必修2 Module 3 Music Grammar 状语从句课件(45张PPT)
文档属性
| 名称 | 必修2 Module 3 Music Grammar 状语从句课件(45张PPT) |  | |
| 格式 | zip | ||
| 文件大小 | 181.8KB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 外研版 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2018-07-21 08:42:50 | ||
图片预览










文档简介
课件45张PPT。Adverbial Clauses of Time 主句是一般将来时,从句用一般现在时表示将来意义。
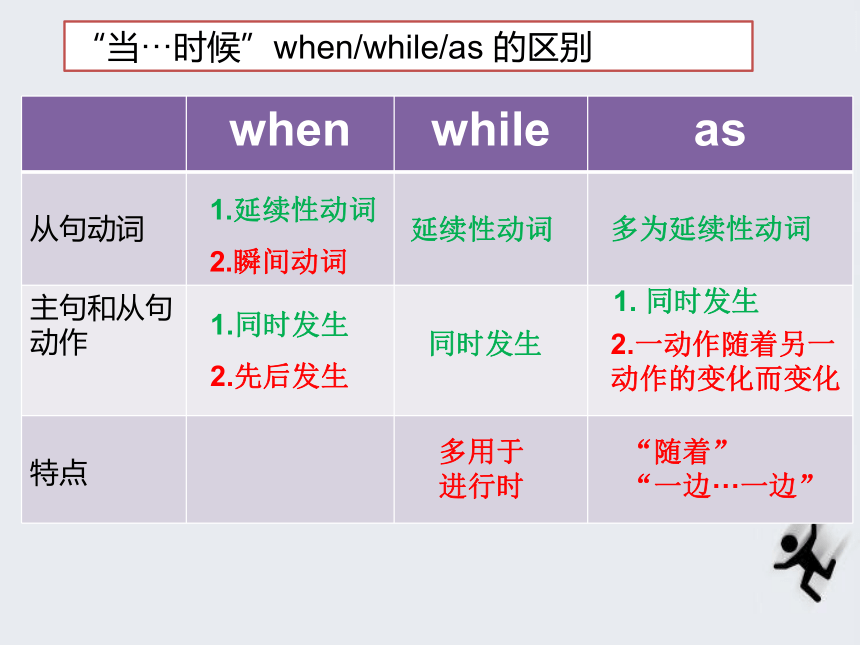
主将从现时间状语从句用表示时间的连词连接一个句子作时间状语,这样的主从复合句就是时间状语从句。01030205Contents连接词04while/when/as一···就···till/until表示时间的名词词组before & since “当……时候” when/ while/ asⅠ1. when
①when引导的从句可用延续性动词也可用瞬间动词;
② 从句动作和主句的动作 可以 同时发生
也可 先后发生When?I?got?to?the?airport, the?guests?had?left.·When I lived there, I used to go to the beach on Sundays. when 特殊用法when 还可做并列连词 连接并列分句,
表示“就在这时“ =at that time
常用结构“be about to… when…”
“正打算···,这时··· ···”
e.g We were about to leave when he came in.2. while① while引导的从句的动作和主句的动作同时发生
② while引导的从句必须使用延续性动词
③ while引导的从句且多用于进行时The doorbell rang while I was watching TV.I met her while I was at school. 3. as① as引导时间状语侧重从句和主句的动作同时发生
② as引导的从句通常使用延续性动词
③还强调一动作随着另一动作的变化而变化
译为: “随着, 一边……一边……”As the children walked along the street, they sang happily.
As China develops, Chinese is becoming more and more important.As we were dancing,a stranger came in.“当···时候”when/while/as 的区别 1.同时发生
2.先后发生1.延续性动词
2.瞬间动词 延续性动词 同时发生 1. 同时发生多为延续性动词多用于
进行时“随着”
“一边···一边”2.一动作随着另一动作的变化而变化用when/while/as完成下列句子。
1. _____ I went into the classroom, he was
reading.
2. _____ he was speaking, everybody
listened carefully.
3. I was about to go out _____ a visitor came.when While When 4.There is plenty of rain in the south _____ there is little in the north.
A. while?? B. as? C. when??? D. so A “一 ··· 就···” Ⅱ1.as soon as+从句
? I'll telephone you?as?soon?as?I get home.
2.the moment/ minute/ second/instant +从句
The moment I saw her, I cried out.
3.immediately/directly/instantly+从句
Immediately he came, I told him the news.
4. no sooner…than…
hardly/scarcely…when…no sooner… than…
hardly/scarcely… when…1.主句谓语用过去完成时,从句谓语用一般过去时。
2.当no sooner和hardly/scarely位于句首时,主句要部分倒装。She had no sooner heard the news than she jumped.No sooner had she heard the news than she jumped.He had hardly/scarcely finished the test when the bell rang. 他一完成测验,铃就响。 ( hardly/scarcely… when…)
Hardly/Scarcely had he finished the test when the bell rang. He had finished the test.The bell rang. “直到… ...” Ⅲtill/untiltill/until注意:till/until都表示“直到···”可互换,但放在句首时只用untilI waited till/until he arrived.He won’t go to bed till/until she returns.在肯定句中表示“直到···为止” 主句通常使用延续性动词。在否定句中表示“直到···才” 主句通常使用瞬间动词。not···until用法注意: ①“no until”可用于强调句式
② “not until” 放在句首时,句子部分倒装。强调结构
“it is/was + not until +从句+that +主句”We did not get off the bus until it stopped.① It was not until it stopped that we get off the bus.② Not until it stopped did we get off the bus.倒装结构
“Not until +从句 +主句(部分倒装)” “表示时间的名词词组” Ⅳ某些表示时间的名词词组,
也可以引导时间状语从句例如:
the day, the year, the morning, every time,
each time, next time, the first time, by the time…① __________ I catch a cold, I have pain in my back.
每一次我感冒的时候,我都会背痛。
② I’m going to see him ________he comes to Shenzhen.
下一次他来深圳的时候, 我会去看他的。
③ He left Europe _________ World War II broke out.
二战爆发的那一年他离开欧洲。
④ He had impressed me that way __________I met him.
我第一次见到他的时候, 他给我留下那样的印象。Every timenext time the year the first time “before & since ” Ⅴbefore引导的时间状语从句before "在...之前“
注意:主句动作发生先于before引导的从句动作发生。It will be half a year before I come back.
It wasn't long before he left the countryIt will be +一段时间+before... (从句一般现在时)
要过...时间才....
It was +一段时间+before... (从句一般过去时)
过了...时间才....Turn off all the lights before you leave. since引导的时间状语从句I?have?distrusted?her?ever?since?she?cheated?me.一般过去时现在完成时注意:since引导的时间从句若用一般过去时,主句则用现在完成时常见句型 “自从...(至今)已经多久了”
“It is/has been +一段时间+since从句”It is three years since I began to smoke.
It is three years since I smoked.(从句动词)瞬间动词:时间从动作开始算起 “自从... 已经多久了”
(从句动词)延续动词:时间从动作结束算起“自从不... 已经多久了”1. I recognized you ____ I saw you at the airport. A. the moment B. while C. after D. once
2. No sooner had I arrived home _____ it began to rain. A. when B. while C. as D. than3. Hardly had he reached the school gate _____the bell rang. A. while B. when C. as D. as soon as4. It seemed only seconds _____ the
boy finished washing his face.
A. when B. before
C. after D. even if
5. Not until I began to work ___ how
much time I had wasted.
A. didn’t I realize B. did I realize
C. I didn’t realize D. I realize 6. It was not until she got home ___ Jennifer realized she had lost her keys.
A. when B. that C. where D. before7. I got to know she was nice and honest ______ I met her.
A. first time B. for the first time
C. the first time D. at the first time8. By this time tomorrow they ___ the
machine.
A. would repair B. will repair
C. will be repairing D. will have repaired
9. By the time you receive this letter, I ___ this city for my home town.
A. have left B. will have left
C. leave D. will leave 翻译句子 我一见到他就告诉他这个消息。(as
soon as)
(2) 她一来到教室,就开始读英语。(as
soon as) I’ll tell him the news as soon as I see him. As soon as she came into the classroom, she began to read English. (3) 我刚一到家天就下雨了。(no
sooner … than …)
(4) 他刚做完试卷,铃声就响了。
(hardly … when …)I had no sooner got home than it began to rain. He had hardly finished the test when the bell rang. (5) 他一来,你就可立即离开。
(immediately)
(6) 我一见到你,就认出你来了。
(the moment)You may leave immediately he comes. I recognized you the moment I saw you. (7) 每次见面,他都向我问候,说“你
好!”(each time / every time)
(8) 到18岁的时候,她已大学毕业了。
(by the time)He greeted with “Hello!” each time he saw me. By the time she was 18, she had already graduated from the university. Grammar (2)Read the following sentences and say which one is better and why. Mike said that he would come to school to see me the next day, but he didn’t come to school to see me the next day.
2. Mike said that he would come to school to see me the next day, but he didn’t.Answer:
The second sentence is better than the first one. Because it left out the same part of one sentence. It can make us easy to understand and easy to read. Ellipses 省略(1) 简单句省略
省略主语 I Beg your pardon. / It Sounds a good idea. / You Take care!
省略谓语 Who comes next? / We’ll do
the best we can do.
省略表语 -- Are you ready?
-- Yes, I am ready.
Tom is not cruel, nor is his sister cruel.省略宾语 Let’s do the dishes. I’ll wash
dishes and you’ll dry dishes.
省略主谓 I am sorry.
省略定语 He spent part of the money,
and the rest of the money he saved.
省略主谓宾-- Do you like English?
-- Yes, I like English very much.(2) 复合句中的省略 so, not的替代性省略
肯定: I think (hope, suppose, believe, expect, guess, am afraid) so.
否定: I don’t think (believe, suppose, expect) so.
I think (suppose, believe, expect, guess, hope, am afraid) not.
e.g. — Do you think it will rain tomorrow?
— I think so. / I don’t think so. / I think not. 状语从句中的省略
由when, while, as, once, whenever引导
的时间状语从句
(b) if, unless引导的条件状语从句
(c) though, although, as if, as引导的方式
状语从句
e.g. When it is heated, a piece of ice will
turn into water.
If it is necessary, I will apologize to him.
Be careful while you are crossing the street.注意如果从句的主语是it或与主句相同, 谓语含有be, 常省略从句的主语和be动词。宾语从句的省略 I believe that you will succeed.
定语从句关系代词的省略(限定性定语从句)
e.g. I’ll give you all that I have.
I don’t like the way that / in which you talk to do others.
Shaoguan is no longer the city which / that it used to be.
I arrived here the day when he left.省略从句与主句相同的部分
Don’t eat more food than it is good for.
(3) 其他省略现象
不定式中的省略(tell, ask, advise, permit, force, etc.)
He may leave if he wishes to leave.
He wanted to go but I told him not to go.
-- Could you come?
-- I’m glad to / would love to come.不定式在happy, glad, eager, ready, willing, love后时可以省略,但要保留to
e.g. --Would you love to come?
-- Yes, I would love to come. 有固定短语引起的疑问句
e.g. What about having a game of chess?
Why not try again?Change the sentences into elliptical sentences.1. She likes singing and she likes dancing.
2. Is this the driver that you talked about
yesterday?
3. The man who is sitting by the window
is Mr. Smith.
4. He could not decide whether to buy the
car or not to buy the car.5. When it is heated, the metal expands.
6. You can do it if you want to do it.
7. My father planed all these houses and
my father built all these houses.
8. He is the last person that I want to see.
9. He worked hard but his brother did
not work hard.
10. While he was reading the newspaper,
grandpa nodded from time to time.
主将从现时间状语从句用表示时间的连词连接一个句子作时间状语,这样的主从复合句就是时间状语从句。01030205Contents连接词04while/when/as一···就···till/until表示时间的名词词组before & since “当……时候” when/ while/ asⅠ1. when
①when引导的从句可用延续性动词也可用瞬间动词;
② 从句动作和主句的动作 可以 同时发生
也可 先后发生When?I?got?to?the?airport, the?guests?had?left.·When I lived there, I used to go to the beach on Sundays. when 特殊用法when 还可做并列连词 连接并列分句,
表示“就在这时“ =at that time
常用结构“be about to… when…”
“正打算···,这时··· ···”
e.g We were about to leave when he came in.2. while① while引导的从句的动作和主句的动作同时发生
② while引导的从句必须使用延续性动词
③ while引导的从句且多用于进行时The doorbell rang while I was watching TV.I met her while I was at school. 3. as① as引导时间状语侧重从句和主句的动作同时发生
② as引导的从句通常使用延续性动词
③还强调一动作随着另一动作的变化而变化
译为: “随着, 一边……一边……”As the children walked along the street, they sang happily.
As China develops, Chinese is becoming more and more important.As we were dancing,a stranger came in.“当···时候”when/while/as 的区别 1.同时发生
2.先后发生1.延续性动词
2.瞬间动词 延续性动词 同时发生 1. 同时发生多为延续性动词多用于
进行时“随着”
“一边···一边”2.一动作随着另一动作的变化而变化用when/while/as完成下列句子。
1. _____ I went into the classroom, he was
reading.
2. _____ he was speaking, everybody
listened carefully.
3. I was about to go out _____ a visitor came.when While When 4.There is plenty of rain in the south _____ there is little in the north.
A. while?? B. as? C. when??? D. so A “一 ··· 就···” Ⅱ1.as soon as+从句
? I'll telephone you?as?soon?as?I get home.
2.the moment/ minute/ second/instant +从句
The moment I saw her, I cried out.
3.immediately/directly/instantly+从句
Immediately he came, I told him the news.
4. no sooner…than…
hardly/scarcely…when…no sooner… than…
hardly/scarcely… when…1.主句谓语用过去完成时,从句谓语用一般过去时。
2.当no sooner和hardly/scarely位于句首时,主句要部分倒装。She had no sooner heard the news than she jumped.No sooner had she heard the news than she jumped.He had hardly/scarcely finished the test when the bell rang. 他一完成测验,铃就响。 ( hardly/scarcely… when…)
Hardly/Scarcely had he finished the test when the bell rang. He had finished the test.The bell rang. “直到… ...” Ⅲtill/untiltill/until注意:till/until都表示“直到···”可互换,但放在句首时只用untilI waited till/until he arrived.He won’t go to bed till/until she returns.在肯定句中表示“直到···为止” 主句通常使用延续性动词。在否定句中表示“直到···才” 主句通常使用瞬间动词。not···until用法注意: ①“no until”可用于强调句式
② “not until” 放在句首时,句子部分倒装。强调结构
“it is/was + not until +从句+that +主句”We did not get off the bus until it stopped.① It was not until it stopped that we get off the bus.② Not until it stopped did we get off the bus.倒装结构
“Not until +从句 +主句(部分倒装)” “表示时间的名词词组” Ⅳ某些表示时间的名词词组,
也可以引导时间状语从句例如:
the day, the year, the morning, every time,
each time, next time, the first time, by the time…① __________ I catch a cold, I have pain in my back.
每一次我感冒的时候,我都会背痛。
② I’m going to see him ________he comes to Shenzhen.
下一次他来深圳的时候, 我会去看他的。
③ He left Europe _________ World War II broke out.
二战爆发的那一年他离开欧洲。
④ He had impressed me that way __________I met him.
我第一次见到他的时候, 他给我留下那样的印象。Every timenext time the year the first time “before & since ” Ⅴbefore引导的时间状语从句before "在...之前“
注意:主句动作发生先于before引导的从句动作发生。It will be half a year before I come back.
It wasn't long before he left the countryIt will be +一段时间+before... (从句一般现在时)
要过...时间才....
It was +一段时间+before... (从句一般过去时)
过了...时间才....Turn off all the lights before you leave. since引导的时间状语从句I?have?distrusted?her?ever?since?she?cheated?me.一般过去时现在完成时注意:since引导的时间从句若用一般过去时,主句则用现在完成时常见句型 “自从...(至今)已经多久了”
“It is/has been +一段时间+since从句”It is three years since I began to smoke.
It is three years since I smoked.(从句动词)瞬间动词:时间从动作开始算起 “自从... 已经多久了”
(从句动词)延续动词:时间从动作结束算起“自从不... 已经多久了”1. I recognized you ____ I saw you at the airport. A. the moment B. while C. after D. once
2. No sooner had I arrived home _____ it began to rain. A. when B. while C. as D. than3. Hardly had he reached the school gate _____the bell rang. A. while B. when C. as D. as soon as4. It seemed only seconds _____ the
boy finished washing his face.
A. when B. before
C. after D. even if
5. Not until I began to work ___ how
much time I had wasted.
A. didn’t I realize B. did I realize
C. I didn’t realize D. I realize 6. It was not until she got home ___ Jennifer realized she had lost her keys.
A. when B. that C. where D. before7. I got to know she was nice and honest ______ I met her.
A. first time B. for the first time
C. the first time D. at the first time8. By this time tomorrow they ___ the
machine.
A. would repair B. will repair
C. will be repairing D. will have repaired
9. By the time you receive this letter, I ___ this city for my home town.
A. have left B. will have left
C. leave D. will leave 翻译句子 我一见到他就告诉他这个消息。(as
soon as)
(2) 她一来到教室,就开始读英语。(as
soon as) I’ll tell him the news as soon as I see him. As soon as she came into the classroom, she began to read English. (3) 我刚一到家天就下雨了。(no
sooner … than …)
(4) 他刚做完试卷,铃声就响了。
(hardly … when …)I had no sooner got home than it began to rain. He had hardly finished the test when the bell rang. (5) 他一来,你就可立即离开。
(immediately)
(6) 我一见到你,就认出你来了。
(the moment)You may leave immediately he comes. I recognized you the moment I saw you. (7) 每次见面,他都向我问候,说“你
好!”(each time / every time)
(8) 到18岁的时候,她已大学毕业了。
(by the time)He greeted with “Hello!” each time he saw me. By the time she was 18, she had already graduated from the university. Grammar (2)Read the following sentences and say which one is better and why. Mike said that he would come to school to see me the next day, but he didn’t come to school to see me the next day.
2. Mike said that he would come to school to see me the next day, but he didn’t.Answer:
The second sentence is better than the first one. Because it left out the same part of one sentence. It can make us easy to understand and easy to read. Ellipses 省略(1) 简单句省略
省略主语 I Beg your pardon. / It Sounds a good idea. / You Take care!
省略谓语 Who comes next? / We’ll do
the best we can do.
省略表语 -- Are you ready?
-- Yes, I am ready.
Tom is not cruel, nor is his sister cruel.省略宾语 Let’s do the dishes. I’ll wash
dishes and you’ll dry dishes.
省略主谓 I am sorry.
省略定语 He spent part of the money,
and the rest of the money he saved.
省略主谓宾-- Do you like English?
-- Yes, I like English very much.(2) 复合句中的省略 so, not的替代性省略
肯定: I think (hope, suppose, believe, expect, guess, am afraid) so.
否定: I don’t think (believe, suppose, expect) so.
I think (suppose, believe, expect, guess, hope, am afraid) not.
e.g. — Do you think it will rain tomorrow?
— I think so. / I don’t think so. / I think not. 状语从句中的省略
由when, while, as, once, whenever引导
的时间状语从句
(b) if, unless引导的条件状语从句
(c) though, although, as if, as引导的方式
状语从句
e.g. When it is heated, a piece of ice will
turn into water.
If it is necessary, I will apologize to him.
Be careful while you are crossing the street.注意如果从句的主语是it或与主句相同, 谓语含有be, 常省略从句的主语和be动词。宾语从句的省略 I believe that you will succeed.
定语从句关系代词的省略(限定性定语从句)
e.g. I’ll give you all that I have.
I don’t like the way that / in which you talk to do others.
Shaoguan is no longer the city which / that it used to be.
I arrived here the day when he left.省略从句与主句相同的部分
Don’t eat more food than it is good for.
(3) 其他省略现象
不定式中的省略(tell, ask, advise, permit, force, etc.)
He may leave if he wishes to leave.
He wanted to go but I told him not to go.
-- Could you come?
-- I’m glad to / would love to come.不定式在happy, glad, eager, ready, willing, love后时可以省略,但要保留to
e.g. --Would you love to come?
-- Yes, I would love to come. 有固定短语引起的疑问句
e.g. What about having a game of chess?
Why not try again?Change the sentences into elliptical sentences.1. She likes singing and she likes dancing.
2. Is this the driver that you talked about
yesterday?
3. The man who is sitting by the window
is Mr. Smith.
4. He could not decide whether to buy the
car or not to buy the car.5. When it is heated, the metal expands.
6. You can do it if you want to do it.
7. My father planed all these houses and
my father built all these houses.
8. He is the last person that I want to see.
9. He worked hard but his brother did
not work hard.
10. While he was reading the newspaper,
grandpa nodded from time to time.
