情态动词[下学期]
图片预览
文档简介
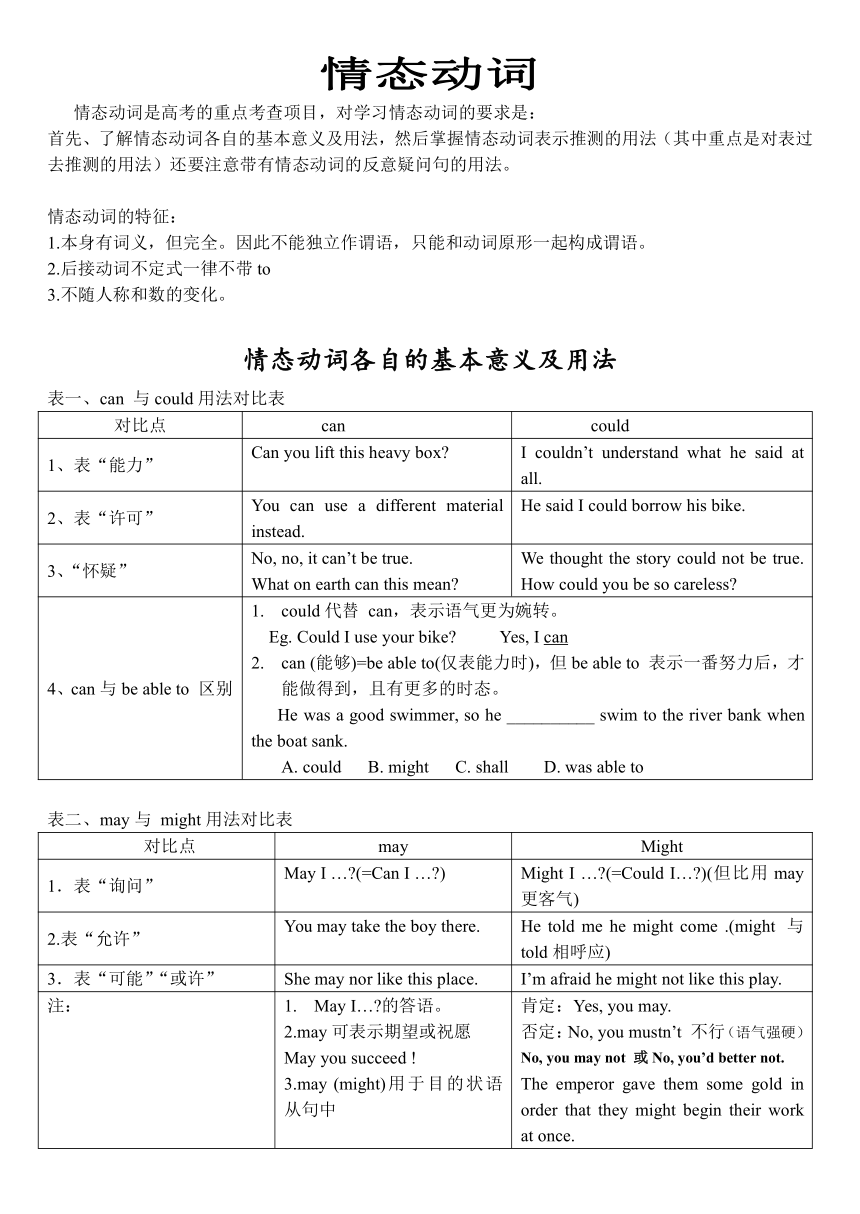
情态动词
情态动词是高考的重点考查项目,对学习情态动词的要求是:
首先、了解情态动词各自的基本意义及用法,然后掌握情态动词表示推测的用法(其中重点是对表过去推测的用法)还要注意带有情态动词的反意疑问句的用法。
情态动词的特征:
1.本身有词义,但完全。因此不能独立作谓语,只能和动词原形一起构成谓语。
2.后接动词不定式一律不带to
3.不随人称和数的变化。
情态动词各自的基本意义及用法
表一、can 与could用法对比表
对比点 can could
1、表“能力” Can you lift this heavy box I couldn’t understand what he said at all.
2、表“许可” You can use a different material instead. He said I could borrow his bike.
3、“怀疑” No, no, it can’t be true.What on earth can this mean We thought the story could not be true. How could you be so careless
4、can与be able to 区别 could代替 can,表示语气更为婉转。 Eg. Could I use your bike Yes, I cancan (能够)=be able to(仅表能力时),但be able to 表示一番努力后,才能做得到,且有更多的时态。He was a good swimmer, so he __________ swim to the river bank when the boat sank.A. could B. might C. shall D. was able to
表二、may与 might用法对比表
对比点 may Might
1.表“询问” May I … (=Can I … ) Might I … (=Could I… )(但比用may 更客气)
2.表“允许” You may take the boy there. He told me he might come .(might 与told相呼应)
3.表“可能”“或许” She may nor like this place. I’m afraid he might not like this play.
注: May I… 的答语。2.may可表示期望或祝愿May you succeed !3.may (might)用于目的状语从句中 肯定:Yes, you may.否定:No, you mustn’t 不行(语气强硬)No, you may not 或No, you’d better not.The emperor gave them some gold in order that they might begin their work at once.
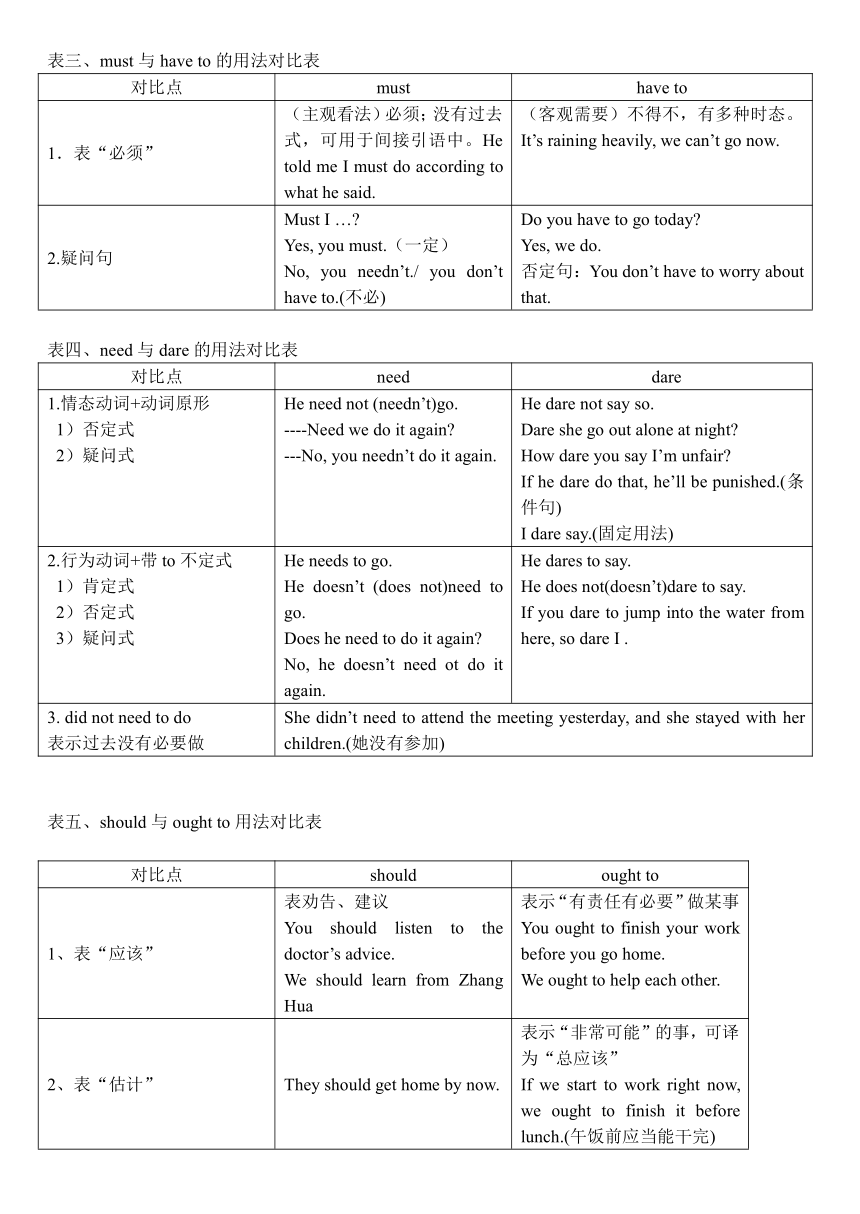
表三、must与have to的用法对比表
对比点 must have to
1.表“必须” (主观看法)必须;没有过去式,可用于间接引语中。He told me I must do according to what he said. (客观需要)不得不,有多种时态。It’s raining heavily, we can’t go now.
2.疑问句 Must I … Yes, you must.(一定)No, you needn’t./ you don’t have to.(不必) Do you have to go today Yes, we do.否定句:You don’t have to worry about that.
表四、need与dare的用法对比表
对比点 need dare
1.情态动词+动词原形 1)否定式 2)疑问式 He need not (needn’t)go.----Need we do it again ---No, you needn’t do it again. He dare not say so.Dare she go out alone at night How dare you say I’m unfair If he dare do that, he’ll be punished.(条件句)I dare say.(固定用法)
2.行为动词+带to不定式 1)肯定式 2)否定式 3)疑问式 He needs to go.He doesn’t (does not)need to go.Does he need to do it again No, he doesn’t need ot do it again. He dares to say.He does not(doesn’t)dare to say.If you dare to jump into the water from here, so dare I .
3. did not need to do表示过去没有必要做 She didn’t need to attend the meeting yesterday, and she stayed with her children.(她没有参加)
表五、should与ought to用法对比表
对比点 should ought to
1、表“应该” 表劝告、建议You should listen to the doctor’s advice.We should learn from Zhang Hua 表示“有责任有必要”做某事You ought to finish your work before you go home.We ought to help each other.
2、表“估计” They should get home by now. 表示“非常可能”的事,可译为“总应该”If we start to work right now, we ought to finish it before lunch.(午饭前应当能干完)
注: 1)、should还可在虚拟语气中的使用2). 注意:ought to的疑问式及否定式----Ought he to go ----Yes, I think he ought to.No, he oughtn’t to. 否定式:ought not to a或oughtn’t to do(不说ought to not do)反疑问句:oughtn’t ______
表六、shall与will的用法对比表
shall Will
征询对方意见或请求指示,用于第一、三人称:Shall I (we)… Shall he (she)… Where shall I (we)wait for you 询问对方的意思或向对方提出要求:Will you(please)… Won’t you… Would you like to… (用would替代will更客气)----Won’t you go and see the film 你不去看电影吗?---Yes, I think I will. 不, 我想去。
2. 表示说话人的“意愿”有“命令”“警告”“强制”“允诺”“决心”等,用于第二、三人称,要重读。You shall do what I tell you ( to do).我叫你干什么你就干什么。Everything shall be done to save the ship.一定要竭尽全力来拯救这艘船。 表示“意志”“意愿”,用于各种人称:I won’t do anything you don’t like.我不会做任何你不喜欢的事。Would表示过去时间的“意志”“意愿”Shylock would not take the money earlier.夏洛克先前是不肯要钱的。
表七:used to与would用法对比表
used to would
1.表示过去的动作、状态,重在与现在情况的对比,不一定要有时间状语。I used to play cards a lot, but now I seldom play.My hometown is not what it used to be. 1.只表示过去动作的重复,有明确的时间状语I would go to see my grandfather on Sunday when he was in the middle school.2.would 后只接表动作的动词,不接表认识或状态动词He used to be nervous in the exam.
2.表示过去的习惯有时可互换:When we were very young, we used to / would go skating every winter.
表示过去的次数时,不能使用:( √)We went to the Great Wall five times when we were young.( X ) We used to go / would go to the Great Wall five times when we were young.
注:used to do的否定式:usedn’t to do 或didn’t use to do (usedn’t也可写作usen’t)疑问式: Did you use to do Didn’t you use to do Used you to do Usedn’t you to do
情态动词表推测
情态动词表推测的意义:
1、大多数情态动词(除表‘能力、许可、意志’外),都可以表示推测,其程度有差异。按其可能性程度的高低排列为:
Must ﹥will ﹥would ﹥ought to ﹥ should ﹥ can ﹥ could﹥ may ﹥ might
肯定 完全可能 很可能 可能 有可能
2.注意区分情态动词的否定的含义:
may not或许不、可能不 might not可能不 can’t 不可能
mustn’t不许、禁止 shouldn’t不应该 needn’t 不必
3.情态动词表推测具体运用:情态动词可以对现在、进行、过去推测
S主+情态动词+be+adj 对“性质”“特征”的推测
S主+情态动词+be+n 对“职业”“事物”的推测
S主+情态动词+V原 对经常性行为的推测
S主+情态动词+be+V-ing 对进行着的行为的推测
S主+情态动词+have+PP 对过去的行为的推测
特别提醒:情态动词表推测时can只能用于否定句和疑问句must只能用于肯定句(它的否定句和疑问句其实就用can来代替了)如句中有情态动词 + 完成时,定是对过去的推测 。句中如有表示不肯定的话语,如:I am not sure; I don’t know 之类,常选may /might的各种形式
4. 记住下面几组表示反劝的特殊的表推测的形式
1). could + have + PP表示本来能做到,但事实上没有做到。 He could have finished the task on time, but the heavy snow came.
2). couldn’t +have + PP表示本来不能做到,但已经做到了。 She could not have covered the whole distance, but in fact she arrived ahead of time.
3) needn’t + have + pp表示本不必做的,但已经做到了。 She needn’t have attended the meeting yesterday, but she did.
4.) should/ought to +have + PP表示 该做而没有做 The plant is dead. I should/ought to have given ot more water.
5) shouldn’t/ oughtn’t to +have + PP表示 不该做而做了。 You oughtn’t to / shouldn’t have taken her bike without permission.
5. 记住下面对比表:
must只能用于肯定句(它的否定句和疑问句其实就用can来代替了)
1.must + have + PP 表示对过去肯定的推测,译为“一定是,准是” The road is wet. It must have rained yesterday.
2.can + have + PP 表示对过去的推测(限于问句中) Can she have said so 他可能这样说吗?
3.can’t + have + PP 表示对过去的否定推测 He cannot have said such a foolish thing.
情态动词表推测的反意疑问句
情态动词表推测的反意疑问句,简单来说,就是以情态动词后的时态为淮,如句子里有明确的时间状语,则以其为准。以 must 为例:
eg. 1. You must be hungry now, aren’t you
2. He must be watching TV , isn’t he
3 Tom must have lived her for a long time, hasn’t he
4. She must have arrived yesterday, didn’t she
注:如选择题中(以She must have arrived yesterday, didn’t she?为例)既有didn’t she又有hasn’t she则以didn’t she?为最佳答案。
情态动词是高考的重点考查项目,对学习情态动词的要求是:
首先、了解情态动词各自的基本意义及用法,然后掌握情态动词表示推测的用法(其中重点是对表过去推测的用法)还要注意带有情态动词的反意疑问句的用法。
情态动词的特征:
1.本身有词义,但完全。因此不能独立作谓语,只能和动词原形一起构成谓语。
2.后接动词不定式一律不带to
3.不随人称和数的变化。
情态动词各自的基本意义及用法
表一、can 与could用法对比表
对比点 can could
1、表“能力” Can you lift this heavy box I couldn’t understand what he said at all.
2、表“许可” You can use a different material instead. He said I could borrow his bike.
3、“怀疑” No, no, it can’t be true.What on earth can this mean We thought the story could not be true. How could you be so careless
4、can与be able to 区别 could代替 can,表示语气更为婉转。 Eg. Could I use your bike Yes, I cancan (能够)=be able to(仅表能力时),但be able to 表示一番努力后,才能做得到,且有更多的时态。He was a good swimmer, so he __________ swim to the river bank when the boat sank.A. could B. might C. shall D. was able to
表二、may与 might用法对比表
对比点 may Might
1.表“询问” May I … (=Can I … ) Might I … (=Could I… )(但比用may 更客气)
2.表“允许” You may take the boy there. He told me he might come .(might 与told相呼应)
3.表“可能”“或许” She may nor like this place. I’m afraid he might not like this play.
注: May I… 的答语。2.may可表示期望或祝愿May you succeed !3.may (might)用于目的状语从句中 肯定:Yes, you may.否定:No, you mustn’t 不行(语气强硬)No, you may not 或No, you’d better not.The emperor gave them some gold in order that they might begin their work at once.
表三、must与have to的用法对比表
对比点 must have to
1.表“必须” (主观看法)必须;没有过去式,可用于间接引语中。He told me I must do according to what he said. (客观需要)不得不,有多种时态。It’s raining heavily, we can’t go now.
2.疑问句 Must I … Yes, you must.(一定)No, you needn’t./ you don’t have to.(不必) Do you have to go today Yes, we do.否定句:You don’t have to worry about that.
表四、need与dare的用法对比表
对比点 need dare
1.情态动词+动词原形 1)否定式 2)疑问式 He need not (needn’t)go.----Need we do it again ---No, you needn’t do it again. He dare not say so.Dare she go out alone at night How dare you say I’m unfair If he dare do that, he’ll be punished.(条件句)I dare say.(固定用法)
2.行为动词+带to不定式 1)肯定式 2)否定式 3)疑问式 He needs to go.He doesn’t (does not)need to go.Does he need to do it again No, he doesn’t need ot do it again. He dares to say.He does not(doesn’t)dare to say.If you dare to jump into the water from here, so dare I .
3. did not need to do表示过去没有必要做 She didn’t need to attend the meeting yesterday, and she stayed with her children.(她没有参加)
表五、should与ought to用法对比表
对比点 should ought to
1、表“应该” 表劝告、建议You should listen to the doctor’s advice.We should learn from Zhang Hua 表示“有责任有必要”做某事You ought to finish your work before you go home.We ought to help each other.
2、表“估计” They should get home by now. 表示“非常可能”的事,可译为“总应该”If we start to work right now, we ought to finish it before lunch.(午饭前应当能干完)
注: 1)、should还可在虚拟语气中的使用2). 注意:ought to的疑问式及否定式----Ought he to go ----Yes, I think he ought to.No, he oughtn’t to. 否定式:ought not to a或oughtn’t to do(不说ought to not do)反疑问句:oughtn’t ______
表六、shall与will的用法对比表
shall Will
征询对方意见或请求指示,用于第一、三人称:Shall I (we)… Shall he (she)… Where shall I (we)wait for you 询问对方的意思或向对方提出要求:Will you(please)… Won’t you… Would you like to… (用would替代will更客气)----Won’t you go and see the film 你不去看电影吗?---Yes, I think I will. 不, 我想去。
2. 表示说话人的“意愿”有“命令”“警告”“强制”“允诺”“决心”等,用于第二、三人称,要重读。You shall do what I tell you ( to do).我叫你干什么你就干什么。Everything shall be done to save the ship.一定要竭尽全力来拯救这艘船。 表示“意志”“意愿”,用于各种人称:I won’t do anything you don’t like.我不会做任何你不喜欢的事。Would表示过去时间的“意志”“意愿”Shylock would not take the money earlier.夏洛克先前是不肯要钱的。
表七:used to与would用法对比表
used to would
1.表示过去的动作、状态,重在与现在情况的对比,不一定要有时间状语。I used to play cards a lot, but now I seldom play.My hometown is not what it used to be. 1.只表示过去动作的重复,有明确的时间状语I would go to see my grandfather on Sunday when he was in the middle school.2.would 后只接表动作的动词,不接表认识或状态动词He used to be nervous in the exam.
2.表示过去的习惯有时可互换:When we were very young, we used to / would go skating every winter.
表示过去的次数时,不能使用:( √)We went to the Great Wall five times when we were young.( X ) We used to go / would go to the Great Wall five times when we were young.
注:used to do的否定式:usedn’t to do 或didn’t use to do (usedn’t也可写作usen’t)疑问式: Did you use to do Didn’t you use to do Used you to do Usedn’t you to do
情态动词表推测
情态动词表推测的意义:
1、大多数情态动词(除表‘能力、许可、意志’外),都可以表示推测,其程度有差异。按其可能性程度的高低排列为:
Must ﹥will ﹥would ﹥ought to ﹥ should ﹥ can ﹥ could﹥ may ﹥ might
肯定 完全可能 很可能 可能 有可能
2.注意区分情态动词的否定的含义:
may not或许不、可能不 might not可能不 can’t 不可能
mustn’t不许、禁止 shouldn’t不应该 needn’t 不必
3.情态动词表推测具体运用:情态动词可以对现在、进行、过去推测
S主+情态动词+be+adj 对“性质”“特征”的推测
S主+情态动词+be+n 对“职业”“事物”的推测
S主+情态动词+V原 对经常性行为的推测
S主+情态动词+be+V-ing 对进行着的行为的推测
S主+情态动词+have+PP 对过去的行为的推测
特别提醒:情态动词表推测时can只能用于否定句和疑问句must只能用于肯定句(它的否定句和疑问句其实就用can来代替了)如句中有情态动词 + 完成时,定是对过去的推测 。句中如有表示不肯定的话语,如:I am not sure; I don’t know 之类,常选may /might的各种形式
4. 记住下面几组表示反劝的特殊的表推测的形式
1). could + have + PP表示本来能做到,但事实上没有做到。 He could have finished the task on time, but the heavy snow came.
2). couldn’t +have + PP表示本来不能做到,但已经做到了。 She could not have covered the whole distance, but in fact she arrived ahead of time.
3) needn’t + have + pp表示本不必做的,但已经做到了。 She needn’t have attended the meeting yesterday, but she did.
4.) should/ought to +have + PP表示 该做而没有做 The plant is dead. I should/ought to have given ot more water.
5) shouldn’t/ oughtn’t to +have + PP表示 不该做而做了。 You oughtn’t to / shouldn’t have taken her bike without permission.
5. 记住下面对比表:
must只能用于肯定句(它的否定句和疑问句其实就用can来代替了)
1.must + have + PP 表示对过去肯定的推测,译为“一定是,准是” The road is wet. It must have rained yesterday.
2.can + have + PP 表示对过去的推测(限于问句中) Can she have said so 他可能这样说吗?
3.can’t + have + PP 表示对过去的否定推测 He cannot have said such a foolish thing.
情态动词表推测的反意疑问句
情态动词表推测的反意疑问句,简单来说,就是以情态动词后的时态为淮,如句子里有明确的时间状语,则以其为准。以 must 为例:
eg. 1. You must be hungry now, aren’t you
2. He must be watching TV , isn’t he
3 Tom must have lived her for a long time, hasn’t he
4. She must have arrived yesterday, didn’t she
注:如选择题中(以She must have arrived yesterday, didn’t she?为例)既有didn’t she又有hasn’t she则以didn’t she?为最佳答案。
