Module 3 Natural elements. Unit 6 Electricity.复习资料(PDF版)
文档属性
| 名称 | Module 3 Natural elements. Unit 6 Electricity.复习资料(PDF版) |
|
|
| 格式 | zip | ||
| 文件大小 | 90.3KB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 牛津深圳版 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2018-04-21 00:00:00 | ||
图片预览




文档简介
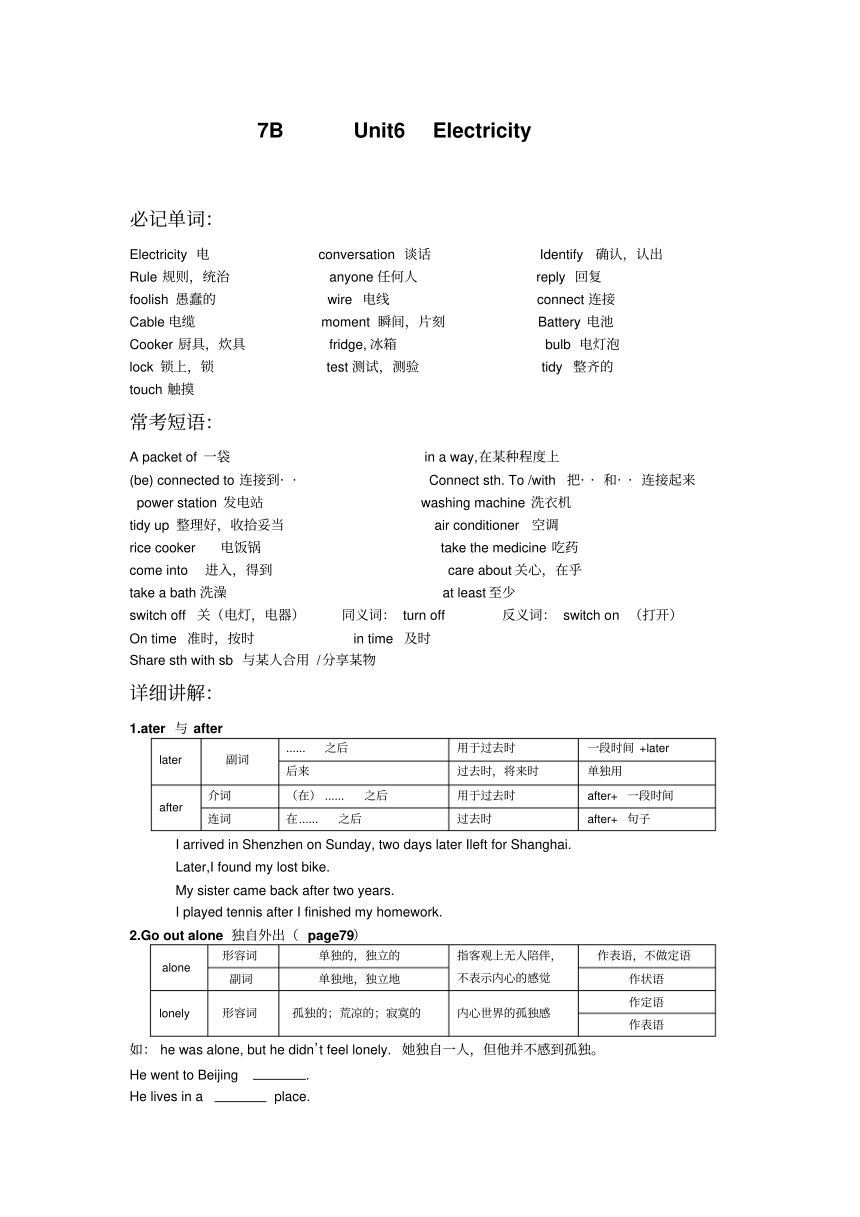
7B
Unit6
Electricity
必记单词:
Electricity
电
conversation
谈话
Identify
确认,认出
Rule
规则,统治
anyone任何人
reply
回复
foolish
愚蠢的
wire
电线
connect连接
Cable电缆
moment
瞬间,片刻
Battery
电池
Cooker
厨具,炊具
fridge,冰箱
bulb
电灯泡
lock
锁上,锁
test测试,测验
tidy
整齐的
touch
触摸
常考短语:
A
packet
of
一袋
in
a
way,在某种程度上
(be)
connected
to
连接到··
Connect
sth.
To
/with
把··和··连接起来
power
station
发电站
washing
machine
洗衣机
tidy
up
整理好,收拾妥当
air
conditioner
空调
rice
cooker
电饭锅
take
the
medicine
吃药
come
into
进入,得到
care
about关心,在乎
take
a
bath洗澡
at
least至少
switch
off
关(电灯,电器)
同义词:
turn
off
反义词:
switch
on
(打开)
On
time
准时,按时
in
time
及时
Share
sth
with
sb
与某人合用
/分享某物
详细讲解:
1.ater
与
after
......
之后
用于过去时
一段时间
+later
later
副词
后来
过去时,将来时
单独用
介词
(在)
......
之后
用于过去时
after+
一段时间
after
连词
在......
之后
过去时
after+
句子
I
arrived
in
Shenzhen
on
Sunday,
two
days
later
Ileft
for
Shanghai.
Later,I
found
my
lost
bike.
My
sister
came
back
after
two
years.
I
played
tennis
after
I
finished
my
homework.
2.Go
out
alone
独自外出(
page79)
形容词
单独的,独立的
指客观上无人陪伴,
作表语,不做定语
alone
副词
单独地,独立地
不表示内心的感觉
作状语
作定语
lonely
形容词
孤独的;荒凉的;寂寞的
内心世界的孤独感
作表语
如:
he
was
alone,
but
he
didn’t
feel
lonely.
她独自一人,但他并不感到孤独。
He
went
to
Beijing
.
He
lives
in
a
place.
He
feels
at
home
himeself.
初中英语情态动词用法详解
【情态动词知识梳理】
情态动词有具体的词义,
但也同助动词一样,
需要与动词原形一起构成句子的谓语,
给
谓语动词添加感彩,表示说话人对有关行为或事物的态度和看法,认为其可能,应该,
必要等。另外情态动词没有人称和数的变化,情态动词后必须跟动词原形。
考点一:
can,may,must等情态动词在陈述句中的用法:
1.
can的用法:
(1)
.表示能力、许可、可能性。表示能力时一般译为
“能、会
”,即有种能力,尤其是生来
具备的能力,此时
may和
must
均不可代替它。如:
She
can
swim
fast,
but
I
can
她’能t
游.
得
很快,但我不能。
I
can
see
with
my
eyes.我用眼睛看。
(2)
.表示许可,常在口语中。如:
You
can
use
my
dictionary.
你可以用我的字典。
(3)
.表示推测,意为
“可能”,常用于否定句和疑问句中,此时
can’译t为“不可能
”。如:
Can
the
news
be
true 这个消息会是真的吗?
—Can
it
be
our
teacher 那个人有可能是我们老师吗?
—No,
it
can
’t
be
our
teacher.
He
is
on
a
visit
to
the
Great
Wa不ll.可能。咱们老师正在游览长城
呢。
【例题】—
I
think
Miss
Gao
must
be
in
the
library.
She
said
she
would
go
there.
—No.
She
__be
there,
I
have
just
been
there.
2.
could的用法:
(1).can的过去式,
意为“能、会”,表示过去的能力。
如:He
could
write
poems
when
he
was
10.
他十岁时就会写诗。
(2).
could
在疑问句中,表示委婉的语气,此时
could
没有过去式的意思。如
:Could
you
do
me
你能帮我个忙吗?
—Could
I
use
your
pen 我能用一下你的钢笔吗
—Yes,
you
can.可以。(注意回答)
3.
may
的用法:
(1)
.表示请求、许可,比
can正式,如:
May
I
borrow
your
bike
我可以借你的自行车吗?
You
may
go
home
now.现在你可以回家了。
【例题】—
_______
I
borrow
your
MP3 —Sure
.
Here
you
are.
A.
May
B.Should
C.Must
D.
Would
(2)
.表示推测,谈论可能性,意为
“可能,或许”,一般用于肯定句中。
如:It
may
rain
tomorrow
.
明天可能会下雨。
She
may
be
at
home.她可能在家呢
.
(3)
.may
的过去式为
might,表示推测时。可能性低于
may。如:He
is
away
from
school.
He
might
be
sick.
他离开学校了,可能是他生病了。
(4)
.
表示希望、
祈求、祝愿,常可译为“祝愿”。
通常是用
may
+主+V
例如:May
you
have
a
good
time.祝你过得愉快。
May
you
be
happy!
祝你幸福!
May
you
succeed!祝你成功!
4.
must的用法:
(1).must
表示主观看法,意为
“必须、一定
”。如:
You
must
stay
here
until
I
come
back.
在我回
来之前你必须呆在这儿。
Must
I
hand
in
my
homework
right
now
我必须现在交作业吗?
(2)对
must引导的疑问句,
肯定回答为
must,否定回答或
don’t
have
to
如.
:—Must
I
finish
my
homework 我现在必须完成作业吗
(4)must
表示有把握的推测,用于肯定句。如
:
The
light
is
on,
so
he
must
be
at
home
now.灯亮
着,他现在肯定在家。
注意其反意问句的构成形式:
当
must
表示肯定的判断、推测时,其反意疑问句要用实际问句的助动词来构成。如:
She
must
have
seen
the
film
before (注意反意疑问句的后半部分
)You
must
have
met
uncle
Wang
in
the
shop
(注意反意疑问句的后半部分
)
5.
need的用法:
(1).need表示需要、
必须,主要用于否定句和疑问句中,
,意为“没有必要,
不必”。用
need
提问时,肯定回答
don’t
have
t。o
如:
—Need
I
stay
here
any
longer
我还有必要留在这儿吗?
—Yes,
you
must
.是的。
/
—No.
you
/don’t
have
to不.,你不必。
(2).need还可以作实义动词,此时有人称、数和时态的变化,如果是人作主语后边多接动
词不定式。
如:I
need
to
do
it
right
now.
我需要马上做这件事。
He
needs
to
learn
more
about
the
girl.他需要多了解那个女孩。
如果是物作主语,一般用
need
doing
与
need
to
be
done这种情况下应注意两点:
①.主动形式的动名词
doing
具有被动的含义;
②.该动名词可以改为其动词不定式的被动形式而句子的意义不变。例如:
The
door
needs
painting.
=
The
door
needs
to
be
painted.那扇门需要油漆一下。
Your
car
needs
mending.
=
Your
car
needs
to
be
repaired.你的车需要维修了。
7.
shall的用法:
shall
表示征求对方意见(多用于第一、三人称)
,如:
Shall
we
go
out
for
a
walk
我们出去散
步好吗?
在英语中,我们可以用其他多种方式提出我们的建议或征求对方意见。
(1).用“
Let's
do...”来提出建议。如:
Let's
go
for
a
walk
after
supper.
(2).用“
What/How
about... ”来提出建议;
about
后接名词或动词
ing
形式。如:
What
about/How
about
a
drink
What
about/How
about
taking
Tom
with
us
(3).用“Why
not... ”来提出建议,表示“何不
,,
”
not
面后接动词原形。“
Why
not... ”
实际上是“
Why
don't
you/we...
”的简略形式。如:
Why
not
meet
at
the
school
gate
at
eight
Why
don't
we
stay
here
another
day
(4).用“Would
you
like...
”来提出建议,意思是“你想要
,,
吗 ”Would
you
like
后可接名
词或不定式。如:
Would
you
like
a
cup
of
tea
Would
you
like
to
go
and
see
her
因此,如果我们说:
“去游泳好吗
”英语中可有这样几种表达法:
Shall
we
go
for
a
swim
Let's
go
for
a
swim
,shall
we
What
about/How
about
going
swimming
Why
not
go
for
a
swim
Would
you
like
to
go
for
a
swim
What
do
you
think
of
going
for
a
swim
8.
should的用法:
(1)should
意为“应该
”,可表示劝告、建议、义务、责任等。如:
We
should
protect
the
environment.我们应该保护环境。
(2)Should
have
done
表示对过去动作的责备、批评。如:
You
should
have
finished
your
homework.
你应该已经完成作业了。
(事实上你没有完成。
)
9.
will
的用法:
will
表示意愿、意志、打算,可用于多种人称。如:
I
will
help
you
if
I
’m
free
this
afternoon.
今天下午如果我有空,我就会帮你。
注意:
(1)、will
在
there
be句型中的形式及其句式变换。
由于“一般将来时”的结构可以用“
will+
动词原形”来表示,
所以
there
be句型的一般将来
时的形式就是
there
will
be
。(一定不能说
there
will
have)例如:There
are
many
students
in
our
school.→There
will
be
many
students
in
our
school.
There
will
be
a
sports
meeting
next
week.
一
定不能说:
There
will
have
a
sports
meeting
next
week.
(2)、will
与
be
going
to
do
something
区别:
①.
be
going
to
表示近期、
眼下就要发生的事情,
will
表示的将来时间则较远一些,
如:He
is
going
to
write
a
letter
tonight.
He
will
write
a
book
one
day.
②.
be
going
to表示根据主观判断将来肯定发生的事情,
will
表示客观上将来势必发生的事
情。
He
is
seriously
ill.
He
is
going
to
die.
He
will
be
twenty
years
old.
③.
be
going
to
含有“计划,
准备”的意思,
而
will
则没有这个意思,
如:She
is
going
to
lend
us
her
book.
He
will
be
here
in
half
an
hour.
④.在有条件从句的主句中,
一般不用
be
going
to,而多用
will,
如:If
any
beasts
comes
at
you,
I'll
stay
with
you
and
help
you.
10.
had
better
的用法:
had
better意为“最好
”,没有人称的变化,后面接不带
to的不定式,其否定形式为:
had
better
not。如:
We
had
better
go
now.我们最好现在就走。
You
had
better
not
give
the
book
to
him.
你最好不要
把这本书给他。
考点二:含有情态动词的疑问句的回答
:
1.对
may
引出的问句,可以有下列回答方式:
Yes,you
may.
Yes,
of
course.
Yes,
certainly.
Sure
.
No,
you
can
’
t.
2.对
must引出的疑问句,回答方式为:
Yes,
must.
No,
don’
t
have
to.
3.could
在疑问句中,表示委婉的语气,此时
could
没有过去式的意思。如
:Could
you
do
me
a
你能帮我个忙吗?—
Could
I
use
your
pen
我能用一下你的钢笔吗
—Yes,
you
can.可以。(注
意回答)
4.
shall
引出的疑问句用于第一人称,表示征求对方意见或客气的请求。其回答方式有以下
几种:
Yes,
please.
All
right.
No,
thank
you.
5.would
you
的回答方式有以下几种:
Yes,
I
will.
(No,
I
won
Su’re
t.
)(I
’m
sorry
,
I
can
’
t.)
All
right/
OK/
With
pleasure.
Certainly.
(No,
thank
you
.)
Yes,
please.
【例题】—
Would
you
do
me
ass
on
my
thanks
to
Lily
—________.
A.That’s
right
B.With
pleasure
D.No
trouble
【解析】
A.意为“对了”,B.意为“乐意效劳
”,
C意.
为
“没关系
”
D意.
为
“不费事
”。答案:
B
考点三
:不同情态动词的否定意义也不同:
1.
(1)
.can’可t译为
“不会”,如:
I
can
’t
play
basketba我ll.不会打篮球。
(2)当句子表推测时,
用
can’表t达不可能,
如:He
can’t
be
ill.
He
is
playing
chess
with
Tom.
他不可能病了,他正和
Tom下棋呢。
(3)can’还t可用来回答
“
May
I
这
”样的问句。
如:May
I
come
in
我可以进来吗?
No,
.
/
can
’不,t.
你不能。
(4)can’还t可用于固定习语中。
can’t
help
doing禁不住,情不自禁
can’
t
wait
to
doso
mething
迫不及待地要做,
如:
She
can’t
help
crying她.
不禁大哭起来。
The
children
can’
t
wait
to
open
the
box.孩子们迫不及待地想打开盒子。
2.
may
的否定式为
may
not,译成
“可能不
”,如:
He
may
not
be
at
home.他也许不在家。
考点四
:情态动词的被动语态
含有情态动词的被动语态的结构为:情态动词
+
be
+
done
(动词的过去分词
)。做题时要
兼顾情态动词和被动语态这两个方面。
She
should
speak
to
her
mother
in
that
way.她不应该用
那种方式和妈妈说话。
More
and
more
trees
must
be
planted
in
China.
在中国必须种植更多的树
木。Many
of
the
stars
can
not
be
seen
because
they
are
far
away
from
us.很多星星我们都看不到,
因为它们离我们太远了。
考点五
:情态动词表示推测的用法
:
一、“情态动词
+动词原形”表示对现在的推测。
1、can表示推测时一般用于否定句或疑问句。如:
That
man
can'
t
be
her
husbandshe
is
still
single.
Who
is
knocking
at
the
door
Can
it
be
the
postman
2、must表示肯定的推测,
一般用于肯定句中。
如:He
must
be
in
his
office
now.Mr
Li
must
be
working
now
,
for
the
lights
in
his
office
are
still
on.
3、might
表示推测时不一定是
may
的过去时,只是表示其可能性较小。
如:The
man
may
be
the
headmaster.
—Where
is
Mr
Li —He
might
be
working
in
his
office.
—May
Mr
Li
come —He
might
not
come
here.
4、Could
表示推测时,语气
can比要弱,说话者留有余地。如:—
Could
it
be
an
animal —
It
could
not
be,because
it
is
not
moving.
5、Should表示推测的可能性比较大,
仅比
must的可能性小一点。
如:It
is
already
10
o
’
clock
now
they
should
be
there.
【情态动词易混点归纳】
易混点一
:
can
和
be
able
to:
两者表示能力时用法相同,但
can只有原形“
can”和过去式“
could”两种形式,在其他时
态中要用
be
able
to来表示。另外
be
able
to
常常指经过努力,花费了时间和劳力之后才能做
到某事。如:
Jim
can’t
speak
English吉.
姆不会说英语。
He
could
speak
English
at
5.
他五岁时
就会说英语。
We’
ll
be
able
to
see
him
next
week.下星期我们将会见到他。
He
has
been
able
to
drive.他已经会开车了。
I
’m
sure
you
’
ll
be
able
to
finish
it
qui我ck相ly.信你能迅速地完成。
We
were
able
to
reach
the
top
of
the
mountain
at
noon.
我们能在中午到达山顶。
易混点二
:can和
may
1.
can和
may
均可用来征求意见或许可,
意为“可以”,
一般可互换使用。
如:Can/
May
I
help
you
我能帮助你吗?
2.
can和
may
表示可能性时的区别:
1)在肯定句中用
might,may,must,不用
can
2)在疑问句中表示推测用
can,不用
might,may,must
3)在否定句中用
can’(t不可能),不用
may,must。如:
She
may
be
in
the
classroom
.她可能
在教室里。
Where
can
they
be
now 他们现在可能在哪儿?
That
can
’t
be
tru那e.不可能是真的。
易混点三
:
may
be和
maybe
用法区别
常用位置
may
be
may为情态动词,
be为动词原形
句中,作谓语
maybe
副词,大概、也许,相当于
perhaps
句首,作状语
例如:
He
may
be
wrong
,
but
I
’m
not
sure.也许他错了,但我也不确定。
易混点四:
can’
t
和
1.
can
’根据t其基本用法可译为:
(1)不会。如:
I
can
’t
speak
English我
.不会说英语。
(2)不能。如:
We
can’t
do
it
now
because
it
’s
to天o
太da黑rk了.
,我们现在干不了。
(3)否定句中表示推测。
“不可能
”,如:
The
man
can’tb
e
our
teacher
because
he
is
much
younger
than
our
teacher..那个人不可能是咱们老师,他年轻得多。
易混点五:
must和
have
to
1.must
侧重于个人意志和主观上的必要。
have
to
侧重于客观上的必要,可用于现在时、过
去时和将来时。
如:I
know
I
must
study
hard.
我知道我必须努力学习。
My
brother
was
very
ill,
so
I
had
to
call
the
doctor
in
the
mid-night.我弟弟病得厉害,我只得半夜里把医生请来。
I
haven’
t
got
any
money
with
me,
so
I
’
ll
have
to
borrow
some
from
my
friend.
我身上没带钱,
只好向朋友借点了。
He
said
they
must
work
hard.
他说他们必须努力工作。
2.
have
to可以用于多种时态;
而
must只用于一般现在或将来。
如:The
composition
is
due
to
hand
in
this
morning,
so
I
had
to
finish
it
last
night.
作文今天早晨到期,因此我不得不昨天晚上
完成。
易混点六
:
used
to
do
/
be
used
to
doing
/
be
used
to
do,
/
be
used
for
doing
used
to
do
表示过去常常发生的动作,强调过去,只用于过去,注意用
to
do,不用
doing
形
式;而
be
used
to
doing
意为“习惯做
,”,
be可有各种时态;
be
used
to
do意为“
,,
被使
用去做
,,
,”为被动语态形式。
be
used
for
doing
用作
,,
”如:
My
father
used
to
eating
meat.我父亲过去起床晚,
但现在不得不早起了。
She
is
used
to
eating
meat.她习惯吃肉。
He
wat
used
to
eating
in
a
restaurant.他不习惯在饭店吃饭。
A
knife
can
be
used
for
cutting
things.(
刀可
以用来割东西
)/
A
knife
can
be
used
to
cut
things.(
刀可以用来割东西
)
Unit6
Electricity
必记单词:
Electricity
电
conversation
谈话
Identify
确认,认出
Rule
规则,统治
anyone任何人
reply
回复
foolish
愚蠢的
wire
电线
connect连接
Cable电缆
moment
瞬间,片刻
Battery
电池
Cooker
厨具,炊具
fridge,冰箱
bulb
电灯泡
lock
锁上,锁
test测试,测验
tidy
整齐的
touch
触摸
常考短语:
A
packet
of
一袋
in
a
way,在某种程度上
(be)
connected
to
连接到··
Connect
sth.
To
/with
把··和··连接起来
power
station
发电站
washing
machine
洗衣机
tidy
up
整理好,收拾妥当
air
conditioner
空调
rice
cooker
电饭锅
take
the
medicine
吃药
come
into
进入,得到
care
about关心,在乎
take
a
bath洗澡
at
least至少
switch
off
关(电灯,电器)
同义词:
turn
off
反义词:
switch
on
(打开)
On
time
准时,按时
in
time
及时
Share
sth
with
sb
与某人合用
/分享某物
详细讲解:
1.ater
与
after
......
之后
用于过去时
一段时间
+later
later
副词
后来
过去时,将来时
单独用
介词
(在)
......
之后
用于过去时
after+
一段时间
after
连词
在......
之后
过去时
after+
句子
I
arrived
in
Shenzhen
on
Sunday,
two
days
later
Ileft
for
Shanghai.
Later,I
found
my
lost
bike.
My
sister
came
back
after
two
years.
I
played
tennis
after
I
finished
my
homework.
2.Go
out
alone
独自外出(
page79)
形容词
单独的,独立的
指客观上无人陪伴,
作表语,不做定语
alone
副词
单独地,独立地
不表示内心的感觉
作状语
作定语
lonely
形容词
孤独的;荒凉的;寂寞的
内心世界的孤独感
作表语
如:
he
was
alone,
but
he
didn’t
feel
lonely.
她独自一人,但他并不感到孤独。
He
went
to
Beijing
.
He
lives
in
a
place.
He
feels
at
home
himeself.
初中英语情态动词用法详解
【情态动词知识梳理】
情态动词有具体的词义,
但也同助动词一样,
需要与动词原形一起构成句子的谓语,
给
谓语动词添加感彩,表示说话人对有关行为或事物的态度和看法,认为其可能,应该,
必要等。另外情态动词没有人称和数的变化,情态动词后必须跟动词原形。
考点一:
can,may,must等情态动词在陈述句中的用法:
1.
can的用法:
(1)
.表示能力、许可、可能性。表示能力时一般译为
“能、会
”,即有种能力,尤其是生来
具备的能力,此时
may和
must
均不可代替它。如:
She
can
swim
fast,
but
I
can
她’能t
游.
得
很快,但我不能。
I
can
see
with
my
eyes.我用眼睛看。
(2)
.表示许可,常在口语中。如:
You
can
use
my
dictionary.
你可以用我的字典。
(3)
.表示推测,意为
“可能”,常用于否定句和疑问句中,此时
can’译t为“不可能
”。如:
Can
the
news
be
true 这个消息会是真的吗?
—Can
it
be
our
teacher 那个人有可能是我们老师吗?
—No,
it
can
’t
be
our
teacher.
He
is
on
a
visit
to
the
Great
Wa不ll.可能。咱们老师正在游览长城
呢。
【例题】—
I
think
Miss
Gao
must
be
in
the
library.
She
said
she
would
go
there.
—No.
She
__be
there,
I
have
just
been
there.
2.
could的用法:
(1).can的过去式,
意为“能、会”,表示过去的能力。
如:He
could
write
poems
when
he
was
10.
他十岁时就会写诗。
(2).
could
在疑问句中,表示委婉的语气,此时
could
没有过去式的意思。如
:Could
you
do
me
你能帮我个忙吗?
—Could
I
use
your
pen 我能用一下你的钢笔吗
—Yes,
you
can.可以。(注意回答)
3.
may
的用法:
(1)
.表示请求、许可,比
can正式,如:
May
I
borrow
your
bike
我可以借你的自行车吗?
You
may
go
home
now.现在你可以回家了。
【例题】—
_______
I
borrow
your
MP3 —Sure
.
Here
you
are.
A.
May
B.Should
C.Must
D.
Would
(2)
.表示推测,谈论可能性,意为
“可能,或许”,一般用于肯定句中。
如:It
may
rain
tomorrow
.
明天可能会下雨。
She
may
be
at
home.她可能在家呢
.
(3)
.may
的过去式为
might,表示推测时。可能性低于
may。如:He
is
away
from
school.
He
might
be
sick.
他离开学校了,可能是他生病了。
(4)
.
表示希望、
祈求、祝愿,常可译为“祝愿”。
通常是用
may
+主+V
例如:May
you
have
a
good
time.祝你过得愉快。
May
you
be
happy!
祝你幸福!
May
you
succeed!祝你成功!
4.
must的用法:
(1).must
表示主观看法,意为
“必须、一定
”。如:
You
must
stay
here
until
I
come
back.
在我回
来之前你必须呆在这儿。
Must
I
hand
in
my
homework
right
now
我必须现在交作业吗?
(2)对
must引导的疑问句,
肯定回答为
must,否定回答或
don’t
have
to
如.
:—Must
I
finish
my
homework 我现在必须完成作业吗
(4)must
表示有把握的推测,用于肯定句。如
:
The
light
is
on,
so
he
must
be
at
home
now.灯亮
着,他现在肯定在家。
注意其反意问句的构成形式:
当
must
表示肯定的判断、推测时,其反意疑问句要用实际问句的助动词来构成。如:
She
must
have
seen
the
film
before (注意反意疑问句的后半部分
)You
must
have
met
uncle
Wang
in
the
shop
(注意反意疑问句的后半部分
)
5.
need的用法:
(1).need表示需要、
必须,主要用于否定句和疑问句中,
,意为“没有必要,
不必”。用
need
提问时,肯定回答
don’t
have
t。o
如:
—Need
I
stay
here
any
longer
我还有必要留在这儿吗?
—Yes,
you
must
.是的。
/
—No.
you
/don’t
have
to不.,你不必。
(2).need还可以作实义动词,此时有人称、数和时态的变化,如果是人作主语后边多接动
词不定式。
如:I
need
to
do
it
right
now.
我需要马上做这件事。
He
needs
to
learn
more
about
the
girl.他需要多了解那个女孩。
如果是物作主语,一般用
need
doing
与
need
to
be
done这种情况下应注意两点:
①.主动形式的动名词
doing
具有被动的含义;
②.该动名词可以改为其动词不定式的被动形式而句子的意义不变。例如:
The
door
needs
painting.
=
The
door
needs
to
be
painted.那扇门需要油漆一下。
Your
car
needs
mending.
=
Your
car
needs
to
be
repaired.你的车需要维修了。
7.
shall的用法:
shall
表示征求对方意见(多用于第一、三人称)
,如:
Shall
we
go
out
for
a
walk
我们出去散
步好吗?
在英语中,我们可以用其他多种方式提出我们的建议或征求对方意见。
(1).用“
Let's
do...”来提出建议。如:
Let's
go
for
a
walk
after
supper.
(2).用“
What/How
about... ”来提出建议;
about
后接名词或动词
ing
形式。如:
What
about/How
about
a
drink
What
about/How
about
taking
Tom
with
us
(3).用“Why
not... ”来提出建议,表示“何不
,,
”
not
面后接动词原形。“
Why
not... ”
实际上是“
Why
don't
you/we...
”的简略形式。如:
Why
not
meet
at
the
school
gate
at
eight
Why
don't
we
stay
here
another
day
(4).用“Would
you
like...
”来提出建议,意思是“你想要
,,
吗 ”Would
you
like
后可接名
词或不定式。如:
Would
you
like
a
cup
of
tea
Would
you
like
to
go
and
see
her
因此,如果我们说:
“去游泳好吗
”英语中可有这样几种表达法:
Shall
we
go
for
a
swim
Let's
go
for
a
swim
,shall
we
What
about/How
about
going
swimming
Why
not
go
for
a
swim
Would
you
like
to
go
for
a
swim
What
do
you
think
of
going
for
a
swim
8.
should的用法:
(1)should
意为“应该
”,可表示劝告、建议、义务、责任等。如:
We
should
protect
the
environment.我们应该保护环境。
(2)Should
have
done
表示对过去动作的责备、批评。如:
You
should
have
finished
your
homework.
你应该已经完成作业了。
(事实上你没有完成。
)
9.
will
的用法:
will
表示意愿、意志、打算,可用于多种人称。如:
I
will
help
you
if
I
’m
free
this
afternoon.
今天下午如果我有空,我就会帮你。
注意:
(1)、will
在
there
be句型中的形式及其句式变换。
由于“一般将来时”的结构可以用“
will+
动词原形”来表示,
所以
there
be句型的一般将来
时的形式就是
there
will
be
。(一定不能说
there
will
have)例如:There
are
many
students
in
our
school.→There
will
be
many
students
in
our
school.
There
will
be
a
sports
meeting
next
week.
一
定不能说:
There
will
have
a
sports
meeting
next
week.
(2)、will
与
be
going
to
do
something
区别:
①.
be
going
to
表示近期、
眼下就要发生的事情,
will
表示的将来时间则较远一些,
如:He
is
going
to
write
a
letter
tonight.
He
will
write
a
book
one
day.
②.
be
going
to表示根据主观判断将来肯定发生的事情,
will
表示客观上将来势必发生的事
情。
He
is
seriously
ill.
He
is
going
to
die.
He
will
be
twenty
years
old.
③.
be
going
to
含有“计划,
准备”的意思,
而
will
则没有这个意思,
如:She
is
going
to
lend
us
her
book.
He
will
be
here
in
half
an
hour.
④.在有条件从句的主句中,
一般不用
be
going
to,而多用
will,
如:If
any
beasts
comes
at
you,
I'll
stay
with
you
and
help
you.
10.
had
better
的用法:
had
better意为“最好
”,没有人称的变化,后面接不带
to的不定式,其否定形式为:
had
better
not。如:
We
had
better
go
now.我们最好现在就走。
You
had
better
not
give
the
book
to
him.
你最好不要
把这本书给他。
考点二:含有情态动词的疑问句的回答
:
1.对
may
引出的问句,可以有下列回答方式:
Yes,you
may.
Yes,
of
course.
Yes,
certainly.
Sure
.
No,
you
can
’
t.
2.对
must引出的疑问句,回答方式为:
Yes,
must.
No,
don’
t
have
to.
3.could
在疑问句中,表示委婉的语气,此时
could
没有过去式的意思。如
:Could
you
do
me
a
你能帮我个忙吗?—
Could
I
use
your
pen
我能用一下你的钢笔吗
—Yes,
you
can.可以。(注
意回答)
4.
shall
引出的疑问句用于第一人称,表示征求对方意见或客气的请求。其回答方式有以下
几种:
Yes,
please.
All
right.
No,
thank
you.
5.would
you
的回答方式有以下几种:
Yes,
I
will.
(No,
I
won
Su’re
t.
)(I
’m
sorry
,
I
can
’
t.)
All
right/
OK/
With
pleasure.
Certainly.
(No,
thank
you
.)
Yes,
please.
【例题】—
Would
you
do
me
ass
on
my
thanks
to
Lily
—________.
A.That’s
right
B.With
pleasure
D.No
trouble
【解析】
A.意为“对了”,B.意为“乐意效劳
”,
C意.
为
“没关系
”
D意.
为
“不费事
”。答案:
B
考点三
:不同情态动词的否定意义也不同:
1.
(1)
.can’可t译为
“不会”,如:
I
can
’t
play
basketba我ll.不会打篮球。
(2)当句子表推测时,
用
can’表t达不可能,
如:He
can’t
be
ill.
He
is
playing
chess
with
Tom.
他不可能病了,他正和
Tom下棋呢。
(3)can’还t可用来回答
“
May
I
这
”样的问句。
如:May
I
come
in
我可以进来吗?
No,
.
/
can
’不,t.
你不能。
(4)can’还t可用于固定习语中。
can’t
help
doing禁不住,情不自禁
can’
t
wait
to
doso
mething
迫不及待地要做,
如:
She
can’t
help
crying她.
不禁大哭起来。
The
children
can’
t
wait
to
open
the
box.孩子们迫不及待地想打开盒子。
2.
may
的否定式为
may
not,译成
“可能不
”,如:
He
may
not
be
at
home.他也许不在家。
考点四
:情态动词的被动语态
含有情态动词的被动语态的结构为:情态动词
+
be
+
done
(动词的过去分词
)。做题时要
兼顾情态动词和被动语态这两个方面。
She
should
speak
to
her
mother
in
that
way.她不应该用
那种方式和妈妈说话。
More
and
more
trees
must
be
planted
in
China.
在中国必须种植更多的树
木。Many
of
the
stars
can
not
be
seen
because
they
are
far
away
from
us.很多星星我们都看不到,
因为它们离我们太远了。
考点五
:情态动词表示推测的用法
:
一、“情态动词
+动词原形”表示对现在的推测。
1、can表示推测时一般用于否定句或疑问句。如:
That
man
can'
t
be
her
husbandshe
is
still
single.
Who
is
knocking
at
the
door
Can
it
be
the
postman
2、must表示肯定的推测,
一般用于肯定句中。
如:He
must
be
in
his
office
now.Mr
Li
must
be
working
now
,
for
the
lights
in
his
office
are
still
on.
3、might
表示推测时不一定是
may
的过去时,只是表示其可能性较小。
如:The
man
may
be
the
headmaster.
—Where
is
Mr
Li —He
might
be
working
in
his
office.
—May
Mr
Li
come —He
might
not
come
here.
4、Could
表示推测时,语气
can比要弱,说话者留有余地。如:—
Could
it
be
an
animal —
It
could
not
be,because
it
is
not
moving.
5、Should表示推测的可能性比较大,
仅比
must的可能性小一点。
如:It
is
already
10
o
’
clock
now
they
should
be
there.
【情态动词易混点归纳】
易混点一
:
can
和
be
able
to:
两者表示能力时用法相同,但
can只有原形“
can”和过去式“
could”两种形式,在其他时
态中要用
be
able
to来表示。另外
be
able
to
常常指经过努力,花费了时间和劳力之后才能做
到某事。如:
Jim
can’t
speak
English吉.
姆不会说英语。
He
could
speak
English
at
5.
他五岁时
就会说英语。
We’
ll
be
able
to
see
him
next
week.下星期我们将会见到他。
He
has
been
able
to
drive.他已经会开车了。
I
’m
sure
you
’
ll
be
able
to
finish
it
qui我ck相ly.信你能迅速地完成。
We
were
able
to
reach
the
top
of
the
mountain
at
noon.
我们能在中午到达山顶。
易混点二
:can和
may
1.
can和
may
均可用来征求意见或许可,
意为“可以”,
一般可互换使用。
如:Can/
May
I
help
you
我能帮助你吗?
2.
can和
may
表示可能性时的区别:
1)在肯定句中用
might,may,must,不用
can
2)在疑问句中表示推测用
can,不用
might,may,must
3)在否定句中用
can’(t不可能),不用
may,must。如:
She
may
be
in
the
classroom
.她可能
在教室里。
Where
can
they
be
now 他们现在可能在哪儿?
That
can
’t
be
tru那e.不可能是真的。
易混点三
:
may
be和
maybe
用法区别
常用位置
may
be
may为情态动词,
be为动词原形
句中,作谓语
maybe
副词,大概、也许,相当于
perhaps
句首,作状语
例如:
He
may
be
wrong
,
but
I
’m
not
sure.也许他错了,但我也不确定。
易混点四:
can’
t
和
1.
can
’根据t其基本用法可译为:
(1)不会。如:
I
can
’t
speak
English我
.不会说英语。
(2)不能。如:
We
can’t
do
it
now
because
it
’s
to天o
太da黑rk了.
,我们现在干不了。
(3)否定句中表示推测。
“不可能
”,如:
The
man
can’tb
e
our
teacher
because
he
is
much
younger
than
our
teacher..那个人不可能是咱们老师,他年轻得多。
易混点五:
must和
have
to
1.must
侧重于个人意志和主观上的必要。
have
to
侧重于客观上的必要,可用于现在时、过
去时和将来时。
如:I
know
I
must
study
hard.
我知道我必须努力学习。
My
brother
was
very
ill,
so
I
had
to
call
the
doctor
in
the
mid-night.我弟弟病得厉害,我只得半夜里把医生请来。
I
haven’
t
got
any
money
with
me,
so
I
’
ll
have
to
borrow
some
from
my
friend.
我身上没带钱,
只好向朋友借点了。
He
said
they
must
work
hard.
他说他们必须努力工作。
2.
have
to可以用于多种时态;
而
must只用于一般现在或将来。
如:The
composition
is
due
to
hand
in
this
morning,
so
I
had
to
finish
it
last
night.
作文今天早晨到期,因此我不得不昨天晚上
完成。
易混点六
:
used
to
do
/
be
used
to
doing
/
be
used
to
do,
/
be
used
for
doing
used
to
do
表示过去常常发生的动作,强调过去,只用于过去,注意用
to
do,不用
doing
形
式;而
be
used
to
doing
意为“习惯做
,”,
be可有各种时态;
be
used
to
do意为“
,,
被使
用去做
,,
,”为被动语态形式。
be
used
for
doing
用作
,,
”如:
My
father
used
to
eating
meat.我父亲过去起床晚,
但现在不得不早起了。
She
is
used
to
eating
meat.她习惯吃肉。
He
wat
used
to
eating
in
a
restaurant.他不习惯在饭店吃饭。
A
knife
can
be
used
for
cutting
things.(
刀可
以用来割东西
)/
A
knife
can
be
used
to
cut
things.(
刀可以用来割东西
)
