备战2018高考英语一轮复习专题讲解(词法部分)介词
文档属性
| 名称 | 备战2018高考英语一轮复习专题讲解(词法部分)介词 |  | |
| 格式 | zip | ||
| 文件大小 | 146.7KB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 通用版 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2017-07-22 10:36:24 | ||
图片预览



文档简介
介词
介词又叫做前置词,是一种虚词,不能单独在句子当中担当成分,它后面必须接名词、代词或相当于名词的其他词类搭配(介词+宾语)构成介词短语;和动词搭配构成短语动词,然后才能够在句子当中充当成分。
介词分为简单介词,如:at,
in,
on,
besides,
since,
for等;合成介词,如:inside,
outside,
without,
within,
into,
onto等;短语介词(或成语介词),如:because
of,
in
front
of,
instead
of,
in
spite
of等;二重介词,如:from
behind,
until
after等。
介词短语的句法功能
介词在句子中可以充当定语、状语、表语、以及宾语补足语等。
作定语
介词短语在句中做定语时须位于被修饰词之后。
The
key
to
the
door
is
missing.
The
water-tower
in
front
of
our
school
was
built
in
1988.
作表语(或称为:主语的补足语)
Some
students
are
in
the
classroom,
and
some
on
the
playground.
As
we
know,
Japan
is
to
the
east
of
China.
作宾语补足语(或称为:宾语的表语)
Did
you
see
a
pen
under
my
desk
this
morning
They
have
sent
another
rocket
into
the
sky.
作状语
On
Sundays,
the
family
are
mostly
out.
(时间状语)
On
top
of
the
hill
stands
a
TV
tower.
(地点状语)
He
is
used
to
sleeping
with
all
the
windows
open.
(伴随状语)
In
the
search
for
the
lost
child,
the
villagers
went
all
out.
(目的状语)
All
the
work
must
be
done
by
hand.
(方式状语)
At
times,
I
go
to
the
cinema.
(频度状语)
She
is
by
far
the
best
student
in
our
class.
(程度状语)
Because
of
poverty,
he
couldn’t
go
to
school.
(原因状语)
To
my
surprise,
he
got
the
first
prize
in
the
contest.
(结果状语
/
或评注性状语)
Without
our
Party,
we
couldn’t
live
a
happy
life.
(条件状语)
In
spite
of
great
efforts
we
failed
to
carry
our
plans
through.
(让步状语)
As
a
matter
of
fact,
nobody
agreed
to
his
project.
(评注性状语)
In
my
opinion,
you’d
better
go
with
us.
介词的复合结构
“介词+宾语+补足语”可以构成介词的复合结构,在句子当中可充当表语、定语、状语、补语等。这种结构中的宾语和补足语之间存在着逻辑上的主谓关系,使得句子意义更加丰富。常见的这类介词有with,
without,
like,
of等。
介词+宾语+形容词
He
is
used
to
sleeping
with
all
the
windows
open.
介词+宾语+分词
Bamboo
leaves
swing
in
the
wind
like
slim
fingers
reaching
to
touch
something.
At
the
beginning
of
school,
the
noise
of
desks
being
opened
and
closed
and
lessons
(of
being)
repeated
at
the
top
of
the
children’s
voices
could
be
heard
out
in
the
street.
The
wounded
boy
glared
at
the
nobleman
with
his
teeth
clenched.
介词+宾语+不定式
The
cat
humped
its
back
just
like
a
fierce
tiger
to
jump
upon
me.
介词+宾语+副词
The
little
boy
rushed
out
of
the
house
without
anything
on.
介词+宾语+介词短语
The
teacher
entered
the
classroom
with
a
book
under
his
arm.
介词的叠用
在少数介词之后还可接另一个介词短语,也就是我们所称的二重介词。如:
The
naughty
boy
suddenly
rushed
out
from
behind
the
tree
to
frighten
the
girl.
In
the
spring,
new
bamboo
shoots
come
out
from
around
their
own
roots.
He
kept
on
working
until
after
lunch.
介词+and+介词
有些介词短语用两个意义相反的介词构成从而使句子精简化。
Not
knowing
what
to
do,
the
worried
officer
walked
up
and
down
the
room.
There
are
many
trees
in
and
outside
the
town.
介词与其同形的与副词区别
有些介词可做副词用,但我们知道副词可以单独在句子中担当成分,而介词须加宾语构成短语才可在句子中充当成分。
试比较:
Please
come
in.
(in为副词
=
into
the
room)
We
have
no
car,
but
we
can
go
there
without.
(without为副词
=
without
a
car)
Although
the
exam
was
difficult,
I
managed
to
get
through.
(through为副词
=
through
the
exam)
常易混用介词的区别
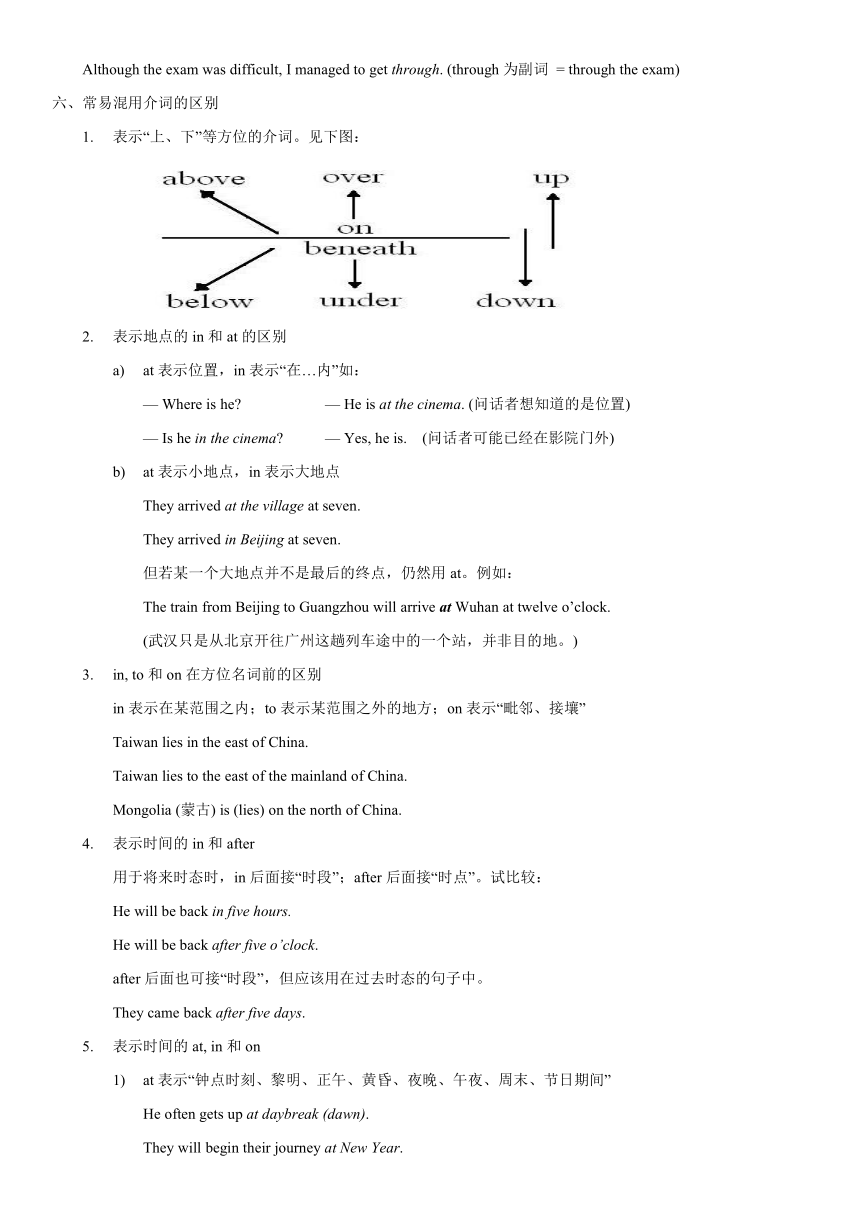
表示“上、下”等方位的介词。见下图:
表示地点的in和at的区别
at表示位置,in表示“在…内”如:
—
Where
is
he
—
He
is
at
the
cinema.
(问话者想知道的是位置)
—
Is
he
in
the
cinema
—
Yes,
he
is.
(问话者可能已经在影院门外)
at表示小地点,in表示大地点
They
arrived
at
the
village
at
seven.
They
arrived
in
Beijing
at
seven.
但若某一个大地点并不是最后的终点,仍然用at。例如:
The
train
from
Beijing
to
Guangzhou
will
arrive
at
Wuhan
at
twelve
o’clock.
(武汉只是从北京开往广州这趟列车途中的一个站,并非目的地。)
in,
to和on在方位名词前的区别
in表示在某范围之内;to表示某范围之外的地方;on表示“毗邻、接壤”
Taiwan
lies
in
the
east
of
China.
Taiwan
lies
to
the
east
of
the
mainland
of
China.
Mongolia
(蒙古)
is
(lies)
on
the
north
of
China.
表示时间的in和after
用于将来时态时,in后面接“时段”;after后面接“时点”。试比较:
He
will
be
back
in
five
hours.
He
will
be
back
after
five
o’clock.
after后面也可接“时段”,但应该用在过去时态的句子中。
They
came
back
after
five
days.
表示时间的at,
in和on
at表示“钟点时刻、黎明、正午、黄昏、夜晚、午夜、周末、节日期间”
He
often
gets
up
at
daybreak
(dawn).
They
will
begin
their
journey
at
New
Year.
in表示“上(下)午、晚间、星期、月份、年份、世纪”
He
was
born
in
1988.
on表示具体日期或具体的上(下)午,节日的当天,美国英语周末前也用on.
He
died
on
the
morning
of
August
15th,
1985.
但若morning,
afternoon,
evening等词前面有early或late等修饰语则仍然用in。如:
He
died
in
the
early
morning
of
August
15th,
1985.
表时间的since和for
since后接时点;for接时段,均常与完成时态连用。
He
has
been
here
since
last
Friday.
He
has
been
here
for
five
days.
当表示“多少次”
时不能用for;
表示“第几次”位于句首时须加for,而位于句尾时for可以省略也可保留。
He
has
been
to
Beijing
three
times.
(不可用for
three
times)
For
the
first
time,
I
have
come
here.
I
have
come
here
(for)
the
first
time.
表示位置的between和among
between表示“个与个之间”,并非只能指两者,可用“…and…”也可接复数名词。如:
The
teacher
sat
between
Tom,
Jack,
Kate,
Jane
and
Mary.
You’d
better
eat
nothing
between
meals.
among则笼统地指“在…之中”,后接复数名词或代词。
The
teacher
sat
among
the
students.
except,
besides,
but,
except
for,
but
for,
except
that/
when
except用作介词,意为“除了”。整个句子所表达的意思重点在except所构成的介词短语上。例如:
Nobody
felt
anxious
except
him.
(只有他才焦虑不安)
except
和
besides
两者都有“除去”之意,但前者指“但并不包括”,是“排除”之意;后者指“除此之外还有”,有“外加”之意。例如:
There
are
six
of
us
besides
Tom.
(除汤姆外,另外我们还有6个人。)
except和
but
but用作介词时,意思是“除…外”,“别无…”,“只有…”;but多与no
one,nothing,who,all,everyone等连用,它可与except互换。例如:
No
one
but
a
fool
would
believe
it.
Who
but
he
would
do
such
a
thing?
except
for
和
except
that/when
二者意为“只是”或“除…外”,表示理由或细节,修正前面所说的情况。except
for后面接单词,except
that/when后面接句子。整个句子所表达的意思重点在主句中,而except所构成的介词短语只是次要的。例如:
Your
composition
is
good
except
for
a
few
spelling
mistakes.
(=
Your
composition
is
good
except
that
there
are
a
few
spelling
mistakes.)
比较:All
the
compositions
are
good
except
Li
Hua’s.
(大家的作文都好,只有李华的除外。)
except
for和but
for
except
for用于陈述语气,but
for用于虚拟语气“要不是…”。例如:
Except
for
its
temples,the
place
is
not
worth
seeing.
But
for
your
help,
I
couldn’t
have
finished
the
work
on
time.
except
but十动词不定式(可带to或不带to,当but或except之前没有动词“do”的某种形式时,其后的不定式要带to。)例如:
They
did
nothing
except/but
watch
TV.
I
could
not
do
anything
except/bur
just
wait
for
him
to
come
round.
巩固训练
Do
you
still
remember
the
film
we
saw
________the
end
of
last
week
A.
in
B.
by
C.
at
D.
to
That
he
had
a
lot
of
practice
________volleyball
was
the
reason
why
he
defeated
all
the
other
players.
A.
in
B.
at
C.
on
D.
about
________the
sound
of
the
knocking
on
the
door,
he
rose
and
went
to
open
it.
A.
At
B.
On
C.
To
D.
Heard
You
can
find
the
store
________No.
19
Beijing
Road.
A.
on
B.
at
C.
near
to
D.
in
Please
wait
for
me
________the
corner
of
that
street
________three
o’clock.
A.
in;
at
B.
at;
on
C.
in;
for
D.
at;
at
I
bought
these
books
________one
yuan
a
copy.
A.
at
B.
by
C.
on
D.
in
I
can’t
buy
it
________such
a
price.
A.
of
B.
for
C.
at
D.
with
The
student
is
sitting
________his
desk.
A.
over
B.
around
C.
at
D.
for
when
the
spaceship
leaves
the
earth
________very
high
speed,
the
astronauts
feel
as
if
they
are
being
crushed
________the
spaceship.
A.
with;
in
B.
at;
on
C.
with;
to
D.
at;
against
The
child
hid
himself
________the
door.
A.
after
B.
behind
C.
in
the
front
of
D.
ago
She
left
the
party
________her
headache.
A.
because
B.
since
C.
in
spite
of
D.
because
of
You
shouldn’t
eat
so
much
chocolate
________meals.
A.
except
B.
between
C.
unless
D.
through
some
animals
sleep
________day
and
wake
up
________night.
A.
by;
by
B.
at;
by
C.
by;
on
D.
on;
in
—What
time
is
it,
please
—It
is
seven
________my
watch.
A.
in
B.
at
C.
for
D.
by
You’ll
be
able
to
speak
English
________practicing
from
time
to
time.
A.
in
B.
by
C.
with
D.
for
________the
end
of
last
year
we
had
leaned
five
English
songs.
A.
At
B.
By
C.
In
D.
On
A
man
should
not
be
judged
always
________what
he
says.
A.
by
B.
in
C.
with
D.
to
The
guests
will
be
here
________two
o’clock.
A.
in
B.
on
C.
for
D.
by
some
people
got
up
and
left
the
hall
________the
show.
A.
while
B.
during
C.
between
D.
through
How
much
must
I
pay
you
________the
tickets
________tonight.
A.
of;
of
B.
for;
for
C.
for;
about
D.
for;
to
I
am
grateful
________your
help
________me.
A.
to;
for
B.
for;
to
C.
to;
to
D.
for;
for
Joan
is
always
praised
________her
cleverness.
A.
of
B.
in
C.
for
D.
by
It’s
quite
warm
today
________January.
A.
for
B.
in
C.
at
D.
on
I
bought
this
book
________fifty
cents.
A.
at
B.
about
C.
at
D.
for
Chinese
is
a
language
________more
native
speakers
than
any
of
the
other
languages.
A.
with
B.
spoken
C.
which
D.
has
Please
write
________pencil,
not
________ink.
A.
in;
with
B.
in
a;
with
C.
with
a
;
in
D.
with;
in
________the
development
of
science
and
technology,
our
country
has
become
richer
and
stronger.
A.
In
B.
By
C.
At
D.
With
________the
rise
in
prices,
life
is
getting
harder.
A.
With
B.
On
C.
As
D.
For
He
has
no
good
pen
________.
A.
to
write
B.
to
write
with
C.
to
write
on
D.
writing
Mary
was
disappointed
when
she
found
but
they
had
gone
to
the
ball
________her.
A.
except
B.
except
for
C.
for
D.
without
Xiao
Li
masters
several
other
foreign
languages
________English.
He
studies
German,
Japanese
and
Russian.
A.
beside
B.
besides
C.
but
D.
except
The
soldier
stood
quite
still,
________his
lips
moved
slightly.
A.
except
that
B.
except
for
C.
except
D.
besides
Your
composition
is
good
________a
few
spelling
mistakes.
A.
besides
B.
except
C.
except
for
D.
except
that
Peter’s
car
is
excellent
________the
color.
A.
except
B.
besides
C.
except
for
D.
only
except
Everybody
went
to
the
exhibition
________Mary.
A.
not
B.
but
C.
for
D.
by
We
live
a
long
way
________the
factory.
A.
to
B.
for
C.
from
D.
in
The
town
lies
________the
west
of
the
river.
A.
at
B.
in
C.
from
D.
to
Let’s
walk
over
________the
sun
on
the
other
side
of
the
street.
A.
in
B.
to
C.
under
D.
by
There
are
a
lot
of
news
________today’s
newspaper.
A.
in
B.
on
C.
at
D.
with
Say
something
about
your
school
________English.
A.
in
B.
with
C.
by
D.
for
The
girl
________will
give
us
a
report.
A.
on
blue
B.
of
blue
C.
in
blue
D.
at
blue
Please
ask
him
if
he
will
join
us
________playing
table
tennis.
A.
on
B.
at
C.
in
D.
with
This
vegetable
is
very
rich
________iron.
A.
of
B.
in
C.
with
D.
for
He
has
been
caught
________the
rain
and
is
wet
through
and
through.
A.
by
B.
in
C.
at
D.
up
with
Look,
there
is
a
hole
________the
wall.
A.
on
B.
at
C.
in
D.
of
What
is
the
difference________
pronunciation
________these
two
words
A.
of;
in
B.
in;
between
C.
in;
among
D.
of;
between
The
doctor
will
be
back
________ten
minutes.
A.
after
B.
in
C.
on
D.
at
The
desk
stands
________the
corner
of
the
room
near
the
window.
A.
on
B.
at
C.
under
D.
in
Do
you
like
dressing
yourself
________new
clothes
A.
on
B.
in
C.
with
D.
by
Please
come
to
see
me
________two
day’s
time.
A.
during
B.
after
C.
for
D.
in
KEY:
1—10.
CBABD
ACCDB
11—20.
DBADB
BADBB
21—30.
BCADA
CDABD
31—40.
BACCB
CDBAA
41—50.
CCBBC
BBDBD
介词又叫做前置词,是一种虚词,不能单独在句子当中担当成分,它后面必须接名词、代词或相当于名词的其他词类搭配(介词+宾语)构成介词短语;和动词搭配构成短语动词,然后才能够在句子当中充当成分。
介词分为简单介词,如:at,
in,
on,
besides,
since,
for等;合成介词,如:inside,
outside,
without,
within,
into,
onto等;短语介词(或成语介词),如:because
of,
in
front
of,
instead
of,
in
spite
of等;二重介词,如:from
behind,
until
after等。
介词短语的句法功能
介词在句子中可以充当定语、状语、表语、以及宾语补足语等。
作定语
介词短语在句中做定语时须位于被修饰词之后。
The
key
to
the
door
is
missing.
The
water-tower
in
front
of
our
school
was
built
in
1988.
作表语(或称为:主语的补足语)
Some
students
are
in
the
classroom,
and
some
on
the
playground.
As
we
know,
Japan
is
to
the
east
of
China.
作宾语补足语(或称为:宾语的表语)
Did
you
see
a
pen
under
my
desk
this
morning
They
have
sent
another
rocket
into
the
sky.
作状语
On
Sundays,
the
family
are
mostly
out.
(时间状语)
On
top
of
the
hill
stands
a
TV
tower.
(地点状语)
He
is
used
to
sleeping
with
all
the
windows
open.
(伴随状语)
In
the
search
for
the
lost
child,
the
villagers
went
all
out.
(目的状语)
All
the
work
must
be
done
by
hand.
(方式状语)
At
times,
I
go
to
the
cinema.
(频度状语)
She
is
by
far
the
best
student
in
our
class.
(程度状语)
Because
of
poverty,
he
couldn’t
go
to
school.
(原因状语)
To
my
surprise,
he
got
the
first
prize
in
the
contest.
(结果状语
/
或评注性状语)
Without
our
Party,
we
couldn’t
live
a
happy
life.
(条件状语)
In
spite
of
great
efforts
we
failed
to
carry
our
plans
through.
(让步状语)
As
a
matter
of
fact,
nobody
agreed
to
his
project.
(评注性状语)
In
my
opinion,
you’d
better
go
with
us.
介词的复合结构
“介词+宾语+补足语”可以构成介词的复合结构,在句子当中可充当表语、定语、状语、补语等。这种结构中的宾语和补足语之间存在着逻辑上的主谓关系,使得句子意义更加丰富。常见的这类介词有with,
without,
like,
of等。
介词+宾语+形容词
He
is
used
to
sleeping
with
all
the
windows
open.
介词+宾语+分词
Bamboo
leaves
swing
in
the
wind
like
slim
fingers
reaching
to
touch
something.
At
the
beginning
of
school,
the
noise
of
desks
being
opened
and
closed
and
lessons
(of
being)
repeated
at
the
top
of
the
children’s
voices
could
be
heard
out
in
the
street.
The
wounded
boy
glared
at
the
nobleman
with
his
teeth
clenched.
介词+宾语+不定式
The
cat
humped
its
back
just
like
a
fierce
tiger
to
jump
upon
me.
介词+宾语+副词
The
little
boy
rushed
out
of
the
house
without
anything
on.
介词+宾语+介词短语
The
teacher
entered
the
classroom
with
a
book
under
his
arm.
介词的叠用
在少数介词之后还可接另一个介词短语,也就是我们所称的二重介词。如:
The
naughty
boy
suddenly
rushed
out
from
behind
the
tree
to
frighten
the
girl.
In
the
spring,
new
bamboo
shoots
come
out
from
around
their
own
roots.
He
kept
on
working
until
after
lunch.
介词+and+介词
有些介词短语用两个意义相反的介词构成从而使句子精简化。
Not
knowing
what
to
do,
the
worried
officer
walked
up
and
down
the
room.
There
are
many
trees
in
and
outside
the
town.
介词与其同形的与副词区别
有些介词可做副词用,但我们知道副词可以单独在句子中担当成分,而介词须加宾语构成短语才可在句子中充当成分。
试比较:
Please
come
in.
(in为副词
=
into
the
room)
We
have
no
car,
but
we
can
go
there
without.
(without为副词
=
without
a
car)
Although
the
exam
was
difficult,
I
managed
to
get
through.
(through为副词
=
through
the
exam)
常易混用介词的区别
表示“上、下”等方位的介词。见下图:
表示地点的in和at的区别
at表示位置,in表示“在…内”如:
—
Where
is
he
—
He
is
at
the
cinema.
(问话者想知道的是位置)
—
Is
he
in
the
cinema
—
Yes,
he
is.
(问话者可能已经在影院门外)
at表示小地点,in表示大地点
They
arrived
at
the
village
at
seven.
They
arrived
in
Beijing
at
seven.
但若某一个大地点并不是最后的终点,仍然用at。例如:
The
train
from
Beijing
to
Guangzhou
will
arrive
at
Wuhan
at
twelve
o’clock.
(武汉只是从北京开往广州这趟列车途中的一个站,并非目的地。)
in,
to和on在方位名词前的区别
in表示在某范围之内;to表示某范围之外的地方;on表示“毗邻、接壤”
Taiwan
lies
in
the
east
of
China.
Taiwan
lies
to
the
east
of
the
mainland
of
China.
Mongolia
(蒙古)
is
(lies)
on
the
north
of
China.
表示时间的in和after
用于将来时态时,in后面接“时段”;after后面接“时点”。试比较:
He
will
be
back
in
five
hours.
He
will
be
back
after
five
o’clock.
after后面也可接“时段”,但应该用在过去时态的句子中。
They
came
back
after
five
days.
表示时间的at,
in和on
at表示“钟点时刻、黎明、正午、黄昏、夜晚、午夜、周末、节日期间”
He
often
gets
up
at
daybreak
(dawn).
They
will
begin
their
journey
at
New
Year.
in表示“上(下)午、晚间、星期、月份、年份、世纪”
He
was
born
in
1988.
on表示具体日期或具体的上(下)午,节日的当天,美国英语周末前也用on.
He
died
on
the
morning
of
August
15th,
1985.
但若morning,
afternoon,
evening等词前面有early或late等修饰语则仍然用in。如:
He
died
in
the
early
morning
of
August
15th,
1985.
表时间的since和for
since后接时点;for接时段,均常与完成时态连用。
He
has
been
here
since
last
Friday.
He
has
been
here
for
five
days.
当表示“多少次”
时不能用for;
表示“第几次”位于句首时须加for,而位于句尾时for可以省略也可保留。
He
has
been
to
Beijing
three
times.
(不可用for
three
times)
For
the
first
time,
I
have
come
here.
I
have
come
here
(for)
the
first
time.
表示位置的between和among
between表示“个与个之间”,并非只能指两者,可用“…and…”也可接复数名词。如:
The
teacher
sat
between
Tom,
Jack,
Kate,
Jane
and
Mary.
You’d
better
eat
nothing
between
meals.
among则笼统地指“在…之中”,后接复数名词或代词。
The
teacher
sat
among
the
students.
except,
besides,
but,
except
for,
but
for,
except
that/
when
except用作介词,意为“除了”。整个句子所表达的意思重点在except所构成的介词短语上。例如:
Nobody
felt
anxious
except
him.
(只有他才焦虑不安)
except
和
besides
两者都有“除去”之意,但前者指“但并不包括”,是“排除”之意;后者指“除此之外还有”,有“外加”之意。例如:
There
are
six
of
us
besides
Tom.
(除汤姆外,另外我们还有6个人。)
except和
but
but用作介词时,意思是“除…外”,“别无…”,“只有…”;but多与no
one,nothing,who,all,everyone等连用,它可与except互换。例如:
No
one
but
a
fool
would
believe
it.
Who
but
he
would
do
such
a
thing?
except
for
和
except
that/when
二者意为“只是”或“除…外”,表示理由或细节,修正前面所说的情况。except
for后面接单词,except
that/when后面接句子。整个句子所表达的意思重点在主句中,而except所构成的介词短语只是次要的。例如:
Your
composition
is
good
except
for
a
few
spelling
mistakes.
(=
Your
composition
is
good
except
that
there
are
a
few
spelling
mistakes.)
比较:All
the
compositions
are
good
except
Li
Hua’s.
(大家的作文都好,只有李华的除外。)
except
for和but
for
except
for用于陈述语气,but
for用于虚拟语气“要不是…”。例如:
Except
for
its
temples,the
place
is
not
worth
seeing.
But
for
your
help,
I
couldn’t
have
finished
the
work
on
time.
except
but十动词不定式(可带to或不带to,当but或except之前没有动词“do”的某种形式时,其后的不定式要带to。)例如:
They
did
nothing
except/but
watch
TV.
I
could
not
do
anything
except/bur
just
wait
for
him
to
come
round.
巩固训练
Do
you
still
remember
the
film
we
saw
________the
end
of
last
week
A.
in
B.
by
C.
at
D.
to
That
he
had
a
lot
of
practice
________volleyball
was
the
reason
why
he
defeated
all
the
other
players.
A.
in
B.
at
C.
on
D.
about
________the
sound
of
the
knocking
on
the
door,
he
rose
and
went
to
open
it.
A.
At
B.
On
C.
To
D.
Heard
You
can
find
the
store
________No.
19
Beijing
Road.
A.
on
B.
at
C.
near
to
D.
in
Please
wait
for
me
________the
corner
of
that
street
________three
o’clock.
A.
in;
at
B.
at;
on
C.
in;
for
D.
at;
at
I
bought
these
books
________one
yuan
a
copy.
A.
at
B.
by
C.
on
D.
in
I
can’t
buy
it
________such
a
price.
A.
of
B.
for
C.
at
D.
with
The
student
is
sitting
________his
desk.
A.
over
B.
around
C.
at
D.
for
when
the
spaceship
leaves
the
earth
________very
high
speed,
the
astronauts
feel
as
if
they
are
being
crushed
________the
spaceship.
A.
with;
in
B.
at;
on
C.
with;
to
D.
at;
against
The
child
hid
himself
________the
door.
A.
after
B.
behind
C.
in
the
front
of
D.
ago
She
left
the
party
________her
headache.
A.
because
B.
since
C.
in
spite
of
D.
because
of
You
shouldn’t
eat
so
much
chocolate
________meals.
A.
except
B.
between
C.
unless
D.
through
some
animals
sleep
________day
and
wake
up
________night.
A.
by;
by
B.
at;
by
C.
by;
on
D.
on;
in
—What
time
is
it,
please
—It
is
seven
________my
watch.
A.
in
B.
at
C.
for
D.
by
You’ll
be
able
to
speak
English
________practicing
from
time
to
time.
A.
in
B.
by
C.
with
D.
for
________the
end
of
last
year
we
had
leaned
five
English
songs.
A.
At
B.
By
C.
In
D.
On
A
man
should
not
be
judged
always
________what
he
says.
A.
by
B.
in
C.
with
D.
to
The
guests
will
be
here
________two
o’clock.
A.
in
B.
on
C.
for
D.
by
some
people
got
up
and
left
the
hall
________the
show.
A.
while
B.
during
C.
between
D.
through
How
much
must
I
pay
you
________the
tickets
________tonight.
A.
of;
of
B.
for;
for
C.
for;
about
D.
for;
to
I
am
grateful
________your
help
________me.
A.
to;
for
B.
for;
to
C.
to;
to
D.
for;
for
Joan
is
always
praised
________her
cleverness.
A.
of
B.
in
C.
for
D.
by
It’s
quite
warm
today
________January.
A.
for
B.
in
C.
at
D.
on
I
bought
this
book
________fifty
cents.
A.
at
B.
about
C.
at
D.
for
Chinese
is
a
language
________more
native
speakers
than
any
of
the
other
languages.
A.
with
B.
spoken
C.
which
D.
has
Please
write
________pencil,
not
________ink.
A.
in;
with
B.
in
a;
with
C.
with
a
;
in
D.
with;
in
________the
development
of
science
and
technology,
our
country
has
become
richer
and
stronger.
A.
In
B.
By
C.
At
D.
With
________the
rise
in
prices,
life
is
getting
harder.
A.
With
B.
On
C.
As
D.
For
He
has
no
good
pen
________.
A.
to
write
B.
to
write
with
C.
to
write
on
D.
writing
Mary
was
disappointed
when
she
found
but
they
had
gone
to
the
ball
________her.
A.
except
B.
except
for
C.
for
D.
without
Xiao
Li
masters
several
other
foreign
languages
________English.
He
studies
German,
Japanese
and
Russian.
A.
beside
B.
besides
C.
but
D.
except
The
soldier
stood
quite
still,
________his
lips
moved
slightly.
A.
except
that
B.
except
for
C.
except
D.
besides
Your
composition
is
good
________a
few
spelling
mistakes.
A.
besides
B.
except
C.
except
for
D.
except
that
Peter’s
car
is
excellent
________the
color.
A.
except
B.
besides
C.
except
for
D.
only
except
Everybody
went
to
the
exhibition
________Mary.
A.
not
B.
but
C.
for
D.
by
We
live
a
long
way
________the
factory.
A.
to
B.
for
C.
from
D.
in
The
town
lies
________the
west
of
the
river.
A.
at
B.
in
C.
from
D.
to
Let’s
walk
over
________the
sun
on
the
other
side
of
the
street.
A.
in
B.
to
C.
under
D.
by
There
are
a
lot
of
news
________today’s
newspaper.
A.
in
B.
on
C.
at
D.
with
Say
something
about
your
school
________English.
A.
in
B.
with
C.
by
D.
for
The
girl
________will
give
us
a
report.
A.
on
blue
B.
of
blue
C.
in
blue
D.
at
blue
Please
ask
him
if
he
will
join
us
________playing
table
tennis.
A.
on
B.
at
C.
in
D.
with
This
vegetable
is
very
rich
________iron.
A.
of
B.
in
C.
with
D.
for
He
has
been
caught
________the
rain
and
is
wet
through
and
through.
A.
by
B.
in
C.
at
D.
up
with
Look,
there
is
a
hole
________the
wall.
A.
on
B.
at
C.
in
D.
of
What
is
the
difference________
pronunciation
________these
two
words
A.
of;
in
B.
in;
between
C.
in;
among
D.
of;
between
The
doctor
will
be
back
________ten
minutes.
A.
after
B.
in
C.
on
D.
at
The
desk
stands
________the
corner
of
the
room
near
the
window.
A.
on
B.
at
C.
under
D.
in
Do
you
like
dressing
yourself
________new
clothes
A.
on
B.
in
C.
with
D.
by
Please
come
to
see
me
________two
day’s
time.
A.
during
B.
after
C.
for
D.
in
KEY:
1—10.
CBABD
ACCDB
11—20.
DBADB
BADBB
21—30.
BCADA
CDABD
31—40.
BACCB
CDBAA
41—50.
CCBBC
BBDBD
