2010年高考英语语法辅导课件-动词时态和语态
文档属性
| 名称 | 2010年高考英语语法辅导课件-动词时态和语态 |  | |
| 格式 | rar | ||
| 文件大小 | 879.1KB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 通用版 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2010-08-08 06:57:00 | ||
图片预览











文档简介
课件55张PPT。动词的时态和语态学习目标:
1、高考考查的八种时态是:一般现在时,一般过去时,一般将来时,现在进行时,过去进行时,现在完成时,过去完成时,过去将来时。
2、容易混淆的三组动词时态是:一般现在时和现在完成时;一般过去时和过去完成时;过去完成时与现在完成时。
3、各种时态及含情态动词的被动形式的应用。学习重点:
1、时态和语态在特定语境中的基本用法。
2、学会根据语境或上下文逻辑关系来判断时态。
3、同题检测时态和语态。
4、被动语态和系表结构,主动形式表被动意义的知识。突破方法:
1、不可脱离语境学习时态和语态,而是要在了解了八种常用时态的一些常用规则后,留心以英语为母语者在实际生活中如何使用各种时态和语态。
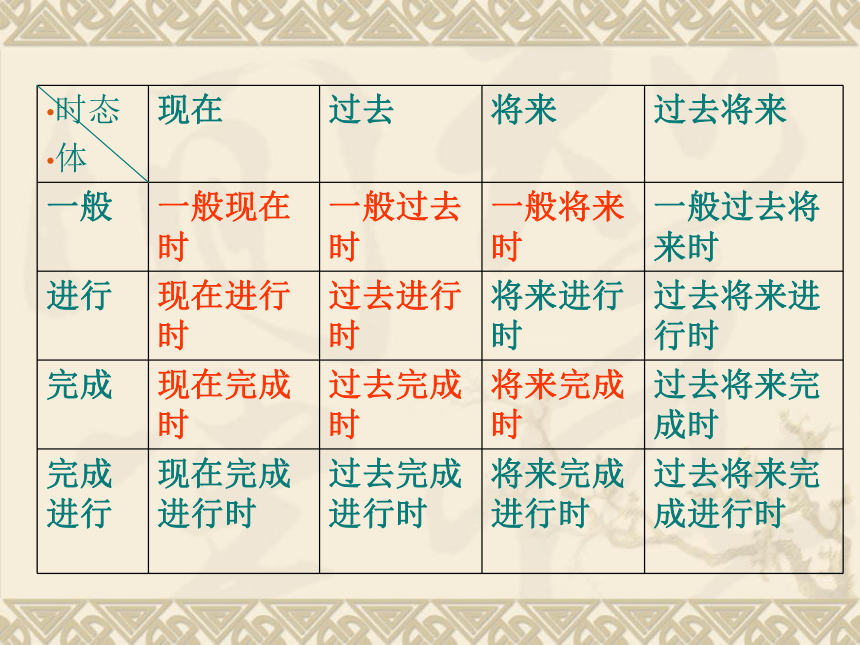
2、建立时态的时、体概念(“时”即现在时、过去时、将来时、过去将来时;每个时又分四个“体”,即一般体、进行体、完成体、完成进行体)。
3、解决时态和语态问题,要遵循如下解题思路:
1)这件事情说的是什么时候的事情或情况? (定“时”)
2)这个动作处于什么状态,是完成了,还是未完成,还是既不表完成又不表进行?(定“体”)
3)这个动词与主语的关系,是主动还是被动? (定“语态”)概念
时态是谓语动词所表示的动作或情况发生时间的各种形式。它是“时”和“体”的组合。“时”有现在、过去、将来、过去将来之分;“体”有一般、进行、完成、完成进行之别。见下表:一、一般现在时
1.一般现在时表示经常发生、习惯性动作或存在的状态;
He takes a walk after supper every day.
He is our English teacher.
客观真理、科学事实、格言;
The sun rises in the east.
Two plus two makes four.
主语的特征、性格、能力等。 He woks hard. The children draw well.
常见时间状语:often, sometimes, seldom, always, every day/month/ year 2.主句是一般将来时,时间、条件状语从句中用一般现在
表示将来。如:
I’ll go there after I finish my work.
If it rains tomorrow, I won’t go there.
3.在以here, there开头的句子里,go, come等少数动词的一般现在时表示正在发生的动作。例如:
There goes the bell.铃响了。
There comes the bus.汽车来了。
Here she comes.她来了。
4. 表示安排或计划好的将来的动作(一般只限于某些表移动的动词,如go,come,leave, start,be ,arrive, begin, return, open, close, depart, end, sail,
finish等).
The train starts at ten o’clock in the morning.
Supper is at five today.二、一般过去时
1)表达特定的过去时间内发生的动作或存在的状况,常与last week/year/ month/ spring, a few days ago, in 1998等时间状语以及when等连词引导的时间状语从句连用。
We had a good swim last Sunday.
When I was young, I took cold baths regularly.
2)叙述过去连续发生的一件件事。
He got up early in the morning, fetched water, swept the yard and then went out to work.
3)表过去某一时间内经常发生或反复发生的动作或行为。 When my brother was a teenager, he played table tennis almost everyday.
4)在条件、时间状语从句中表示过去将来的动作。
They said they would let us know if they heard any news about him.题组练习:用所给动词的适当形式填空
---Your baby is too thin.
---- It could gain weight, but it _____(not eat) much.
2. It won’t be long before such a thing _____ (happen) again.
3. I won’t speak to him unless he ____
(apologize) to me.doesn’t eathappensapologizes4. The careless driver has just been fined $ 10 for stopping his car at a sign that ____ (read) “NO PARKING”.
5. --- Nancy is not coming tonight.
---- But she _______ . (promise).readspromised三. 一般将来时
一般将来时表示将来要发生的动作和存在的状况。有下列一些形式:
1.will/shall do (侧重将来行为,不突出计划安排去做某事,与tomorrow,next week, soon, in 2018等连用)
My daughter will be twelve years old tommorrow.
I shall go back to see my childhood friends in the summer vacation.
We shall work in this factory every day.
(表将来经常发生的动作)2. be going to do (主观上打算、决心或客观上可能发生)
We are going to visit the Museum of Chinese History.
Tom studies very hard, and he is going to try for a scholarship.
Look at those clouds. It’s going to rain. 3. be about to (表即将发生的动作,立即的将来,此句型很少与表示将来的具体时间状语连用。)
The English evening is about to begin.
We are about to leave, so there is no time to visit him now.
4. be to do
1)(按计划或安排即将发生)
The boys are to go to school next week.
He and I are to meet at the Shanghai Railway Station.这种结构也可用于过去,was / were to do sth表示曾经计划要做的事,但不表明计划是否被执行,或表示命运(即命中注定要发生的事),而非计划;was / were to have done sth 表示未曾实现的计划。
I felt nervous, I was soon to leave home for the first time.我感到很紧张,因为我很快就要首次离开家了。
They said goodbye, little knowing that they were never to meet again.他们告了别,不知道以后再也不会见面了。
We were to have told you, but you were not in. 我们本想告诉你的,但你不在家。2)表示“应该”,相当于should ,ought to ,
You are to report to the police.
What is to be done?应该怎么办呢?
3) 表示“必须”, 相当于must ,have to
The letter is to be handed to him in person.
4) You are to do your homework before you watch TV.
表示“想,打算”,相当于intend,want ,
If we are to be there before ten, we’ll have to go now. 5)用于第一人称疑问句,表示征求对方意见。
Am I to go on with the work?
What are we to do next?
6)用于否定句,表示“禁止”, 相当于“mustn’t”
The books in this room are not to be taken outside.
7)表示“可能,可以”, 相当于may, can
The news is to be found in the evening paper.
Such people are to be found everywhere. 9) were to do sth用于if 或 even if /even though 从句中,表示对未来的假设。
If I were to tell you that I killed him, would you believe me?
Even if the sun were to rise in the west, I would never do such a thing.
10) be to blame(该受责备,对某坏事应负责任)与 be to let (待出租)两种结构中,用不定式的主动形式表示被动含义。
Which driver is to blame for the accident? 这事故是哪个司机的责任?
This house is to let. 这房子要出租。题组练习:单项填空6. We have been looking for the boy all the afternoon but he is nowhere_____.
to see B. seeing C. seen D. to be seen
7. As early as his second film, Chaplin had developed his own manner of acting, the one that ____ world famous.
A. Would become B. became
C. was to become D. had become8. --- We just saw John at the bookstore.
---- That’s strange. I didn’t think he ___back until tomorrow.
A. will come B. was to come
C. is coming D. is to come
9. If the sun ____ tomorrow, what would we do?
A. were not to raise B. does not rise
C. would not rise D. were not to rise10. Look at these clouds, ___.
A. It’s going to rain B. It’s raining
C. It is to rain D. It can rain
11. Who do you think ____ for the failure of their marriage?
A. to blame B. to be blame
C. is to blame D. is to be blamed 四、现在进行时
1.表示正在进行的动作或存在的状态。
We are having an English lesson.
He is translating a novel.
--- Have you moved into the new house?
---- Not yet. The rooms are being painted.
2.有些动词,如come,go,leave,return,arrive,begin,start,stay等,它们的现在进行时表示按计划安排在不远的将来即将发生的动作。
例如:She is leaving for Beijing.她要去北京。
He is working as a teacher tomorrow.
从明天起他要做老师。
My father is coming to see me this Saturday.
这个星期六我爸爸要来看我。3.代替一般现在时,描绘更加生动。例如:The Changjiang River is flowing into the east.江水滚滚向东流。The sun is rising in the east.太阳从东方冉冉升起。
4. 表示反复出现或习惯性动作,往往含有赞赏、厌恶、遗憾等情绪,常与always, continually, constantly连用, 如:
He is always thinking of others first.
He is always making the same mistake.
5.大多数动词可用于进行时,但也有些动词不用于进行时。常见的有:exist,live,understand,mean,owe,belong to ,know,doubt,suppose,remember,forget,
believe,trust,want,wish,refuse,like,hate,dislike,
prefer,mind,hope等。五、过去进行时
1.表示过去某一时刻或某一段时间内正在进行的动作(这一过去时间须用时间状语表示)。
例如:He was preparing his lecture all day yesterday.
2.表示动作在另一过去动作发生时进行。
例如:They were still working when I left.
3.用在两个过去进行时动作同时发生。
例如:I was writing while he was watching TV.4.表示过去将来动作。例如:He said she was arriving the next day.
5.一个长动作作为背景,被一个短动作打断,长动作往往用进行体,短动作用一般体。
My brother fell while he was riding his bicycle and hurt himself.
Tom slipped into the house when on one was looking.题组训练:用所给单词的适当形式填空。12) You _____ always ______ (watch) TV. Why not do something more active?
13) ---- Watch!
----- I ______ (watch) but I ______ (not see ) anything unusual.
14) Listen ! The couple _______ (quarrel) in the room.
15) ---- You’re drinking too much!
---- No one ____ (see) me but you. arewatchingam watchingdon’t seeare quarrellingsees六、过去将来时
1.表从过去某时间看将要发生的事情,多用在在间接引语或宾语从句中,还可表示过去的倾向
或过去经常发生的事情
They asked me if I would go to Guangzhou soon.
He’d play the violin when he was in low spirits.
2 . 用于“was/were going to+动词原形”句型中,表示过去的安排、打算或确信某事会发生,
多用于口语。 I told her I was going to see her that afternoon.
I’m sure (that) they were going to do that. 七、将来进行时
1)表示在将来某一时间正在进行的动作;
They will be meeting us at the station. I will be seeing Mr Smith tomorrow.
2)表示原因、结果或猜测;
Please come tomorrow afternoon, tomorrow morning I’ll be having a meeting.
Stop the child or he will be falling over.
You will be making a mistake.
3)用在问句中,表示委婉礼貌;
Will you be reading anything else?
When shall we be meeting again?
4)表示稍后一点的安排
My duties will end in July and I will be returning to Shanghai.八、现在完成时
1.表示过去发生的动作对现在产生的影响或结果,或说话时已完成的动作,常与so far, in
the past/ last few years, recently, lately, twice, for two years, how long, since (…ago) 用。
例如:I have finished one third of the report so far. She has cleand the room.
2.表示从过去开始,待续到现在的动作或状态,往往和“for…”, “since…”表述的一段时间状语连用。例如:He has learned English for six years./ They have worked here since they left college.3.现在完成时与一般过去时的区别:
1)用两种时态来表述发生在过去的某一动作,现在完成时强调这一过去动作对现在产生的影响或结果,而一般过去时只表达过去的动作或状态,和现在关系不大。例如:She has cleaned the room.It’s very clean now.(此句has cleaned就不能改为cleaned.一是因为cleaned与现状无关,二是因为一般过去时不可突然跳到It’s这样的一般现在时。)
2)汉语中的“了”、“过”、“曾”等词常用完成表达,如:I have seen that film.(我看过那部电影了。)但是如果是在特定的过去时间“看了”、“做过”,就不可用完成时而必须用一般过去进来表达。例如:When did you see that film? I saw it yesterday.(你什么时候看了那部电影?我昨天看的。)不能说:When have you seen that film?I have seen it yesterday. 4. 表示“曾经到过某地(人已回来)”用“have/has been to”,表示“到某地去了(还未回来)”用“have/has gone to”.例如:
——Where is Li Hua?
-He has gone to the reading-room.
——She knows a lot about Shanghai.
-She has been there.
5. 短暂动词(即瞬间动词),join,lose,buy,borrow,leave,go,come,arrive,
die,marry, finish,complete,begin,start,
break out等,在完成时态中,其肯定式不能和表示一段时间的状语连用。
例如不能说:He has finished the work for three hours.
要翻译“他已完成工作三小时了。”可采用
1)“ago法”:He finished the work three hours ago.
2)“延续法”:He has been through(with)the work for three hours.
3)“since法”:It is/has been three hours since he finished the work.
题组训练: 句型转换
16) He left his office 3 hours ago.
He _____ _______ ______ from his office for 3 hours.
It ______ ______ 3 hours since he left his office.
17) He has been dead for 4 years.
He ______ ______ ______ ago.
It has been _____ ______ ______ he died. has been awayhas beendied four years four years since九、过去完成时
1.表示在过去某一时间以前已经完成的动作,常与by
(the end of)+过去时间状语,by then等时间状语连用, 也可用before等介词短语或一个时间状语从句来表示,
还可通过上下文来表示。
He had shut the door before the dog came up.
Everything had been all right up till this morning.
By then he had learned English for 3 years.
2.表示动作或状态从过去某个时刻开始一直延续到另一个过去时刻才完成,甚至还要继续下去。
例如:At the age of ten,he had learned 500 English words.
He had been ill for a week when we learned about it.3.常用hope,expect,think,intend,want,suppose等动词的过去完成时来表示未实现的希望、打算或意图。例如:We had expected that you would be able to win the match.
4.用于hardly / scarcely / barely had ... done…when…和no sooner…had...done...than…引导的复合句的主句中,常用倒装语序。When 和than从句里用一般过去时,表示“刚刚、、、就、、、”
Hardly (No sooner) had I got home when (than) the rain poured down.我们刚到家大雨就倾盆而下。
Hardly had we started when the car got a flat tyre. 我们才刚刚开动,汽车的轮胎就漏气了 5. It was / had been + 一段时间+ since从句. Since 从句中的谓语动词用过去完成时。
It was ten years since we had had such a wonderful time. 我们10年没这么高兴了。
6. This / That / It was the first / second ...time + that 从句。 that从句中的谓语动词用过去完成时。
It was the third time (that) he had made the same mistake. 这是他第三次犯同样的错误了。
That was the first time (that) I had passed the exam. 那是我第一次考试及格。 十、将来完成时
用来表示在将来某个时刻(前)将完成的动作。常和by短语,when,before引起的时间状语连用。例如:We will have finished senior Book 2 by the end of this term.
十一、现在完成进行时
1.用来表示从过去某一时刻开始一直持续到现在(或今后还要继续一去)的动作。完成进行体是完成体和进行体的组合,因此,它具备完成体和进行体的一些因素,如它具备进行体的“未完性、暂时性、感彩”等特点。例如:He has been learning English for 6 years.(从过去某一时间开始学英语,强调到现在还在学)
It has been raining for three days.(强调说话者抱怨的感彩)
2.凡是不能用于现在进行时的动词均不能用于现成完成进行时。 题组训练:用所给动词的适当形式填空.
18) Helen _______ (leave) her keys in the office so she had to wait until her husband _____ (come ) home.
19) I _____ (hope) to meet Mr. Thompson this morning, but I found nobody left in the room. had left camehad hoped20) We plan to reach the North Pole in mid-July, and by then we _____
(walk)for six weeks.
21) By the time you arrive in New York, you will ____ (away) for two weeks.
22) --- Did you find the missing couple in the mountain yesterday?
--- No, but we _____ (try) to get in touch with them ever since. will have walkedhave been away have been trying(2006年高考全国卷I)
The house belongs to my aunt but she ____ here any more.
A.hasn’t lived B. didn’t live
C. hadn’t lived D. doesn’t live高考感悟【解析】 本题考查动词的时态。其句意为“这所房子是我阿姨的,但她(现在)不住这儿了。”指的是现在的居住情况,故D项符合。【命题立意】 时态题要依据句中出现的动词的时态或时间状语来判断。2 (2006年高考全国卷II)
John, a friend of mine, who got married only last week, spent $ 3,000 more than he for the wedding.
will plan B. has planned
C. would plan D. had planned
【解析】 plan表示的动作发生在spent这一过去动作之前,应该用过去完成时。此句意为“我的朋友约翰上周结婚了,婚礼花去了3000美元,超过了原计划。”
【答案】D 【命题立意】 本题考查过去完成时态。3 (2006年高考北京卷)
- leave at the end of this month.
-I don’t think you should do that until ____ another job.
A. I’m going to; you’d found
B. I’m going to; you’ve found
C. I’ll; you’ll find
D. I’ll; you’d find
【解析】 be going to 按计划,打算将要做某事。此句意为“我打算在这个月末离开。”“我认为在你没有找到另一份工作之前你不应该离开。”
【答案】B
【命题立意】本题是对时态基本用法的考查。4 (2006年高考北京卷)
-Your job open for your return.
-Thanks.
A. will be kept B. will keep
C. had kept D. had been kept
【解析】 keep the job/ the position open 使工作、职位等处于空缺状态,由句意“随时欢迎你回来工作”可知用将来时。
【答案】A
【命题立意】此题考查一般将来时的被动语态,时态的判定要根据句意来确定。 5 (2006年高考北京卷)
-Where did you put the car keys?
-Oh, I put them on the chair because the phone rang as I in.
remembered; come
remembered; was coming
C. remember; came
D. remember; was coming
【解析】 remember是说话者说话时的思维活动,应用一般现在时。remember宾语从句的内容发生在以前,故用过去时态。
【答案】C
【命题立意】 本题考查时态的基本用法,做题时要将自己融入题目,身临其境。6 (2006年高考天津卷)
What we used to think impossible now does seem possible.
is B. was C. has been D. will be
【解析】 由句意“我们以前认为不可能的事现在看起来的确是可能的”和谓语动词used to think可知空格处的谓语部分应该表达过去意义。【答案】B
【命题立意】本题考查时态用法,应善于抓住句中含有时间概念的动词或时间状语的暗示,如本句中的used to和now。7 (2006年高考上海卷)
When he turned professional at the age of 11, Mike to become a world champion by his coach and parents.
A. expected B. was expecting
C. was expected D. would be expected
【解析】Mike与expect之间为动宾关系,故需用被动语态,由从句含义可以确定其时态为过去时。
【答案】C
【命题立意】本题综合考查时态与语态,注意谓语动词与主语的逻辑关系及上下文体现的时间含义。8 (2006年高考广东卷)The young girl sitting next to me on the plane was very nervous. She before.
A. hadn’t flown B. didn’t fly
C. hadn’t flown D. wasn’t flying
【解析】动作发生在was nervous之前
【答案】C
【命题立意】本题考查过去完成时态。9.——Can I join your club,dad?
——You can when you______a bit older. (NMET)
A.get B.will get
C.are getting D.will have got
析:“You can”是将来意,when引导的时间状语从句要用一般现在时表将来所以此题答案为A.10.—— Oh,it’s you!I______you.
—— I’ve just had my hair cut and I’m wearing new glasses.
A.didn’t recognize
B.hadn’t recognized
C.haven’t recognized
D.don’t recongnize
析:从“Oh,it’s you!”可知说话时已认出对方。“没有认出”是在此之前为过去情况,所以应选A 11. I don’t think Jim saw me; he______into space. (NMET)
A.just stared
B.was just staring
C.has just stared
D.had just stared
析:B, 在空白处应选一个与“saw”相配,能解释Jim didn’t see me 这一原因的选项,只有着眼于A、B。若选A不能体观他“当时正在做”某事,故排除A而选B。这样因为“他正在望宇宙天空”所以“未看到我”。12. ——______my glasses?
——Yes,I saw them on your bed a minute ago. (NMET)
A.Do you see B.Had you seen
C.Would you see D.Have you seen
析:现在完成时可表过去发生的事情对现在产生的影响或结果,问话人以这样的时态发问可作现焦急的心情。故答案为D。
13.You don’t need to describe her.I______her several times. (NMET)
A.had met B.have met C.met D.meet
析:答案B。道理同12。14.——Do you know our town at all?
——No,this is the first time I______here.
A.was B.have been
C.came D.am going
析:根据this/it is the first/second/…time sb.has done sth.句型,可定答案为B。 又如:This is the second time he has visited the Great Wall.15. I don’t really work here.I______until the new secretary arrives. (NMET)
A.just help out
B.have just helped out
C.am just helping out
D.will just help out
析:根据I don’t really work here.以及…until the new secretary arrives,可知说话人所要做的事是计划安排行为,C、D两个选项都表将来动作,但D非计划安排,C则体现按计划去做,所以此题答案为C。16. ——Is this raincoat yours?
——No,mine______there behind the door. (NMET)
A.is hanging
B.has hung
C.hangs
D.hung
析:此题的“悬挂”是指现状而言,故表过去“挂”的B、D项可排除。C项虽指“现在挂”,但侧重在常规,习惯。为了突出“你所指的那件雨衣不是我的,我的正挂在门后”这一意思,选A是极为合情理的。Thank you
1、高考考查的八种时态是:一般现在时,一般过去时,一般将来时,现在进行时,过去进行时,现在完成时,过去完成时,过去将来时。
2、容易混淆的三组动词时态是:一般现在时和现在完成时;一般过去时和过去完成时;过去完成时与现在完成时。
3、各种时态及含情态动词的被动形式的应用。学习重点:
1、时态和语态在特定语境中的基本用法。
2、学会根据语境或上下文逻辑关系来判断时态。
3、同题检测时态和语态。
4、被动语态和系表结构,主动形式表被动意义的知识。突破方法:
1、不可脱离语境学习时态和语态,而是要在了解了八种常用时态的一些常用规则后,留心以英语为母语者在实际生活中如何使用各种时态和语态。
2、建立时态的时、体概念(“时”即现在时、过去时、将来时、过去将来时;每个时又分四个“体”,即一般体、进行体、完成体、完成进行体)。
3、解决时态和语态问题,要遵循如下解题思路:
1)这件事情说的是什么时候的事情或情况? (定“时”)
2)这个动作处于什么状态,是完成了,还是未完成,还是既不表完成又不表进行?(定“体”)
3)这个动词与主语的关系,是主动还是被动? (定“语态”)概念
时态是谓语动词所表示的动作或情况发生时间的各种形式。它是“时”和“体”的组合。“时”有现在、过去、将来、过去将来之分;“体”有一般、进行、完成、完成进行之别。见下表:一、一般现在时
1.一般现在时表示经常发生、习惯性动作或存在的状态;
He takes a walk after supper every day.
He is our English teacher.
客观真理、科学事实、格言;
The sun rises in the east.
Two plus two makes four.
主语的特征、性格、能力等。 He woks hard. The children draw well.
常见时间状语:often, sometimes, seldom, always, every day/month/ year 2.主句是一般将来时,时间、条件状语从句中用一般现在
表示将来。如:
I’ll go there after I finish my work.
If it rains tomorrow, I won’t go there.
3.在以here, there开头的句子里,go, come等少数动词的一般现在时表示正在发生的动作。例如:
There goes the bell.铃响了。
There comes the bus.汽车来了。
Here she comes.她来了。
4. 表示安排或计划好的将来的动作(一般只限于某些表移动的动词,如go,come,leave, start,be ,arrive, begin, return, open, close, depart, end, sail,
finish等).
The train starts at ten o’clock in the morning.
Supper is at five today.二、一般过去时
1)表达特定的过去时间内发生的动作或存在的状况,常与last week/year/ month/ spring, a few days ago, in 1998等时间状语以及when等连词引导的时间状语从句连用。
We had a good swim last Sunday.
When I was young, I took cold baths regularly.
2)叙述过去连续发生的一件件事。
He got up early in the morning, fetched water, swept the yard and then went out to work.
3)表过去某一时间内经常发生或反复发生的动作或行为。 When my brother was a teenager, he played table tennis almost everyday.
4)在条件、时间状语从句中表示过去将来的动作。
They said they would let us know if they heard any news about him.题组练习:用所给动词的适当形式填空
---Your baby is too thin.
---- It could gain weight, but it _____(not eat) much.
2. It won’t be long before such a thing _____ (happen) again.
3. I won’t speak to him unless he ____
(apologize) to me.doesn’t eathappensapologizes4. The careless driver has just been fined $ 10 for stopping his car at a sign that ____ (read) “NO PARKING”.
5. --- Nancy is not coming tonight.
---- But she _______ . (promise).readspromised三. 一般将来时
一般将来时表示将来要发生的动作和存在的状况。有下列一些形式:
1.will/shall do (侧重将来行为,不突出计划安排去做某事,与tomorrow,next week, soon, in 2018等连用)
My daughter will be twelve years old tommorrow.
I shall go back to see my childhood friends in the summer vacation.
We shall work in this factory every day.
(表将来经常发生的动作)2. be going to do (主观上打算、决心或客观上可能发生)
We are going to visit the Museum of Chinese History.
Tom studies very hard, and he is going to try for a scholarship.
Look at those clouds. It’s going to rain. 3. be about to (表即将发生的动作,立即的将来,此句型很少与表示将来的具体时间状语连用。)
The English evening is about to begin.
We are about to leave, so there is no time to visit him now.
4. be to do
1)(按计划或安排即将发生)
The boys are to go to school next week.
He and I are to meet at the Shanghai Railway Station.这种结构也可用于过去,was / were to do sth表示曾经计划要做的事,但不表明计划是否被执行,或表示命运(即命中注定要发生的事),而非计划;was / were to have done sth 表示未曾实现的计划。
I felt nervous, I was soon to leave home for the first time.我感到很紧张,因为我很快就要首次离开家了。
They said goodbye, little knowing that they were never to meet again.他们告了别,不知道以后再也不会见面了。
We were to have told you, but you were not in. 我们本想告诉你的,但你不在家。2)表示“应该”,相当于should ,ought to ,
You are to report to the police.
What is to be done?应该怎么办呢?
3) 表示“必须”, 相当于must ,have to
The letter is to be handed to him in person.
4) You are to do your homework before you watch TV.
表示“想,打算”,相当于intend,want ,
If we are to be there before ten, we’ll have to go now. 5)用于第一人称疑问句,表示征求对方意见。
Am I to go on with the work?
What are we to do next?
6)用于否定句,表示“禁止”, 相当于“mustn’t”
The books in this room are not to be taken outside.
7)表示“可能,可以”, 相当于may, can
The news is to be found in the evening paper.
Such people are to be found everywhere. 9) were to do sth用于if 或 even if /even though 从句中,表示对未来的假设。
If I were to tell you that I killed him, would you believe me?
Even if the sun were to rise in the west, I would never do such a thing.
10) be to blame(该受责备,对某坏事应负责任)与 be to let (待出租)两种结构中,用不定式的主动形式表示被动含义。
Which driver is to blame for the accident? 这事故是哪个司机的责任?
This house is to let. 这房子要出租。题组练习:单项填空6. We have been looking for the boy all the afternoon but he is nowhere_____.
to see B. seeing C. seen D. to be seen
7. As early as his second film, Chaplin had developed his own manner of acting, the one that ____ world famous.
A. Would become B. became
C. was to become D. had become8. --- We just saw John at the bookstore.
---- That’s strange. I didn’t think he ___back until tomorrow.
A. will come B. was to come
C. is coming D. is to come
9. If the sun ____ tomorrow, what would we do?
A. were not to raise B. does not rise
C. would not rise D. were not to rise10. Look at these clouds, ___.
A. It’s going to rain B. It’s raining
C. It is to rain D. It can rain
11. Who do you think ____ for the failure of their marriage?
A. to blame B. to be blame
C. is to blame D. is to be blamed 四、现在进行时
1.表示正在进行的动作或存在的状态。
We are having an English lesson.
He is translating a novel.
--- Have you moved into the new house?
---- Not yet. The rooms are being painted.
2.有些动词,如come,go,leave,return,arrive,begin,start,stay等,它们的现在进行时表示按计划安排在不远的将来即将发生的动作。
例如:She is leaving for Beijing.她要去北京。
He is working as a teacher tomorrow.
从明天起他要做老师。
My father is coming to see me this Saturday.
这个星期六我爸爸要来看我。3.代替一般现在时,描绘更加生动。例如:The Changjiang River is flowing into the east.江水滚滚向东流。The sun is rising in the east.太阳从东方冉冉升起。
4. 表示反复出现或习惯性动作,往往含有赞赏、厌恶、遗憾等情绪,常与always, continually, constantly连用, 如:
He is always thinking of others first.
He is always making the same mistake.
5.大多数动词可用于进行时,但也有些动词不用于进行时。常见的有:exist,live,understand,mean,owe,belong to ,know,doubt,suppose,remember,forget,
believe,trust,want,wish,refuse,like,hate,dislike,
prefer,mind,hope等。五、过去进行时
1.表示过去某一时刻或某一段时间内正在进行的动作(这一过去时间须用时间状语表示)。
例如:He was preparing his lecture all day yesterday.
2.表示动作在另一过去动作发生时进行。
例如:They were still working when I left.
3.用在两个过去进行时动作同时发生。
例如:I was writing while he was watching TV.4.表示过去将来动作。例如:He said she was arriving the next day.
5.一个长动作作为背景,被一个短动作打断,长动作往往用进行体,短动作用一般体。
My brother fell while he was riding his bicycle and hurt himself.
Tom slipped into the house when on one was looking.题组训练:用所给单词的适当形式填空。12) You _____ always ______ (watch) TV. Why not do something more active?
13) ---- Watch!
----- I ______ (watch) but I ______ (not see ) anything unusual.
14) Listen ! The couple _______ (quarrel) in the room.
15) ---- You’re drinking too much!
---- No one ____ (see) me but you. arewatchingam watchingdon’t seeare quarrellingsees六、过去将来时
1.表从过去某时间看将要发生的事情,多用在在间接引语或宾语从句中,还可表示过去的倾向
或过去经常发生的事情
They asked me if I would go to Guangzhou soon.
He’d play the violin when he was in low spirits.
2 . 用于“was/were going to+动词原形”句型中,表示过去的安排、打算或确信某事会发生,
多用于口语。 I told her I was going to see her that afternoon.
I’m sure (that) they were going to do that. 七、将来进行时
1)表示在将来某一时间正在进行的动作;
They will be meeting us at the station. I will be seeing Mr Smith tomorrow.
2)表示原因、结果或猜测;
Please come tomorrow afternoon, tomorrow morning I’ll be having a meeting.
Stop the child or he will be falling over.
You will be making a mistake.
3)用在问句中,表示委婉礼貌;
Will you be reading anything else?
When shall we be meeting again?
4)表示稍后一点的安排
My duties will end in July and I will be returning to Shanghai.八、现在完成时
1.表示过去发生的动作对现在产生的影响或结果,或说话时已完成的动作,常与so far, in
the past/ last few years, recently, lately, twice, for two years, how long, since (…ago) 用。
例如:I have finished one third of the report so far. She has cleand the room.
2.表示从过去开始,待续到现在的动作或状态,往往和“for…”, “since…”表述的一段时间状语连用。例如:He has learned English for six years./ They have worked here since they left college.3.现在完成时与一般过去时的区别:
1)用两种时态来表述发生在过去的某一动作,现在完成时强调这一过去动作对现在产生的影响或结果,而一般过去时只表达过去的动作或状态,和现在关系不大。例如:She has cleaned the room.It’s very clean now.(此句has cleaned就不能改为cleaned.一是因为cleaned与现状无关,二是因为一般过去时不可突然跳到It’s这样的一般现在时。)
2)汉语中的“了”、“过”、“曾”等词常用完成表达,如:I have seen that film.(我看过那部电影了。)但是如果是在特定的过去时间“看了”、“做过”,就不可用完成时而必须用一般过去进来表达。例如:When did you see that film? I saw it yesterday.(你什么时候看了那部电影?我昨天看的。)不能说:When have you seen that film?I have seen it yesterday. 4. 表示“曾经到过某地(人已回来)”用“have/has been to”,表示“到某地去了(还未回来)”用“have/has gone to”.例如:
——Where is Li Hua?
-He has gone to the reading-room.
——She knows a lot about Shanghai.
-She has been there.
5. 短暂动词(即瞬间动词),join,lose,buy,borrow,leave,go,come,arrive,
die,marry, finish,complete,begin,start,
break out等,在完成时态中,其肯定式不能和表示一段时间的状语连用。
例如不能说:He has finished the work for three hours.
要翻译“他已完成工作三小时了。”可采用
1)“ago法”:He finished the work three hours ago.
2)“延续法”:He has been through(with)the work for three hours.
3)“since法”:It is/has been three hours since he finished the work.
题组训练: 句型转换
16) He left his office 3 hours ago.
He _____ _______ ______ from his office for 3 hours.
It ______ ______ 3 hours since he left his office.
17) He has been dead for 4 years.
He ______ ______ ______ ago.
It has been _____ ______ ______ he died. has been awayhas beendied four years four years since九、过去完成时
1.表示在过去某一时间以前已经完成的动作,常与by
(the end of)+过去时间状语,by then等时间状语连用, 也可用before等介词短语或一个时间状语从句来表示,
还可通过上下文来表示。
He had shut the door before the dog came up.
Everything had been all right up till this morning.
By then he had learned English for 3 years.
2.表示动作或状态从过去某个时刻开始一直延续到另一个过去时刻才完成,甚至还要继续下去。
例如:At the age of ten,he had learned 500 English words.
He had been ill for a week when we learned about it.3.常用hope,expect,think,intend,want,suppose等动词的过去完成时来表示未实现的希望、打算或意图。例如:We had expected that you would be able to win the match.
4.用于hardly / scarcely / barely had ... done…when…和no sooner…had...done...than…引导的复合句的主句中,常用倒装语序。When 和than从句里用一般过去时,表示“刚刚、、、就、、、”
Hardly (No sooner) had I got home when (than) the rain poured down.我们刚到家大雨就倾盆而下。
Hardly had we started when the car got a flat tyre. 我们才刚刚开动,汽车的轮胎就漏气了 5. It was / had been + 一段时间+ since从句. Since 从句中的谓语动词用过去完成时。
It was ten years since we had had such a wonderful time. 我们10年没这么高兴了。
6. This / That / It was the first / second ...time + that 从句。 that从句中的谓语动词用过去完成时。
It was the third time (that) he had made the same mistake. 这是他第三次犯同样的错误了。
That was the first time (that) I had passed the exam. 那是我第一次考试及格。 十、将来完成时
用来表示在将来某个时刻(前)将完成的动作。常和by短语,when,before引起的时间状语连用。例如:We will have finished senior Book 2 by the end of this term.
十一、现在完成进行时
1.用来表示从过去某一时刻开始一直持续到现在(或今后还要继续一去)的动作。完成进行体是完成体和进行体的组合,因此,它具备完成体和进行体的一些因素,如它具备进行体的“未完性、暂时性、感彩”等特点。例如:He has been learning English for 6 years.(从过去某一时间开始学英语,强调到现在还在学)
It has been raining for three days.(强调说话者抱怨的感彩)
2.凡是不能用于现在进行时的动词均不能用于现成完成进行时。 题组训练:用所给动词的适当形式填空.
18) Helen _______ (leave) her keys in the office so she had to wait until her husband _____ (come ) home.
19) I _____ (hope) to meet Mr. Thompson this morning, but I found nobody left in the room. had left camehad hoped20) We plan to reach the North Pole in mid-July, and by then we _____
(walk)for six weeks.
21) By the time you arrive in New York, you will ____ (away) for two weeks.
22) --- Did you find the missing couple in the mountain yesterday?
--- No, but we _____ (try) to get in touch with them ever since. will have walkedhave been away have been trying(2006年高考全国卷I)
The house belongs to my aunt but she ____ here any more.
A.hasn’t lived B. didn’t live
C. hadn’t lived D. doesn’t live高考感悟【解析】 本题考查动词的时态。其句意为“这所房子是我阿姨的,但她(现在)不住这儿了。”指的是现在的居住情况,故D项符合。【命题立意】 时态题要依据句中出现的动词的时态或时间状语来判断。2 (2006年高考全国卷II)
John, a friend of mine, who got married only last week, spent $ 3,000 more than he for the wedding.
will plan B. has planned
C. would plan D. had planned
【解析】 plan表示的动作发生在spent这一过去动作之前,应该用过去完成时。此句意为“我的朋友约翰上周结婚了,婚礼花去了3000美元,超过了原计划。”
【答案】D 【命题立意】 本题考查过去完成时态。3 (2006年高考北京卷)
- leave at the end of this month.
-I don’t think you should do that until ____ another job.
A. I’m going to; you’d found
B. I’m going to; you’ve found
C. I’ll; you’ll find
D. I’ll; you’d find
【解析】 be going to 按计划,打算将要做某事。此句意为“我打算在这个月末离开。”“我认为在你没有找到另一份工作之前你不应该离开。”
【答案】B
【命题立意】本题是对时态基本用法的考查。4 (2006年高考北京卷)
-Your job open for your return.
-Thanks.
A. will be kept B. will keep
C. had kept D. had been kept
【解析】 keep the job/ the position open 使工作、职位等处于空缺状态,由句意“随时欢迎你回来工作”可知用将来时。
【答案】A
【命题立意】此题考查一般将来时的被动语态,时态的判定要根据句意来确定。 5 (2006年高考北京卷)
-Where did you put the car keys?
-Oh, I put them on the chair because the phone rang as I in.
remembered; come
remembered; was coming
C. remember; came
D. remember; was coming
【解析】 remember是说话者说话时的思维活动,应用一般现在时。remember宾语从句的内容发生在以前,故用过去时态。
【答案】C
【命题立意】 本题考查时态的基本用法,做题时要将自己融入题目,身临其境。6 (2006年高考天津卷)
What we used to think impossible now does seem possible.
is B. was C. has been D. will be
【解析】 由句意“我们以前认为不可能的事现在看起来的确是可能的”和谓语动词used to think可知空格处的谓语部分应该表达过去意义。【答案】B
【命题立意】本题考查时态用法,应善于抓住句中含有时间概念的动词或时间状语的暗示,如本句中的used to和now。7 (2006年高考上海卷)
When he turned professional at the age of 11, Mike to become a world champion by his coach and parents.
A. expected B. was expecting
C. was expected D. would be expected
【解析】Mike与expect之间为动宾关系,故需用被动语态,由从句含义可以确定其时态为过去时。
【答案】C
【命题立意】本题综合考查时态与语态,注意谓语动词与主语的逻辑关系及上下文体现的时间含义。8 (2006年高考广东卷)The young girl sitting next to me on the plane was very nervous. She before.
A. hadn’t flown B. didn’t fly
C. hadn’t flown D. wasn’t flying
【解析】动作发生在was nervous之前
【答案】C
【命题立意】本题考查过去完成时态。9.——Can I join your club,dad?
——You can when you______a bit older. (NMET)
A.get B.will get
C.are getting D.will have got
析:“You can”是将来意,when引导的时间状语从句要用一般现在时表将来所以此题答案为A.10.—— Oh,it’s you!I______you.
—— I’ve just had my hair cut and I’m wearing new glasses.
A.didn’t recognize
B.hadn’t recognized
C.haven’t recognized
D.don’t recongnize
析:从“Oh,it’s you!”可知说话时已认出对方。“没有认出”是在此之前为过去情况,所以应选A 11. I don’t think Jim saw me; he______into space. (NMET)
A.just stared
B.was just staring
C.has just stared
D.had just stared
析:B, 在空白处应选一个与“saw”相配,能解释Jim didn’t see me 这一原因的选项,只有着眼于A、B。若选A不能体观他“当时正在做”某事,故排除A而选B。这样因为“他正在望宇宙天空”所以“未看到我”。12. ——______my glasses?
——Yes,I saw them on your bed a minute ago. (NMET)
A.Do you see B.Had you seen
C.Would you see D.Have you seen
析:现在完成时可表过去发生的事情对现在产生的影响或结果,问话人以这样的时态发问可作现焦急的心情。故答案为D。
13.You don’t need to describe her.I______her several times. (NMET)
A.had met B.have met C.met D.meet
析:答案B。道理同12。14.——Do you know our town at all?
——No,this is the first time I______here.
A.was B.have been
C.came D.am going
析:根据this/it is the first/second/…time sb.has done sth.句型,可定答案为B。 又如:This is the second time he has visited the Great Wall.15. I don’t really work here.I______until the new secretary arrives. (NMET)
A.just help out
B.have just helped out
C.am just helping out
D.will just help out
析:根据I don’t really work here.以及…until the new secretary arrives,可知说话人所要做的事是计划安排行为,C、D两个选项都表将来动作,但D非计划安排,C则体现按计划去做,所以此题答案为C。16. ——Is this raincoat yours?
——No,mine______there behind the door. (NMET)
A.is hanging
B.has hung
C.hangs
D.hung
析:此题的“悬挂”是指现状而言,故表过去“挂”的B、D项可排除。C项虽指“现在挂”,但侧重在常规,习惯。为了突出“你所指的那件雨衣不是我的,我的正挂在门后”这一意思,选A是极为合情理的。Thank you
