Module 3 The Violence of Nature 教案-grammar(外研版必修3)
文档属性
| 名称 | Module 3 The Violence of Nature 教案-grammar(外研版必修3) |  | |
| 格式 | rar | ||
| 文件大小 | 26.6KB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 外研版 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2009-07-14 17:38:00 | ||
图片预览

文档简介
本资料来自于资源最齐全的21世纪教育网www.21cnjy.com
Module 3 The Violence of Nature-Grammar
Grammar—教案
■Goals
●To learn about the past perfect passive and indirect speech
■Procedures
Step 1: Learning about the past perfect passive
Active Passive
They had given us visas for three months. We had been given visas for three months.
Step 2: Making sentences with the past perfect passive
1. A rotating column of air from a thunderstorm to the ground had been discovered before the fireman arrived.
2. The most violent tornado had been observed then.
3. The wallet had been picked up and handed in before the owner found it missing.
4. By the time the fire engines arrived the fire had been put down.
5. By the time he returned home the house had been destroyed.
6. The map had been left inside exactly where it was when we came into the room.
7. The east coast of the US had been affected greatly before the rescue arrived.
8. The city had been hit three times by the earthquake before the people moved out of it.
9. The man had been buried for five days when he was located.
10. He had been killed before we found him in the room.
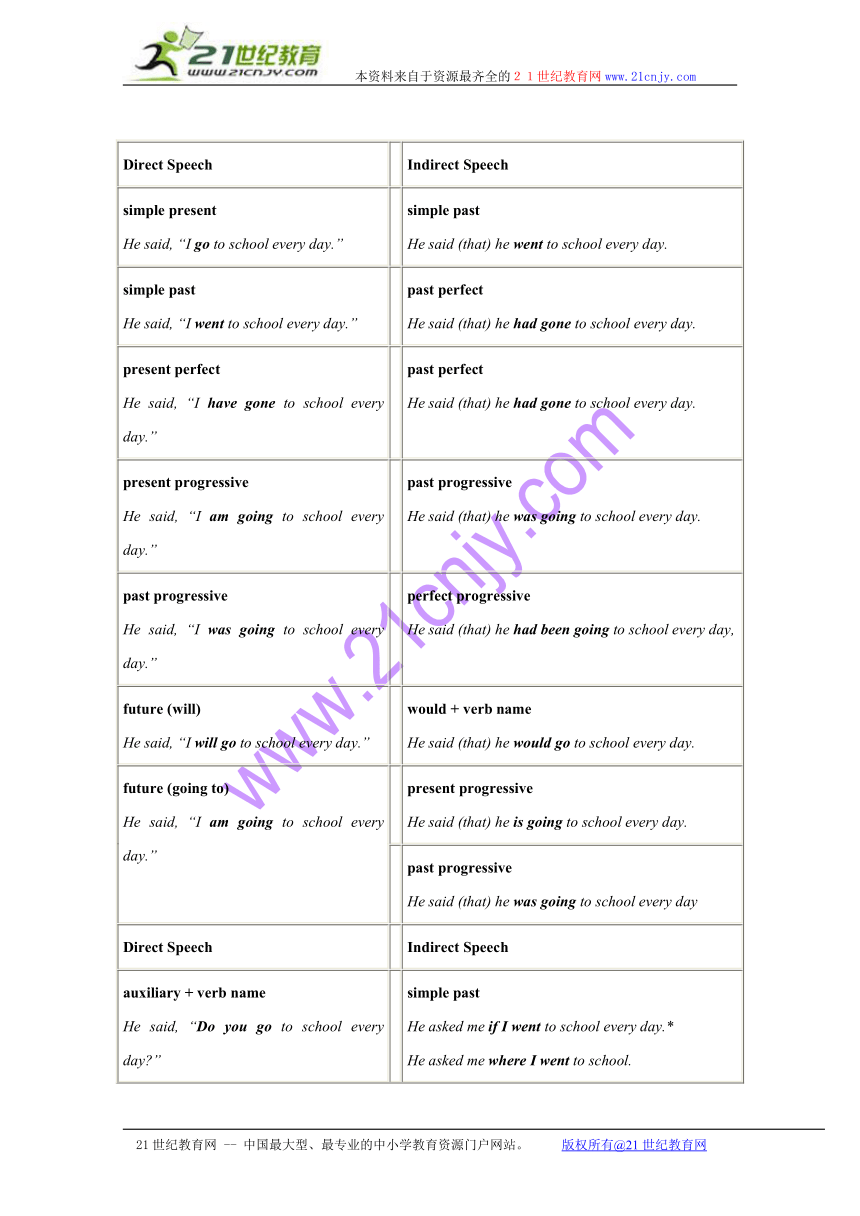
Step 3: Learning about indirect speech
When using indirect or reported speech, the form changes. Usually indirect speech is introduced by the verb said, as in I said, Bill said, or they said.
Direct Speech Indirect Speech
simple present
He said, “I go to school every day.” simple past
He said (that) he went to school every day.
simple past
He said, “I went to school every day.” past perfect
He said (that) he had gone to school every day.
present perfect
He said, “I have gone to school every day.” past perfect
He said (that) he had gone to school every day.
present progressive
He said, “I am going to school every day.” past progressive
He said (that) he was going to school every day.
past progressive
He said, “I was going to school every day.” perfect progressive
He said (that) he had been going to school every day,
future (will)
He said, “I will go to school every day.” would + verb name
He said (that) he would go to school every day.
future (going to)
He said, “I am going to school every day.” present progressive
He said (that) he is going to school every day.
past progressive
He said (that) he was going to school every day
Direct Speech Indirect Speech
auxiliary + verb name
He said, “Do you go to school every day ”
He said, “Where do you go to school ” simple past
He asked me if I went to school every day.*
He asked me where I went to school.
imperative
He said, “Go to school every day.” infinitive
He said to go to school every day.
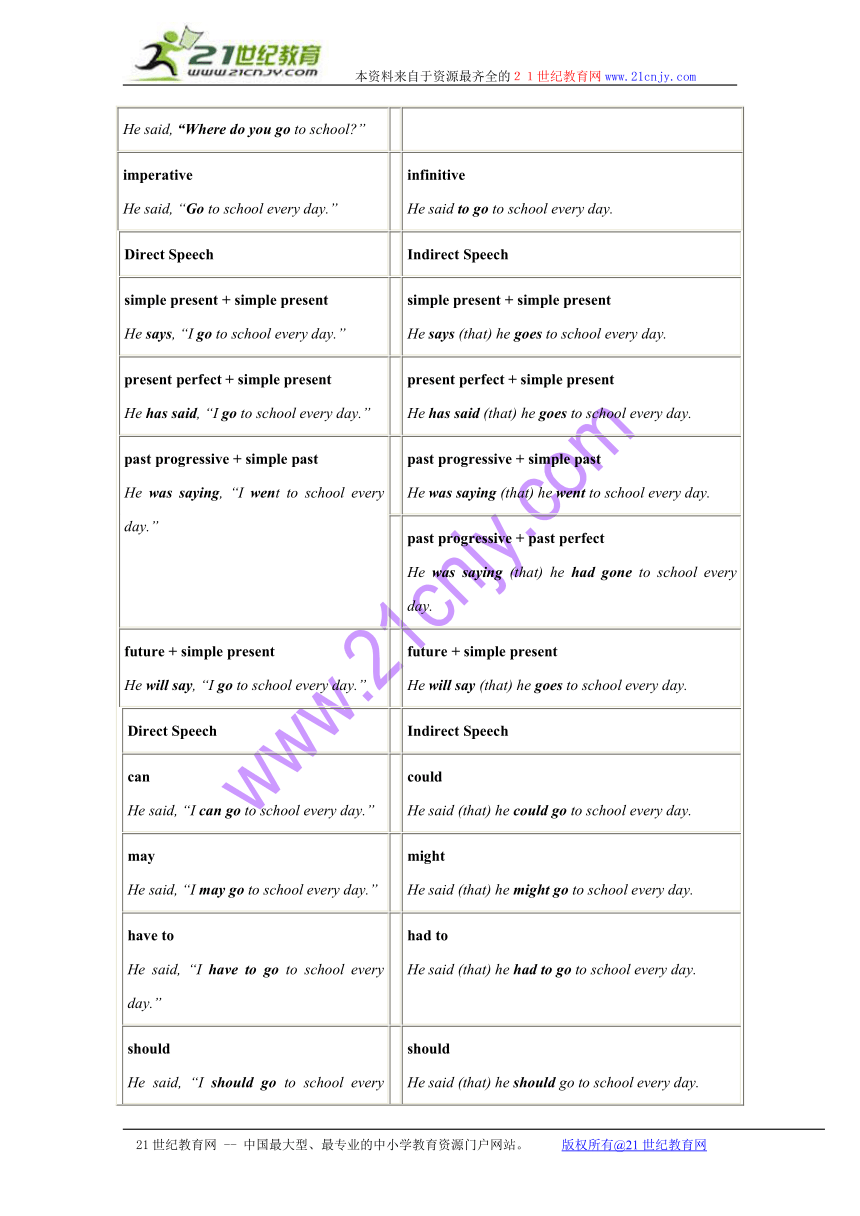
Direct Speech Indirect Speech
simple present + simple present
He says, “I go to school every day.” simple present + simple present
He says (that) he goes to school every day.
present perfect + simple present
He has said, “I go to school every day.” present perfect + simple present
He has said (that) he goes to school every day.
past progressive + simple past
He was saying, “I went to school every day.” past progressive + simple past
He was saying (that) he went to school every day.
past progressive + past perfect
He was saying (that) he had gone to school every day.
future + simple present
He will say, “I go to school every day.” future + simple present
He will say (that) he goes to school every day.
Direct Speech Indirect Speech
can
He said, “I can go to school every day.” could
He said (that) he could go to school every day.
may
He said, “I may go to school every day.” might
He said (that) he might go to school every day.
have to
He said, “I have to go to school every day.” had to
He said (that) he had to go to school every day.
should
He said, “I should go to school every day.” should
He said (that) he should go to school every day.
ought to
He said, “I ought to go to school every day.” ought to
He said (that) he ought to go to school every day.
Step 4 Absorb information concerning National College Entrance Examination
高考链接
动词时态题在高考单项填空题中一般占2至4分。高考时态题常考一般现在时、一般过去时、现在进行时、过去进行时、现在完成时、过去完成时、一般将来时与过去将来时等。高考时态题大致有以下特点:
一、某些题无明确时间状语 考生必须从已知条件中推出其时间状语。这样的考题很多,如:
1. ---You’ve left the light on.
---Oh, so I have. ______ and turn it off. (2000全国)
A. I’ll go B. I’ve gone C. I go D. I’m going
此题没有明确的时间状语提示,但从已知条件中我们可以知道去关灯这一动作应是将来的事。选项D在形式上有误,因此答案为A。
2. ---We could have walked to the station, it was so near.
---Yes. A taxi _____ at all necessary. (1992全国)
A. wasn’t B. hadn’t been C. wouldn’t be D. won’t be
从已知条件“We could have walked to the station, it was so near.”可知“我们没有走路而是坐出租车”的动作发生在过去。因此出租车没有必要应是过去(当时)的事,而不可能是过去之前,更不可能是现在或将来的事。答案为A。
二、某些题虽有时间状语,但极具干扰性 考生应排除干扰。如:
3. ---How are you today
---Oh, I ______ as ill as I do now for a very long time. (2000全国)
A. didn’t feel B. wasn’t feeling C. don’t feel D. haven’t felt
此题虽然有时间状语now和for a very long time, 但学生会误把该题看成是过去和现在的对比而选A。其实该题是最近一段时间的情况与现在的情况作对比:我身体最近很长一段时间都没有现在这样差。答案为D。
4. ---Can I help you, sir
---Yes. I bought this radio here yesterday, but it ______. (1996全国)
A. didn’t work B. won’t work C. can’t work D. doesn’t work
表面上看起来,此题好像讲的是昨天的事,但信息词but表明收音机不work应是现在的情况。所以答案应选D。
三、瞬时过去的动作 这种情况在英语里很多,在汉语里不多,因此不大为学生所理解。近年来这类考题很常见,应引起特别注意。如:
5. ---Hey, look where you are going
---Oh, I’m terribly sorry. ______. (1999全国)
A. I’m not noticing B. I wasn’t noticing C. I haven’t noticed D. I don’t notice
此题中“我没有注意到”应是过去的事。当对方提醒后,“我”又道歉了,这表明“我”不可能到现在还没注意到。因此只能是刚才没注意到,属瞬间的过去。故选B。
6. ---Your phone number again I_____ quite catch it.
---It’s 9568442. (1995全国)
A.didn't B.couldn't C.don't D.can't
这里“我”没听清电话号码,应是没听清刚才对方说的,而不可能是没听清现在对方说的。选项B虽是过去,但它表示没有这种可能性,不符题意,故选A。
7. ---Oh, it’s you! I ________ you.
---I’ve just had my hair cut and I’m wearing new glasses. (1997全国)
A. didn’t recognize B. hadn’t recognized C. haven’t recognized D. don’t recognize
已知条件Oh, it’s you!表明“我”现在已认出“你”了。因此“我”没认出“你”只能是刚才(瞬时过去)的事。不会是过去之前的事(B);也不是到现在为止的事(C);更不能是现在的事(D)。故答案为A。
1. The house belongs to my aunt but she ____ here any more. (2006全国I) A. hasn’t lived B. didn’t live C. hadn’t lived D. doesn’t live2. John, a friend of mine, who got married only last week, spent $3,000 more than he ____ for the wedding. (2006全国II) A. will plan B. has planned C. would plan D. had planned3. ---____ leave at the end of this month. ---I don’t think you should do that until ____ another job. (2006北京) A. I’m going to; you’d found B. I’m going to; you’ve found C. I’ll; you’ll find D. I’ll; you’d find4. What we used to think ____ impossible now does seem possible. (2006天津) A. is B. was C. has been D. will be5. Look at the timetable. Hurry up! Flight 4026 ____ off at 18:20. (2006四川) A. takes B. took C. will be taken D. has taken6. The young girl sitting next to me on the plane was very nervous. She ____ before. (2006广东) A. hasn’t flown B. didn’t fly C. hadn’t flown D. wasn’t flying7. Send my regards to your lovely wife when you ____ home. (2006上海) A. wrote B. will write C. have written D. write8. Although medical science ____ control over several dangerous diseases, what worries us is that some of them are returning. (2006江苏) A. achieved B. has achieved C. will achieve D. had achieved9. I ____ along the street looking for a place to park when the accident ____. (2006安徽) A. went; was occurring B. went; occurred C. was going; occurred D. was going; had occurred10. Ladies and gentlemen, please fasten your seat belts. The plane ____. (2006福建) A. takes off B. is taking off C. has taken off D. took offKeys: 1-5 DDBBA 6-10 CDBCB
21世纪教育网 -- 中国最大型、最专业的中小学教育资源门户网站。 版权所有@21世纪教育网
Module 3 The Violence of Nature-Grammar
Grammar—教案
■Goals
●To learn about the past perfect passive and indirect speech
■Procedures
Step 1: Learning about the past perfect passive
Active Passive
They had given us visas for three months. We had been given visas for three months.
Step 2: Making sentences with the past perfect passive
1. A rotating column of air from a thunderstorm to the ground had been discovered before the fireman arrived.
2. The most violent tornado had been observed then.
3. The wallet had been picked up and handed in before the owner found it missing.
4. By the time the fire engines arrived the fire had been put down.
5. By the time he returned home the house had been destroyed.
6. The map had been left inside exactly where it was when we came into the room.
7. The east coast of the US had been affected greatly before the rescue arrived.
8. The city had been hit three times by the earthquake before the people moved out of it.
9. The man had been buried for five days when he was located.
10. He had been killed before we found him in the room.
Step 3: Learning about indirect speech
When using indirect or reported speech, the form changes. Usually indirect speech is introduced by the verb said, as in I said, Bill said, or they said.
Direct Speech Indirect Speech
simple present
He said, “I go to school every day.” simple past
He said (that) he went to school every day.
simple past
He said, “I went to school every day.” past perfect
He said (that) he had gone to school every day.
present perfect
He said, “I have gone to school every day.” past perfect
He said (that) he had gone to school every day.
present progressive
He said, “I am going to school every day.” past progressive
He said (that) he was going to school every day.
past progressive
He said, “I was going to school every day.” perfect progressive
He said (that) he had been going to school every day,
future (will)
He said, “I will go to school every day.” would + verb name
He said (that) he would go to school every day.
future (going to)
He said, “I am going to school every day.” present progressive
He said (that) he is going to school every day.
past progressive
He said (that) he was going to school every day
Direct Speech Indirect Speech
auxiliary + verb name
He said, “Do you go to school every day ”
He said, “Where do you go to school ” simple past
He asked me if I went to school every day.*
He asked me where I went to school.
imperative
He said, “Go to school every day.” infinitive
He said to go to school every day.
Direct Speech Indirect Speech
simple present + simple present
He says, “I go to school every day.” simple present + simple present
He says (that) he goes to school every day.
present perfect + simple present
He has said, “I go to school every day.” present perfect + simple present
He has said (that) he goes to school every day.
past progressive + simple past
He was saying, “I went to school every day.” past progressive + simple past
He was saying (that) he went to school every day.
past progressive + past perfect
He was saying (that) he had gone to school every day.
future + simple present
He will say, “I go to school every day.” future + simple present
He will say (that) he goes to school every day.
Direct Speech Indirect Speech
can
He said, “I can go to school every day.” could
He said (that) he could go to school every day.
may
He said, “I may go to school every day.” might
He said (that) he might go to school every day.
have to
He said, “I have to go to school every day.” had to
He said (that) he had to go to school every day.
should
He said, “I should go to school every day.” should
He said (that) he should go to school every day.
ought to
He said, “I ought to go to school every day.” ought to
He said (that) he ought to go to school every day.
Step 4 Absorb information concerning National College Entrance Examination
高考链接
动词时态题在高考单项填空题中一般占2至4分。高考时态题常考一般现在时、一般过去时、现在进行时、过去进行时、现在完成时、过去完成时、一般将来时与过去将来时等。高考时态题大致有以下特点:
一、某些题无明确时间状语 考生必须从已知条件中推出其时间状语。这样的考题很多,如:
1. ---You’ve left the light on.
---Oh, so I have. ______ and turn it off. (2000全国)
A. I’ll go B. I’ve gone C. I go D. I’m going
此题没有明确的时间状语提示,但从已知条件中我们可以知道去关灯这一动作应是将来的事。选项D在形式上有误,因此答案为A。
2. ---We could have walked to the station, it was so near.
---Yes. A taxi _____ at all necessary. (1992全国)
A. wasn’t B. hadn’t been C. wouldn’t be D. won’t be
从已知条件“We could have walked to the station, it was so near.”可知“我们没有走路而是坐出租车”的动作发生在过去。因此出租车没有必要应是过去(当时)的事,而不可能是过去之前,更不可能是现在或将来的事。答案为A。
二、某些题虽有时间状语,但极具干扰性 考生应排除干扰。如:
3. ---How are you today
---Oh, I ______ as ill as I do now for a very long time. (2000全国)
A. didn’t feel B. wasn’t feeling C. don’t feel D. haven’t felt
此题虽然有时间状语now和for a very long time, 但学生会误把该题看成是过去和现在的对比而选A。其实该题是最近一段时间的情况与现在的情况作对比:我身体最近很长一段时间都没有现在这样差。答案为D。
4. ---Can I help you, sir
---Yes. I bought this radio here yesterday, but it ______. (1996全国)
A. didn’t work B. won’t work C. can’t work D. doesn’t work
表面上看起来,此题好像讲的是昨天的事,但信息词but表明收音机不work应是现在的情况。所以答案应选D。
三、瞬时过去的动作 这种情况在英语里很多,在汉语里不多,因此不大为学生所理解。近年来这类考题很常见,应引起特别注意。如:
5. ---Hey, look where you are going
---Oh, I’m terribly sorry. ______. (1999全国)
A. I’m not noticing B. I wasn’t noticing C. I haven’t noticed D. I don’t notice
此题中“我没有注意到”应是过去的事。当对方提醒后,“我”又道歉了,这表明“我”不可能到现在还没注意到。因此只能是刚才没注意到,属瞬间的过去。故选B。
6. ---Your phone number again I_____ quite catch it.
---It’s 9568442. (1995全国)
A.didn't B.couldn't C.don't D.can't
这里“我”没听清电话号码,应是没听清刚才对方说的,而不可能是没听清现在对方说的。选项B虽是过去,但它表示没有这种可能性,不符题意,故选A。
7. ---Oh, it’s you! I ________ you.
---I’ve just had my hair cut and I’m wearing new glasses. (1997全国)
A. didn’t recognize B. hadn’t recognized C. haven’t recognized D. don’t recognize
已知条件Oh, it’s you!表明“我”现在已认出“你”了。因此“我”没认出“你”只能是刚才(瞬时过去)的事。不会是过去之前的事(B);也不是到现在为止的事(C);更不能是现在的事(D)。故答案为A。
1. The house belongs to my aunt but she ____ here any more. (2006全国I) A. hasn’t lived B. didn’t live C. hadn’t lived D. doesn’t live2. John, a friend of mine, who got married only last week, spent $3,000 more than he ____ for the wedding. (2006全国II) A. will plan B. has planned C. would plan D. had planned3. ---____ leave at the end of this month. ---I don’t think you should do that until ____ another job. (2006北京) A. I’m going to; you’d found B. I’m going to; you’ve found C. I’ll; you’ll find D. I’ll; you’d find4. What we used to think ____ impossible now does seem possible. (2006天津) A. is B. was C. has been D. will be5. Look at the timetable. Hurry up! Flight 4026 ____ off at 18:20. (2006四川) A. takes B. took C. will be taken D. has taken6. The young girl sitting next to me on the plane was very nervous. She ____ before. (2006广东) A. hasn’t flown B. didn’t fly C. hadn’t flown D. wasn’t flying7. Send my regards to your lovely wife when you ____ home. (2006上海) A. wrote B. will write C. have written D. write8. Although medical science ____ control over several dangerous diseases, what worries us is that some of them are returning. (2006江苏) A. achieved B. has achieved C. will achieve D. had achieved9. I ____ along the street looking for a place to park when the accident ____. (2006安徽) A. went; was occurring B. went; occurred C. was going; occurred D. was going; had occurred10. Ladies and gentlemen, please fasten your seat belts. The plane ____. (2006福建) A. takes off B. is taking off C. has taken off D. took offKeys: 1-5 DDBBA 6-10 CDBCB
21世纪教育网 -- 中国最大型、最专业的中小学教育资源门户网站。 版权所有@21世纪教育网
