Unit 18[下学期]
图片预览











文档简介
课件85张PPT。The plan for Unit 18The teaching aims:
1. Improving the students’ skills in
speaking ,(Talk about inventions)
listening and reading
2. Word study and grammarFunctional SentencesThis invention can help people…
This is a new way of…
This new invention will make it possible for people to…
I think… is much more useful than…
It can make / help people…
I’d like to invent… because it can…I’d like to invent… which can…
If people can create…
I suppose…
It must be very convenient if people could invent…
I dreamed I could invent…
Vocabulary 1. 四会词汇
vest, heel, patent, officer, petrol, background, reject, possibility, otherwise, connection, previous, aware, trial, rider, dusty, pilot, storage, glue, typewriter 2. 认读词汇
edible, flavour, laptop, inflatable, creative, rephrase, partial, perception, visible, Mozart, relativity, Samuel Morse, desktop, palmtop, Mona Lisa, Charles Chaplin, John Denver, Isaac Newton, Abraham Lincoln, Eve, Helen Keller, metaphor, paste, electronics, Eniac3. 词组
allow for, get stuck, break away from, be aware of, trial and error, after all, keep track of
4. 重点词汇
vest, office, background, reject, possibility, otherwise, aware, allow for, get stuck, break away from, be aware of, after all, keep track of
Time periodsSix periods
1. Word Study , Warming up, Listening 2. 2. Word Study and Speaking
3. Word Study and Reading
4. Important points
5. Integrating skill skills
6. Grammar and Writing
Warming upWarming upStep One
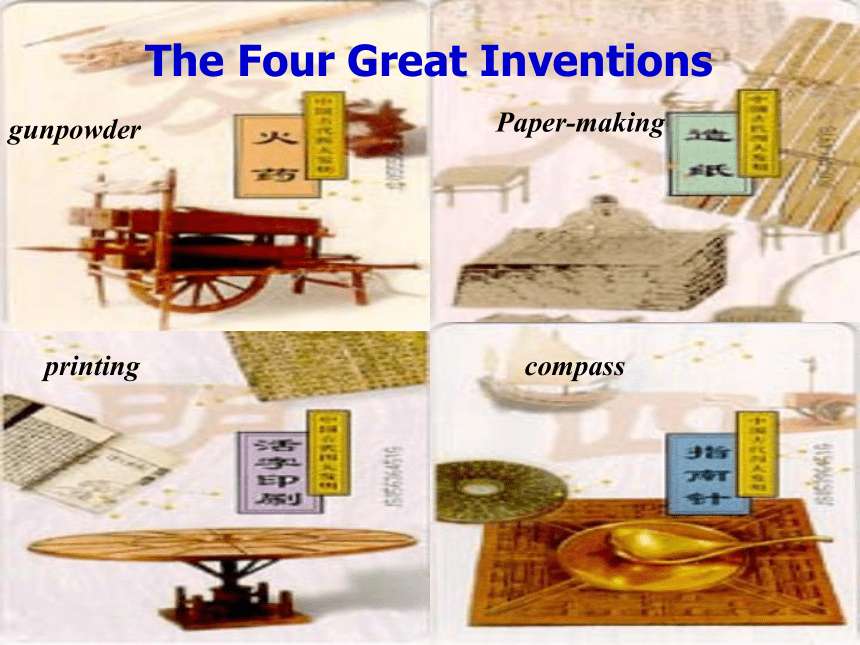
Introducing four great inventions and some other inventions in modern times .
gunpowderPaper-makingprintingcompassThe Four Great Inventions The first twenty years in the 20th century: Inventions in the 20th century:planepaper cupsIn the 1920s :
electric shaver,TV,the first film with sound (美国华纳兄弟电影公司拍摄的《爵士乐歌手》),frozen food,traffic lights,penicillin 青霉素In the 1930s :
sunglasses,zebra crossing,canned beer,
ball-pen,computer , tape-recorderIn the 1940s and 1950s :
nylon stockings, color TV,atomic bomb ,microwave oven,jeep,credit card, cable TV,pocket transistor radio(晶体管收音机),weight-reducing drink,video recorder(录像机),,hydrogen bomb(氢弹), laser(激光) In the 1960s and 80s :
mouse ,cassette ,sleeping pill ,laptop computer ,scanner , e-mail, word processor software , mobile phone and walkman, CD ROM,…. In the last ten years :
DVD,Pentium“奔腾”处理器,the cloned sheep Dolly, message / MS
N(短信), man-made liver (人造肝脏)Step TwoLook at the pictures and match picture with the correct description at the bottom of Page 57.
Learn the new words :
edible 可以吃的
laptop 笔记本电(nose-top/ desktop/palmtop computer)
flavour 味道
vest 背心,马甲
heel 鞋跟,脚后跟
inflatable 可充气的,可膨胀的
Discussion:
Is there anything you would like to invent? If so , what and why ?
Discussion:What can you do to improve them?What should we do after inventing new things? What are the disadvantages in them? Go to the patent office to ask for a patentListeningPre-Listening :
Learn the new words in the listening materials.
Patent 专利,专利权
a patent 专利(权);专利品;专利证书
a patent device专利发明 patent right 专利权 apply for a patent申请专利权
patent marking 专利标记
The Patent Office专利局
patent number 专利号
Officer 公务员,官员
vehicle 交通工具
bucket 水桶
groceries 食品,杂货
Listening :Listen to the dialogue
on the tape and answer the questions below:
Dialogue 1
What are the advantages of Mr. Jones’ new invention?
How does it work?
What can it be used for?
Why does the patent officer not want to give Mr. Jones a patent?What are the advantages of
Mr. Jones’ new invention?
The new invention is clean and cheap.
How does it work?
It’s a vehicle that doesn’t need an engine or fuel. The vehicle is powered by the person who uses it.What can it be used for?
The invention can be used as a means of transportation, instead of cars and buses.
Why does the patent officer not want to give Mr. Jones a patent?
Because the vehicle described by the inventor has already been invented —— it’s a bike-like two-wheel car.Dialogue 2
What has Mr.Butler invented?
Why did he invent it?
How does it work?
Why does the patent officer not want to give Mr. Butler a patent?Listening :Dialogue 2
What has Mr.Butler invented?
He invented a device for helping people carry heavy objects.
Why did he invent it?
He was tired of carrying heavy grocery bags.
/ He got the idea when he saw a woman carrying some heavy bags.Dialogue 2
How does it work?
If you put the bags into a large bucket of water, the bags will float and you won’t have to carry them.
Why does the patent officer not want to give Mr. Butler a patent?
Because his idea doesn’t work ( is not practical) —— You would still have to carry the large buckets. Post- Listening : Discuss: What should a new thing be like in order to be given a patent?Three criteria must be met before
Patent right may be granted.
They are novelty (新颖性), creativity,
and practicality.
SpeakingStep One
Read the useful expressions.
This invention can help people…
This is a new way of…
This new invention will make it possible for people to…
I think… is much more useful than…
It can make / help people…
I’d like to invent… because it can…I’d like to invent…
which can…
If people can create…
I suppose…
It must be very convenient if people could invent…
I dreamed I could invent…
Step TwoAccording to the clues in the textbook , ask the students to suppose they have invented a car / a flying bicycle / a pen or a machine that makes it possible for people to see the future and ask them to make sentences with the useful expressions.
ReadingWhat will you think of next ?Pre – reading: All the contents of Warming up and Listening are about inventions. Ask the students to guess what the text is about .
the great thinkers’ ideas for new inventions Reading : ScanningHow do the great thinkers come up with ideas for new inventions ? (paying attention to the new words and trying to understand them )
Thinking outside the box
Taking another look at it
Making connections
Keeping trying
Think outside the boxTake another look at itMake connectionsKeep tryingFind out what the following ways mean.Try new ways to solve
a problem.Look at a problem in
as many ways as
possible.Try to combine new
and old ideas in as
many different ways
as possible.Have a long process
of trial and error.Read the text carefully and try to answer the questions below . (making marks under the new words)Ask the students to find the main idea of the second paragraphCreative thinking is a conscious effort to break away from old thought patterns in order to explore new possibilities .Ask the students to find the main idea of the third paragraphBy looking at a problem in as many ways as possible , some solutions that would otherwise remain invisible can be found .Ask the students to find the main idea of the fourth paragraphCombining new and old ideas in as many different ways as possible is very important for inventions .Ask the students to find the main idea of the fourth paragraphGood ideas are no accident . They are the result of a long process of trial and error .Post-ReadingTrue or False 1 Most inventors have high IQs.
2 The things we know can sometimes make
it more difficult for us to understand.
3 It’s impossible to learn how to be creative.
4 The best way to find a good solution is to
look for one good answer.
5 Inventors try to avoid failure.
6 The more ways we have of looking at a
problem, the more likely it is that we can
find a solution.
7 Most good ideas are the result of a long
process of trial and error. FFFFTTTThe new words in the text .creative /background /visible
/rephrase/allow for /reject /
get stuck//partial /break away
from/possibility /perception
/otherwise/connection/previous/aware/
be aware of /trial and error /relativity
PointsUseful expressions to be explained1.be tired of 对…感到厌倦,对…不感兴趣
be tired from 因…而疲惫
2.break away form (the police / al his friends / a habit / the Union…)
3.the possibility of … / that…4.attempt sth.
attempt to do sth.
attempt doing sth.
make an attempt to do sth.
in one’s attempt to do sth.
5. be aware of/that-clause
6. let … out 放出,放掉;泄露,说出;放大(衣服等);出租;终止,结束
7.come up with 想到或提出(答案、办法等) 8.have … in common : share interests, characteristics, etc. 有共同之处,有共同的利益、特点等 out of common 异乎寻常 in common with 像…样 9. allow for :考虑;顾及;对…做准备;体谅 allow sb. to do sth. / allow doing sth allow of sth. 允许,容许 10.get stuck 陷进去,被捆住 11.otherwise (adv.) 不然,否则;不同地;在其他方面,除此之外 12.as with : like 正如…一样 13.trial and error 反复试验,不断摸索 14.reject 拒绝,丢弃 15. attempt ,尝试,企图,试图 16.be said to do it’s said that … 据说 17.be similar to … 与…相类似 18. keep pace with… = keep up with 跟上 Grammar
The Attributive Clause
●The restrictive & non-restrictive attributive clauses
●The attributive clause & the appositive clause
●The attributive clause & the emphasis structureThe use of the relative pronouns:person(s) subject/object person(s)object person(s)/thing(s)subject/objectthing(s)subject/object person(s)/thing(s)
(of whom/which)attributiveThe use of the relative adverbs:timeadverbial of timeplace adverbial of placereasonadverbial of reasonPractice: complete the sentences with suitable relatives.
1. I know the reason ____ he came late.
2. Do you know the woman, ________ son went to
college last year?
3. The house ________ color is red is John’s.
The house, the color of which is red, is John’s.
4. This is the best film _____ I’ve ever seen.
5. That’s the town _______ he worked in 1987.
That’s the town in which he worked in 1987.
6. I have 2 brothers, _____ are both soldiers.
7. Next week, ______ you’ll spend in your
hometown ,is coming.
8. I’ve tried 2 pairs of shoes, neither of _____ fits me well.whywhosewhosethatwherewhowhichwhichNotice:
Pay more attention to the agreement between
the verb and the antecedent in person and
number in the attributive clause, and then
complete the sentences:
Those who ____ to go to the cinema must
be at the school gate by 3:30 p.m. (want)
2. He who ___________ the great wall is not
a true man. (not reach)
3. She is the only one of the girls who ____
been to Beijing. (have)
4. He is one of the boys who ____ seen the
film. (have)wantdoesn’t reachhashave
When a relative pronoun is used as a subject
in the clause, the verb must agree with the
antecedent in person and number.
(2) When the antecedent is the structure “one
of +n. (pl.)”, the verb in the clause must be plural,
agrees with the plural form. However, if there
is “the” or “the only very” before “one”, the
verb in the clause must be singular, agrees with
the word “one”.Conclusion 1:Practice: Complete the following sentences with suitable relatives:
The time ___________ I went to Tokyo is in 1982.
2. I’ll never forget the time __________ I spent at college.
3. The shop __________ I bought the book in
is big.
4. The shop _____________ I bought the book is big.
Conclusion 2: when the antecedent is a noun for time or place “when” or “where” is not always used to introduce the clause. It depends on the fun_ction of the relative word in the clause.whenwhich/thatwhich/thatwhere/in whichThe Difference Between “that” and “which”.
Complete the following sentences with “that”
or “which”.
This is the 2nd article ____ I have written
in English.
2. It is the best film _____ he has ever seen.
3. This is the very book _____ I want to read.
4. All ____ they told me surprised me.
5. They talked about the teachers and schools
_____ they had visited.thatthatthatthatthat6. Who is the comrade ______ was there?
7. There is a bed in the room _____is still vacant.
8. Our village is no longer the place _______ it
used to be.
He paid the boy $10 for washing the windows,
most of _______ hadn’t been cleaned at least
a year.
10. The weather turned out to be very good,
_______ was more than we could expect.
11. The clever boy made a hole in the wall,
through _______ he could see what was going on
inside the house.thatthatthatwhich whichwhichConclusion 3:
When the antecedent refers to thing(s), “that” is often used in the following cases:(1) After ordinal number and superlatives
(2) After the following words: all, only, little,
few, much, very, none, last, just, any(thing),
every(thing), some(thing), no(thing).
(3) After two or more antecedents, referring
to both person(s) and thing(s).
(4) After interrogative pronouns “which” or
“who”.(5) When the relative pronoun is used as a predictive
in the clause.
(6) When the main clause begins with “there be ”.
In the following cases, “which” is always used.
①After prepositions
②to introduce a non-restrictive attributive
clause.
③The whole main sentence is the “antecedent”
of the relative clause, and there is
always a comma.
Tell me the reason ____ you were late for class.
2. Who is the girl _____ is speaking there ?
3. This is Mr. Smith, _____ has something interesting to tell you.
4. The computer ________ CPU doesn’t work has to be
repaired.whythatwhowhoseFill in the blanks with suitable relatives to complete the following sentences.5. This kind of computer, _____ is well-known ,
is out of date.
6. This is just the place ___ I’ve been longing
to visit for years.
7. His mother is an engineer, ____ makes him
very proud.
8. The old man has 4 sons, three of ____ are
doctors.
whichthatwhichwhom一、从词类上区别
同位语从句前面的名词只能是idea, fact, news, hope,
belief, suggestion, proposal, word, thought, doubt,
truth, possibility, promise, order等表示抽象意义的名
词。而定语从句的先行词可以是名词、代词、主句的一部
分或整个主句。
如:
We are looking into the question whether he is worth
trusting.
我们正在调查的是他是否值得信赖的问题(同位语从句)
Word came that he had gone abroad.
据说他已经出国了。(同位语从句)The Difference Between the Attributive Clause and the
Appositive Clause The doctor whom you are looking for is in
the room.
你找的那位医生在房间里面。
(定语从句,名词the doctor作先行词)
Our team has won the game, which makes us
very happy.
(定语从句,which代表前面提到的整个句子)
His mother did all she could to help him with
his study.
他妈妈尽最大努力帮他学习。
(定语从句,代词all作先行词)二、从性质上区别
定语从句是从句对其先行词的修饰或限制,
属于形容词性从句的范畴;而同位语从句是
从句对前面抽象名词的进一步说明和解释,
属于名词性从句的范畴。如:
The news that our team has won the game
is true.
我们队赢了那场比赛的消息是真的。
(同位语从句,补充说明news的内容。)
The news (that) he told me yesterday is true.
昨天他告诉我的那个消息是真的。
(定语从句,that 从句作定语修饰news)I made a promise that if anyone set me free
I would make him very rich.
我许诺如果谁让我自由,我就让他非常富有。
(同位语从句,补充说明promise)
The mother made a promise that pleased all her
children.
妈妈做出了一个令她的孩子们高兴的许诺。
(定语从句,that从句作定语修饰promise。)三、从引导词及其在句子中的成份上区别有些引导词
如how, whether, what可以引导同位语从句,但不能
引导定语从句。如:
That question whether we need it has not been
considered.
我们是否需要它这个问题还没有考虑。(同位语从句)
I have no idea what has happened to him.
我不知道他发生了什么事。(同位语从句)
引导词that引导定语从句时,在从句中一般作主语
或宾语(指物时还可以用which代替),并且作宾语时
常常省略。That在同位语从句中仅起连接作用,不充当
任何成份,并且不能省略,也不能用which来代替。 The order that we (should) send a few people
to help the other groups was received yesterday.
我们应派几个人去帮助别的几个小组的命令昨天
已收到了。(同位语从句,是对order的具体解释,
that虽不作成份,但不能省略)
The order (that) we received yesterday was
that we (should) send a few people to help the
other groups.
我们昨天收到的命令是我们应该派几个人去帮助别
的几个小组。(定语从句,是名词order的修饰语,
that在从句中作received的宾语,可以省略)从A、B、C、D四个选项中,选出可以填入
空白处的最佳选项。
Along with the letter was his promise ____
he would visit me this coming Christmas.
A. which B. that C. what D. whether
2. Luckily, we’d brought a road map without___
we would have lost our way.
A. it B. that C. this D. which
3. There is a new problem involved in the
popularity of private cars ___road conditions need _________ .
A. that; to be improved B. which; to be improved
C. where; improving D. when; improvingBDA5. Information has been put forward ____
more middle school graduates will be
admitted into universities.
A. while B. that C. when D. as
6. The fact came up ___ specific speech sounds are
recognized by babies as young as 6 months old.
A. what B. which C. that D. whose
7. A decision was made ____ those who
wanted to get a job in the factory would not
be allowed to stay.
A. what B. when C. which D. thatBCD8. The question came up at the meeting ____
we had enough money for our research.
that B. what C. which D. whether
9. The reason ____ he is late is ____ there was
a breakdown on the railway.
A. why; why B. why; that
C. because; that D. that; becauseDB强调句型的句式结构为:“It is/was + 被强调部
分 + that/who从句”。
在强调时间、地点、原因或方式状语时,一律
用that,而不用when, why或how;
在强调主语和宾语时,如果主语和宾语指代人,
则可用who和whom来代替that,
但是从句中的人称和数要与被强调的主语和宾语
保持一致。这些都容易与定语从句混淆。The Difference Between the Attributive Clause
and the Emphasis Structure定语从句和强调句型的判断方法:若将句中的
“It is/was”和“that/who”去掉,而句子不缺成分,
结构完整,说明原句是强调句型;若句子结构不
完整,则说明原句为定语从句。
1. It was not until 1920 ____ regular radio
broadcasts began.(1995高考卷)
A. while B. which C. that D. since
2. ____ was his kindness that everyone praised
him.
A. It B. What C. So D. SuchCA3. It is the ability to do the job ____ matters not where
you come from or what you are. (2000高考卷)
A. one B. that C. what D. it
4. It was ____ he came to Macao ____ he knew what
kind of place it was.
A. that; when B. until; that
C. not until; when D. not until; that
5. ____ is a fact that English is being accepted as an
international language.
A. There B. This C. That D. ItBDD6. It was not until we came back from outside ____
out of his bed.
A. did he get B. when he got
C. that he got D. then he got
7. When was it ____ you met him in the library?
A. where B. that C. in which D. which
8. It was near the place ____ there is a bomb
____ we found the dead man.
A. where; where B. where; that
C. that; where D. that; thatCBB The order that we (should) send a few people
to help the other groups was received yesterday.
我们应派几个人去帮助别的几个小组的命令昨天
已收到了。(同位语从句,是对order的具体解释,
that虽不作成份,但不能省略)
The order (that) we received yesterday was
that we (should) send a few people to help the
other groups.
我们昨天收到的命令是我们应该派几个人去帮助别
的几个小组。(定语从句,是名词order的修饰语,
that在从句中作received的宾语,可以省略)Answers to Ex 2 on page 61:The wires that/which the machines were connected with were very old.
The wires with which the machines were connected were very old.
Leonardo da Vinci who/that painted the “Mona Lisa” was interested in both literature and science.
The pilot who/that/whom we had dinner with told us stories about his travels.
The pilot with whom we had dinner told us stories about his travels.The four ancient Chinese inventions which/that we are proud of have remained important in human history for thousands of years.
Mozart whose music is popular all over the world showed his talent for music at a very young age.
The photos are kept in the cupboard which/ that our parents left to us ten years ago.
The photos are kept in the cupboard which/ that was left by our parents ten years ago.The country which/that this news report is coming from is on the other side of the world.
The country from which this news report is coming is on the other side of the world.
从A、B、C、D四个选项中,选出可以填入
空白处的最佳选项。
Along with the letter was his promise ____
he would visit me this coming Christmas.
A. which B. that C. what D. whether
2. Luckily, we’d brought a road map without___
we would have lost our way.
A. it B. that C. this D. which
3. There is a new problem involved in the
popularity of private cars ___road conditions need _________ .
A. that; to be improved B. which; to be improved
C. where; improving D. when; improvingBDA5. Information has been put forward ____
more middle school graduates will be
admitted into universities.
A. while B. that C. when D. as
6. The fact came up ___ specific speech sounds are
recognized by babies as young as 6 months old.
A. what B. which C. that D. whose
7. A decision was made ____ those who
wanted to get a job in the factory would not
be allowed to stay.
A. what B. when C. which D. thatBCD8. The question came up at the meeting ____
we had enough money for our research.
that B. what C. which D. whether
9. The reason ____ he is late is ____ there was
a breakdown on the railway.
A. why; why B. why; that
C. because; that D. that; becauseDB强调句型的句式结构为:“It is/was + 被强调部
分 + that/who从句”。
在强调时间、地点、原因或方式状语时,一律
用that,而不用when, why或how;
在强调主语和宾语时,如果主语和宾语指代人,
则可用who和whom来代替that,
但是从句中的人称和数要与被强调的主语和宾语
保持一致。这些都容易与定语从句混淆。The Difference Between the Attributive Clause
and the Emphasis Structure定语从句和强调句型的判断方法:若将句中的
“It is/was”和“that/who”去掉,而句子不缺成分,
结构完整,说明原句是强调句型;若句子结构不
完整,则说明原句为定语从句。
1. It was not until 1920 ____ regular radio
broadcasts began.(1995高考卷)
A. while B. which C. that D. since
2. ____ was his kindness that everyone praised
him.
A. It B. What C. So D. SuchCA3. It is the ability to do the job ____ matters not where
you come from or what you are. (2000高考卷)
A. one B. that C. what D. it
4. It was ____ he came to Macao ____ he knew what
kind of place it was.
A. that; when B. until; that
C. not until; when D. not until; that
5. ____ is a fact that English is being accepted as an
international language.
A. There B. This C. That D. ItBDD6. It was not until we came back from outside ____
out of his bed.
A. did he get B. when he got
C. that he got D. then he got
7. When was it ____ you met him in the library?
A. where B. that C. in which D. which
8. It was near the place ____ there is a bomb
____ we found the dead man.
A. where; where B. where; that
C. that; where D. that; thatCBBWritingwriting Before we start writing, we should list ideas and information and think about the organization of our articles.
Step1 Computer is part of our life
Step2 The development of computer
Step 3 The way we use computers will change
1. Improving the students’ skills in
speaking ,(Talk about inventions)
listening and reading
2. Word study and grammarFunctional SentencesThis invention can help people…
This is a new way of…
This new invention will make it possible for people to…
I think… is much more useful than…
It can make / help people…
I’d like to invent… because it can…I’d like to invent… which can…
If people can create…
I suppose…
It must be very convenient if people could invent…
I dreamed I could invent…
Vocabulary 1. 四会词汇
vest, heel, patent, officer, petrol, background, reject, possibility, otherwise, connection, previous, aware, trial, rider, dusty, pilot, storage, glue, typewriter 2. 认读词汇
edible, flavour, laptop, inflatable, creative, rephrase, partial, perception, visible, Mozart, relativity, Samuel Morse, desktop, palmtop, Mona Lisa, Charles Chaplin, John Denver, Isaac Newton, Abraham Lincoln, Eve, Helen Keller, metaphor, paste, electronics, Eniac3. 词组
allow for, get stuck, break away from, be aware of, trial and error, after all, keep track of
4. 重点词汇
vest, office, background, reject, possibility, otherwise, aware, allow for, get stuck, break away from, be aware of, after all, keep track of
Time periodsSix periods
1. Word Study , Warming up, Listening 2. 2. Word Study and Speaking
3. Word Study and Reading
4. Important points
5. Integrating skill skills
6. Grammar and Writing
Warming upWarming upStep One
Introducing four great inventions and some other inventions in modern times .
gunpowderPaper-makingprintingcompassThe Four Great Inventions The first twenty years in the 20th century: Inventions in the 20th century:planepaper cupsIn the 1920s :
electric shaver,TV,the first film with sound (美国华纳兄弟电影公司拍摄的《爵士乐歌手》),frozen food,traffic lights,penicillin 青霉素In the 1930s :
sunglasses,zebra crossing,canned beer,
ball-pen,computer , tape-recorderIn the 1940s and 1950s :
nylon stockings, color TV,atomic bomb ,microwave oven,jeep,credit card, cable TV,pocket transistor radio(晶体管收音机),weight-reducing drink,video recorder(录像机),,hydrogen bomb(氢弹), laser(激光) In the 1960s and 80s :
mouse ,cassette ,sleeping pill ,laptop computer ,scanner , e-mail, word processor software , mobile phone and walkman, CD ROM,…. In the last ten years :
DVD,Pentium“奔腾”处理器,the cloned sheep Dolly, message / MS
N(短信), man-made liver (人造肝脏)Step TwoLook at the pictures and match picture with the correct description at the bottom of Page 57.
Learn the new words :
edible 可以吃的
laptop 笔记本电(nose-top/ desktop/palmtop computer)
flavour 味道
vest 背心,马甲
heel 鞋跟,脚后跟
inflatable 可充气的,可膨胀的
Discussion:
Is there anything you would like to invent? If so , what and why ?
Discussion:What can you do to improve them?What should we do after inventing new things? What are the disadvantages in them? Go to the patent office to ask for a patentListeningPre-Listening :
Learn the new words in the listening materials.
Patent 专利,专利权
a patent 专利(权);专利品;专利证书
a patent device专利发明 patent right 专利权 apply for a patent申请专利权
patent marking 专利标记
The Patent Office专利局
patent number 专利号
Officer 公务员,官员
vehicle 交通工具
bucket 水桶
groceries 食品,杂货
Listening :Listen to the dialogue
on the tape and answer the questions below:
Dialogue 1
What are the advantages of Mr. Jones’ new invention?
How does it work?
What can it be used for?
Why does the patent officer not want to give Mr. Jones a patent?What are the advantages of
Mr. Jones’ new invention?
The new invention is clean and cheap.
How does it work?
It’s a vehicle that doesn’t need an engine or fuel. The vehicle is powered by the person who uses it.What can it be used for?
The invention can be used as a means of transportation, instead of cars and buses.
Why does the patent officer not want to give Mr. Jones a patent?
Because the vehicle described by the inventor has already been invented —— it’s a bike-like two-wheel car.Dialogue 2
What has Mr.Butler invented?
Why did he invent it?
How does it work?
Why does the patent officer not want to give Mr. Butler a patent?Listening :Dialogue 2
What has Mr.Butler invented?
He invented a device for helping people carry heavy objects.
Why did he invent it?
He was tired of carrying heavy grocery bags.
/ He got the idea when he saw a woman carrying some heavy bags.Dialogue 2
How does it work?
If you put the bags into a large bucket of water, the bags will float and you won’t have to carry them.
Why does the patent officer not want to give Mr. Butler a patent?
Because his idea doesn’t work ( is not practical) —— You would still have to carry the large buckets. Post- Listening : Discuss: What should a new thing be like in order to be given a patent?Three criteria must be met before
Patent right may be granted.
They are novelty (新颖性), creativity,
and practicality.
SpeakingStep One
Read the useful expressions.
This invention can help people…
This is a new way of…
This new invention will make it possible for people to…
I think… is much more useful than…
It can make / help people…
I’d like to invent… because it can…I’d like to invent…
which can…
If people can create…
I suppose…
It must be very convenient if people could invent…
I dreamed I could invent…
Step TwoAccording to the clues in the textbook , ask the students to suppose they have invented a car / a flying bicycle / a pen or a machine that makes it possible for people to see the future and ask them to make sentences with the useful expressions.
ReadingWhat will you think of next ?Pre – reading: All the contents of Warming up and Listening are about inventions. Ask the students to guess what the text is about .
the great thinkers’ ideas for new inventions Reading : ScanningHow do the great thinkers come up with ideas for new inventions ? (paying attention to the new words and trying to understand them )
Thinking outside the box
Taking another look at it
Making connections
Keeping trying
Think outside the boxTake another look at itMake connectionsKeep tryingFind out what the following ways mean.Try new ways to solve
a problem.Look at a problem in
as many ways as
possible.Try to combine new
and old ideas in as
many different ways
as possible.Have a long process
of trial and error.Read the text carefully and try to answer the questions below . (making marks under the new words)Ask the students to find the main idea of the second paragraphCreative thinking is a conscious effort to break away from old thought patterns in order to explore new possibilities .Ask the students to find the main idea of the third paragraphBy looking at a problem in as many ways as possible , some solutions that would otherwise remain invisible can be found .Ask the students to find the main idea of the fourth paragraphCombining new and old ideas in as many different ways as possible is very important for inventions .Ask the students to find the main idea of the fourth paragraphGood ideas are no accident . They are the result of a long process of trial and error .Post-ReadingTrue or False 1 Most inventors have high IQs.
2 The things we know can sometimes make
it more difficult for us to understand.
3 It’s impossible to learn how to be creative.
4 The best way to find a good solution is to
look for one good answer.
5 Inventors try to avoid failure.
6 The more ways we have of looking at a
problem, the more likely it is that we can
find a solution.
7 Most good ideas are the result of a long
process of trial and error. FFFFTTTThe new words in the text .creative /background /visible
/rephrase/allow for /reject /
get stuck//partial /break away
from/possibility /perception
/otherwise/connection/previous/aware/
be aware of /trial and error /relativity
PointsUseful expressions to be explained1.be tired of 对…感到厌倦,对…不感兴趣
be tired from 因…而疲惫
2.break away form (the police / al his friends / a habit / the Union…)
3.the possibility of … / that…4.attempt sth.
attempt to do sth.
attempt doing sth.
make an attempt to do sth.
in one’s attempt to do sth.
5. be aware of/that-clause
6. let … out 放出,放掉;泄露,说出;放大(衣服等);出租;终止,结束
7.come up with 想到或提出(答案、办法等) 8.have … in common : share interests, characteristics, etc. 有共同之处,有共同的利益、特点等 out of common 异乎寻常 in common with 像…样 9. allow for :考虑;顾及;对…做准备;体谅 allow sb. to do sth. / allow doing sth allow of sth. 允许,容许 10.get stuck 陷进去,被捆住 11.otherwise (adv.) 不然,否则;不同地;在其他方面,除此之外 12.as with : like 正如…一样 13.trial and error 反复试验,不断摸索 14.reject 拒绝,丢弃 15. attempt ,尝试,企图,试图 16.be said to do it’s said that … 据说 17.be similar to … 与…相类似 18. keep pace with… = keep up with 跟上 Grammar
The Attributive Clause
●The restrictive & non-restrictive attributive clauses
●The attributive clause & the appositive clause
●The attributive clause & the emphasis structureThe use of the relative pronouns:person(s) subject/object person(s)object person(s)/thing(s)subject/objectthing(s)subject/object person(s)/thing(s)
(of whom/which)attributiveThe use of the relative adverbs:timeadverbial of timeplace adverbial of placereasonadverbial of reasonPractice: complete the sentences with suitable relatives.
1. I know the reason ____ he came late.
2. Do you know the woman, ________ son went to
college last year?
3. The house ________ color is red is John’s.
The house, the color of which is red, is John’s.
4. This is the best film _____ I’ve ever seen.
5. That’s the town _______ he worked in 1987.
That’s the town in which he worked in 1987.
6. I have 2 brothers, _____ are both soldiers.
7. Next week, ______ you’ll spend in your
hometown ,is coming.
8. I’ve tried 2 pairs of shoes, neither of _____ fits me well.whywhosewhosethatwherewhowhichwhichNotice:
Pay more attention to the agreement between
the verb and the antecedent in person and
number in the attributive clause, and then
complete the sentences:
Those who ____ to go to the cinema must
be at the school gate by 3:30 p.m. (want)
2. He who ___________ the great wall is not
a true man. (not reach)
3. She is the only one of the girls who ____
been to Beijing. (have)
4. He is one of the boys who ____ seen the
film. (have)wantdoesn’t reachhashave
When a relative pronoun is used as a subject
in the clause, the verb must agree with the
antecedent in person and number.
(2) When the antecedent is the structure “one
of +n. (pl.)”, the verb in the clause must be plural,
agrees with the plural form. However, if there
is “the” or “the only very” before “one”, the
verb in the clause must be singular, agrees with
the word “one”.Conclusion 1:Practice: Complete the following sentences with suitable relatives:
The time ___________ I went to Tokyo is in 1982.
2. I’ll never forget the time __________ I spent at college.
3. The shop __________ I bought the book in
is big.
4. The shop _____________ I bought the book is big.
Conclusion 2: when the antecedent is a noun for time or place “when” or “where” is not always used to introduce the clause. It depends on the fun_ction of the relative word in the clause.whenwhich/thatwhich/thatwhere/in whichThe Difference Between “that” and “which”.
Complete the following sentences with “that”
or “which”.
This is the 2nd article ____ I have written
in English.
2. It is the best film _____ he has ever seen.
3. This is the very book _____ I want to read.
4. All ____ they told me surprised me.
5. They talked about the teachers and schools
_____ they had visited.thatthatthatthatthat6. Who is the comrade ______ was there?
7. There is a bed in the room _____is still vacant.
8. Our village is no longer the place _______ it
used to be.
He paid the boy $10 for washing the windows,
most of _______ hadn’t been cleaned at least
a year.
10. The weather turned out to be very good,
_______ was more than we could expect.
11. The clever boy made a hole in the wall,
through _______ he could see what was going on
inside the house.thatthatthatwhich whichwhichConclusion 3:
When the antecedent refers to thing(s), “that” is often used in the following cases:(1) After ordinal number and superlatives
(2) After the following words: all, only, little,
few, much, very, none, last, just, any(thing),
every(thing), some(thing), no(thing).
(3) After two or more antecedents, referring
to both person(s) and thing(s).
(4) After interrogative pronouns “which” or
“who”.(5) When the relative pronoun is used as a predictive
in the clause.
(6) When the main clause begins with “there be ”.
In the following cases, “which” is always used.
①After prepositions
②to introduce a non-restrictive attributive
clause.
③The whole main sentence is the “antecedent”
of the relative clause, and there is
always a comma.
Tell me the reason ____ you were late for class.
2. Who is the girl _____ is speaking there ?
3. This is Mr. Smith, _____ has something interesting to tell you.
4. The computer ________ CPU doesn’t work has to be
repaired.whythatwhowhoseFill in the blanks with suitable relatives to complete the following sentences.5. This kind of computer, _____ is well-known ,
is out of date.
6. This is just the place ___ I’ve been longing
to visit for years.
7. His mother is an engineer, ____ makes him
very proud.
8. The old man has 4 sons, three of ____ are
doctors.
whichthatwhichwhom一、从词类上区别
同位语从句前面的名词只能是idea, fact, news, hope,
belief, suggestion, proposal, word, thought, doubt,
truth, possibility, promise, order等表示抽象意义的名
词。而定语从句的先行词可以是名词、代词、主句的一部
分或整个主句。
如:
We are looking into the question whether he is worth
trusting.
我们正在调查的是他是否值得信赖的问题(同位语从句)
Word came that he had gone abroad.
据说他已经出国了。(同位语从句)The Difference Between the Attributive Clause and the
Appositive Clause The doctor whom you are looking for is in
the room.
你找的那位医生在房间里面。
(定语从句,名词the doctor作先行词)
Our team has won the game, which makes us
very happy.
(定语从句,which代表前面提到的整个句子)
His mother did all she could to help him with
his study.
他妈妈尽最大努力帮他学习。
(定语从句,代词all作先行词)二、从性质上区别
定语从句是从句对其先行词的修饰或限制,
属于形容词性从句的范畴;而同位语从句是
从句对前面抽象名词的进一步说明和解释,
属于名词性从句的范畴。如:
The news that our team has won the game
is true.
我们队赢了那场比赛的消息是真的。
(同位语从句,补充说明news的内容。)
The news (that) he told me yesterday is true.
昨天他告诉我的那个消息是真的。
(定语从句,that 从句作定语修饰news)I made a promise that if anyone set me free
I would make him very rich.
我许诺如果谁让我自由,我就让他非常富有。
(同位语从句,补充说明promise)
The mother made a promise that pleased all her
children.
妈妈做出了一个令她的孩子们高兴的许诺。
(定语从句,that从句作定语修饰promise。)三、从引导词及其在句子中的成份上区别有些引导词
如how, whether, what可以引导同位语从句,但不能
引导定语从句。如:
That question whether we need it has not been
considered.
我们是否需要它这个问题还没有考虑。(同位语从句)
I have no idea what has happened to him.
我不知道他发生了什么事。(同位语从句)
引导词that引导定语从句时,在从句中一般作主语
或宾语(指物时还可以用which代替),并且作宾语时
常常省略。That在同位语从句中仅起连接作用,不充当
任何成份,并且不能省略,也不能用which来代替。 The order that we (should) send a few people
to help the other groups was received yesterday.
我们应派几个人去帮助别的几个小组的命令昨天
已收到了。(同位语从句,是对order的具体解释,
that虽不作成份,但不能省略)
The order (that) we received yesterday was
that we (should) send a few people to help the
other groups.
我们昨天收到的命令是我们应该派几个人去帮助别
的几个小组。(定语从句,是名词order的修饰语,
that在从句中作received的宾语,可以省略)从A、B、C、D四个选项中,选出可以填入
空白处的最佳选项。
Along with the letter was his promise ____
he would visit me this coming Christmas.
A. which B. that C. what D. whether
2. Luckily, we’d brought a road map without___
we would have lost our way.
A. it B. that C. this D. which
3. There is a new problem involved in the
popularity of private cars ___road conditions need _________ .
A. that; to be improved B. which; to be improved
C. where; improving D. when; improvingBDA5. Information has been put forward ____
more middle school graduates will be
admitted into universities.
A. while B. that C. when D. as
6. The fact came up ___ specific speech sounds are
recognized by babies as young as 6 months old.
A. what B. which C. that D. whose
7. A decision was made ____ those who
wanted to get a job in the factory would not
be allowed to stay.
A. what B. when C. which D. thatBCD8. The question came up at the meeting ____
we had enough money for our research.
that B. what C. which D. whether
9. The reason ____ he is late is ____ there was
a breakdown on the railway.
A. why; why B. why; that
C. because; that D. that; becauseDB强调句型的句式结构为:“It is/was + 被强调部
分 + that/who从句”。
在强调时间、地点、原因或方式状语时,一律
用that,而不用when, why或how;
在强调主语和宾语时,如果主语和宾语指代人,
则可用who和whom来代替that,
但是从句中的人称和数要与被强调的主语和宾语
保持一致。这些都容易与定语从句混淆。The Difference Between the Attributive Clause
and the Emphasis Structure定语从句和强调句型的判断方法:若将句中的
“It is/was”和“that/who”去掉,而句子不缺成分,
结构完整,说明原句是强调句型;若句子结构不
完整,则说明原句为定语从句。
1. It was not until 1920 ____ regular radio
broadcasts began.(1995高考卷)
A. while B. which C. that D. since
2. ____ was his kindness that everyone praised
him.
A. It B. What C. So D. SuchCA3. It is the ability to do the job ____ matters not where
you come from or what you are. (2000高考卷)
A. one B. that C. what D. it
4. It was ____ he came to Macao ____ he knew what
kind of place it was.
A. that; when B. until; that
C. not until; when D. not until; that
5. ____ is a fact that English is being accepted as an
international language.
A. There B. This C. That D. ItBDD6. It was not until we came back from outside ____
out of his bed.
A. did he get B. when he got
C. that he got D. then he got
7. When was it ____ you met him in the library?
A. where B. that C. in which D. which
8. It was near the place ____ there is a bomb
____ we found the dead man.
A. where; where B. where; that
C. that; where D. that; thatCBB The order that we (should) send a few people
to help the other groups was received yesterday.
我们应派几个人去帮助别的几个小组的命令昨天
已收到了。(同位语从句,是对order的具体解释,
that虽不作成份,但不能省略)
The order (that) we received yesterday was
that we (should) send a few people to help the
other groups.
我们昨天收到的命令是我们应该派几个人去帮助别
的几个小组。(定语从句,是名词order的修饰语,
that在从句中作received的宾语,可以省略)Answers to Ex 2 on page 61:The wires that/which the machines were connected with were very old.
The wires with which the machines were connected were very old.
Leonardo da Vinci who/that painted the “Mona Lisa” was interested in both literature and science.
The pilot who/that/whom we had dinner with told us stories about his travels.
The pilot with whom we had dinner told us stories about his travels.The four ancient Chinese inventions which/that we are proud of have remained important in human history for thousands of years.
Mozart whose music is popular all over the world showed his talent for music at a very young age.
The photos are kept in the cupboard which/ that our parents left to us ten years ago.
The photos are kept in the cupboard which/ that was left by our parents ten years ago.The country which/that this news report is coming from is on the other side of the world.
The country from which this news report is coming is on the other side of the world.
从A、B、C、D四个选项中,选出可以填入
空白处的最佳选项。
Along with the letter was his promise ____
he would visit me this coming Christmas.
A. which B. that C. what D. whether
2. Luckily, we’d brought a road map without___
we would have lost our way.
A. it B. that C. this D. which
3. There is a new problem involved in the
popularity of private cars ___road conditions need _________ .
A. that; to be improved B. which; to be improved
C. where; improving D. when; improvingBDA5. Information has been put forward ____
more middle school graduates will be
admitted into universities.
A. while B. that C. when D. as
6. The fact came up ___ specific speech sounds are
recognized by babies as young as 6 months old.
A. what B. which C. that D. whose
7. A decision was made ____ those who
wanted to get a job in the factory would not
be allowed to stay.
A. what B. when C. which D. thatBCD8. The question came up at the meeting ____
we had enough money for our research.
that B. what C. which D. whether
9. The reason ____ he is late is ____ there was
a breakdown on the railway.
A. why; why B. why; that
C. because; that D. that; becauseDB强调句型的句式结构为:“It is/was + 被强调部
分 + that/who从句”。
在强调时间、地点、原因或方式状语时,一律
用that,而不用when, why或how;
在强调主语和宾语时,如果主语和宾语指代人,
则可用who和whom来代替that,
但是从句中的人称和数要与被强调的主语和宾语
保持一致。这些都容易与定语从句混淆。The Difference Between the Attributive Clause
and the Emphasis Structure定语从句和强调句型的判断方法:若将句中的
“It is/was”和“that/who”去掉,而句子不缺成分,
结构完整,说明原句是强调句型;若句子结构不
完整,则说明原句为定语从句。
1. It was not until 1920 ____ regular radio
broadcasts began.(1995高考卷)
A. while B. which C. that D. since
2. ____ was his kindness that everyone praised
him.
A. It B. What C. So D. SuchCA3. It is the ability to do the job ____ matters not where
you come from or what you are. (2000高考卷)
A. one B. that C. what D. it
4. It was ____ he came to Macao ____ he knew what
kind of place it was.
A. that; when B. until; that
C. not until; when D. not until; that
5. ____ is a fact that English is being accepted as an
international language.
A. There B. This C. That D. ItBDD6. It was not until we came back from outside ____
out of his bed.
A. did he get B. when he got
C. that he got D. then he got
7. When was it ____ you met him in the library?
A. where B. that C. in which D. which
8. It was near the place ____ there is a bomb
____ we found the dead man.
A. where; where B. where; that
C. that; where D. that; thatCBBWritingwriting Before we start writing, we should list ideas and information and think about the organization of our articles.
Step1 Computer is part of our life
Step2 The development of computer
Step 3 The way we use computers will change
