虚拟语气
图片预览





文档简介
(共29张PPT)
*
虚拟语气
SUBJUNCTIVE MOOD
GRAMMER 语法
1 Brief introduction
2 Classification of the subjunctive mood
3 Some common sentence patterns
4 Conclusion
*
What’s the subjected mood
. He hopes that he will play football with him tomorrow
He wishes that he would play football with him tomorrow.
.If it rains tomorrow, I won’t go camping.
If the sun turned around the earth, I would marry you.
.Providing that he has recovered from his cold, he will be at school next week.
Providing that you were left on a desert island, what would you do
*
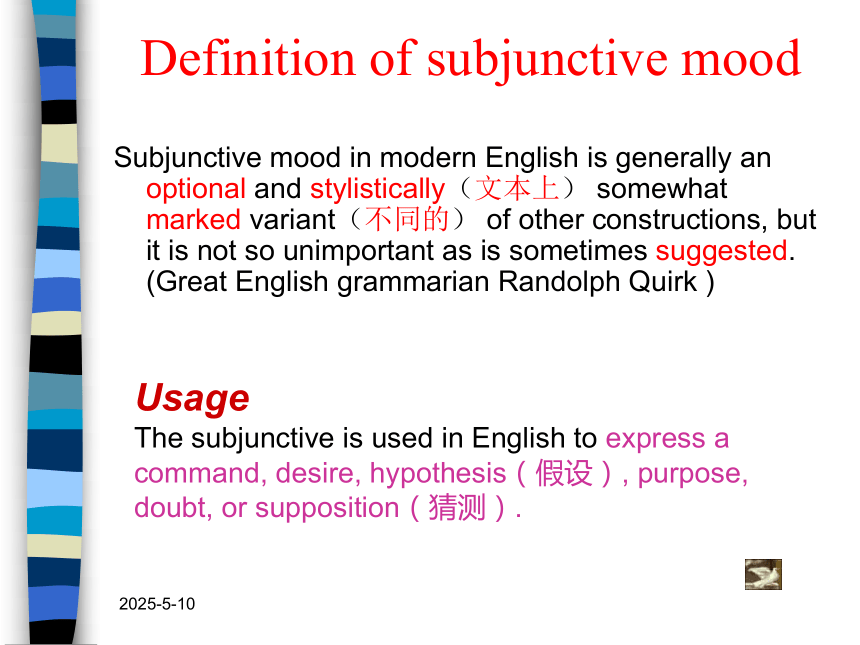
Definition of subjunctive mood
Subjunctive mood in modern English is generally an optional and stylistically(文本上) somewhat marked variant(不同的) of other constructions, but it is not so unimportant as is sometimes suggested. (Great English grammarian Randolph Quirk )
Usage
The subjunctive is used in English to express a command, desire, hypothesis(假设), purpose, doubt, or supposition(猜测).
*
a. the base form (do)
b. past form (did)
c. had + past participle (had+done)
d. should + the base form (should+ do)
e. should have + past participle(should have done)
f. should / would + the base form(should/would do)
g. should /would + have + past participle
(should /would+have+done)
Seven verb forms
*
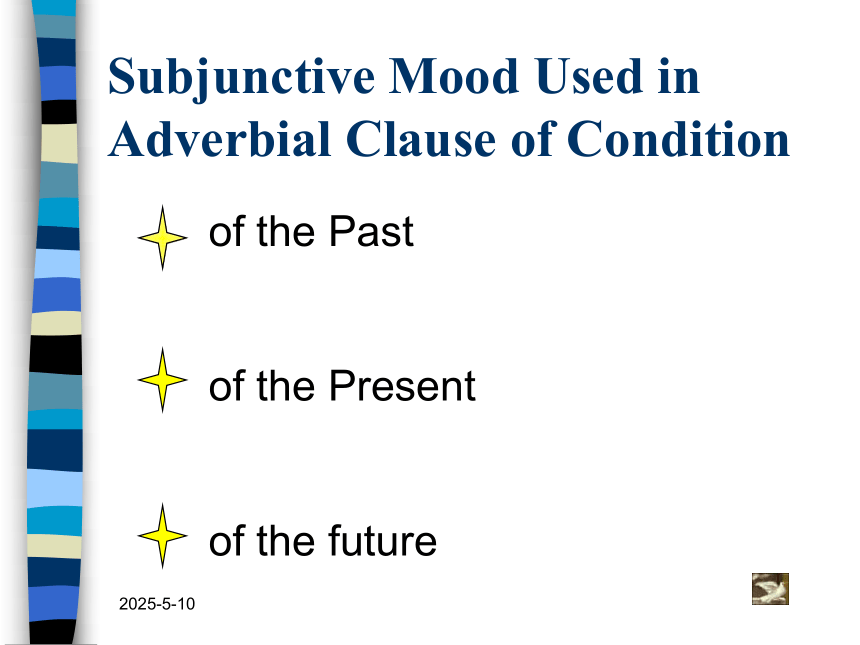
Subjunctive Mood Used in Adverbial Clause of Condition
of the Past
of the Present
of the future
*
situation in the past
Used to describe events that could have happened in the past but did not actually happen
e.g
If I had seen the film, I would have told you about it.
If I had realized that, he would have run away.
Basic form: had done sth+would have done sth
*
Situation in the present
PRACTICE
(1)When you are talking about something that is generally true or happens often
e.g
If they lose weight during an illness, they soon regain it afterwards.
If the baby is crying, it is probably hungry
Basic form: present tense
Warning:you do not use the present continuous in both clauses
If they are losing money, they are being angry.
*
END
(2)When you are talking about something that you think is unlikely to happen.
If I were as big as you, I would kill you.
If I had enough money, I would buy the car.
Basic form: past simple / past continuous + would do
Warning : “were” is sometimes used instead of “was”, especially after “I”
And you often say “ if I were you” when you are giving advice.
*
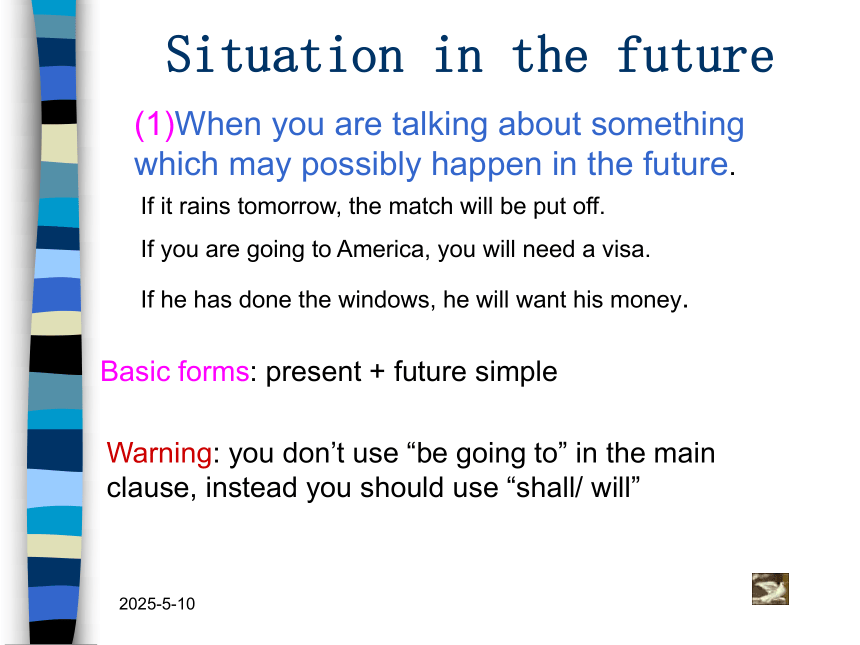
Situation in the future
(1)When you are talking about something which may possibly happen in the future.
If it rains tomorrow, the match will be put off.
If you are going to America, you will need a visa.
If he has done the windows, he will want his money.
Basic forms: present + future simple
Warning: you don’t use “be going to” in the main clause, instead you should use “shall/ will”
*
(2) A future subjunctive can be constructed using the conjugated form of the verb "to be" plus the infinitive or with the usage of the modal auxiliary verb "should"
If you were to give the money to me, then I would say no more about it.
If I should go, then will you feed the hens
Warning: the "were" clauses result in the present conditional, while the "should" clauses result in the future indicative.
Basic form: be to /should do + would/will do
*
Basic rules and features
KEYs
When it is possible to happen or is true
(conditional clause) present+(main clause)present /simple future
When it is unlikely to happen or on contrary to
the truth
(conditional clause) past+(main clause) would do/have done
do/ be doing/have done
do/ will do
did/ had done
*
PRACTICE1
①从句的动作与过去事实相反,而主句的动作与现在或现在正在发生的事实不符。如:
If I had worked hard at school, I would be an engineer, too.
Had done + would do sth
Sometimes the action in the conditional clause and main clause do not match in time.
*
②从句的动作与现在事实相反,而主句的动作与过去事实不符。如: If he knew her, he would have greeted her.
要是他认识她的话,他肯定会去问候她了
Did + would have done
③从句的动作与过去发生的情况相反,而主句的动作与现在正在发生的情况相反。如:
If he had been working hard, he would be working in the office now. 要是他工作一直努力的话,他现在已进了办公室了。
Had done + would do
*
If there is a helping verb, modal verb , be or have in the subordinate clause and the clause is placed at the beginning, we can place these words before the subject
KEYs
The inversion form(倒装)
*
PRACTICE
Had it not been for the PLA,we wouldn‘t have been able to beat the flood. =If it hadn't been for the PLA,we wouldn't … Were he here now,he would certainly help me. = If he were here, he would certainly help me.
Attention: 1).In the inversion sentence, we should put “not” behind the subject . 2).Sometimes in spoken language, when the subject is the singular form of the first and third person, we can use was instead of were, but in the inversion sentences, we must use were.
*
Common sentence patterns
1. SM in object clause
1) As the object of wish
E.g. I wish I were as young as you.
In this kind of clause, we use past simple tense of the verb to refer to sth contrary to the fact at present; while past perfect tense to the fact in the past and past future tense to the fact in the future.
*
I wish I had enough money to buy a car.(表示的是现在)
He whishes he had not lost the chance.(表示的是过去)
I wish I would join the army when I grow up.(表示的是将来)
*
2).As the object to make a command, demand, propose…
In the object clause of these kinds of verbs, we should use (should) + do as the predicate.
E.g. I recommend that you all be diligent if you want to pass the exam.
It is demanded that we (should) get everything ready by tonight.
Common words are: command, demand, require, recommend, propose, desire, order, suggest, ask, insist, decide, advise
*
2. SM in the subject clause: It is + adj. + that-clause
In the clause, we should also use (should) + do as its predicate.
e.g. It is necessary that he (should)be sent to the hospital at once.
The adj. could be: necessary, important, essential, strange, natural ,vital,urgent,
recommended…
*
3. SM in the attribute clause:
It is (about/high) time that…
Its predicate should use past tense or should +do.
E.g. It’s time that we began our meeting.
It is high time that we should tell him the truth.
Note: should can’t be omitted
*
4. SM in the predicative and appositive clauses 表语从句和同位语从句
His proposal is that we turn off TV for half an hour every day.
I offered the advice that we stay here.
In the clauses introduced by words as proposal and advice, we should use (should) + do as the predicate.
More such words are: decision, demand, desire, necessity, recommendation…
*
4. SM in the adverbial clause of concession(让步状语从句)
1) introduced by as if/though
If the clause is contrary to the fact, its predicate should use past tense or past perfect tense or would + do.
E.g. She talked about the film as if she had really seen it.
You look as if you had seen a ghost.
*
2). introduced by lest(以防、以免) /in case /for fear that
In these clauses, their predicates must be (should) + do
E.g. The old woman walked slowly lest she(should)slip.
*
5.SM in the sentences expressing wishes
if only & if...only (但愿、要是……就好了)
E.g. If only I could see Jordan.
If only I didn’t oversleep.
In these sentences, we can only use past tense.
*
KEYs
Exercises
You didn’t let me drive. If we ___ in turn, you _____ so tired.
A. drove; didn’t get
B. drove; wouldn’t get
C. were driving; wouldn’t get
D. had driven; wouldn’t have got
2. When a pencil is partly in a glass of water, it looks as if it _____.
A. breaks B. has broken
C. were broken D. had been broken
D
C
*
PRACTICE
3. ____ it rain tomorrow, we should have to put off the visit to the Yangpu Bridge.
A. Were B. Should
C. Would D. Will
4. Jane’s face suggested that she _____ ill, and her parents suggested that she _____ a medical examination.
A. be; should have B. was; have
C. should be; had D. was; has
5. Without electricity human life _____ quite different today.
A. is B. will be
C. would have been D. would be
B
B
D
*
翻译题
山无棱.天地合,乃敢以君决
KEYs
If all the mountains became flat and the Heaven mingled with the Earth, I would break up with you!
*
References: http://baike./view/26751.htm
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Subjunctive
http://www./qk/88585X/200404/23349073.html
*
*
虚拟语气
SUBJUNCTIVE MOOD
GRAMMER 语法
1 Brief introduction
2 Classification of the subjunctive mood
3 Some common sentence patterns
4 Conclusion
*
What’s the subjected mood
. He hopes that he will play football with him tomorrow
He wishes that he would play football with him tomorrow.
.If it rains tomorrow, I won’t go camping.
If the sun turned around the earth, I would marry you.
.Providing that he has recovered from his cold, he will be at school next week.
Providing that you were left on a desert island, what would you do
*
Definition of subjunctive mood
Subjunctive mood in modern English is generally an optional and stylistically(文本上) somewhat marked variant(不同的) of other constructions, but it is not so unimportant as is sometimes suggested. (Great English grammarian Randolph Quirk )
Usage
The subjunctive is used in English to express a command, desire, hypothesis(假设), purpose, doubt, or supposition(猜测).
*
a. the base form (do)
b. past form (did)
c. had + past participle (had+done)
d. should + the base form (should+ do)
e. should have + past participle(should have done)
f. should / would + the base form(should/would do)
g. should /would + have + past participle
(should /would+have+done)
Seven verb forms
*
Subjunctive Mood Used in Adverbial Clause of Condition
of the Past
of the Present
of the future
*
situation in the past
Used to describe events that could have happened in the past but did not actually happen
e.g
If I had seen the film, I would have told you about it.
If I had realized that, he would have run away.
Basic form: had done sth+would have done sth
*
Situation in the present
PRACTICE
(1)When you are talking about something that is generally true or happens often
e.g
If they lose weight during an illness, they soon regain it afterwards.
If the baby is crying, it is probably hungry
Basic form: present tense
Warning:you do not use the present continuous in both clauses
If they are losing money, they are being angry.
*
END
(2)When you are talking about something that you think is unlikely to happen.
If I were as big as you, I would kill you.
If I had enough money, I would buy the car.
Basic form: past simple / past continuous + would do
Warning : “were” is sometimes used instead of “was”, especially after “I”
And you often say “ if I were you” when you are giving advice.
*
Situation in the future
(1)When you are talking about something which may possibly happen in the future.
If it rains tomorrow, the match will be put off.
If you are going to America, you will need a visa.
If he has done the windows, he will want his money.
Basic forms: present + future simple
Warning: you don’t use “be going to” in the main clause, instead you should use “shall/ will”
*
(2) A future subjunctive can be constructed using the conjugated form of the verb "to be" plus the infinitive or with the usage of the modal auxiliary verb "should"
If you were to give the money to me, then I would say no more about it.
If I should go, then will you feed the hens
Warning: the "were" clauses result in the present conditional, while the "should" clauses result in the future indicative.
Basic form: be to /should do + would/will do
*
Basic rules and features
KEYs
When it is possible to happen or is true
(conditional clause) present+(main clause)present /simple future
When it is unlikely to happen or on contrary to
the truth
(conditional clause) past+(main clause) would do/have done
do/ be doing/have done
do/ will do
did/ had done
*
PRACTICE1
①从句的动作与过去事实相反,而主句的动作与现在或现在正在发生的事实不符。如:
If I had worked hard at school, I would be an engineer, too.
Had done + would do sth
Sometimes the action in the conditional clause and main clause do not match in time.
*
②从句的动作与现在事实相反,而主句的动作与过去事实不符。如: If he knew her, he would have greeted her.
要是他认识她的话,他肯定会去问候她了
Did + would have done
③从句的动作与过去发生的情况相反,而主句的动作与现在正在发生的情况相反。如:
If he had been working hard, he would be working in the office now. 要是他工作一直努力的话,他现在已进了办公室了。
Had done + would do
*
If there is a helping verb, modal verb , be or have in the subordinate clause and the clause is placed at the beginning, we can place these words before the subject
KEYs
The inversion form(倒装)
*
PRACTICE
Had it not been for the PLA,we wouldn‘t have been able to beat the flood. =If it hadn't been for the PLA,we wouldn't … Were he here now,he would certainly help me. = If he were here, he would certainly help me.
Attention: 1).In the inversion sentence, we should put “not” behind the subject . 2).Sometimes in spoken language, when the subject is the singular form of the first and third person, we can use was instead of were, but in the inversion sentences, we must use were.
*
Common sentence patterns
1. SM in object clause
1) As the object of wish
E.g. I wish I were as young as you.
In this kind of clause, we use past simple tense of the verb to refer to sth contrary to the fact at present; while past perfect tense to the fact in the past and past future tense to the fact in the future.
*
I wish I had enough money to buy a car.(表示的是现在)
He whishes he had not lost the chance.(表示的是过去)
I wish I would join the army when I grow up.(表示的是将来)
*
2).As the object to make a command, demand, propose…
In the object clause of these kinds of verbs, we should use (should) + do as the predicate.
E.g. I recommend that you all be diligent if you want to pass the exam.
It is demanded that we (should) get everything ready by tonight.
Common words are: command, demand, require, recommend, propose, desire, order, suggest, ask, insist, decide, advise
*
2. SM in the subject clause: It is + adj. + that-clause
In the clause, we should also use (should) + do as its predicate.
e.g. It is necessary that he (should)be sent to the hospital at once.
The adj. could be: necessary, important, essential, strange, natural ,vital,urgent,
recommended…
*
3. SM in the attribute clause:
It is (about/high) time that…
Its predicate should use past tense or should +do.
E.g. It’s time that we began our meeting.
It is high time that we should tell him the truth.
Note: should can’t be omitted
*
4. SM in the predicative and appositive clauses 表语从句和同位语从句
His proposal is that we turn off TV for half an hour every day.
I offered the advice that we stay here.
In the clauses introduced by words as proposal and advice, we should use (should) + do as the predicate.
More such words are: decision, demand, desire, necessity, recommendation…
*
4. SM in the adverbial clause of concession(让步状语从句)
1) introduced by as if/though
If the clause is contrary to the fact, its predicate should use past tense or past perfect tense or would + do.
E.g. She talked about the film as if she had really seen it.
You look as if you had seen a ghost.
*
2). introduced by lest(以防、以免) /in case /for fear that
In these clauses, their predicates must be (should) + do
E.g. The old woman walked slowly lest she(should)slip.
*
5.SM in the sentences expressing wishes
if only & if...only (但愿、要是……就好了)
E.g. If only I could see Jordan.
If only I didn’t oversleep.
In these sentences, we can only use past tense.
*
KEYs
Exercises
You didn’t let me drive. If we ___ in turn, you _____ so tired.
A. drove; didn’t get
B. drove; wouldn’t get
C. were driving; wouldn’t get
D. had driven; wouldn’t have got
2. When a pencil is partly in a glass of water, it looks as if it _____.
A. breaks B. has broken
C. were broken D. had been broken
D
C
*
PRACTICE
3. ____ it rain tomorrow, we should have to put off the visit to the Yangpu Bridge.
A. Were B. Should
C. Would D. Will
4. Jane’s face suggested that she _____ ill, and her parents suggested that she _____ a medical examination.
A. be; should have B. was; have
C. should be; had D. was; has
5. Without electricity human life _____ quite different today.
A. is B. will be
C. would have been D. would be
B
B
D
*
翻译题
山无棱.天地合,乃敢以君决
KEYs
If all the mountains became flat and the Heaven mingled with the Earth, I would break up with you!
*
References: http://baike./view/26751.htm
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Subjunctive
http://www./qk/88585X/200404/23349073.html
*
