高中英语人教版 必修一 Unit 3 Travel journal 全单元课件(共77张)
文档属性
| 名称 | 高中英语人教版 必修一 Unit 3 Travel journal 全单元课件(共77张) |  | |
| 格式 | zip | ||
| 文件大小 | 1.8MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 人教版(新课程标准) | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2019-02-16 19:27:37 | ||
图片预览








文档简介
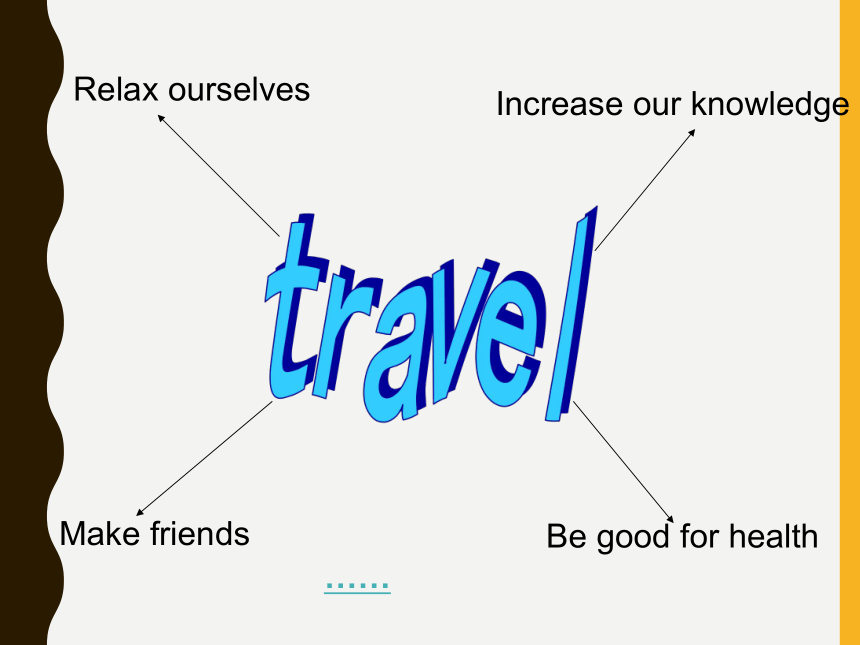
课件77张PPT。 Unit 3 Travel Journal Do you like travelling?
Why do you like traveling?
Where have you been?
How did you get there? Warming Up travelRelax ourselvesIncrease our knowledgeMake friendsBe good for health……The Great WallHe who does not reach the Great Wall is not a true man.GuilinGuilin scenery stands out as the world's best. 桂林山水甲天下by busby plane / by airWhich kind of transport do you prefer to use?by bikeon footby car Fill in the chart on page17.You can finish this part by considering the following aspects. Cost(花费) pollution(污染)
Safety(安全) Comfort (舒适)
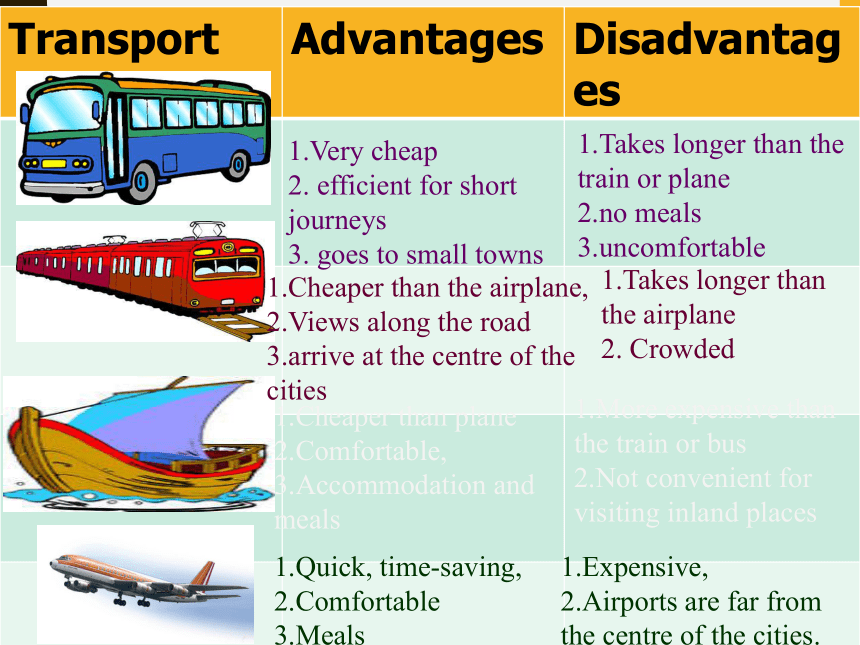
Quickness(迅速) Convenience (方便)1.Very cheap
2. efficient for short journeys
3. goes to small towns1.Takes longer than the train or plane
2.no meals
3.uncomfortable1.Cheaper than the airplane,
2.Views along the road
3.arrive at the centre of the cities1.Takes longer than the airplane
2. Crowded 1.Cheaper than plane
2.Comfortable,
3.Accommodation and meals 1.More expensive than the train or bus
2.Not convenient for visiting inland places1.Quick, time-saving,
2.Comfortable
3.Meals 1.Expensive,
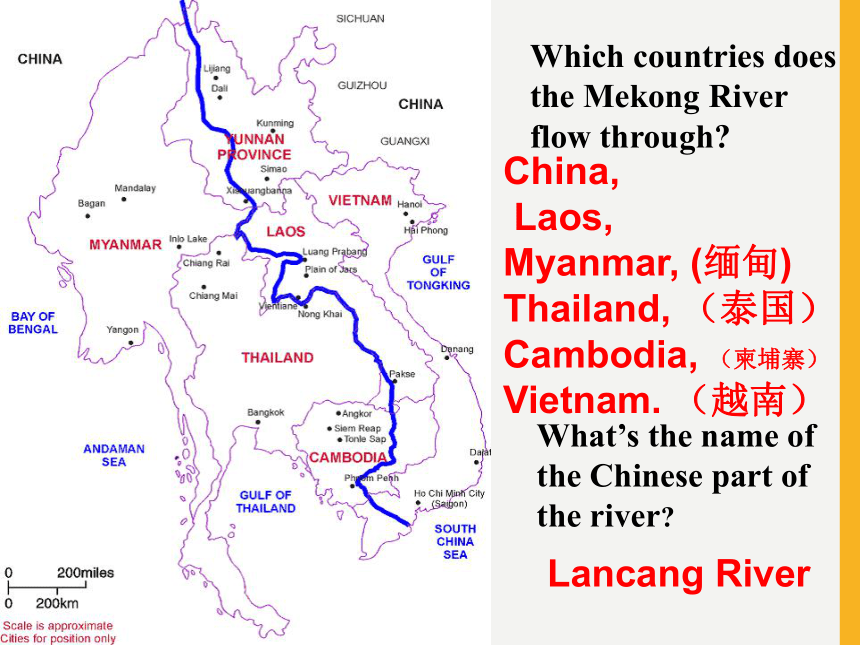
2.Airports are far from the centre of the cities.How do people who live along a river use it? Pre-readingIrrigate(灌溉)their fieldsmake electricitygo swimminggo fishingtravel along the river……Lancang River---Mekong RiverThe Source of the Mekong RiverThe Length:The longest river in the world.the Jifu Mountains in Zaduo County, Yushu Tibet Autonomous Region of northwest China's Qinghai Province, which is about 5,200 meters above sea level.
青海省玉树藏族自治区杂多县境内的吉富山。4880km12thThe name of the Chinese part:Lancang River(澜沧江)Which countries does the Mekong River flow through?China,
Laos,
Myanmar, (缅甸)
Thailand, (泰国)Cambodia, (柬埔寨)Vietnam. (越南)What’s the name of the Chinese part of the river?Lancang River The countries that the Mekong River flows through.LaosThailandMyanmarCambodiaVietnamChinaSkimmingSkim the text in two minutes and tell the main idea of the whole passage.Main idea of the passageThe passage is mainly about__________and
his sister's ______and _______ for taking a great_______trip along the __________.Wang kundreambikeplanMekong River*Match the main idea with each paragraphPara.1
Para.2
Para.3
A.The preparation before the
trip and details about Mekong
river
B. Dream of travelling along the Mekong River by bike.
C. Plan for the trip and different attitudes between Wang Kun and Wang Wei.
Structure of the text Group1(para.1)
1. Who takes part in the journey?
2. What’s their dream?
3. Who are Dao Wei and Yu Hang?
4.Who planned the trip to the Mekong?
Group2(para.2)
1. Did Wang Wei know the best way of getting to places?
2. Where is the source of the Mekong River?
3. Is it a difficult journey to cycle along the Mekong River? Why?
Group3(para.3)
1. What can you see when you travel along the Mekong River?
2. How does the scenery change when you travel along the Mekong River? Order the sentences.
a.The Mekong River enters the South China Sea.
b.The Mekong River begins at a glacier on a Tibetan mountain.
c.At first, the river is small and the water is clear and cold.
d.The Mekong River enters Southeast Asia.
e.The Mekong River travels across western Yunnan Province.
f.The Mekong River leaves China.
Group workRead the 1st paragraph:1. Who takes part in the journey?
2. What’s their dream?
3. Who are Dao Wei and Yu Hang?
4.Who planned the trip to the Mekong?
Wang Wei, Wang Kun, Dao Wei and Yu Hang. To take a great bike trip.Wang Kun’s cousins who are at a college in Kunming.Wang Wei planned the trip.Read the 2nd paragraph:1. Did Wang Wei know the best way of getting to places?
2. Where is the source of the Mekong River?
3. Is it a difficult journey to cycle along the Mekong River? Why?
No, she didn’t. It is in Qinghai Province. Yes, because the journey begins at an altitude of more than 5,000 meters where it is hard to breathe and very cold.
Read the 3rd paragraph:1. What can you see when you travel along the Mekong River?
We can see glacier, rapids, hills, valleys, waterfalls and plains.2. How does the scenery change when you travel along the
Mekong River? Order the sentences.
The Mekong River enters the South China Sea.
The Mekong River begins at a glacier on a Tibetan mountain.
At first, the river is small and the water is clear and cold.
The Mekong River enters Southeast Asia.
The Mekong River travels across western Yunnan Province.
The Mekong River leaves China.
(b c e f d a)Summary Wang Kun and his sister Wang Wei_____________ (dream) about taking a great bike trip ever ____________middle school. After________ from college, they_______ (final) got the chance to take a bike trip. _____ was Wang Wei who first got the idea to cycle along the Mekong River. Then Wang Wei plan the ________ for the trip. Although Wang Kun had some doubts, Wang Wei was ________ (determine) and insisted that she ______ the trip properly. Knowing that Wang Wei was a _______ girl,whose decision could not be changed once she had made up her mind .Wang Kun had to give_____.have dreamedsincegraduatingfinally Itscheduledeterminedorganizestubbornin现在进行时:1.现在进行时的构成:助动词am/is/are+现在分词
2.现在进行时的适用情况:
①表示说话时正在进行的动作。
②近来一段时间一直在进行的动作,但说话时动作不一定进行。
He is learning driving these days.
这些日子他正在学开车。
③表示发展中或正在改变的情况。
The weather is going colder and colder.
④表示在做某事的过程,通常是一个习惯性、经常性的动作
You look pretty when you are smiling.
你微笑时看上去很美。
⑤与always, forever 等副词连用,表示反复发生的或习惯性的动作,往往含有赞赏、抱怨、生气、厌烦等情绪。
She is always complaining about others.现在进行时表将来1.表示即将发生的动作,常有“意图”、“安排”或“打算”的含义,使句子更加生动,给人以期待感。此时多使用表示位置转移的动词(come, go, start, begin, arrive, leave, move, stay,etc)
E.g We are leaving early tomorrow morning.
我们明天一早就出发。
2.表示将来的现在进行时除使用位移动词外,也可使用某些非位移动词(do, buy, have, meet, play,spend,etc),此时句中一般要有表将来的时间状语。
My mother is buying me a bike soon.
Tom is having a party tomorrow.
3.偶尔也可以表示较远的将来
When I grow up, I'm going to join the army.现在进行时表将来4.表示将来的进行时有时含有“决心”的意思,此用法多用于否定结构中。
E.g I'm not going to the cinema.
我不去电影院了。
I'm not waiting for him any longer.
我不再等他了。 1.Ever since middle school, my sister Wang Wei and I have dreamed about taking a great bike trip.
1). dream n./ v. dreamed/dreamt
Language points dream (v.)of/about sth. 梦想;梦见;做梦
a…dream 做了一个……的梦
that…
sb. to be … 梦想某人成为……1.She always dreams of running her own business. 她一直梦想着经营自己的生意。2.I dreamed about you last night.
我昨晚梦见你了。3.I dreamed a happy dream yesterday.
我昨天做了一个幸福的梦。4. I never dreamed him to be a liar.我做梦都没有想到他会是一个撒谎的人。 They are Dai and grew up in western Yunnan Province near the Lancang River, the Chinese part of the river that is called the Mekong River in other countries.
"the Chinese part......other countries"作“the Lancang River"的同位语。
名词或代词在句中作同位语,在同位语后跟一个定语从句加以修饰限制。
e.g It's a world full of wonders, one where anything can happen.
She gave me a determined look--the kind that said she wouldn't change her mind. Exercise:
Meeting my uncle after so many years was an unforgettable moment,___I'll always treasure.
A. that B. one C. it D. whatB After graduating from college, we finally got the chance to take a bike trip.
"graduating from college"作伴随状语。
分词作状语时,其形式主要看分词与句子主语之间的关系:
主谓----现在分词; 动宾----过去分词
e.g They came into the classroom, laughing and talking.
他们说笑着走进了教室。
The pop star hurried up to his car, followed by his fans.
那个明星匆忙走进自己的车,后面跟着他的粉丝。 Exercise:
He had a wonderful childhood,___with his mother to all over the world.
A. travel B. traveled C. to travel D. traveling D finally adv. 终于;最后;(用于列举)最后地;决定性地
finally, in the end 和at last 的区别 :
① finally用来在列举事物或论点时引出最后一项内容,一般无感彩。
② at last表示”等候或耽误了很久才...",强调经过一番拖延或曲折后,常带有较厚的感彩。
③ in the end也表示经过一定的耽误、等待之后“终于”;同时也可用于预测未来。
e.g At last, we found out what had really happened.
我们终于查明真正发生了什么事。
My dream will come true in the end.
我的梦想终会实现。 Exercise:
She put some soil in the box, then sowed the seed carefully, and covered it with more soil.__ she kept the box in the shade.
A. In the end B. At last
C. to the end D. FinallyD It was my sister who first had the idea to cycle along the entire Mekong River from where it begins to where it ends.
it was...who的强调句型,被强调部分是句子的主语“my sister"。
被强调部分若是”人“,则用who/that;若是其它”时间、地点“等一律用that。
e.g It was Tom who brought the book here yesterday.
是汤姆昨天把这本书拿到这里来的。 注意:
①若被强调部分是原句的主语,who/that后的谓语动词在人称和数上与该主语一致。
e.g It is I that/who am your true friend .
②被强调部分不管单复数如何,始终用"it is/was".
Exercise:
① 就是因为坏天气导致足球比赛不得不被推迟。It was because of bad weather that the football match had to be put off.②是孩子们在花园里制造噪音吗?Is it the children who are making noise in the garden? Although she didn't know the best way of getting to places, she insisted that she organize the trip properly.
本句中insist 的宾语从句用了虚拟语气。
insist+宾语从句:
①表示个人建议、主张,意为”坚持要求“时,从句需用虚拟语气,即(should)+do;
②表示主语认定一个事实,意为”坚持说;坚持认为“时,从句应用陈述句语气。
e.g He insisted that we (should)accept these gifts.
The boy insisted that he hadn't broken the window. insist①on/upon (doing) sth.坚持要求干......;强调......
e.g He insisted on going with me.
他坚持跟我一起去。
He insists upon the importance of correct pronunciation.
他强调正确发音的重要性。
②on sb.'s doing sth. 坚持要求某人干某事
Mother insisted on my staying at home.
母亲坚持要求我呆在家里。
注:insist之后不能直接跟名词、代词或动名词作宾语,
需加介词on/upon. Exercise:
1.I insisted that a doctor__immediately.
A.has been sent for B. sent for
C.will be sent for D. be sent for
2. The doctor insisted that I__a high fever and that I__a rest for a few days.
A. had; had B. have; have
C. had; have D. have; hadDC 3. The man insisted__a taxi for me.
A.find B.to find C.on finding D. in finding
4. The lady insisted that the young man ___her wallet and insisted on__ to the police station at once.
A. had stolen; be sent B. should steal; sending
C. had stolen; his being sent D. should steal; sendingCC When I told her that our journey would begin at an altitude of more than 5,000meters, she seemed to be excited about it.
sb. seemed/seems to be/do..., "seem"常用作系动词,意为”看起来“
①seem+adj./n.(to sb.) (在某人看来)好像......
e.g You seem happy today. 你今天好像很高兴。
He seems a nice man. 他好像是个好人。
②seem like+n./pron. 看起来······
It seems like a good idea. 这看起来是个好主意。
③sb. seems/seemed to do/be... 某人好像······
They seem to know what they are doing.
看来他们明白自己在干什么。 ④It seems/seemed that ... 似乎······;看来······
It seems that he doesn't agree with us.
看来他不同意我们的观点。
⑤It seems seemed as if/though... 看来好像······
It seemed as if they would married then.
那时看起来好像他们要结婚了。
⑥It seems/seemed +adj.+to do... 干······好像······
It seems reasonable to ask students to buy a dictionary.
要学生买一本词典好像也没什么不合理。 When I told her the air would be hard to breathe and it would be very cold, she said it would be an interesting experience.
当我告诉她哪里空气稀薄,呼吸困难,而且天气很冷时,她 却说这将是一次有趣的经历。
the air would be hard to breathe :“air”是”breathe”的逻辑宾语。
主语+be+ adj. +to do: 不定式与主语之间是逻辑上的动宾关系时,常用主动表被动。(用于此类结构的形容词有:hard difficult, easy, impossible, comfortable, pleasant, dangerous, fit, bad, good等。)
E.g The problem is difficult to solve.
这个问题很难解决。
The air is bad to breathe.
呼吸这种空气对身体有害。
注: 此结构中,不定式的动词若为不及物动词时,要加相应的介词。
E.g
Exercise:
1. In many people’s opinion, that company, though relatively small, is pleasant___.
A. to deal with(与·····做生意) B. dealing with
C. to be dealed with D. deal with
2.英语难以在短时间内学好。
AEnglish is difficult to learn well in a short time.汤姆是一个很难相处的人 Once she has made up her mind, nothing can change it.
“Once”引导时间状语从句,意为“一旦······,就······”
E.g Once you start, you’ll never give up.
一旦你开始了,就不要放弃。
Physics is easy to learn once you understand the rules.
一旦你理解了规则,物理就不难学了。 Exercise:
__they decide which college to go to, students should research the admission procedures.
A. As B. While C. Until D. OnceD 辨析:once 与 as soon as
同:二者都可译为“一······就······”,引导时间状语。
异:once引导的时间状语从句带有条件的意味,常译为“一旦······”。
as soon as引导的时间状语从句强调时间衔接的紧促性,常译为“一······就······;刚······就······”。
E.g Once you’ve seen it, you’ll never forget it.
一旦你见到它,你将永远忘不掉它。
I’ll inform you as soon as I get in touch with her.
我一联系上她就马上通知你。
It becomes rapids as it passes through deep valleys, travelling across western Yunnan Province. 当河水穿过深谷,流经云南西部时, 它变成了急流。
as 在该句中用作连词,引导时间状语从句,意为“当······的时候;随着;一边······一边······”。
E.g As the sun rose, the fog disappeared.
当太阳出来的时候,雾就消散了。
He smiled as he passed.
他路过时笑了笑。
Exercise:
他一边沿着河边走,一边读这封信。He read the letter as he walked along the river. 拓展表将来的其它表达方式:
1.be going to do:
①表示人主观上近期的“打算、意图、计划”等
E.g Are you going to visit the museum this afternoon?
②表示有某种迹象表明最近将会发生的事。
Look! It's going to rain.
看!天要下雨了。(可通过天上的云等迹象看出来)
2.wil/shall+do: 表达单纯的将来,是对未来事情发生的“预见”。will用于各种人称,shall一般用于第一人称。
We shall/will be there by twelve. 我们将于12点到那儿。
I‘ll go back to my hometown next month. 下个月我要回老家。
3.be+to do: 表示预定,按计划或安排将发生某事,有时也表示命令、禁止或可能性。
The French President is to visit China next month.
No one is to leave the room without permission.
4.一般现在时表示将来: 常用于表示按计划、按规定或是按时刻表来进行的未来动作,仅限于一些转移动词。
The plane arrives at 2:00 this afternoon.
飞机将于今天下午2:00抵达。
5.be about to do: 正要,即将。表示马上要发生的动作。不能与表示将来时间的状语连用,常用于:
be about to do...when... 正要做......,这时......
I was just about to go to work when someone called
me up.
法国总统将于下个月访华。未经允许,任何人不得离开这个房间。我正要去上班的时候,这时有人打电话给我。Exercise:--I have not finished my dinner yet.
--But our friends___ for us.
A. will wait B. wait
C. have waited D. are waiting
I've won a holiday for two to Florida. I___ my mum with me to have fun there.
A. am taking B. have taken
C. take D. will have taken ADExercise:Ladies and gentlemen, please fasten your seat belts. The plane__.
A. takes off B. is taking off
C. has taken off D. took off
Hurry up! The train___. You know it___ at 8:30 am.
A. leaves; leaves B. is leaving; leaves
C. leaves; is leaving D. is leaving; is leavingBBWhat do you think about Wang Kun and Wang Wei?Wang kun’s character: enthusiastic, critical and sensible
Wang Wei’s character: imaginative, organized,
eager, persistent, stubborn and risk-takingA Summary Wang Kun and Wang Wei have _________ about taking a great bike trip. when they __________ from college. They _______ to _____ along the Mekong River with their ________. Wang Wei is very _________. Once she is __________ to do something she will never _______ her mind. Although it is difficult to travel along the Mekong River by bike, she ________ that they find the ________ of the river and begin their journey there.dreamedgraduateddecidedcyclecousinsstubborndeterminedchangeinsistedsource
Using LanguageJouney Down The MekongPart2 A night in the mountainsThe Tibetan Mountains Fast reading What’s the main idea of the passage?
1.When and where does it happen?
2.What items are Wang Kun and Wang Wei carrying with them?
3.Where are they reaching? 1.When and where does it happen?
2. What items are Wang Kun and Wang Wei carrying with them?
a tent, a cooker and food, pillow, water bottles caps, coats, gloves, trousers, T-shirts and shorts.
3. Where are they reaching?
At night in autumn in Tibetan mountainDali, Yunnan True or falseThey reached Tibet in winter. ( )
Wang Wei always rode in front of me. ( )
3. When they reached a valley, it became warmer.( )
4. They went to sleep early in their tent. ( )
5. There was almost no wind on that night.( )
6. Their cousins will join them in Dali.( )FTTFTTDetailed reading Read Para 2 and fill the blanks We __ __ .Wang Wei__ __ __
but I__ __
The sky__ __
The stars __ __
There was only the sound of _In the early eveningAfter supperAt midnightmake campwent to sleepstayed awakebecame clearergrew brighterfire Along the way children dressed in long wool coats stopped to look at us.
一路上,穿着羊毛大衣的孩子们停下来看我们。
"dressed in wool long coats"为过去分词短语作children的后置定语,为动宾关系。等同于一个定语从句:who are dressed in long wool coats.
E.g Do you know the girl dressed in red?
Do you know the girl who is dressed in red?
dress的用法:
1.dress sb./oneself 给某人/自己穿衣服
The mother is dressing her baby.
母亲正为婴儿穿衣。
2. be dressed in+衣服/颜色 穿着······
She is dressed in black today.
今天她穿了一身黑。
To climb the mountains was hard work...
爬山是一件辛苦的事······
不定式"to climb the mountains"作主语。
不定式作主语时经常用it充当形式主语,而将真正的主语放到谓语动词之后。
E.g To master a foreign language is necessary nowadays.
=It is necessary to master a foreign language. At one point we were so high that we found ourselves cycling through clouds.
find+宾语(ourselves)+宾语补足语(cycling)
在此结构中,宾补可以为:形容词、现在分词、过去分词、介词短语等表示find之后的宾语的状态。
E.g We came home and found him asleep on the sofa.
我们回到家发现他躺在沙发上。 Exercise:
1. 他发现自己被一个贼跟着。
2.她醒来发现自己躺在医院的床上。He found himself followed by a thief.She wake up and found herself in a
hospital bed. We had to change our caps, coats, gloves and trousers for T-shirts and shorts.
我们不得不把帽子、外套、手套和长裤换下,床上T恤和短裤。
change: (n.) 变化;零钱
(v.)换衣;更换
Wait, it won’t take me long to change.
Prases:
change …for… 用…换….
change into… 把…变成
get changed 换好衣服
change A for B 用A换B
change one’s mind 改变主意
Sara, hurry up. I’m afraid you won’t have time to____ before the party.
get changed B. get change
C. get changing D. get to changeExercise 他们正在使沙漠变成农田。
.They are changing desert into farmland. We put up our tents and then we ate. 我们先搭起帐篷然后吃饭。put up① 举起, 抬起 = raise
② 挂起, 张贴
③ 建造, 搭起 = build
④ 住宿, 留宿e.g.
1. He put up his hand to catch the teacher’s attention.
2. A new notice has been put up on the board.
3. A new theatre will be put up.
4. Will you put me up for the night?举起, 抬起挂起, 张贴建造, 搭起住宿, 留宿 company n. :
1.for company 作伴;陪伴
E.g He'll go with you as far as the station for company.
他将陪你到车站。
2.in company 在(客人)面前
Don't yawn in company.
在客人面前别打呵欠。
3.in company with 与······在一起
She came in company with a group of girls.
她同一群女孩一起来。
4.keep company with 与······在一起
She stayed at home to keep company with her mother.
她呆在家里陪伴她妈妈。 关于lie和lay:
lie—lied—lied—lying 撒谎
lie—lay—lain—lying 躺,位于
lay—laid—laid—laying 下蛋,产卵;放置
巧计lie与lay的口诀:
规则的撒谎,不规则的躺
躺过就下蛋,下蛋不规则
注:这里的“规则”与“不规则”是指动词过去式与过去分词的变化是否规则。 Exercise:
1. 他没有说出真相,又撒谎了。
2.她把头放在他的肩膀上。
3.当我进来的时候,他的书摊开放在桌上。
4.母鸡正下蛋。
5.这座城市位于中国西部。She laid her head on my shoulder.When I went in, his books lay open on the desk.The hen is laying an egg.The city lies in the north of China.He wasn’t telling the truth and lied again. We can hardly wait to see them!
我们迫不及待地想见到他们!
can hardly wait to do sth. 迫不及待想做某事
for sth. 迫不及待想得到···
(=can't wait to do sth./for sth.)
1.我迫不及待想要看到他的新小说。
2.汤姆迫不及待地想得到一份新工作。I can't wait to see his new novel. Tom can hardly wait for a new job.
Why do you like traveling?
Where have you been?
How did you get there? Warming Up travelRelax ourselvesIncrease our knowledgeMake friendsBe good for health……The Great WallHe who does not reach the Great Wall is not a true man.GuilinGuilin scenery stands out as the world's best. 桂林山水甲天下by busby plane / by airWhich kind of transport do you prefer to use?by bikeon footby car Fill in the chart on page17.You can finish this part by considering the following aspects. Cost(花费) pollution(污染)
Safety(安全) Comfort (舒适)
Quickness(迅速) Convenience (方便)1.Very cheap
2. efficient for short journeys
3. goes to small towns1.Takes longer than the train or plane
2.no meals
3.uncomfortable1.Cheaper than the airplane,
2.Views along the road
3.arrive at the centre of the cities1.Takes longer than the airplane
2. Crowded 1.Cheaper than plane
2.Comfortable,
3.Accommodation and meals 1.More expensive than the train or bus
2.Not convenient for visiting inland places1.Quick, time-saving,
2.Comfortable
3.Meals 1.Expensive,
2.Airports are far from the centre of the cities.How do people who live along a river use it? Pre-readingIrrigate(灌溉)their fieldsmake electricitygo swimminggo fishingtravel along the river……Lancang River---Mekong RiverThe Source of the Mekong RiverThe Length:The longest river in the world.the Jifu Mountains in Zaduo County, Yushu Tibet Autonomous Region of northwest China's Qinghai Province, which is about 5,200 meters above sea level.
青海省玉树藏族自治区杂多县境内的吉富山。4880km12thThe name of the Chinese part:Lancang River(澜沧江)Which countries does the Mekong River flow through?China,
Laos,
Myanmar, (缅甸)
Thailand, (泰国)Cambodia, (柬埔寨)Vietnam. (越南)What’s the name of the Chinese part of the river?Lancang River The countries that the Mekong River flows through.LaosThailandMyanmarCambodiaVietnamChinaSkimmingSkim the text in two minutes and tell the main idea of the whole passage.Main idea of the passageThe passage is mainly about__________and
his sister's ______and _______ for taking a great_______trip along the __________.Wang kundreambikeplanMekong River*Match the main idea with each paragraphPara.1
Para.2
Para.3
A.The preparation before the
trip and details about Mekong
river
B. Dream of travelling along the Mekong River by bike.
C. Plan for the trip and different attitudes between Wang Kun and Wang Wei.
Structure of the text Group1(para.1)
1. Who takes part in the journey?
2. What’s their dream?
3. Who are Dao Wei and Yu Hang?
4.Who planned the trip to the Mekong?
Group2(para.2)
1. Did Wang Wei know the best way of getting to places?
2. Where is the source of the Mekong River?
3. Is it a difficult journey to cycle along the Mekong River? Why?
Group3(para.3)
1. What can you see when you travel along the Mekong River?
2. How does the scenery change when you travel along the Mekong River? Order the sentences.
a.The Mekong River enters the South China Sea.
b.The Mekong River begins at a glacier on a Tibetan mountain.
c.At first, the river is small and the water is clear and cold.
d.The Mekong River enters Southeast Asia.
e.The Mekong River travels across western Yunnan Province.
f.The Mekong River leaves China.
Group workRead the 1st paragraph:1. Who takes part in the journey?
2. What’s their dream?
3. Who are Dao Wei and Yu Hang?
4.Who planned the trip to the Mekong?
Wang Wei, Wang Kun, Dao Wei and Yu Hang. To take a great bike trip.Wang Kun’s cousins who are at a college in Kunming.Wang Wei planned the trip.Read the 2nd paragraph:1. Did Wang Wei know the best way of getting to places?
2. Where is the source of the Mekong River?
3. Is it a difficult journey to cycle along the Mekong River? Why?
No, she didn’t. It is in Qinghai Province. Yes, because the journey begins at an altitude of more than 5,000 meters where it is hard to breathe and very cold.
Read the 3rd paragraph:1. What can you see when you travel along the Mekong River?
We can see glacier, rapids, hills, valleys, waterfalls and plains.2. How does the scenery change when you travel along the
Mekong River? Order the sentences.
The Mekong River enters the South China Sea.
The Mekong River begins at a glacier on a Tibetan mountain.
At first, the river is small and the water is clear and cold.
The Mekong River enters Southeast Asia.
The Mekong River travels across western Yunnan Province.
The Mekong River leaves China.
(b c e f d a)Summary Wang Kun and his sister Wang Wei_____________ (dream) about taking a great bike trip ever ____________middle school. After________ from college, they_______ (final) got the chance to take a bike trip. _____ was Wang Wei who first got the idea to cycle along the Mekong River. Then Wang Wei plan the ________ for the trip. Although Wang Kun had some doubts, Wang Wei was ________ (determine) and insisted that she ______ the trip properly. Knowing that Wang Wei was a _______ girl,whose decision could not be changed once she had made up her mind .Wang Kun had to give_____.have dreamedsincegraduatingfinally Itscheduledeterminedorganizestubbornin现在进行时:1.现在进行时的构成:助动词am/is/are+现在分词
2.现在进行时的适用情况:
①表示说话时正在进行的动作。
②近来一段时间一直在进行的动作,但说话时动作不一定进行。
He is learning driving these days.
这些日子他正在学开车。
③表示发展中或正在改变的情况。
The weather is going colder and colder.
④表示在做某事的过程,通常是一个习惯性、经常性的动作
You look pretty when you are smiling.
你微笑时看上去很美。
⑤与always, forever 等副词连用,表示反复发生的或习惯性的动作,往往含有赞赏、抱怨、生气、厌烦等情绪。
She is always complaining about others.现在进行时表将来1.表示即将发生的动作,常有“意图”、“安排”或“打算”的含义,使句子更加生动,给人以期待感。此时多使用表示位置转移的动词(come, go, start, begin, arrive, leave, move, stay,etc)
E.g We are leaving early tomorrow morning.
我们明天一早就出发。
2.表示将来的现在进行时除使用位移动词外,也可使用某些非位移动词(do, buy, have, meet, play,spend,etc),此时句中一般要有表将来的时间状语。
My mother is buying me a bike soon.
Tom is having a party tomorrow.
3.偶尔也可以表示较远的将来
When I grow up, I'm going to join the army.现在进行时表将来4.表示将来的进行时有时含有“决心”的意思,此用法多用于否定结构中。
E.g I'm not going to the cinema.
我不去电影院了。
I'm not waiting for him any longer.
我不再等他了。 1.Ever since middle school, my sister Wang Wei and I have dreamed about taking a great bike trip.
1). dream n./ v. dreamed/dreamt
Language points dream (v.)of/about sth. 梦想;梦见;做梦
a…dream 做了一个……的梦
that…
sb. to be … 梦想某人成为……1.She always dreams of running her own business. 她一直梦想着经营自己的生意。2.I dreamed about you last night.
我昨晚梦见你了。3.I dreamed a happy dream yesterday.
我昨天做了一个幸福的梦。4. I never dreamed him to be a liar.我做梦都没有想到他会是一个撒谎的人。 They are Dai and grew up in western Yunnan Province near the Lancang River, the Chinese part of the river that is called the Mekong River in other countries.
"the Chinese part......other countries"作“the Lancang River"的同位语。
名词或代词在句中作同位语,在同位语后跟一个定语从句加以修饰限制。
e.g It's a world full of wonders, one where anything can happen.
She gave me a determined look--the kind that said she wouldn't change her mind. Exercise:
Meeting my uncle after so many years was an unforgettable moment,___I'll always treasure.
A. that B. one C. it D. whatB After graduating from college, we finally got the chance to take a bike trip.
"graduating from college"作伴随状语。
分词作状语时,其形式主要看分词与句子主语之间的关系:
主谓----现在分词; 动宾----过去分词
e.g They came into the classroom, laughing and talking.
他们说笑着走进了教室。
The pop star hurried up to his car, followed by his fans.
那个明星匆忙走进自己的车,后面跟着他的粉丝。 Exercise:
He had a wonderful childhood,___with his mother to all over the world.
A. travel B. traveled C. to travel D. traveling D finally adv. 终于;最后;(用于列举)最后地;决定性地
finally, in the end 和at last 的区别 :
① finally用来在列举事物或论点时引出最后一项内容,一般无感彩。
② at last表示”等候或耽误了很久才...",强调经过一番拖延或曲折后,常带有较厚的感彩。
③ in the end也表示经过一定的耽误、等待之后“终于”;同时也可用于预测未来。
e.g At last, we found out what had really happened.
我们终于查明真正发生了什么事。
My dream will come true in the end.
我的梦想终会实现。 Exercise:
She put some soil in the box, then sowed the seed carefully, and covered it with more soil.__ she kept the box in the shade.
A. In the end B. At last
C. to the end D. FinallyD It was my sister who first had the idea to cycle along the entire Mekong River from where it begins to where it ends.
it was...who的强调句型,被强调部分是句子的主语“my sister"。
被强调部分若是”人“,则用who/that;若是其它”时间、地点“等一律用that。
e.g It was Tom who brought the book here yesterday.
是汤姆昨天把这本书拿到这里来的。 注意:
①若被强调部分是原句的主语,who/that后的谓语动词在人称和数上与该主语一致。
e.g It is I that/who am your true friend .
②被强调部分不管单复数如何,始终用"it is/was".
Exercise:
① 就是因为坏天气导致足球比赛不得不被推迟。It was because of bad weather that the football match had to be put off.②是孩子们在花园里制造噪音吗?Is it the children who are making noise in the garden? Although she didn't know the best way of getting to places, she insisted that she organize the trip properly.
本句中insist 的宾语从句用了虚拟语气。
insist+宾语从句:
①表示个人建议、主张,意为”坚持要求“时,从句需用虚拟语气,即(should)+do;
②表示主语认定一个事实,意为”坚持说;坚持认为“时,从句应用陈述句语气。
e.g He insisted that we (should)accept these gifts.
The boy insisted that he hadn't broken the window. insist①on/upon (doing) sth.坚持要求干......;强调......
e.g He insisted on going with me.
他坚持跟我一起去。
He insists upon the importance of correct pronunciation.
他强调正确发音的重要性。
②on sb.'s doing sth. 坚持要求某人干某事
Mother insisted on my staying at home.
母亲坚持要求我呆在家里。
注:insist之后不能直接跟名词、代词或动名词作宾语,
需加介词on/upon. Exercise:
1.I insisted that a doctor__immediately.
A.has been sent for B. sent for
C.will be sent for D. be sent for
2. The doctor insisted that I__a high fever and that I__a rest for a few days.
A. had; had B. have; have
C. had; have D. have; hadDC 3. The man insisted__a taxi for me.
A.find B.to find C.on finding D. in finding
4. The lady insisted that the young man ___her wallet and insisted on__ to the police station at once.
A. had stolen; be sent B. should steal; sending
C. had stolen; his being sent D. should steal; sendingCC When I told her that our journey would begin at an altitude of more than 5,000meters, she seemed to be excited about it.
sb. seemed/seems to be/do..., "seem"常用作系动词,意为”看起来“
①seem+adj./n.(to sb.) (在某人看来)好像......
e.g You seem happy today. 你今天好像很高兴。
He seems a nice man. 他好像是个好人。
②seem like+n./pron. 看起来······
It seems like a good idea. 这看起来是个好主意。
③sb. seems/seemed to do/be... 某人好像······
They seem to know what they are doing.
看来他们明白自己在干什么。 ④It seems/seemed that ... 似乎······;看来······
It seems that he doesn't agree with us.
看来他不同意我们的观点。
⑤It seems seemed as if/though... 看来好像······
It seemed as if they would married then.
那时看起来好像他们要结婚了。
⑥It seems/seemed +adj.+to do... 干······好像······
It seems reasonable to ask students to buy a dictionary.
要学生买一本词典好像也没什么不合理。 When I told her the air would be hard to breathe and it would be very cold, she said it would be an interesting experience.
当我告诉她哪里空气稀薄,呼吸困难,而且天气很冷时,她 却说这将是一次有趣的经历。
the air would be hard to breathe :“air”是”breathe”的逻辑宾语。
主语+be+ adj. +to do: 不定式与主语之间是逻辑上的动宾关系时,常用主动表被动。(用于此类结构的形容词有:hard difficult, easy, impossible, comfortable, pleasant, dangerous, fit, bad, good等。)
E.g The problem is difficult to solve.
这个问题很难解决。
The air is bad to breathe.
呼吸这种空气对身体有害。
注: 此结构中,不定式的动词若为不及物动词时,要加相应的介词。
E.g
Exercise:
1. In many people’s opinion, that company, though relatively small, is pleasant___.
A. to deal with(与·····做生意) B. dealing with
C. to be dealed with D. deal with
2.英语难以在短时间内学好。
AEnglish is difficult to learn well in a short time.汤姆是一个很难相处的人 Once she has made up her mind, nothing can change it.
“Once”引导时间状语从句,意为“一旦······,就······”
E.g Once you start, you’ll never give up.
一旦你开始了,就不要放弃。
Physics is easy to learn once you understand the rules.
一旦你理解了规则,物理就不难学了。 Exercise:
__they decide which college to go to, students should research the admission procedures.
A. As B. While C. Until D. OnceD 辨析:once 与 as soon as
同:二者都可译为“一······就······”,引导时间状语。
异:once引导的时间状语从句带有条件的意味,常译为“一旦······”。
as soon as引导的时间状语从句强调时间衔接的紧促性,常译为“一······就······;刚······就······”。
E.g Once you’ve seen it, you’ll never forget it.
一旦你见到它,你将永远忘不掉它。
I’ll inform you as soon as I get in touch with her.
我一联系上她就马上通知你。
It becomes rapids as it passes through deep valleys, travelling across western Yunnan Province. 当河水穿过深谷,流经云南西部时, 它变成了急流。
as 在该句中用作连词,引导时间状语从句,意为“当······的时候;随着;一边······一边······”。
E.g As the sun rose, the fog disappeared.
当太阳出来的时候,雾就消散了。
He smiled as he passed.
他路过时笑了笑。
Exercise:
他一边沿着河边走,一边读这封信。He read the letter as he walked along the river. 拓展表将来的其它表达方式:
1.be going to do:
①表示人主观上近期的“打算、意图、计划”等
E.g Are you going to visit the museum this afternoon?
②表示有某种迹象表明最近将会发生的事。
Look! It's going to rain.
看!天要下雨了。(可通过天上的云等迹象看出来)
2.wil/shall+do: 表达单纯的将来,是对未来事情发生的“预见”。will用于各种人称,shall一般用于第一人称。
We shall/will be there by twelve. 我们将于12点到那儿。
I‘ll go back to my hometown next month. 下个月我要回老家。
3.be+to do: 表示预定,按计划或安排将发生某事,有时也表示命令、禁止或可能性。
The French President is to visit China next month.
No one is to leave the room without permission.
4.一般现在时表示将来: 常用于表示按计划、按规定或是按时刻表来进行的未来动作,仅限于一些转移动词。
The plane arrives at 2:00 this afternoon.
飞机将于今天下午2:00抵达。
5.be about to do: 正要,即将。表示马上要发生的动作。不能与表示将来时间的状语连用,常用于:
be about to do...when... 正要做......,这时......
I was just about to go to work when someone called
me up.
法国总统将于下个月访华。未经允许,任何人不得离开这个房间。我正要去上班的时候,这时有人打电话给我。Exercise:--I have not finished my dinner yet.
--But our friends___ for us.
A. will wait B. wait
C. have waited D. are waiting
I've won a holiday for two to Florida. I___ my mum with me to have fun there.
A. am taking B. have taken
C. take D. will have taken ADExercise:Ladies and gentlemen, please fasten your seat belts. The plane__.
A. takes off B. is taking off
C. has taken off D. took off
Hurry up! The train___. You know it___ at 8:30 am.
A. leaves; leaves B. is leaving; leaves
C. leaves; is leaving D. is leaving; is leavingBBWhat do you think about Wang Kun and Wang Wei?Wang kun’s character: enthusiastic, critical and sensible
Wang Wei’s character: imaginative, organized,
eager, persistent, stubborn and risk-takingA Summary Wang Kun and Wang Wei have _________ about taking a great bike trip. when they __________ from college. They _______ to _____ along the Mekong River with their ________. Wang Wei is very _________. Once she is __________ to do something she will never _______ her mind. Although it is difficult to travel along the Mekong River by bike, she ________ that they find the ________ of the river and begin their journey there.dreamedgraduateddecidedcyclecousinsstubborndeterminedchangeinsistedsource
Using LanguageJouney Down The MekongPart2 A night in the mountainsThe Tibetan Mountains Fast reading What’s the main idea of the passage?
1.When and where does it happen?
2.What items are Wang Kun and Wang Wei carrying with them?
3.Where are they reaching? 1.When and where does it happen?
2. What items are Wang Kun and Wang Wei carrying with them?
a tent, a cooker and food, pillow, water bottles caps, coats, gloves, trousers, T-shirts and shorts.
3. Where are they reaching?
At night in autumn in Tibetan mountainDali, Yunnan True or falseThey reached Tibet in winter. ( )
Wang Wei always rode in front of me. ( )
3. When they reached a valley, it became warmer.( )
4. They went to sleep early in their tent. ( )
5. There was almost no wind on that night.( )
6. Their cousins will join them in Dali.( )FTTFTTDetailed reading Read Para 2 and fill the blanks We __ __ .Wang Wei__ __ __
but I__ __
The sky__ __
The stars __ __
There was only the sound of _In the early eveningAfter supperAt midnightmake campwent to sleepstayed awakebecame clearergrew brighterfire Along the way children dressed in long wool coats stopped to look at us.
一路上,穿着羊毛大衣的孩子们停下来看我们。
"dressed in wool long coats"为过去分词短语作children的后置定语,为动宾关系。等同于一个定语从句:who are dressed in long wool coats.
E.g Do you know the girl dressed in red?
Do you know the girl who is dressed in red?
dress的用法:
1.dress sb./oneself 给某人/自己穿衣服
The mother is dressing her baby.
母亲正为婴儿穿衣。
2. be dressed in+衣服/颜色 穿着······
She is dressed in black today.
今天她穿了一身黑。
To climb the mountains was hard work...
爬山是一件辛苦的事······
不定式"to climb the mountains"作主语。
不定式作主语时经常用it充当形式主语,而将真正的主语放到谓语动词之后。
E.g To master a foreign language is necessary nowadays.
=It is necessary to master a foreign language. At one point we were so high that we found ourselves cycling through clouds.
find+宾语(ourselves)+宾语补足语(cycling)
在此结构中,宾补可以为:形容词、现在分词、过去分词、介词短语等表示find之后的宾语的状态。
E.g We came home and found him asleep on the sofa.
我们回到家发现他躺在沙发上。 Exercise:
1. 他发现自己被一个贼跟着。
2.她醒来发现自己躺在医院的床上。He found himself followed by a thief.She wake up and found herself in a
hospital bed. We had to change our caps, coats, gloves and trousers for T-shirts and shorts.
我们不得不把帽子、外套、手套和长裤换下,床上T恤和短裤。
change: (n.) 变化;零钱
(v.)换衣;更换
Wait, it won’t take me long to change.
Prases:
change …for… 用…换….
change into… 把…变成
get changed 换好衣服
change A for B 用A换B
change one’s mind 改变主意
Sara, hurry up. I’m afraid you won’t have time to____ before the party.
get changed B. get change
C. get changing D. get to changeExercise 他们正在使沙漠变成农田。
.They are changing desert into farmland. We put up our tents and then we ate. 我们先搭起帐篷然后吃饭。put up① 举起, 抬起 = raise
② 挂起, 张贴
③ 建造, 搭起 = build
④ 住宿, 留宿e.g.
1. He put up his hand to catch the teacher’s attention.
2. A new notice has been put up on the board.
3. A new theatre will be put up.
4. Will you put me up for the night?举起, 抬起挂起, 张贴建造, 搭起住宿, 留宿 company n. :
1.for company 作伴;陪伴
E.g He'll go with you as far as the station for company.
他将陪你到车站。
2.in company 在(客人)面前
Don't yawn in company.
在客人面前别打呵欠。
3.in company with 与······在一起
She came in company with a group of girls.
她同一群女孩一起来。
4.keep company with 与······在一起
She stayed at home to keep company with her mother.
她呆在家里陪伴她妈妈。 关于lie和lay:
lie—lied—lied—lying 撒谎
lie—lay—lain—lying 躺,位于
lay—laid—laid—laying 下蛋,产卵;放置
巧计lie与lay的口诀:
规则的撒谎,不规则的躺
躺过就下蛋,下蛋不规则
注:这里的“规则”与“不规则”是指动词过去式与过去分词的变化是否规则。 Exercise:
1. 他没有说出真相,又撒谎了。
2.她把头放在他的肩膀上。
3.当我进来的时候,他的书摊开放在桌上。
4.母鸡正下蛋。
5.这座城市位于中国西部。She laid her head on my shoulder.When I went in, his books lay open on the desk.The hen is laying an egg.The city lies in the north of China.He wasn’t telling the truth and lied again. We can hardly wait to see them!
我们迫不及待地想见到他们!
can hardly wait to do sth. 迫不及待想做某事
for sth. 迫不及待想得到···
(=can't wait to do sth./for sth.)
1.我迫不及待想要看到他的新小说。
2.汤姆迫不及待地想得到一份新工作。I can't wait to see his new novel. Tom can hardly wait for a new job.
