《高中英语》(Senior High English)总体编写思路 [北京师范大学出版社曹瑞珍][上学期]
文档属性
| 名称 | 《高中英语》(Senior High English)总体编写思路 [北京师范大学出版社曹瑞珍][上学期] |  | |
| 格式 | rar | ||
| 文件大小 | 3.6MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 北师大版 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2006-10-22 23:43:00 | ||
图片预览







文档简介
课件70张PPT。《高中英语》
Senior High English 总体编写思路 北京师范大学出版社
曹瑞珍高中英语课程目标语言技能 Language Skills
听、说、读、写
语言知识 Language Items
语音、词汇、语法、功能、话题
情感态度 Emotions and Attitudes
兴趣、动机、自信、合作
学习策略 Learning Strategies
认知、调控、交际、资源
文化意识 Cultural Awareness
英语国家的文化、中外文化比较
教材编写原则以语言技能和语言知识为主线,融入学习策略的教学以及情感态度和文化意识的培养;
Input + Practice = Output
Interest → Motivation → Makes learning and teaching easier
Integrated skills approach
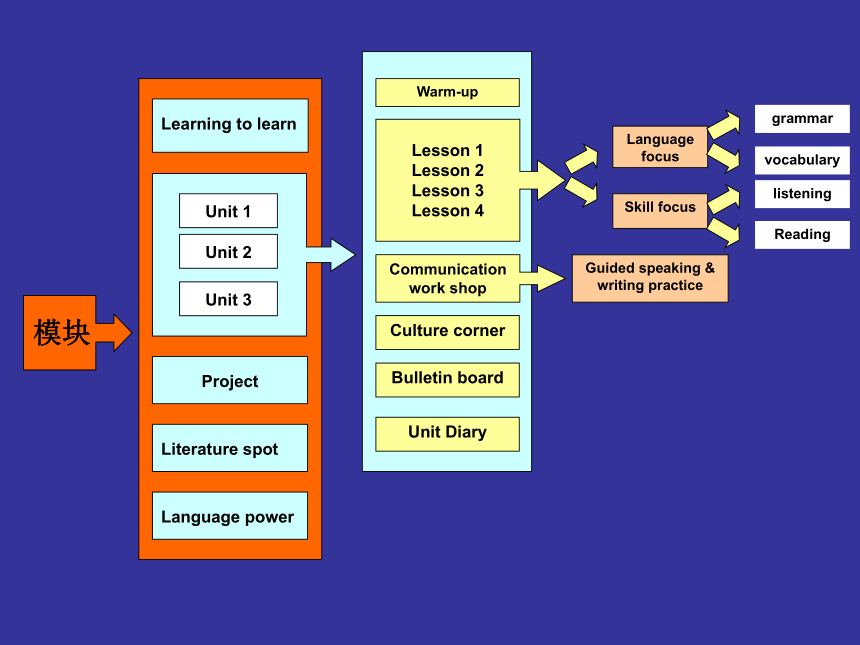
grammarvocabularylisteningReadingWarm-upProjectLearning to learnLiterature spotLanguage powerCulture cornerBulletin boardUnit DiaryLanguage focusSkill focusGuided speaking & writing practiceUnit 1Unit 2Unit 3Communication work shopLesson 1
Lesson 2
Lesson 3
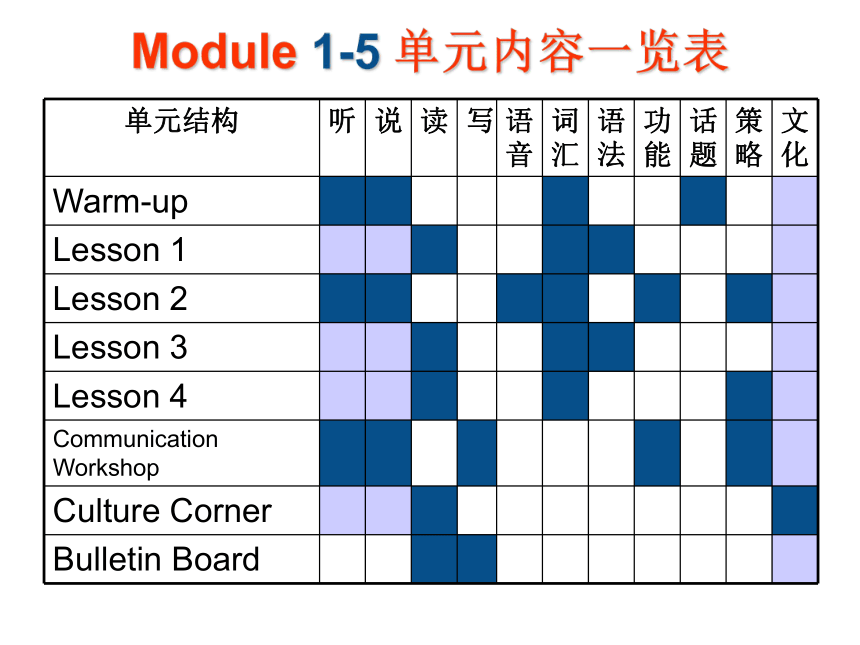
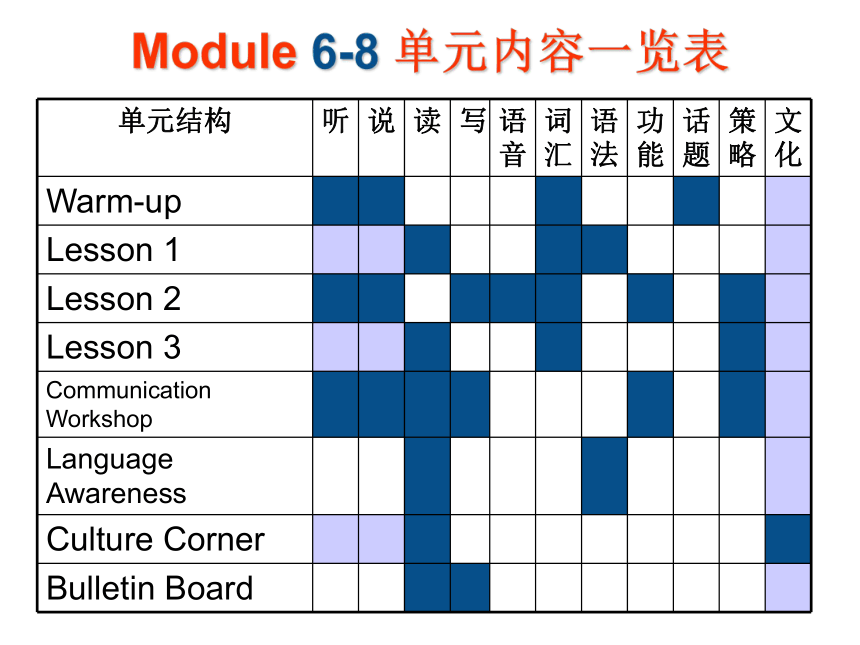
Lesson 4 模块Module 1-5 单元内容一览表 Module 6-8 单元内容一览表 语言技能Reading
Listening
Speaking
Writing
语言技能Integrated skills 的几种方式
Speaking Reading (Listening) Speaking (Writing)
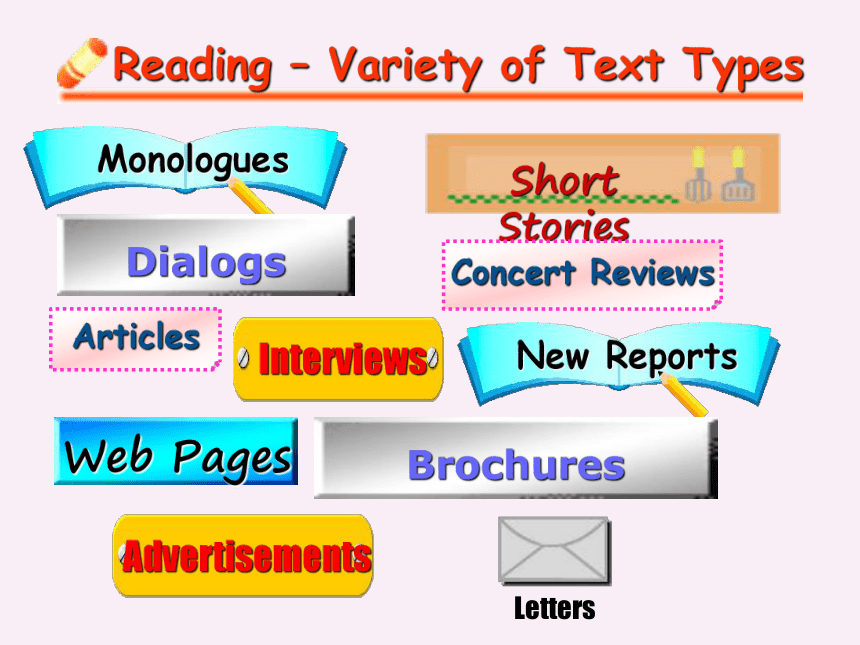
Reading Reading (Listening) Speaking (Writing)语言技能From Module 1 onwards, strategies for reading, listening, writing, organising your vocabulary, and organising your learning encourage independent learning and good learning habits for life.Reading – Variety of Text TypesMonologuesNew ReportsDialogsArticlesInterviewsWeb PagesShort StoriesConcert ReviewsBrochuresAdvertisementsLettersReading StrategiesPrediction
Reading for details
Reading for main ideas
Sequencing
Dealing with difficult words
Completing notes
Identifying facts and opinions
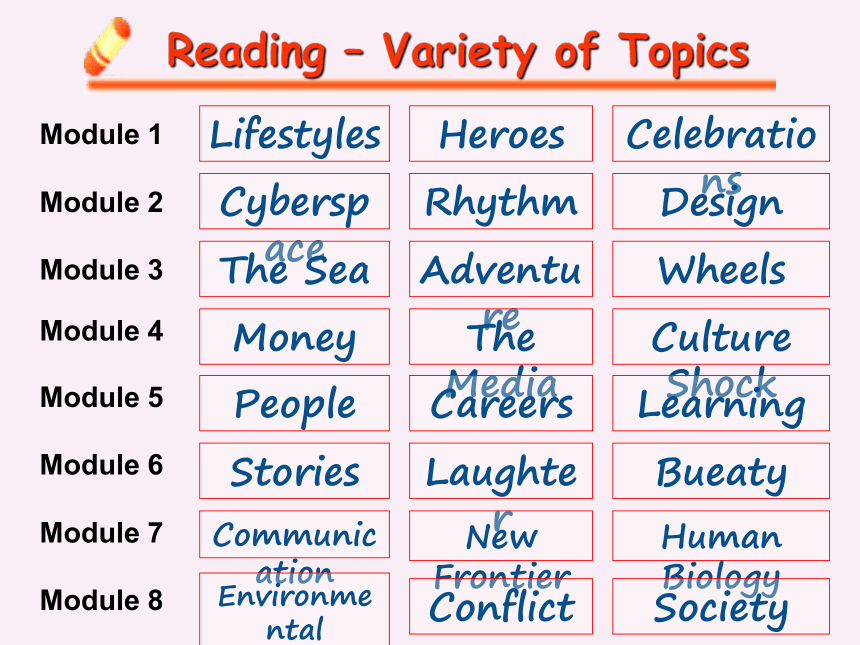
Dealing with culture referencesReading – Variety of TopicsLifestylesHeroesModule 1CelebrationsCyberspaceRhythmModule 2DesignThe SeaAdventureModule 3WheelsMoneyThe MediaModule 4Culture ShockPeopleCareersModule 5LearningStoriesLaughterModule 6BueatyCommunicationNew FrontierModule 7Human BiologyConflictModule 8SocietyEnvironmental ProtectionReading StrategiesParagraphs and headings
Identifying accurate information
Completing texts with sentence gaps
Reading under pressure
Summarising
Reading StrategiesReading Strategies:
Facts and opinions
To find opinions, look for adjectives (e.g. amazing / attractive).
Facts give information which is, in theory, true (e.g. has an automatic focus)
Reading in lessonsTo provide language input
To teach grammar or reading skills
To practice reading skills
To practice grammar
To learn and practice vocabularyExampleExample Readings in Communication Workshop and Bulletin Board To provide models for writing
Reading StagesBefore reading
While reading
Post reading
ExampleFocus on ReadingListening – Variety of Text TypesMonologuesNew ReportsDialogsArticlesInterviewsShort StoriesAdvertisementsListening in Warm-up 4-5 short dialogues
To introduce the unit topic
To prompt students to talk about the topicListening StrategiesPreparations
Listening for specific information
Focus on situation
Identifying people
Identifying style
Identifying different English accents
Completing texts
Identifying moods
Understanding culture references
ExampleListening in Lessons To provide audio language input
To teach listening strategies
To practise listening skills
To teach functions
To practise pronunciation
Listening in StagesBefore listening
While listening
Post listeningListening in Communication Workshop Speaking – Before you start
To provide language input for speaking task
Song
To arouse students’ interest
Speaking in Warm-up To get students familiar with the topicRead the questions. Then, in pairs, tell your partner about yourself.
Example I listen to the radio every morning while I’m getting ready for school. And you?
Do you listen to the radio much? Which programmes?
How many hours of TV do you watch each week?
What are your favourite TV programmes?
What magazines do you read regularly?
Do you often read a newspaper? If so, which one?
Which paper do your parents read?
Do you sometimes use the Internet? What for?Speaking in Lessons 1-4 To practise using the language taught in the lesson
To practise functions
To share views and opinions
Mostly teacher / student interaction or pair workSpeaking in Communication Workshop To practise using the language taught in the unit
To practise functions
To share views and opinions
Full speaking task involving group work and several stepsWriting in Communication Workshop Teaching writing by showing the process step by step
There is always a model to follow.
Talkback – for students to share ideas Focus on WritingPractise using linking wordsGuided writing with exampleTranslation语言知识Grammar
Vocabulary
Functions
PronunciationGrammar – discovery approachThe discovery or inductive approach of grammar provides students with a challenge. They are not simply given the rules. The process of rule-discovery ensures the rules are better internalized. A staging method has also been implemented---revise, practice, rehearse, perform, which takes students from more controlled to freer practiceContrastive grammar approachStudents not only have to discover the rules on their own, they are also given a chance of comparing various tenses in different combinations (Present Perfect versus Past Simple, Present Simple versus Present Continuous, etc.). This allows them to better understand the differences in usage.
The contrastive approach to grammar deals with common problem areas that students face.Contextualized Presentation of GrammarGrammar is always presented in a context, so that students start out with meaning rather than form.Contextualized Presentation of GrammarAfrica on G8 Agenda
The Group of Eight, or G8, was formed by eight of the world’s wealthiest nations in 1998. The G8 is made up of political leaders from France, the United States, Britain, Germany, Japan, Italy, Canada and Russia. They meet every summer to discuss major problems that concern the whole world.
It is going to be remembered as a historical meeting. This year, the topic of Africa will be discussed in detail. Widespread poverty there means that many people cannot get the water, clothing, housing, electricity or education they need. AIDS is another problem of great concern so sex education and health care administration is extremely important.
Reforms have been demanded by people from all over the world. They want the leaders to cancel the debt of Africa’s poorest countries so that the problems there can be prevented from getting any worse. Their belief is that this is the only way for many of these nations to escape their painful pasts. Grammar - PresentationSTATE OR ACTIVITY VERBS
4 Look at the blue words in the text. Can they be used in simple and continuous tenses or only simple tenses? Complete the table.
Blue words:
arrive watch talk feel
understand know realise
believe prepare carry means
want like prefer need
Can you add more verbs to each column? Students are given lot of examples and are required to discover grammar rules themselves.Read these pairs of sentences. Compare the verbs. Does the verb mean the same in both sentences?
a) All our guides have several years of experience in leading hiking trips in the Himalayas.
b) You are having a hot cup of tea.
a) You are feeling tired.
b) At Adventure 2000 we feel that we understand the needs of hikers.
a) We also think that good travel arrangements are important.
b) You are thinking about how far there is to go.
? Grammar Summary 3, on page 93Grammar - Practice Guided practice: more controlled6 Which of the sentences cannot be changed into the Present Continuous?
The coffee tastes awful.
We have breakfast very early.
She thinks she is the best.
They feel they need more time.
I have a serious headache.
She thinks about her mother a lot.
Which of these expressions an be used in both Present Continuous and Present Simple, and which only in the Present Simple?
have a shower, play football, think about, know, look awful, want, see the boss, like, sound interesting, watch TV, believe, taste good, look at
Grammar - Practice Less guided practice: less controlled8 Read the interview with a Tibetan guide and put the verbs in brackets in the Present Continuous or Present Simple.
Reporter: Do you (1) ________ (like) your job?
Guide: Oh, yes. I (2) ________ (love) it. I (3) ________ (enjoy) meeting new people and travelling a lot.
Reporter: What do you (4) ________ (think) about the tourists who (5) ________ (come) to Tibet?
Guide: Most of them already (6) ________ (know) a lot about mountains and (7) ________ (want) to see as much as possible. Right now, I (8) ________ (work) for a group of Austrian hikers who have all been here before. They (9) ________ (understand) all about hiking and I’m sure they (10) ________ (enjoy) themselves. That’s great because it (11) ________ (mean) that the hike is good fun for me too.
Language in Use Free Practice11 Work in pairs. Use the verbs above to tell your partner about what you do/don’t do and what you are/aren’t doing.
Example have a shower
I always have a shower in the morning.
I’m not having a shower now.
Vocabulary developmentModule 1-5
specific focus is put on working out the meaning of unknown vocabulary
Multi-part verbs/Phrasal verbs
Preposition bank
Module 6-8
Idiomatic bank--- the focus moves to more colloquial language and multi-word verbs
Vocabulary developmentFocusing on lexical development through longer, more detailed reading texts
Vocabulary work looking at issues such as worldbuilding, multi-part verbs, collocations, idiomatic language and word families;
chatroom---focus on the colloquial uses of the language
Lexican---gives instant reference for students dealing with the increased load of vocabulary associated with Module 6-8
Vocabulary developmentLanguage Power
Word power
Key Word Bank
Word tips---present strategies for expanding vocabulary, e.g. start your own vocabulary book
Working with dictionaries
Phrase builder and lexicon ---invaluable resource both in the classroom as well as out and for both teachers and studentsVocabulary – Topic WordsWarm-up
1 Look at the types of transport in the Key Words and complete the table.KEY WORDS
plane, balloon, bicycle, boat, bus, car, ferry, helicopter, lorry, motorcycle, ship, train, the underground, minibus Topic words to help recycle known vocabulary
Help students to remember new wordsTrain students to categorize words, which helps their memoryVocabulary – Traget New WordsComplete the sentences using the words below.
innocent, fiction, strawberry, spokesman, contemporary, sew, as long as, load, in favour of, bush, evidence, electricity
1 The lights won’t work because there is no __________.
2 I will help you with your homework __________ you stop watching TV now.
3 Can I help you? That is a heavy __________ you are carrying.
4 Are you __________ this new law to stop people smoking?
5 My mum __________ all my clothes for me.
6 There is a lot of __________ that he was the person who stole the book.
7 I don’t think he did it. I think he’s __________.
8 I love to eat __________ with cream.
9 He hid the knife under a __________ in the garden.
10 The __________ has to explain what the team thinks.
11 I like to read books that are __________.
12 David really likes __________ art. He doesn’t like old paintings very much.Practice in both the main lessons and in Language powerVocabulary – Key Word BankFood: bacon, barbecues, dessert, fusion, garlic, hamburger, hot dogs, lemon, mushroom, roast beef, steak, toast
Places: Big Ben, Buckingham Palace, Sydney Opera House, the Great Barrier Reef, World Trace Centre, the Statue of Liberty
Sports: American football, basketball, fishing, soccer, golf, hiking, horse-riding, rugby, sailing, surfing, tennis
Adjectives: amazing, brilliant, broad, cautious, contrary, cosy, curious, delicious, dull, familiar, foggy, informal, interesting, limited, lively, modest, muddy, multi-cultural, outgoing, poor, popular, reasonable, splendid, tasty, top. unfair, well-off, yummy
Phrasal verbs: drop (somebody) off, go back, hang on, hurry up, look after, look back, look for, look forward to, look in, look up, pick (somebody) up
Money: bank, cash, credit card, coin, notes, traveller’s cheques
Australia: coal, desert, diamond, export, flavour, mine, outdoors
The UK: bed and breakfast, comfort, hotel, phone box, the underground
Beijing polite: Excuse me. Of course (not). Thank you. That’s very kind of you. Would you mind doing ... Vocabulary – Others Wordbuilding
Phrasal verbs
Matching of words (collocations)
FunctionContextualized Presentation of functions
fun_ction is always presented in real life context, so that students start out with discourse rather than isolated sentences.Function PresentedInteraction
Giving opinions
Preferences
Travel situations
Discussing suggestions
Shopping and bargaining
Interrupting people
Being polite
Showing Sympathy
Clarifying and asking
Presenting
Giving and asking for adviceExamplePronunciationPronunciation is presented with language functions.
Culture content The textbook incorporates culture throughout the course.
Culture corner in each unit
Literature spot in each module
Comparing culture
A Unit on Culture Shock
Reading texts about Life in the Arctic, Christmas in Britain, how to behave in different cultures and seasonal festivals around the world…Culture ContentCultures about English speaking countries and other countries in the world.
Chinese culture Culture content Reading texts about Life in the Arctic, Christmas in Britain, how to behave in different cultures and seasonal festivals around the world…
Quote….Unquote
starting point for further discussion either in English or Chinese;
to stimulate both teachers and students to extra activities and work
To provide students with examples of real speech that they can further explore or use
Culture – Culture CornerCulture – Comparing CulturesBenefits for studentsInductive methodology promotes student autonomy.
Provide opportunities to personalise learning and discover grammar rules on their own.
Its mature approach treats students like young adults and expect them to participate and take responsibility for their learning.Benefits for studentsGraded exercises in LP allow everyone to proceed at the appropriate pace.
Writing Help and Grammar Summary in SB help students to study on their own.
Key words, Function File and Learning Strategies make learning even easier.
Opportunity to learn about other cultures and compare them to one’s own.Benefits for studentsReliable preparation for school leaving exams---grammar, skills and vocabulary that students really need.
Gaining knowledge beyond the English language classroom.
Opportunities to help students to become independent learners.
Benefits for teachersEasy to teach thanks to learner training aspects of the course---it allows students to become independent learners.
Tasks are broken into their constituent parts or marked for difficulty to allow easy exploitation in mixed ability classes.
Thorough coverage of grammar, skills and vocabulary.
Benefits for teachersTopics which keep students interested and willing to take part
Teaching skills development through the extended TB introduction
The Warm-up sections help teachers find interesting ways to start their lessons
Extended reading texts make revision more interesting and create motivating options for all students
Benefits for teachersCommunication Workshops provide further skills development
TB offers options to the lesson plans to cut activities or develop themKey featuresKeeps students interested
Offers students a challenge
Supplies enough grammar and vocabulary input
Personalises the language they learn
Offers plenty of opportunities to practice
Regular recycle the material
Integrates grammar and vocabulary with skills work
Makes students see that what they learn is relevant to the exams they face.高中英语课程目标语言技能 Language Skills
听、说、读、写
语言知识 Language Items
语音、词汇、语法、功能、话题
情感态度 Emotions and Attitudes
兴趣、动机、自信、合作
学习策略 Learning Strategies
认知、调控、交际、资源
文化意识 Cultural Awareness
英语国家的文化、中外文化比较
曹瑞珍:010-58802782
王 源:010-58802831
E-mail: bnupress@263.net
基础教育教材网:http://gbjc.bnup.com.cn/
Thank you!
听、说、读、写
语言知识 Language Items
语音、词汇、语法、功能、话题
情感态度 Emotions and Attitudes
兴趣、动机、自信、合作
学习策略 Learning Strategies
认知、调控、交际、资源
文化意识 Cultural Awareness
英语国家的文化、中外文化比较
教材编写原则以语言技能和语言知识为主线,融入学习策略的教学以及情感态度和文化意识的培养;
Input + Practice = Output
Interest → Motivation → Makes learning and teaching easier
Integrated skills approach
grammarvocabularylisteningReadingWarm-upProjectLearning to learnLiterature spotLanguage powerCulture cornerBulletin boardUnit DiaryLanguage focusSkill focusGuided speaking & writing practiceUnit 1Unit 2Unit 3Communication work shopLesson 1
Lesson 2
Lesson 3
Lesson 4 模块Module 1-5 单元内容一览表 Module 6-8 单元内容一览表 语言技能Reading
Listening
Speaking
Writing
语言技能Integrated skills 的几种方式
Speaking Reading (Listening) Speaking (Writing)
Reading Reading (Listening) Speaking (Writing)语言技能From Module 1 onwards, strategies for reading, listening, writing, organising your vocabulary, and organising your learning encourage independent learning and good learning habits for life.Reading – Variety of Text TypesMonologuesNew ReportsDialogsArticlesInterviewsWeb PagesShort StoriesConcert ReviewsBrochuresAdvertisementsLettersReading StrategiesPrediction
Reading for details
Reading for main ideas
Sequencing
Dealing with difficult words
Completing notes
Identifying facts and opinions
Dealing with culture referencesReading – Variety of TopicsLifestylesHeroesModule 1CelebrationsCyberspaceRhythmModule 2DesignThe SeaAdventureModule 3WheelsMoneyThe MediaModule 4Culture ShockPeopleCareersModule 5LearningStoriesLaughterModule 6BueatyCommunicationNew FrontierModule 7Human BiologyConflictModule 8SocietyEnvironmental ProtectionReading StrategiesParagraphs and headings
Identifying accurate information
Completing texts with sentence gaps
Reading under pressure
Summarising
Reading StrategiesReading Strategies:
Facts and opinions
To find opinions, look for adjectives (e.g. amazing / attractive).
Facts give information which is, in theory, true (e.g. has an automatic focus)
Reading in lessonsTo provide language input
To teach grammar or reading skills
To practice reading skills
To practice grammar
To learn and practice vocabularyExampleExample Readings in Communication Workshop and Bulletin Board To provide models for writing
Reading StagesBefore reading
While reading
Post reading
ExampleFocus on ReadingListening – Variety of Text TypesMonologuesNew ReportsDialogsArticlesInterviewsShort StoriesAdvertisementsListening in Warm-up 4-5 short dialogues
To introduce the unit topic
To prompt students to talk about the topicListening StrategiesPreparations
Listening for specific information
Focus on situation
Identifying people
Identifying style
Identifying different English accents
Completing texts
Identifying moods
Understanding culture references
ExampleListening in Lessons To provide audio language input
To teach listening strategies
To practise listening skills
To teach functions
To practise pronunciation
Listening in StagesBefore listening
While listening
Post listeningListening in Communication Workshop Speaking – Before you start
To provide language input for speaking task
Song
To arouse students’ interest
Speaking in Warm-up To get students familiar with the topicRead the questions. Then, in pairs, tell your partner about yourself.
Example I listen to the radio every morning while I’m getting ready for school. And you?
Do you listen to the radio much? Which programmes?
How many hours of TV do you watch each week?
What are your favourite TV programmes?
What magazines do you read regularly?
Do you often read a newspaper? If so, which one?
Which paper do your parents read?
Do you sometimes use the Internet? What for?Speaking in Lessons 1-4 To practise using the language taught in the lesson
To practise functions
To share views and opinions
Mostly teacher / student interaction or pair workSpeaking in Communication Workshop To practise using the language taught in the unit
To practise functions
To share views and opinions
Full speaking task involving group work and several stepsWriting in Communication Workshop Teaching writing by showing the process step by step
There is always a model to follow.
Talkback – for students to share ideas Focus on WritingPractise using linking wordsGuided writing with exampleTranslation语言知识Grammar
Vocabulary
Functions
PronunciationGrammar – discovery approachThe discovery or inductive approach of grammar provides students with a challenge. They are not simply given the rules. The process of rule-discovery ensures the rules are better internalized. A staging method has also been implemented---revise, practice, rehearse, perform, which takes students from more controlled to freer practiceContrastive grammar approachStudents not only have to discover the rules on their own, they are also given a chance of comparing various tenses in different combinations (Present Perfect versus Past Simple, Present Simple versus Present Continuous, etc.). This allows them to better understand the differences in usage.
The contrastive approach to grammar deals with common problem areas that students face.Contextualized Presentation of GrammarGrammar is always presented in a context, so that students start out with meaning rather than form.Contextualized Presentation of GrammarAfrica on G8 Agenda
The Group of Eight, or G8, was formed by eight of the world’s wealthiest nations in 1998. The G8 is made up of political leaders from France, the United States, Britain, Germany, Japan, Italy, Canada and Russia. They meet every summer to discuss major problems that concern the whole world.
It is going to be remembered as a historical meeting. This year, the topic of Africa will be discussed in detail. Widespread poverty there means that many people cannot get the water, clothing, housing, electricity or education they need. AIDS is another problem of great concern so sex education and health care administration is extremely important.
Reforms have been demanded by people from all over the world. They want the leaders to cancel the debt of Africa’s poorest countries so that the problems there can be prevented from getting any worse. Their belief is that this is the only way for many of these nations to escape their painful pasts. Grammar - PresentationSTATE OR ACTIVITY VERBS
4 Look at the blue words in the text. Can they be used in simple and continuous tenses or only simple tenses? Complete the table.
Blue words:
arrive watch talk feel
understand know realise
believe prepare carry means
want like prefer need
Can you add more verbs to each column? Students are given lot of examples and are required to discover grammar rules themselves.Read these pairs of sentences. Compare the verbs. Does the verb mean the same in both sentences?
a) All our guides have several years of experience in leading hiking trips in the Himalayas.
b) You are having a hot cup of tea.
a) You are feeling tired.
b) At Adventure 2000 we feel that we understand the needs of hikers.
a) We also think that good travel arrangements are important.
b) You are thinking about how far there is to go.
? Grammar Summary 3, on page 93Grammar - Practice Guided practice: more controlled6 Which of the sentences cannot be changed into the Present Continuous?
The coffee tastes awful.
We have breakfast very early.
She thinks she is the best.
They feel they need more time.
I have a serious headache.
She thinks about her mother a lot.
Which of these expressions an be used in both Present Continuous and Present Simple, and which only in the Present Simple?
have a shower, play football, think about, know, look awful, want, see the boss, like, sound interesting, watch TV, believe, taste good, look at
Grammar - Practice Less guided practice: less controlled8 Read the interview with a Tibetan guide and put the verbs in brackets in the Present Continuous or Present Simple.
Reporter: Do you (1) ________ (like) your job?
Guide: Oh, yes. I (2) ________ (love) it. I (3) ________ (enjoy) meeting new people and travelling a lot.
Reporter: What do you (4) ________ (think) about the tourists who (5) ________ (come) to Tibet?
Guide: Most of them already (6) ________ (know) a lot about mountains and (7) ________ (want) to see as much as possible. Right now, I (8) ________ (work) for a group of Austrian hikers who have all been here before. They (9) ________ (understand) all about hiking and I’m sure they (10) ________ (enjoy) themselves. That’s great because it (11) ________ (mean) that the hike is good fun for me too.
Language in Use Free Practice11 Work in pairs. Use the verbs above to tell your partner about what you do/don’t do and what you are/aren’t doing.
Example have a shower
I always have a shower in the morning.
I’m not having a shower now.
Vocabulary developmentModule 1-5
specific focus is put on working out the meaning of unknown vocabulary
Multi-part verbs/Phrasal verbs
Preposition bank
Module 6-8
Idiomatic bank--- the focus moves to more colloquial language and multi-word verbs
Vocabulary developmentFocusing on lexical development through longer, more detailed reading texts
Vocabulary work looking at issues such as worldbuilding, multi-part verbs, collocations, idiomatic language and word families;
chatroom---focus on the colloquial uses of the language
Lexican---gives instant reference for students dealing with the increased load of vocabulary associated with Module 6-8
Vocabulary developmentLanguage Power
Word power
Key Word Bank
Word tips---present strategies for expanding vocabulary, e.g. start your own vocabulary book
Working with dictionaries
Phrase builder and lexicon ---invaluable resource both in the classroom as well as out and for both teachers and studentsVocabulary – Topic WordsWarm-up
1 Look at the types of transport in the Key Words and complete the table.KEY WORDS
plane, balloon, bicycle, boat, bus, car, ferry, helicopter, lorry, motorcycle, ship, train, the underground, minibus Topic words to help recycle known vocabulary
Help students to remember new wordsTrain students to categorize words, which helps their memoryVocabulary – Traget New WordsComplete the sentences using the words below.
innocent, fiction, strawberry, spokesman, contemporary, sew, as long as, load, in favour of, bush, evidence, electricity
1 The lights won’t work because there is no __________.
2 I will help you with your homework __________ you stop watching TV now.
3 Can I help you? That is a heavy __________ you are carrying.
4 Are you __________ this new law to stop people smoking?
5 My mum __________ all my clothes for me.
6 There is a lot of __________ that he was the person who stole the book.
7 I don’t think he did it. I think he’s __________.
8 I love to eat __________ with cream.
9 He hid the knife under a __________ in the garden.
10 The __________ has to explain what the team thinks.
11 I like to read books that are __________.
12 David really likes __________ art. He doesn’t like old paintings very much.Practice in both the main lessons and in Language powerVocabulary – Key Word BankFood: bacon, barbecues, dessert, fusion, garlic, hamburger, hot dogs, lemon, mushroom, roast beef, steak, toast
Places: Big Ben, Buckingham Palace, Sydney Opera House, the Great Barrier Reef, World Trace Centre, the Statue of Liberty
Sports: American football, basketball, fishing, soccer, golf, hiking, horse-riding, rugby, sailing, surfing, tennis
Adjectives: amazing, brilliant, broad, cautious, contrary, cosy, curious, delicious, dull, familiar, foggy, informal, interesting, limited, lively, modest, muddy, multi-cultural, outgoing, poor, popular, reasonable, splendid, tasty, top. unfair, well-off, yummy
Phrasal verbs: drop (somebody) off, go back, hang on, hurry up, look after, look back, look for, look forward to, look in, look up, pick (somebody) up
Money: bank, cash, credit card, coin, notes, traveller’s cheques
Australia: coal, desert, diamond, export, flavour, mine, outdoors
The UK: bed and breakfast, comfort, hotel, phone box, the underground
Beijing polite: Excuse me. Of course (not). Thank you. That’s very kind of you. Would you mind doing ... Vocabulary – Others Wordbuilding
Phrasal verbs
Matching of words (collocations)
FunctionContextualized Presentation of functions
fun_ction is always presented in real life context, so that students start out with discourse rather than isolated sentences.Function PresentedInteraction
Giving opinions
Preferences
Travel situations
Discussing suggestions
Shopping and bargaining
Interrupting people
Being polite
Showing Sympathy
Clarifying and asking
Presenting
Giving and asking for adviceExamplePronunciationPronunciation is presented with language functions.
Culture content The textbook incorporates culture throughout the course.
Culture corner in each unit
Literature spot in each module
Comparing culture
A Unit on Culture Shock
Reading texts about Life in the Arctic, Christmas in Britain, how to behave in different cultures and seasonal festivals around the world…Culture ContentCultures about English speaking countries and other countries in the world.
Chinese culture Culture content Reading texts about Life in the Arctic, Christmas in Britain, how to behave in different cultures and seasonal festivals around the world…
Quote….Unquote
starting point for further discussion either in English or Chinese;
to stimulate both teachers and students to extra activities and work
To provide students with examples of real speech that they can further explore or use
Culture – Culture CornerCulture – Comparing CulturesBenefits for studentsInductive methodology promotes student autonomy.
Provide opportunities to personalise learning and discover grammar rules on their own.
Its mature approach treats students like young adults and expect them to participate and take responsibility for their learning.Benefits for studentsGraded exercises in LP allow everyone to proceed at the appropriate pace.
Writing Help and Grammar Summary in SB help students to study on their own.
Key words, Function File and Learning Strategies make learning even easier.
Opportunity to learn about other cultures and compare them to one’s own.Benefits for studentsReliable preparation for school leaving exams---grammar, skills and vocabulary that students really need.
Gaining knowledge beyond the English language classroom.
Opportunities to help students to become independent learners.
Benefits for teachersEasy to teach thanks to learner training aspects of the course---it allows students to become independent learners.
Tasks are broken into their constituent parts or marked for difficulty to allow easy exploitation in mixed ability classes.
Thorough coverage of grammar, skills and vocabulary.
Benefits for teachersTopics which keep students interested and willing to take part
Teaching skills development through the extended TB introduction
The Warm-up sections help teachers find interesting ways to start their lessons
Extended reading texts make revision more interesting and create motivating options for all students
Benefits for teachersCommunication Workshops provide further skills development
TB offers options to the lesson plans to cut activities or develop themKey featuresKeeps students interested
Offers students a challenge
Supplies enough grammar and vocabulary input
Personalises the language they learn
Offers plenty of opportunities to practice
Regular recycle the material
Integrates grammar and vocabulary with skills work
Makes students see that what they learn is relevant to the exams they face.高中英语课程目标语言技能 Language Skills
听、说、读、写
语言知识 Language Items
语音、词汇、语法、功能、话题
情感态度 Emotions and Attitudes
兴趣、动机、自信、合作
学习策略 Learning Strategies
认知、调控、交际、资源
文化意识 Cultural Awareness
英语国家的文化、中外文化比较
曹瑞珍:010-58802782
王 源:010-58802831
E-mail: bnupress@263.net
基础教育教材网:http://gbjc.bnup.com.cn/
Thank you!
同课章节目录
