Unit 2 Section A (GF-4c)课件 2025-2026学年度人教版英语九年级全册【Unit 2 I think that mooncakes are delicious!】
文档属性
| 名称 | Unit 2 Section A (GF-4c)课件 2025-2026学年度人教版英语九年级全册【Unit 2 I think that mooncakes are delicious!】 |  | |
| 格式 | pptx | ||
| 文件大小 | 1.3MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 试卷 | ||
| 版本资源 | 人教新目标(Go for it)版 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2025-08-19 20:55:53 | ||
图片预览










文档简介
(共32张PPT)
Section A (GF-4c)
Unit 2 I think that mooncakes
are delicious!
Learning Goals
Key words & phrases:
tie, objective clause
Key sentences:
1. Do you know that there are two special days for parents in America
2. I heard that it is becoming more and more popular to celebrate
Mother’s Day and Father’s Day in China.
Students can use the objective clauses and the exclamatory statements properly.
Words & Expressions
tie
objective clause
n.领带 / v.捆;束
宾语从句
Warming up
Which festival do these pictures remind you of
Qing Ming Festival
What do people do on Qing Ming Festival
People will pay respect to their ancestors(祭拜祖先) and pray for family proserity(繁荣). In some places, people eat Qing Tuan — a kind of green glutinous(黏的) rice ball on Qing Ming Festival. Because during the time of Qing Ming, the bright sunshine brings everything back to life, so it is the best time to go out and enjoy the beautiful scenes outside.
Activity: What do you know about Qing Ming Festival
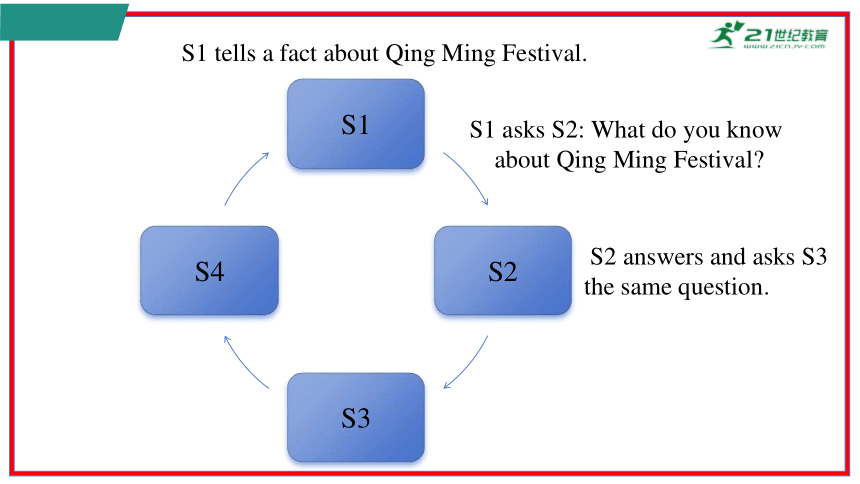
Step 1 Work in a group of four.
Step 2 S1 tells a fact about Qing Ming Festival using the sentence
structure “ I know / I think that ...”. Then S1 asks S2: What
do you know about Qing Ming Festival
Step 3 S2 answers the question and asks S3: What do you know
about Qing Ming Festival
Step 4 Repeat the previous steps till all the students in the group
have answered the question.
S1 tells a fact about Qing Ming Festival.
S1 asks S2: What do you know
about Qing Ming Festival
S2 answers and asks S3 the same question.
Grammar Focus
Read the sentences and find out the common features.
I know that the Water Festival is really fun.
I wonder if they’ll have the races again next year.
I wonder whether June is a good time to visit Hong Kong.
I believe that April is the hottest month in Thailand.
主语+谓语
that/if/whether
宾语从句
Objective Clause (宾语从句)
在复合句中作宾语的从句叫宾语从句, 它通常位于主句谓语动词(及物动词)或介词之后。宾语从句通常由从属连词(that / whether / if)、连接代词(who / whom / whose / what / which)或连接副词(when / where / how / why)引导。
Tips:
简单句指只包含一个主谓结构, 并且句子的各个成分都只由单词或短语构成的独立句子或者是分句。例如:
I don’t like the film. (主语:I, 谓语:don’t like, 宾语:the film)
复合句包含一个主句、一个或一个以上的从句; 或只包含一个从句, 但有两个或两个以上的主句。例如:
We know he likes English.
主 + 谓
主 + 谓 + 宾
Can you find out more sentences that contain the objective clauses from the conversations or passage that you’ve learned in Section A
Mary thinks that the teams were fantastic.
I believe that April is the hottest month in Thailand.
He found that the moon was so bright and round.
Bill wonders whether they’ll have zongzi again next year.
I wonder if it is similar to the Water Festival of the Dai
people in Yunnan Province.
由that引导的宾语从句
由whether / if引导的宾语从句
由that引导的宾语从句
当宾语从句是陈述句时, 用that引导。that无词义, 在从句中不充当成分, 在口语和非正式文体中常常省略。
All the students think (that) Mr. Zhang is humorous.
当主句的主语是第一人称(I / we), 并且谓语动词是think, guess, believe, suppose等时, 如果宾语从句要表达否定意思, 一般将否定转移到主句上来, 即“否定前移”。
I don’t think the girl can do the work alone.
that在宾语从句中的省略与保留
a. 在主语+谓语+it(形式宾语)+宾补+that从句(真正宾语)的句
型中不省略。
We must make it clear that we mean what we say.
b. 由连词and连接的两个由that引导的宾语从句中,第二个that
不省略。
He told me (that) he would come and that he would come on time.
c.当that作介词except, in等的宾语时不省略。
They believe in that she must still be single.
I know nothing about him except that he is living in Beijing.
由if / whether引导的宾语从句
当宾语从句的语义相当于一个一般疑问句时, 常用if / whether引导, 表示 “是否” 。if / whether在句中不充当句子成分, 但不能省略。
I wonder if / whether you want to attend the meeting.
由if / whether引导的宾语从句
一般情况下二者没有区别, 可以互换。但是以下情况不可互换:
whether之后紧跟or not时不可与if互换。
Nobody knows whether or not it will rain tomorrow.
在介词后只能用whether不能用if。
The boy worries about whether he has broken his computer.
与动词不定式连用时, 只能用whether不能用if。
I can’t decide whether to go or to stay.
宾语从句的语序
无论主句是陈述句还是疑问句,宾语从句都用陈述句的语序,即“主语在前,谓语在后”的顺序。
Danny says that he will learn English.
Do you know where he came from
Please tell me how I can get to the bus station.
宾语从句的时态
当主句是一般现在时,宾语从句的时态不作限制,我们可以根据句子的意思来使用需要的任何一种时态。
I hear (that)
Jim went to work an hour ago.
he is interested in English.
she will come tomorrow.
Tom has been to London twice.
当主句是一般过去时的时候,宾语从句必须运用相应的过去的某一种时态,从而达到主句和从句的相互一致。例如,把左侧的四句话变为宾语从句是:
He will go to Hong Kong .
He is sick.
He is reading a book .
He has finished his work.
He said
He had finished his work.
He would go to Hong Kong.
He was sick.
He was reading a book.
当宾语从句说明的是客观存在的事实或者是客观存在的真理时就不用受到主句时态的限制,仍是用一般现在时态。
the sun is much bigger than the moon .
summer is after spring .
the earth moves around the sun.
He told me (that)
We knew (that)
The teacher told us (that)
宾语从句的总结
宾语从句三要素
引导词
that
if/whether
特殊疑问词
时态
主句为一般现在时
主句为一般过去时
一般过去时
过去将来时
过去进行时
过去完成时
语序
宾语从句的语序都为陈述句语序
从句客观真理时态不变
从句可为任何时态
Read the sentences and find out the common features.
What fun the Water Festival is!
How fantasic the dragon boat teams were!
How pretty the dragon boats were!
How delicious the food is in Hong Kong!
What / How
名词/形容词/副词
主语+谓语+其他!
Exclamatory Statements (感叹句)
感叹句是表示赞美、惊叹、喜悦等感情的句子。感叹句的句尾用感叹号“!”,读降调。
What引导的感叹句
What + a / an + adj. + 可数名词单数 + 陈述句!
What a beautiful girl she is!
What + adj. + 可数名词复数 + 陈述句!
What big coconuts these are!
What + adj. + 不可数名词 + 陈述句!
What nice weather it is!
How引导的感叹句
How + adj. / adv. + 陈述句(主语 + 谓语)!
How fine the weather is!
How hot it is today!
How high the kite is flying!
How+ 主语 + 谓语!
How time flies!
4a
Write sentences using the words given.
1. think / Lantern Festival / beautiful
___________________________________________________
2. don’t know / whether / he / come home / for the festival
___________________________________________________
3. believe / Water Festival / most / fun
___________________________________________________
I think that the Lantern Festival is beautiful.
I don’t know whether he will come home for the festival.
I believe that the Water Festival is the most fun.
4. wonder / if / mooncakes / delicious
_______________________________________________
5. how / exciting / races
______________________________________________
6. what / nice / a / treat
_______________________________________________
I wonder if the mooncakes are delicious.
How exciting the races were!
What a nice treat!
4b
Read the passage below and underline the objective clauses. If possible, write your own sentences about Mother’s Day and Father’s Day using objective clauses.
Dear Xia Yu,
Do you know that there are two special days for parents in America One is Mother’s Day on the second Sunday of May, and the other is Father’s Day on the third Sunday of June. On these two days, American children often give gifts to their parents or take them out for lunch or dinner.
one ... the other ...
一个......另一个......
表示特定范围内两个事物的不同情况。
Common gifts are flowers and cards for mothers and shirts or ties for fathers. I heard that it is becoming more and more popular to celebrate Mother’s Day and Father’s Day in China. I wonder if children over there also give similar gifts to their parents. I believe that there are many ways to show our love. Actually, we don’t have to spend a lot of money. It is also a good idea to help parents to do something instead.
June
n. 领带 v. 捆;束
当其作动词时, 过去式和过去分词均为tied, 现在分词为tying。
4c
Which festival do you like best Ask your group and report to the class.
e.g. In our group, David’s favorite festival is ... He thinks
that ...
Name Favorite festival Reason(s)
Exercises
根据句意选出恰当的一项填空。
1. ______ (What / What a) fine weather it is now!
2. ______ (What / How) warm it is in the classroom!
3. ________ (What / What a) nice shirt you bought!
4. _____ (What / How) fast the young man is walking!
What
How
What a
How
将下列句子改为感叹句。
1. The girl is very clever.
_____ ______ the girl is!
2. It is a wonderful experience.
_____ ______ wonderful experience it is!
3. The wind is blowing strongly.
_____ _______ the wind is blowing!
4. The news is exciting.
_____ _______ news it is!
5. The sweaters are very nice.
_____ ______ sweaters they are!
How clever
What a
How strongly
What exciting
What nice
Homework
Preview Section B 1a-1d.
Do the exercises in students’ book.
Thank you!
Section A (GF-4c)
Unit 2 I think that mooncakes
are delicious!
Learning Goals
Key words & phrases:
tie, objective clause
Key sentences:
1. Do you know that there are two special days for parents in America
2. I heard that it is becoming more and more popular to celebrate
Mother’s Day and Father’s Day in China.
Students can use the objective clauses and the exclamatory statements properly.
Words & Expressions
tie
objective clause
n.领带 / v.捆;束
宾语从句
Warming up
Which festival do these pictures remind you of
Qing Ming Festival
What do people do on Qing Ming Festival
People will pay respect to their ancestors(祭拜祖先) and pray for family proserity(繁荣). In some places, people eat Qing Tuan — a kind of green glutinous(黏的) rice ball on Qing Ming Festival. Because during the time of Qing Ming, the bright sunshine brings everything back to life, so it is the best time to go out and enjoy the beautiful scenes outside.
Activity: What do you know about Qing Ming Festival
Step 1 Work in a group of four.
Step 2 S1 tells a fact about Qing Ming Festival using the sentence
structure “ I know / I think that ...”. Then S1 asks S2: What
do you know about Qing Ming Festival
Step 3 S2 answers the question and asks S3: What do you know
about Qing Ming Festival
Step 4 Repeat the previous steps till all the students in the group
have answered the question.
S1 tells a fact about Qing Ming Festival.
S1 asks S2: What do you know
about Qing Ming Festival
S2 answers and asks S3 the same question.
Grammar Focus
Read the sentences and find out the common features.
I know that the Water Festival is really fun.
I wonder if they’ll have the races again next year.
I wonder whether June is a good time to visit Hong Kong.
I believe that April is the hottest month in Thailand.
主语+谓语
that/if/whether
宾语从句
Objective Clause (宾语从句)
在复合句中作宾语的从句叫宾语从句, 它通常位于主句谓语动词(及物动词)或介词之后。宾语从句通常由从属连词(that / whether / if)、连接代词(who / whom / whose / what / which)或连接副词(when / where / how / why)引导。
Tips:
简单句指只包含一个主谓结构, 并且句子的各个成分都只由单词或短语构成的独立句子或者是分句。例如:
I don’t like the film. (主语:I, 谓语:don’t like, 宾语:the film)
复合句包含一个主句、一个或一个以上的从句; 或只包含一个从句, 但有两个或两个以上的主句。例如:
We know he likes English.
主 + 谓
主 + 谓 + 宾
Can you find out more sentences that contain the objective clauses from the conversations or passage that you’ve learned in Section A
Mary thinks that the teams were fantastic.
I believe that April is the hottest month in Thailand.
He found that the moon was so bright and round.
Bill wonders whether they’ll have zongzi again next year.
I wonder if it is similar to the Water Festival of the Dai
people in Yunnan Province.
由that引导的宾语从句
由whether / if引导的宾语从句
由that引导的宾语从句
当宾语从句是陈述句时, 用that引导。that无词义, 在从句中不充当成分, 在口语和非正式文体中常常省略。
All the students think (that) Mr. Zhang is humorous.
当主句的主语是第一人称(I / we), 并且谓语动词是think, guess, believe, suppose等时, 如果宾语从句要表达否定意思, 一般将否定转移到主句上来, 即“否定前移”。
I don’t think the girl can do the work alone.
that在宾语从句中的省略与保留
a. 在主语+谓语+it(形式宾语)+宾补+that从句(真正宾语)的句
型中不省略。
We must make it clear that we mean what we say.
b. 由连词and连接的两个由that引导的宾语从句中,第二个that
不省略。
He told me (that) he would come and that he would come on time.
c.当that作介词except, in等的宾语时不省略。
They believe in that she must still be single.
I know nothing about him except that he is living in Beijing.
由if / whether引导的宾语从句
当宾语从句的语义相当于一个一般疑问句时, 常用if / whether引导, 表示 “是否” 。if / whether在句中不充当句子成分, 但不能省略。
I wonder if / whether you want to attend the meeting.
由if / whether引导的宾语从句
一般情况下二者没有区别, 可以互换。但是以下情况不可互换:
whether之后紧跟or not时不可与if互换。
Nobody knows whether or not it will rain tomorrow.
在介词后只能用whether不能用if。
The boy worries about whether he has broken his computer.
与动词不定式连用时, 只能用whether不能用if。
I can’t decide whether to go or to stay.
宾语从句的语序
无论主句是陈述句还是疑问句,宾语从句都用陈述句的语序,即“主语在前,谓语在后”的顺序。
Danny says that he will learn English.
Do you know where he came from
Please tell me how I can get to the bus station.
宾语从句的时态
当主句是一般现在时,宾语从句的时态不作限制,我们可以根据句子的意思来使用需要的任何一种时态。
I hear (that)
Jim went to work an hour ago.
he is interested in English.
she will come tomorrow.
Tom has been to London twice.
当主句是一般过去时的时候,宾语从句必须运用相应的过去的某一种时态,从而达到主句和从句的相互一致。例如,把左侧的四句话变为宾语从句是:
He will go to Hong Kong .
He is sick.
He is reading a book .
He has finished his work.
He said
He had finished his work.
He would go to Hong Kong.
He was sick.
He was reading a book.
当宾语从句说明的是客观存在的事实或者是客观存在的真理时就不用受到主句时态的限制,仍是用一般现在时态。
the sun is much bigger than the moon .
summer is after spring .
the earth moves around the sun.
He told me (that)
We knew (that)
The teacher told us (that)
宾语从句的总结
宾语从句三要素
引导词
that
if/whether
特殊疑问词
时态
主句为一般现在时
主句为一般过去时
一般过去时
过去将来时
过去进行时
过去完成时
语序
宾语从句的语序都为陈述句语序
从句客观真理时态不变
从句可为任何时态
Read the sentences and find out the common features.
What fun the Water Festival is!
How fantasic the dragon boat teams were!
How pretty the dragon boats were!
How delicious the food is in Hong Kong!
What / How
名词/形容词/副词
主语+谓语+其他!
Exclamatory Statements (感叹句)
感叹句是表示赞美、惊叹、喜悦等感情的句子。感叹句的句尾用感叹号“!”,读降调。
What引导的感叹句
What + a / an + adj. + 可数名词单数 + 陈述句!
What a beautiful girl she is!
What + adj. + 可数名词复数 + 陈述句!
What big coconuts these are!
What + adj. + 不可数名词 + 陈述句!
What nice weather it is!
How引导的感叹句
How + adj. / adv. + 陈述句(主语 + 谓语)!
How fine the weather is!
How hot it is today!
How high the kite is flying!
How+ 主语 + 谓语!
How time flies!
4a
Write sentences using the words given.
1. think / Lantern Festival / beautiful
___________________________________________________
2. don’t know / whether / he / come home / for the festival
___________________________________________________
3. believe / Water Festival / most / fun
___________________________________________________
I think that the Lantern Festival is beautiful.
I don’t know whether he will come home for the festival.
I believe that the Water Festival is the most fun.
4. wonder / if / mooncakes / delicious
_______________________________________________
5. how / exciting / races
______________________________________________
6. what / nice / a / treat
_______________________________________________
I wonder if the mooncakes are delicious.
How exciting the races were!
What a nice treat!
4b
Read the passage below and underline the objective clauses. If possible, write your own sentences about Mother’s Day and Father’s Day using objective clauses.
Dear Xia Yu,
Do you know that there are two special days for parents in America One is Mother’s Day on the second Sunday of May, and the other is Father’s Day on the third Sunday of June. On these two days, American children often give gifts to their parents or take them out for lunch or dinner.
one ... the other ...
一个......另一个......
表示特定范围内两个事物的不同情况。
Common gifts are flowers and cards for mothers and shirts or ties for fathers. I heard that it is becoming more and more popular to celebrate Mother’s Day and Father’s Day in China. I wonder if children over there also give similar gifts to their parents. I believe that there are many ways to show our love. Actually, we don’t have to spend a lot of money. It is also a good idea to help parents to do something instead.
June
n. 领带 v. 捆;束
当其作动词时, 过去式和过去分词均为tied, 现在分词为tying。
4c
Which festival do you like best Ask your group and report to the class.
e.g. In our group, David’s favorite festival is ... He thinks
that ...
Name Favorite festival Reason(s)
Exercises
根据句意选出恰当的一项填空。
1. ______ (What / What a) fine weather it is now!
2. ______ (What / How) warm it is in the classroom!
3. ________ (What / What a) nice shirt you bought!
4. _____ (What / How) fast the young man is walking!
What
How
What a
How
将下列句子改为感叹句。
1. The girl is very clever.
_____ ______ the girl is!
2. It is a wonderful experience.
_____ ______ wonderful experience it is!
3. The wind is blowing strongly.
_____ _______ the wind is blowing!
4. The news is exciting.
_____ _______ news it is!
5. The sweaters are very nice.
_____ ______ sweaters they are!
How clever
What a
How strongly
What exciting
What nice
Homework
Preview Section B 1a-1d.
Do the exercises in students’ book.
Thank you!
同课章节目录
- Unit 1 How can we become good learners.
- Section A
- Section B
- Unit 2 I think that mooncakes are delicious!
- Section A
- Section B
- Unit 3 Could you please tell me where the restroom
- Section A
- Section B
- Unit 4 I used to be afraid of the dark.
- Section A
- Section B
- Unit 5 What are the shirts made of?
- Section A
- Section B
- Review of Units 1-5
- Unit 6 When was it invented?
- Section A
- Section B
- Unit 7 Teenagers should be allowed to choose their
- Section A
- Section B
- Unit 8 It must belong to Carla.
- Section A
- Section B
- Unit 9 I like music that I can dance to.
- Section A
- Section B
- Unit 10 You're supposed to shake hands.
- Section A
- Section B
- Review of Units 6-10
- Unit 11 Sad movies make me cry.
- Section A
- Section B
- Unit 12 Life is full of the unexpected
- Section A
- Section B
- Unit 13 We're trying to save the earth!
- Section A
- Section B
- Unit 14 I remember meeting all of you in Grade 7.
- Section A
- Section B
- Review of Units 11-14
