人教版 m8 u5 using language listening[下学期]
文档属性
| 名称 | 人教版 m8 u5 using language listening[下学期] | 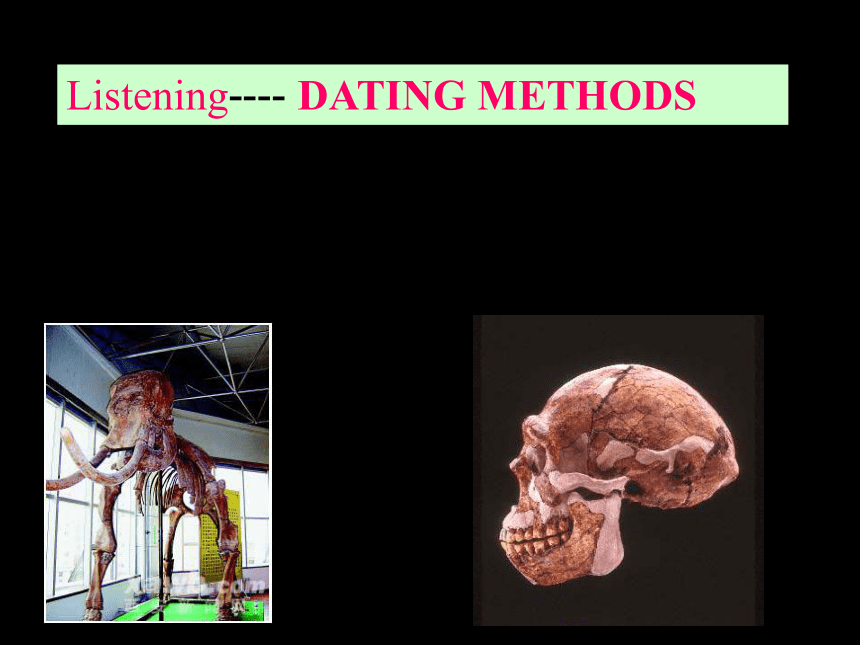 | |
| 格式 | rar | ||
| 文件大小 | 1.4MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 人教版(新课程标准) | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2006-09-06 09:03:00 | ||
图片预览




文档简介
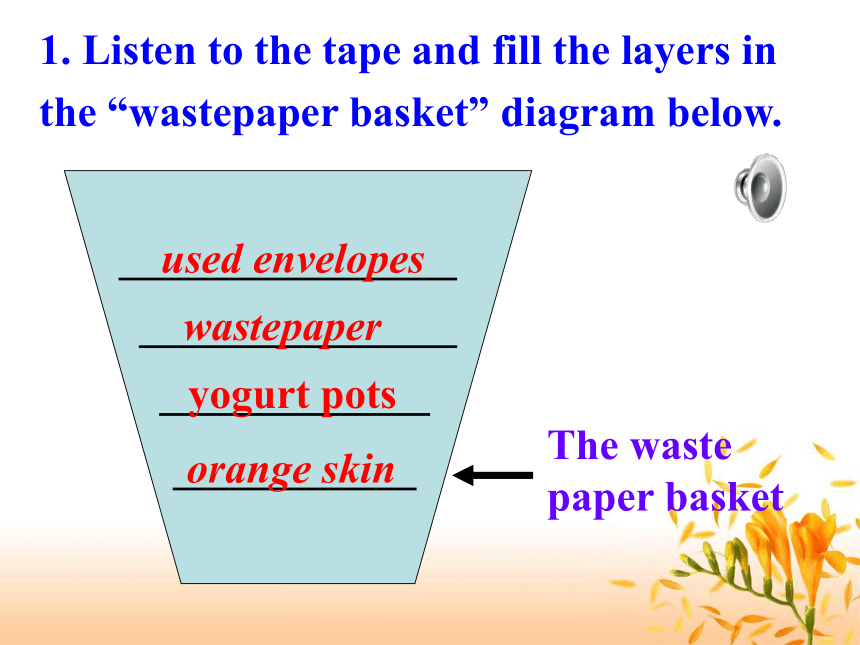
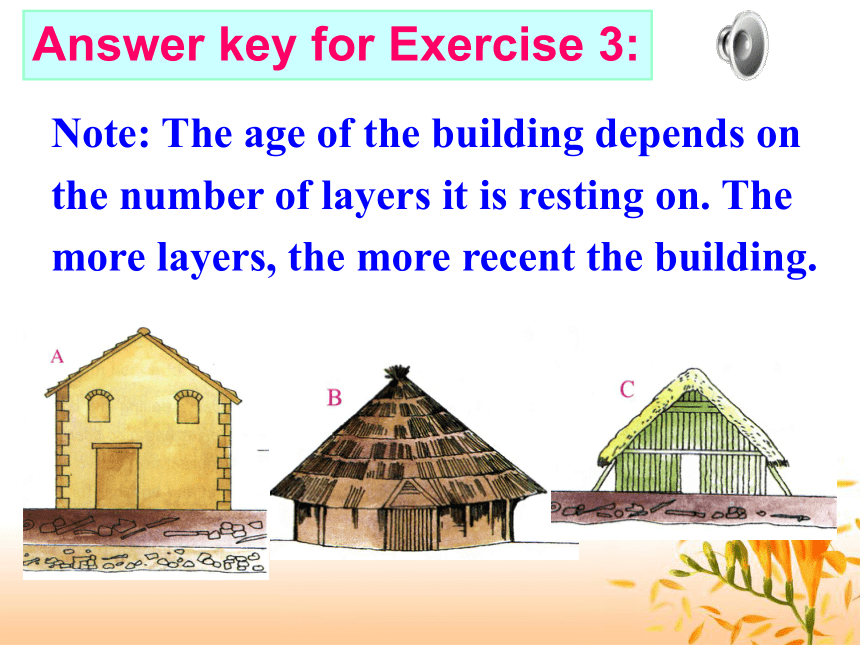
课件15张PPT。Listening---- DATING METHODS1. Listen to the tape and fill the layers in the “wastepaper basket” diagram below. yogurt potsorange skinwastepaperused envelopesAnswer key for Exercise 2Each layer looks different as they are uncovered, so you can tell where one layer starts and another finishes. In the wastepaper basket, the most recent layer is _________, an older layer is below that and the oldest layer is ____________. at the topat the bottomAll living things have ______ in their bodies. When they die, the carbon ________________ at a ____ rate. The method measures __________ of carbon in bones or plants using radioactivity and can ________ how old the remains are. starts to disappearfixedthe amountwork outcarbon Note: The age of the building depends on the number of layers it is resting on. The more layers, the more recent the building. Answer key for Exercise 3: The oldest building is B because it has no layers underneath it.
The second oldest building is C because it has one layer underneath it.
The most recent building is building A. It has two layers underneath. ZH: How can you tell how old the bones
are when you find them?LISTENING TEXT(P42)DATING METHODSZhou Heping has come to ask the archaeologist, Richard Leakey, how he dates the bones he finds.RL: There are two main ways: the first uses layers in the ground and the second uses the radiocarbon dating.
ZH: How does the layer method work?
RL: Well, many layers of soil were produced at different times. Each time people build houses and live somewhere, they make an occupation layer. Each has a different color and texture.
ZH: How does that help?
RL: Look at the diagram in your book. Think of your wastepaper basket. When you came into work you threw the orange skin into it. Later someone threw their empty yogurt pots into it. Then some waste paper was added. Finally someone threw away some used envelopes. How many layers are there?
ZH: There are four layers.
RL: Good. Now which layer is the latest? ZH: Now, let me think! Yes, it'll be the one on the top, which is the used envelopes.
RL: And where's the oldest layer?
ZH: At the bottom.
RL: Well done. When we find bones in layers of soil, we know they are the same age as the soil.
ZH: I see. RL: Now let's think about the second method.
ZH: I remember. It's called the radiocarbon dating method. That's a strange name.
RL: Yes. It uses the radioactivity to measure the amount of carbon in living things. The carbon in a dead body disappears at a fixed rate. We know how long this takes, so we can measure the amount of carbon and work out how old a bone or plant is.
ZH: That's very clever. Is it very accurate too?
RL: There are some problems, so you are always given a date plus or minus some years. For example, your bone may be dated to 10,000 years ago plus or minus 100 years. This means the bone is between 9,900 years and 10,100 years old.
ZH: How clever! How old are the bones from the Zhoukoudian Caves? RL: They are between 250,000 and 40,000 years old.
ZH: Perhaps we can go and visit the site together sometime?
RL: Of course. Whenever you like!
The second oldest building is C because it has one layer underneath it.
The most recent building is building A. It has two layers underneath. ZH: How can you tell how old the bones
are when you find them?LISTENING TEXT(P42)DATING METHODSZhou Heping has come to ask the archaeologist, Richard Leakey, how he dates the bones he finds.RL: There are two main ways: the first uses layers in the ground and the second uses the radiocarbon dating.
ZH: How does the layer method work?
RL: Well, many layers of soil were produced at different times. Each time people build houses and live somewhere, they make an occupation layer. Each has a different color and texture.
ZH: How does that help?
RL: Look at the diagram in your book. Think of your wastepaper basket. When you came into work you threw the orange skin into it. Later someone threw their empty yogurt pots into it. Then some waste paper was added. Finally someone threw away some used envelopes. How many layers are there?
ZH: There are four layers.
RL: Good. Now which layer is the latest? ZH: Now, let me think! Yes, it'll be the one on the top, which is the used envelopes.
RL: And where's the oldest layer?
ZH: At the bottom.
RL: Well done. When we find bones in layers of soil, we know they are the same age as the soil.
ZH: I see. RL: Now let's think about the second method.
ZH: I remember. It's called the radiocarbon dating method. That's a strange name.
RL: Yes. It uses the radioactivity to measure the amount of carbon in living things. The carbon in a dead body disappears at a fixed rate. We know how long this takes, so we can measure the amount of carbon and work out how old a bone or plant is.
ZH: That's very clever. Is it very accurate too?
RL: There are some problems, so you are always given a date plus or minus some years. For example, your bone may be dated to 10,000 years ago plus or minus 100 years. This means the bone is between 9,900 years and 10,100 years old.
ZH: How clever! How old are the bones from the Zhoukoudian Caves? RL: They are between 250,000 and 40,000 years old.
ZH: Perhaps we can go and visit the site together sometime?
RL: Of course. Whenever you like!
