高中英语人教版(新课程标准)选修6【全单元教学课件】 Unit 2 Poems(120张PPT)
文档属性
| 名称 | 高中英语人教版(新课程标准)选修6【全单元教学课件】 Unit 2 Poems(120张PPT) |  | |
| 格式 | zip | ||
| 文件大小 | 2.4MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 人教版(新课程标准) | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2018-04-19 08:20:40 | ||
图片预览











文档简介
课件120张PPT。A few simple forms
of English poemsReading Do you remember any little poems or songs you learned when you were a child?
Do you remember any poems you have read in high school, either in Chinese or in English? Can you recite any? What are the characteristics of poems? Can you give me some examples?
Poems have beats. They may rhyme or may not rhyme — but they have to have rhythms.
This beat is not always obvious, but it’s usually there.Twinkle, twinkle, little ____,
How I wonder what you ____,
Up above the world so ____ ,
Like a diamond in the _____.star.are.high.skyCan you find something
like a poem?Rhyme and rhythm are essential to poetry. Without rhythm, there wouldn’t be poems.Twinkle twinkle little star
How I wonder what you are,
Up above the world so high
Like a diamond in the sky. 强 弱 强 弱 强 弱 强唐诗分五言,七言。根据韵节来分
英诗可分为单韵诗、双韵诗、三韵诗……至八韵诗。构成一个韵节的四种情况: 强 + 弱, 强 + 弱弱
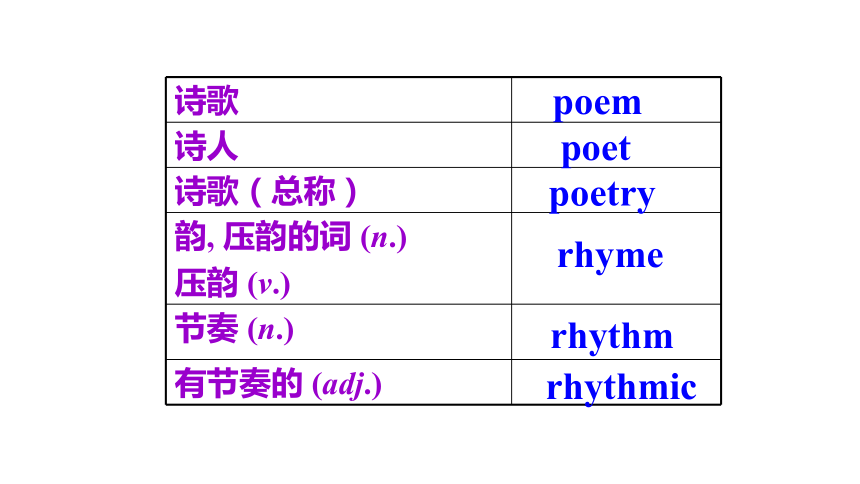
弱 + 强, 弱 + 强 poempoetpoetryrhymerhythmrhythmicThere are many reasons why people write poems. In small groups make a list of these reasons. Why do people write poems?People write poems
to tell a story
to express feelings
to make others laugh to tell the life or friendship
to delight the kids
to tell stories
to describe the seasons or scenes
for entertainment
as the lyric of a song SkimmingScan the text for the two questions.
1. What is the main idea of the reading passage?
2. What five kinds of poems does the reading passage talk about? Some simple forms of English poems.Nursery rhymes, list poems, the cinquain, haiku and Tang poems.Read the text carefully and fill in the blanks.Nursery
rhymes rhythm and rhymereciteList poems phrasesfive linesstrongtranslations17 syllablesclearHush, little baby, don’t say a word, Papa’s going to buy you a mockingbird.
If that mockingbird won’t sing, Papa’s going to buy you a diamond ring.
If that diamond ring turns to brass, Papa’s going to buy you a looking-grass.2. Read and answer questions.AIf that looking-grass gets broke, Papa’s going to buy you a billy-goat.
If that billy-goat runs away, Papa’s going to buy you another today. What is the baby’s father going to
buy if the mirror gets broken?
If the mirror gets broken, the baby’s father will buy a billy-goat instead.
2. What is the baby’s father going to do if the goat runs away?
He’s going to buy the baby another billy-goat. 3. What is the poem A about? Use
your own words to explain it.
Poem A is a nursery thyme that
illustrates a father’s love for his baby.I saw a fish-pond all on fire,
I saw a house bow to a squire,
I saw a person twelve-feet high,
I saw a cottage in the sky,
I saw a balloon made of lead,
I saw a coffin drop down dead,I saw a fish-pond all on fireBI saw two sparrows run a race,
I saw two horses making lace,
I saw a girl just like a cat,
I saw a kitten wear a hat,
I saw a man who saw these too,
And said though strange they all were true.What is the poem B about?
Poem B is an amusing nonsense poem which describes images of some ridiculous things.We should have won …
If Jack had scored that goal,
If we’d had just a few more minutes,
If we had trained harder,
If Ben had passed the ball to Joe,
If we’d had thousands of fans screaming,Our first football matchCIf I hadn’t taken my eye off the ball,
If we hadn’t stayed up so late the night before,
If we hadn’t take it easy,
If we hadn’t run out of energy.
We should have won …
If we’d been better! What is the poem C about?
Why didn’t the players win the match?
Does the author really believe his or her excuses? How do you know?Answer these questions.Sample answers:
Poem C is about losing a football match and the writer lists a lot of excuses for their failure. What is the poem C about?They didn’t win because they didn’t have enough time; they didn’t have thousands of fans screaming; they stayed up too late the night before; they ran out of energy. 2. Why didn’t the players win the match?No. The author doesn’t believe his excuses, because at the end of the poem the speaker admits that they just did not play well enough to win …3. Does the author really believe his or her excuses? How do you know?Brother
Beautiful, athletic
Teasing, shouting, laughing
Friend and enemy too Mine Summer
Sleepy, salty
Drying, drooping, dreading
Week in, week out
EndlessDE1. What are the poems about?
2. Do the authors like the subjects? Give
your reasons. Poem D is a description of a lovely brother.
Poem E is a description of hot and boring summer. Poem D: Yes, the author likes his subject. Although the speaker describes a couple of negative aspects of his / her brother, the reader can feel the affection that the speaker feels for his / her brother. Poem E: No, the author doesn’t like his subject. The reader gets the feeling that the speaker cannot wait until the summer is over. The words drooping, dreading, week in, week out and endless convey this feeling.FA fallen blossom
Is coming back to the branch.
Look, a butterfly! GSnow having melted.
The whole village is brimful
Of happy children.What are the poems about?
Poem F describes how a butterfly rests on a tree.
Poem G describes that the weather is warmer and the village is full of happy children.Where she awaits her husband on and on the river flows.
Never looking back, transformed into stone.
Day by day upon the mountain top, wind and rain revolve.
Should the journeyer return, this stone would utter speech.H望夫石望夫处,江悠悠,
化为石,不回头。
山头日日风复雨,
行人归来石应语。What is the story that the poem tells? Tell the story in your own words.
2. Circle one or more of the feelings below that you think the woman has. Give reasons for your answers:
loneliness joy love trust
anger hate sorrow1. A woman’s husband has gone away. The woman waits for him by the river where she last saw him. She waits and waits, never moving from that spot and never speaking, while the river continues to flow and the wind and rain come and go.2. The woman has the feelings of:
Loneliness: she was alone watching her husband on the mountain top.
Love: she waited year after year despite wind and rain.
Trust: she believed her husband would come back one day.Sorrow: year after year, she waited and waited without seeing any hope of her husband’s coming back, she was very sad.一首诗 a poem1. There are various reasons why people write poetry. 1) various: different, its root is vary.
2) poetry is a collective noun, used as
an uncountable noun.2. Others try to convey certain emotions.
1) convey
★ 作“传达,表达(思想或感情等)”讲
时,常用于convey sth. (to sb.)结构。
e.g. 1. Colours like red convey a sense of
energy and strength.
2. Please convey my thanks to your
wife. ★ 作“传送,运送,输送”讲时,常用于convey sb. / sth. (from ...) (to ...) 结构。
e.g. 1. This train conveys over five
hundred passengers every day.
2. A taxi conveyed us to the train
station.
3. Wires convey electricity from
power stations to the user. 3. The language is concrete but imaginative, and they delight small children because they rhyme, have strong rhythm and a lot of repetition.
本句是一个由and连接的并列复合句,两个分句分别是 _______________________
_______________ 和they delight small children ... a lot of repetition; The language is concrete but imaginativeb. 第二个分句中含有一个由because引导的原因状语从句。4. List poems have a flexible line length
and repeated phrases which give both a
pattern and a rhythm to the poem.
flexible灵活的,可弯曲的,柔顺的。5. Another simple form of poem that
students can easily write is the
cinquain, a poem made up of five lines.
本句的主干为:Another simple form
of poem is the cinquain;
b. that引导定语从句students can easily write,修饰先行词 _______;
c. a poem made up of five lines作cinquain同位语;poemd. 在同位语中,made up of five lines是
过去分词短语作后置定语,修饰
poem,可以改为定语从句which is
made up of five lines。
这句话还可以这样表达:
The cinquain is another simple form of poem. It is made up of five lines and students can easily write it. 6. We would have won ... ... if we hadn’t run out of energy.
run out of ... 为及物动词短语,意为“用完了……”,而run out为不及物动词短语,后不能接宾语,意为“被用完”。
e.g. I have run out of money.
My money has run out.7. It is easy to write and, like the cinquain, can give a clear picture and create a special feeling using the minimum of words.
本句包含三个并列的谓语,分别是:
_____________, can give和(can) create;
b. like the cinquain作插入语;
c. using the minimum of words是动词-ing形式作方式状语。is easy to write8. Should the journeyer return, this
stone would utter speech.
当if引导的虚拟条件句中有had, were, should时,可将if省去,将had, were, should提前,构成倒装语序。9. Did you know that English speakers
also enjoy other forms of Asian poetry — Tang poems from China in particular?
in particular 尤其,特别,其中,形容词particular意为“特指的,特别的”。另外,particular还可表示“讲究,挑剔”,可构成be particular about,意为“对……挑剔 / 讲究”。1. Read the text aloud and recite Paragraph 1.
2. Prepare your favorite Tang poem (s) and translate it/them into English.Using languageSpeaking请阅读下面的短文,以帮助你理解课本上的诗歌“I’ve saved the summer”。
I’ve saved the summer
I’ve saved the summer for you. And when the snow begins to fall on cold
winter mornings, I’ll give it all to you to keep you warm. I’ve saved some sunlight in case you need it. I believe it will drive off darkness and light your way. When you were nineteen, I kept the image of your smile in my mind. When you get older, you will know the meaning of brave young smiles.
I don’t know how I can help you to start your journey through life. However, there will be solutions somewhere before the day is through.
Whenever you need love, I’ll offer all I have. It might help you as you travel on your way, till you find the love that belongs to you.1. Listen to the poem ‘I’ve saved the summer’ and answer these questions. (answers are free)
1) Do you think the speaker in the poem is more likely to be a girlfriend /boyfriend or parent?
2) Does the poem have a rhythmic pattern?3) Does the poem have rhyming words?
4) When you were listening to the poem, did it make you feel something or think about something? What did it make you feel or think about?2. Now read “I’ve saved the summer”.
1) Circle the words that rhyme. What is unusual about the rhyming words in the last four lines?
2) Try beating or clapping the strong beats of the rhythm as you read the poem to yourself. Now listen to the poem again and clap the strong beats.Rod McKuen I’ve saved the summer
And I give it all to you
To hold on winter mornings
When the snow is new.I’ve saved some sunlight
If you should ever need
A place away from darkness
Where your mind can feed.人民教育出版社 | 选修六 And for myself I’ve kept your
smile
When you were but nineteen,
Till you’re older you’ll not know
What brave young smiles can
mean.I know no answers
To help you on your way
The answers lie somewhere
At the bottom of the day. But if you’ve a need for love
I’ll give you all I own
It might help you down the road
Till you’ve found your own.
(by Rod McKuen)人民教育出版社 | 选修六 1. Who is the speaker in the poem and who is he /she speaking to? Give reasons to support your answer.
Maybe a parent speaking to a young adult child. 2. Which of the following is the closest to the speaker’s message? Give a reason for your choice.
A. If it’s cold, I’ll warm you; if it’s dark, I’ll give you light; if you’re hungry, I’ll feed you; if you want love, I’ll give it to you.B. Although the future may be difficult for you, whenever you need warmth and love, remember I’ll have some to give you.
C. While you’re away I’ll remember your smile and I’ll love you always. When you return, I hope you will love me.人民教育出版社 | 选修六 1. Does the poem have a rhyming pattern?
pattern:
n. (1) 图案
e.g. This cloth has a pattern of blue and
white squares.
这种布有蓝白格子的图案。Language points(2) 模板, 式样
e.g. They like new?patterns?of family life.? 他们喜欢新的家庭生活方式。
v. form a pattern
e.g. He patterned himself upon a man he admired.
他模仿一个他钦佩的人。人民教育出版社 | 选修六 2. Till you’re older you’ll not know what
brave young smiles can mean.
等你长大成人以后,才知道年轻勇敢的
微笑的奥秘。
till 用在肯定句中,意为“直到……为
止”,通常表示动作的终点,因此,动
词必须是延续性的。如:We must stick to our task till it is finished. 我们必须继续工作, 直到做完为止。
Just wait till you see it. It’s great.
你就等着直到看见它吧。好看极了。
用在否定句中,意为“直到……才”,通常表示动作的起点,动词可以是延续性的也可以是非延续性的。如:She didn’t sleep till her son came back.
直到她儿子回来她才睡着。
(sleep为延续性动词)
I didn’t begin work till he had gone.
直到他走了我才开始工作。
(begin为非延续性动词)3. I’ll also try out his way some time.
try out: trying something to find
out about it 试用, 试验
e.g. Please try out red wine.
请试试我们的红葡萄酒。try one’s best
try on
try doing sth.
try to do sth.尽最大努力
试穿
试着做某事
尽力做某事ListeningListeningQuestion 1: What inspires you to write poetry?
Question 2: In what kind of place do you like to write poetry?
Question 3: What conditions do you need to be able to write poetry? (Does it have to be quite, do you need to be alone, do you need to listen to music and so on?)1. Listen to Part 1 and answer these questions.
(1)Who has written a poem already and is ready to enter the competition?
(2) Who is not going to enter a poem for the competition this year? LucyPitt(3) Who plans to write at the weekend?
Jack
(4) When is the deadline for the competition?
the 24th of the month.Listen to Part 2 of the tape and
fill in the chart.by going for a hike in the countryside
and then sitting quietly by himselfby surrounding herself with familiar
things in her own house. Listen to the two parts again and note down the expressions about intention and plans.possibly by listening to his favourite
music though he has never written
poetry beforeI’m ___________ enter a poem this year.
I haven’t begun mine yet but I _________
___ this weekend.
How ____ inspire yourself this weekend?
I ________ go for a hike in the
countryside and sit quietly somewhere
by myself.not going to plan to do
itwillintend toSubjunctive Mood(II)虚拟语气Learning study虚拟语气(二)
本节课我们巩固复习虚拟语气,主要复习if条件从句和wish宾语从句中表示过去情况的虚拟语气的用法,以及虚拟语气在其他从句中的运用。虚拟语气特殊句型1. wish 的宾语从句现在: 过去时(were)
过去: 过去完成时
将来: would/could/might +
v. should下面我们再来看看其他形式的虚拟语气的用法。1. I wish I were a bird. (现在)
2. I wish I hadn’t made such a mistake. (过去)
3. We wish our parents wouldn’t punish us. (将来)I wish I were as tall as you.
我希望和你一样高。
He wished he hadn’t said that.
他希望他没讲那样的话。
I wish it would rain tomorrow.
我希望明天下雨就好了。2) wish to do 表达法 wish sb. / sth. to do I wish to see the manager. = I want to see the manager.
I wish the manager to be informed
at once. = I want the manager to be informed at once.2. would rather that现在:
过去:
将来:e.g. I would rather you paid me now.
I would rather you had gone, too.
Don’t come. I would rather you
came tomorrow.过去时过去时过去完成时3. as if /though + clause 现在:
过去:过去时过去完成时在as if / as though后的从句中,常用一般过去时或“would / could / should / might + 动词原形”来表示与现在或将来的事实相反或不太可能实现的事情。 They talked as if they had been
friends for years.
He looks as if he were drunk.e.g. She loves the baby as if it were
her own son.
I remember the whole thing as if
it had happened yesterday.4. It’s (about/high) time + that过去时
should + v.你该走了。It’s high time that you went.
It’s high time that you were
going.
It’s high time that you should
go.我们该去睡觉了。It’s time that we went to bed.
It’s time that we should go to bed. 5. without和but for 构成虚拟。
but for要不是
Without sunlight, people’s life would be different from today.
But for your help, I wouldn’t have finished the work.6. If only … 要是就好了
e.g. If only I knew his name!
If only we had followed your advice!
If only I could see him again!要是我们的父母能和我们住在一起就好了!
If only our parents could live with us!
要是我没错过火车就好了!
If only I hadn’t missed the train!7. 在主语、表语、同位语从句中,虚拟语气用“should + 动词原形”或动词原形来表示。这样的句型有:It is strange / natural / important / no wonder / impossible / necessary / a pity / ... that ...;My advice / suggestion / requirement / ... is that ... 等。It is important that we (should) master a foreign language.
It is strange that she refuse to come to the party.
It’s necessary that we should study hard.WritingWriting如 何 写 英 语 诗 歌
诗歌是各种英语文体中最富有激情和感彩的一种。诗歌往往用高度凝练的语言来表达诗人的喜怒哀乐,诗人把自己对生活和客观世界的理解和感悟融入诗歌,当我们在欣赏一首诗时,可以通过文字捕捉到诗人的内心情感。一首优秀的诗可以以其特有的节奏与方式影响人们的精神世界。【写作指导】
一、诗歌的篇幅一般短小精悍,语言精练,感情强烈;在格式上,英语诗歌同汉语诗歌一样讲究押韵。诗的押韵是指通过重复元音或辅音以达到一定的音韵效果,一首诗的押韵具有带规律性的一致性,尤其是在诗句的末尾,称尾韵。下面我们来看Thomas Nash的一首诗:Spring
Spring, the sweet Spring, is the year’s pleasant king;
Then blooms each thing, then maids dance in a ring,
Cold doth not sting, the pretty birds do sing,
Cuckoo, jug-jug, pu-we, to-witta-woo!The palm and may make country houses gay,
Lambs frisk and play, the shepherds pipe all day,
And we hear aye birds tune this merry lay,
Cuckoo, jug-jug, pu-we, to-witta-woo!The fields breathe sweet, the daisies kiss our feet,
Young lovers meet, old wives a-sunning sit,
In every street theses tunes our ears do greet,
Cuckoo, jug-jug, pu-we, to-witta-woo!
Spring! the sweet Spring!这首诗押韵整齐,读起来很有节奏感。表现了春天里万物复苏、生机盎然、一派欢乐祥和的生动景象。
二、现代诗歌可以押韵,也可以不押韵,但是写作时需注意两点:
1. 要有节奏感。没有节奏感的诗歌,不能算诗,最多是分行的散文。2. 要把握句子结构的平衡。也就是诗句长短不要相差太远,否则读起来给人不平衡、不舒服之感。The Significance of Failure
Failure doesn’t mean you are a failure,
It does mean you haven’t succeeded yet.
Failure doesn’t mean you have accomplished nothing,It does mean you have learned something.
Failure doesn’t mean you have been a fool,
It does mean you had a lot of faith.
Failure doesn’t mean you’ve been disgraced,
It does mean you were willing to try.
Failure doesn’t mean you don’t have it, 人民教育出版社 | 选修六 It does mean you have to do something
in a different way.
Failure doesn’t mean you are inferior,
It does mean you are not perfect.
Failure doesn’t mean you’ve wasted your life,
It does mean you have a reason to start afresh.
Failure doesn’t mean you should give up,
It does mean you must try harder. Failure doesn’t mean you’ll never make it,
It does mean it will take a little longer.
Failure doesn’t mean God has abandoned you,
It does mean God has a better idea. 【佳作赏析】
When You Are Old
When you are old and grey and full of sleep,
And nodding by the fire, take down this book,
And slowly read, and dream of the soft lookYour eyes had once, and of their shadows deep;
How many loved your moments of glad grace,
And loved your beauty with love false or true,
But one man loved the pilgrim soul in you,And loved the sorrows of your changing face;
And bending down beside the glowing bars,
Murmur, a little sadly, how Love fled
And paced upon the mountains overhead
And hid his face amid a crowd of stars. 这首诗的作者是William Butler Yeats(威廉·巴特勒·叶芝)。叶芝是爱尔兰最伟大的诗人之一 ,对现代诗很有影响。这首诗是叶芝写给自己心爱的人的情诗。诗中的主人公“你”指的是爱尔兰革命家Maud Gonne,诗人遇见她并爱上她,曾多次向其求婚,均未成功,但诗人对她爱慕终生,于是就有了这篇经典之作。全诗共三节,前两节均是对 Maud Gonne的爱意的倾诉。第一节中虽然多次用第二人称“你”,但实际上是描述作者自己心中的所思所想。第二节中诗人采用了对比的手法,讲述了对 Maud Gonne的爱慕之情,突出自己永恒的爱。最后一节诗人描述了自己内心悲伤的感情。诗中sleep / deep, book / look, grace / face, bars / stars, fled / overhead这几组韵调使诗歌富于音韵感,有音律美,节奏感强,读起来琅琅上口。纵观全诗,没有华丽的辞藻,也找不到甜蜜的情话,有的只是平淡的文字背后寄予的永恒的爱意和深情,反而能让读者久久回味。1. Write a list poem starting with “If
I …” like poem C on page 10.
2. Write a poem that starts with “Slowly …” and make each pair of lines rhyme. Write about 6 lines. Homework
of English poemsReading Do you remember any little poems or songs you learned when you were a child?
Do you remember any poems you have read in high school, either in Chinese or in English? Can you recite any? What are the characteristics of poems? Can you give me some examples?
Poems have beats. They may rhyme or may not rhyme — but they have to have rhythms.
This beat is not always obvious, but it’s usually there.Twinkle, twinkle, little ____,
How I wonder what you ____,
Up above the world so ____ ,
Like a diamond in the _____.star.are.high.skyCan you find something
like a poem?Rhyme and rhythm are essential to poetry. Without rhythm, there wouldn’t be poems.Twinkle twinkle little star
How I wonder what you are,
Up above the world so high
Like a diamond in the sky. 强 弱 强 弱 强 弱 强唐诗分五言,七言。根据韵节来分
英诗可分为单韵诗、双韵诗、三韵诗……至八韵诗。构成一个韵节的四种情况: 强 + 弱, 强 + 弱弱
弱 + 强, 弱 + 强 poempoetpoetryrhymerhythmrhythmicThere are many reasons why people write poems. In small groups make a list of these reasons. Why do people write poems?People write poems
to tell a story
to express feelings
to make others laugh to tell the life or friendship
to delight the kids
to tell stories
to describe the seasons or scenes
for entertainment
as the lyric of a song SkimmingScan the text for the two questions.
1. What is the main idea of the reading passage?
2. What five kinds of poems does the reading passage talk about? Some simple forms of English poems.Nursery rhymes, list poems, the cinquain, haiku and Tang poems.Read the text carefully and fill in the blanks.Nursery
rhymes rhythm and rhymereciteList poems phrasesfive linesstrongtranslations17 syllablesclearHush, little baby, don’t say a word, Papa’s going to buy you a mockingbird.
If that mockingbird won’t sing, Papa’s going to buy you a diamond ring.
If that diamond ring turns to brass, Papa’s going to buy you a looking-grass.2. Read and answer questions.AIf that looking-grass gets broke, Papa’s going to buy you a billy-goat.
If that billy-goat runs away, Papa’s going to buy you another today. What is the baby’s father going to
buy if the mirror gets broken?
If the mirror gets broken, the baby’s father will buy a billy-goat instead.
2. What is the baby’s father going to do if the goat runs away?
He’s going to buy the baby another billy-goat. 3. What is the poem A about? Use
your own words to explain it.
Poem A is a nursery thyme that
illustrates a father’s love for his baby.I saw a fish-pond all on fire,
I saw a house bow to a squire,
I saw a person twelve-feet high,
I saw a cottage in the sky,
I saw a balloon made of lead,
I saw a coffin drop down dead,I saw a fish-pond all on fireBI saw two sparrows run a race,
I saw two horses making lace,
I saw a girl just like a cat,
I saw a kitten wear a hat,
I saw a man who saw these too,
And said though strange they all were true.What is the poem B about?
Poem B is an amusing nonsense poem which describes images of some ridiculous things.We should have won …
If Jack had scored that goal,
If we’d had just a few more minutes,
If we had trained harder,
If Ben had passed the ball to Joe,
If we’d had thousands of fans screaming,Our first football matchCIf I hadn’t taken my eye off the ball,
If we hadn’t stayed up so late the night before,
If we hadn’t take it easy,
If we hadn’t run out of energy.
We should have won …
If we’d been better! What is the poem C about?
Why didn’t the players win the match?
Does the author really believe his or her excuses? How do you know?Answer these questions.Sample answers:
Poem C is about losing a football match and the writer lists a lot of excuses for their failure. What is the poem C about?They didn’t win because they didn’t have enough time; they didn’t have thousands of fans screaming; they stayed up too late the night before; they ran out of energy. 2. Why didn’t the players win the match?No. The author doesn’t believe his excuses, because at the end of the poem the speaker admits that they just did not play well enough to win …3. Does the author really believe his or her excuses? How do you know?Brother
Beautiful, athletic
Teasing, shouting, laughing
Friend and enemy too Mine Summer
Sleepy, salty
Drying, drooping, dreading
Week in, week out
EndlessDE1. What are the poems about?
2. Do the authors like the subjects? Give
your reasons. Poem D is a description of a lovely brother.
Poem E is a description of hot and boring summer. Poem D: Yes, the author likes his subject. Although the speaker describes a couple of negative aspects of his / her brother, the reader can feel the affection that the speaker feels for his / her brother. Poem E: No, the author doesn’t like his subject. The reader gets the feeling that the speaker cannot wait until the summer is over. The words drooping, dreading, week in, week out and endless convey this feeling.FA fallen blossom
Is coming back to the branch.
Look, a butterfly! GSnow having melted.
The whole village is brimful
Of happy children.What are the poems about?
Poem F describes how a butterfly rests on a tree.
Poem G describes that the weather is warmer and the village is full of happy children.Where she awaits her husband on and on the river flows.
Never looking back, transformed into stone.
Day by day upon the mountain top, wind and rain revolve.
Should the journeyer return, this stone would utter speech.H望夫石望夫处,江悠悠,
化为石,不回头。
山头日日风复雨,
行人归来石应语。What is the story that the poem tells? Tell the story in your own words.
2. Circle one or more of the feelings below that you think the woman has. Give reasons for your answers:
loneliness joy love trust
anger hate sorrow1. A woman’s husband has gone away. The woman waits for him by the river where she last saw him. She waits and waits, never moving from that spot and never speaking, while the river continues to flow and the wind and rain come and go.2. The woman has the feelings of:
Loneliness: she was alone watching her husband on the mountain top.
Love: she waited year after year despite wind and rain.
Trust: she believed her husband would come back one day.Sorrow: year after year, she waited and waited without seeing any hope of her husband’s coming back, she was very sad.一首诗 a poem1. There are various reasons why people write poetry. 1) various: different, its root is vary.
2) poetry is a collective noun, used as
an uncountable noun.2. Others try to convey certain emotions.
1) convey
★ 作“传达,表达(思想或感情等)”讲
时,常用于convey sth. (to sb.)结构。
e.g. 1. Colours like red convey a sense of
energy and strength.
2. Please convey my thanks to your
wife. ★ 作“传送,运送,输送”讲时,常用于convey sb. / sth. (from ...) (to ...) 结构。
e.g. 1. This train conveys over five
hundred passengers every day.
2. A taxi conveyed us to the train
station.
3. Wires convey electricity from
power stations to the user. 3. The language is concrete but imaginative, and they delight small children because they rhyme, have strong rhythm and a lot of repetition.
本句是一个由and连接的并列复合句,两个分句分别是 _______________________
_______________ 和they delight small children ... a lot of repetition; The language is concrete but imaginativeb. 第二个分句中含有一个由because引导的原因状语从句。4. List poems have a flexible line length
and repeated phrases which give both a
pattern and a rhythm to the poem.
flexible灵活的,可弯曲的,柔顺的。5. Another simple form of poem that
students can easily write is the
cinquain, a poem made up of five lines.
本句的主干为:Another simple form
of poem is the cinquain;
b. that引导定语从句students can easily write,修饰先行词 _______;
c. a poem made up of five lines作cinquain同位语;poemd. 在同位语中,made up of five lines是
过去分词短语作后置定语,修饰
poem,可以改为定语从句which is
made up of five lines。
这句话还可以这样表达:
The cinquain is another simple form of poem. It is made up of five lines and students can easily write it. 6. We would have won ... ... if we hadn’t run out of energy.
run out of ... 为及物动词短语,意为“用完了……”,而run out为不及物动词短语,后不能接宾语,意为“被用完”。
e.g. I have run out of money.
My money has run out.7. It is easy to write and, like the cinquain, can give a clear picture and create a special feeling using the minimum of words.
本句包含三个并列的谓语,分别是:
_____________, can give和(can) create;
b. like the cinquain作插入语;
c. using the minimum of words是动词-ing形式作方式状语。is easy to write8. Should the journeyer return, this
stone would utter speech.
当if引导的虚拟条件句中有had, were, should时,可将if省去,将had, were, should提前,构成倒装语序。9. Did you know that English speakers
also enjoy other forms of Asian poetry — Tang poems from China in particular?
in particular 尤其,特别,其中,形容词particular意为“特指的,特别的”。另外,particular还可表示“讲究,挑剔”,可构成be particular about,意为“对……挑剔 / 讲究”。1. Read the text aloud and recite Paragraph 1.
2. Prepare your favorite Tang poem (s) and translate it/them into English.Using languageSpeaking请阅读下面的短文,以帮助你理解课本上的诗歌“I’ve saved the summer”。
I’ve saved the summer
I’ve saved the summer for you. And when the snow begins to fall on cold
winter mornings, I’ll give it all to you to keep you warm. I’ve saved some sunlight in case you need it. I believe it will drive off darkness and light your way. When you were nineteen, I kept the image of your smile in my mind. When you get older, you will know the meaning of brave young smiles.
I don’t know how I can help you to start your journey through life. However, there will be solutions somewhere before the day is through.
Whenever you need love, I’ll offer all I have. It might help you as you travel on your way, till you find the love that belongs to you.1. Listen to the poem ‘I’ve saved the summer’ and answer these questions. (answers are free)
1) Do you think the speaker in the poem is more likely to be a girlfriend /boyfriend or parent?
2) Does the poem have a rhythmic pattern?3) Does the poem have rhyming words?
4) When you were listening to the poem, did it make you feel something or think about something? What did it make you feel or think about?2. Now read “I’ve saved the summer”.
1) Circle the words that rhyme. What is unusual about the rhyming words in the last four lines?
2) Try beating or clapping the strong beats of the rhythm as you read the poem to yourself. Now listen to the poem again and clap the strong beats.Rod McKuen I’ve saved the summer
And I give it all to you
To hold on winter mornings
When the snow is new.I’ve saved some sunlight
If you should ever need
A place away from darkness
Where your mind can feed.人民教育出版社 | 选修六 And for myself I’ve kept your
smile
When you were but nineteen,
Till you’re older you’ll not know
What brave young smiles can
mean.I know no answers
To help you on your way
The answers lie somewhere
At the bottom of the day. But if you’ve a need for love
I’ll give you all I own
It might help you down the road
Till you’ve found your own.
(by Rod McKuen)人民教育出版社 | 选修六 1. Who is the speaker in the poem and who is he /she speaking to? Give reasons to support your answer.
Maybe a parent speaking to a young adult child. 2. Which of the following is the closest to the speaker’s message? Give a reason for your choice.
A. If it’s cold, I’ll warm you; if it’s dark, I’ll give you light; if you’re hungry, I’ll feed you; if you want love, I’ll give it to you.B. Although the future may be difficult for you, whenever you need warmth and love, remember I’ll have some to give you.
C. While you’re away I’ll remember your smile and I’ll love you always. When you return, I hope you will love me.人民教育出版社 | 选修六 1. Does the poem have a rhyming pattern?
pattern:
n. (1) 图案
e.g. This cloth has a pattern of blue and
white squares.
这种布有蓝白格子的图案。Language points(2) 模板, 式样
e.g. They like new?patterns?of family life.? 他们喜欢新的家庭生活方式。
v. form a pattern
e.g. He patterned himself upon a man he admired.
他模仿一个他钦佩的人。人民教育出版社 | 选修六 2. Till you’re older you’ll not know what
brave young smiles can mean.
等你长大成人以后,才知道年轻勇敢的
微笑的奥秘。
till 用在肯定句中,意为“直到……为
止”,通常表示动作的终点,因此,动
词必须是延续性的。如:We must stick to our task till it is finished. 我们必须继续工作, 直到做完为止。
Just wait till you see it. It’s great.
你就等着直到看见它吧。好看极了。
用在否定句中,意为“直到……才”,通常表示动作的起点,动词可以是延续性的也可以是非延续性的。如:She didn’t sleep till her son came back.
直到她儿子回来她才睡着。
(sleep为延续性动词)
I didn’t begin work till he had gone.
直到他走了我才开始工作。
(begin为非延续性动词)3. I’ll also try out his way some time.
try out: trying something to find
out about it 试用, 试验
e.g. Please try out red wine.
请试试我们的红葡萄酒。try one’s best
try on
try doing sth.
try to do sth.尽最大努力
试穿
试着做某事
尽力做某事ListeningListeningQuestion 1: What inspires you to write poetry?
Question 2: In what kind of place do you like to write poetry?
Question 3: What conditions do you need to be able to write poetry? (Does it have to be quite, do you need to be alone, do you need to listen to music and so on?)1. Listen to Part 1 and answer these questions.
(1)Who has written a poem already and is ready to enter the competition?
(2) Who is not going to enter a poem for the competition this year? LucyPitt(3) Who plans to write at the weekend?
Jack
(4) When is the deadline for the competition?
the 24th of the month.Listen to Part 2 of the tape and
fill in the chart.by going for a hike in the countryside
and then sitting quietly by himselfby surrounding herself with familiar
things in her own house. Listen to the two parts again and note down the expressions about intention and plans.possibly by listening to his favourite
music though he has never written
poetry beforeI’m ___________ enter a poem this year.
I haven’t begun mine yet but I _________
___ this weekend.
How ____ inspire yourself this weekend?
I ________ go for a hike in the
countryside and sit quietly somewhere
by myself.not going to plan to do
itwillintend toSubjunctive Mood(II)虚拟语气Learning study虚拟语气(二)
本节课我们巩固复习虚拟语气,主要复习if条件从句和wish宾语从句中表示过去情况的虚拟语气的用法,以及虚拟语气在其他从句中的运用。虚拟语气特殊句型1. wish 的宾语从句现在: 过去时(were)
过去: 过去完成时
将来: would/could/might +
v. should下面我们再来看看其他形式的虚拟语气的用法。1. I wish I were a bird. (现在)
2. I wish I hadn’t made such a mistake. (过去)
3. We wish our parents wouldn’t punish us. (将来)I wish I were as tall as you.
我希望和你一样高。
He wished he hadn’t said that.
他希望他没讲那样的话。
I wish it would rain tomorrow.
我希望明天下雨就好了。2) wish to do 表达法 wish sb. / sth. to do I wish to see the manager. = I want to see the manager.
I wish the manager to be informed
at once. = I want the manager to be informed at once.2. would rather that现在:
过去:
将来:e.g. I would rather you paid me now.
I would rather you had gone, too.
Don’t come. I would rather you
came tomorrow.过去时过去时过去完成时3. as if /though + clause 现在:
过去:过去时过去完成时在as if / as though后的从句中,常用一般过去时或“would / could / should / might + 动词原形”来表示与现在或将来的事实相反或不太可能实现的事情。 They talked as if they had been
friends for years.
He looks as if he were drunk.e.g. She loves the baby as if it were
her own son.
I remember the whole thing as if
it had happened yesterday.4. It’s (about/high) time + that过去时
should + v.你该走了。It’s high time that you went.
It’s high time that you were
going.
It’s high time that you should
go.我们该去睡觉了。It’s time that we went to bed.
It’s time that we should go to bed. 5. without和but for 构成虚拟。
but for要不是
Without sunlight, people’s life would be different from today.
But for your help, I wouldn’t have finished the work.6. If only … 要是就好了
e.g. If only I knew his name!
If only we had followed your advice!
If only I could see him again!要是我们的父母能和我们住在一起就好了!
If only our parents could live with us!
要是我没错过火车就好了!
If only I hadn’t missed the train!7. 在主语、表语、同位语从句中,虚拟语气用“should + 动词原形”或动词原形来表示。这样的句型有:It is strange / natural / important / no wonder / impossible / necessary / a pity / ... that ...;My advice / suggestion / requirement / ... is that ... 等。It is important that we (should) master a foreign language.
It is strange that she refuse to come to the party.
It’s necessary that we should study hard.WritingWriting如 何 写 英 语 诗 歌
诗歌是各种英语文体中最富有激情和感彩的一种。诗歌往往用高度凝练的语言来表达诗人的喜怒哀乐,诗人把自己对生活和客观世界的理解和感悟融入诗歌,当我们在欣赏一首诗时,可以通过文字捕捉到诗人的内心情感。一首优秀的诗可以以其特有的节奏与方式影响人们的精神世界。【写作指导】
一、诗歌的篇幅一般短小精悍,语言精练,感情强烈;在格式上,英语诗歌同汉语诗歌一样讲究押韵。诗的押韵是指通过重复元音或辅音以达到一定的音韵效果,一首诗的押韵具有带规律性的一致性,尤其是在诗句的末尾,称尾韵。下面我们来看Thomas Nash的一首诗:Spring
Spring, the sweet Spring, is the year’s pleasant king;
Then blooms each thing, then maids dance in a ring,
Cold doth not sting, the pretty birds do sing,
Cuckoo, jug-jug, pu-we, to-witta-woo!The palm and may make country houses gay,
Lambs frisk and play, the shepherds pipe all day,
And we hear aye birds tune this merry lay,
Cuckoo, jug-jug, pu-we, to-witta-woo!The fields breathe sweet, the daisies kiss our feet,
Young lovers meet, old wives a-sunning sit,
In every street theses tunes our ears do greet,
Cuckoo, jug-jug, pu-we, to-witta-woo!
Spring! the sweet Spring!这首诗押韵整齐,读起来很有节奏感。表现了春天里万物复苏、生机盎然、一派欢乐祥和的生动景象。
二、现代诗歌可以押韵,也可以不押韵,但是写作时需注意两点:
1. 要有节奏感。没有节奏感的诗歌,不能算诗,最多是分行的散文。2. 要把握句子结构的平衡。也就是诗句长短不要相差太远,否则读起来给人不平衡、不舒服之感。The Significance of Failure
Failure doesn’t mean you are a failure,
It does mean you haven’t succeeded yet.
Failure doesn’t mean you have accomplished nothing,It does mean you have learned something.
Failure doesn’t mean you have been a fool,
It does mean you had a lot of faith.
Failure doesn’t mean you’ve been disgraced,
It does mean you were willing to try.
Failure doesn’t mean you don’t have it, 人民教育出版社 | 选修六 It does mean you have to do something
in a different way.
Failure doesn’t mean you are inferior,
It does mean you are not perfect.
Failure doesn’t mean you’ve wasted your life,
It does mean you have a reason to start afresh.
Failure doesn’t mean you should give up,
It does mean you must try harder. Failure doesn’t mean you’ll never make it,
It does mean it will take a little longer.
Failure doesn’t mean God has abandoned you,
It does mean God has a better idea. 【佳作赏析】
When You Are Old
When you are old and grey and full of sleep,
And nodding by the fire, take down this book,
And slowly read, and dream of the soft lookYour eyes had once, and of their shadows deep;
How many loved your moments of glad grace,
And loved your beauty with love false or true,
But one man loved the pilgrim soul in you,And loved the sorrows of your changing face;
And bending down beside the glowing bars,
Murmur, a little sadly, how Love fled
And paced upon the mountains overhead
And hid his face amid a crowd of stars. 这首诗的作者是William Butler Yeats(威廉·巴特勒·叶芝)。叶芝是爱尔兰最伟大的诗人之一 ,对现代诗很有影响。这首诗是叶芝写给自己心爱的人的情诗。诗中的主人公“你”指的是爱尔兰革命家Maud Gonne,诗人遇见她并爱上她,曾多次向其求婚,均未成功,但诗人对她爱慕终生,于是就有了这篇经典之作。全诗共三节,前两节均是对 Maud Gonne的爱意的倾诉。第一节中虽然多次用第二人称“你”,但实际上是描述作者自己心中的所思所想。第二节中诗人采用了对比的手法,讲述了对 Maud Gonne的爱慕之情,突出自己永恒的爱。最后一节诗人描述了自己内心悲伤的感情。诗中sleep / deep, book / look, grace / face, bars / stars, fled / overhead这几组韵调使诗歌富于音韵感,有音律美,节奏感强,读起来琅琅上口。纵观全诗,没有华丽的辞藻,也找不到甜蜜的情话,有的只是平淡的文字背后寄予的永恒的爱意和深情,反而能让读者久久回味。1. Write a list poem starting with “If
I …” like poem C on page 10.
2. Write a poem that starts with “Slowly …” and make each pair of lines rhyme. Write about 6 lines. Homework
