B9U2 Reading(人教版 )[上学期]
文档属性
| 名称 | B9U2 Reading(人教版 )[上学期] |

|
|
| 格式 | rar | ||
| 文件大小 | 4.6MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 人教版(新课程标准) | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2007-12-21 00:00:00 | ||
图片预览

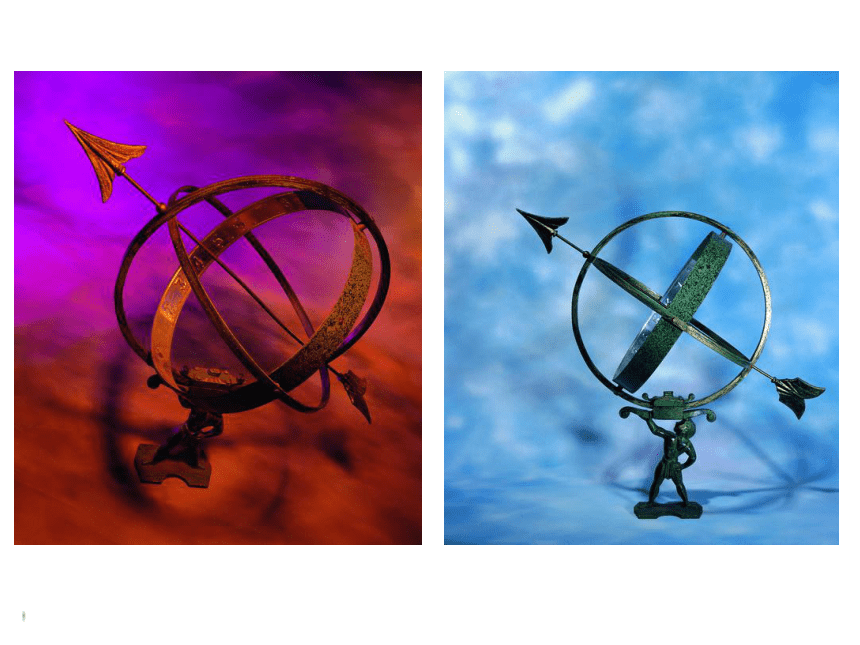


文档简介
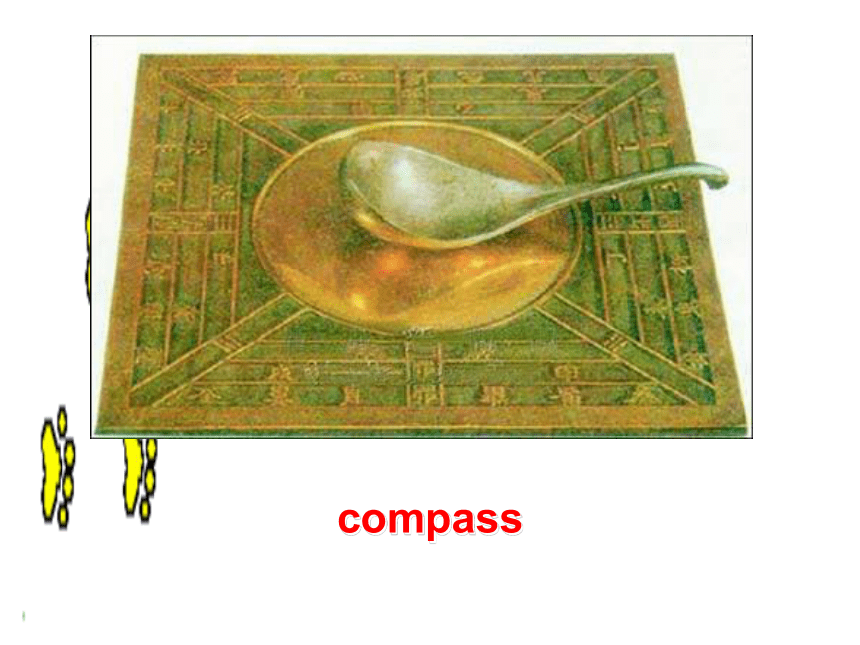
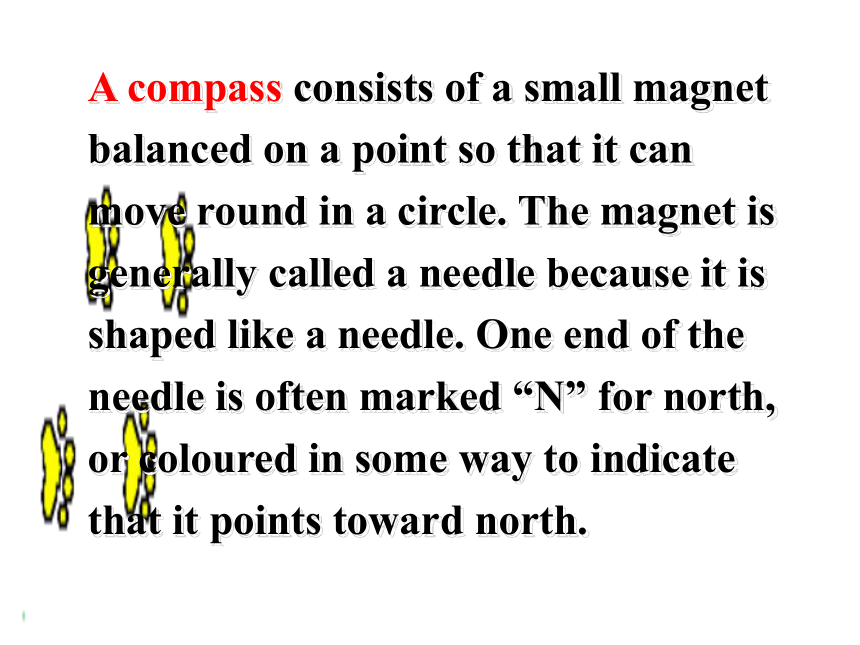
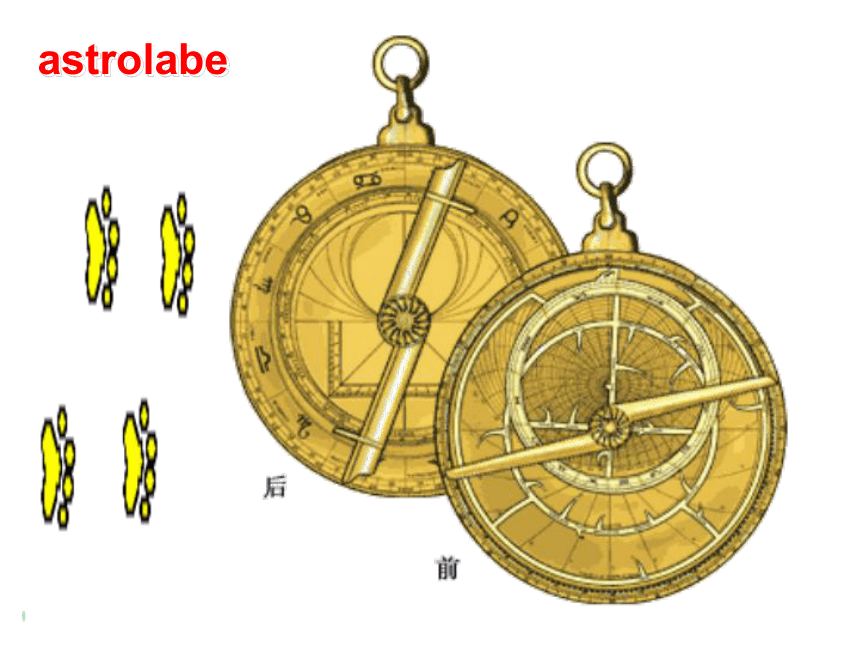
课件135张PPT。ReadingcompassA compass consists of a small magnet balanced on a point so that it can move round in a circle. The magnet is generally called a needle because it is shaped like a needle. One end of the needle is often marked “N” for north, or coloured in some way to indicate that it points toward north.astrolabeThe astrolabe measures the height and position of the sun. If you can measure this accurately, a sailor can tell how many degrees the boat is from the North Pole. From this he can tell where the boat is in the ocean.sextantThe sextant is a navigational instrument for measuring the angle between the horizon and some object in the sky. First a sailor looks at the horizon through an eyepiece. At the same time he can see light from the sun or a star reflected off a small mirror on top of the instrument, onto a second mirror and into the eyepiece. The navigator can then see two images, the horizon and the sun side by side. He can then measure the angle between them on a scale at the bottom of the instrument. The scale goes from 0 to 120 degrees. An earlier instrument, called a quadrant, measured in angle in the same way but it could only measure angles from 0 to 90 degrees.quadrantnautical chartZheng He’s VoyageZheng He’s VoyageNautical charts are maps of the depth of the sea and the currents of the oceans. They provide modern sailors with routes through the seas, rather like roads through the countryside. The information began to be collected in the nineteenth century and has continued to be updated ever since. These charts were not available to Captain Bligh or Zheng He.Discuss1. How do you think seamen found their way before modern accurate methods of navigation were invented?Kept close to the shore, used nature such as the sun, wind, birds, tide, etc, to help them, and used some of the instruments including a compass, astrolabe, etc.2. Which do you think was easier to work out: latitude or longitude?Latitude, because it was used to measure how far you had traveled from land on a straight line. It was discovered a long time before longitude.3. Can you identify these early navigational instruments seamen used and explain how they are used?1) compass ( in ancient China)
2) astrolabe
3) sextant
4) sea / nautical / marine chart4. Which ones do you think are still used
today?Sea charts are still used today.ReadingComprehending1. Read the passage and answer the following questions.
What is the use of a bearing circle,
astrolabe, quadrant or sextant? ( )
What is the use of a compass? ( )
A. To set the course of the ship
B. To measure the position of the ship
C. To measure the speed of the ship
D. To tell the timeAB2) Why are speed and time important in working out the longitude of a ship? Speed and time are important in finding out the longitude of a ship because the earth moves fifteen degrees westwards every hour. If you know your direction, speed and time, you can work out the approximate longitude or change in your position in relation to the stars.3) Why is the position of the sun and various stars useful for working out latitude?
The position of the sun and stars are useful for working out latitude because they are fixed points in the sky and their movements in relation to the earth are already known. So they can be used to measure a ship's position.2. Suppose you were a sea captain aiming to sail round Africa. Discuss in groups:
1) What skills would you seek in your sailors?
2) What problems would you anticipate for this journey?3. What would you do if you came across the following problems during your voyage? Read the chart below and fill in your plans of action to deal with them.Wait till the storm is over, and then find your new position and return to your original course. Use knots to find your speed and work out your approximate longitude.Use the compass and the astrolabe , quadrant or sextant to find out your position , return to your former course. Follow nesting birds to shore ;
look for special cloud formations or fog over streams to find land. Use a compass.Measure your position using the sun or stars; look for sea birds, cloud formations, fog or sea-weed to show that land is nearby.4. Read the passage again and use the information to analyse the navigational skills.1. To find the ship’s position at sea a sailor used the North Star and the sun.
2. A sailor knew that land was nearby if he saw _________________________________
_______________________.
3. Sailors used ________________________
________to increase their speed. fresh seaweed, nesting birds returning home in the evening or fog sea currents or tides and winds4. There were two methods to find longitude:
1)_______________________
2)__________________________________
measuring time and speedcompass and complicated mathematical tables5 Write down the working principles of the following instruments:
Bearing circle:
Astrolabe:
to compare the height of the sun now with the position of the sun at midday. to compare the position of the ship in relation to some stars or the sun Quadrant: a more precise form of the astrolabe, to measure how high stars are above the horizon, and compare that measurement with previous measurements (using the ship as one of the fixed points to find its position) Sextant:
an updated version of the quadrant and so it was more accurate, to measure the angle between two fixed points outside the ship (using two mirrors to find the ship's position). 5. Imagine you are on a boat with twenty-nine other people. You have a small box for your personal things but it can only hole ten items. What would you need for a week’s journey across the North Sea to England?soapblanketcards, chessshirt, trousersknife, scissorssea-sick tablets, cold medicinenovels, essay collectionswaterproof boots Discuss your list with your partner and combine the two sets of choices to make a third and better list. Be prepared to justify your choices to the class.1. How do you think seamen found their way before modern accurate methods of navigation were invented?
在现代精确的导航法尚未发明之前, 你认为航海员是怎样探路的?①这是一个“特殊疑问词+do you think…” 的双重疑问句结构。除think以外believe,guess, suppose等词也可以用于此结构。
What do you suppose has happened to him?
在I think/believe/guess/suppose/ imagine等词的句式中,如果从句有否定,否定词应该前移,即否定转移。
I don’t think he will come.
I think he will not come.[正][误]② invent vt.发明,创作;虚构,杜撰
Alexander Graham Bell invented the telephone in 1876.
1876年阿历山大·格雷厄姆·贝尔发明了电话。
The whole story was invented.
整个故事是虚构的。
inventor n.发明者,发明家,创造者
invention n.发明,创造;发明物discover:
invent:
Gilbert ___________electricity, but Edison _________the electric light bulb.
Who _____________America?
Who _____________the computer?
客观存在,被人发现客观没有,被人发明discoveredinventeddiscoveredinvented吉尔伯特发现了电,爱迪生发明了电灯。谁发现了美洲?谁发明了电脑?2. work out
① to calculate an answer, amount, price, or value 计算
② to think about sth. and manage to understand it 设法弄懂
③ to think carefully about how you are going to do sth. and plan a good way of doing it 精心制定出,安排eg.
⑴ See if you can work out this bill
out.
⑵ The plot is so complicated that it’ll
take you a while to work it out.计算弄明白⑶ I can’t work out Geoff ; one day he’s friendly ,the next day he ignores me completely.
⑷ I haven’t worked out who’s gong to look after the kids tonight.明白计划3. latitude
The angular distance north or south of the earth's equator, measured in degrees along a meridian, as on a map or globe.
纬度:地球赤道北或南的角距离,例如在地图或地球仪上沿着子午线用度数测量
e.g.
Our position is latitude 40 degrees north.
我们的位置是北纬40度。4. longitude
The angular distance on the earth's surface, measured east or west from the prime meridian at Greenwich, England, to the meridian passing through a position, expressed in degrees (or hours), minutes, and seconds.经线:地球表面的成角距离,从英国格林威治的本初子午线向东或向西至经过某一点的子午线计量,以度(或小时)、分和秒表示。
e.g.
Our position is longitude 116 degrees east.
我们的位置是东经116度。5. identify
vt.把…等同于;认出,鉴定, 认为同一
I identified the jacket at once;it was my brother’s.
He identifies beauty with goodness.
identify oneself with 与……有联系,支持
He preferred not to identify himself with that group.identification
n. 辨认, 鉴定, 证明, 视为同一
identity n.
同一性, 身份, 一致, 特性, 恒等式
identity card 身份证1. We may well wonder how seamen explored the oceans before latitude and longitude made it possible to plot a ship’s position on a map. 在经纬度未能绘出航船在地图上的位置之前,我们很想知道航海员是怎样在海上探险的。 Page 1 ① may/might well 很可能,极有可能
These are excellent photographs and we may well use them in our magazine.
这些是很不错的照片,我们很有可能把它们用在我们的杂志上。
You might well find that you’ll need more by the weekend.
到周末你很可能会发现你需要更多东西。② 主语+think/feel/make/consider…+it +n./adj.+ for/of sb. to do…
其中it为形式宾语,for/of引出动词不定式的逻辑主语。
I think it important for him to learn English well.
我认为学好英语对他很重要。
I have made it clear that I object to the plan.
我已经表明我反对这个计划。2. The voyages of travelers before the 17th century show that they were not at the mercy of the sea even though they did not have modern navigational aids.
17世纪前的海上航行表明,即使没有现代航海术的帮助,旅行者也没有受大海的支配。① voyage n./ vi. 航海, 航行
The voyage from England to India used to take six months.
过去从英国航行到印度要六个月。
go on/make/take a sea voyage
去航海旅行
voyager n.
航行者, 航海者trip 指休闲或因商的短途旅行
journey 指从一地出发直达目的地的长途陆路旅行或旅程,不含回到原出发点之意。
travel 常指到国外或某个遥远的地方去,不强调具体目的地。指具体的旅行时常用复数,用单数一般表示旅行的抽象概念。trip, journey, travel, voyage, tourvoyage 强调较远距离的水上或空中旅行或游历。
tour 指周游或巡回旅行,常常是访问一系列地方后再回到原出发点。e.g.
We will have a comfortable voyage to the Far East through air.
我们乘飞机去远东旅游将会非常舒适。The journey to the seaside will take not more than two days.
到海边去旅行最多需要花费两天时间。
I at once began making preparations for a trip home.
我马上开始为回家做准备。Our American friends are making a tour of Shanghai.
我们的美国朋友正在对上海进行巡回旅行。
He came back home after years of foreign travel.
在多年的国外旅行后他回到了家。 They have got everything ready to make a _____ across the Atlantic.
A. trip B. travel
C. voyage D. tour② at the mercy of
without any protection against; helpless before 任由…摆布;在…面前无助
They were lost at sea, at the mercy of wind and weather.
他们在海上迷失了方向,任凭风和天气的摆布。
I don’t like to be at the mercy of such a man.
我不愿受这样一个人的摆布。have mercy on/ show mercy to
对……表示怜悯
The terrorists showed no mercy to the hostages.
恐怖分子对人质残酷无情。
without mercy 毫不留情地
The mother left the dying baby in the hospital without mercy.
那位母亲狠心地把垂死的婴儿丢弃在医院。It’s a mercy (that) (口)幸运的是,幸亏
(用于表示更遭的情况得以避免总算是幸运)
It’s a mercy the accident happened so near the hospital.
幸亏事故发生在离医院很近的地方。
It’s a mercy she wasn’t seriously hurt.
幸运的是她伤势不重。③ even though = even if
虽然,即使 引导让步状语从句
A.引导把握不大或假设的事情
Even if we achieve great success in our work, we should not be proud.
即使我们在工作上取得了巨大的胜利,也不能骄傲。 He will have problems in finding a
job even if he can pass the exam.
即便他能通过考试,以后找工作也成
问题。
They wouldn’t lose heart even if
they failed ten times.
即使他们失败十次也不灰心丧气。B.引出事实
Even though he was late, he was not criticized by the teacher.
他虽然迟到了,也没有挨老师的批评。
I can still remember, even though it was so long ago.
虽然这是很久以前的事,我还记得。* There was never any time for Kate to feel lonely, she was an only child.
A. ever since B. now that
C. even though D. even as* Allow children the space to voice their opinions, _____ they are different from your own. (05湖南)
A. until B. even if
C. unless D. as though3. alongside
prep. = by the side of; side by side with在……旁边;与……并排
adv. = along, near, at, or to the side
在……旁边,近旁,沿着边
He parked his car alongside the fence.
他把车沿着围墙停放。
A car drew up alongside.
一辆汽车开上来并排而行。4. minimum (min)
adj. 最小的, 最低的
n. 最小值, 最小化。
其反义词为maximum (max)
adj. 最高的, 最多的, 最大极限的
n. 最大量, 最大限度, 极大 The minimum requirements for the job
are a degree and two years’ experience.
该工作的最低要求是要有学位和两年
的工作经验。
You must get a minimum of 40
questions right to pass the examination.
你最少必须答对40道题才能通过考试。 keep/reduce sth. to a minimum
将某物保持在/降低到最低限度
The school manages to keep bullying to a minimum.
学校设法最低限度得减少恃强凌弱的行为。
The maximum number of students in each class is 58.
每个班学生人数的最高限额是58名。 We must make maximum use of the resources available.
我们必须最大限度地利用可得到的资源。
Temperature will reach a maximum of 40℃ here.
这儿的最高气温将达40摄氏度。5. indicate vt.
指出, 显示, 象征, 预示, 需要, 简要地说明
I asked him where my sister was and he indicated the shop opposite.
我问他姐姐在哪儿, 他朝对面的商店指了一下。
I indicated that his help was not welcome.
我表明他的帮助不受欢迎。6. close adj.
①near in space or time
空间上或时间上靠近的
②likely 可能的
③careful 小心的close to death
离死亡不远
take a close look at sth.
严密注意某物
keep a close watch/eye on
仔细地看
They chose a spot close to the river for their picnic.
他们选择了一个离河不远的地方进行野餐。
Your birthday is close to mine.
你的生日离我的生日相隔不长。
The two countries are close to signing a peace agreement.
两国即将签署和平协议。7. used to do
表过去习惯化的动作或状态
be/become/get used to doing/n.
习惯于(to为介词)
be used to do
为被动语态,表示“被用来做某事”
I used to go swimming on Saturdays but now I don’t.The country life he was used to _____
greatly since 1992. (2005 山东)
A. change B. has changed
C. changing D. have changedI’m not used to getting up so early.
Cloth is used to make clothes.used to do与 would 用法对比
1. used to do表示过去的动作、状态, 重在与现在情况的对比,不一定要有时间状语。would 只表示过去动作的重复, 有明确的时间状语。
I would go to see my grandfather on Sunday when he was in the middle school.
I used to play cards a lot, but now I seldom play. 2.表示过去的习惯, 可互换。
When we were very young, we used to/would go skating every winter.
注: used to do 的否定式:
usedn’t to do/didn’t use to do
(usedn’t也可写作usen’t.)
疑问式:
Did you use to do…?/ Used you to do…?
Didn’t you use to do…?/ Usedn’t you to do…?8. nowhere adv.
无处, 到处都无
该词用于句首时,要用倒装语序。
I have no job and nowhere to live.
我没工作,也没地方住。
Nowhere could I see him.
我哪儿也看不到他。 Maybe you have been to many countries, but nowhere else _____ such a beautiful palace. (2004 辽宁)
A. can you find
B. you could find
C. you can find
D. could you find9. offshore adj./adv.
向海面吹的, 离岸的, 海面上的, 海上/下作业的
offshore workers
海上作业的工人
offshore bank/company/investment
境外银行/公司/投资offshore wind/current etc.
从陆地吹向海面的风/离岸的潮流
The storm moved offshore.
风暴离岸移动。
A boat moored offshore.
船在近海下锚。10. accelerate vi./vt.
= to (cause to ) move faster 加速, 促进
She accelerated her car and passed the bus in front.
她加快车速超过了前面的公共汽车。
The car suddenly accelerated.
那辆车突然开始加速。1. secure
adj.安全的, 可靠的, 放心的, 无虑的
v. 保护,使安全
Our house is secure from flood.
我们的房子没有被淹的危险。
Some measures are needed to secure the bank from a flood.
这道堤防需要采取一些措施, 免得被洪水冲坏。Page2security n.安全,保安,保护
Security was tight during the President’s visit.
总统来访期间,保安工作十分严密。
For security reasons the visitors were searched.
为了安全起见,来宾受到了检查。2. no/not/never … until…
直到……才---Was his father very strict with him
when he was at school?
---Yes. He had never praised him _____
he became one of the top students
in his grade. (03 北京春)
A. after B. unless
C. until D. when3. knot
n.(绳等的)结, (树的)节; 船速,=海里/小时
v.打结
He tied his belt with a knot.
他把带子打了个结。
The wire is too stiff to knot easily.
这根铁丝太硬了, 不容易打结。4. involve vt.
包括,使陷于,使参与,影响
Don’t involve other people in your mistakes.
别把别人牵涉到你的错误中去。
All the children were involved in the school play.
所有的孩子都参加了学校排练的戏剧。
The matter is serious because it involves your reputation.
这件事很严重,因为它影响到你的声誉。 involve 指必然包括的结果
include 指包括属于整体的部分
contain 指包含在内或含有几种成分
hold 常指含有多少容量,可与contain互换involve, include, contain, holdTaking the job _________living abroad.
接受这项工作就一定要住在国外。
The price __________postage charges.
价格包括邮资在内。
Beer ___________alcohol.
啤酒里含有酒精。
How much water does the pan_______?
那盘子能盛多少水?involvesincludescontainshold5. nautical mile
海里(合1.852公里)在航海和航空上应用的长度单位,按地球大圆一弧分长计,尤指国际和美国单位。6. magnetic
adj. 磁的, 有磁性的, 有吸引力的
magnet
n. 磁体, 磁铁
a magnetic recorder
磁录音机 a magnetic compass bearing
可分辨磁极方向的罗盘
a magnetic person
有魅力的人
The iron has lost its magnetic force.
这铁已失去磁力。7. direction n.方向;指导;趋势
(常用复数)指示, 用法, 说明(书), 收件人地址
Full directions inside.
内附详细说明书。
in all directions = in every direction
向四面八方follow one’s directions 遵照某人的指示
In which direction are you going, north or south?
你准备朝哪个方向走?向北还是向南?
This team is under my direction.
这个小队由我指挥。 8. random n. 随意, 任意
adj. 任意的, 随便的, 胡乱的
make a random choice
任意选择
at random = aimlessly; without any plan 随机,随便 The travelers at the airport were searched at random.
(搜查人员对)机场上的旅客随便选几个人加以搜查。
Soiled dishes were piled at random.
脏碟子乱七八糟地堆着。9. awkward adj.
难使用的, 笨拙的, 尴尬的;
棘手的,难处理的
an awkward remark
令人窘迫的评论
There was an awkward silence, when no one knew what to say.
当谁都不知道说什么时,出现了令人尴尬的沉默。他很笨,总是丢东西。He is awkward; he keeps dropping things.An awkward situation arose during the peace talks.
在和平谈判中出现了棘手的情况。10. reference n.
提及, 涉及, 参考, 参考书目,
证明书(人), 介绍信(人)
At the meeting the teacher made references to his heroic deeds.
在会上老师提到了他的英雄事迹。
These are reference books for teachers.
这些是教师参考书。refer v.
提到, 涉及, 查阅, 咨询
The teacher often refers her pupils to this dictionary.
老师经常让她的学生查这本字典。
Her pupils often refer to this dictionary.
她的学会经常查这本字典。
Don’t refer to it again.
别再提那件事。11. precise adj. 精确的, 准确的
precision n. 精确(性), 精密(度)
A lawyer needs a precise mind.
律师需要一丝不苟的精神。
A camera is an instrument of precision.
照相机是一种精密仪器。 accurate
= correct, free of mistakes
准确的,无误的
precise
= exact in form, detail, measurements, time, etc
精密的,精确的accurate, precise, exactexact
= correct and without mistake (of things that can be measured)
精密的,准确的12. simplify vt. 单一化, 简单化
simple adj. 简单的
The English in this story has been simplified to make it easier to understand.
这个故事里的英语被简写以便更容易理解。
His father lived a simple life in the country.
他父亲在农村过着简朴的生活。 13. portable adj.
轻便的, 手提(式)的, 便携式的
a portable typewriter
提式打字机
a portable generator
便携式发电机14. shortcoming n.
缺点, 短处(常用复数)
In spite of all her shortcomings, she is still the best teacher the school has.
他尽管有些缺点,但仍然是该校最好的教师。
15. update
v. 使现代化, 修正, 校正, 更新
n. 现代化, 更新
updated
adj. 最新的,现代化的,适时的
an updated and revised edition
最新修订本16.tendency n. 趋向, 倾向
We’ve noticed a growing tendency for people to work at home instead of in offices.
我们注意到一种趋势,越来越多的人在家里工作而不在办公室里上班。 have a tendency to do sth.
倾向于做某事,往往会做某事
Jean’s nice but she has a tendency to talk too much.
简人倒不错,就是往往太唠叨。17. reliable adj. 可靠的, 可信赖的
rely v.依赖, 依靠, 信赖, 信任, 依赖于
reliability n.可靠性
She may forget to come --- she is not very reliable.
她可能忘了来,她不太可信赖。Language points on P141. course n. 过程, 经过, 进程, 方针, 路线, 跑道, 课程, 一道菜
Tom made much noise in the course of discussion.
在讨论期间汤姆弄出了很大的响声。 The ship was blown off course.
那船被吹离了航向。
We made three courses: soup, meat and vegetables, and fruit.
我们有三道菜: 汤, 肉和蔬菜, 还有水果。Phrases with “course”
in course of 正在……过程中, 在……期间
in due course = at the proper or right time
在合适或正好的时间
of course
① in the natural or expected order of
things; naturally.
按事物自然的或预期的顺序;自然地2. aim
n.目标, 目的, 瞄准
v. 对...瞄准, 打算
He aimed the gun at the enemy officer.
他用枪瞄准了敌军官。
The hunter took aim at a wolf.
猎手瞄准了一匹狼。②without any doubt; certainly.
无疑地;当然地3. be prepared to do
准备做某事(思想上准备好了)
prepare to do
准备做某事(强调动作)
They are prepared to do it.
(准备好或愿意)
They are preparing to do it.
(正在准备) prepare sth. 准备……
prepare for sth. 为……做准备
The teacher is preparing the reviewing exercises, and the students are preparing for the final examination.
老师正在准备复习用的练习, 而学生们正在为期末考试做准备。4. justify v.
证明……是正当的;为……辩护
The course of events fully justifies our views.
事情的发展完全证明我们的意见是正确的。
How can you justify your rude and foolish behavior?
你怎样为你粗鲁而愚蠢的行为辩护?Homework 1. Review this passage.
2. Preview Learning about
language.
2) astrolabe
3) sextant
4) sea / nautical / marine chart4. Which ones do you think are still used
today?Sea charts are still used today.ReadingComprehending1. Read the passage and answer the following questions.
What is the use of a bearing circle,
astrolabe, quadrant or sextant? ( )
What is the use of a compass? ( )
A. To set the course of the ship
B. To measure the position of the ship
C. To measure the speed of the ship
D. To tell the timeAB2) Why are speed and time important in working out the longitude of a ship? Speed and time are important in finding out the longitude of a ship because the earth moves fifteen degrees westwards every hour. If you know your direction, speed and time, you can work out the approximate longitude or change in your position in relation to the stars.3) Why is the position of the sun and various stars useful for working out latitude?
The position of the sun and stars are useful for working out latitude because they are fixed points in the sky and their movements in relation to the earth are already known. So they can be used to measure a ship's position.2. Suppose you were a sea captain aiming to sail round Africa. Discuss in groups:
1) What skills would you seek in your sailors?
2) What problems would you anticipate for this journey?3. What would you do if you came across the following problems during your voyage? Read the chart below and fill in your plans of action to deal with them.Wait till the storm is over, and then find your new position and return to your original course. Use knots to find your speed and work out your approximate longitude.Use the compass and the astrolabe , quadrant or sextant to find out your position , return to your former course. Follow nesting birds to shore ;
look for special cloud formations or fog over streams to find land. Use a compass.Measure your position using the sun or stars; look for sea birds, cloud formations, fog or sea-weed to show that land is nearby.4. Read the passage again and use the information to analyse the navigational skills.1. To find the ship’s position at sea a sailor used the North Star and the sun.
2. A sailor knew that land was nearby if he saw _________________________________
_______________________.
3. Sailors used ________________________
________to increase their speed. fresh seaweed, nesting birds returning home in the evening or fog sea currents or tides and winds4. There were two methods to find longitude:
1)_______________________
2)__________________________________
measuring time and speedcompass and complicated mathematical tables5 Write down the working principles of the following instruments:
Bearing circle:
Astrolabe:
to compare the height of the sun now with the position of the sun at midday. to compare the position of the ship in relation to some stars or the sun Quadrant: a more precise form of the astrolabe, to measure how high stars are above the horizon, and compare that measurement with previous measurements (using the ship as one of the fixed points to find its position) Sextant:
an updated version of the quadrant and so it was more accurate, to measure the angle between two fixed points outside the ship (using two mirrors to find the ship's position). 5. Imagine you are on a boat with twenty-nine other people. You have a small box for your personal things but it can only hole ten items. What would you need for a week’s journey across the North Sea to England?soapblanketcards, chessshirt, trousersknife, scissorssea-sick tablets, cold medicinenovels, essay collectionswaterproof boots Discuss your list with your partner and combine the two sets of choices to make a third and better list. Be prepared to justify your choices to the class.1. How do you think seamen found their way before modern accurate methods of navigation were invented?
在现代精确的导航法尚未发明之前, 你认为航海员是怎样探路的?①这是一个“特殊疑问词+do you think…” 的双重疑问句结构。除think以外believe,guess, suppose等词也可以用于此结构。
What do you suppose has happened to him?
在I think/believe/guess/suppose/ imagine等词的句式中,如果从句有否定,否定词应该前移,即否定转移。
I don’t think he will come.
I think he will not come.[正][误]② invent vt.发明,创作;虚构,杜撰
Alexander Graham Bell invented the telephone in 1876.
1876年阿历山大·格雷厄姆·贝尔发明了电话。
The whole story was invented.
整个故事是虚构的。
inventor n.发明者,发明家,创造者
invention n.发明,创造;发明物discover:
invent:
Gilbert ___________electricity, but Edison _________the electric light bulb.
Who _____________America?
Who _____________the computer?
客观存在,被人发现客观没有,被人发明discoveredinventeddiscoveredinvented吉尔伯特发现了电,爱迪生发明了电灯。谁发现了美洲?谁发明了电脑?2. work out
① to calculate an answer, amount, price, or value 计算
② to think about sth. and manage to understand it 设法弄懂
③ to think carefully about how you are going to do sth. and plan a good way of doing it 精心制定出,安排eg.
⑴ See if you can work out this bill
out.
⑵ The plot is so complicated that it’ll
take you a while to work it out.计算弄明白⑶ I can’t work out Geoff ; one day he’s friendly ,the next day he ignores me completely.
⑷ I haven’t worked out who’s gong to look after the kids tonight.明白计划3. latitude
The angular distance north or south of the earth's equator, measured in degrees along a meridian, as on a map or globe.
纬度:地球赤道北或南的角距离,例如在地图或地球仪上沿着子午线用度数测量
e.g.
Our position is latitude 40 degrees north.
我们的位置是北纬40度。4. longitude
The angular distance on the earth's surface, measured east or west from the prime meridian at Greenwich, England, to the meridian passing through a position, expressed in degrees (or hours), minutes, and seconds.经线:地球表面的成角距离,从英国格林威治的本初子午线向东或向西至经过某一点的子午线计量,以度(或小时)、分和秒表示。
e.g.
Our position is longitude 116 degrees east.
我们的位置是东经116度。5. identify
vt.把…等同于;认出,鉴定, 认为同一
I identified the jacket at once;it was my brother’s.
He identifies beauty with goodness.
identify oneself with 与……有联系,支持
He preferred not to identify himself with that group.identification
n. 辨认, 鉴定, 证明, 视为同一
identity n.
同一性, 身份, 一致, 特性, 恒等式
identity card 身份证1. We may well wonder how seamen explored the oceans before latitude and longitude made it possible to plot a ship’s position on a map. 在经纬度未能绘出航船在地图上的位置之前,我们很想知道航海员是怎样在海上探险的。 Page 1 ① may/might well 很可能,极有可能
These are excellent photographs and we may well use them in our magazine.
这些是很不错的照片,我们很有可能把它们用在我们的杂志上。
You might well find that you’ll need more by the weekend.
到周末你很可能会发现你需要更多东西。② 主语+think/feel/make/consider…+it +n./adj.+ for/of sb. to do…
其中it为形式宾语,for/of引出动词不定式的逻辑主语。
I think it important for him to learn English well.
我认为学好英语对他很重要。
I have made it clear that I object to the plan.
我已经表明我反对这个计划。2. The voyages of travelers before the 17th century show that they were not at the mercy of the sea even though they did not have modern navigational aids.
17世纪前的海上航行表明,即使没有现代航海术的帮助,旅行者也没有受大海的支配。① voyage n./ vi. 航海, 航行
The voyage from England to India used to take six months.
过去从英国航行到印度要六个月。
go on/make/take a sea voyage
去航海旅行
voyager n.
航行者, 航海者trip 指休闲或因商的短途旅行
journey 指从一地出发直达目的地的长途陆路旅行或旅程,不含回到原出发点之意。
travel 常指到国外或某个遥远的地方去,不强调具体目的地。指具体的旅行时常用复数,用单数一般表示旅行的抽象概念。trip, journey, travel, voyage, tourvoyage 强调较远距离的水上或空中旅行或游历。
tour 指周游或巡回旅行,常常是访问一系列地方后再回到原出发点。e.g.
We will have a comfortable voyage to the Far East through air.
我们乘飞机去远东旅游将会非常舒适。The journey to the seaside will take not more than two days.
到海边去旅行最多需要花费两天时间。
I at once began making preparations for a trip home.
我马上开始为回家做准备。Our American friends are making a tour of Shanghai.
我们的美国朋友正在对上海进行巡回旅行。
He came back home after years of foreign travel.
在多年的国外旅行后他回到了家。 They have got everything ready to make a _____ across the Atlantic.
A. trip B. travel
C. voyage D. tour② at the mercy of
without any protection against; helpless before 任由…摆布;在…面前无助
They were lost at sea, at the mercy of wind and weather.
他们在海上迷失了方向,任凭风和天气的摆布。
I don’t like to be at the mercy of such a man.
我不愿受这样一个人的摆布。have mercy on/ show mercy to
对……表示怜悯
The terrorists showed no mercy to the hostages.
恐怖分子对人质残酷无情。
without mercy 毫不留情地
The mother left the dying baby in the hospital without mercy.
那位母亲狠心地把垂死的婴儿丢弃在医院。It’s a mercy (that) (口)幸运的是,幸亏
(用于表示更遭的情况得以避免总算是幸运)
It’s a mercy the accident happened so near the hospital.
幸亏事故发生在离医院很近的地方。
It’s a mercy she wasn’t seriously hurt.
幸运的是她伤势不重。③ even though = even if
虽然,即使 引导让步状语从句
A.引导把握不大或假设的事情
Even if we achieve great success in our work, we should not be proud.
即使我们在工作上取得了巨大的胜利,也不能骄傲。 He will have problems in finding a
job even if he can pass the exam.
即便他能通过考试,以后找工作也成
问题。
They wouldn’t lose heart even if
they failed ten times.
即使他们失败十次也不灰心丧气。B.引出事实
Even though he was late, he was not criticized by the teacher.
他虽然迟到了,也没有挨老师的批评。
I can still remember, even though it was so long ago.
虽然这是很久以前的事,我还记得。* There was never any time for Kate to feel lonely, she was an only child.
A. ever since B. now that
C. even though D. even as* Allow children the space to voice their opinions, _____ they are different from your own. (05湖南)
A. until B. even if
C. unless D. as though3. alongside
prep. = by the side of; side by side with在……旁边;与……并排
adv. = along, near, at, or to the side
在……旁边,近旁,沿着边
He parked his car alongside the fence.
他把车沿着围墙停放。
A car drew up alongside.
一辆汽车开上来并排而行。4. minimum (min)
adj. 最小的, 最低的
n. 最小值, 最小化。
其反义词为maximum (max)
adj. 最高的, 最多的, 最大极限的
n. 最大量, 最大限度, 极大 The minimum requirements for the job
are a degree and two years’ experience.
该工作的最低要求是要有学位和两年
的工作经验。
You must get a minimum of 40
questions right to pass the examination.
你最少必须答对40道题才能通过考试。 keep/reduce sth. to a minimum
将某物保持在/降低到最低限度
The school manages to keep bullying to a minimum.
学校设法最低限度得减少恃强凌弱的行为。
The maximum number of students in each class is 58.
每个班学生人数的最高限额是58名。 We must make maximum use of the resources available.
我们必须最大限度地利用可得到的资源。
Temperature will reach a maximum of 40℃ here.
这儿的最高气温将达40摄氏度。5. indicate vt.
指出, 显示, 象征, 预示, 需要, 简要地说明
I asked him where my sister was and he indicated the shop opposite.
我问他姐姐在哪儿, 他朝对面的商店指了一下。
I indicated that his help was not welcome.
我表明他的帮助不受欢迎。6. close adj.
①near in space or time
空间上或时间上靠近的
②likely 可能的
③careful 小心的close to death
离死亡不远
take a close look at sth.
严密注意某物
keep a close watch/eye on
仔细地看
They chose a spot close to the river for their picnic.
他们选择了一个离河不远的地方进行野餐。
Your birthday is close to mine.
你的生日离我的生日相隔不长。
The two countries are close to signing a peace agreement.
两国即将签署和平协议。7. used to do
表过去习惯化的动作或状态
be/become/get used to doing/n.
习惯于(to为介词)
be used to do
为被动语态,表示“被用来做某事”
I used to go swimming on Saturdays but now I don’t.The country life he was used to _____
greatly since 1992. (2005 山东)
A. change B. has changed
C. changing D. have changedI’m not used to getting up so early.
Cloth is used to make clothes.used to do与 would 用法对比
1. used to do表示过去的动作、状态, 重在与现在情况的对比,不一定要有时间状语。would 只表示过去动作的重复, 有明确的时间状语。
I would go to see my grandfather on Sunday when he was in the middle school.
I used to play cards a lot, but now I seldom play. 2.表示过去的习惯, 可互换。
When we were very young, we used to/would go skating every winter.
注: used to do 的否定式:
usedn’t to do/didn’t use to do
(usedn’t也可写作usen’t.)
疑问式:
Did you use to do…?/ Used you to do…?
Didn’t you use to do…?/ Usedn’t you to do…?8. nowhere adv.
无处, 到处都无
该词用于句首时,要用倒装语序。
I have no job and nowhere to live.
我没工作,也没地方住。
Nowhere could I see him.
我哪儿也看不到他。 Maybe you have been to many countries, but nowhere else _____ such a beautiful palace. (2004 辽宁)
A. can you find
B. you could find
C. you can find
D. could you find9. offshore adj./adv.
向海面吹的, 离岸的, 海面上的, 海上/下作业的
offshore workers
海上作业的工人
offshore bank/company/investment
境外银行/公司/投资offshore wind/current etc.
从陆地吹向海面的风/离岸的潮流
The storm moved offshore.
风暴离岸移动。
A boat moored offshore.
船在近海下锚。10. accelerate vi./vt.
= to (cause to ) move faster 加速, 促进
She accelerated her car and passed the bus in front.
她加快车速超过了前面的公共汽车。
The car suddenly accelerated.
那辆车突然开始加速。1. secure
adj.安全的, 可靠的, 放心的, 无虑的
v. 保护,使安全
Our house is secure from flood.
我们的房子没有被淹的危险。
Some measures are needed to secure the bank from a flood.
这道堤防需要采取一些措施, 免得被洪水冲坏。Page2security n.安全,保安,保护
Security was tight during the President’s visit.
总统来访期间,保安工作十分严密。
For security reasons the visitors were searched.
为了安全起见,来宾受到了检查。2. no/not/never … until…
直到……才---Was his father very strict with him
when he was at school?
---Yes. He had never praised him _____
he became one of the top students
in his grade. (03 北京春)
A. after B. unless
C. until D. when3. knot
n.(绳等的)结, (树的)节; 船速,=海里/小时
v.打结
He tied his belt with a knot.
他把带子打了个结。
The wire is too stiff to knot easily.
这根铁丝太硬了, 不容易打结。4. involve vt.
包括,使陷于,使参与,影响
Don’t involve other people in your mistakes.
别把别人牵涉到你的错误中去。
All the children were involved in the school play.
所有的孩子都参加了学校排练的戏剧。
The matter is serious because it involves your reputation.
这件事很严重,因为它影响到你的声誉。 involve 指必然包括的结果
include 指包括属于整体的部分
contain 指包含在内或含有几种成分
hold 常指含有多少容量,可与contain互换involve, include, contain, holdTaking the job _________living abroad.
接受这项工作就一定要住在国外。
The price __________postage charges.
价格包括邮资在内。
Beer ___________alcohol.
啤酒里含有酒精。
How much water does the pan_______?
那盘子能盛多少水?involvesincludescontainshold5. nautical mile
海里(合1.852公里)在航海和航空上应用的长度单位,按地球大圆一弧分长计,尤指国际和美国单位。6. magnetic
adj. 磁的, 有磁性的, 有吸引力的
magnet
n. 磁体, 磁铁
a magnetic recorder
磁录音机 a magnetic compass bearing
可分辨磁极方向的罗盘
a magnetic person
有魅力的人
The iron has lost its magnetic force.
这铁已失去磁力。7. direction n.方向;指导;趋势
(常用复数)指示, 用法, 说明(书), 收件人地址
Full directions inside.
内附详细说明书。
in all directions = in every direction
向四面八方follow one’s directions 遵照某人的指示
In which direction are you going, north or south?
你准备朝哪个方向走?向北还是向南?
This team is under my direction.
这个小队由我指挥。 8. random n. 随意, 任意
adj. 任意的, 随便的, 胡乱的
make a random choice
任意选择
at random = aimlessly; without any plan 随机,随便 The travelers at the airport were searched at random.
(搜查人员对)机场上的旅客随便选几个人加以搜查。
Soiled dishes were piled at random.
脏碟子乱七八糟地堆着。9. awkward adj.
难使用的, 笨拙的, 尴尬的;
棘手的,难处理的
an awkward remark
令人窘迫的评论
There was an awkward silence, when no one knew what to say.
当谁都不知道说什么时,出现了令人尴尬的沉默。他很笨,总是丢东西。He is awkward; he keeps dropping things.An awkward situation arose during the peace talks.
在和平谈判中出现了棘手的情况。10. reference n.
提及, 涉及, 参考, 参考书目,
证明书(人), 介绍信(人)
At the meeting the teacher made references to his heroic deeds.
在会上老师提到了他的英雄事迹。
These are reference books for teachers.
这些是教师参考书。refer v.
提到, 涉及, 查阅, 咨询
The teacher often refers her pupils to this dictionary.
老师经常让她的学生查这本字典。
Her pupils often refer to this dictionary.
她的学会经常查这本字典。
Don’t refer to it again.
别再提那件事。11. precise adj. 精确的, 准确的
precision n. 精确(性), 精密(度)
A lawyer needs a precise mind.
律师需要一丝不苟的精神。
A camera is an instrument of precision.
照相机是一种精密仪器。 accurate
= correct, free of mistakes
准确的,无误的
precise
= exact in form, detail, measurements, time, etc
精密的,精确的accurate, precise, exactexact
= correct and without mistake (of things that can be measured)
精密的,准确的12. simplify vt. 单一化, 简单化
simple adj. 简单的
The English in this story has been simplified to make it easier to understand.
这个故事里的英语被简写以便更容易理解。
His father lived a simple life in the country.
他父亲在农村过着简朴的生活。 13. portable adj.
轻便的, 手提(式)的, 便携式的
a portable typewriter
提式打字机
a portable generator
便携式发电机14. shortcoming n.
缺点, 短处(常用复数)
In spite of all her shortcomings, she is still the best teacher the school has.
他尽管有些缺点,但仍然是该校最好的教师。
15. update
v. 使现代化, 修正, 校正, 更新
n. 现代化, 更新
updated
adj. 最新的,现代化的,适时的
an updated and revised edition
最新修订本16.tendency n. 趋向, 倾向
We’ve noticed a growing tendency for people to work at home instead of in offices.
我们注意到一种趋势,越来越多的人在家里工作而不在办公室里上班。 have a tendency to do sth.
倾向于做某事,往往会做某事
Jean’s nice but she has a tendency to talk too much.
简人倒不错,就是往往太唠叨。17. reliable adj. 可靠的, 可信赖的
rely v.依赖, 依靠, 信赖, 信任, 依赖于
reliability n.可靠性
She may forget to come --- she is not very reliable.
她可能忘了来,她不太可信赖。Language points on P141. course n. 过程, 经过, 进程, 方针, 路线, 跑道, 课程, 一道菜
Tom made much noise in the course of discussion.
在讨论期间汤姆弄出了很大的响声。 The ship was blown off course.
那船被吹离了航向。
We made three courses: soup, meat and vegetables, and fruit.
我们有三道菜: 汤, 肉和蔬菜, 还有水果。Phrases with “course”
in course of 正在……过程中, 在……期间
in due course = at the proper or right time
在合适或正好的时间
of course
① in the natural or expected order of
things; naturally.
按事物自然的或预期的顺序;自然地2. aim
n.目标, 目的, 瞄准
v. 对...瞄准, 打算
He aimed the gun at the enemy officer.
他用枪瞄准了敌军官。
The hunter took aim at a wolf.
猎手瞄准了一匹狼。②without any doubt; certainly.
无疑地;当然地3. be prepared to do
准备做某事(思想上准备好了)
prepare to do
准备做某事(强调动作)
They are prepared to do it.
(准备好或愿意)
They are preparing to do it.
(正在准备) prepare sth. 准备……
prepare for sth. 为……做准备
The teacher is preparing the reviewing exercises, and the students are preparing for the final examination.
老师正在准备复习用的练习, 而学生们正在为期末考试做准备。4. justify v.
证明……是正当的;为……辩护
The course of events fully justifies our views.
事情的发展完全证明我们的意见是正确的。
How can you justify your rude and foolish behavior?
你怎样为你粗鲁而愚蠢的行为辩护?Homework 1. Review this passage.
2. Preview Learning about
language.
