Unit 1 Where did you go on vacation? Section A 1a-1c 课件(27张PPT)
文档属性
| 名称 | Unit 1 Where did you go on vacation? Section A 1a-1c 课件(27张PPT) |  | |
| 格式 | zip | ||
| 文件大小 | 651.5KB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 人教新目标(Go for it)版 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2018-10-31 21:00:29 | ||
图片预览








文档简介
Unit 1
Where did you go on vacation?
备注:见flash课件 Section A
1c Make conversations about the
people in 1a.
A: Where did Tina go on vacation?
B: She went to the mountains.
c
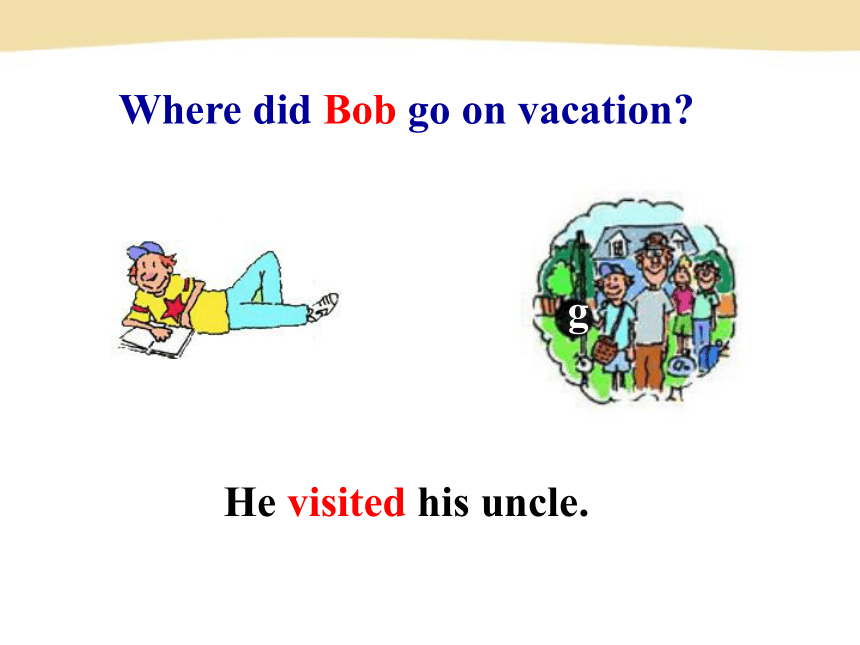
Where did Bob go on vacation?
He visited his uncle.
g
Where did Tom go on vacation?
He went to summer camp.
d
Where did Sally go on
vacation?
She stayed at home.
f
Where did Xiang Hua go on vacation?
He went to New York City.
b
Where did he go on
vacation?
He went to the beach.
a
动词过去式 动词原形
went
stayed
visited
did
was
had
go
stay
visit
do
is
have
1. --Where did you go on vacation?
你去哪儿度假了?
--I went to the mountains. 我去了山区。
1) 这是一个特殊疑问句。由“特殊疑问词
+助动词+主语+动词+其它?” 构成。
由于是询问已发生的动作(过去的事情),
所以助动词用过去式did, 其后的动词用原形。
Language Points
e.g. --Where did you go yesterday?
你昨天去了哪儿?
--I visited my friends.
我去拜访了朋友。
2) 与go to the mountains结构类似的词组还有:
go to the beach 去海边
go to summer camp 去夏令营
go to New York City 去纽约市
go on vacation 去度假
go to a trip 去旅行
go to the movies 去看电影
2. -- Did you go to Central Park?
你去中心公园了吗?
-- Yes, I did. 是的, 去了。
这是一个一般疑问句, 由助动词提问,
回答也用助动词。由于询问的是发生在
过去的事, 所以助动词用过去式did。
一般过去时的一般疑问句的句子结构:
Did+主语+动词原形+其它+?
回答: Yes, 主+did. / No, 主+didn’t.
在过去时态中, 无论主语是第几人称,
是单数还是复数, 助动词一律用 did。如:
--Did you/he/she/they go to the park
last night?
--Yes, I/he/she/they did.
3. I stayed at home. 我待在家里。
1) stay可以作及物动词, 也可以作不及
物动词。当它作不及物动词时就不能直接
接宾语, 其后接相应的介词短语, 表地点
(留在某地)或表状态(保持某种状态)。
e.g. stay in the office 继续任职 (掌权)
stay awake 不睡 (醒着)
stay in the army 留在部队中
stay at home 呆在家中
We're staying in the same hotel.
我们住在同一家旅馆。
2) home与house, family的区别
home指“家”这个概念, 包括“住处”和
“家人”。 house则指“房子”、“住宅”,
侧重于建筑结构。family则指“家庭成员”。
※当family作整体概念时, 谓语动词用单数;
看作一个个成员时, 谓语动词用复数。
e.g. I watched TV at home last might.
我昨晚在家里看电视。
This house is very beautiful.
这房子真漂亮。
My family is a small but happy one.
我家人不多但很幸福。
My family are watching TV.
家人在看电视。
2)如果动词是延续性动词,则一般它即可表示动作,也可以表示状态。 如:live/stay/work等就是此类。
3)如果是单独的瞬间性动词,则它只表示动作。 如:get up/put on/begin就属于此类。
5. Did you buy anything special?
在英语中,anything, something, nothing 和everything是用于指代事物的复合不定代词,与之相对应的复合不定代词 anyone, someone, no one 和everyone ( anybody, somebody, nobody 和 everybody) 用于指人。
与形容词连时, 形容词必须放在复合不定
代词之后,语法上称作“后置”。例如:
something important—— 重要的事
I can see someone new in your group.
我看出你们小组里有新人。
There’s nothing interesting in the news today.
今天的新闻里没有什么有趣的新闻。
6. We took quite a few photos there.
此句中 quite a few 是一个整体结构,表
示“相当多”, 修饰可数名词,请不要与a
few(少数几个) 混淆。比较下面例句中quite
a few 和a few的区别。
There are only a few books on the table,
but I still have quite a few in the bookcase.
虽然桌上只有几本书,但我的书柜里还有
很多书。
7. She?visited?her?uncle.??
①句中visit是及物动词直接跟宾语,当其后接表示人的词语时译为 “拜访”。当其后接表示地点的名词时,译为“参观”。
? visit?the??Summer?Palace----参观颐和园
???②visit还可以作名词“拜访,参观”,构成短语 pay?a?visit?to…/be?on?a?visit?to…译为 “访问(某人)”“参观(某地)”????
1.We?paid?a?visit?to?our?teacher?yesterday.?
???我昨天拜访了我的老师。
2.?We?are __a visit __our?English?teacher ?now.
? A. on;on??? B. to;on???
C.?to;to? D. on;to?
3. 谢谢你的请柬。
Thanks for your invitation.
4. 玛丽在歌唱比赛中得了奖。
Mary won a prize in the singing
competition.
5. 你远足愉快吗?
Did you have fun hiking?
Homework
Make a conversation about what did you do last week.
Master the words in this unit and pre-view next part.
Where did you go on vacation?
备注:见flash课件 Section A
1c Make conversations about the
people in 1a.
A: Where did Tina go on vacation?
B: She went to the mountains.
c
Where did Bob go on vacation?
He visited his uncle.
g
Where did Tom go on vacation?
He went to summer camp.
d
Where did Sally go on
vacation?
She stayed at home.
f
Where did Xiang Hua go on vacation?
He went to New York City.
b
Where did he go on
vacation?
He went to the beach.
a
动词过去式 动词原形
went
stayed
visited
did
was
had
go
stay
visit
do
is
have
1. --Where did you go on vacation?
你去哪儿度假了?
--I went to the mountains. 我去了山区。
1) 这是一个特殊疑问句。由“特殊疑问词
+助动词+主语+动词+其它?” 构成。
由于是询问已发生的动作(过去的事情),
所以助动词用过去式did, 其后的动词用原形。
Language Points
e.g. --Where did you go yesterday?
你昨天去了哪儿?
--I visited my friends.
我去拜访了朋友。
2) 与go to the mountains结构类似的词组还有:
go to the beach 去海边
go to summer camp 去夏令营
go to New York City 去纽约市
go on vacation 去度假
go to a trip 去旅行
go to the movies 去看电影
2. -- Did you go to Central Park?
你去中心公园了吗?
-- Yes, I did. 是的, 去了。
这是一个一般疑问句, 由助动词提问,
回答也用助动词。由于询问的是发生在
过去的事, 所以助动词用过去式did。
一般过去时的一般疑问句的句子结构:
Did+主语+动词原形+其它+?
回答: Yes, 主+did. / No, 主+didn’t.
在过去时态中, 无论主语是第几人称,
是单数还是复数, 助动词一律用 did。如:
--Did you/he/she/they go to the park
last night?
--Yes, I/he/she/they did.
3. I stayed at home. 我待在家里。
1) stay可以作及物动词, 也可以作不及
物动词。当它作不及物动词时就不能直接
接宾语, 其后接相应的介词短语, 表地点
(留在某地)或表状态(保持某种状态)。
e.g. stay in the office 继续任职 (掌权)
stay awake 不睡 (醒着)
stay in the army 留在部队中
stay at home 呆在家中
We're staying in the same hotel.
我们住在同一家旅馆。
2) home与house, family的区别
home指“家”这个概念, 包括“住处”和
“家人”。 house则指“房子”、“住宅”,
侧重于建筑结构。family则指“家庭成员”。
※当family作整体概念时, 谓语动词用单数;
看作一个个成员时, 谓语动词用复数。
e.g. I watched TV at home last might.
我昨晚在家里看电视。
This house is very beautiful.
这房子真漂亮。
My family is a small but happy one.
我家人不多但很幸福。
My family are watching TV.
家人在看电视。
2)如果动词是延续性动词,则一般它即可表示动作,也可以表示状态。 如:live/stay/work等就是此类。
3)如果是单独的瞬间性动词,则它只表示动作。 如:get up/put on/begin就属于此类。
5. Did you buy anything special?
在英语中,anything, something, nothing 和everything是用于指代事物的复合不定代词,与之相对应的复合不定代词 anyone, someone, no one 和everyone ( anybody, somebody, nobody 和 everybody) 用于指人。
与形容词连时, 形容词必须放在复合不定
代词之后,语法上称作“后置”。例如:
something important—— 重要的事
I can see someone new in your group.
我看出你们小组里有新人。
There’s nothing interesting in the news today.
今天的新闻里没有什么有趣的新闻。
6. We took quite a few photos there.
此句中 quite a few 是一个整体结构,表
示“相当多”, 修饰可数名词,请不要与a
few(少数几个) 混淆。比较下面例句中quite
a few 和a few的区别。
There are only a few books on the table,
but I still have quite a few in the bookcase.
虽然桌上只有几本书,但我的书柜里还有
很多书。
7. She?visited?her?uncle.??
①句中visit是及物动词直接跟宾语,当其后接表示人的词语时译为 “拜访”。当其后接表示地点的名词时,译为“参观”。
? visit?the??Summer?Palace----参观颐和园
???②visit还可以作名词“拜访,参观”,构成短语 pay?a?visit?to…/be?on?a?visit?to…译为 “访问(某人)”“参观(某地)”????
1.We?paid?a?visit?to?our?teacher?yesterday.?
???我昨天拜访了我的老师。
2.?We?are __a visit __our?English?teacher ?now.
? A. on;on??? B. to;on???
C.?to;to? D. on;to?
3. 谢谢你的请柬。
Thanks for your invitation.
4. 玛丽在歌唱比赛中得了奖。
Mary won a prize in the singing
competition.
5. 你远足愉快吗?
Did you have fun hiking?
Homework
Make a conversation about what did you do last week.
Master the words in this unit and pre-view next part.
同课章节目录
- Unit 1 Where did you go on vacation?
- Section A
- Section B
- Unit 2 How often do you exercise?
- Section A
- Section B
- Unit 3 I'm more outgoing than my sister.
- Section A
- Section B
- Unit 4 What's the best movie theater?
- Section A
- Section B
- Unit 5 Do you want to watch a game show?
- Section A
- Section B
- Unit 6 I'm going to study computer science.
- Section A
- Section B
- Unit 7 Will people have robots?
- Section A
- Section B
- Unit 8 How do you make a banana milk shake?
- Section A
- Section B
- Unit 9 Can you come to my party?
- Section A
- Section B
- Unit 10 If you go to the party, you'll have a grea
- Section A
- Section B
