
4.She ______ (study) English in 2019.
答案:studied
解析:“in 2019” 提示用一般过去时,study 以 “辅音字母 + y” 结尾,过去式变 y 为 i 加 - ed,即 studied。
5.She ______ (not eat) breakfast this morning.
答案:didn’t eat
解析:“this morning”(今天早上,已过去)提示用一般过去时,否定句用 didn’t + 动词原形 eat。
小试牛刀
6.— ______ your brother ______ (be) in Shanghai last year
— No, he ______.
A. Was; wasn’t B. Were; weren’t
答案:A
解析:“last year” 提示用一般过去时,主语 “your brother” 是单数,be 动词用 was,否定回答用 wasn’t,故选 A。
Part Five-形容词比较级/最高级
比较级(-er/more)、最高级(-est/most)
结构
单音节 / 多音节词变化规则、than 和 the的使用、特殊变化(good→better→best)
考点
每年2-3 题,占比约 10%
真题频次
一、变化规则
形容词比较级用于两者之间的比较,表示 “更……”;最高级用于三者及以上的比较,表示 “最……”。两者均有规则变化和不规则变化,且句式结构有明确区别。
规则变化 情况 比较级(+er) 最高级(+est) 例词
单音节词(一般) 直接加 er 直接加 est tall → taller → tallest
以不发音 e 结尾 加 r 加 st nice → nicer → nicest
以 “辅音 + y” 结尾 变 y 为 i 加 er 变 y 为 i 加 est happy → happier → happiest
以 “辅 + 元 + 辅” 结尾(重读闭音节) 双写尾字母加 er 双写尾字母加 est big → bigger → biggest
多音节词(3 个及以上) 在词前加 more 在词前加 most beautiful → more beautiful → most beautiful
不规则变化(需特殊记忆) 原级 比较级 最高级
good/well better best
bad/ill worse worst
many/much more most
little less least
far farther/further farthest/furthest
二、句式结构
比较级(两者比较)
基本结构:A + be + 比较级 + than + B
例:Tom is taller than John.(汤姆比约翰高。)
修饰比较级:可用 much, a little, even 等
例:This book is much more interesting than that one.(这本书比那本有趣得多。)
01
最高级(三者及以上比较)
基本结构:A + be + the + 最高级 + 范围(of/in 短语)
例:She is the youngest in her family.(她是家里最小的。)
注意:最高级前必须加定冠词the,且需明确比较范围(如 of the three, in the class)。
02
三、常用易错点提示
01
比较级后漏用 than
错误:She is taller her sister.
正确:She is taller than her sister.(比较级需用 than 连接比较对象)
最高级前漏用 the
错误:He is tallest in the team.
正确:He is the tallest in the team.(最高级前必须加 the)
02
多音节词误用 - er/-est
错误:This story is interestinger than that one.
正确:This story is more interesting than that one.(多音节词用 more/most,不用 - er/-est)
03
比较对象不一致
错误:The population of China is larger than Japan.(中国人口与日本比较,对象不一致)
正确:The population of China is larger than that of Japan.(用 that 代替前面的 population,确保比较对象一致)
04
误用 “比较级 + and + 比较级” 表示 “越来越……” 时的结构
错误:It’s getting more and more cold.
正确:It’s getting colder and colder.(单音节词用 “比较级 + and + 比较级”,多音节词用 “more and more + 原级”)
05
1.This box is ______ (heavy) than that one.
答案:heavier
解析:两者比较用比较级,heavy 是 “辅 + 元 + 辅” 结尾,双写尾字母加 - er。
2.Which is ______ (big), the sun or the moon
答案:bigger
解析:两者比较用比较级,big 的比较级是 bigger。
小试牛刀
3.She is ______ (good) at English than her brother.
答案:better
解析:good 的比较级是不规则变化 better。
4.This is ______ (interesting) book I have ever read.
答案:the most interesting
解析:“I have ever read” 表示范围(三者及以上),用最高级,多音节词前加 most,且加 the。
5.— Who runs ______, Tom or Jack
— Tom does.
A. fast B. faster C. fastest
答案:B
解析:两者比较用比较级,fast 的比较级是 faster,故选 B。
小试牛刀
6.The weather is getting ______ (bad) these days.
答案:worse
解析:“these days” 暗示变化,bad 的比较级是不规则变化 worse,此处表示 “越来越糟”。
Part Six-疑问句
一般疑问句:Do/Does/Did + 主语 + 动词原形?
特殊疑问句:疑问词(what, where, how) + 一般疑问句?
结构
疑问词选择、助动词正确形式、回答完整性
考点
每年 3-4 题,占比约 15%
真题频次
一、分类及句式结构(1)
疑问句是用来提出问题的句子,通常以问号 “ ” 结尾。根据提问方式和功能,英语中疑问句可分为四类:一般疑问句、特殊疑问句、选择疑问句和反意疑问句。
一般疑问句(General Questions)
功能:询问一件事是否属实,通常用 “是 / 否”(Yes/No)回答。
结构:
含 be 动词(am/is/are/was/were):be 动词 + 主语 + 其他?
例:Is she a student (她是学生吗?)→ Yes, she is./No, she isn’t.
含情态动词(can/may/must/should 等):情态动词 + 主语 + 动词原形 + 其他?
例:Can you swim (你会游泳吗?)→ Yes, I can./No, I can’t.
含实义动词:助动词(do/does/did) + 主语 + 动词原形 + 其他?
例:Do you like apples (你喜欢苹果吗?)→ Yes, I do./No, I don’t.
01
特殊疑问句(Special Questions)
功能:对句子中的某一具体成分(如人、物、时间、地点等)提问,需用特殊疑问词引导。
常用特殊疑问词:
问人:who(主格)/whom(宾格)
问物 / 事情:what
问时间:when/what time
问地点:where
问原因:why
问方式:how
问数量:how many(可数名词)/how much(不可数名词)
问年龄:how old
问频率:how often
What is your name (你叫什么名字?)→ My name is Lily.
Where do you live (你住在哪里?)→ I live in Beijing.
How did you go to school yesterday (你昨天怎么去学校的?)→ By bike.
02
二、分类及句式结构(2)
选择疑问句(Alternative Questions)
功能:提出两个或多个选项,让对方选择其中一个回答,不能用 Yes/No 回答。
结构:
一般疑问句 + or + 选项?
例:Do you like tea or coffee (你喜欢茶还是咖啡?)→ Coffee, please.
特殊疑问句 + A + or + B?
例:Which is bigger, the earth or the moon (地球和月球哪个更大?)→ The earth.
03
反意疑问句(Tag Questions)
功能:对自己提出的观点或事实进行反问,希望得到对方的确认。
结构:陈述句 + 简短疑问句?(前肯后否,前否后肯)
前句为肯定:简短疑问句用否定(be 动词 / 助动词 / 情态动词的否定形式 + 主语代词)
例:He is a teacher, isn’t he (他是老师,不是吗?)→ Yes, he is./No, he isn’t.
前句为否定:简短疑问句用肯定(be 动词 / 助动词 / 情态动词 + 主语代词)
例:She doesn’t like sports, does she (她不喜欢运动,是吗?)→ Yes, she does./No, she doesn’t.
04
三、常用易错点提示
01
一般疑问句中实义动词的形式
错误:He likes music, does he like
正确:Does he like music (助动词 does 提前后,实义动词用原形 like)
特殊疑问句中 “主谓倒装” 的遗漏
错误:What you are doing
正确:What are you doing (特殊疑问词后需用一般疑问句语序,即 be 动词提前)
02
反意疑问句的 “前否后肯” 判断
错误:She never late for school, isn’t she
正确:She is never late for school, is she (never 表否定,前句视为否定,后句用肯定)
03
选择疑问句的回答误区
错误:— Do you want red or blue — Yes, I want red.
正确:— Do you want red or blue — Red.(选择疑问句不能用 Yes/No 回答,直接选选项)
04
特殊疑问词的混淆
错误:How is your name (how 问方式,问名字需用 what)
正确:What is your name
05
1.______ you speak French
A. Do B. Does C. Are
答案:A
解析:句中 “speak” 是实义动词,主语是 “you”,一般疑问句需用助动词 do,故选 A。
2.— ______ is the post office
— It’s next to the bank.
A. What B. Where C. How
答案:B
解析:答语 “next to the bank” 表示地点,用 where 提问,故选 B。
小试牛刀
3.______ he ______ to school by bus every day
A. Do; go B. Does; go C. Does; goes
答案:B
解析:主语 “he” 是第三人称单数,助动词用 does,后接动词原形 go,故选 B。
4.— ______ apples do you need
— Five, please.
A. How much B. How many C. How old
答案:B
解析:“apples” 是可数名词复数,用 how many 提问数量,故选 B。
小试牛刀
Part Seven-祈使句
动词原形+ 其他成分(否定句:Don't + 动词原形)
结构
礼貌用语(Please)、否定形式、情境应用(如警告、建议)
考点
每年1-2 题,占比约 5%
真题频次
一、基本结构及用法(1)
谓语动词用原形,句末用感叹号 “!” 或句号 “.”,语气强烈时用感叹号。
1. 肯定形式
结构:动词原形 + 其他成分(宾语 / 状语等)
表命令:Stand up!(站起来!)
表请求:Pass me the pen, please.(请递给我那支笔。)
表劝告:Eat more vegetables.(多吃点蔬菜。)
表邀请:Come to my party this weekend.(这周末来参加我的派对吧。)
注意:为使语气委婉,可在句首或句末加 “please”(句末加时,前面通常用逗号隔开)。
例:Please close the window. = Close the window, please.(请关窗。)
2. 第三人称祈使句
有时祈使句会以 “Let + 第三人称代词 / 名词 + 动词原形” 开头,表 “让某人做某事”。
例:Let him try again.(让他再试一次。)
Let the children play outside.(让孩子们在外面玩。)
一、基本结构及用法(2)
3. 否定形式
结构:Don’t + 动词原形 + 其他成分
表禁止:Don’t smoke here.(禁止吸烟。)
表劝阻:Don’t play with fire.(别玩火。)
表提醒:Don’t forget to lock the door.(别忘了锁门。)
特殊否定:对于以 let 开头的祈使句,否定形式有两种:
Let’s(包括说话者和听话者)的否定:Let’s not + 动词原形
例:Let’s not go out in the rain.(咱们别在雨天出去了。)
Let sb.(不包括说话者)的否定:Don’t let sb. + 动词原形
例:Don’t let him go alone.(别让他一个人走。)
4. 强调形式
为加强语气,可在肯定祈使句前加 “Do”(重读),意为 “务必、一定”。
例:Do come early!(一定要早点来!)
二、常见句式及场景应用
句式类型 结构示例 适用场景
基础肯定句 Open the door. 日常指令、操作提示
委婉请求句 Could you pass the salt (虽含情态动词,但本质是祈使语气) 礼貌请求
禁止警告句 No parking!(省略动词的简洁形式) 公共标识、安全警告
建议劝告句 Let’s go for a walk. 提议、邀请
三、常用易错点提示
01
谓语动词形式错误
错误:He closes the window!(祈使句省略主语 you,不能用第三人称单数形式 closes)
正确:Close the window!(用动词原形 close)
否定形式遗漏 “Don’t”
错误:Not run in the hallways!
正确:Don’t run in the hallways!(否定祈使句必须用 Don’t 开头)
02
“Let’s” 与 “Let us” 混淆
Let’s go(包括听话者:“咱们一起去”),Let us go(不包括听话者,需对方允许:“让我们去”)
例:Let’s play football.(邀请对方一起踢球)。Let us play football, mom.(请求妈妈允许 “我们” 踢球)
03
语气词 “please” 的位置不当
错误:Close please the door.
正确:Please close the door. 或 Close the door, please.(please 可放句首或句末,句末需加逗号)
04
误用主语
错误:You be quiet!(祈使句通常省略主语 you,加主语会使语气生硬,多用于训斥)
正确:Be quiet!(自然表达)
05
1.______ the lights when you leave the room.
A. Turn off B. Turns off C. Turning off
答案:A
解析:祈使句用动词原形开头,“turn off” 表示 “关掉”,故选 A。
2.______ late for class again.
A. Don’t be B. Not be C. Don’t are
答案:A
解析:否定祈使句用 “Don’t + 动词原形”,“be late” 是固定搭配,故选 A。
小试牛刀
3.______ quiet in the library, please.
A. Be B. Are C. Is
答案:the most interesting
解析:“I have ever read” 表示范围(三者及以上),用最高级,多音节词前加 most,且加 the。
4.— ______ me your phone number
— Sure, it’s 138xxxx5678.
A. Give B. To give C. Giving
答案:A
解析:此处是委婉请求的祈使句,用动词原形开头,故选 A。
小试牛刀
Part Eight-情态动词
can/can't, must/mustn't, should/shouldn't
结构
情态动词后接动词原形、否定句(直接加 not)、情境应用(能力、义务)
考点
每年 2-3 题,占比约 10%
真题频次
一、常用情态动词的基本用法(1)
情态动词是表示说话人对动作或状态的语气、态度(如能力、可能性、许可、义务、推测等)的动词,本身有一定意义,但不能单独作谓语,需与动词原形连用构成谓语。常见情态动词包括:can, could, may, might, must, shall, should, will, would, need, dare 等。
注意:could 表请求时,回答仍用 can(不用 could):
— Could I use your phone — Yes, you can.(√) / Yes, you could.(×)
can(现在时):表示 “能力、许可、可能性(用于否定 / 疑问句)”。
能力:She can speak three languages.(她会说三种语言。)
许可(口语,较随意):Can I borrow your pen (我能借你的笔吗?)
否定可能性:He can’t be at home.(他不可能在家。)
1
could(过去时 / 委婉语气):
过去的能力:I could swim when I was five.(我五岁时会游泳。)
委婉请求(比 can 更礼貌):Could you help me (你能帮我吗?)
推测(可能性比 may/might 小):This could be his book.(这可能是他的书。)
2
一、常用情态动词的基本用法(2)
must / have to
must:表示 “必须、肯定推测(语气最强)”,否定形式为 mustn’t(禁止)。
义务:You must wear a seatbelt.(你必须系安全带。)
肯定推测:This must be Tom’s bag.(这一定是汤姆的包。)
禁止:You mustn’t park here.(禁止在此停车。)
have to:强调 “客观需要、不得不”,有人称 / 时态变化(has to, had to)。
客观要求:I have to work overtime today.(我今天不得不加班。)
过去时:She had to walk home yesterday.(她昨天不得不步行回家。)
区别:must 强调主观意愿,have to 强调客观压力。
may / might
may:表示 “许可、可能性(用于肯定 / 否定句)”。
许可(较正式):May I come in (我可以进来吗?)
肯定推测:He may be late.(他可能会迟到。)
might:过去时 / 更委婉的推测(可能性比 may 小)。
过去的许可:She said I might leave early.(她说我可以早点走。)
推测(更不确定):It might rain tomorrow.(明天可能会下雨。)
注意:may 的否定回答用 mustn’t(禁止)或 can’t(不允许):
— May I smoke here — No, you mustn’t.(不,禁止吸烟。)
一、常用情态动词的基本用法(3)
shall / should
shall:用于第一人称(I/we),表示 “建议、征求意见”。
Shall we go to the park (我们去公园好吗?)
should:表示 “应该、建议、推测(按道理)”。
建议:You should exercise more.(你应该多锻炼。)
推测:They should be here by now.(他们现在应该到了。)
will:表示 “意愿、将来、请求(用于第二人称)”。
意愿:I will help you.(我会帮你。)
请求(口语):Will you pass the salt (能把盐递给我吗?)
would:过去的意愿 / 将来、委婉请求(比 will 礼貌)。
过去习惯:He would walk to school.(他过去常步行上学。)
委婉请求:Would you mind opening the window (你介意开窗吗?)
will / would
need:表示 “需要”,可作情态动词(多用于否定 / 疑问句,后接原形)或实义动词(有人称 / 时态变化,后接 to do)。
情态动词:You needn’t hurry.(你不必着急。)
实义动词:She needs to finish the work.(她需要完成工作。)
dare:表示 “敢于”,用法同 need。
情态动词:Dare he speak in public (他敢在公共场合讲话吗?)
实义动词:She dares to argue with him.(她敢和他争论。)
need / dare
二、情态动词表 “推测” 的用法对比
情态动词 推测语气 适用句式 例句
must 肯定(100%) 肯定句 He must be tired.(他一定累了。)
may 可能(50%) 肯定句 / 否定句(may not) She may come tomorrow.(她可能明天来。)
might 或许(30%) 肯定句 / 否定句(might not) It might rain.(可能会下雨。)
can 可能(否定 / 疑问) 否定句 / 疑问句 He can’t be a doctor.(他不可能是医生。)
should 按道理应该 肯定句 They should arrive soon.(他们应该很快到。
三、常用易错点提示
01
must 的否定混淆
错误:You mustn’t go(禁止去)≠ You needn’t go(不必去)。
例:Must I finish it today — No, you needn’t.(不必)/ Yes, you must.(必须)
03
may 与 might 表推测的时态误区
might 不只是 may 的过去时,还可表示 “可能性更小”,与时态无关。
例:She might come tomorrow.(明天可能来,可能性比 may 小)
05
need 作情态动词与实义动词的区别
情态动词:Need he go (他需要去吗?)→ 否定:He needn’t go.
实义动词:Does he need to go (他需要去吗?)→ 否定:He doesn’t need to go.
02
can 与 be able to 混淆
can 只有现在时(can)和过去时(could),其他时态需用 be able to。
错误:He will can swim next year.
正确:He will be able to swim next year.(他明年将学会游泳。)
04
should 与 ought to 混淆
should 后接动词原形,ought to 后接 to do,意义相近(“应该”)。
错误:You should to apologize.
正确:You should apologize. = You ought to apologize.(你应该道歉。)
06
推测时的时态错误
对过去的推测需用 “情态动词 + have done”。
错误:He must be late yesterday.
正确:He must have been late yesterday.(他昨天一定迟到了。)
1.— ______ I use your dictionary
— Sure, here you are.
A. Must B. May C. Need
答案:B
解析:表示请求许可,用 may(较正式),故选 B。
小试牛刀
2.You ______ play with fire. It’s dangerous.
A. mustn ’t B. needn’t C. wouldn’t
答案:A
解析:表示 “禁止”,用 mustn’t,故选 A。
3.They ______ have finished the work. I saw them resting just now.
A. must B. can C. need
答案:A
解析:对过去的肯定推测,用 must have done,故选 A。
小试牛刀
4.— ______ we go out for dinner
— Good idea!
A. Shall B. Will C. Would
答案:A
解析:第一人称征求意见,用 shall,故选 A。
谢 谢!
THANK YOU
