unit 4 earthquake whole unit[上学期]
文档属性
| 名称 | unit 4 earthquake whole unit[上学期] |  | |
| 格式 | rar | ||
| 文件大小 | 2.3MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 人教版(新课程标准) | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2006-10-26 14:05:00 | ||
图片预览








文档简介
课件114张PPT。 Unit 4
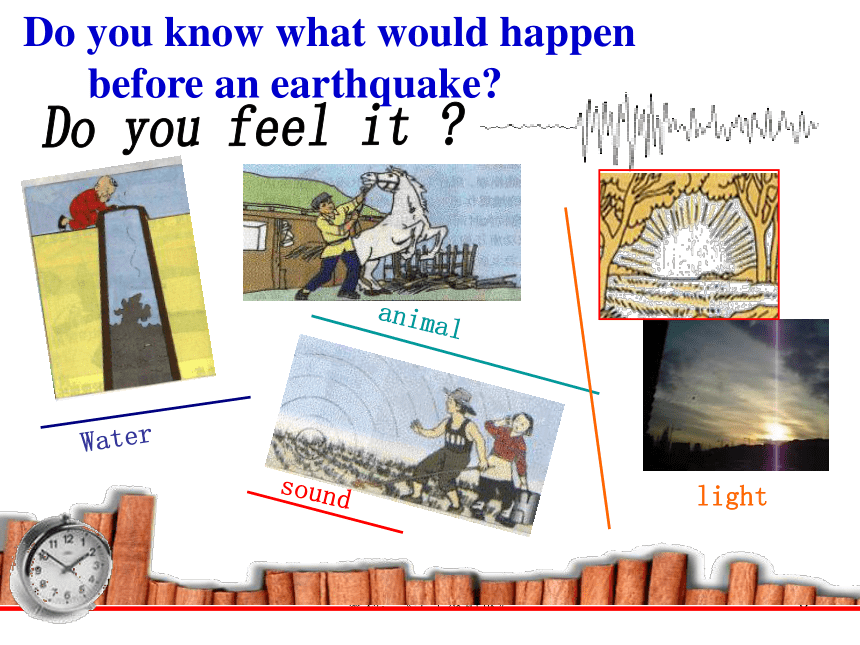
Warming up and Reading IEarthquakeNatural DisasterstyphoonflooddroughttsunamiearthquakeWhich disaster may cause the worst damage? earthquakeWarming up-II----sharing (1m)What causes an earthquake?The movement of the platesIt is always calm before a storm.策划:《学生双语报》6Do you feel it ?WateranimallightsoundDo you know what would happen
before an earthquake?Reading A NIGHT
THE EARTH DIDN’T SLEEPFast reading What does the passage mainly talk about?
How many parts can we divide the text into?An earthquake happened
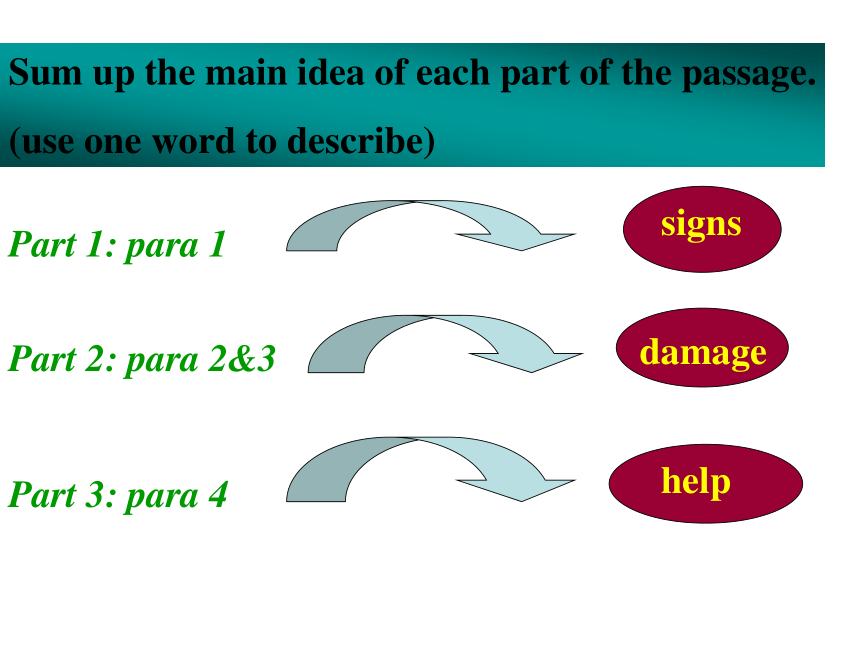
in Tangshan in 1976Sum up the main idea of each part of the passage.
(use one word to describe)Part 1: para 1Part 2: para 2&3Part 3: para 4signsdamagehelp signs
before
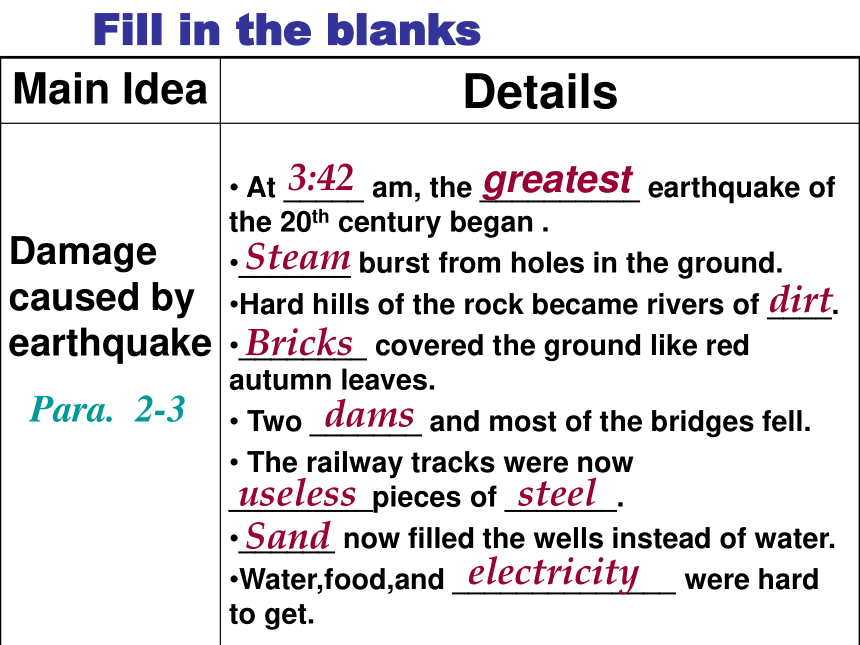
Earthquake Para.1Fill in the blanksStrangerosefellsmellynervouseatjumpedran3:00bright lightsDamage
caused by
earthquakePara. 2-3Fill in the blanks3:42greatestSteamdirtBricksdamsuselesssteelSandelectricityData(数据) of the nation felt the earthquake .
A huge crack that was kilometres long and
metres wide cut across houses.
In terrible seconds a large city lay in ruins.
of the people died or were injured during the earthquake.
The number of people who were killed or injured reached more than .
All of the city’s hospitals, _ of its factories and buildings and of its homes were gone.
1/3830152/3400,00075%90%Para. 2-3What can we conclude from the data?who came to rescue them? 150,000 soldiersHow did the army help to rescue the survivors?dig out… and bury…
built shelters…
fresh water…by…. Retell the storyStrange things; water in the wells; smelly gas; animals; shake;at an end;
Lay in ruins; died or injured; people began to wonder……; hope not lost;
Soldiers; city breathe again Retell the story ____________ happened in Tang Shan. For a few days, water in the wells _____________. From the ______ of wells __________come out. Mice, chicken, pigs and even fish became ________. At 3:00 am, everything began to ______.It seemed that the world was _________. _________ of the nation ____ it. ___________cut across the city. The city lay _______. Strange thingsrose and fellcrackssmelly gasnervousshakeat an endOne-thirdfeltA huge crackin ruinsTwo-thirds of the people _____ or ___________. Then later that afternoon, another big quake ______ Tang Shan. People began to wonder ___________________________. But all hope ____________. _______ came to help those ________. Slowly, the city began to _____________.diedwere injuredshookhow long the disaster would lastwas not lostSoldiersbreathe againsurvivors What shall we do if an earthquake happens?DiscussionDiscussion (3m) Don’t be nervous and keep calm.
Don’t try to run out of the classroom.
Protect your head by putting your bag on your head.
Squat or sit down beside your desk.
Leave the classroom after the earthquake.A night the earth didn’t sleepSlowly, the city began to breathe again.What lessons should we learn from the Tangshan Earthquake?Discussion (group work)Tang shan’s new lookHomework1. find more information about earthquakes.
2.Finish the “learning about language” part on page 27.
3.Finish exercise 1 on page 63.Language Points
for Reading ITake a break! Unit 4
Period 3 learning about languageEarthquakePeriod 3: 幻灯片33-57页1. Answer keys for Ex1 on Page27:1 pipe
2 dam
3 shocked
4 injured
5 well
6 canal
7 ruins
8 a great number of
9 at an end
10 bury
11 rise
12 rescue
13 steamWord-consolidation-I (2m)2. Answer keys for Ex. 2 on page 28: It was a frightening night because a great number of things happened at the same time. The wall of the dam cracked, so the water went all over the fields. It filled the canals and the wells. The water pipes in some buildings burst. The water covered the buildings and had fallen in ruins around the dead and injured animals. People were shocked. They had to bury many of them for health reasons. It was a very sad time.Word-consolidation-II (2m)3. Answer keys for Ex.3 on page 28:1.one million
2.two-thirds
3.one-third
4.seventy-five percent
5.ninety percent
6.ten thousand
7.one hundred and fifty thousand
8. half a millionC
H
F
E
A
B
D
GWord-consolidation-III(2m)Grammar 定语从句 The Attributive Clause Grammar (5m)
Titanic is the ship that sank after hitting an iceberg.Rose and Jack are the lovers who met on the ship.Rosethe lady/meet Jack on TitanicRose is
met Jack on TitanicJackthe young man /want to save Rosethe man /want to kill JackCalJack is
wanted to save RoseCal is wanted to kill Jack.the lady whothe young man whothe man whothe ship/sink into the oceanthe ship/is the most beautiful
in the world at that time Titanic is
sank into the ocean.Titanic is
was the most beautiful in the word at that time.the ship thatthe ship thatthe Heart of Oceanthe diamond/is worn by RoseThe Heart of Ocean is
was worn by Rose.the diamond/is dropped
into the ocean by RoseThe Heart of Ocean is
was dropped into the ocean by Rose the diamond
thatthe diamond that
born in 1847/ man/ invent the first telephone
Bell who was born in 1847 is the man that invented the first telephone. 引导定语从句关系代词的用法: that which who whom whose 1.that在从句中作主语或宾语,指人和物 1)A plane is a machine that can fly.( 主语)2)The noodles that I looked were delicious.(宾语)3)Let’s ask the man that is reading the book over there.(主语)4)The girl that we saw yesterday is Jim’sister.(宾语) 2. Which 在从句中作主语或宾语,指物1) They planted the trees which didn’t need much water. (主语 )3. who whom 在从句中分别作主语和宾语 (口语中who也可作宾语)1) The foreigner who visited our school yesterday is from Canada.(主语)2) The fish which we bought were not fresh. (宾语)2) The boy who broke the window is called Michael.(主语) 4) Mr. Read is the professor to whom you should write . (宾语)3) The person to whom you just talked is Mr. Li. (宾语) 3) This is the book whose cover is blue.4. whose 在从句中作定语,指人或物1) Miss Flower is the teacher whose house caught fire last week.2) This is the boy whose composition the teacher talked of . The boss in whose company my father worked is a very kind person. 关系代词whose还可以在从句中与它所修饰的词一起作介词宾语NOTE that和which在指物的情况下一般都可以互换, 但在下列情况下, 一般用that而不用which。I am sure she has something (that) you can borrow.I’ve read all the books that are not mine. This is the first book (that) he has read.This is the very book that belongs to him.(1) 先行词为all, everything, nothing, something,
anything, little, much 等不定代词时。(2)先行词被all, every, no, some, any, little, much等
修饰时。(3)先行词被序数词或最高级修饰时。(4)先行词被the only, the very, the same, the last修饰时。NOTEeg. He talked about the things and persons he had visited in the city. * 在 who 或 which 引导的特殊疑问句中,限制性定语从句必须用 that 引导。that eg. Who is the man is standing over there.that* 先行词在从句中作表语时, 限制性定语从句通常用 that 引导。(常可省略) eg. She is no longer the girl that she was before she went to the country.3. The house ____________ they built in 1987 stayed up in the earthquake. Fill in the blanks with who, whom, that, which or whose1. The earthquake___________ hit the city in 1906 was the biggest in American history.2. We don’t know the number of people ____________ lost their homes in 1906 earthquakethat / which that / who which /that 6. Harry is the boy ________ mother is our maths teacher .4. A house ____________ is built on sand may fall down in a earthquake. 5. Luckily none of the people ______________ I know were killed in the earthquake .which / thatwho/whom/thatwhoseAnswer keys for “Discovering useful structures”Ex. 2 on Page 281 who
2 that/which
3 which/that
4 whose
5 whoseFunction-II----practice (2m)1.The famous basketball star, _______ tried to make a comeback, attracted a lot of attention. (北京 2002春季)
A、where B、when C、which D、who
答案 D
真题解析:本题考察定语从句关联词的选择,从句意可知先行词the famous basketball star(著名的篮球明星)是人,所以应用表示人的关联词who。
高考链接The film brought the hours back to me _____ I was taken good care of in that far-away village.(NMET 2001)
A、until B、that C、when D、where
答案 C
真题解析:本题考察定语从句的连接词,主句中的先行词the hours被其它成分分割,只要考生能够认清真正的先行词,就不难得出答案,the hours表示时间,所以应该选择一个表示时间的关系副词,即when。高考链接3._____ is known to everybody, the moon travels around the earth once every month. (NMET2001) A、It B、As C、That D、what
答案 B
真题解析:本题考察as引导非限定性定语从句。as引导从句的意思是“正如……..”,引导的非限定性定语从句修饰整个句子,当as在从句中充当主语时,常用下面的结构:as is know,as is said,as is reported 等,所以本题的答案是B。高考链接Homework1.finish the exercises on page 28.
2.surf the internet to find more information about the attributive clause and sum up the rules of it.Take a break! Unit 4
Period 4 Reading IIEarthquakePeriod 4: 幻灯片58-75页Do you know any other place where the earthquakes easily happen in the world? Warming up----Brainstorming (2m)Pacific plateAmerican
plateEurasian plate India plateAfrican
plateAntarctic plateSan FranciscoUS Map?
?Pacific
plate
NorthSouthWestEast↖American plateThe plates are moving constantly. Sometimes these two plates stop and do not move for years. Then Suddenly, they jump and an earthquake is felt. As a result of the movement of these plates, west America near the sea has always been a bad place for earthquakes. ContinentOceanic plate★★San Francisco (before the earthquake)San Francisco (after the earthquake)Read the passage and finish the following exercises.1.Write an adjective to describe how the author feels about the earthquake and what it did.
___________________
Why did you choose these word?
__________________________________Reading I----scanning (2m)2.Write an adjective to describe how the author feels about the people of San Francisco.
___________________
Why did you choose these word?
__________________________________Read the first paragraph in this passage. Then go back and read again the first paragraph of the passage on page 26.Compare the ways both writers give you details about the earthquakes.Reading II----detailed reading (3m)How do you know?
______________________________1.Which writer shows more feeling about the earthquake?
A. The writer of the Tangshan quake in 1976
B The writer of the San Francisco in 1906Both writers give similar details about_________________________
and___________________________
_______________________________3.Which one of the following statements is true?
A. Both writers give details of big events before little events.
B Both writers give details of little events before big events.
C Neither writer gives details of big events before little events.3.Which one of the following statements is not true?
Both writers saw the earthquake he wrote about.
B. Only one writer saw the earthquake he wrote about.
C. Neither writer saw the earthquake he wrote about.Thinking:
If you are going to make a speech to honor those who died in the terrible disaster and those who helped the survivors in Tangshan, what would you say?Thinking &writing (5m)HomeworkRead the letter and then write a short speech, in which you should follow the following points on page 29.Take a break! Unit 4
Period 5 Listening EarthquakePeriod 5: 幻灯片76-85页Question: Have you ever experienced a terrible disaster and became a survivor?Pre-listening----prediction (1m)Listen to the tape as it tells the story of a man who was a survivor of the great San Francisco earthquake of 1906.Read the following statements and tell whether they are true or false.1.F 2.F 3.T 4.T 5.F 6.F
Listening----(5m)Listen to the tape and answer the following questions. When did the man talk about the earthquake: while it was happening or after it had happened? How do you know?
After the earthquake had happened.
The last sentence gives information about the next day.Listening----answering the following questions (5m)Listen to the tape and answer the following questions. Is the man calm as he talks about he earthquake? Why or why not?
Yes, the man is calm because he is writing about something a long time after it happened.
Listen to the tape and answer the following questions.What was the biggest danger for the man: fires, cows or falling buildings? Why? The falling buildings were his biggest danger and he didn’t know when one might fall on him. He could at least see the fires and cows coming towards him.
Listen to the tape and answer the following questions. Where was the man going? He was going to the bay to get on a boat.
Listen to the tape and answer the following questions. Have you got any ideas to help this man during the earthquake?
______________________________________
______________________________________(The students’ answers may vary but should demonstrate an understanding of the listening text.)
HomeworkFinish the listening task on workbook, page 66.Take a break! Unit 4
Period 6 Speaking and WritingEarthquakePeriod 6: 幻灯片86-109页What kind of
newspaper
do you usually read?
Speaking task:China daily21 centuryNew York TimesWashington postEnglish weekly……Speaking (4m)Have you ever read any
English newspaper or chinese
newspaper? What are they?
Which would you prefer, English newspaper or Chinese newspaper? Why?Discussion:
Discussion (3m)an interesting title that
tells the reader what your topic is
Headline
Main ideasDetailsDo you know what an outline is?outlineBrainstorming for writing (3m)QuestionsWhy an outline is important?
What should an outline conclude?
Why a headline is important?
What are the steps to finish a newspaper story?
What is the feature of the newspaper story?Why an outline is important?
Because an outline will prepare you to write a better story.
What should an outline conclude?
A good outline should have a headline, a list of main idea and a list of important details.
Why a headline is important?
A headline can tell the reader what the topic is, so it can attract the reader’s attention since the reader may not have bought the newspaper before they read the headline.
What are the steps to finish a newspaper story?
First, organize the main ideas. Next, put some details into each paragraph.
What is the feature of the newspaper story?
A newspaper story gives the most important news first and the least important news last.
Read the example of a newspaper
story on P31.
How many parts is the story divided?
Find the headline, main ideas and details of each paragraph.Pre-writing (3m)
Headline :
Main ideasDetailsoutline
importantThe most important news first
the least important news lastExample of newspaper story China leads world in traffic death Experts say that road traffic accidents are on the rise and China ranks first in the world in traffic death tolls. Worldwide Statistics show that the global traffic accident death toll amounted to 500,000 in 2003, with the largest share,104,000
reported in China, followed by India with 86,000, the U.S. with 40,000, and Russia with 26,000, said Duan Liren , former deputy director of the Beijing Traffic Management Bureau. Road accidents are
The seventh leading killer in China. Prepare the outline for a short
newspaper story for China Daily.
Use the example to help you organize
Your outline. AssignmentTake a break!Language Data BankLanguage Points for Reading IImagine your home begins to shake and you must leave it right away. (P25)
Shake : vi /vt (shook ,shaken)
Shake hands with sb
Shake one’s head over /at sth
The whole house shook during the explosion.
The explosion shook the house.
Please shake the bottle before taking.
The host shook hands with all the guests.
Nothing can shake our determination to overcome the difficulty.
He shook his head in answer to my question.
right away: right now ; at once ; immediately
I am getting in touch with him right away.
Language Points for Reading I2. For three days the water in the village wells rose and fell, rose and fell. (Para 1, Line 1)
rise(rose,risen) vi
go up; get higher; (of the sun, moon, stars,etc.)
come above the horizon; stand up ,
get out of bed
The flood has risen two feet.
She usually rises early in the morning.rise & raiserise: 升起; 上升; 上涨(不能用于被动语态)
raise: 举起 ; 使升起; 提高(可用于被动语态)
He raised a heavy box over his head.
We must raise the living standard of the people .
Food prices are still rising.
3. A smelly gas came out of the cracks. In the farmyards, the chickens and even the pigs were too nervous to eat. (Para 1, Line 3)
smelly adj. 发臭的
wind----windy dream----dreamy ice----icy
too···to ·····=so that
This book is too difficult for me to read.
=This book is so difficult that I can not read.
4. In the city, the water pipes in some buildings cracked and burst. (Para 1, L6)
burst (burst, burst)
(1).vi. break open or in pieces suddenly;
e.g. When he was riding ,the tire burst.
(2).vi. come or go suddenly or violently
e.g. The house burst into flames.
The girl burst into tear.
(3).n. bursting, outbreak
e.g. a burst of laughter/applause
5. …went to bed as usual that night. (Para1, Line 8)
as usual 照常,惯常
As usual, it rained on my birthday.
6. It seemed that the world was at an end.(Para 2, Line 1)
at an end 世界末日 come to an end 结束
The meeting came to an end at midnight.
at the end of 在……的尽头/最后
At the end of the road you’ll find a shop.
He is at the end of his patience.7. In fifteen terrible seconds a large city lay in ruin. (Para 2, Line 5)
lie(lay,lain) (v.)
to be, remain or be kept in a certain state
e.g. The village lay in ruins after the war.
in ruins: severly damaged or destroyed 毁坏
e.g. An earthquake left the whole town in ruins.
n. be/lie in ruins
sth. left after destruction,decay or downfall 废墟 ,遗迹
v. damage , destroyed 损坏,毁灭
e.g. The fire ruined the house8. Two-thirds of the people died or were injured during the earthquake.(para 2, Line 6)
injure : v. to hurt oneself /sb /sth physically受伤
e,.g. He fell of the bicycle in car accident.
Smoking will injure your health.
two-thirds
分子用基数(one, two…),分母用序数词(first, second…..),当分子超过1时,分母的词尾加s
1/6 one-sixth
1/3 one-third
2/3 two-thirds
9.People were shocked. (Para 3, Line 7)
shock :n. [U] [C] 打击;震惊, 震动
vt. 使震惊,使惊愕
shocking : adj. 使人震惊的
The news of his wife’s death was a terrible
shock to him.
You will get a shock if you touch the live wire.
I was shocked by his rudeness.
His failure in the exam was shocking to his parents.the number of : a quantity of people or things.
a number of : a lot of
reach(v) to achieve or obtain sth.
达成(某事物);达到,获得
e.g. At last we reached a decision.
You’ll understand it when you reach my age.
destroy: v. to damage sth severely; ruin
e.g. An atom bomb would destroy a city.
All his hopes are destroyed.
instead of : in place of; rather than
代替,而不是
e.g. He did the work instead of his father.
I’ll go to the cinema this afternoon
instead of doing my homework. rescue: to save or set free from harm,
danger,or loss
e.g. He rescued the man from drowning.
n. Act of rescuing 解救; 营救
All hope was not lost.不是所有的希望都破灭了。
all not = not all; some but not all .一些,但不是全部
e.g. Not all the boys left.(=Only some of them left)
The End
Warming up and Reading IEarthquakeNatural DisasterstyphoonflooddroughttsunamiearthquakeWhich disaster may cause the worst damage? earthquakeWarming up-II----sharing (1m)What causes an earthquake?The movement of the platesIt is always calm before a storm.策划:《学生双语报》6Do you feel it ?WateranimallightsoundDo you know what would happen
before an earthquake?Reading A NIGHT
THE EARTH DIDN’T SLEEPFast reading What does the passage mainly talk about?
How many parts can we divide the text into?An earthquake happened
in Tangshan in 1976Sum up the main idea of each part of the passage.
(use one word to describe)Part 1: para 1Part 2: para 2&3Part 3: para 4signsdamagehelp signs
before
Earthquake Para.1Fill in the blanksStrangerosefellsmellynervouseatjumpedran3:00bright lightsDamage
caused by
earthquakePara. 2-3Fill in the blanks3:42greatestSteamdirtBricksdamsuselesssteelSandelectricityData(数据) of the nation felt the earthquake .
A huge crack that was kilometres long and
metres wide cut across houses.
In terrible seconds a large city lay in ruins.
of the people died or were injured during the earthquake.
The number of people who were killed or injured reached more than .
All of the city’s hospitals, _ of its factories and buildings and of its homes were gone.
1/3830152/3400,00075%90%Para. 2-3What can we conclude from the data?who came to rescue them? 150,000 soldiersHow did the army help to rescue the survivors?dig out… and bury…
built shelters…
fresh water…by…. Retell the storyStrange things; water in the wells; smelly gas; animals; shake;at an end;
Lay in ruins; died or injured; people began to wonder……; hope not lost;
Soldiers; city breathe again Retell the story ____________ happened in Tang Shan. For a few days, water in the wells _____________. From the ______ of wells __________come out. Mice, chicken, pigs and even fish became ________. At 3:00 am, everything began to ______.It seemed that the world was _________. _________ of the nation ____ it. ___________cut across the city. The city lay _______. Strange thingsrose and fellcrackssmelly gasnervousshakeat an endOne-thirdfeltA huge crackin ruinsTwo-thirds of the people _____ or ___________. Then later that afternoon, another big quake ______ Tang Shan. People began to wonder ___________________________. But all hope ____________. _______ came to help those ________. Slowly, the city began to _____________.diedwere injuredshookhow long the disaster would lastwas not lostSoldiersbreathe againsurvivors What shall we do if an earthquake happens?DiscussionDiscussion (3m) Don’t be nervous and keep calm.
Don’t try to run out of the classroom.
Protect your head by putting your bag on your head.
Squat or sit down beside your desk.
Leave the classroom after the earthquake.A night the earth didn’t sleepSlowly, the city began to breathe again.What lessons should we learn from the Tangshan Earthquake?Discussion (group work)Tang shan’s new lookHomework1. find more information about earthquakes.
2.Finish the “learning about language” part on page 27.
3.Finish exercise 1 on page 63.Language Points
for Reading ITake a break! Unit 4
Period 3 learning about languageEarthquakePeriod 3: 幻灯片33-57页1. Answer keys for Ex1 on Page27:1 pipe
2 dam
3 shocked
4 injured
5 well
6 canal
7 ruins
8 a great number of
9 at an end
10 bury
11 rise
12 rescue
13 steamWord-consolidation-I (2m)2. Answer keys for Ex. 2 on page 28: It was a frightening night because a great number of things happened at the same time. The wall of the dam cracked, so the water went all over the fields. It filled the canals and the wells. The water pipes in some buildings burst. The water covered the buildings and had fallen in ruins around the dead and injured animals. People were shocked. They had to bury many of them for health reasons. It was a very sad time.Word-consolidation-II (2m)3. Answer keys for Ex.3 on page 28:1.one million
2.two-thirds
3.one-third
4.seventy-five percent
5.ninety percent
6.ten thousand
7.one hundred and fifty thousand
8. half a millionC
H
F
E
A
B
D
GWord-consolidation-III(2m)Grammar 定语从句 The Attributive Clause Grammar (5m)
Titanic is the ship that sank after hitting an iceberg.Rose and Jack are the lovers who met on the ship.Rosethe lady/meet Jack on TitanicRose is
met Jack on TitanicJackthe young man /want to save Rosethe man /want to kill JackCalJack is
wanted to save RoseCal is wanted to kill Jack.the lady whothe young man whothe man whothe ship/sink into the oceanthe ship/is the most beautiful
in the world at that time Titanic is
sank into the ocean.Titanic is
was the most beautiful in the word at that time.the ship thatthe ship thatthe Heart of Oceanthe diamond/is worn by RoseThe Heart of Ocean is
was worn by Rose.the diamond/is dropped
into the ocean by RoseThe Heart of Ocean is
was dropped into the ocean by Rose the diamond
thatthe diamond that
born in 1847/ man/ invent the first telephone
Bell who was born in 1847 is the man that invented the first telephone. 引导定语从句关系代词的用法: that which who whom whose 1.that在从句中作主语或宾语,指人和物 1)A plane is a machine that can fly.( 主语)2)The noodles that I looked were delicious.(宾语)3)Let’s ask the man that is reading the book over there.(主语)4)The girl that we saw yesterday is Jim’sister.(宾语) 2. Which 在从句中作主语或宾语,指物1) They planted the trees which didn’t need much water. (主语 )3. who whom 在从句中分别作主语和宾语 (口语中who也可作宾语)1) The foreigner who visited our school yesterday is from Canada.(主语)2) The fish which we bought were not fresh. (宾语)2) The boy who broke the window is called Michael.(主语) 4) Mr. Read is the professor to whom you should write . (宾语)3) The person to whom you just talked is Mr. Li. (宾语) 3) This is the book whose cover is blue.4. whose 在从句中作定语,指人或物1) Miss Flower is the teacher whose house caught fire last week.2) This is the boy whose composition the teacher talked of . The boss in whose company my father worked is a very kind person. 关系代词whose还可以在从句中与它所修饰的词一起作介词宾语NOTE that和which在指物的情况下一般都可以互换, 但在下列情况下, 一般用that而不用which。I am sure she has something (that) you can borrow.I’ve read all the books that are not mine. This is the first book (that) he has read.This is the very book that belongs to him.(1) 先行词为all, everything, nothing, something,
anything, little, much 等不定代词时。(2)先行词被all, every, no, some, any, little, much等
修饰时。(3)先行词被序数词或最高级修饰时。(4)先行词被the only, the very, the same, the last修饰时。NOTEeg. He talked about the things and persons he had visited in the city. * 在 who 或 which 引导的特殊疑问句中,限制性定语从句必须用 that 引导。that eg. Who is the man is standing over there.that* 先行词在从句中作表语时, 限制性定语从句通常用 that 引导。(常可省略) eg. She is no longer the girl that she was before she went to the country.3. The house ____________ they built in 1987 stayed up in the earthquake. Fill in the blanks with who, whom, that, which or whose1. The earthquake___________ hit the city in 1906 was the biggest in American history.2. We don’t know the number of people ____________ lost their homes in 1906 earthquakethat / which that / who which /that 6. Harry is the boy ________ mother is our maths teacher .4. A house ____________ is built on sand may fall down in a earthquake. 5. Luckily none of the people ______________ I know were killed in the earthquake .which / thatwho/whom/thatwhoseAnswer keys for “Discovering useful structures”Ex. 2 on Page 281 who
2 that/which
3 which/that
4 whose
5 whoseFunction-II----practice (2m)1.The famous basketball star, _______ tried to make a comeback, attracted a lot of attention. (北京 2002春季)
A、where B、when C、which D、who
答案 D
真题解析:本题考察定语从句关联词的选择,从句意可知先行词the famous basketball star(著名的篮球明星)是人,所以应用表示人的关联词who。
高考链接The film brought the hours back to me _____ I was taken good care of in that far-away village.(NMET 2001)
A、until B、that C、when D、where
答案 C
真题解析:本题考察定语从句的连接词,主句中的先行词the hours被其它成分分割,只要考生能够认清真正的先行词,就不难得出答案,the hours表示时间,所以应该选择一个表示时间的关系副词,即when。高考链接3._____ is known to everybody, the moon travels around the earth once every month. (NMET2001) A、It B、As C、That D、what
答案 B
真题解析:本题考察as引导非限定性定语从句。as引导从句的意思是“正如……..”,引导的非限定性定语从句修饰整个句子,当as在从句中充当主语时,常用下面的结构:as is know,as is said,as is reported 等,所以本题的答案是B。高考链接Homework1.finish the exercises on page 28.
2.surf the internet to find more information about the attributive clause and sum up the rules of it.Take a break! Unit 4
Period 4 Reading IIEarthquakePeriod 4: 幻灯片58-75页Do you know any other place where the earthquakes easily happen in the world? Warming up----Brainstorming (2m)Pacific plateAmerican
plateEurasian plate India plateAfrican
plateAntarctic plateSan FranciscoUS Map?
?Pacific
plate
NorthSouthWestEast↖American plateThe plates are moving constantly. Sometimes these two plates stop and do not move for years. Then Suddenly, they jump and an earthquake is felt. As a result of the movement of these plates, west America near the sea has always been a bad place for earthquakes. ContinentOceanic plate★★San Francisco (before the earthquake)San Francisco (after the earthquake)Read the passage and finish the following exercises.1.Write an adjective to describe how the author feels about the earthquake and what it did.
___________________
Why did you choose these word?
__________________________________Reading I----scanning (2m)2.Write an adjective to describe how the author feels about the people of San Francisco.
___________________
Why did you choose these word?
__________________________________Read the first paragraph in this passage. Then go back and read again the first paragraph of the passage on page 26.Compare the ways both writers give you details about the earthquakes.Reading II----detailed reading (3m)How do you know?
______________________________1.Which writer shows more feeling about the earthquake?
A. The writer of the Tangshan quake in 1976
B The writer of the San Francisco in 1906Both writers give similar details about_________________________
and___________________________
_______________________________3.Which one of the following statements is true?
A. Both writers give details of big events before little events.
B Both writers give details of little events before big events.
C Neither writer gives details of big events before little events.3.Which one of the following statements is not true?
Both writers saw the earthquake he wrote about.
B. Only one writer saw the earthquake he wrote about.
C. Neither writer saw the earthquake he wrote about.Thinking:
If you are going to make a speech to honor those who died in the terrible disaster and those who helped the survivors in Tangshan, what would you say?Thinking &writing (5m)HomeworkRead the letter and then write a short speech, in which you should follow the following points on page 29.Take a break! Unit 4
Period 5 Listening EarthquakePeriod 5: 幻灯片76-85页Question: Have you ever experienced a terrible disaster and became a survivor?Pre-listening----prediction (1m)Listen to the tape as it tells the story of a man who was a survivor of the great San Francisco earthquake of 1906.Read the following statements and tell whether they are true or false.1.F 2.F 3.T 4.T 5.F 6.F
Listening----(5m)Listen to the tape and answer the following questions. When did the man talk about the earthquake: while it was happening or after it had happened? How do you know?
After the earthquake had happened.
The last sentence gives information about the next day.Listening----answering the following questions (5m)Listen to the tape and answer the following questions. Is the man calm as he talks about he earthquake? Why or why not?
Yes, the man is calm because he is writing about something a long time after it happened.
Listen to the tape and answer the following questions.What was the biggest danger for the man: fires, cows or falling buildings? Why? The falling buildings were his biggest danger and he didn’t know when one might fall on him. He could at least see the fires and cows coming towards him.
Listen to the tape and answer the following questions. Where was the man going? He was going to the bay to get on a boat.
Listen to the tape and answer the following questions. Have you got any ideas to help this man during the earthquake?
______________________________________
______________________________________(The students’ answers may vary but should demonstrate an understanding of the listening text.)
HomeworkFinish the listening task on workbook, page 66.Take a break! Unit 4
Period 6 Speaking and WritingEarthquakePeriod 6: 幻灯片86-109页What kind of
newspaper
do you usually read?
Speaking task:China daily21 centuryNew York TimesWashington postEnglish weekly……Speaking (4m)Have you ever read any
English newspaper or chinese
newspaper? What are they?
Which would you prefer, English newspaper or Chinese newspaper? Why?Discussion:
Discussion (3m)an interesting title that
tells the reader what your topic is
Headline
Main ideasDetailsDo you know what an outline is?outlineBrainstorming for writing (3m)QuestionsWhy an outline is important?
What should an outline conclude?
Why a headline is important?
What are the steps to finish a newspaper story?
What is the feature of the newspaper story?Why an outline is important?
Because an outline will prepare you to write a better story.
What should an outline conclude?
A good outline should have a headline, a list of main idea and a list of important details.
Why a headline is important?
A headline can tell the reader what the topic is, so it can attract the reader’s attention since the reader may not have bought the newspaper before they read the headline.
What are the steps to finish a newspaper story?
First, organize the main ideas. Next, put some details into each paragraph.
What is the feature of the newspaper story?
A newspaper story gives the most important news first and the least important news last.
Read the example of a newspaper
story on P31.
How many parts is the story divided?
Find the headline, main ideas and details of each paragraph.Pre-writing (3m)
Headline :
Main ideasDetailsoutline
importantThe most important news first
the least important news lastExample of newspaper story China leads world in traffic death Experts say that road traffic accidents are on the rise and China ranks first in the world in traffic death tolls. Worldwide Statistics show that the global traffic accident death toll amounted to 500,000 in 2003, with the largest share,104,000
reported in China, followed by India with 86,000, the U.S. with 40,000, and Russia with 26,000, said Duan Liren , former deputy director of the Beijing Traffic Management Bureau. Road accidents are
The seventh leading killer in China. Prepare the outline for a short
newspaper story for China Daily.
Use the example to help you organize
Your outline. AssignmentTake a break!Language Data BankLanguage Points for Reading IImagine your home begins to shake and you must leave it right away. (P25)
Shake : vi /vt (shook ,shaken)
Shake hands with sb
Shake one’s head over /at sth
The whole house shook during the explosion.
The explosion shook the house.
Please shake the bottle before taking.
The host shook hands with all the guests.
Nothing can shake our determination to overcome the difficulty.
He shook his head in answer to my question.
right away: right now ; at once ; immediately
I am getting in touch with him right away.
Language Points for Reading I2. For three days the water in the village wells rose and fell, rose and fell. (Para 1, Line 1)
rise(rose,risen) vi
go up; get higher; (of the sun, moon, stars,etc.)
come above the horizon; stand up ,
get out of bed
The flood has risen two feet.
She usually rises early in the morning.rise & raiserise: 升起; 上升; 上涨(不能用于被动语态)
raise: 举起 ; 使升起; 提高(可用于被动语态)
He raised a heavy box over his head.
We must raise the living standard of the people .
Food prices are still rising.
3. A smelly gas came out of the cracks. In the farmyards, the chickens and even the pigs were too nervous to eat. (Para 1, Line 3)
smelly adj. 发臭的
wind----windy dream----dreamy ice----icy
too···to ·····=so that
This book is too difficult for me to read.
=This book is so difficult that I can not read.
4. In the city, the water pipes in some buildings cracked and burst. (Para 1, L6)
burst (burst, burst)
(1).vi. break open or in pieces suddenly;
e.g. When he was riding ,the tire burst.
(2).vi. come or go suddenly or violently
e.g. The house burst into flames.
The girl burst into tear.
(3).n. bursting, outbreak
e.g. a burst of laughter/applause
5. …went to bed as usual that night. (Para1, Line 8)
as usual 照常,惯常
As usual, it rained on my birthday.
6. It seemed that the world was at an end.(Para 2, Line 1)
at an end 世界末日 come to an end 结束
The meeting came to an end at midnight.
at the end of 在……的尽头/最后
At the end of the road you’ll find a shop.
He is at the end of his patience.7. In fifteen terrible seconds a large city lay in ruin. (Para 2, Line 5)
lie(lay,lain) (v.)
to be, remain or be kept in a certain state
e.g. The village lay in ruins after the war.
in ruins: severly damaged or destroyed 毁坏
e.g. An earthquake left the whole town in ruins.
n. be/lie in ruins
sth. left after destruction,decay or downfall 废墟 ,遗迹
v. damage , destroyed 损坏,毁灭
e.g. The fire ruined the house8. Two-thirds of the people died or were injured during the earthquake.(para 2, Line 6)
injure : v. to hurt oneself /sb /sth physically受伤
e,.g. He fell of the bicycle in car accident.
Smoking will injure your health.
two-thirds
分子用基数(one, two…),分母用序数词(first, second…..),当分子超过1时,分母的词尾加s
1/6 one-sixth
1/3 one-third
2/3 two-thirds
9.People were shocked. (Para 3, Line 7)
shock :n. [U] [C] 打击;震惊, 震动
vt. 使震惊,使惊愕
shocking : adj. 使人震惊的
The news of his wife’s death was a terrible
shock to him.
You will get a shock if you touch the live wire.
I was shocked by his rudeness.
His failure in the exam was shocking to his parents.the number of : a quantity of people or things.
a number of : a lot of
reach(v) to achieve or obtain sth.
达成(某事物);达到,获得
e.g. At last we reached a decision.
You’ll understand it when you reach my age.
destroy: v. to damage sth severely; ruin
e.g. An atom bomb would destroy a city.
All his hopes are destroyed.
instead of : in place of; rather than
代替,而不是
e.g. He did the work instead of his father.
I’ll go to the cinema this afternoon
instead of doing my homework. rescue: to save or set free from harm,
danger,or loss
e.g. He rescued the man from drowning.
n. Act of rescuing 解救; 营救
All hope was not lost.不是所有的希望都破灭了。
all not = not all; some but not all .一些,但不是全部
e.g. Not all the boys left.(=Only some of them left)
The End
