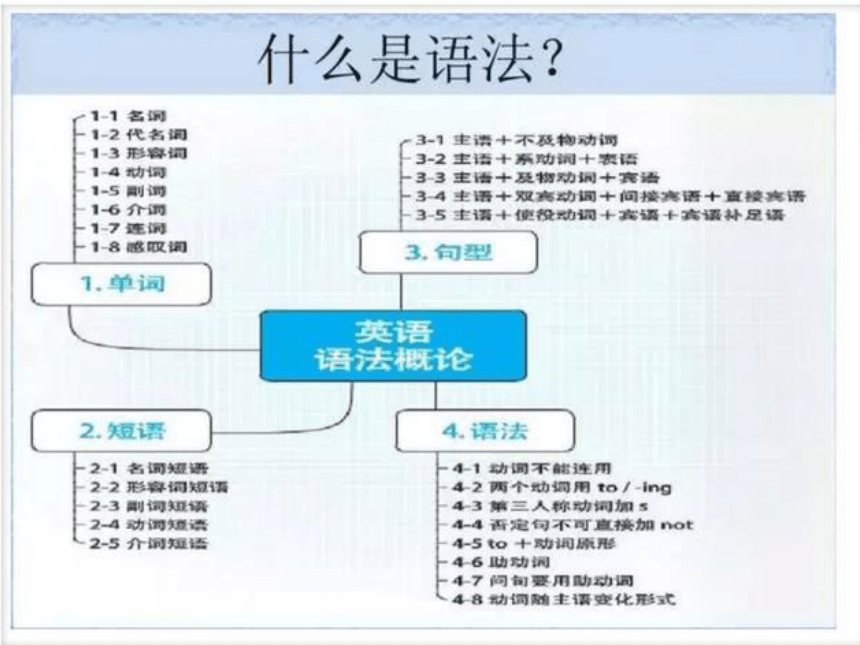
初高中英语动词时态
图片预览









文档简介
英语时态解析
主讲:高福静
时态是谓语动词的形式,表示动作发生的时间或所处的状态,是由动词的不同形式来表现的,这就是动词的时态。
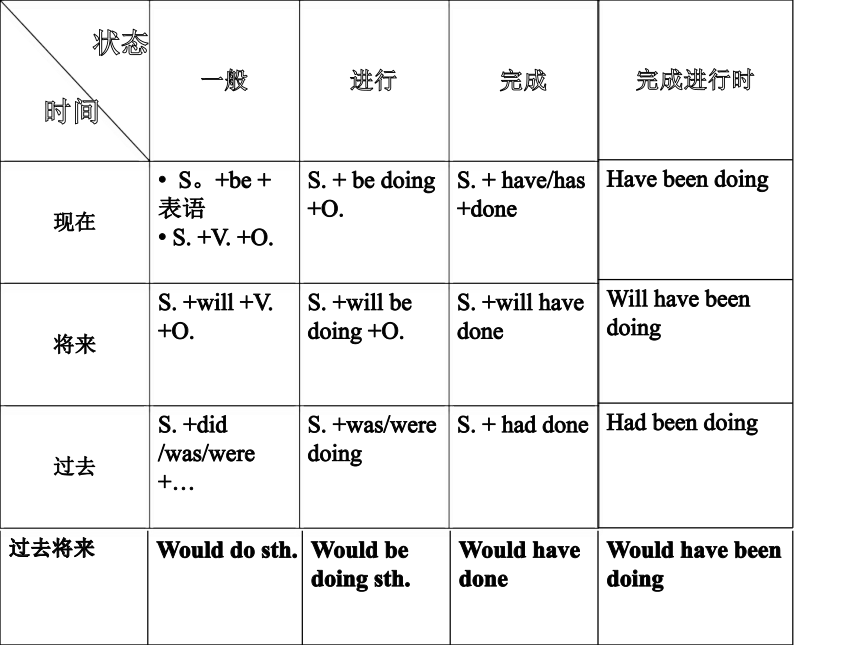
英语时态共有16种,常考的有10种:
状态
时间
一般 进行 完成
现在 S。+be +表语
S. +V. +O. S. + be doing +O. S. + have/has +done
将来 S. +will +V. +O. S. +will be doing +O. S. +will have done
过去 S. +did /was/were+… S. +was/were doing S. + had done
完成进行时
Have been doing
Will have been doing
Had been doing
过去将来 Would do sth. Would be doing sth. Would have done Would have been doing
一般现在时
定义
结构
标志词
用法
练习
【定 义】
一般现在时表示现在经常反复发生的动作、存在的状态或习惯性的动作。即描述我们日常生活中的衣食住行等活动。
结构:
Be 动词:She’s a worker. Is she a worker? She isn’t a worker.
情态动词:I can play the piano. Can you play the piano? I can’t play the piano.
行为动词:They want to eat some tomatoes. Do they want to eat any tomatoes? They don’t want to eat any tomatoes.
Gina has a nice watch. Does Gina have a nice watch? Gina doesn’t have a watch.
变形:
肯定句: 主语+ be+ 其它。
否定句: 主语+ be+not + 其它。
一般问句: Be+主语+ 其它,
特殊疑问句: 特殊疑问词+be+主语+其它,
含实义动词的一般现在时结构:
肯定句:主语+动词原形/动词三单形式+其它。
否定句:主语+don’t/doesn’t+动词原形+其它。
一般问句: Do/Does+主语+动词原形+其它,
特殊疑问句: 特殊疑问词+do/does+主语+动词原形+其它,
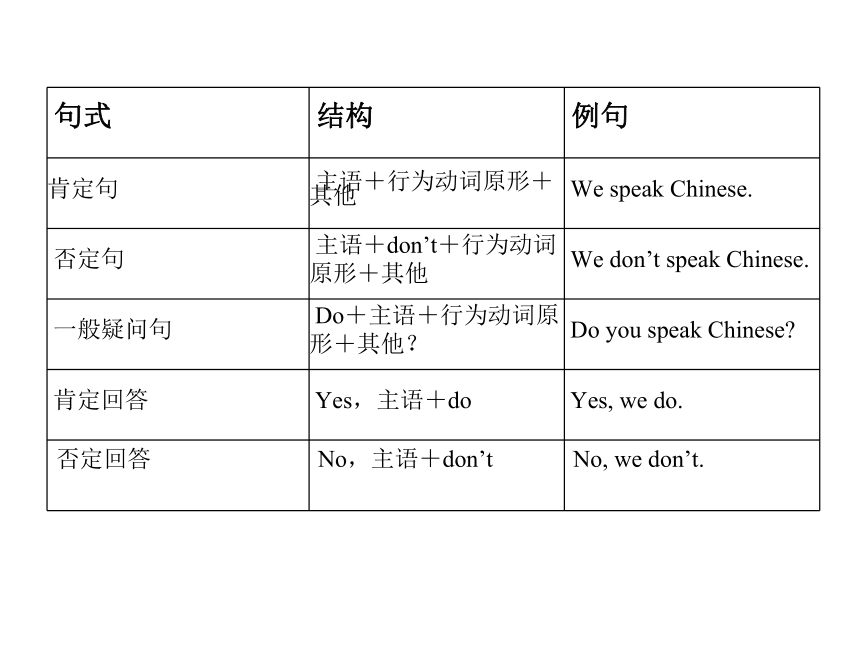
?句式 ?结构 ?例句
肯定句 ?主语+行为动词原形+其他 ?We speak Chinese.
?否定句 ?主语+don’t+行为动词
原形+其他 ?We don’t speak Chinese.
?一般疑问句 ?Do+主语+行为动词原
形+其他? ?Do you speak Chinese?
?肯定回答 ?Yes,主语+do ?Yes, we do.
否定回答
No,主语+don’t
No, we don’t.
标志词:
时间状语与时态有着极为密切的关系,以下常与各种时态连用的时间状语:常与表频度的adv.或时间状语连用。 always, usually, often, frequently, seldom,sometimes, occasionally,every day, once a week etc.
2.
有些句子没有明显的时间状语,这时就可以根据上下文内容来判断时间关系,确定正确的时态。
She lives in the city, but she doesn’t like the life in the city.
1. 表示现在的状态或经常性的动作:
The boy is ill.这男孩病了We need a lot of money. 我们需要大笔钱。He gets up at six every day. 他每天六点起床。
2. 表示现在的能力、特征、职业等:She dances well. 她跳舞跳得好。My father teaches physics. 我父亲教物理。
3. 表示普遍真理或客观事实:
Summer follows spring. 春去夏来。
A plane is faster than a car.
The earth turns around the sun. 地球绕着太阳转。
即使是在主句为过去时态的宾语从句中,表示客观真理的句也用一般现在时态: The teacher told us that the earth turns around the sun.
Columbus proved that the earth is round.
As the saying goes, it is the early bird that catches the worm.
用法
4)表示人的心理活动和感官动作通常用一般现在时,常见动词有:like, love, hate, dislike, want, wish, hope, think, understand, remember, forget, mean, need, hear, feel, see
e.g. He really hopes you can enjoy your stay here.
I: 一般现在时代替进行时
用法:在某些习惯性表达法中,一般现在时可以用来表示现正在发生的动作或存在的状态
e.g. 车来了。
Here comes the bus! = The bus is coming.
There goes the bell. = The bell is ringing.
Attention: 一般现在时的特殊用法
II: 一般现在时表将来时
1. 表示已安排或计划好,将来必定会发生的动作或存在的状态时,这类动词常见为be, arrive, begin, go, leave, start, return等
e.g. Tomorrow we start for Shanghai.
2. 在含有条件、让步、时间状语从句的复合句中,从句用一般现在时表将来的动作.(主将从现)
e.g. We will try to go there in time although it rains heavily tomorrow.
动词第三人称变化规则
第三人称单数的构成方法与名词的单数变复数规则大致一样,即:
1. 一般情况下由动词后加-s构成:work-works, read-reads, look-looks come-comes, live-lives ,listen--listens
2. 以s, x, z, sh, ch 以及字母o结构的动词,后加-es:
Watch—watches;wash—washes; wish-wishes
Guess-guesses 猜, mix--mixes 混和, go--goes 去,finish-finishes 完成,catch--catches 抓住
3. 以辅音字母加y结尾的动词,应将y改为i 再加-es:
以元音字母加y结尾的直接加s。如:plays, says, stays, enjoys, buys
Fly-flies 飞行, study-studies 学习, carry-carries 带,扛
4.以o结尾加es。如:does, goes
5.有个别的变化不规则,如have-has, be-is / am / are, 等。
发音规则:
-词尾-s和-es 读音规则是:在s, x, z, sh, ch 后的es读作[iz],其余的读作[z]。
一般过去式
定 义
时间标志性词
用法
【定 义】
一般过去时表示过确切时间发生过了的动作或存在过的状态。即描述已经发生过了的事情。
【时间标志性词】 yesterday,the day before yesterday, in 2010, (three days) ago,last (night, month, year, weekend), just now,
另,一般过去时也表示经常或反复发生的动作,常和often, sometimes, always, never, used to等表示频率的时间状语连用。
例如:
When I was a child, I often played football in the street.
He is no longer what he used to be.
一般过去式
【用 法】
A(be型
这一类型由be动词,was和were,+名词、形容词、副词、代词、数词或介词短语等一起构成谓语~表示主语以前或过去的个性、特征或状态。如:
?I was a student ten years ago.(主语+be动词+名词)
?They were hungry just now.,主语+be动词+形容词,
?The bike was under the tree yesterday.(主语+be动词+介词短语)
?It was rainy last Sunday.
?They were very happy at Kangkang’s birthday party.
B(did型
did型由行为动词过去式充当谓语~表示以前做过的某事~其构成为―主语+动词过去式动词‖。如:
?I knew him when I was young. ?He believed me at that time .
C(there be(was/were)型
there be型句子表示―某地曾经存在…‖~其构成为―there be(was/were)+主语 +其他‖。用法遵循“就近原则‖~
D(情态动词型
情态动词型句子的构成为―主语+情态动词过去式could+动词原形‖~情态动词过去式和动词原形一起构成谓语~表示主语过去或曾经能做的事情。如:
?He could speak a little English last year.(could+speak)
?What could she do when he was ten.
动词过去式变化规则
1. 一般加ed helped; learned(learnt)
2. e结尾的动词,?直接加d:?smiled;?hoped;?died;tied.
3.一个元音+一个辅音结尾的情况:双写最后一个辅音字母加ed.(重读闭音节)
stopped; planned; preferred(重读在fer前); admitted(重读在mit前); referred; deferred;
4.辅音+y结尾动词,y变i加ed: worried;studied.
5.以t结尾的词,过去式与原形相同。如:put—put, let—let, cut—cut, beat—beat read—read
6.以d结尾的词,把d变成t。如:build—built, lend—lent, send—sent, spend—spent
7.以n结尾的词,在词后加t。如:mean—meant, burn—burnt, learn—learnt
8.以ow / aw结尾的词,把ow / aw变成ew。如:blow—blew, draw—drew, know—knew, grow—grew throw—threw(动词show除外,show—showed)
9.含有双写字母的词,将双写改为单写,在词尾加t。如:keep—kept, sleep—slept, feel—felt, smell—smelt sweep—swept
10.含有元音字母o / i的词,将o / i变成a。如:come—came become—became sing—sang, give—gave, sit—sat, drink—drank
11.把重读开音节中的i改为o,变成过去式。如:drive—drove,ride—rode,write—wrote
动词原形中的e改为o,如: get—got,forget—forgot
动词原形中的ee改为e,如: feed—fed,meet—met
12.动词原形中的eak改为oke,如: break—broke,speak—spoke
13.动词原形中的ell改为old,如: sell—sold,tell—told
14.在动词原形后加d或t变成过去式,并且发生音变。如:
hear—heard, say—said,mean—meant〔m
15.不符合上述规律的动词过去式。如:
am,is—was,are—were,build—built,do—did,eat—ate,fall—fell,find—found,fly—flew,go—went,have /has— had,hold—held,leave—left,make—made,may—might,run—ran,see—saw,take—took
一般将来时
【定义】 一般将来时的基本用法是表示单纯的将来事实:
It will rain tomorrow. 明天会下雨。 He will arrive next Monday. 他将于下周星期一到。
I shall never forget it. 我将永远不会忘记。
【结构】一般将来时通常由“will / shall + 动词原形”构成。
标志词:tomorrow, next year, one day, soon, someday, sometime, in the future
We’ll go at six o’clock tonight.
I will/shall graduate form this school soon.
英语中除了“will / shall+动词原形”表示将来时态外,还可以有以下方法: 1.用“be going to+动词原形”表示
(1)表示主观计划、安排要发生的事
e.g. The play is going to be produced next month.
We are going to see a movie tonight.
(2) 有迹象表明很可能要发生的事
Look at the dark clouds; there is going to be a storm.
2.用“be to+动词原形”表示。表示客观安排或受人指示而做某事。
e.g. We are to discuss the report next Saturday.
I am to play football tomorrow afternoon.
I am going to play football tomorrow afternoon.
3.用“be about to+动词原形”表示。主要表示即将要发生的事:
The train is about to leave. 火车即将开出。
The film is about to start. 电影马上就要开始了。
注意:该结构不与tomorrow, next week等表示明确的将来的时间状语连用。
如不用:He is about to leave for Qingdao ./The train is about to leave soon.
注:be about to…when 就要做…这时…
e.g. I was about to go out when the telephone
rang.
4. 瞬间动词如begin, start ,come, go, leave等的一般现在时或现在进行时表即将发生的动作。
The students are leaving on Sunday. 学生们星期日出发。
We’re having a party next week. 我们下星期将开一个晚会。
该用法有时表示即将发生的动作:I’m leaving. 我要走了。
5.用一般现在时表示。表示按规定或时间表预计要发生的事:
The train leaves at 7:25 this evening. 火车今晚7:25分开。
We have a holiday tomorrow. 我们明天放假。
will [shall] be going to 区别
两者均可表示将来时间和意图,有时可换用:
I think it’ll rain this evening. / I think it’s going to rain this evening. 我想今晚会下雨。
I won’t tell you about it. / I’m not going to tell you about it. 我不会把这事告诉你的。
两者的区别是:若强调某个意图是经过事先考虑好的,要用 be going to;若表示某个意图没有经过事先考虑,而是在说话的当时才临时想到的,则要用 will。
比较:
“Come to the party.” “OK, I’ll bring my boyfriend.” “来参加晚会吧。”“好的,我把我的男朋友也带来。”(临时想法,不能用 be going to)
“Why are you taking it out?” ”I’m going to wash it.” “干吗要把它拿出来?”“我想把它洗一洗。”(事先考虑的意图,不能用 will)
另外,若表示有迹象表明要发生某事,只用 be going to,不用 will:
Look at those black clouds. It’s going to rain. 看那些乌云,要下雨了。
过去将来时
结构:would do
表示在过去预计将要发生的动作,常用于宾从中.
e.g. (1)The students said they would go to visit the Great Wall the next day.
(2) When it rained, he would bring an umbrella with him.(表示过去经常性的动作)
现在进行时
现在进行时 表示动词在此时(说话的瞬间)正在发生或进行就使用进行时态,
结构为sb +be+ v-ing +sth + 其它.
1. 表此时此刻正在进行的动作,常与now, at the moment, for the time being, for the present等表示现在时间的状语连用.
e.g. We are having classes now.
2. 表示近段时间正发生而此刻不一定在进行的动作。
e.g. (1) Mr. Green is writing another novel.
(2) She is learning piano under Mr. Smith.
3. 进行时与always, usually, often, constantly, continually等频度词连用,表经常或反复发生的动作,而且表示批评、不满、讨厌、赞扬或惊讶等感彩。
e.g. (1) You are always forgetting the important thing.
(2) You are constantly finding fault with me.
(3) He is always thinking of others.
肯定句形式:
I + am 动词ing. 如:I am reading (read) an interesting story book now.
She/He/It + is 动词ing. 如:Tom is reading (read) an interesting story book now. We/You/They + are动词ing. 如:They are reading (read) an interesting story book now. 否定句形式:
直接在be,am, is, are,之后加not~其余照抄。
如: I am not reading ( not read) an interesting story book now.
Tom isn’t reading ( not read) an interesting story book now.
They aren’t reading ( not read) an interesting story book now.
一般疑问句:
直接将be,am, is, are,提到主语之前~其余照抄。
如:Is Tom reading (read) an interesting story book now?
Are they reading (read) an interesting story book now?
特殊疑问句:首先分析划线部分的意思~确定用哪个疑问词,what, where, who, when, which, whose, how, how many, how much, what shape, what colour, what … doing, where … going, what … do,,然后再将原句变为一般疑问句形式,即将be动词提到主语之前~其余的不变,。
如:What time is Tom reading(read) an interesting story book?
Where are they taking(take) pictures?
现在分词 当我们说某人正在做什么事时,动词要使用分词形式,不能用原形,构成如下:
一)一般在后加ing。如:spell-spelling, sing-singing, see-seeing, train-training, play-playing, hurry-hurrying, watch-watching, go-going, do-doing
二)以不发音e的结尾的去掉e再加ing。如:dance-dancing, wake-waking, take-taking, practice-practicing, write-writing, have-having
三)以重读闭音节结尾且一个元音字母+一个辅音字母(注意除开字母组合如show –showing, draw-drawing)要双写最后的辅音字母再加ing。如:put-putting, run-running, get-getting, let-letting, begin-beginning
四)以ie结尾的变ie为y再加ing。
如:tie-tying系; die-dying死 ;lie-lying 位于
动词现在分词变化规则
现在进行时的时间标志短语汇总:
现在(正在)进行时常与一些固定的时间短语搭配使用:
now“现在”
如: Jim is playing soccer now.
Look! Listen! “看啊~听啊~”
如:Look! Mr. Lee is working on the computer.
Listen! The birds are sing in the tree.
right now= at the moment“此刻”
如:The monkeys are climbing up the trees at the momnet.
Where is…? 问题的回答,暗指说话的时候。
如:—Where is your mom, Tom?
—Oh, she is cooking in the kitchen.
前面早就阐明是现在的短文中。
过去进行时
结构:was/were +doing
表示过去某一时刻正在进行的动作,时间状语为:at that time, at the moment, this time yesterday, when, while.
e.g. He was cooking supper this time yesterday.
.
将来进行时
结构:will / shall be doing
表将来某时刻或某一阶段正在进行的动作或状态。
e.g. My parents will be waiting for me at the airport tomorrow afternoon.
Dear, when you read this letter I shall be living in the heaven.
现在完成时
结构:has/have done
1. 表示动作发生并结束在过去,但对现在仍有影响。常与already, yet,just, ever, never等副词连用。
e.g. (1) We have just finished the work.
(2)The trees have already been planted.
2. 表从过去某一时刻开始的动作或状态持续到了现在,并还有可能继续下去。常和下列时状连用:
during/in the past few years, so far,
up to now, until now, for+时间段, since, since then, recently, these days, all day
e.g. (1) Tom left Beijing for Shanghai and has worked there ever since.
(2) I enjoyed Shakespeare’s works. Up to now I have read three of his plays.
一般过去时与现在完成时的区别
一般过去时:表示的动作或状态都已成
为过去, 现已不复在。
现在完成时:强调过去的动作对现在产
生的结果或影响。
3. 注意:使用现在完成时的固定句型:
It/This is the first/second time that +主+现在完成时
It/This was the first/second time that + 主+过去完成时
e.g. This is the second time that he has been fired.
过去完成时
结构:had done
表示在过去某一时刻或某一动作之前已经完成的动作,即“过去的过去”。(必须有一个过去的时间或动作作参考)
e.g. (1) When I got to the cinema, the film had begun.
(2) By the end of last month, they had finished two thirds of the work.
过去完成时用在某些句型中。
No sooner…than…
Hardly/Scarcely…when…
e.g. 我们刚一到车站,火车就开了
No sooner had we arrived at the station than the train left.
一…就…
一、用动词的正确时态填空:
What we used to think _____(be) impossible does seem possible now.
When I was at college I _______(speak) three foreign languages, but I _______________(forget) all except a few words of each.
was
spoke
have forgotten
3. My friend, who _________(serve) on the International Olympic Committee all his life, is retiring next week.
4. The new secretary will report to the manager as soon as she ___________(arrive).
has served
arrives
5. Mary ____________(make) a dress when she cut her finger.
6. Shirley ____________(write) a book about China’s railway construction last year. But I have no idea whether she has finished it .
was making
was writing
7. Thank you so much for the Longman English-English Dictionary. I _____________(want) one for ages.
8. He said that he ____________ (not lend) me a penny.
have been wanting
wouldn’t lend
9. I ____________ (write) to Mr. Pitt and tell him about Tom’s new house.
10. Hurry up! The train __________ (leave).
11. This was the best film that I ___________ (see).
will write
is leaving
had seen
9. I ____________ (write) to Mr. Pitt and tell him about Tom’s new house.
10. Hurry up! The train __________ (leave).
11. This was the best film that I ___________ (see).
will write
is leaving
had seen
高考真题:
The house belongs to my aunt but she ____________(not live) here any more.
This machine ____________(not work). It hasn’t worked for years.
If their marketing plans succeed, they ___________(increase) their sales by 20 percent.
doesn’t live
doesn’t work
will increase
4. Population experts predict that most people ___________(live) in cities in the near future.
5. He ___________(play) football regularly when he was young.
6. —Have you known Dr. Jackson for a long time?
—Yes, since he _______(join) the Chinese Society.
will live
played
joined
7. I called Hnnah many times yesterday evening, but I couldn’t get through. Her brother ___________ (talk) on the phone all the time!
8. John promised his doctor he _________________ (not smoke), and he has not smoked ever since.
was talking
would not smoke
12. We first met on a train in 2000. We both felt immediately that we ____________ (know) each other for years.
13. — I’m sure Andrew will win the first prize in the final.
— I think so. He ____________ (prepare) for it for months.
had known
has been preparing
14. The telephone __________ (ring), but by the time I got indoors, it stopped.
15. —What’s that noise?
—Oh, I forgot to tell you. The new machine _______________ (test).
16. I like these English songs and they _________________(teach) many times on the radio.
was ringing
is being tested
have been taught
17. No decision ____________ (make) about any future appointment until all the candidates have been interviewed.
18. Do you have any problems if you ___________ (offer).
will be made
are offered
骄者必败。
我们小时候常在一起玩。
这些天我在上夜校。
她老是帮助别人。
我已经看过那部电影了。
警察到达时,小偷们早就跑了。
如果你告诉他真相,他会原谅你的。
你看天上的云,快下雨了。
他们将在六月结婚。
他马上就去北京。
骄者必败。
Pride goes before a fall.
2. 我们小时候常在一起玩。
We often played together when we were children.
3. 这些天我在上夜校。
I’m studying at an evening school these day.
4. 她老是帮助别人。
She is always helping others.
5. 我已经看过那部电影了。
I have seen the film already.
6. 警察到达时,小偷们早就跑了。
When the police arrived, the thieves had run away.
7. 如果你告诉他真相,他会原谅你的。
He will forgive you if you tell him the truth.
8. 你看天上的云,快下雨了。
Look at the clouds; it’s going to rain./ it’s raining.
9. 他们将在六月结婚。
They are going to marry in June.
They are to marry in June.
10. 他马上就去北京。
He is about to leave for Beijing.
He is leaving for Beijing.
Thanks
主讲:高福静
时态是谓语动词的形式,表示动作发生的时间或所处的状态,是由动词的不同形式来表现的,这就是动词的时态。
英语时态共有16种,常考的有10种:
状态
时间
一般 进行 完成
现在 S。+be +表语
S. +V. +O. S. + be doing +O. S. + have/has +done
将来 S. +will +V. +O. S. +will be doing +O. S. +will have done
过去 S. +did /was/were+… S. +was/were doing S. + had done
完成进行时
Have been doing
Will have been doing
Had been doing
过去将来 Would do sth. Would be doing sth. Would have done Would have been doing
一般现在时
定义
结构
标志词
用法
练习
【定 义】
一般现在时表示现在经常反复发生的动作、存在的状态或习惯性的动作。即描述我们日常生活中的衣食住行等活动。
结构:
Be 动词:She’s a worker. Is she a worker? She isn’t a worker.
情态动词:I can play the piano. Can you play the piano? I can’t play the piano.
行为动词:They want to eat some tomatoes. Do they want to eat any tomatoes? They don’t want to eat any tomatoes.
Gina has a nice watch. Does Gina have a nice watch? Gina doesn’t have a watch.
变形:
肯定句: 主语+ be+ 其它。
否定句: 主语+ be+not + 其它。
一般问句: Be+主语+ 其它,
特殊疑问句: 特殊疑问词+be+主语+其它,
含实义动词的一般现在时结构:
肯定句:主语+动词原形/动词三单形式+其它。
否定句:主语+don’t/doesn’t+动词原形+其它。
一般问句: Do/Does+主语+动词原形+其它,
特殊疑问句: 特殊疑问词+do/does+主语+动词原形+其它,
?句式 ?结构 ?例句
肯定句 ?主语+行为动词原形+其他 ?We speak Chinese.
?否定句 ?主语+don’t+行为动词
原形+其他 ?We don’t speak Chinese.
?一般疑问句 ?Do+主语+行为动词原
形+其他? ?Do you speak Chinese?
?肯定回答 ?Yes,主语+do ?Yes, we do.
否定回答
No,主语+don’t
No, we don’t.
标志词:
时间状语与时态有着极为密切的关系,以下常与各种时态连用的时间状语:常与表频度的adv.或时间状语连用。 always, usually, often, frequently, seldom,sometimes, occasionally,every day, once a week etc.
2.
有些句子没有明显的时间状语,这时就可以根据上下文内容来判断时间关系,确定正确的时态。
She lives in the city, but she doesn’t like the life in the city.
1. 表示现在的状态或经常性的动作:
The boy is ill.这男孩病了We need a lot of money. 我们需要大笔钱。He gets up at six every day. 他每天六点起床。
2. 表示现在的能力、特征、职业等:She dances well. 她跳舞跳得好。My father teaches physics. 我父亲教物理。
3. 表示普遍真理或客观事实:
Summer follows spring. 春去夏来。
A plane is faster than a car.
The earth turns around the sun. 地球绕着太阳转。
即使是在主句为过去时态的宾语从句中,表示客观真理的句也用一般现在时态: The teacher told us that the earth turns around the sun.
Columbus proved that the earth is round.
As the saying goes, it is the early bird that catches the worm.
用法
4)表示人的心理活动和感官动作通常用一般现在时,常见动词有:like, love, hate, dislike, want, wish, hope, think, understand, remember, forget, mean, need, hear, feel, see
e.g. He really hopes you can enjoy your stay here.
I: 一般现在时代替进行时
用法:在某些习惯性表达法中,一般现在时可以用来表示现正在发生的动作或存在的状态
e.g. 车来了。
Here comes the bus! = The bus is coming.
There goes the bell. = The bell is ringing.
Attention: 一般现在时的特殊用法
II: 一般现在时表将来时
1. 表示已安排或计划好,将来必定会发生的动作或存在的状态时,这类动词常见为be, arrive, begin, go, leave, start, return等
e.g. Tomorrow we start for Shanghai.
2. 在含有条件、让步、时间状语从句的复合句中,从句用一般现在时表将来的动作.(主将从现)
e.g. We will try to go there in time although it rains heavily tomorrow.
动词第三人称变化规则
第三人称单数的构成方法与名词的单数变复数规则大致一样,即:
1. 一般情况下由动词后加-s构成:work-works, read-reads, look-looks come-comes, live-lives ,listen--listens
2. 以s, x, z, sh, ch 以及字母o结构的动词,后加-es:
Watch—watches;wash—washes; wish-wishes
Guess-guesses 猜, mix--mixes 混和, go--goes 去,finish-finishes 完成,catch--catches 抓住
3. 以辅音字母加y结尾的动词,应将y改为i 再加-es:
以元音字母加y结尾的直接加s。如:plays, says, stays, enjoys, buys
Fly-flies 飞行, study-studies 学习, carry-carries 带,扛
4.以o结尾加es。如:does, goes
5.有个别的变化不规则,如have-has, be-is / am / are, 等。
发音规则:
-词尾-s和-es 读音规则是:在s, x, z, sh, ch 后的es读作[iz],其余的读作[z]。
一般过去式
定 义
时间标志性词
用法
【定 义】
一般过去时表示过确切时间发生过了的动作或存在过的状态。即描述已经发生过了的事情。
【时间标志性词】 yesterday,the day before yesterday, in 2010, (three days) ago,last (night, month, year, weekend), just now,
另,一般过去时也表示经常或反复发生的动作,常和often, sometimes, always, never, used to等表示频率的时间状语连用。
例如:
When I was a child, I often played football in the street.
He is no longer what he used to be.
一般过去式
【用 法】
A(be型
这一类型由be动词,was和were,+名词、形容词、副词、代词、数词或介词短语等一起构成谓语~表示主语以前或过去的个性、特征或状态。如:
?I was a student ten years ago.(主语+be动词+名词)
?They were hungry just now.,主语+be动词+形容词,
?The bike was under the tree yesterday.(主语+be动词+介词短语)
?It was rainy last Sunday.
?They were very happy at Kangkang’s birthday party.
B(did型
did型由行为动词过去式充当谓语~表示以前做过的某事~其构成为―主语+动词过去式动词‖。如:
?I knew him when I was young. ?He believed me at that time .
C(there be(was/were)型
there be型句子表示―某地曾经存在…‖~其构成为―there be(was/were)+主语 +其他‖。用法遵循“就近原则‖~
D(情态动词型
情态动词型句子的构成为―主语+情态动词过去式could+动词原形‖~情态动词过去式和动词原形一起构成谓语~表示主语过去或曾经能做的事情。如:
?He could speak a little English last year.(could+speak)
?What could she do when he was ten.
动词过去式变化规则
1. 一般加ed helped; learned(learnt)
2. e结尾的动词,?直接加d:?smiled;?hoped;?died;tied.
3.一个元音+一个辅音结尾的情况:双写最后一个辅音字母加ed.(重读闭音节)
stopped; planned; preferred(重读在fer前); admitted(重读在mit前); referred; deferred;
4.辅音+y结尾动词,y变i加ed: worried;studied.
5.以t结尾的词,过去式与原形相同。如:put—put, let—let, cut—cut, beat—beat read—read
6.以d结尾的词,把d变成t。如:build—built, lend—lent, send—sent, spend—spent
7.以n结尾的词,在词后加t。如:mean—meant, burn—burnt, learn—learnt
8.以ow / aw结尾的词,把ow / aw变成ew。如:blow—blew, draw—drew, know—knew, grow—grew throw—threw(动词show除外,show—showed)
9.含有双写字母的词,将双写改为单写,在词尾加t。如:keep—kept, sleep—slept, feel—felt, smell—smelt sweep—swept
10.含有元音字母o / i的词,将o / i变成a。如:come—came become—became sing—sang, give—gave, sit—sat, drink—drank
11.把重读开音节中的i改为o,变成过去式。如:drive—drove,ride—rode,write—wrote
动词原形中的e改为o,如: get—got,forget—forgot
动词原形中的ee改为e,如: feed—fed,meet—met
12.动词原形中的eak改为oke,如: break—broke,speak—spoke
13.动词原形中的ell改为old,如: sell—sold,tell—told
14.在动词原形后加d或t变成过去式,并且发生音变。如:
hear—heard, say—said,mean—meant〔m
15.不符合上述规律的动词过去式。如:
am,is—was,are—were,build—built,do—did,eat—ate,fall—fell,find—found,fly—flew,go—went,have /has— had,hold—held,leave—left,make—made,may—might,run—ran,see—saw,take—took
一般将来时
【定义】 一般将来时的基本用法是表示单纯的将来事实:
It will rain tomorrow. 明天会下雨。 He will arrive next Monday. 他将于下周星期一到。
I shall never forget it. 我将永远不会忘记。
【结构】一般将来时通常由“will / shall + 动词原形”构成。
标志词:tomorrow, next year, one day, soon, someday, sometime, in the future
We’ll go at six o’clock tonight.
I will/shall graduate form this school soon.
英语中除了“will / shall+动词原形”表示将来时态外,还可以有以下方法: 1.用“be going to+动词原形”表示
(1)表示主观计划、安排要发生的事
e.g. The play is going to be produced next month.
We are going to see a movie tonight.
(2) 有迹象表明很可能要发生的事
Look at the dark clouds; there is going to be a storm.
2.用“be to+动词原形”表示。表示客观安排或受人指示而做某事。
e.g. We are to discuss the report next Saturday.
I am to play football tomorrow afternoon.
I am going to play football tomorrow afternoon.
3.用“be about to+动词原形”表示。主要表示即将要发生的事:
The train is about to leave. 火车即将开出。
The film is about to start. 电影马上就要开始了。
注意:该结构不与tomorrow, next week等表示明确的将来的时间状语连用。
如不用:He is about to leave for Qingdao ./The train is about to leave soon.
注:be about to…when 就要做…这时…
e.g. I was about to go out when the telephone
rang.
4. 瞬间动词如begin, start ,come, go, leave等的一般现在时或现在进行时表即将发生的动作。
The students are leaving on Sunday. 学生们星期日出发。
We’re having a party next week. 我们下星期将开一个晚会。
该用法有时表示即将发生的动作:I’m leaving. 我要走了。
5.用一般现在时表示。表示按规定或时间表预计要发生的事:
The train leaves at 7:25 this evening. 火车今晚7:25分开。
We have a holiday tomorrow. 我们明天放假。
will [shall] be going to 区别
两者均可表示将来时间和意图,有时可换用:
I think it’ll rain this evening. / I think it’s going to rain this evening. 我想今晚会下雨。
I won’t tell you about it. / I’m not going to tell you about it. 我不会把这事告诉你的。
两者的区别是:若强调某个意图是经过事先考虑好的,要用 be going to;若表示某个意图没有经过事先考虑,而是在说话的当时才临时想到的,则要用 will。
比较:
“Come to the party.” “OK, I’ll bring my boyfriend.” “来参加晚会吧。”“好的,我把我的男朋友也带来。”(临时想法,不能用 be going to)
“Why are you taking it out?” ”I’m going to wash it.” “干吗要把它拿出来?”“我想把它洗一洗。”(事先考虑的意图,不能用 will)
另外,若表示有迹象表明要发生某事,只用 be going to,不用 will:
Look at those black clouds. It’s going to rain. 看那些乌云,要下雨了。
过去将来时
结构:would do
表示在过去预计将要发生的动作,常用于宾从中.
e.g. (1)The students said they would go to visit the Great Wall the next day.
(2) When it rained, he would bring an umbrella with him.(表示过去经常性的动作)
现在进行时
现在进行时 表示动词在此时(说话的瞬间)正在发生或进行就使用进行时态,
结构为sb +be+ v-ing +sth + 其它.
1. 表此时此刻正在进行的动作,常与now, at the moment, for the time being, for the present等表示现在时间的状语连用.
e.g. We are having classes now.
2. 表示近段时间正发生而此刻不一定在进行的动作。
e.g. (1) Mr. Green is writing another novel.
(2) She is learning piano under Mr. Smith.
3. 进行时与always, usually, often, constantly, continually等频度词连用,表经常或反复发生的动作,而且表示批评、不满、讨厌、赞扬或惊讶等感彩。
e.g. (1) You are always forgetting the important thing.
(2) You are constantly finding fault with me.
(3) He is always thinking of others.
肯定句形式:
I + am 动词ing. 如:I am reading (read) an interesting story book now.
She/He/It + is 动词ing. 如:Tom is reading (read) an interesting story book now. We/You/They + are动词ing. 如:They are reading (read) an interesting story book now. 否定句形式:
直接在be,am, is, are,之后加not~其余照抄。
如: I am not reading ( not read) an interesting story book now.
Tom isn’t reading ( not read) an interesting story book now.
They aren’t reading ( not read) an interesting story book now.
一般疑问句:
直接将be,am, is, are,提到主语之前~其余照抄。
如:Is Tom reading (read) an interesting story book now?
Are they reading (read) an interesting story book now?
特殊疑问句:首先分析划线部分的意思~确定用哪个疑问词,what, where, who, when, which, whose, how, how many, how much, what shape, what colour, what … doing, where … going, what … do,,然后再将原句变为一般疑问句形式,即将be动词提到主语之前~其余的不变,。
如:What time is Tom reading(read) an interesting story book?
Where are they taking(take) pictures?
现在分词 当我们说某人正在做什么事时,动词要使用分词形式,不能用原形,构成如下:
一)一般在后加ing。如:spell-spelling, sing-singing, see-seeing, train-training, play-playing, hurry-hurrying, watch-watching, go-going, do-doing
二)以不发音e的结尾的去掉e再加ing。如:dance-dancing, wake-waking, take-taking, practice-practicing, write-writing, have-having
三)以重读闭音节结尾且一个元音字母+一个辅音字母(注意除开字母组合如show –showing, draw-drawing)要双写最后的辅音字母再加ing。如:put-putting, run-running, get-getting, let-letting, begin-beginning
四)以ie结尾的变ie为y再加ing。
如:tie-tying系; die-dying死 ;lie-lying 位于
动词现在分词变化规则
现在进行时的时间标志短语汇总:
现在(正在)进行时常与一些固定的时间短语搭配使用:
now“现在”
如: Jim is playing soccer now.
Look! Listen! “看啊~听啊~”
如:Look! Mr. Lee is working on the computer.
Listen! The birds are sing in the tree.
right now= at the moment“此刻”
如:The monkeys are climbing up the trees at the momnet.
Where is…? 问题的回答,暗指说话的时候。
如:—Where is your mom, Tom?
—Oh, she is cooking in the kitchen.
前面早就阐明是现在的短文中。
过去进行时
结构:was/were +doing
表示过去某一时刻正在进行的动作,时间状语为:at that time, at the moment, this time yesterday, when, while.
e.g. He was cooking supper this time yesterday.
.
将来进行时
结构:will / shall be doing
表将来某时刻或某一阶段正在进行的动作或状态。
e.g. My parents will be waiting for me at the airport tomorrow afternoon.
Dear, when you read this letter I shall be living in the heaven.
现在完成时
结构:has/have done
1. 表示动作发生并结束在过去,但对现在仍有影响。常与already, yet,just, ever, never等副词连用。
e.g. (1) We have just finished the work.
(2)The trees have already been planted.
2. 表从过去某一时刻开始的动作或状态持续到了现在,并还有可能继续下去。常和下列时状连用:
during/in the past few years, so far,
up to now, until now, for+时间段, since, since then, recently, these days, all day
e.g. (1) Tom left Beijing for Shanghai and has worked there ever since.
(2) I enjoyed Shakespeare’s works. Up to now I have read three of his plays.
一般过去时与现在完成时的区别
一般过去时:表示的动作或状态都已成
为过去, 现已不复在。
现在完成时:强调过去的动作对现在产
生的结果或影响。
3. 注意:使用现在完成时的固定句型:
It/This is the first/second time that +主+现在完成时
It/This was the first/second time that + 主+过去完成时
e.g. This is the second time that he has been fired.
过去完成时
结构:had done
表示在过去某一时刻或某一动作之前已经完成的动作,即“过去的过去”。(必须有一个过去的时间或动作作参考)
e.g. (1) When I got to the cinema, the film had begun.
(2) By the end of last month, they had finished two thirds of the work.
过去完成时用在某些句型中。
No sooner…than…
Hardly/Scarcely…when…
e.g. 我们刚一到车站,火车就开了
No sooner had we arrived at the station than the train left.
一…就…
一、用动词的正确时态填空:
What we used to think _____(be) impossible does seem possible now.
When I was at college I _______(speak) three foreign languages, but I _______________(forget) all except a few words of each.
was
spoke
have forgotten
3. My friend, who _________(serve) on the International Olympic Committee all his life, is retiring next week.
4. The new secretary will report to the manager as soon as she ___________(arrive).
has served
arrives
5. Mary ____________(make) a dress when she cut her finger.
6. Shirley ____________(write) a book about China’s railway construction last year. But I have no idea whether she has finished it .
was making
was writing
7. Thank you so much for the Longman English-English Dictionary. I _____________(want) one for ages.
8. He said that he ____________ (not lend) me a penny.
have been wanting
wouldn’t lend
9. I ____________ (write) to Mr. Pitt and tell him about Tom’s new house.
10. Hurry up! The train __________ (leave).
11. This was the best film that I ___________ (see).
will write
is leaving
had seen
9. I ____________ (write) to Mr. Pitt and tell him about Tom’s new house.
10. Hurry up! The train __________ (leave).
11. This was the best film that I ___________ (see).
will write
is leaving
had seen
高考真题:
The house belongs to my aunt but she ____________(not live) here any more.
This machine ____________(not work). It hasn’t worked for years.
If their marketing plans succeed, they ___________(increase) their sales by 20 percent.
doesn’t live
doesn’t work
will increase
4. Population experts predict that most people ___________(live) in cities in the near future.
5. He ___________(play) football regularly when he was young.
6. —Have you known Dr. Jackson for a long time?
—Yes, since he _______(join) the Chinese Society.
will live
played
joined
7. I called Hnnah many times yesterday evening, but I couldn’t get through. Her brother ___________ (talk) on the phone all the time!
8. John promised his doctor he _________________ (not smoke), and he has not smoked ever since.
was talking
would not smoke
12. We first met on a train in 2000. We both felt immediately that we ____________ (know) each other for years.
13. — I’m sure Andrew will win the first prize in the final.
— I think so. He ____________ (prepare) for it for months.
had known
has been preparing
14. The telephone __________ (ring), but by the time I got indoors, it stopped.
15. —What’s that noise?
—Oh, I forgot to tell you. The new machine _______________ (test).
16. I like these English songs and they _________________(teach) many times on the radio.
was ringing
is being tested
have been taught
17. No decision ____________ (make) about any future appointment until all the candidates have been interviewed.
18. Do you have any problems if you ___________ (offer).
will be made
are offered
骄者必败。
我们小时候常在一起玩。
这些天我在上夜校。
她老是帮助别人。
我已经看过那部电影了。
警察到达时,小偷们早就跑了。
如果你告诉他真相,他会原谅你的。
你看天上的云,快下雨了。
他们将在六月结婚。
他马上就去北京。
骄者必败。
Pride goes before a fall.
2. 我们小时候常在一起玩。
We often played together when we were children.
3. 这些天我在上夜校。
I’m studying at an evening school these day.
4. 她老是帮助别人。
She is always helping others.
5. 我已经看过那部电影了。
I have seen the film already.
6. 警察到达时,小偷们早就跑了。
When the police arrived, the thieves had run away.
7. 如果你告诉他真相,他会原谅你的。
He will forgive you if you tell him the truth.
8. 你看天上的云,快下雨了。
Look at the clouds; it’s going to rain./ it’s raining.
9. 他们将在六月结婚。
They are going to marry in June.
They are to marry in June.
10. 他马上就去北京。
He is about to leave for Beijing.
He is leaving for Beijing.
Thanks
