牛津英语模块3 unit3 back to the past Grammar and usage
文档属性
| 名称 | 牛津英语模块3 unit3 back to the past Grammar and usage |

|
|
| 格式 | rar | ||
| 文件大小 | 521.3KB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 牛津译林版 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2009-04-13 00:00:00 | ||
图片预览










文档简介
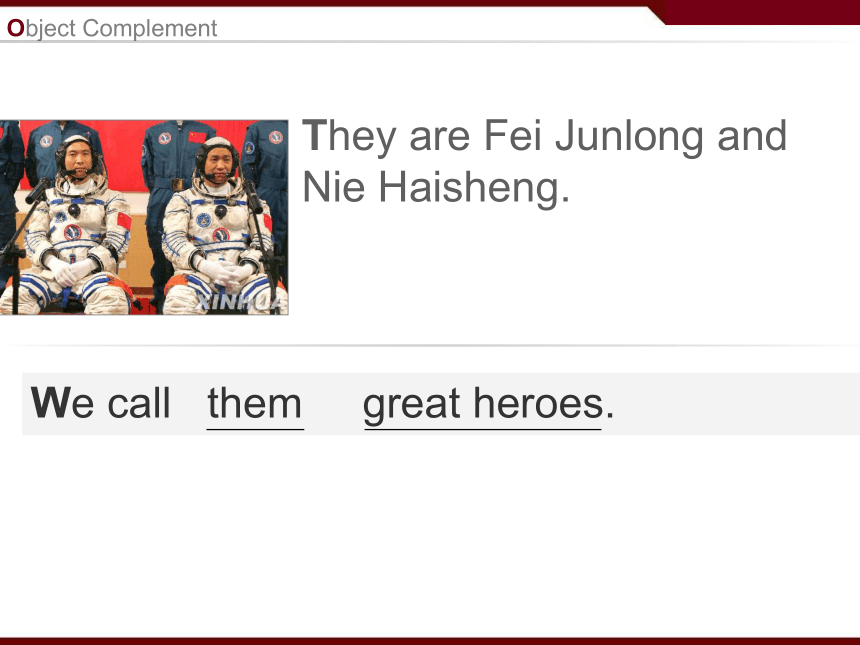
课件186张PPT。3unitBACK TO THE PASTGrammar and usageObject ComplementObject ComplementWho are they?Object ComplementThey are Fei Junlong and
Nie Haisheng.Object ComplementThey are Fei Junlong and
Nie Haisheng.We call them great heroes.Object ComplementThey are Fei Junlong and
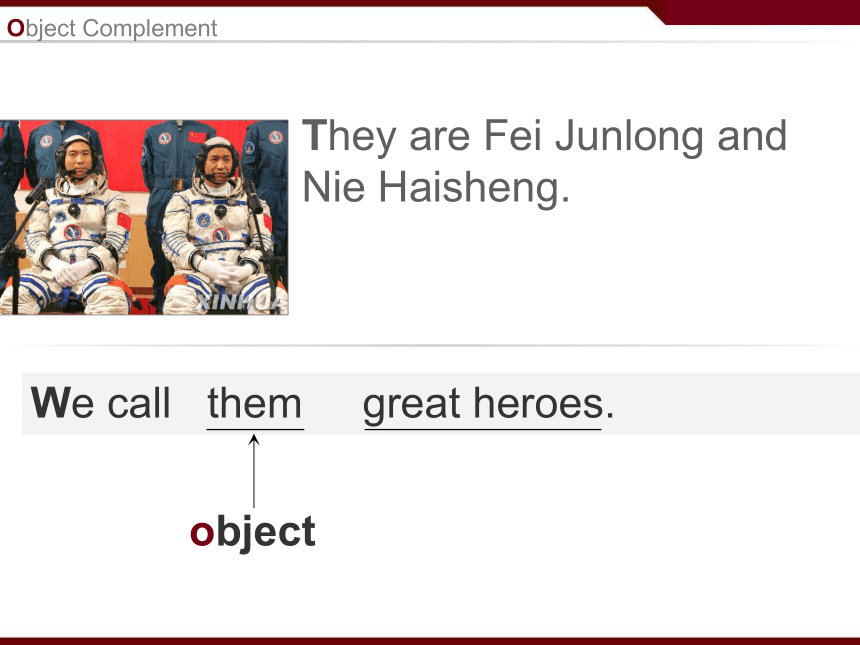
Nie Haisheng.We call them great heroes. object Object ComplementThey are Fei Junlong and
Nie Haisheng.We call them great heroes. object object complement Pay attention to the following:Pay attention to the following:1. The object complement gives more
information abut the object.Pay attention to the following:1. The object complement gives more
information abut the object.
They called the young man Great Hero.Pay attention to the following:1. The object complement gives more
information abut the object.
They called the young man Great Hero.2. An object complement always occurs in this
pattern: verb + object + object complement.
The object complement can often be a noun
phrase or an adjective.Pay attention to the following:1. The object complement gives more
information abut the object.
They called the young man Great Hero.2. An object complement always occurs in this
pattern: verb + object + object complement.
The object complement can often be a noun
phrase or an adjective.
They made Yu Tong monitor of their class.Pay attention to the following:1. The object complement gives more
information abut the object.
They called the young man Great Hero.2. An object complement always occurs in this
pattern: verb + object + object complement.
The object complement can often be a noun
phrase or an adjective.
They made Yu Tong monitor of their class.
You must keep the room clean all the time.Pay attention to the following:3. Sometimes a to-infinitive or bare
infinitive can be an object complement.Pay attention to the following:3. Sometimes a to-infinitive or bare
infinitive can be an object complement.
I’d like all of you to work still harder.Pay attention to the following:4. An object complement can be a prepositional
phrase.Pay attention to the following:4. An object complement can be a prepositional
phrase.
If you keep the new dress in hot water, the
colors will run.Pay attention to the following:4. An object complement can be a prepositional
phrase.
If you keep the new dress in hot water, the
colors will run.5. An object complement can also be a present
participle phrase or a past participle phrase.Pay attention to the following:4. An object complement can be a prepositional
phrase.
If you keep the new dress in hot water, the
colors will run.5. An object complement can also be a present
participle phrase or a past participle phrase.
The most exciting thing for the old man was
to watch the children playing in the garden.Pay attention to the following:4. An object complement can be a prepositional
phrase.
If you keep the new dress in hot water, the
colors will run.5. An object complement can also be a present
participle phrase or a past participle phrase.
The most exciting thing for the old man was
to watch the children playing in the garden.
They told me to have my car repaired as
soon as possible.Pay attention to the following:6. An object complement usually agrees with
the object in number.Pay attention to the following:6. An object complement usually agrees with
the object in number.
After that people called the boy a little hero.Summary Summary 1. The following verbs are often followed by an
object and a noun or a noun phrase as an
object complement:Summary 1. The following verbs are often followed by an
object and a noun or a noun phrase as an
object complement:
name, call, choose, elect, make,…Summary 1. The following verbs are often followed by an
object and a noun or a noun phrase as an
object complement:
name, call, choose, elect, make,…e.g.We elected John chairman of our club after
the former one retired.Summary 1. The following verbs are often followed by an
object and a noun or a noun phrase as an
object complement:
name, call, choose, elect, make,…e.g.We elected John chairman of our club after
the former one retired.
When we were working on the farm, we all
call Iron Ox.Summary 2. The following verbs are often followed by an
object and an adjective as an object
complement:Summary 2. The following verbs are often followed by an
object and an adjective as an object
complement:
make, get, keep, find, consider, …Summary 2. The following verbs are often followed by an
object and an adjective as an object
complement:
make, get, keep, find, consider, …e.g.Though he did not mean to hurt her, yet his
joke did make her angry.Summary 2. The following verbs are often followed by an
object and an adjective as an object
complement:
make, get, keep, find, consider, …e.g.Though he did not mean to hurt her, yet his
joke did make her angry.
After many years of hard work, he found it
impossible to carry on with his experiments.Summary 3. The following verbs are often followed by a
to-infinitive as an object complement:Summary 3. The following verbs are often followed by a
to-infinitive as an object complement:
ask, tell, beg, invite, order, advise, warn,
want, get, wish, expect, persuade, allow,
permit, forbid, help,…Summary 3. The following verbs are often followed by a
to-infinitive as an object complement:
ask, tell, beg, invite, order, advise, warn,
want, get, wish, expect, persuade, allow,
permit, forbid, help,…e.g.She asked me to answer the question at once.Summary 3. The following verbs are often followed by a
to-infinitive as an object complement:
ask, tell, beg, invite, order, advise, warn,
want, get, wish, expect, persuade, allow,
permit, forbid, help,…e.g.She asked me to answer the question at once.
The teacher did not allow us to talk to each
other in class.Summary 4. The following verbs are often followed by a
bare infinitive as an object complementSummary 4. The following verbs are often followed by a
bare infinitive as an object complement
have, make, let, help, see, hear, watch,
notice, find, observe, look at, listen toSummary 4. The following verbs are often followed by a
bare infinitive as an object complement
have, make, let, help, see, hear, watch,
notice, find, observe, look at, listen toe.g.In that factory, the boss always has his
workers work more than fifteen hours a day. Summary 4. The following verbs are often followed by a
bare infinitive as an object complement
have, make, let, help, see, hear, watch,
notice, find, observe, look at, listen toe.g.In that factory, the boss always has his
workers work more than fifteen hours a day.
The Most exciting thing for the old man was to
watch his grandchildren play in the garden.Summary 5. The following verbs are often followed by a
present participle as an object complement:Summary 5. The following verbs are often followed by a
present participle as an object complement:
have, keep, get, feel, see, hear, watch, find,
notice, observe,…Summary 5. The following verbs are often followed by a
present participle as an object complement:
have, keep, get, feel, see, hear, watch, find,
notice, observe,…e.g.As we got to the top of the mountain, we saw
the sun rising in the east.Summary 5. The following verbs are often followed by a
present participle as an object complement:
have, keep, get, feel, see, hear, watch, find,
notice, observe,…e.g.As we got to the top of the mountain, we saw
the sun rising in the east.
Some villagers reported that they saw the
missing boy playing near the river toward
evening.Summary 6. The following verbs are often followed by a
past participle as an object complement:Summary 6. The following verbs are often followed by a
past participle as an object complement:
have, make, get, see feel, hear, watch, find…Summary 6. The following verbs are often followed by a
past participle as an object complement:
have, make, get, see feel, hear, watch, find…e.g.When you speak English you should try your
best to make yourself understood.Summary 6. The following verbs are often followed by a
past participle as an object complement:
have, make, get, see feel, hear, watch, find…e.g.When you speak English you should try your
best to make yourself understood.
I was surprised to find my room thoroughly
cleaned and everything arranged in good
order.Please go through
Lost civilizations again
and find as many sentences
with an object complement
as you can.ExamplesSven found the remains of buildings buried
under the sand, together with a lot of treasures,
such as coins, painted pots, silk materials,
documents and wall paintings.ExamplesSven found the remains of buildings buried
under the sand, together with a lot of treasures,
such as coins, painted pots, silk materials,
documents and wall paintings.remains of buildings is the object, and
buried under the sand is the object
complement, which gives information
about the situation of the object.ExamplesWe found the ruins most interesting.ExamplesWe found the ruins most interesting.the ruins is the object, and interesting is
the object complement, which gives
information about the object.Read the next excerpt from
Ann's diary entry on page 48 and
use proper object complements to
complete it. Try to understand what
these phrases in the box mean.Please do C1 on page 108 in
your Workbook to practise
what you have learnt in this part.Either…or, neither…norYou must pay attention that either...or...,
neither…nor… can connect the coordinate
subject, verb, object and adverbial in
sentences.1. Connecting the coordinate subjects 1. Connecting the coordinate subjects Either your mother or your father, or both your
parents can come with you.1. Connecting the coordinate subjects Either your mother or your father, or both your
parents can come with you.
Either Tim or his brothers have to water the
trees every other day.1. Connecting the coordinate subjects Either your mother or your father, or both your
parents can come with you.
Either Tim or his brothers have to water the
trees every other day.
Neither your aunt nor I have any other thought
but what is the best for you?1. Connecting the coordinate subjects Either your mother or your father, or both your
parents can come with you.
Either Tim or his brothers have to water the
trees every other day.
Neither your aunt nor I have any other thought
but what is the best for you?
But neither his daughter nor his son would
listen to his suggestions.2. Connecting the coordinate objects2. Connecting the coordinate objectsAt school we may have either rice or noodles
for supper every day.2. Connecting the coordinate objectsAt school we may have either rice or noodles
for supper every day.
You may choose either physics or chemistry
as your major.2. Connecting the coordinate objectsAt school we may have either rice or noodles
for supper every day.
You may choose either physics or chemistry
as your major.
They have neither steam heat nor running
water.2. Connecting the coordinate objectsAt school we may have either rice or noodles
for supper every day.
You may choose either physics or chemistry
as your major.
They have neither steam heat nor running
water.
I won’t take a trip for I have neither the time
nor money.3. Connecting the coordinate predicates or
predicatives3. Connecting the coordinate predicates or
predicatives“Either go to the concert or stay at home.
Don’t go anywhere else,” father shouted.3. Connecting the coordinate predicates or
predicatives“Either go to the concert or stay at home.
Don’t go anywhere else,” father shouted.3. Connecting the coordinate predicates or
predicatives“Either go to the concert or stay at home.
Don’t go anywhere else,” father shouted.
The books there are either books on travel or
detective novels.3. Connecting the coordinate predicates or
predicatives“Either go to the concert or stay at home.
Don’t go anywhere else,” father shouted.
The books there are either books on travel or
detective novels.
That is neither my fault nor his.3. Connecting the coordinate predicates or
predicatives“Either go to the concert or stay at home.
Don’t go anywhere else,” father shouted.
The books there are either books on travel or
detective novels.
That is neither my fault nor his.
He was neither clever nor stupid, but good
enough at his work.3. Connecting the coordinate predicates or
predicatives“Either go to the concert or stay at home.
Don’t go anywhere else,” father shouted.
The books there are either books on travel or
detective novels.
That is neither my fault nor his.
He was neither clever nor stupid, but good
enough at his work.
One third of the men could neither read nor
write.4. Connecting the coordinate adverbials or
attributes:4. Connecting the coordinate adverbials or
attributes:We are going to return to our home town
either today or tomorrow. You may take either
the blue or the green one.4. Connecting the coordinate adverbials or
attributes:We are going to return to our home town
either today or tomorrow. You may take either
the blue or the green one.
The two men walked very fast, looking neither
to the right nor to the left.4. Connecting the coordinate adverbials or
attributes:We are going to return to our home town
either today or tomorrow. You may take either
the blue or the green one.
The two men walked very fast, looking neither
to the right nor to the left.
Paul came at the right time, neither too early
nor too late.5. Connecting the coordinate clauses:5. Connecting the coordinate clauses:Either you must improve your work, or I will
dismiss you.5. Connecting the coordinate clauses:Either you must improve your work, or I will
dismiss you.
Either you cut it out, or we shall have to wash
our hands of the whole business.例1 Not only I but Jane and Mary ______
tired of having one examination after
another.
A. is B. are C. am D. be例1 Not only I but Jane and Mary ______
tired of having one examination after
another.
A. is B. are C. am D. be析: 由“or, either…or, neither…nor,
not…but, not only… but also”连接两个
并列主语时,动词与靠近的主语保持一致。例1 Not only I but Jane and Mary ______
tired of having one examination after
another.
A. is B. are C. am D. be析: 由“or, either…or, neither…nor,
not…but, not only… but also”连接两个
并列主语时,动词与靠近的主语保持一致。______ you or he the teacher of English?
Neither my sister nor my mother ______
present at the meeting.
A. Are, was B. Is, were
C. Are, are D. Is, is e.g.______ you or he the teacher of English?
Neither my sister nor my mother ______
present at the meeting.
A. Are, was B. Is, were
C. Are, are D. Is, is e.g.Subject-verb agreement例2 A library with five thousand books
______ to the nation as a gift.
A. is offered B. has offered
C. are offered D. have offered例2 A library with five thousand books
______ to the nation as a gift.
A. is offered B. has offered
C. are offered D. have offered析: 一般说来,主语后带有with, together
with, as well as, along with, in addition to,
like, including, but, rather than, no less
than等词语时,其谓语动词随主语。The monitor as well as his classmates
was given a reward for working hard.e.g.例2 A library with five thousand books
______ to the nation as a gift.
A. is offered B. has offered
C. are offered D. have offered析: 一般说来,主语后带有with, together
with, as well as, along with, in addition to,
like, including, but, rather than, no less
than等词语时,其谓语动词随主语。The monitor as well as his classmates
was given a reward for working hard.e.g.例3 When and where to build the new
factory ______ yet.
A. is not decided B. are not decided
C. has not decided D. have not decided例3 When and where to build the new
factory ______ yet.
A. is not decided B. are not decided
C. has not decided D. have not decided析: 当when和where加不定式指的是同一
件事时,谓语动词用单数。不定式,动名
词短语或从句作主语,谓语动词用单数。Reading aloud is very important in learning
a foreign language.e.g.例3 When and where to build the new
factory ______ yet.
A. is not decided B. are not decided
C. has not decided D. have not decided析: 当when和where加不定式指的是同一
件事时,谓语动词用单数。不定式,动名
词短语或从句作主语,谓语动词用单数。Reading aloud is very important in learning
a foreign language.e.g.例4 Every boy and every girl ______ that
each day and each hour brings _____duty
A. know, their B. knows, their
C. knows, its D. know, its例4 Every boy and every girl ______ that
each day and each hour brings _____duty
A. know, their B. knows, their
C. knows, its D. know, its析:every/each/ no+单数名词+and every/
each / no+单数名词短语做主语,谓语动
词用单数。No teacher and no student agrees to have
classes on Sunday.e.g.例4 Every boy and every girl ______ that
each day and each hour brings _____duty
A. know, their B. knows, their
C. knows, its D. know, its析:every/each/ no+单数名词+and every/
each / no+单数名词短语做主语,谓语动
词用单数。No teacher and no student agrees to have
classes on Sunday.e.g.例5 We live day by day, but in the great
things, the time of days and weeks _____
so small that a day is unimportant. 07 湖南
A. is B. are
C. has been D. have been 例6 A survey of the opinions of experts __
that three hours of outdoor exercise a
week ____ good for one’s health. 07 江西
A. show; are B. shows; is
C. show; is D. shows; are例5 We live day by day, but in the great
things, the time of days and weeks _____
so small that a day is unimportant. 07 湖南
A. is B. are
C. has been D. have been 例6 A survey of the opinions of experts __
that three hours of outdoor exercise a
week ____ good for one’s health. 07 江西
A. show; are B. shows; is
C. show; is D. shows; are例5 We live day by day, but in the great
things, the time of days and weeks _____
so small that a day is unimportant. 07 湖南
A. is B. are
C. has been D. have been 例6 A survey of the opinions of experts __
that three hours of outdoor exercise a
week ____ good for one’s health. 07 江西
A. show; are B. shows; is
C. show; is D. shows; areⅠ由and连接的名词作主语时:1. 由and连接的两个不同概念的名词作主语
时,动词要用复数:Both you and I are going to attend the
meeting.When he will go to BJ and how he will go
to BJ have not been decided yet.e.g.2. 如果后面加作为插入语,谓语也用单数
形式。Black, and not Mary, was chosen
monitor.She, and not you, is going to speak at
the meeting.All work, and no play, has made you a
fool.e.g.3. 以many a或more than one修饰的单数名
词后面的谓语用单数形式,但其意义是
复数性的。Many a boy is fond of playing football.
More than one student enjoys folk-music.e.g.The boy and the girl were each given
an apple.e.g.注:在以each,every,no修饰的并列主
语中的两个名词前不能加冠词。如果并列
的两个名词前分别加定冠词变成复数概念,
此时,放在后面作同位语,动词仍用复数
形式。4. 当and连接的为同一人、事或概念时,这
时and后的名词前没有冠词,其动词用单
数:The singer and composer is coming to
our school.
Bread and butter is often served for
breakfast.
Pork and Chinese cabbage is one of my
favourite dishes.e.g.常见的由and连接的指一个概念的有:
The needle and thread, salt and water,
the folk and knife, soap and water,
iron and steel,a watch and chain,
the bread and butter, truth and honesty,
a cup and saucer(茶托)等。Ⅱ当主语后面接说明主语的 修饰词或插入语时:谓语动词的数不受修饰成分的影响,仍与
主语一致。常见的有:
with, along with, together with,as well as,
like, no less than, rather than,more than,
as much as, but, except, besides,
including等。Bamboo, like a tree, grows tall and
straight.
The house, including the garden and the
garage, was sold out.e.g.Ⅲ 当集合名词做主语时:根据句子内容,谓语动词既可是单数,也
可是复数。常用人的集合名词有:
group, class, team, family, nation, army,
audience, crowd, public, governmentMy family is a happy family. My family
all love music. / The audience was in
good order. (指整体状态). The audience
were greatly encouraged. ( 指具体的人)e.g.注:有些集合名词如people、cattle等在任
何情况下都与复数形式搭配。Ⅳ 就近原则:以连词or,either…or,nor,neither…nor,
not only…but (also)...连接的名词或代词
作主语时,谓语与其相邻的保持一致。Among the boys, one or two are able to
jump 1.6 metres.
There is a bed, a table and two chairs in
her room.e.g.Ⅴ 以某些“不定代词或
表示数量的词+of+名词”结构,
谓语形式要与of后边的名词保持一致。70 percent of the surface is covered with
water.
70 percent of the farmers have improved
their living conditions.
The rest of his journey was pleasant.
The rest of the girls are fond of music.
All of your work is well done.
All of your answers are correct.e.g.注意1. one of +复数名词+(单)谓语,如:One of the students is from the south.2. one of+复数名词+定语从句(从句动词
用复数),如: He is one of the boys who are ready to
help others.注意3. the (only) one of+名词(复数)+定语
从句,从句中谓语动词用单数,表示众多
中只有一个,如:He is the only one of the students who
comes early.4. a number of和the number ofThe number of the students in the school
is 1,250.
A number of students are waiting outside
the gate.Ⅵ “the + adj.(分词或数词)”
结构起名词作用时:如果这个结构表示的是一类人,谓语动词
用复数形式,如果这个结构表示抽象概念
(或具体的某个人),谓语用单数形式。The old are being taken good care of.
There is an old man and a young man in
the room now. The old is the father of the
young.
The unexpected was not prevented in
those days.Ⅶ 表示重量、距离、金钱、
一段时间及由one and a half修饰的
复数名词作主语时,谓语动词用单数形式:Twenty dollars isn’t enough to buy the
book.
Ten miles isn’t long.
Five times five is twenty-five.
One and a half apples is lying on the plate.练习exercise1. Do you know _____________.
A. what is the police looking for
B. what are the police looking for
C. what the police are looking for
D. what the police is looking for1. Do you know _____________.
A. what is the police looking for
B. what are the police looking for
C. what the police are looking for
D. what the police is looking for2. ____he ____I finished the experiment?
A. Have neither/nor B. Has neither/nor
C. Have neither/or D. Have either /or2. ____he ____I finished the experiment?
A. Have neither/nor B. Has neither/nor
C. Have neither/or D. Have either /or3. The old ____ well looked after by the
government in China.
A. is B. are
C. has been D. was3. The old ____ well looked after by the
government in China.
A. is B. are
C. has been D. was4. The secretary and manager _____ very
busy now.
A. is B. are
C. has been D. were4. The secretary and manager _____ very
busy now.
A. is B. are
C. has been D. were5. Both the secretary and the manager
________ agreed to attend the meeting.
A. has B. have
C. are D. is 5. Both the secretary and the manager
________ agreed to attend the meeting.
A. has B. have
C. are D. is 6. During the holidays every train and ship
______ crowded.
A. are B. were
C. was D. has6. During the holidays every train and ship
______ crowded.
A. are B. were
C. was D. has7. Tom as well as two of his classmates
_____ invited to the party.
A. was B. were
C. have been D. had been7. Tom as well as two of his classmates
_____ invited to the party.
A. was B. were
C. have been D. had been8. Most of his spare time _____spent in
reading.
A. are B. were
C. was D. have been8. Most of his spare time _____spent in
reading.
A. are B. were
C. was D. have been9. Ten thousand dollars ______ quite a
large sum.
A. are B. is
C. has D. have9. Ten thousand dollars ______ quite a
large sum.
A. are B. is
C. has D. have10. About 20 percent of the work ______
done yesterday.
A. are B. is
C. were D. was10. About 20 percent of the work ______
done yesterday.
A. are B. is
C. were D. was11. The United States _____ founded in
1776.
A. was B. is
C. were D. are11. The United States _____ founded in
1776.
A. was B. is
C. were D. are12. This pair of shoes _____ made in our
factory.
A. is B. are
C. have been D. had been12. This pair of shoes _____ made in our
factory.
A. is B. are
C. have been D. had been13. No one except my parents ________
anything about it.
A. know B. knows
C. is knowing D. have known13. No one except my parents ________
anything about it.
A. know B. knows
C. is knowing D. have known14. A number of students ______ from
the south.
A. are B. is
C. have D. has14. A number of students ______ from
the south.
A. are B. is
C. have D. has15. The number of students from the
south _____ small.
A. are B. is
C. have D. has15. The number of students from the
south _____ small.
A. are B. is
C. have D. has16. John is the only one of the students
in our class who ____ to school on foot.
A. go B. goes
C. have gone D. are going16. John is the only one of the students
in our class who ____ to school on foot.
A. go B. goes
C. have gone D. are going17. It is not I who ______ wrong.
A. is B. are
C. am D. has been17. It is not I who ______ wrong.
A. is B. are
C. am D. has been18. He said that his family ____ all very
well.
A. are B. were
C. is D. was 18. He said that his family ____ all very
well.
A. are B. were
C. is D. was 19. One and a half apples _______ on
the table.
A. is leaving B. is left
C. are left D. left19. One and a half apples _______ on
the table.
A. is leaving B. is left
C. are left D. left20. Where ____ that five pounds I lent
you?
A. is B. have
C. was D. were20. Where ____ that five pounds I lent
you?
A. is B. have
C. was D. were21. " I " ____the ninth letter of the English
alphabet.
A. are B. be
C. is D. am21. " I " ____the ninth letter of the English
alphabet.
A. are B. be
C. is D. am22. Six times seven ______ forty-two.
A. are B. is
C. have D. was22. Six times seven ______ forty-two.
A. are B. is
C. have D. was23. The United States_____made up of
50 states, one of which______Kentucky.
A. is/are B. is/is
C. are/is D. are/are23. The United States_____made up of
50 states, one of which______Kentucky.
A. is/are B. is/is
C. are/is D. are/are24. The population of the city__increasing
fast.
A. were B. be
C. is D. are24. The population of the city__increasing
fast.
A. were B. be
C. is D. are25. One third of the population here____
workers.
A. is B. have
C. be D. are25. One third of the population here____
workers.
A. is B. have
C. be D. are26. Now the police ____ searching the
town for the lost child.
A. was B. were
C. is D. are26. Now the police ____ searching the
town for the lost child.
A. was B. were
C. is D. are27. Two of them will go first, the rest ____
to stay.
A. is B. are
C. used D. have27. Two of them will go first, the rest ____
to stay.
A. is B. are
C. used D. have28. He was the one of the students who
______ praised at the meeting.
A. was B. were
C. is D. are 28. He was the one of the students who
______ praised at the meeting.
A. was B. were
C. is D. are 29. The scientist and professor ____ left
for Russia.
A. have B. has
C. is D. are29. The scientist and professor ____ left
for Russia.
A. have B. has
C. is D. are30. Many a boy ______ made such a
funny experiment.
A. have B. are
C. has D. is 30. Many a boy ______ made such a
funny experiment.
A. have B. are
C. has D. is 31. Every means _______ been tried
since then.
A. has B. were
C. was D. has been31. Every means _______ been tried
since then.
A. has B. were
C. was D. has beenRead Part A on page 51. It is another of
Ann's diary entries. Try your best to
understand the article and choose the
correct verb forms. Then go through
Part B on page 51. It is a letter in a local
newspaper. Read the letter and finish the
exercise individually, using the correct
forms of the given verbs.
Nie Haisheng.Object ComplementThey are Fei Junlong and
Nie Haisheng.We call them great heroes.Object ComplementThey are Fei Junlong and
Nie Haisheng.We call them great heroes. object Object ComplementThey are Fei Junlong and
Nie Haisheng.We call them great heroes. object object complement Pay attention to the following:Pay attention to the following:1. The object complement gives more
information abut the object.Pay attention to the following:1. The object complement gives more
information abut the object.
They called the young man Great Hero.Pay attention to the following:1. The object complement gives more
information abut the object.
They called the young man Great Hero.2. An object complement always occurs in this
pattern: verb + object + object complement.
The object complement can often be a noun
phrase or an adjective.Pay attention to the following:1. The object complement gives more
information abut the object.
They called the young man Great Hero.2. An object complement always occurs in this
pattern: verb + object + object complement.
The object complement can often be a noun
phrase or an adjective.
They made Yu Tong monitor of their class.Pay attention to the following:1. The object complement gives more
information abut the object.
They called the young man Great Hero.2. An object complement always occurs in this
pattern: verb + object + object complement.
The object complement can often be a noun
phrase or an adjective.
They made Yu Tong monitor of their class.
You must keep the room clean all the time.Pay attention to the following:3. Sometimes a to-infinitive or bare
infinitive can be an object complement.Pay attention to the following:3. Sometimes a to-infinitive or bare
infinitive can be an object complement.
I’d like all of you to work still harder.Pay attention to the following:4. An object complement can be a prepositional
phrase.Pay attention to the following:4. An object complement can be a prepositional
phrase.
If you keep the new dress in hot water, the
colors will run.Pay attention to the following:4. An object complement can be a prepositional
phrase.
If you keep the new dress in hot water, the
colors will run.5. An object complement can also be a present
participle phrase or a past participle phrase.Pay attention to the following:4. An object complement can be a prepositional
phrase.
If you keep the new dress in hot water, the
colors will run.5. An object complement can also be a present
participle phrase or a past participle phrase.
The most exciting thing for the old man was
to watch the children playing in the garden.Pay attention to the following:4. An object complement can be a prepositional
phrase.
If you keep the new dress in hot water, the
colors will run.5. An object complement can also be a present
participle phrase or a past participle phrase.
The most exciting thing for the old man was
to watch the children playing in the garden.
They told me to have my car repaired as
soon as possible.Pay attention to the following:6. An object complement usually agrees with
the object in number.Pay attention to the following:6. An object complement usually agrees with
the object in number.
After that people called the boy a little hero.Summary Summary 1. The following verbs are often followed by an
object and a noun or a noun phrase as an
object complement:Summary 1. The following verbs are often followed by an
object and a noun or a noun phrase as an
object complement:
name, call, choose, elect, make,…Summary 1. The following verbs are often followed by an
object and a noun or a noun phrase as an
object complement:
name, call, choose, elect, make,…e.g.We elected John chairman of our club after
the former one retired.Summary 1. The following verbs are often followed by an
object and a noun or a noun phrase as an
object complement:
name, call, choose, elect, make,…e.g.We elected John chairman of our club after
the former one retired.
When we were working on the farm, we all
call Iron Ox.Summary 2. The following verbs are often followed by an
object and an adjective as an object
complement:Summary 2. The following verbs are often followed by an
object and an adjective as an object
complement:
make, get, keep, find, consider, …Summary 2. The following verbs are often followed by an
object and an adjective as an object
complement:
make, get, keep, find, consider, …e.g.Though he did not mean to hurt her, yet his
joke did make her angry.Summary 2. The following verbs are often followed by an
object and an adjective as an object
complement:
make, get, keep, find, consider, …e.g.Though he did not mean to hurt her, yet his
joke did make her angry.
After many years of hard work, he found it
impossible to carry on with his experiments.Summary 3. The following verbs are often followed by a
to-infinitive as an object complement:Summary 3. The following verbs are often followed by a
to-infinitive as an object complement:
ask, tell, beg, invite, order, advise, warn,
want, get, wish, expect, persuade, allow,
permit, forbid, help,…Summary 3. The following verbs are often followed by a
to-infinitive as an object complement:
ask, tell, beg, invite, order, advise, warn,
want, get, wish, expect, persuade, allow,
permit, forbid, help,…e.g.She asked me to answer the question at once.Summary 3. The following verbs are often followed by a
to-infinitive as an object complement:
ask, tell, beg, invite, order, advise, warn,
want, get, wish, expect, persuade, allow,
permit, forbid, help,…e.g.She asked me to answer the question at once.
The teacher did not allow us to talk to each
other in class.Summary 4. The following verbs are often followed by a
bare infinitive as an object complementSummary 4. The following verbs are often followed by a
bare infinitive as an object complement
have, make, let, help, see, hear, watch,
notice, find, observe, look at, listen toSummary 4. The following verbs are often followed by a
bare infinitive as an object complement
have, make, let, help, see, hear, watch,
notice, find, observe, look at, listen toe.g.In that factory, the boss always has his
workers work more than fifteen hours a day. Summary 4. The following verbs are often followed by a
bare infinitive as an object complement
have, make, let, help, see, hear, watch,
notice, find, observe, look at, listen toe.g.In that factory, the boss always has his
workers work more than fifteen hours a day.
The Most exciting thing for the old man was to
watch his grandchildren play in the garden.Summary 5. The following verbs are often followed by a
present participle as an object complement:Summary 5. The following verbs are often followed by a
present participle as an object complement:
have, keep, get, feel, see, hear, watch, find,
notice, observe,…Summary 5. The following verbs are often followed by a
present participle as an object complement:
have, keep, get, feel, see, hear, watch, find,
notice, observe,…e.g.As we got to the top of the mountain, we saw
the sun rising in the east.Summary 5. The following verbs are often followed by a
present participle as an object complement:
have, keep, get, feel, see, hear, watch, find,
notice, observe,…e.g.As we got to the top of the mountain, we saw
the sun rising in the east.
Some villagers reported that they saw the
missing boy playing near the river toward
evening.Summary 6. The following verbs are often followed by a
past participle as an object complement:Summary 6. The following verbs are often followed by a
past participle as an object complement:
have, make, get, see feel, hear, watch, find…Summary 6. The following verbs are often followed by a
past participle as an object complement:
have, make, get, see feel, hear, watch, find…e.g.When you speak English you should try your
best to make yourself understood.Summary 6. The following verbs are often followed by a
past participle as an object complement:
have, make, get, see feel, hear, watch, find…e.g.When you speak English you should try your
best to make yourself understood.
I was surprised to find my room thoroughly
cleaned and everything arranged in good
order.Please go through
Lost civilizations again
and find as many sentences
with an object complement
as you can.ExamplesSven found the remains of buildings buried
under the sand, together with a lot of treasures,
such as coins, painted pots, silk materials,
documents and wall paintings.ExamplesSven found the remains of buildings buried
under the sand, together with a lot of treasures,
such as coins, painted pots, silk materials,
documents and wall paintings.remains of buildings is the object, and
buried under the sand is the object
complement, which gives information
about the situation of the object.ExamplesWe found the ruins most interesting.ExamplesWe found the ruins most interesting.the ruins is the object, and interesting is
the object complement, which gives
information about the object.Read the next excerpt from
Ann's diary entry on page 48 and
use proper object complements to
complete it. Try to understand what
these phrases in the box mean.Please do C1 on page 108 in
your Workbook to practise
what you have learnt in this part.Either…or, neither…norYou must pay attention that either...or...,
neither…nor… can connect the coordinate
subject, verb, object and adverbial in
sentences.1. Connecting the coordinate subjects 1. Connecting the coordinate subjects Either your mother or your father, or both your
parents can come with you.1. Connecting the coordinate subjects Either your mother or your father, or both your
parents can come with you.
Either Tim or his brothers have to water the
trees every other day.1. Connecting the coordinate subjects Either your mother or your father, or both your
parents can come with you.
Either Tim or his brothers have to water the
trees every other day.
Neither your aunt nor I have any other thought
but what is the best for you?1. Connecting the coordinate subjects Either your mother or your father, or both your
parents can come with you.
Either Tim or his brothers have to water the
trees every other day.
Neither your aunt nor I have any other thought
but what is the best for you?
But neither his daughter nor his son would
listen to his suggestions.2. Connecting the coordinate objects2. Connecting the coordinate objectsAt school we may have either rice or noodles
for supper every day.2. Connecting the coordinate objectsAt school we may have either rice or noodles
for supper every day.
You may choose either physics or chemistry
as your major.2. Connecting the coordinate objectsAt school we may have either rice or noodles
for supper every day.
You may choose either physics or chemistry
as your major.
They have neither steam heat nor running
water.2. Connecting the coordinate objectsAt school we may have either rice or noodles
for supper every day.
You may choose either physics or chemistry
as your major.
They have neither steam heat nor running
water.
I won’t take a trip for I have neither the time
nor money.3. Connecting the coordinate predicates or
predicatives3. Connecting the coordinate predicates or
predicatives“Either go to the concert or stay at home.
Don’t go anywhere else,” father shouted.3. Connecting the coordinate predicates or
predicatives“Either go to the concert or stay at home.
Don’t go anywhere else,” father shouted.3. Connecting the coordinate predicates or
predicatives“Either go to the concert or stay at home.
Don’t go anywhere else,” father shouted.
The books there are either books on travel or
detective novels.3. Connecting the coordinate predicates or
predicatives“Either go to the concert or stay at home.
Don’t go anywhere else,” father shouted.
The books there are either books on travel or
detective novels.
That is neither my fault nor his.3. Connecting the coordinate predicates or
predicatives“Either go to the concert or stay at home.
Don’t go anywhere else,” father shouted.
The books there are either books on travel or
detective novels.
That is neither my fault nor his.
He was neither clever nor stupid, but good
enough at his work.3. Connecting the coordinate predicates or
predicatives“Either go to the concert or stay at home.
Don’t go anywhere else,” father shouted.
The books there are either books on travel or
detective novels.
That is neither my fault nor his.
He was neither clever nor stupid, but good
enough at his work.
One third of the men could neither read nor
write.4. Connecting the coordinate adverbials or
attributes:4. Connecting the coordinate adverbials or
attributes:We are going to return to our home town
either today or tomorrow. You may take either
the blue or the green one.4. Connecting the coordinate adverbials or
attributes:We are going to return to our home town
either today or tomorrow. You may take either
the blue or the green one.
The two men walked very fast, looking neither
to the right nor to the left.4. Connecting the coordinate adverbials or
attributes:We are going to return to our home town
either today or tomorrow. You may take either
the blue or the green one.
The two men walked very fast, looking neither
to the right nor to the left.
Paul came at the right time, neither too early
nor too late.5. Connecting the coordinate clauses:5. Connecting the coordinate clauses:Either you must improve your work, or I will
dismiss you.5. Connecting the coordinate clauses:Either you must improve your work, or I will
dismiss you.
Either you cut it out, or we shall have to wash
our hands of the whole business.例1 Not only I but Jane and Mary ______
tired of having one examination after
another.
A. is B. are C. am D. be例1 Not only I but Jane and Mary ______
tired of having one examination after
another.
A. is B. are C. am D. be析: 由“or, either…or, neither…nor,
not…but, not only… but also”连接两个
并列主语时,动词与靠近的主语保持一致。例1 Not only I but Jane and Mary ______
tired of having one examination after
another.
A. is B. are C. am D. be析: 由“or, either…or, neither…nor,
not…but, not only… but also”连接两个
并列主语时,动词与靠近的主语保持一致。______ you or he the teacher of English?
Neither my sister nor my mother ______
present at the meeting.
A. Are, was B. Is, were
C. Are, are D. Is, is e.g.______ you or he the teacher of English?
Neither my sister nor my mother ______
present at the meeting.
A. Are, was B. Is, were
C. Are, are D. Is, is e.g.Subject-verb agreement例2 A library with five thousand books
______ to the nation as a gift.
A. is offered B. has offered
C. are offered D. have offered例2 A library with five thousand books
______ to the nation as a gift.
A. is offered B. has offered
C. are offered D. have offered析: 一般说来,主语后带有with, together
with, as well as, along with, in addition to,
like, including, but, rather than, no less
than等词语时,其谓语动词随主语。The monitor as well as his classmates
was given a reward for working hard.e.g.例2 A library with five thousand books
______ to the nation as a gift.
A. is offered B. has offered
C. are offered D. have offered析: 一般说来,主语后带有with, together
with, as well as, along with, in addition to,
like, including, but, rather than, no less
than等词语时,其谓语动词随主语。The monitor as well as his classmates
was given a reward for working hard.e.g.例3 When and where to build the new
factory ______ yet.
A. is not decided B. are not decided
C. has not decided D. have not decided例3 When and where to build the new
factory ______ yet.
A. is not decided B. are not decided
C. has not decided D. have not decided析: 当when和where加不定式指的是同一
件事时,谓语动词用单数。不定式,动名
词短语或从句作主语,谓语动词用单数。Reading aloud is very important in learning
a foreign language.e.g.例3 When and where to build the new
factory ______ yet.
A. is not decided B. are not decided
C. has not decided D. have not decided析: 当when和where加不定式指的是同一
件事时,谓语动词用单数。不定式,动名
词短语或从句作主语,谓语动词用单数。Reading aloud is very important in learning
a foreign language.e.g.例4 Every boy and every girl ______ that
each day and each hour brings _____duty
A. know, their B. knows, their
C. knows, its D. know, its例4 Every boy and every girl ______ that
each day and each hour brings _____duty
A. know, their B. knows, their
C. knows, its D. know, its析:every/each/ no+单数名词+and every/
each / no+单数名词短语做主语,谓语动
词用单数。No teacher and no student agrees to have
classes on Sunday.e.g.例4 Every boy and every girl ______ that
each day and each hour brings _____duty
A. know, their B. knows, their
C. knows, its D. know, its析:every/each/ no+单数名词+and every/
each / no+单数名词短语做主语,谓语动
词用单数。No teacher and no student agrees to have
classes on Sunday.e.g.例5 We live day by day, but in the great
things, the time of days and weeks _____
so small that a day is unimportant. 07 湖南
A. is B. are
C. has been D. have been 例6 A survey of the opinions of experts __
that three hours of outdoor exercise a
week ____ good for one’s health. 07 江西
A. show; are B. shows; is
C. show; is D. shows; are例5 We live day by day, but in the great
things, the time of days and weeks _____
so small that a day is unimportant. 07 湖南
A. is B. are
C. has been D. have been 例6 A survey of the opinions of experts __
that three hours of outdoor exercise a
week ____ good for one’s health. 07 江西
A. show; are B. shows; is
C. show; is D. shows; are例5 We live day by day, but in the great
things, the time of days and weeks _____
so small that a day is unimportant. 07 湖南
A. is B. are
C. has been D. have been 例6 A survey of the opinions of experts __
that three hours of outdoor exercise a
week ____ good for one’s health. 07 江西
A. show; are B. shows; is
C. show; is D. shows; areⅠ由and连接的名词作主语时:1. 由and连接的两个不同概念的名词作主语
时,动词要用复数:Both you and I are going to attend the
meeting.When he will go to BJ and how he will go
to BJ have not been decided yet.e.g.2. 如果后面加作为插入语,谓语也用单数
形式。Black, and not Mary, was chosen
monitor.She, and not you, is going to speak at
the meeting.All work, and no play, has made you a
fool.e.g.3. 以many a或more than one修饰的单数名
词后面的谓语用单数形式,但其意义是
复数性的。Many a boy is fond of playing football.
More than one student enjoys folk-music.e.g.The boy and the girl were each given
an apple.e.g.注:在以each,every,no修饰的并列主
语中的两个名词前不能加冠词。如果并列
的两个名词前分别加定冠词变成复数概念,
此时,放在后面作同位语,动词仍用复数
形式。4. 当and连接的为同一人、事或概念时,这
时and后的名词前没有冠词,其动词用单
数:The singer and composer is coming to
our school.
Bread and butter is often served for
breakfast.
Pork and Chinese cabbage is one of my
favourite dishes.e.g.常见的由and连接的指一个概念的有:
The needle and thread, salt and water,
the folk and knife, soap and water,
iron and steel,a watch and chain,
the bread and butter, truth and honesty,
a cup and saucer(茶托)等。Ⅱ当主语后面接说明主语的 修饰词或插入语时:谓语动词的数不受修饰成分的影响,仍与
主语一致。常见的有:
with, along with, together with,as well as,
like, no less than, rather than,more than,
as much as, but, except, besides,
including等。Bamboo, like a tree, grows tall and
straight.
The house, including the garden and the
garage, was sold out.e.g.Ⅲ 当集合名词做主语时:根据句子内容,谓语动词既可是单数,也
可是复数。常用人的集合名词有:
group, class, team, family, nation, army,
audience, crowd, public, governmentMy family is a happy family. My family
all love music. / The audience was in
good order. (指整体状态). The audience
were greatly encouraged. ( 指具体的人)e.g.注:有些集合名词如people、cattle等在任
何情况下都与复数形式搭配。Ⅳ 就近原则:以连词or,either…or,nor,neither…nor,
not only…but (also)...连接的名词或代词
作主语时,谓语与其相邻的保持一致。Among the boys, one or two are able to
jump 1.6 metres.
There is a bed, a table and two chairs in
her room.e.g.Ⅴ 以某些“不定代词或
表示数量的词+of+名词”结构,
谓语形式要与of后边的名词保持一致。70 percent of the surface is covered with
water.
70 percent of the farmers have improved
their living conditions.
The rest of his journey was pleasant.
The rest of the girls are fond of music.
All of your work is well done.
All of your answers are correct.e.g.注意1. one of +复数名词+(单)谓语,如:One of the students is from the south.2. one of+复数名词+定语从句(从句动词
用复数),如: He is one of the boys who are ready to
help others.注意3. the (only) one of+名词(复数)+定语
从句,从句中谓语动词用单数,表示众多
中只有一个,如:He is the only one of the students who
comes early.4. a number of和the number ofThe number of the students in the school
is 1,250.
A number of students are waiting outside
the gate.Ⅵ “the + adj.(分词或数词)”
结构起名词作用时:如果这个结构表示的是一类人,谓语动词
用复数形式,如果这个结构表示抽象概念
(或具体的某个人),谓语用单数形式。The old are being taken good care of.
There is an old man and a young man in
the room now. The old is the father of the
young.
The unexpected was not prevented in
those days.Ⅶ 表示重量、距离、金钱、
一段时间及由one and a half修饰的
复数名词作主语时,谓语动词用单数形式:Twenty dollars isn’t enough to buy the
book.
Ten miles isn’t long.
Five times five is twenty-five.
One and a half apples is lying on the plate.练习exercise1. Do you know _____________.
A. what is the police looking for
B. what are the police looking for
C. what the police are looking for
D. what the police is looking for1. Do you know _____________.
A. what is the police looking for
B. what are the police looking for
C. what the police are looking for
D. what the police is looking for2. ____he ____I finished the experiment?
A. Have neither/nor B. Has neither/nor
C. Have neither/or D. Have either /or2. ____he ____I finished the experiment?
A. Have neither/nor B. Has neither/nor
C. Have neither/or D. Have either /or3. The old ____ well looked after by the
government in China.
A. is B. are
C. has been D. was3. The old ____ well looked after by the
government in China.
A. is B. are
C. has been D. was4. The secretary and manager _____ very
busy now.
A. is B. are
C. has been D. were4. The secretary and manager _____ very
busy now.
A. is B. are
C. has been D. were5. Both the secretary and the manager
________ agreed to attend the meeting.
A. has B. have
C. are D. is 5. Both the secretary and the manager
________ agreed to attend the meeting.
A. has B. have
C. are D. is 6. During the holidays every train and ship
______ crowded.
A. are B. were
C. was D. has6. During the holidays every train and ship
______ crowded.
A. are B. were
C. was D. has7. Tom as well as two of his classmates
_____ invited to the party.
A. was B. were
C. have been D. had been7. Tom as well as two of his classmates
_____ invited to the party.
A. was B. were
C. have been D. had been8. Most of his spare time _____spent in
reading.
A. are B. were
C. was D. have been8. Most of his spare time _____spent in
reading.
A. are B. were
C. was D. have been9. Ten thousand dollars ______ quite a
large sum.
A. are B. is
C. has D. have9. Ten thousand dollars ______ quite a
large sum.
A. are B. is
C. has D. have10. About 20 percent of the work ______
done yesterday.
A. are B. is
C. were D. was10. About 20 percent of the work ______
done yesterday.
A. are B. is
C. were D. was11. The United States _____ founded in
1776.
A. was B. is
C. were D. are11. The United States _____ founded in
1776.
A. was B. is
C. were D. are12. This pair of shoes _____ made in our
factory.
A. is B. are
C. have been D. had been12. This pair of shoes _____ made in our
factory.
A. is B. are
C. have been D. had been13. No one except my parents ________
anything about it.
A. know B. knows
C. is knowing D. have known13. No one except my parents ________
anything about it.
A. know B. knows
C. is knowing D. have known14. A number of students ______ from
the south.
A. are B. is
C. have D. has14. A number of students ______ from
the south.
A. are B. is
C. have D. has15. The number of students from the
south _____ small.
A. are B. is
C. have D. has15. The number of students from the
south _____ small.
A. are B. is
C. have D. has16. John is the only one of the students
in our class who ____ to school on foot.
A. go B. goes
C. have gone D. are going16. John is the only one of the students
in our class who ____ to school on foot.
A. go B. goes
C. have gone D. are going17. It is not I who ______ wrong.
A. is B. are
C. am D. has been17. It is not I who ______ wrong.
A. is B. are
C. am D. has been18. He said that his family ____ all very
well.
A. are B. were
C. is D. was 18. He said that his family ____ all very
well.
A. are B. were
C. is D. was 19. One and a half apples _______ on
the table.
A. is leaving B. is left
C. are left D. left19. One and a half apples _______ on
the table.
A. is leaving B. is left
C. are left D. left20. Where ____ that five pounds I lent
you?
A. is B. have
C. was D. were20. Where ____ that five pounds I lent
you?
A. is B. have
C. was D. were21. " I " ____the ninth letter of the English
alphabet.
A. are B. be
C. is D. am21. " I " ____the ninth letter of the English
alphabet.
A. are B. be
C. is D. am22. Six times seven ______ forty-two.
A. are B. is
C. have D. was22. Six times seven ______ forty-two.
A. are B. is
C. have D. was23. The United States_____made up of
50 states, one of which______Kentucky.
A. is/are B. is/is
C. are/is D. are/are23. The United States_____made up of
50 states, one of which______Kentucky.
A. is/are B. is/is
C. are/is D. are/are24. The population of the city__increasing
fast.
A. were B. be
C. is D. are24. The population of the city__increasing
fast.
A. were B. be
C. is D. are25. One third of the population here____
workers.
A. is B. have
C. be D. are25. One third of the population here____
workers.
A. is B. have
C. be D. are26. Now the police ____ searching the
town for the lost child.
A. was B. were
C. is D. are26. Now the police ____ searching the
town for the lost child.
A. was B. were
C. is D. are27. Two of them will go first, the rest ____
to stay.
A. is B. are
C. used D. have27. Two of them will go first, the rest ____
to stay.
A. is B. are
C. used D. have28. He was the one of the students who
______ praised at the meeting.
A. was B. were
C. is D. are 28. He was the one of the students who
______ praised at the meeting.
A. was B. were
C. is D. are 29. The scientist and professor ____ left
for Russia.
A. have B. has
C. is D. are29. The scientist and professor ____ left
for Russia.
A. have B. has
C. is D. are30. Many a boy ______ made such a
funny experiment.
A. have B. are
C. has D. is 30. Many a boy ______ made such a
funny experiment.
A. have B. are
C. has D. is 31. Every means _______ been tried
since then.
A. has B. were
C. was D. has been31. Every means _______ been tried
since then.
A. has B. were
C. was D. has beenRead Part A on page 51. It is another of
Ann's diary entries. Try your best to
understand the article and choose the
correct verb forms. Then go through
Part B on page 51. It is a letter in a local
newspaper. Read the letter and finish the
exercise individually, using the correct
forms of the given verbs.
