高三英语一轮复习情态动词课件(共23张PPT)
文档属性
| 名称 | 高三英语一轮复习情态动词课件(共23张PPT) |

|
|
| 格式 | zip | ||
| 文件大小 | 337.8KB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 通用版 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2018-12-02 09:34:43 | ||
图片预览








文档简介
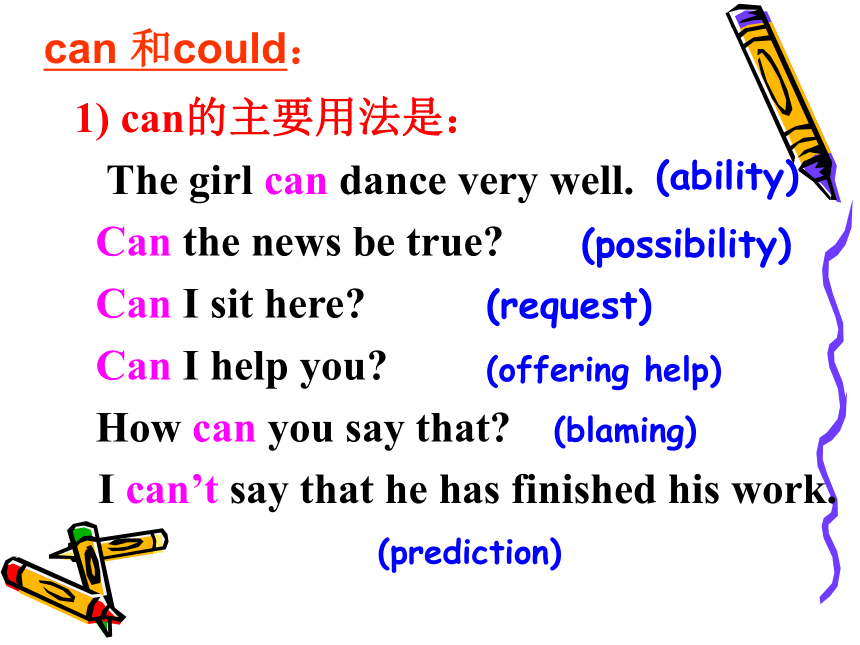
课件23张PPT。情态动词用法情态动词的语法特征1)?情态动词?不能单独做谓语,除ought ?和have?外,后面只能接动词原形。2)?情态动词没有人称,数的变化,但有些情态动词,如can、will也有一般式和过去式的变化。3)?情态动词的“时态”形式并不是时间区别的主要标志,情态动词的现在式形式和过去式形式都可用来表示现在时间、过去时间和将来时间。 1) can的主要用法是:
The girl can dance very well.
Can the news be true?
Can I sit here?
Can I help you?
How can you say that?
I can’t say that he has finished his work. can 和could:(ability)(possibility)(request)(offering help)(blaming)(prediction)2) could的主要用法是:
A. could 是can的过去式, 表示与过去 有关的能力和推测:
We all knew that the young man couldn’t be a doctor.(prediction)(request)B. could可以代替can表示请求, 但语气较can客气、委婉:
Could you lend me your dictionary?
Could I use your bike?3) can和could接动词的完成时
They could have stayed at my home, but they chose to stay at a hotel.
You could have had a better mark.
They can't have gone out because the light is still on.
(can/could have done) 表示对过去发生的事情做出的判断“本可以,本可能做某事” 。
Can, could 用在否定和疑问句中, 表示推测,不相信、怀疑等态度。may 和might :
may 的基本用法有三种:
?A. 表示请求、许可;比can较为正式:
?? May I come in ?
You may go now.
B. 表示 “也许” “可能”: 通常只用于肯定句和否定句中。 --I believe the man is from England.
--But I may be wrong.
The guest may arrive this afternoon.
The road may be blocked.
这条路可能不通了。
在疑问句中,表示可能性用can, could,不用may
在否定句中,都可以用,但意思不同. “cannot”: 不可能. “may not”: 可能不.
Where can he be? 他会在哪呢? C. 表示祝愿;但语气较正式:
May you succeed!
May you have a good journey!
might 的用法有:
She said that he might take her bike. 在间接引语中表示 “过去的可能和允许”
除了在间接引语以外,might 一般不表示过去的可能或者许可。 may ,might 都可以表示现在的“可能性”,但might 的可能性要小.
Our football team didn’t play very well today, but we might do better tomorrow.
Might I have a word with you?might表示 “现在的许可”, 语气比may 较委婉will和would:1. will可以作助动词和情态动词
I will tell you something important now.
He said he would tell me……
Would you like to have a try ?
When she was young,she would read fairy tales.
will用于构成将来时是助动词.
will用于表示“意志”“决心”“请求”是情态动词.
would亦同理.
Would you help us, please?Would比will委婉shall和should:1. shall用于构成将来时是助动词,用于第一人称
shall用于征求对方的意见,表示 “决心” 是情态动词。
Perhaps I shall pay a visit to England this winter.
(构成一般将来时, 助动词)
Shall we go by train, Mom?
(用于征求对方的意见,情态动词)
I shall go at once.
(表 “决心”,情态动词)
2. should表示义务、建议、劝告,意为 “应该”。 You should keep your promise.
She should have passed the exam.
She shouldn’t have left without saying a word.
“should+ have+过去分词”
表示本应该已做某事但没有做,表示责备对方.
“shouldn’t+ have+过去分词”
表示责备或批评,意为“本应该…但” must和 have?to1.Must 有两种基本用法. 一是表示 “必须”.
?— Must?I?finish?all?assignments?at?a?time? ??—Yes, you must.
No,?you?needn't. 用于一般问句中,肯定回答用must;
否定回答用?needn’t或don’t have to,“不必”;
mustn’t表示“禁止,不允许”cf: must表主观 表客观have to1) You mustn’t tell George.=Don’t tell George.2) You don’t have to tell George.= You can tell
George If you like. But it isn’t necessary.3)You have a high fever. You mustn’t go to school.4) –Must I study in bed all day? --No, You needn’t.否定式:mustn’t “不得做某事,禁止”否定式: don’t have to =needn’t doI don’t like this TV set. We must buy a new one.
There was no more bus. They had to walk home.2.表示“必须”时,must?和have?to?的区别:must着重说明主观看法,have?to?强调客观需要。另外,have?to?能用于更多时态。 3 .Must 表示推测时, 只能用于肯定句。must do 对一般时的肯定推测must have done 对过去发生的事情作出的肯 定判断must be doing 对现在的动作进行肯定推测 You?must?be?the?new?teacher. ?
He?must?be?joking. There?is?nobody?here.?They?must?have?all gone?home.
2. A: ___________ Xiao Feng find the origin of Easter from that book?
B: No, he _____________. 1. A: ______ you like to go to a special event with us on Saturday?
B: Yes, I __________Would’d like to Can/Couldcan’t/couldn’t Exercise 3. A: __________ I go with my friend to the harvest festival?
B: Yes, you __________. 4. A: If I want to be a doctor, _______ I study science?
B: Yes, you _________. shouldMay/Can may/canshould5. A: He is very handsome. ____ he play the role of the prince?
B: No, he _______________________ ______. can’t (play the role of theCanPrince) 6. A: The neighbour’ s children are older this year. _______________ they stop playing tricks at Halloween?
B: Perhaps, they __________ ________________________.
__________________________
____________.Canor Shouldmay stopor should stop playing tricksplaying tricks at Halloweenat Halloween 拓展: 情态动词+不定式完成式可表示“推测”、“责备”、“怀疑”等多种意义。
must have done 肯定做了
may/might have done 可能已做了
can’t/ couldn’t have done 不可能做了
should have done 本该做但没做
shouldn’t have done 本不该做但做了
could have done 本来能够做但没做1. The ground is rather wet, so it ________________(rain) last night, didn’t it?
2. Tom ______________(go) to Shanghai, but I’m still not sure about it.
3. The ground is very dry, so it _______________(rain) last night.
4. Someone must have broken into our bedroom. Who _________________ (do)it?
5. I really regretted wasting the hours when I __________________(study) hard, but it was too late.must have rained may have gone can’t have rainedcould have doneshould have studied6. I’m very sorry for the words I_________________(say) to you at that moment.
7. ---I paid a visit to New York last month and
we stayed at a nice hotel.
---Oh,you _______________(stay) with Barbara.
She is always willing to do you a favour.shouldn’t have said
could have stayed
The girl can dance very well.
Can the news be true?
Can I sit here?
Can I help you?
How can you say that?
I can’t say that he has finished his work. can 和could:(ability)(possibility)(request)(offering help)(blaming)(prediction)2) could的主要用法是:
A. could 是can的过去式, 表示与过去 有关的能力和推测:
We all knew that the young man couldn’t be a doctor.(prediction)(request)B. could可以代替can表示请求, 但语气较can客气、委婉:
Could you lend me your dictionary?
Could I use your bike?3) can和could接动词的完成时
They could have stayed at my home, but they chose to stay at a hotel.
You could have had a better mark.
They can't have gone out because the light is still on.
(can/could have done) 表示对过去发生的事情做出的判断“本可以,本可能做某事” 。
Can, could 用在否定和疑问句中, 表示推测,不相信、怀疑等态度。may 和might :
may 的基本用法有三种:
?A. 表示请求、许可;比can较为正式:
?? May I come in ?
You may go now.
B. 表示 “也许” “可能”: 通常只用于肯定句和否定句中。 --I believe the man is from England.
--But I may be wrong.
The guest may arrive this afternoon.
The road may be blocked.
这条路可能不通了。
在疑问句中,表示可能性用can, could,不用may
在否定句中,都可以用,但意思不同. “cannot”: 不可能. “may not”: 可能不.
Where can he be? 他会在哪呢? C. 表示祝愿;但语气较正式:
May you succeed!
May you have a good journey!
might 的用法有:
She said that he might take her bike. 在间接引语中表示 “过去的可能和允许”
除了在间接引语以外,might 一般不表示过去的可能或者许可。 may ,might 都可以表示现在的“可能性”,但might 的可能性要小.
Our football team didn’t play very well today, but we might do better tomorrow.
Might I have a word with you?might表示 “现在的许可”, 语气比may 较委婉will和would:1. will可以作助动词和情态动词
I will tell you something important now.
He said he would tell me……
Would you like to have a try ?
When she was young,she would read fairy tales.
will用于构成将来时是助动词.
will用于表示“意志”“决心”“请求”是情态动词.
would亦同理.
Would you help us, please?Would比will委婉shall和should:1. shall用于构成将来时是助动词,用于第一人称
shall用于征求对方的意见,表示 “决心” 是情态动词。
Perhaps I shall pay a visit to England this winter.
(构成一般将来时, 助动词)
Shall we go by train, Mom?
(用于征求对方的意见,情态动词)
I shall go at once.
(表 “决心”,情态动词)
2. should表示义务、建议、劝告,意为 “应该”。 You should keep your promise.
She should have passed the exam.
She shouldn’t have left without saying a word.
“should+ have+过去分词”
表示本应该已做某事但没有做,表示责备对方.
“shouldn’t+ have+过去分词”
表示责备或批评,意为“本应该…但” must和 have?to1.Must 有两种基本用法. 一是表示 “必须”.
?— Must?I?finish?all?assignments?at?a?time? ??—Yes, you must.
No,?you?needn't. 用于一般问句中,肯定回答用must;
否定回答用?needn’t或don’t have to,“不必”;
mustn’t表示“禁止,不允许”cf: must表主观 表客观have to1) You mustn’t tell George.=Don’t tell George.2) You don’t have to tell George.= You can tell
George If you like. But it isn’t necessary.3)You have a high fever. You mustn’t go to school.4) –Must I study in bed all day? --No, You needn’t.否定式:mustn’t “不得做某事,禁止”否定式: don’t have to =needn’t doI don’t like this TV set. We must buy a new one.
There was no more bus. They had to walk home.2.表示“必须”时,must?和have?to?的区别:must着重说明主观看法,have?to?强调客观需要。另外,have?to?能用于更多时态。 3 .Must 表示推测时, 只能用于肯定句。must do 对一般时的肯定推测must have done 对过去发生的事情作出的肯 定判断must be doing 对现在的动作进行肯定推测 You?must?be?the?new?teacher. ?
He?must?be?joking. There?is?nobody?here.?They?must?have?all gone?home.
2. A: ___________ Xiao Feng find the origin of Easter from that book?
B: No, he _____________. 1. A: ______ you like to go to a special event with us on Saturday?
B: Yes, I __________Would’d like to Can/Couldcan’t/couldn’t Exercise 3. A: __________ I go with my friend to the harvest festival?
B: Yes, you __________. 4. A: If I want to be a doctor, _______ I study science?
B: Yes, you _________. shouldMay/Can may/canshould5. A: He is very handsome. ____ he play the role of the prince?
B: No, he _______________________ ______. can’t (play the role of theCanPrince) 6. A: The neighbour’ s children are older this year. _______________ they stop playing tricks at Halloween?
B: Perhaps, they __________ ________________________.
__________________________
____________.Canor Shouldmay stopor should stop playing tricksplaying tricks at Halloweenat Halloween 拓展: 情态动词+不定式完成式可表示“推测”、“责备”、“怀疑”等多种意义。
must have done 肯定做了
may/might have done 可能已做了
can’t/ couldn’t have done 不可能做了
should have done 本该做但没做
shouldn’t have done 本不该做但做了
could have done 本来能够做但没做1. The ground is rather wet, so it ________________(rain) last night, didn’t it?
2. Tom ______________(go) to Shanghai, but I’m still not sure about it.
3. The ground is very dry, so it _______________(rain) last night.
4. Someone must have broken into our bedroom. Who _________________ (do)it?
5. I really regretted wasting the hours when I __________________(study) hard, but it was too late.must have rained may have gone can’t have rainedcould have doneshould have studied6. I’m very sorry for the words I_________________(say) to you at that moment.
7. ---I paid a visit to New York last month and
we stayed at a nice hotel.
---Oh,you _______________(stay) with Barbara.
She is always willing to do you a favour.shouldn’t have said
could have stayed
