unit 13[下学期]
图片预览
文档简介
Unit 13 The water planet (First period)
Teaching procedures: 教学步骤
Step I. Warming up 热身
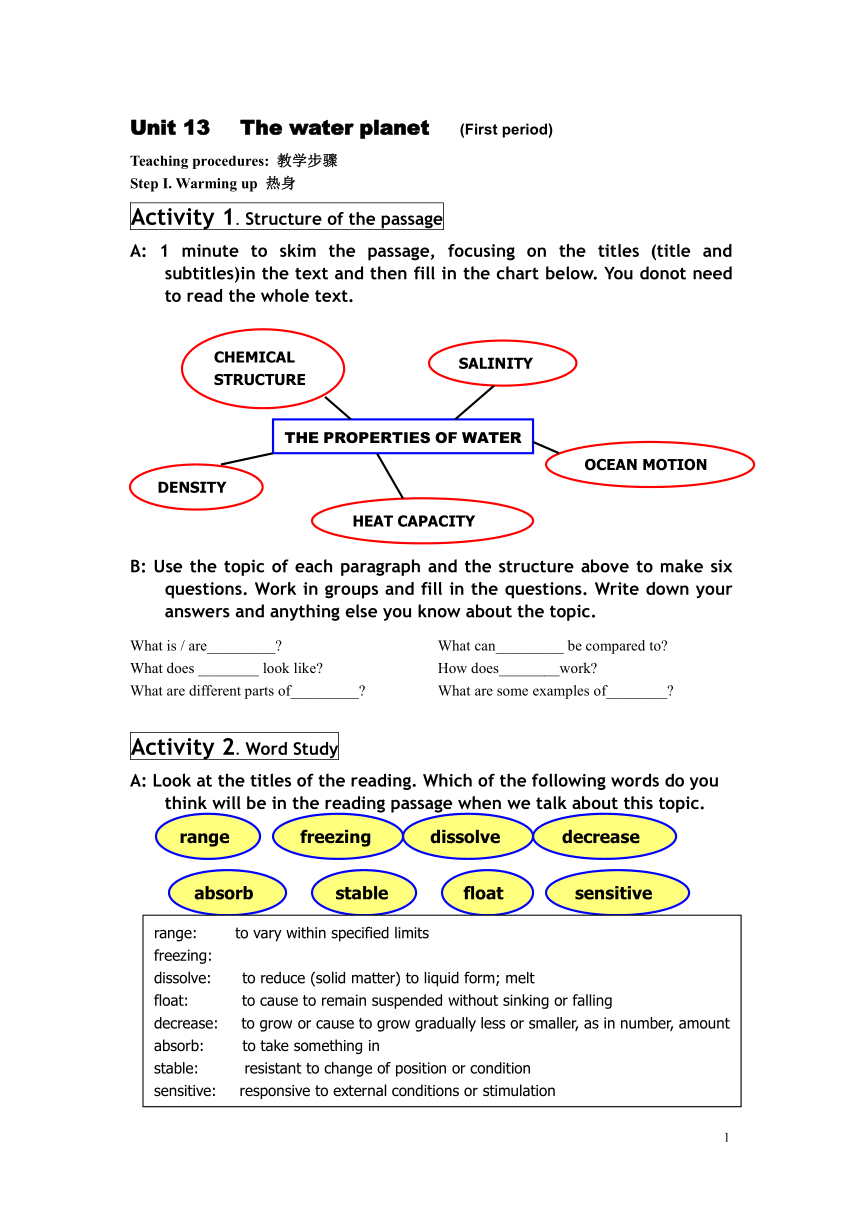
Activity 1. Structure of the passage
A: 1 minute to skim the passage, focusing on the titles (title and subtitles)in the text and then fill in the chart below. You donot need to read the whole text.
B: Use the topic of each paragraph and the structure above to make six questions. Work in groups and fill in the questions. Write down your answers and anything else you know about the topic.
What is / are_________ What can_________ be compared to
What does ________ look like How does________work
What are different parts of_________ What are some examples of________
Activity 2. Word Study
A: Look at the titles of the reading. Which of the following words do you
think will be in the reading passage when we talk about this topic.
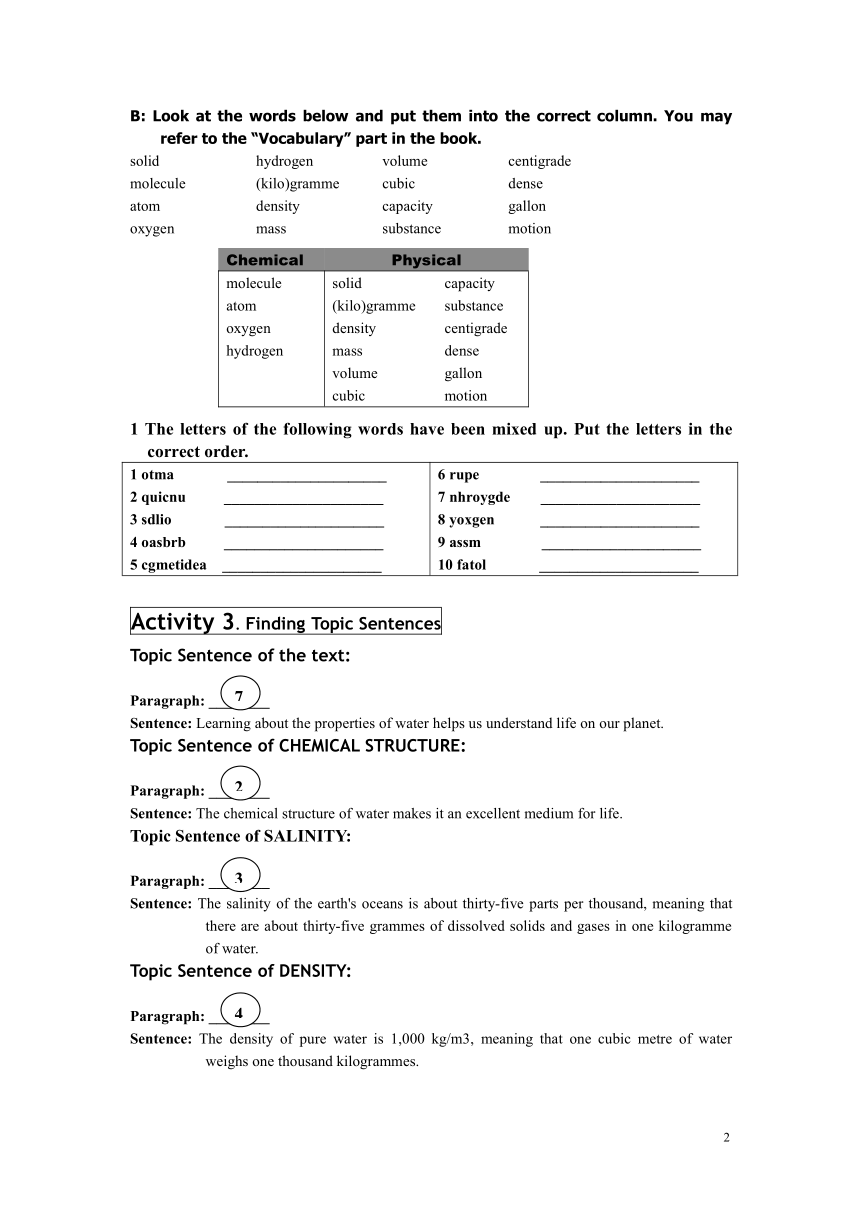
B: Look at the words below and put them into the correct column. You may refer to the “Vocabulary” part in the book.
solid
molecule
atom
oxygen
hydrogen
(kilo)gramme density
mass
volume
cubic
capacity
substance
centigrade
dense
gallon
motion
Chemical Physical
moleculeatomoxygenhydrogen solid(kilo)grammedensitymassvolumecubic capacitysubstancecentigradedensegallonmotion
1 The letters of the following words have been mixed up. Put the letters in the correct order.
1 otma _____________________2 quicnu _____________________3 sdlio _____________________4 oasbrb _____________________5 cgmetidea _____________________ 6 rupe _____________________7 nhroygde _____________________8 yoxgen _____________________9 assm _____________________10 fatol _____________________
Activity 3. Finding Topic Sentences
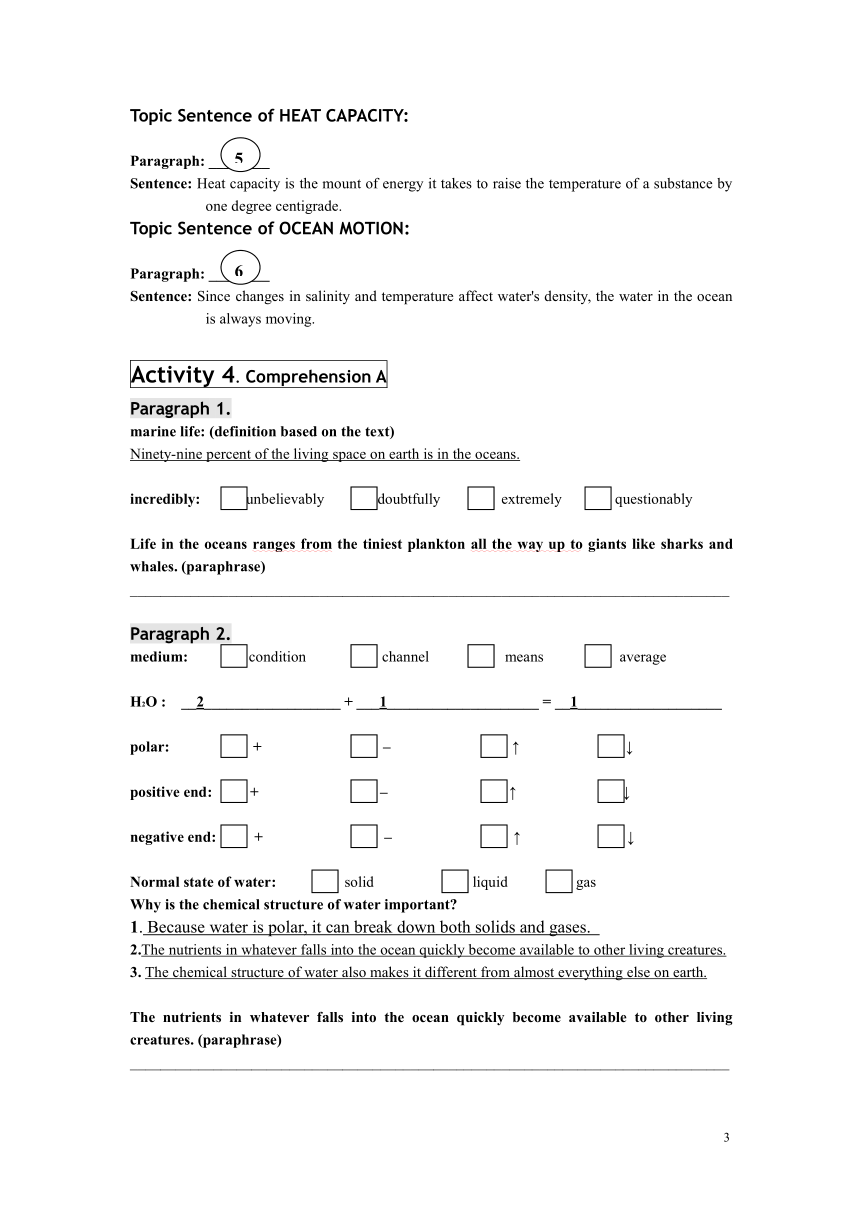
Topic Sentence of the text:
Paragraph: ________
Sentence: Learning about the properties of water helps us understand life on our planet.
Topic Sentence of CHEMICAL STRUCTURE:
Paragraph: ________
Sentence: The chemical structure of water makes it an excellent medium for life.
Topic Sentence of SALINITY:
Paragraph: ________
Sentence: The salinity of the earth's oceans is about thirty-five parts per thousand, meaning that there are about thirty-five grammes of dissolved solids and gases in one kilogramme of water.
Topic Sentence of DENSITY:
Paragraph: ________
Sentence: The density of pure water is 1,000 kg/m3, meaning that one cubic metre of water weighs one thousand kilogrammes.
Topic Sentence of HEAT CAPACITY:
Paragraph: ________
Sentence: Heat capacity is the mount of energy it takes to raise the temperature of a substance by one degree centigrade.
Topic Sentence of OCEAN MOTION:
Paragraph: ________
Sentence: Since changes in salinity and temperature affect water's density, the water in the ocean is always moving.
Activity 4. Comprehension A
Paragraph 1.
marine life: (definition based on the text)
Ninety-nine percent of the living space on earth is in the oceans.
incredibly: unbelievably doubtfully extremely questionably
Life in the oceans ranges from the tiniest plankton all the way up to giants like sharks and whales. (paraphrase)
_______________________________________________________________________________
Paragraph 2.
medium: condition channel means average
H2O : __2__________________ + ___1____________________ = __1___________________
polar: + – ↑ ↓
positive end: + – ↑ ↓
negative end: + – ↑ ↓
Normal state of water: solid liquid gas
Why is the chemical structure of water important
1. Because water is polar, it can break down both solids and gases.
2.The nutrients in whatever falls into the ocean quickly become available to other living creatures.
3. The chemical structure of water also makes it different from almost everything else on earth.
The nutrients in whatever falls into the ocean quickly become available to other living creatures. (paraphrase)
_______________________________________________________________________________
Paragraph 3.
sea water (salt water) = dissolved gases + dissolved solids + pure water
salinity of sea water: 35‰ 35%
salinity of sea water affects: weight and freezing point
Paragraph 4.
Factors of density: mass and volume
Unit of density: kg/m3 = (kilogrammes per cubic metre)
Density of pure water: 1,000 kg/m3 = (one cubic metre of water weighs one thousand kilogrammes )
When water freezes, its density decreases. If it did not, the oceans would be frozen solid.
(paraphrase)
______________________________________________________________________________
Paragraph 5.
Heat capacity: energy temperature substanc water
Opposite word/phrase of absorb: give off change create
Paragraph 6.
How does the water in the ocean move
Dense water sinks and less dense water is pushed to the surface.
Paragraph 7.
Main idea: significance of water to nature
Water, which seems so simple and common, is what makes life possible. Of all the resources on earth -- oil, gas, gold and so on -- nothing is as precious as a drop of rain. (paraphrase)
______________________________________________________________________________
Activity 4. Comprehension B
Complete the chart below. P21
Property What is it What is it good for
Chemical structure
Density
Heat capacity
Activity 5. Language Study
Word study P21
2 Fill in the blanks with the proper words. The first letter has been given.
1 The water molecule is made up of two h________ atoms and one o___________ atom.
2 Water is a liquid at room temperature, but it turns into a s________ when the temperature drops below 0℃ and into a gas when heated above 100℃.
3 The soil can a__________ water, so it helps to keep water from flowing away.
4 Marine scientists study the r_________ between living creatures and their habitat in the ocean.
5 Life in the oceans appears in different sizes, r__________ from the tiniest fish all the way up to the biggest blue whales.
6 Oil has a density lower than 1,000 kg/m3, so it will f_________ on water.
Activity 6. Summary
Features of Science Exposition:
A. Stentence Structure:
B. Vocabulary:
C. Tense:
D. Text Structure:
INTEGRATING SKILLS
Reading NATURE'S NURSERY: ESTUARIES
As the oceans are the source of life on earth, the estuaries are our planet's nurseries. An estuary is the body of water where a river meets the ocean. Salt water from the ocean and fresh water from the fiver mix together in an estuary. This mixing of fresh and salt water creates a unique environment filled with life of all kinds -- a zone between the land and the sea. Estuaries are the homes of thousands of animals and plants. Many cities and towns are built near estuaries, and a lot of fish is caught in estuaries.
Estuaries are great places for nature's young ones. Here, animals can enjoy all the benefits of the oceans without having to face many of the dangers. Tides provide energy for the ecosystems, but estuaries are protected from waves and storms by islands, mud or sand. Nutrients arrive in estuaries from both the land and the ocean. The density of living creatures is higher than in any other habitat on earth. The diversity of life in estuaries is incredible-- birds, fish, marine mammals, shellfish and other species all come here to live, feed and reproduce.
Estuaries are also important because they absorb nutrients and pollutants from water coming from inland sources, thus cleaning our water. Unfortunately, this function also makes estuaries very sensitive to environmental pollution. Since estuaries protect animals and plants from storms and floods and prevent erosion, protecting estuaries is very important.
Finally, estuaries provide both recreation and education for human beings. Most of us enjoy fishing, swimming and having fun on the beach, and scientists and students have endless opportunities to study a variety of life in the habitat. Estuaries also contribute to the economy through tourism and fishing.
Activity 1. Finding Topic Sentences
Topic Sentence of Paragraph: _____
Sentence: As the oceans are the source of life on earth, the estuaries are our planet's nurseries.
Topic Sentence of Paragraph: _____
Sentence: Estuaries are great places for nature's young ones.
Topic Sentence of Paragraph: _____
Sentence: Estuaries are also important because they absorb nutrients and pollutants from water coming from inland sources, thus cleaning our water.
Topic Sentence of Paragraph: _____
Sentence: Estuaries provide both recreation and education for human beings.
Activity 2. Structure of the passage
Activity 3. Answering the questions
1 Why are estuaries such good places for nature's young ones
2 What does density mean in this passage
3 How do estuaries affect the water that passes through them
4 Why are estuaries more sensitive to pollution than other areas
5 Why are estuaries important to human beings
Activity 4. Word Study
THE PROPERTIES OF WATER
CHEMICAL STRUCTURE
SALINITY
DENSITY
HEAT CAPACITY
OCEAN MOTION
range
freezing
dissolve
sensitive
float
decrease
absorb
stable
range: to vary within specified limits
freezing:
dissolve: to reduce (solid matter) to liquid form; melt
float: to cause to remain suspended without sinking or falling
decrease: to grow or cause to grow gradually less or smaller, as in number, amount
absorb: to take something in
stable: resistant to change of position or condition
sensitive: responsive to external conditions or stimulation
7
6
5
3
2
4
2
3
4
1
3
4
2
1
3
4
2
1
4
3
2
1
estuary
mammal
reproduce
pollutant
erosion
recreation
Estuary : the body of water where a river meets the ocean
Mammal : warm-blooded vertebrate animals
Reproduce : to generate (offspring) by sexual or asexual means.
Pollutant : something that pollutes, especially a waste material
Erosion : the process of eroding or the condition of being eroded
Recreation : refreshment of one's mind or body after work through activity that amuses or stimulates
PAGE
2
Teaching procedures: 教学步骤
Step I. Warming up 热身
Activity 1. Structure of the passage
A: 1 minute to skim the passage, focusing on the titles (title and subtitles)in the text and then fill in the chart below. You donot need to read the whole text.
B: Use the topic of each paragraph and the structure above to make six questions. Work in groups and fill in the questions. Write down your answers and anything else you know about the topic.
What is / are_________ What can_________ be compared to
What does ________ look like How does________work
What are different parts of_________ What are some examples of________
Activity 2. Word Study
A: Look at the titles of the reading. Which of the following words do you
think will be in the reading passage when we talk about this topic.
B: Look at the words below and put them into the correct column. You may refer to the “Vocabulary” part in the book.
solid
molecule
atom
oxygen
hydrogen
(kilo)gramme density
mass
volume
cubic
capacity
substance
centigrade
dense
gallon
motion
Chemical Physical
moleculeatomoxygenhydrogen solid(kilo)grammedensitymassvolumecubic capacitysubstancecentigradedensegallonmotion
1 The letters of the following words have been mixed up. Put the letters in the correct order.
1 otma _____________________2 quicnu _____________________3 sdlio _____________________4 oasbrb _____________________5 cgmetidea _____________________ 6 rupe _____________________7 nhroygde _____________________8 yoxgen _____________________9 assm _____________________10 fatol _____________________
Activity 3. Finding Topic Sentences
Topic Sentence of the text:
Paragraph: ________
Sentence: Learning about the properties of water helps us understand life on our planet.
Topic Sentence of CHEMICAL STRUCTURE:
Paragraph: ________
Sentence: The chemical structure of water makes it an excellent medium for life.
Topic Sentence of SALINITY:
Paragraph: ________
Sentence: The salinity of the earth's oceans is about thirty-five parts per thousand, meaning that there are about thirty-five grammes of dissolved solids and gases in one kilogramme of water.
Topic Sentence of DENSITY:
Paragraph: ________
Sentence: The density of pure water is 1,000 kg/m3, meaning that one cubic metre of water weighs one thousand kilogrammes.
Topic Sentence of HEAT CAPACITY:
Paragraph: ________
Sentence: Heat capacity is the mount of energy it takes to raise the temperature of a substance by one degree centigrade.
Topic Sentence of OCEAN MOTION:
Paragraph: ________
Sentence: Since changes in salinity and temperature affect water's density, the water in the ocean is always moving.
Activity 4. Comprehension A
Paragraph 1.
marine life: (definition based on the text)
Ninety-nine percent of the living space on earth is in the oceans.
incredibly: unbelievably doubtfully extremely questionably
Life in the oceans ranges from the tiniest plankton all the way up to giants like sharks and whales. (paraphrase)
_______________________________________________________________________________
Paragraph 2.
medium: condition channel means average
H2O : __2__________________ + ___1____________________ = __1___________________
polar: + – ↑ ↓
positive end: + – ↑ ↓
negative end: + – ↑ ↓
Normal state of water: solid liquid gas
Why is the chemical structure of water important
1. Because water is polar, it can break down both solids and gases.
2.The nutrients in whatever falls into the ocean quickly become available to other living creatures.
3. The chemical structure of water also makes it different from almost everything else on earth.
The nutrients in whatever falls into the ocean quickly become available to other living creatures. (paraphrase)
_______________________________________________________________________________
Paragraph 3.
sea water (salt water) = dissolved gases + dissolved solids + pure water
salinity of sea water: 35‰ 35%
salinity of sea water affects: weight and freezing point
Paragraph 4.
Factors of density: mass and volume
Unit of density: kg/m3 = (kilogrammes per cubic metre)
Density of pure water: 1,000 kg/m3 = (one cubic metre of water weighs one thousand kilogrammes )
When water freezes, its density decreases. If it did not, the oceans would be frozen solid.
(paraphrase)
______________________________________________________________________________
Paragraph 5.
Heat capacity: energy temperature substanc water
Opposite word/phrase of absorb: give off change create
Paragraph 6.
How does the water in the ocean move
Dense water sinks and less dense water is pushed to the surface.
Paragraph 7.
Main idea: significance of water to nature
Water, which seems so simple and common, is what makes life possible. Of all the resources on earth -- oil, gas, gold and so on -- nothing is as precious as a drop of rain. (paraphrase)
______________________________________________________________________________
Activity 4. Comprehension B
Complete the chart below. P21
Property What is it What is it good for
Chemical structure
Density
Heat capacity
Activity 5. Language Study
Word study P21
2 Fill in the blanks with the proper words. The first letter has been given.
1 The water molecule is made up of two h________ atoms and one o___________ atom.
2 Water is a liquid at room temperature, but it turns into a s________ when the temperature drops below 0℃ and into a gas when heated above 100℃.
3 The soil can a__________ water, so it helps to keep water from flowing away.
4 Marine scientists study the r_________ between living creatures and their habitat in the ocean.
5 Life in the oceans appears in different sizes, r__________ from the tiniest fish all the way up to the biggest blue whales.
6 Oil has a density lower than 1,000 kg/m3, so it will f_________ on water.
Activity 6. Summary
Features of Science Exposition:
A. Stentence Structure:
B. Vocabulary:
C. Tense:
D. Text Structure:
INTEGRATING SKILLS
Reading NATURE'S NURSERY: ESTUARIES
As the oceans are the source of life on earth, the estuaries are our planet's nurseries. An estuary is the body of water where a river meets the ocean. Salt water from the ocean and fresh water from the fiver mix together in an estuary. This mixing of fresh and salt water creates a unique environment filled with life of all kinds -- a zone between the land and the sea. Estuaries are the homes of thousands of animals and plants. Many cities and towns are built near estuaries, and a lot of fish is caught in estuaries.
Estuaries are great places for nature's young ones. Here, animals can enjoy all the benefits of the oceans without having to face many of the dangers. Tides provide energy for the ecosystems, but estuaries are protected from waves and storms by islands, mud or sand. Nutrients arrive in estuaries from both the land and the ocean. The density of living creatures is higher than in any other habitat on earth. The diversity of life in estuaries is incredible-- birds, fish, marine mammals, shellfish and other species all come here to live, feed and reproduce.
Estuaries are also important because they absorb nutrients and pollutants from water coming from inland sources, thus cleaning our water. Unfortunately, this function also makes estuaries very sensitive to environmental pollution. Since estuaries protect animals and plants from storms and floods and prevent erosion, protecting estuaries is very important.
Finally, estuaries provide both recreation and education for human beings. Most of us enjoy fishing, swimming and having fun on the beach, and scientists and students have endless opportunities to study a variety of life in the habitat. Estuaries also contribute to the economy through tourism and fishing.
Activity 1. Finding Topic Sentences
Topic Sentence of Paragraph: _____
Sentence: As the oceans are the source of life on earth, the estuaries are our planet's nurseries.
Topic Sentence of Paragraph: _____
Sentence: Estuaries are great places for nature's young ones.
Topic Sentence of Paragraph: _____
Sentence: Estuaries are also important because they absorb nutrients and pollutants from water coming from inland sources, thus cleaning our water.
Topic Sentence of Paragraph: _____
Sentence: Estuaries provide both recreation and education for human beings.
Activity 2. Structure of the passage
Activity 3. Answering the questions
1 Why are estuaries such good places for nature's young ones
2 What does density mean in this passage
3 How do estuaries affect the water that passes through them
4 Why are estuaries more sensitive to pollution than other areas
5 Why are estuaries important to human beings
Activity 4. Word Study
THE PROPERTIES OF WATER
CHEMICAL STRUCTURE
SALINITY
DENSITY
HEAT CAPACITY
OCEAN MOTION
range
freezing
dissolve
sensitive
float
decrease
absorb
stable
range: to vary within specified limits
freezing:
dissolve: to reduce (solid matter) to liquid form; melt
float: to cause to remain suspended without sinking or falling
decrease: to grow or cause to grow gradually less or smaller, as in number, amount
absorb: to take something in
stable: resistant to change of position or condition
sensitive: responsive to external conditions or stimulation
7
6
5
3
2
4
2
3
4
1
3
4
2
1
3
4
2
1
4
3
2
1
estuary
mammal
reproduce
pollutant
erosion
recreation
Estuary : the body of water where a river meets the ocean
Mammal : warm-blooded vertebrate animals
Reproduce : to generate (offspring) by sexual or asexual means.
Pollutant : something that pollutes, especially a waste material
Erosion : the process of eroding or the condition of being eroded
Recreation : refreshment of one's mind or body after work through activity that amuses or stimulates
PAGE
2
