英语复习 动词时态 课件(共56张ppt)
文档属性
| 名称 | 英语复习 动词时态 课件(共56张ppt) |  | |
| 格式 | zip | ||
| 文件大小 | 279.9KB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 通用版 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2018-11-30 09:23:48 | ||
图片预览











文档简介
课件56张PPT。English Verb Tense一般现在时
一般过去时
一般将来时
一般过去将来时 英语动词时态Grammar Focusthe Simple Present Tense
the Simple Past Tense
the Simple Future Tense
the Simple Past-future Tensethe Simple Present Tense1.表示现在的状态和经常发生的动作。
Lisa has two sisters and a brother.
We go to school at 6:30 every morning.
She often rides her bike to work.
He often gets up at six every morning.
I usually watch TV news at home on Saturday.
Alice is always late for class.
2. 表示客观真理、事实和规律。
The earth goes around the sun.
We live a happy life in China.
Light travels faster than sound.一般现在时3.表示一个人的爱好、习惯、性格、能力等。
Maria likes listening to MP3.
I can play tennis and ping-pong.
We are all hard-working and thrifty.
He works in a company.
They know French.
4.用于祈使句、条件状语和时间状语从句或格言警句中。
Brush your teeth after meal, Tom.
She won't go to bed until her mom gets back.
When he arrives there, he will be caught in a heavy rain.
Cats catch mice.the Simple Present Tense一般现在时一般现在时的谓语构成
1.表示状态的be动词(即am, is, are)
She is an English girl. I am her boyfriend.
We are from Yunnan. They are friendly to us.
The girl in red is Gina from Canada.
The man in a car is my pen pal from the US.
How are you? / How is your mom?the Simple Present Tense一般现在时2. 谓语动词是实义动词时,用动词原形(主语是单数第三人称除外)。
We often play basketball after school.
They usually watch TV at home on weekends.
I always help my parents water our fruit trees.
Do you go to visit the museums on Saturdays?
We come over to see him.
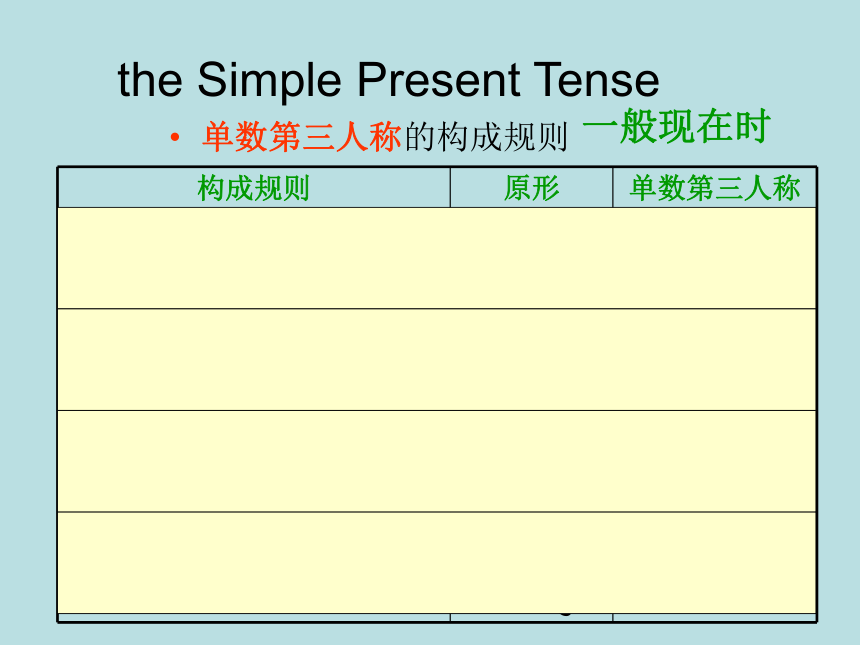
Do they clean their classroom after class?the Simple Present Tense一般现在时主语是单数第三人称时,谓语动词用单数第三人称形式。
Jim often goes to school by bike.
She always gets up late in the morning.
He usually plays ping-pong with his friends.
Alice has a cute pet at home.
Does she watch TV with her parents at night?
What does he do on weekends?the Simple Present Tense一般现在时单数第三人称的构成规则the Simple Present Tense一般现在时含be动词的变化(be是连系动词)
1.肯定句 主语+be+表语
He is a Chinese boy. We are at school.
2.否定句 主语+be + not+表语
He is not a Japanese boy. We are not at home.
3. 疑问句(一般疑问句):Be+主语+表语?
Is he a Chinese boy? Are you at school?the Simple Present Tense一般现在时一般现在时的句子变化含行为动词的变化
1.肯定句 主语+动词原形(+其它)
We often play ping-pong after school.
They usually clean their classroom after class.
主语是单数第三人称时,动词用单数第三人称形式
She always does her homework at school.
Lucy runs fastest in her class.
He has lunch with his classmates at school.the Simple Present Tense一般现在时一般现在时的句子变化2.否定句 主语+do not + 动词原形+其它
We don’t often play ping-pong after school.
They don’t usually clean their classroom after class.
主语是单数第三人称时,助动词用does, 即does + not+动词原形+其它
She doesn’t always do her homework at school.
Lucy doesn’t run fastest in her class.
He doesn’t have lunch with his classmates at school.the Simple Present Tense一般现在时一般现在时的句子变化3.疑问句(一般疑问句)Do(Does)+主语+动词原形+其它?
Do you often play ping-pong after school?
Do they usually clean their classroom after class?
Does she always do her homework at school?
Does Lucy run fastest in her class?
Does he have lunch with his classmates at school?the Simple Present Tense一般现在时一般现在时的句子变化一般现在时的时间状语
always, usually, often, sometimes, hardly, ever, never, every day, on weekends, once a week 等。一般现在时the Simple Present Tense1 Tim ______ (go) to work every morning. He _______ (work) hard.
2 The sun always _______ (rise) in the east.
3 _____ you often _______ (water) these flowers?
4 We know that light _______ (travel) very fast.
5 Sometimes he ___( be) right . But sometimes he _______ (make) mistakes. goesworksrisesDowater用所给动词的适当形式填空。travelsismakes6 He ______ (have) lunch at home every day.
7 She ___________ (not go) shopping on Sunday.
8 Mr. Zhang _____ (be) a good teacher.
9 Tom _______ (like) swimming in summer.
10 They often _______ (visit) a farm.
11 _______ Mike usually ______(see) the film?
12 Dr. Lee usually _______(visit) this museum once a month. the Simple Present Tense一般现在时用所给动词的适当形式填空。hasdoesn’t goislikesvisitDoesseevisits Mr. Smith _____ up late in the morning, so his wife always ______ him to make sure he isn’t late for work. One day they _________ with each other for some reason and they stop __________ to each other. That evening Mr. Smith ______ his wife a piece of paper which says “Call me at 7:00 in the morning.” Then he ______ to sleep without saying anything. When he _______ up the next morning, it’s 9:30. He gets up and ______ on his clothes quickly. As he _______ the bedroom, he ______ a piece of paper on the table which says “it’s 7 o’clock. Get up!”the Simple Present Tense一般现在时用所给动词的适当形式填空。get call quarrel speak give go wake put leave findgetscallsquarrelspeakinggivesgoeswakesputsleavesfinds( ) 1.---What do you often do at weekends?
---I often ______ my grandparents.
A. visit B.visited C.have visited D.will visit
( ) 2.---Do you know if Jack will drive to London this weekend?
---Jack? Never! He ______ driving so far.
A. has hated B.will hate C.hated D.hates
( ) 3.---Tina, breakfast is ready. Dad cooked it for us.
---It can't have been Father. He _____ early on Sundays.
A. always gets up B. often got up
C. had got up D. never gets upthe Simple Present Tense一般现在时选择填空。( ) 4.If it _____ rain tomorrow, we'll go hiking.
A. won't B. doesn't C. don't D. didn't
( ) 5.Alice likes doing housework. She ____ her room every afternoon.
A. cleans B. cleaned C. is cleaning D. has cleaned
( ) 6.Now my dad _____ his bike to work every day instead of driving.
A. ride B. rode C. will ride D. rides
the Simple Present Tense一般现在时the Simple Past Tense表示过去某个时间所发生的动作或存在的状态,谓语动词用过去式,常与过去时间状语连用。
I worked in London last year.
She went to a movie yesterday evening.
Gina played tennis after school yesterday.
Tony had an apple and a glass of milk for breakfast yesterday morning.
Alice watched TV at home last Friday night.一般过去时表示过去经常或反复发生的动作,常和often, usually, always 等表示频度的时间状语连用。
I often watched TV news at home last summer.
Lucy usually went shopping with her mom last year.
He always sent some food to the charity a few years ago.the Simple Past Tense一般过去时英语动词过去式的构成规则规则变化
1.一般情况下在原形动词后加-ed 如:watched, worked, played, looked, started, visited, walked, enjoyed
2.以e字母结尾的动词只加-d 如: lived , hoped, used, loved, liked, danced 3.末尾只有一个辅音字母的重读闭音节动词,构成过去式时,先双写这个辅音字母,再加-ed 如: clapped, planned, stopped
4.以辅音字母加-y 结尾的动词,先去掉-y 字母,再加-ied 如: study ——— studied carry ——— carried worry ——— worried the Simple Past Tense一般过去时英语动词过去式的构成规则不规则变化
常见的不规则动词 put let hurt cut
am/is – was are – were become – became begin – began bring – brought buy – bought catch – caught come – came do (does) – did eat – ate feel – felt find – found give – gave get – got go – went grow – grew run – ran have (has) – had hear – heard know – knew make – made say – said see – saw sit – sat stand– stood take – took teach – taught write – wrote tell – toldthe Simple Past Tense一般过去时英语动词过去式的构成规则含连系动词be (was/were)的变化
1.肯定句 主语+be+表语
He was a Chinese driver.We were at school.
2.否定句 主语+be + not+表语
He was not a writer. They were not at home.
3. 疑问句(一般疑问句) Be+主语+表语?
Was he an engineer? Were you at school?the Simple Past Tense一般过去时一般过去时的句子变化含行为动词的变化
1.肯定句 主语+动词过去式(+其它)
We usually played ping-pong a few years ago.
They cleaned their bedroom last weekend.
She did her homework at school yesterday.
Lucy watched TV news last night.
He had lunch at school.the Simple Past Tense一般过去时一般过去时的句子变化2.否定句 主语+did not + 动词原形+其它
We didn’t play ping-pong yesterday afternoon.
They didn’t clean their classroom after school.
She didn’t do her homework at school.
Mom didn’t cook dinner for us last Friday.
Lucy didn’t run to school yesterday morning.
He didn’t have lunch at school this morning.
Gina didn’t get an MP4 for her brother.the Simple Past Tense一般过去时一般过去时的句子变化3.疑问句(一般疑问句)Did+主语+动词原形+其它?
Did you play ping-pong after school?
Did they clean their classroom after class?
Did she do her homework at school?
Did Lucy speak at the meeting?
Did he have lunch at school?
Did Gina get an MP4 for her brother?the Simple Past Tense一般过去时一般过去时的句子变化the Simple Past Tense一般过去时( )1.After Steven sent some e-mails, he ___ surfing the Internet.
A. starts B. has started C. will start D. started
( )2.The teacher is already standing here. Do you know when she ___?
A. comes B. came C. is coming D. was coming
( )3.---Have you ever been to Kunming?
---Yes. I ___ there last month.
A. have been B. went C. was going D. have gone选择填空。一般现在时态和一般过去时态比较 一般现在时态
1.表示经常性、习惯性的动作或存在的状态。
常与often, usually, every day, sometimes, always, never, once a week, on Sunday等时间状语连用。例如:
I often get up at 6 o’clock.
She usually plays piano.
They always stay at home.
I am sometimes busy.
He is 13 years old this year.
He often watches TV after school. 一般过去时态
1.表示过去某一时间发的动作或存在的状态。
常与yesterday, yesterday evening, last night, last Saturday, last month, last year 等过去时间状语连用。例如:
I got up at 6 yesterday.
She played piano this afternoon.
I was busy yesterday morning.
He was 12 years old last year.
He watched TV after school yesterday. 2.表示客观事实和普遍真理。例如:
The earth moves around the sun.
The light travels faster than sound.
一般现在时态
动词用原形,若主语为单数第三人时,用单数第三人称形式。例如:
I often watch TV.
She often watches TV.
Do you play chess?
Does he play chess?一般现在时态和一般过去时态比较2.表示过去经常和反复做的动作。例如:
I often went to fish last summer.
We usually played cards last year.
一般过去时态
无论主语是第几人称、单数还是复数,谓语动词都用动词过去式。例如:
I watched TV yesterday.
She played piano last night.
He did his homework.一般过去时态 表示过去某时发生的动作或存在的状态。
过去进行时态 表示过去某时刻或某段时间正在进行的动作。
Alice wrote to Li Ming last Friday night.
Alice was writing to Li Ming last Friday night.
I watched TV yesterday afternoon.
I was watching TV yesterday afternoon. 一般过去时态和过去进行时态比较the Simple Future Tense一般将来时一般将来时的表达方法
I.“be going to + verb”结构 表示将要发生的事或打算、计划、决定要做的事情。例如:
I am going to go shopping with mom this afternoon.
We are going to visit Tibet for a week.
They are going to have a party for Mary’s birthday this evening.
She is going to work in Japan next week.
He is going to ride his bike to the Great Wall this Saturday.the Simple Future Tense一般将来时II. will + verb 表示将来某时要发生的动作或存在的状态,也表示将来经常或反复发生的动作。例如:
I will go to see my uncle this afternoon.
We will visit the Great Wall next week.
She will watch TV play at home tonight.
My mom will get me an MP3 tomorrow.
People will have robots in the future.III. 现在进行时态 也可以表示当前一段时间内的活动或现阶段正在进行的动作。
They are working on a farm with the farmers these days.
He is writing a book this month.
My grandparents are living with my uncle in Beijing these years.
The bus is coming soon.the Simple Future Tense一般将来时现在进行时态 还可以用来表示按计划或安排将要进行的动作,有“意图、打算”之意。
--What are you doing for summer vacation?
--I am visiting my aunt in Australia.
--When are you going?
--I am going on this Sunday.
We are going to the Summer Palace next Sunday morning.
She is going to Tibet for two weeks.
I am coming to see my grandma.the Simple Future Tense一般将来时*shall和will 都是一般将来时态的助动词。
疑问句中,主语是第一人称(I和we)时,常用助动词shall。
When shall we meet tomorrow morning?
Shall I open the door? Shall we sing?
书面语中,主语是第一人称(I和we)时,也常用助动词shall。但在口语中,可用will。
I shall go to Japan with mom next month.
We shall have a birthday party for Lucy.the Simple Future Tense一般将来时Shall and willwillwill( ) 1.Whenever a person ___ difficulties, he ___ two choices. One is to give up, the other is to face them bravely and try to overcome them.
A. meets; had B. meets; will have C. will meet; has D. will meet; had
( ) 2.I' m busy now. I ___ to you after school this afternoon.
A. talk B. talked C. will talk D. have talked
( ) 3.---What's your plan for your vacation? ---We ___ to Hong Kong for a visit.
A. were flying B. have flown C. will flythe Simple Future Tense一般将来时选择填空( ) 4.If we ___ take environmental problems seriously, the earth ___ worse and worse.
A. don't; will be B. won't; isn't
C. won't; is D. don't; won't be
( ) 5.Hurry up! The sky is covered with black clouds. I'm afraid it ___ .
A. rains B. is going to rain
C. rained D. was raining
( ) 6.---Have you ever been to the Great Wall?
---Not yet. I ___ it this year.
A. visited B. have visited
C. was visiting D. will visitthe Simple Future Tense一般将来时( ) 7.---Does the bus go to the beach?
---No. You ___ the wrong way. You want the No. 11.
A. go B. were going C. are going D. would go
( ) 8.Mr. Wang has left for Guangzhou. He ___ a speech there in two days.
A. gives B. gave C. will give D. has given
( ) 9.Robots ___ more heavy work for us in the future.
A. will do B. did C. have done D. were doing
( )10.---Do you think gradpa and grandma ___ late?
---No, the train is usually on time.
A. were B. will be C. was D. have beenthe Simple Future Tense一般将来时构成 助动词 would + 动词原形
用法 主要用于宾语从句中,表示从过去某个时间看来将要发生的动作或存在的状态。
She said (that) she would go to the zoo this Saturday.
Mom told me (that) she would take us to the science museum next weekend.
Mr. White said (that) he would fly to Australia this afternoon.the Simple Past-future Tense一般过去将来时Dad told us (that) he would make a toy bear for us.
My aunt said (that) she would get a soft toy for me as a gift on my sixth birthday.
Mr. Yang asked us if we would have a party for Ms Anna.
I wondered if you would go shopping with me if you are free.一般过去将来时the Simple Past-future TenseEnglish Verb Tensethe Present Progressive Tense the Past Progressive Tense the Present Perfect Progressive TenseGrammar Focus英语动词时态现在进行时
过去进行时
现在完成进行时构成 be 动词的一般式(am/is/are) + 现在分词(doing) 例如:
I am listening to my MP3 now.
We are having a math class.
She is watching TV news at home.
He is playing basketball now.
Gina is making dinner for us now.the Present Progressive Tense现在进行时用法 现在进行时态是表示现在(说话瞬间)正在进行或发生的动作。
What are you doing now?
We are listening to some pop songs.
Lucy is playing the piano.
Are you studying at the computer?
No, I’m not. I am playing games.
Is she cooking at home? Yes, she is.the Present Progressive Tense现在进行时构成 be 动词的过去式(was/were)+现在分词(doing) 例如:
I was watching TV news at home.
We were having lunch at school.
She was shopping with her mom.
He was cutting hair at the barber.
They were flying a kite in the park.the Past Progressive Tense过去进行时用法 过去进行时态 表示在过去某时刻或某段时间正在进行的动作。※ 一般用时间状语(从句)来表示这一过去时间。例如:
What were you doing at nine last night?
What was she doing when the UFO arrived?
He was sleeping when you called him.
We were watching a football match on TV at this time yesterday evening.the Past Progressive Tense过去进行时构成 助动词have (has)+ been +动词的现在分词 (doing)
I have been teaching for many years.
She has been playing volleyball since she was young.
We have been waiting for you all the afternoon.
He has been watching TV at home.the Present perfect Progressive Tense现在完成进行时用法 现在完成进行时 表示从过去开始一直在进行的动作,可能还要进行下去,也可能刚结束。
How long have you been skating?
I have been cleaning the classroom.
We have been waiting for the bus for an hour.
Alice has been watching TV all the afternoon.
Mr. White has been working here for 10 years.the Present perfect Progressive Tense现在完成进行时English Verb Tensethe Present Perfect Tense the Past Perfect TenseGrammar Focus英语动词时态现在完成时
过去完成时构成 助动词have (has)+过去分词 (done)
I have lived in Kunming for ten years.
She has learned Spanish since five years ago.
We have worked here since 2001.
He has played the violin since he was a child.
They have ever eaten hamburgers in China.
I have just had my lunch at school.
Gina has just left the Junior High School.
Uncle Wang has already gone to Shanghai.the Present Perfect Tense现在完成时用法 a.表示过去发生或已完成的动作对现在造成的影响或结果。
Have you had your lunch yet?
Has the student on duty erased the blackboard?
Have you finished doing your homework?
Has Gina come here? Has she played tennis?
I have my hair cut already.
Has Leo his bike mended yet?
You have played basketball before class.the Present Perfect Tense现在完成时I haven’t seen her these days.
We have known Celia for many years.
She has lived in Nanjian since 1978.
Alison has played the guitar since he was young.
They have bought an apartment in 1980s.
She has taught us English since 2012.
Mr. Yang has been at this school for 20 years.the Present Perfect Tense现在完成时b.表示从过去某时开始的动作或状态,一直持续到现在,可能刚刚结束,也可能还要继续下去。when she was a baby.for nearly 40 years.for almost 20 years.for almost two years.for over 6 years.since 1994.Have (has) been
Have (has) gone
Where has she been?
She has been to the bank.
Where has she gone?
She has gone to the bank.
Has Nicole been to Beijing yet?
Oh, Nicole has gone to Beijing. the Present Perfect Tense现在完成时Have (has) been & have (has) gone曾经到过某地去某地了(不在这儿)already backnot herenot here现在完成时 表示过去发生的动作对现在造成影响或结果,强调的是现在,因此,不和过去时间状语连用。
一般过去时 表示过去的动作和状态,和现在不发生联系,所以,可以和过去时间状语连用。
I have seen the film.
I saw the film last weekend.
She has lived in Kunming since 1999.
She lived in Kunming in 1999.
Lily has come to China for twice.
Lily came to China last month.现在完成时态和一般过去时态比较现在完成进行时 从过去开始一直在进行的动作,可能还要进行下去,也可能刚结束。
现在完成时 过去开始的动作到现在刚结束;或对现在造成了一定的影响,产生结果。
How long have you collected the shells?
How long have you been skating?
I have already erased the blackboard.
I’ve been cleaning the classroom for an hour.
We have waited for the bus for an hour.
We have been waiting for the bus for an hour.现在完成时态和现在完成进行时态比较构成 助动词had+过去分词(done)
I had lived in Kunming before I came here.
She had learned Spanish five years ago.
We had worked here for ten years before.
He had played the violin when he was a child.
They had ever eaten hamburgers in China.
I had just been to my old primary school.
The movie had begun when we got there.
Alice had slept when Mom got back home.the Present Perfect Tense过去完成时用法 a.表示过去发生或已完成的动作对过去造成的影响或结果。
Had you had your lunch before you came here?
Had she erased the blackboard before class?
Had you learned Spanish in Spain?
Had Gina played tennis before she came here?
I had my hair cut already by Friday.
Had Leo his bike mended yet?
You had played basketball before class.the Present Perfect Tense过去完成时I hadn’t seen her before she came here.
We had known Celia before she went to the US.
She had lived in Nanjian from 1978 to 1993.
Alison had played the guitar before he was sang.
They had bought an apartment in 1980s.
She had taught English before she taught math.
Mr. Yang had been at this school for 20 years.the Present Perfect Tense过去完成时b.表示从过去某时开始的动作或状态,持续到过去某时 并对当时造成了影响和结果,也就说,过去完成时表示的是过去的过去的动作。Thank you for your watching!
Catch you on the next time!
一般过去时
一般将来时
一般过去将来时 英语动词时态Grammar Focusthe Simple Present Tense
the Simple Past Tense
the Simple Future Tense
the Simple Past-future Tensethe Simple Present Tense1.表示现在的状态和经常发生的动作。
Lisa has two sisters and a brother.
We go to school at 6:30 every morning.
She often rides her bike to work.
He often gets up at six every morning.
I usually watch TV news at home on Saturday.
Alice is always late for class.
2. 表示客观真理、事实和规律。
The earth goes around the sun.
We live a happy life in China.
Light travels faster than sound.一般现在时3.表示一个人的爱好、习惯、性格、能力等。
Maria likes listening to MP3.
I can play tennis and ping-pong.
We are all hard-working and thrifty.
He works in a company.
They know French.
4.用于祈使句、条件状语和时间状语从句或格言警句中。
Brush your teeth after meal, Tom.
She won't go to bed until her mom gets back.
When he arrives there, he will be caught in a heavy rain.
Cats catch mice.the Simple Present Tense一般现在时一般现在时的谓语构成
1.表示状态的be动词(即am, is, are)
She is an English girl. I am her boyfriend.
We are from Yunnan. They are friendly to us.
The girl in red is Gina from Canada.
The man in a car is my pen pal from the US.
How are you? / How is your mom?the Simple Present Tense一般现在时2. 谓语动词是实义动词时,用动词原形(主语是单数第三人称除外)。
We often play basketball after school.
They usually watch TV at home on weekends.
I always help my parents water our fruit trees.
Do you go to visit the museums on Saturdays?
We come over to see him.
Do they clean their classroom after class?the Simple Present Tense一般现在时主语是单数第三人称时,谓语动词用单数第三人称形式。
Jim often goes to school by bike.
She always gets up late in the morning.
He usually plays ping-pong with his friends.
Alice has a cute pet at home.
Does she watch TV with her parents at night?
What does he do on weekends?the Simple Present Tense一般现在时单数第三人称的构成规则the Simple Present Tense一般现在时含be动词的变化(be是连系动词)
1.肯定句 主语+be+表语
He is a Chinese boy. We are at school.
2.否定句 主语+be + not+表语
He is not a Japanese boy. We are not at home.
3. 疑问句(一般疑问句):Be+主语+表语?
Is he a Chinese boy? Are you at school?the Simple Present Tense一般现在时一般现在时的句子变化含行为动词的变化
1.肯定句 主语+动词原形(+其它)
We often play ping-pong after school.
They usually clean their classroom after class.
主语是单数第三人称时,动词用单数第三人称形式
She always does her homework at school.
Lucy runs fastest in her class.
He has lunch with his classmates at school.the Simple Present Tense一般现在时一般现在时的句子变化2.否定句 主语+do not + 动词原形+其它
We don’t often play ping-pong after school.
They don’t usually clean their classroom after class.
主语是单数第三人称时,助动词用does, 即does + not+动词原形+其它
She doesn’t always do her homework at school.
Lucy doesn’t run fastest in her class.
He doesn’t have lunch with his classmates at school.the Simple Present Tense一般现在时一般现在时的句子变化3.疑问句(一般疑问句)Do(Does)+主语+动词原形+其它?
Do you often play ping-pong after school?
Do they usually clean their classroom after class?
Does she always do her homework at school?
Does Lucy run fastest in her class?
Does he have lunch with his classmates at school?the Simple Present Tense一般现在时一般现在时的句子变化一般现在时的时间状语
always, usually, often, sometimes, hardly, ever, never, every day, on weekends, once a week 等。一般现在时the Simple Present Tense1 Tim ______ (go) to work every morning. He _______ (work) hard.
2 The sun always _______ (rise) in the east.
3 _____ you often _______ (water) these flowers?
4 We know that light _______ (travel) very fast.
5 Sometimes he ___( be) right . But sometimes he _______ (make) mistakes. goesworksrisesDowater用所给动词的适当形式填空。travelsismakes6 He ______ (have) lunch at home every day.
7 She ___________ (not go) shopping on Sunday.
8 Mr. Zhang _____ (be) a good teacher.
9 Tom _______ (like) swimming in summer.
10 They often _______ (visit) a farm.
11 _______ Mike usually ______(see) the film?
12 Dr. Lee usually _______(visit) this museum once a month. the Simple Present Tense一般现在时用所给动词的适当形式填空。hasdoesn’t goislikesvisitDoesseevisits Mr. Smith _____ up late in the morning, so his wife always ______ him to make sure he isn’t late for work. One day they _________ with each other for some reason and they stop __________ to each other. That evening Mr. Smith ______ his wife a piece of paper which says “Call me at 7:00 in the morning.” Then he ______ to sleep without saying anything. When he _______ up the next morning, it’s 9:30. He gets up and ______ on his clothes quickly. As he _______ the bedroom, he ______ a piece of paper on the table which says “it’s 7 o’clock. Get up!”the Simple Present Tense一般现在时用所给动词的适当形式填空。get call quarrel speak give go wake put leave findgetscallsquarrelspeakinggivesgoeswakesputsleavesfinds( ) 1.---What do you often do at weekends?
---I often ______ my grandparents.
A. visit B.visited C.have visited D.will visit
( ) 2.---Do you know if Jack will drive to London this weekend?
---Jack? Never! He ______ driving so far.
A. has hated B.will hate C.hated D.hates
( ) 3.---Tina, breakfast is ready. Dad cooked it for us.
---It can't have been Father. He _____ early on Sundays.
A. always gets up B. often got up
C. had got up D. never gets upthe Simple Present Tense一般现在时选择填空。( ) 4.If it _____ rain tomorrow, we'll go hiking.
A. won't B. doesn't C. don't D. didn't
( ) 5.Alice likes doing housework. She ____ her room every afternoon.
A. cleans B. cleaned C. is cleaning D. has cleaned
( ) 6.Now my dad _____ his bike to work every day instead of driving.
A. ride B. rode C. will ride D. rides
the Simple Present Tense一般现在时the Simple Past Tense表示过去某个时间所发生的动作或存在的状态,谓语动词用过去式,常与过去时间状语连用。
I worked in London last year.
She went to a movie yesterday evening.
Gina played tennis after school yesterday.
Tony had an apple and a glass of milk for breakfast yesterday morning.
Alice watched TV at home last Friday night.一般过去时表示过去经常或反复发生的动作,常和often, usually, always 等表示频度的时间状语连用。
I often watched TV news at home last summer.
Lucy usually went shopping with her mom last year.
He always sent some food to the charity a few years ago.the Simple Past Tense一般过去时英语动词过去式的构成规则规则变化
1.一般情况下在原形动词后加-ed 如:watched, worked, played, looked, started, visited, walked, enjoyed
2.以e字母结尾的动词只加-d 如: lived , hoped, used, loved, liked, danced 3.末尾只有一个辅音字母的重读闭音节动词,构成过去式时,先双写这个辅音字母,再加-ed 如: clapped, planned, stopped
4.以辅音字母加-y 结尾的动词,先去掉-y 字母,再加-ied 如: study ——— studied carry ——— carried worry ——— worried the Simple Past Tense一般过去时英语动词过去式的构成规则不规则变化
常见的不规则动词 put let hurt cut
am/is – was are – were become – became begin – began bring – brought buy – bought catch – caught come – came do (does) – did eat – ate feel – felt find – found give – gave get – got go – went grow – grew run – ran have (has) – had hear – heard know – knew make – made say – said see – saw sit – sat stand– stood take – took teach – taught write – wrote tell – toldthe Simple Past Tense一般过去时英语动词过去式的构成规则含连系动词be (was/were)的变化
1.肯定句 主语+be+表语
He was a Chinese driver.We were at school.
2.否定句 主语+be + not+表语
He was not a writer. They were not at home.
3. 疑问句(一般疑问句) Be+主语+表语?
Was he an engineer? Were you at school?the Simple Past Tense一般过去时一般过去时的句子变化含行为动词的变化
1.肯定句 主语+动词过去式(+其它)
We usually played ping-pong a few years ago.
They cleaned their bedroom last weekend.
She did her homework at school yesterday.
Lucy watched TV news last night.
He had lunch at school.the Simple Past Tense一般过去时一般过去时的句子变化2.否定句 主语+did not + 动词原形+其它
We didn’t play ping-pong yesterday afternoon.
They didn’t clean their classroom after school.
She didn’t do her homework at school.
Mom didn’t cook dinner for us last Friday.
Lucy didn’t run to school yesterday morning.
He didn’t have lunch at school this morning.
Gina didn’t get an MP4 for her brother.the Simple Past Tense一般过去时一般过去时的句子变化3.疑问句(一般疑问句)Did+主语+动词原形+其它?
Did you play ping-pong after school?
Did they clean their classroom after class?
Did she do her homework at school?
Did Lucy speak at the meeting?
Did he have lunch at school?
Did Gina get an MP4 for her brother?the Simple Past Tense一般过去时一般过去时的句子变化the Simple Past Tense一般过去时( )1.After Steven sent some e-mails, he ___ surfing the Internet.
A. starts B. has started C. will start D. started
( )2.The teacher is already standing here. Do you know when she ___?
A. comes B. came C. is coming D. was coming
( )3.---Have you ever been to Kunming?
---Yes. I ___ there last month.
A. have been B. went C. was going D. have gone选择填空。一般现在时态和一般过去时态比较 一般现在时态
1.表示经常性、习惯性的动作或存在的状态。
常与often, usually, every day, sometimes, always, never, once a week, on Sunday等时间状语连用。例如:
I often get up at 6 o’clock.
She usually plays piano.
They always stay at home.
I am sometimes busy.
He is 13 years old this year.
He often watches TV after school. 一般过去时态
1.表示过去某一时间发的动作或存在的状态。
常与yesterday, yesterday evening, last night, last Saturday, last month, last year 等过去时间状语连用。例如:
I got up at 6 yesterday.
She played piano this afternoon.
I was busy yesterday morning.
He was 12 years old last year.
He watched TV after school yesterday. 2.表示客观事实和普遍真理。例如:
The earth moves around the sun.
The light travels faster than sound.
一般现在时态
动词用原形,若主语为单数第三人时,用单数第三人称形式。例如:
I often watch TV.
She often watches TV.
Do you play chess?
Does he play chess?一般现在时态和一般过去时态比较2.表示过去经常和反复做的动作。例如:
I often went to fish last summer.
We usually played cards last year.
一般过去时态
无论主语是第几人称、单数还是复数,谓语动词都用动词过去式。例如:
I watched TV yesterday.
She played piano last night.
He did his homework.一般过去时态 表示过去某时发生的动作或存在的状态。
过去进行时态 表示过去某时刻或某段时间正在进行的动作。
Alice wrote to Li Ming last Friday night.
Alice was writing to Li Ming last Friday night.
I watched TV yesterday afternoon.
I was watching TV yesterday afternoon. 一般过去时态和过去进行时态比较the Simple Future Tense一般将来时一般将来时的表达方法
I.“be going to + verb”结构 表示将要发生的事或打算、计划、决定要做的事情。例如:
I am going to go shopping with mom this afternoon.
We are going to visit Tibet for a week.
They are going to have a party for Mary’s birthday this evening.
She is going to work in Japan next week.
He is going to ride his bike to the Great Wall this Saturday.the Simple Future Tense一般将来时II. will + verb 表示将来某时要发生的动作或存在的状态,也表示将来经常或反复发生的动作。例如:
I will go to see my uncle this afternoon.
We will visit the Great Wall next week.
She will watch TV play at home tonight.
My mom will get me an MP3 tomorrow.
People will have robots in the future.III. 现在进行时态 也可以表示当前一段时间内的活动或现阶段正在进行的动作。
They are working on a farm with the farmers these days.
He is writing a book this month.
My grandparents are living with my uncle in Beijing these years.
The bus is coming soon.the Simple Future Tense一般将来时现在进行时态 还可以用来表示按计划或安排将要进行的动作,有“意图、打算”之意。
--What are you doing for summer vacation?
--I am visiting my aunt in Australia.
--When are you going?
--I am going on this Sunday.
We are going to the Summer Palace next Sunday morning.
She is going to Tibet for two weeks.
I am coming to see my grandma.the Simple Future Tense一般将来时*shall和will 都是一般将来时态的助动词。
疑问句中,主语是第一人称(I和we)时,常用助动词shall。
When shall we meet tomorrow morning?
Shall I open the door? Shall we sing?
书面语中,主语是第一人称(I和we)时,也常用助动词shall。但在口语中,可用will。
I shall go to Japan with mom next month.
We shall have a birthday party for Lucy.the Simple Future Tense一般将来时Shall and willwillwill( ) 1.Whenever a person ___ difficulties, he ___ two choices. One is to give up, the other is to face them bravely and try to overcome them.
A. meets; had B. meets; will have C. will meet; has D. will meet; had
( ) 2.I' m busy now. I ___ to you after school this afternoon.
A. talk B. talked C. will talk D. have talked
( ) 3.---What's your plan for your vacation? ---We ___ to Hong Kong for a visit.
A. were flying B. have flown C. will flythe Simple Future Tense一般将来时选择填空( ) 4.If we ___ take environmental problems seriously, the earth ___ worse and worse.
A. don't; will be B. won't; isn't
C. won't; is D. don't; won't be
( ) 5.Hurry up! The sky is covered with black clouds. I'm afraid it ___ .
A. rains B. is going to rain
C. rained D. was raining
( ) 6.---Have you ever been to the Great Wall?
---Not yet. I ___ it this year.
A. visited B. have visited
C. was visiting D. will visitthe Simple Future Tense一般将来时( ) 7.---Does the bus go to the beach?
---No. You ___ the wrong way. You want the No. 11.
A. go B. were going C. are going D. would go
( ) 8.Mr. Wang has left for Guangzhou. He ___ a speech there in two days.
A. gives B. gave C. will give D. has given
( ) 9.Robots ___ more heavy work for us in the future.
A. will do B. did C. have done D. were doing
( )10.---Do you think gradpa and grandma ___ late?
---No, the train is usually on time.
A. were B. will be C. was D. have beenthe Simple Future Tense一般将来时构成 助动词 would + 动词原形
用法 主要用于宾语从句中,表示从过去某个时间看来将要发生的动作或存在的状态。
She said (that) she would go to the zoo this Saturday.
Mom told me (that) she would take us to the science museum next weekend.
Mr. White said (that) he would fly to Australia this afternoon.the Simple Past-future Tense一般过去将来时Dad told us (that) he would make a toy bear for us.
My aunt said (that) she would get a soft toy for me as a gift on my sixth birthday.
Mr. Yang asked us if we would have a party for Ms Anna.
I wondered if you would go shopping with me if you are free.一般过去将来时the Simple Past-future TenseEnglish Verb Tensethe Present Progressive Tense the Past Progressive Tense the Present Perfect Progressive TenseGrammar Focus英语动词时态现在进行时
过去进行时
现在完成进行时构成 be 动词的一般式(am/is/are) + 现在分词(doing) 例如:
I am listening to my MP3 now.
We are having a math class.
She is watching TV news at home.
He is playing basketball now.
Gina is making dinner for us now.the Present Progressive Tense现在进行时用法 现在进行时态是表示现在(说话瞬间)正在进行或发生的动作。
What are you doing now?
We are listening to some pop songs.
Lucy is playing the piano.
Are you studying at the computer?
No, I’m not. I am playing games.
Is she cooking at home? Yes, she is.the Present Progressive Tense现在进行时构成 be 动词的过去式(was/were)+现在分词(doing) 例如:
I was watching TV news at home.
We were having lunch at school.
She was shopping with her mom.
He was cutting hair at the barber.
They were flying a kite in the park.the Past Progressive Tense过去进行时用法 过去进行时态 表示在过去某时刻或某段时间正在进行的动作。※ 一般用时间状语(从句)来表示这一过去时间。例如:
What were you doing at nine last night?
What was she doing when the UFO arrived?
He was sleeping when you called him.
We were watching a football match on TV at this time yesterday evening.the Past Progressive Tense过去进行时构成 助动词have (has)+ been +动词的现在分词 (doing)
I have been teaching for many years.
She has been playing volleyball since she was young.
We have been waiting for you all the afternoon.
He has been watching TV at home.the Present perfect Progressive Tense现在完成进行时用法 现在完成进行时 表示从过去开始一直在进行的动作,可能还要进行下去,也可能刚结束。
How long have you been skating?
I have been cleaning the classroom.
We have been waiting for the bus for an hour.
Alice has been watching TV all the afternoon.
Mr. White has been working here for 10 years.the Present perfect Progressive Tense现在完成进行时English Verb Tensethe Present Perfect Tense the Past Perfect TenseGrammar Focus英语动词时态现在完成时
过去完成时构成 助动词have (has)+过去分词 (done)
I have lived in Kunming for ten years.
She has learned Spanish since five years ago.
We have worked here since 2001.
He has played the violin since he was a child.
They have ever eaten hamburgers in China.
I have just had my lunch at school.
Gina has just left the Junior High School.
Uncle Wang has already gone to Shanghai.the Present Perfect Tense现在完成时用法 a.表示过去发生或已完成的动作对现在造成的影响或结果。
Have you had your lunch yet?
Has the student on duty erased the blackboard?
Have you finished doing your homework?
Has Gina come here? Has she played tennis?
I have my hair cut already.
Has Leo his bike mended yet?
You have played basketball before class.the Present Perfect Tense现在完成时I haven’t seen her these days.
We have known Celia for many years.
She has lived in Nanjian since 1978.
Alison has played the guitar since he was young.
They have bought an apartment in 1980s.
She has taught us English since 2012.
Mr. Yang has been at this school for 20 years.the Present Perfect Tense现在完成时b.表示从过去某时开始的动作或状态,一直持续到现在,可能刚刚结束,也可能还要继续下去。when she was a baby.for nearly 40 years.for almost 20 years.for almost two years.for over 6 years.since 1994.Have (has) been
Have (has) gone
Where has she been?
She has been to the bank.
Where has she gone?
She has gone to the bank.
Has Nicole been to Beijing yet?
Oh, Nicole has gone to Beijing. the Present Perfect Tense现在完成时Have (has) been & have (has) gone曾经到过某地去某地了(不在这儿)already backnot herenot here现在完成时 表示过去发生的动作对现在造成影响或结果,强调的是现在,因此,不和过去时间状语连用。
一般过去时 表示过去的动作和状态,和现在不发生联系,所以,可以和过去时间状语连用。
I have seen the film.
I saw the film last weekend.
She has lived in Kunming since 1999.
She lived in Kunming in 1999.
Lily has come to China for twice.
Lily came to China last month.现在完成时态和一般过去时态比较现在完成进行时 从过去开始一直在进行的动作,可能还要进行下去,也可能刚结束。
现在完成时 过去开始的动作到现在刚结束;或对现在造成了一定的影响,产生结果。
How long have you collected the shells?
How long have you been skating?
I have already erased the blackboard.
I’ve been cleaning the classroom for an hour.
We have waited for the bus for an hour.
We have been waiting for the bus for an hour.现在完成时态和现在完成进行时态比较构成 助动词had+过去分词(done)
I had lived in Kunming before I came here.
She had learned Spanish five years ago.
We had worked here for ten years before.
He had played the violin when he was a child.
They had ever eaten hamburgers in China.
I had just been to my old primary school.
The movie had begun when we got there.
Alice had slept when Mom got back home.the Present Perfect Tense过去完成时用法 a.表示过去发生或已完成的动作对过去造成的影响或结果。
Had you had your lunch before you came here?
Had she erased the blackboard before class?
Had you learned Spanish in Spain?
Had Gina played tennis before she came here?
I had my hair cut already by Friday.
Had Leo his bike mended yet?
You had played basketball before class.the Present Perfect Tense过去完成时I hadn’t seen her before she came here.
We had known Celia before she went to the US.
She had lived in Nanjian from 1978 to 1993.
Alison had played the guitar before he was sang.
They had bought an apartment in 1980s.
She had taught English before she taught math.
Mr. Yang had been at this school for 20 years.the Present Perfect Tense过去完成时b.表示从过去某时开始的动作或状态,持续到过去某时 并对当时造成了影响和结果,也就说,过去完成时表示的是过去的过去的动作。Thank you for your watching!
Catch you on the next time!
