人教版高中英语必修一unit 2 English around the world单词讲解课件(45张ppt)
文档属性
| 名称 | 人教版高中英语必修一unit 2 English around the world单词讲解课件(45张ppt) |  | |
| 格式 | zip | ||
| 文件大小 | 224.5KB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 人教版(新课程标准) | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2019-06-28 17:24:09 | ||
图片预览








文档简介
Unit 2
单词讲解
练习
课文介绍
课文朗读
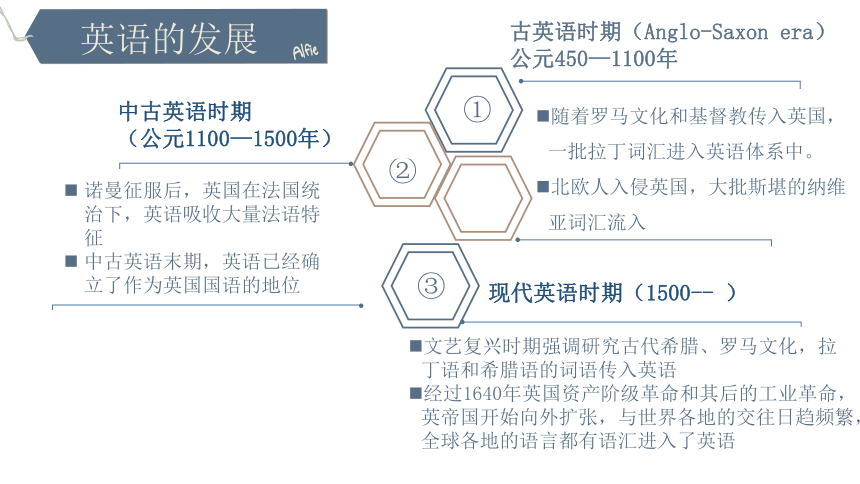
随着罗马文化和基督教传入英国,一批拉丁词汇进入英语体系中。
北欧人入侵英国,大批斯堪的纳维亚词汇流入
①
诺曼征服后,英国在法国统治下,英语吸收大量法语特征
中古英语末期,英语已经确立了作为英国国语的地位
②
古英语时期(Anglo-Saxon era)
公元450—1100年
③
文艺复兴时期强调研究古代希腊、罗马文化,拉丁语和希腊语的词语传入英语
经过1640年英国资产阶级革命和其后的工业革命,英帝国开始向外扩张,与世界各地的交往日趋频繁,全球各地的语言都有语汇进入了英语
英语的发展
中古英语时期
(公元1100—1500年)
现代英语时期(1500-- )
单词讲解
more than
(1) +数字 超过,超出(=over)
e.g. We have 48 classes in three grades with more than 3,000 students.
我们三个年级一共有48个班级,超过3.000名学生。
e.g. It costs her more than 20 dollars a week.
?(2)+名词、代词动词 不仅仅,不只是(=not only)
e.g. The Summer Palace is more than a park.
e.g. 学校不仅我们学习的地方,还是我们人生第二个家。
The school is more than a place to study, and also is our second home in our lives.
(1)vt.以……为根据
base ... on/upon ... 把……建立于……基础之上
be based on/upon 以……为基础;依据……
e.g. We should base the theory on careful research.
我们应该把理论建立在仔细研究的基础上。
e.g. The film based on the novel by Mo Yan is well worth seeing.
根据莫言的小说改编的电影非常值得观看。
e.g. It was based more on German than the English we
speak at present.
当时的英语更多是以德语为基础,而我们今天所说的英语不是。
base
at the base of 以……为基点;在……的底部
e.g. At the base of the pine tree, there was a nest containing four eggs.
(3) basic adj. 基本的;基础的
e.g. The government provides them with not only food and shelter, but also the basic skills for their living.
政府不仅为他们提供食物和住处,还为他们提供基本的谋生技能。
(4) basis n. 基础;基本原则
e.g. Our theory builds on a solid basis.
我们的理论建立在牢固的基础上。
(2)n.基部;基地;基础
________ an important decision(决定) more on emotion than on reason, you will regret(后悔) it sooner or later(早晚,迟早).
A.Based B.Basing C.Base D.To base
主谓宾
动词非谓语
P.P 被动
Ing 主动
To do 目的,表将来
(1) [C] 命令;指令;
at sb.’s command 听某人支配
e.g. I’m at your command — what would you like me to do?
我听从你的吩咐——你要我做什么?
under one’s command = under the command of sb.
由某人指挥
e.g. Under the command of Mao, the People’ s Army of
Liberation(人民解放军) defeated the enemy successfully.
take command of 控制
e.g. I had to take command of my temper.
我必须控制我的脾气。
Mother often takes command of her children’s behavor.
command n.
have a good command of 掌握;精通(尤指语言)
e.g. Applicants will be expected to have a good command of English.
申请人必须精通英语。
e.g. Only when you have a_good_command_of vocabulary,
will reading no longer be your obstacle.
只有掌握充足的词汇,阅读才不会成为你的拦路虎。
e.g. 精通英语的人更容易找工作。
People that have a good command of English are easier to find a job.
(2)[U] 掌握
?
command sb. to do sth. 命令某人做某事
command that ... (should) do ... 命令……
e.g.He commanded that we_(should)_finish the work in an hour.
=He commanded us_to_finish the work in an hour.
他命令我们一个小时内完成这项工作。
e.g. 导演叫这个演员在半个小时内背下新增的台词。
(导演:director 台词:script)within在…之内 recite/remember
The director commanded the actor to remember the newly added script within half an hour.
(3)vt.命令;指挥;支配;博得;赢得
n.请求;要求
make (a) request for ... 请求;要求……
at sb.’s request = at the request of sb. 应某人之要求
e.g. The kidnappers were merciless and Getty’s son made
repeated requests for help from his father.
绑架者毫无慈悲之心,Getty的儿子不断向他的父亲求助。
e.g. 应校长之邀,马云来我们学校开了个讲座。
At President of school’s request, MY came to our school and made a speech
At President of school’s request, MY came to our school to make a speech
At President of school’s request, MY came to our school. He made a speech
request
request sb. to do sth. 请求某人做某事
request that ... (should) do sth. 请求……
e.g. All members of the club are requested to attend the annual meeting.
请俱乐部的全体会员务必参加年会。
e.g. My parents requested that I should learn a second foreign language.
= My parents requested me to learn a second foreign language.
我父母要求我再学一门外语。
It is requested that ... (should) do sth. 据要求……
e.g. It is requested that all the articles should be related to the students’ life.
要求所有的文章与学生的生活有关。
vt.请求;要求
后跟虚拟语气的动词:
一坚持:insist;
二命令:order, command;
三建议:suggest, advise, recommend;
四要求:demand, request, require, desire;
再加一个敦促:urge。That (should) do
1. He suggested that they _____ use a trick instead of fighting.
A. should B. would C. do D. had
2. My father did not go to New York; the doctor suggested that he _____ there.
A. not went B. won’t go C. not go D. not to go
3. His doctor suggested that he _____ a short trip abroad.
A. will take B. would take C. take D. took
4. The law requires that everyone _____ his car checked at least
once a year.
A. has B. had C. have D. will have
5. The librarian insists that John _____ no more books from the library before he returns all the books he has borrowed.
A. will take B. took C. take D. takes
6. He insisted that we all _____ in his office at one o’clock.
A. be B. to be C. would be D. shall be
7. I must go there earlier. John has suggested that I _____ an
hour before the discussion begins.
A. go B. shall go C. will go D. would go
come up
(1)走近;上来
e.g. Her cat came up and rubbed itself against their legs.
她的猫上前来蹭了他们的腿。
(2)发生 happen
e.g. I’m afraid something urgent has come up.
恐怕有紧急事情发生了。
e.g. I was delayed – something came up at home.
我耽搁了–家里有事意外发生。
(3)被提出
e.g. The subject came up at work.
这一话题在工作时被提及。
(4)(太阳、月亮等)升起
e.g. It will be so great watching the sun come up.
看着太阳升起将会很美妙。
①An old lady came up to me and asked for directions.
②As soon as the project came up at the meeting, it attracted many people’s attention.
③When the moon came up, the young people began their celebration.
④I’ll let him know if anything comes up.
走近
被提出
升起
发生
come up with 想出;提出
e.g. The designer says he came up with the idea after watching people get wet on streets in Russia.
这位设计师说他是在看到俄罗斯街头有人被淋湿后提出这个点子的。
e.g. Have you ever noticed how easy it is to come up with a
reason to do nothing?
你有没有感觉在不想做什么的时候,很容易就会想出一个理由去逃避?
e.g. When you come across something important, write it down.
当你遇到重要的事情时,把它记下来.
e.g. Have you ever come across a great, but long, article online?
你可曾在网上看到一篇好看到时很长的文章?
?
When it comes to 名词/名词性的短语/ doing ... 当谈到……
e.g. I can use the computer. When_it_comes_to repairing it,
I know nothing.
我能使用电脑,但谈到修电脑,我一无所知。
come across 穿过(路、桥);(偶然)遇见;发现
make use of 利用;使用
e.g. My experience tells me that it is not what you are given but how you make use of it that determines who you are.
我的经历告诉我不是你拥有什么而是你怎样利用你所拥有的决定了你的未来。
e.g. 利用这个机遇,他创办了自己的公司,并大赚了一笔。
Opportunity 机会
Making use of this opportunity, he set up his/a company and made some money.
make full/good use of 充分利用
=make the best/most of 充分利用
=take (full) advantage of (充分)利用
e.g. In my opinion, every minute should be made full use of to learn well.
依我看来,我们应充分利用分分秒秒把学习搞好。
e.g. Last but not least, it’s everyone’s responsibility to make
the most of water.
最后但同等重要的是,充分利用水资源是每个人的责任。
It is no use doing sth. 做……是没用的
e.g. It is no use crying over spilt milk.
打翻牛奶,哭也没用(覆水难收)。
e.g. It is no use doing what you like; you have got to like what you do.
做你喜欢的事是没用的,你必须喜欢你所做的事。
play a/an (vital/ important) part in 参与;起作用;扮演角色
=play a/an (vital/ important) role in
e.g. Taiwan issue plays an important part in Sino- US relationships.
e.g. At present, China plays a vital role in the international arena.
e.g. 大学对许多人一生有极其重要的影响。
e.g. 阅读在学习中占关键性地位。
Reading plays a key part in study.
key
because of 因为(后接名词或名词性短语)
because 因为(后接句子)
e.g. They were there because of me.
= they were there because I was there.
他们来这里是因为我。
e.g. 因为考试失败,她哭得很伤心。Fail/ failure
Because she failed the exam, she cries sadly.
Because of the failure of exam, she cries sadly.
believe it or not 信不信由你
e.g. Believe it or not, I met a super football star this morning on the street.
信不信由你,我今天早晨在街上遇到一个超级球星。
e.g. 信不信由你,数学的作用远超出你的想象。
e.g. 信不信由你,我永远不会骗你。Cheat
Believe it or not, I won’t cheat you forever.
more than, believe it or not, because of, come up, at present, make use of, play a part in, base ...on
1.—I’m happy to take you there in my car.
—You are so nice. Thank you.
2.There is no way of predicting what the long?term effects of the accident will be.
3.I believe Mary as she always her ideas scientific experiments.
4.At the meeting many questions about the quality of the new bridge.
5. the thick fog, the return flight of the aircraft had to be put off.
6.They tried their best to the chance that their school offered to study hard.
7. ,_they will not carry out their promise.
8.Friends our lives, although we may take friendship for granted.
adj.本国的;本地的
native speaker/ language
be native to ... 产于…… silk
e.g. It is wel-l?known that the panda is native to China.
众所周知,大熊猫产于中国。
n.本地人;本国人
e.g. a native of Switzerland 一个出生在瑞士的人
A native of China found that silk was native to China in Tang dynasty.
native
latter adj.较后的;后半的;(两者中的)后者 later
the former ...the latter ...前者……后者……
e.g. Mary and Jane are both my friends. The former is a clerk in a bank and the latter teaches English in a middle school.
玛丽和简都是我的朋友,前者是银行的职员,后者在中学教英语。
e.g. Celebrations are planned for the latter part of November.
庆祝活动计划在11月的下半月举行。
The latter part of 19c
?
n.(1)街区
e.g. She grew up playing with the other kids on the block.
她是和街区里其他孩子一起玩大的。
(2)块;木块;石块;
a block of… 一块〔指木头、石头等有直边的坚硬物体〕
?
v. 阻挡,堵塞
e.g. A fallen tree is blocking the road.
一棵倒下的树把路阻断了。
e.g. I tried to get through, but there were people blocking my way.
我想过去,但是有人挡着路。
block
?
Let’s walk round the block.
Seeing the road blocked with snow, we had to spend the holiday at home, watching TV.
Before us stands a wall made of concrete blocks.
街区
2. 阻挡
3. 石板
e.g. Number sense is not the ability to count. It is the ability to recognize a change in number.
数字感并不只是数数的能力,它是识别数字变化的能力。
recognize sb./one’s voice 认出某人/听出某人的声音
e.g. At any case, I can recognize my mother’s voice.
e.g. I recognized his voice the moment he opened his mouth.
他一张嘴说话,我就听出了他的声音。
recognize vt. 辨认出;承认;公认
e.g. Picasso Pablo and Vincent van Gogh have been recognized to be/ as the most influential painters all around the world.
e.g. Sharing bike is recognized as one of new Chinese Four Inventions.
?
recognize that ... 承认…… realize
e.g. We also recognize that we need to do more.
同时,我们也认识到,我们还要开展更多工作。
e.g. We need to recognize that health is an investment.
我们必须认识到健康是一种投资。
be recognized to be/as ... 被认作……/被认为是……
It is recognized that ... 人们公认……
?
e.g. It is recognized that he is a good teacher.
大家都公认他是一个好老师。
e.g. It is recognized that environment pollution has become one of the most serious problems that people face.
入们一致认为环境污染已经成了人们面对的最严重的问题之一。
e.g. It is recognized that in the Information Age, Internet
commerce is a powerful tool in the economic growth of developing countries.
大家都认可,在信息时代网络贸易是发展中国家经济发展强有力的工具。
recognition n. 认出;认识
beyond (all) recognition 认不出来
e.g. The city has been built up so fast that it’s changed
beyond_recognition.
这城市建设得真快,已看不出它原来的面貌了。
Information
communication
e.g. Now it is different from the past.
现在和过去不同了。
e.g. This place is very quiet, quite different from the hustle and bustle
of the cities.
这个地方很安静, 与城市的拥挤喧嚣十分不同。
e.g. My scores are the same as yours.
My scores are different from yours
be different from 与…不同
be the same as 与…一样
e.g. There is a shop at the end of the street.
这条街走到头有一个商店。
e.g. 月底我们会有一次月考。
We will have a monthly exam at the end of this month.
e.g.观众在歌剧结束时报以热烈的掌声。
Audience观众 opera歌剧 applause
Audience made hot applause at the end of the opera.
at the end of 在…结束时 ,在…末
a large number of 大量的,很多(修饰主语,谓语动词用复数)
a small number of 少量,些许
e.g. The city have attracted a large number of homosexuals.
e.g. A small number of hit songs like those of Jay Chou have
received worldwide fame.
the number of …的数量(作主语,谓语动词用单数)
e.g. The number of unemployment has hit record high at the end of this year.
in fact
= actually
= as a matter of fact 事实上
The number of the students in this city _____ increased 6 times in comparison with 2001.
The number of the volunteers ________ 100 now. And a small number of them ________ already gone to the workplace.
A.is; have B.are; have C.is; are D.is; has
(一) 祈使句的变化规则
如果直接引语是祈使句,变为间接引语时,
根据句子意思在不定式前加上tell/ask/order等动词
将祈使句的动词原形变为带to的不定式
如果祈使句是否定句,在不定式前面还要加上not
e.g. The hostess said to us, “Please sit down.”
→ The hostess asked us to sit down.
e.g. He said, “Don’t make so much noise, boys.”
→ He told the boys not to make so much noise.
直接引语与间接引语
1)一般疑问句
谓语动词是say或said要改为 ask 或asked
把疑问句语序变为陈述句语序,句末用句号
变为由if/whether 引导的宾语从句
e.g. “Do you think a diary can become your friend?” the writer says.
→ The writer asks us if we think a diary can become our friend.
2) 特殊疑问句
保留原来的引导词
疑问句要变为陈述句,句末用句号
e.g. “What do you want?” he asked me.
→ He asked me what I wanted.
(二)疑问句的变化规则
1.The monitor said to me, “Don’t forget to turn off the lights when you leave.”
→The monitor _ forget to turn off the lights when I left.
2.Mr Brown said to Mary, “Will you write Tom a letter in English or send him an e?mail?”
→Mr Brown asked Mary write Tom a letter in English or send him an e?mail.
3.He asked, “Haven’t you finished your English homework?”
→He asked me if I have finished my English homework or not.
4.Mum said to me, “How do you deal with the disagreement between the company and the customers?”
→Mum asked me how I deal with the disagreement between the company and the customers.
命令语气:表示直接命令某人做某事,语气比较重,不怎么礼貌,一般用于上级 对下级
e.g. “ Look at the example”, the teacher said to us.
e.g. Open the window!
请求语气:表示请求某人做某事,语气比较缓和,非常礼貌
e.g. “ Would you like to see my flat?” She asked.
e.g. Would you please open the window?
命令(command)语气和请求(request)语气
单词讲解
练习
课文介绍
课文朗读
随着罗马文化和基督教传入英国,一批拉丁词汇进入英语体系中。
北欧人入侵英国,大批斯堪的纳维亚词汇流入
①
诺曼征服后,英国在法国统治下,英语吸收大量法语特征
中古英语末期,英语已经确立了作为英国国语的地位
②
古英语时期(Anglo-Saxon era)
公元450—1100年
③
文艺复兴时期强调研究古代希腊、罗马文化,拉丁语和希腊语的词语传入英语
经过1640年英国资产阶级革命和其后的工业革命,英帝国开始向外扩张,与世界各地的交往日趋频繁,全球各地的语言都有语汇进入了英语
英语的发展
中古英语时期
(公元1100—1500年)
现代英语时期(1500-- )
单词讲解
more than
(1) +数字 超过,超出(=over)
e.g. We have 48 classes in three grades with more than 3,000 students.
我们三个年级一共有48个班级,超过3.000名学生。
e.g. It costs her more than 20 dollars a week.
?(2)+名词、代词动词 不仅仅,不只是(=not only)
e.g. The Summer Palace is more than a park.
e.g. 学校不仅我们学习的地方,还是我们人生第二个家。
The school is more than a place to study, and also is our second home in our lives.
(1)vt.以……为根据
base ... on/upon ... 把……建立于……基础之上
be based on/upon 以……为基础;依据……
e.g. We should base the theory on careful research.
我们应该把理论建立在仔细研究的基础上。
e.g. The film based on the novel by Mo Yan is well worth seeing.
根据莫言的小说改编的电影非常值得观看。
e.g. It was based more on German than the English we
speak at present.
当时的英语更多是以德语为基础,而我们今天所说的英语不是。
base
at the base of 以……为基点;在……的底部
e.g. At the base of the pine tree, there was a nest containing four eggs.
(3) basic adj. 基本的;基础的
e.g. The government provides them with not only food and shelter, but also the basic skills for their living.
政府不仅为他们提供食物和住处,还为他们提供基本的谋生技能。
(4) basis n. 基础;基本原则
e.g. Our theory builds on a solid basis.
我们的理论建立在牢固的基础上。
(2)n.基部;基地;基础
________ an important decision(决定) more on emotion than on reason, you will regret(后悔) it sooner or later(早晚,迟早).
A.Based B.Basing C.Base D.To base
主谓宾
动词非谓语
P.P 被动
Ing 主动
To do 目的,表将来
(1) [C] 命令;指令;
at sb.’s command 听某人支配
e.g. I’m at your command — what would you like me to do?
我听从你的吩咐——你要我做什么?
under one’s command = under the command of sb.
由某人指挥
e.g. Under the command of Mao, the People’ s Army of
Liberation(人民解放军) defeated the enemy successfully.
take command of 控制
e.g. I had to take command of my temper.
我必须控制我的脾气。
Mother often takes command of her children’s behavor.
command n.
have a good command of 掌握;精通(尤指语言)
e.g. Applicants will be expected to have a good command of English.
申请人必须精通英语。
e.g. Only when you have a_good_command_of vocabulary,
will reading no longer be your obstacle.
只有掌握充足的词汇,阅读才不会成为你的拦路虎。
e.g. 精通英语的人更容易找工作。
People that have a good command of English are easier to find a job.
(2)[U] 掌握
?
command sb. to do sth. 命令某人做某事
command that ... (should) do ... 命令……
e.g.He commanded that we_(should)_finish the work in an hour.
=He commanded us_to_finish the work in an hour.
他命令我们一个小时内完成这项工作。
e.g. 导演叫这个演员在半个小时内背下新增的台词。
(导演:director 台词:script)within在…之内 recite/remember
The director commanded the actor to remember the newly added script within half an hour.
(3)vt.命令;指挥;支配;博得;赢得
n.请求;要求
make (a) request for ... 请求;要求……
at sb.’s request = at the request of sb. 应某人之要求
e.g. The kidnappers were merciless and Getty’s son made
repeated requests for help from his father.
绑架者毫无慈悲之心,Getty的儿子不断向他的父亲求助。
e.g. 应校长之邀,马云来我们学校开了个讲座。
At President of school’s request, MY came to our school and made a speech
At President of school’s request, MY came to our school to make a speech
At President of school’s request, MY came to our school. He made a speech
request
request sb. to do sth. 请求某人做某事
request that ... (should) do sth. 请求……
e.g. All members of the club are requested to attend the annual meeting.
请俱乐部的全体会员务必参加年会。
e.g. My parents requested that I should learn a second foreign language.
= My parents requested me to learn a second foreign language.
我父母要求我再学一门外语。
It is requested that ... (should) do sth. 据要求……
e.g. It is requested that all the articles should be related to the students’ life.
要求所有的文章与学生的生活有关。
vt.请求;要求
后跟虚拟语气的动词:
一坚持:insist;
二命令:order, command;
三建议:suggest, advise, recommend;
四要求:demand, request, require, desire;
再加一个敦促:urge。That (should) do
1. He suggested that they _____ use a trick instead of fighting.
A. should B. would C. do D. had
2. My father did not go to New York; the doctor suggested that he _____ there.
A. not went B. won’t go C. not go D. not to go
3. His doctor suggested that he _____ a short trip abroad.
A. will take B. would take C. take D. took
4. The law requires that everyone _____ his car checked at least
once a year.
A. has B. had C. have D. will have
5. The librarian insists that John _____ no more books from the library before he returns all the books he has borrowed.
A. will take B. took C. take D. takes
6. He insisted that we all _____ in his office at one o’clock.
A. be B. to be C. would be D. shall be
7. I must go there earlier. John has suggested that I _____ an
hour before the discussion begins.
A. go B. shall go C. will go D. would go
come up
(1)走近;上来
e.g. Her cat came up and rubbed itself against their legs.
她的猫上前来蹭了他们的腿。
(2)发生 happen
e.g. I’m afraid something urgent has come up.
恐怕有紧急事情发生了。
e.g. I was delayed – something came up at home.
我耽搁了–家里有事意外发生。
(3)被提出
e.g. The subject came up at work.
这一话题在工作时被提及。
(4)(太阳、月亮等)升起
e.g. It will be so great watching the sun come up.
看着太阳升起将会很美妙。
①An old lady came up to me and asked for directions.
②As soon as the project came up at the meeting, it attracted many people’s attention.
③When the moon came up, the young people began their celebration.
④I’ll let him know if anything comes up.
走近
被提出
升起
发生
come up with 想出;提出
e.g. The designer says he came up with the idea after watching people get wet on streets in Russia.
这位设计师说他是在看到俄罗斯街头有人被淋湿后提出这个点子的。
e.g. Have you ever noticed how easy it is to come up with a
reason to do nothing?
你有没有感觉在不想做什么的时候,很容易就会想出一个理由去逃避?
e.g. When you come across something important, write it down.
当你遇到重要的事情时,把它记下来.
e.g. Have you ever come across a great, but long, article online?
你可曾在网上看到一篇好看到时很长的文章?
?
When it comes to 名词/名词性的短语/ doing ... 当谈到……
e.g. I can use the computer. When_it_comes_to repairing it,
I know nothing.
我能使用电脑,但谈到修电脑,我一无所知。
come across 穿过(路、桥);(偶然)遇见;发现
make use of 利用;使用
e.g. My experience tells me that it is not what you are given but how you make use of it that determines who you are.
我的经历告诉我不是你拥有什么而是你怎样利用你所拥有的决定了你的未来。
e.g. 利用这个机遇,他创办了自己的公司,并大赚了一笔。
Opportunity 机会
Making use of this opportunity, he set up his/a company and made some money.
make full/good use of 充分利用
=make the best/most of 充分利用
=take (full) advantage of (充分)利用
e.g. In my opinion, every minute should be made full use of to learn well.
依我看来,我们应充分利用分分秒秒把学习搞好。
e.g. Last but not least, it’s everyone’s responsibility to make
the most of water.
最后但同等重要的是,充分利用水资源是每个人的责任。
It is no use doing sth. 做……是没用的
e.g. It is no use crying over spilt milk.
打翻牛奶,哭也没用(覆水难收)。
e.g. It is no use doing what you like; you have got to like what you do.
做你喜欢的事是没用的,你必须喜欢你所做的事。
play a/an (vital/ important) part in 参与;起作用;扮演角色
=play a/an (vital/ important) role in
e.g. Taiwan issue plays an important part in Sino- US relationships.
e.g. At present, China plays a vital role in the international arena.
e.g. 大学对许多人一生有极其重要的影响。
e.g. 阅读在学习中占关键性地位。
Reading plays a key part in study.
key
because of 因为(后接名词或名词性短语)
because 因为(后接句子)
e.g. They were there because of me.
= they were there because I was there.
他们来这里是因为我。
e.g. 因为考试失败,她哭得很伤心。Fail/ failure
Because she failed the exam, she cries sadly.
Because of the failure of exam, she cries sadly.
believe it or not 信不信由你
e.g. Believe it or not, I met a super football star this morning on the street.
信不信由你,我今天早晨在街上遇到一个超级球星。
e.g. 信不信由你,数学的作用远超出你的想象。
e.g. 信不信由你,我永远不会骗你。Cheat
Believe it or not, I won’t cheat you forever.
more than, believe it or not, because of, come up, at present, make use of, play a part in, base ...on
1.—I’m happy to take you there in my car.
—You are so nice. Thank you.
2.There is no way of predicting what the long?term effects of the accident will be.
3.I believe Mary as she always her ideas scientific experiments.
4.At the meeting many questions about the quality of the new bridge.
5. the thick fog, the return flight of the aircraft had to be put off.
6.They tried their best to the chance that their school offered to study hard.
7. ,_they will not carry out their promise.
8.Friends our lives, although we may take friendship for granted.
adj.本国的;本地的
native speaker/ language
be native to ... 产于…… silk
e.g. It is wel-l?known that the panda is native to China.
众所周知,大熊猫产于中国。
n.本地人;本国人
e.g. a native of Switzerland 一个出生在瑞士的人
A native of China found that silk was native to China in Tang dynasty.
native
latter adj.较后的;后半的;(两者中的)后者 later
the former ...the latter ...前者……后者……
e.g. Mary and Jane are both my friends. The former is a clerk in a bank and the latter teaches English in a middle school.
玛丽和简都是我的朋友,前者是银行的职员,后者在中学教英语。
e.g. Celebrations are planned for the latter part of November.
庆祝活动计划在11月的下半月举行。
The latter part of 19c
?
n.(1)街区
e.g. She grew up playing with the other kids on the block.
她是和街区里其他孩子一起玩大的。
(2)块;木块;石块;
a block of… 一块〔指木头、石头等有直边的坚硬物体〕
?
v. 阻挡,堵塞
e.g. A fallen tree is blocking the road.
一棵倒下的树把路阻断了。
e.g. I tried to get through, but there were people blocking my way.
我想过去,但是有人挡着路。
block
?
Let’s walk round the block.
Seeing the road blocked with snow, we had to spend the holiday at home, watching TV.
Before us stands a wall made of concrete blocks.
街区
2. 阻挡
3. 石板
e.g. Number sense is not the ability to count. It is the ability to recognize a change in number.
数字感并不只是数数的能力,它是识别数字变化的能力。
recognize sb./one’s voice 认出某人/听出某人的声音
e.g. At any case, I can recognize my mother’s voice.
e.g. I recognized his voice the moment he opened his mouth.
他一张嘴说话,我就听出了他的声音。
recognize vt. 辨认出;承认;公认
e.g. Picasso Pablo and Vincent van Gogh have been recognized to be/ as the most influential painters all around the world.
e.g. Sharing bike is recognized as one of new Chinese Four Inventions.
?
recognize that ... 承认…… realize
e.g. We also recognize that we need to do more.
同时,我们也认识到,我们还要开展更多工作。
e.g. We need to recognize that health is an investment.
我们必须认识到健康是一种投资。
be recognized to be/as ... 被认作……/被认为是……
It is recognized that ... 人们公认……
?
e.g. It is recognized that he is a good teacher.
大家都公认他是一个好老师。
e.g. It is recognized that environment pollution has become one of the most serious problems that people face.
入们一致认为环境污染已经成了人们面对的最严重的问题之一。
e.g. It is recognized that in the Information Age, Internet
commerce is a powerful tool in the economic growth of developing countries.
大家都认可,在信息时代网络贸易是发展中国家经济发展强有力的工具。
recognition n. 认出;认识
beyond (all) recognition 认不出来
e.g. The city has been built up so fast that it’s changed
beyond_recognition.
这城市建设得真快,已看不出它原来的面貌了。
Information
communication
e.g. Now it is different from the past.
现在和过去不同了。
e.g. This place is very quiet, quite different from the hustle and bustle
of the cities.
这个地方很安静, 与城市的拥挤喧嚣十分不同。
e.g. My scores are the same as yours.
My scores are different from yours
be different from 与…不同
be the same as 与…一样
e.g. There is a shop at the end of the street.
这条街走到头有一个商店。
e.g. 月底我们会有一次月考。
We will have a monthly exam at the end of this month.
e.g.观众在歌剧结束时报以热烈的掌声。
Audience观众 opera歌剧 applause
Audience made hot applause at the end of the opera.
at the end of 在…结束时 ,在…末
a large number of 大量的,很多(修饰主语,谓语动词用复数)
a small number of 少量,些许
e.g. The city have attracted a large number of homosexuals.
e.g. A small number of hit songs like those of Jay Chou have
received worldwide fame.
the number of …的数量(作主语,谓语动词用单数)
e.g. The number of unemployment has hit record high at the end of this year.
in fact
= actually
= as a matter of fact 事实上
The number of the students in this city _____ increased 6 times in comparison with 2001.
The number of the volunteers ________ 100 now. And a small number of them ________ already gone to the workplace.
A.is; have B.are; have C.is; are D.is; has
(一) 祈使句的变化规则
如果直接引语是祈使句,变为间接引语时,
根据句子意思在不定式前加上tell/ask/order等动词
将祈使句的动词原形变为带to的不定式
如果祈使句是否定句,在不定式前面还要加上not
e.g. The hostess said to us, “Please sit down.”
→ The hostess asked us to sit down.
e.g. He said, “Don’t make so much noise, boys.”
→ He told the boys not to make so much noise.
直接引语与间接引语
1)一般疑问句
谓语动词是say或said要改为 ask 或asked
把疑问句语序变为陈述句语序,句末用句号
变为由if/whether 引导的宾语从句
e.g. “Do you think a diary can become your friend?” the writer says.
→ The writer asks us if we think a diary can become our friend.
2) 特殊疑问句
保留原来的引导词
疑问句要变为陈述句,句末用句号
e.g. “What do you want?” he asked me.
→ He asked me what I wanted.
(二)疑问句的变化规则
1.The monitor said to me, “Don’t forget to turn off the lights when you leave.”
→The monitor _ forget to turn off the lights when I left.
2.Mr Brown said to Mary, “Will you write Tom a letter in English or send him an e?mail?”
→Mr Brown asked Mary write Tom a letter in English or send him an e?mail.
3.He asked, “Haven’t you finished your English homework?”
→He asked me if I have finished my English homework or not.
4.Mum said to me, “How do you deal with the disagreement between the company and the customers?”
→Mum asked me how I deal with the disagreement between the company and the customers.
命令语气:表示直接命令某人做某事,语气比较重,不怎么礼貌,一般用于上级 对下级
e.g. “ Look at the example”, the teacher said to us.
e.g. Open the window!
请求语气:表示请求某人做某事,语气比较缓和,非常礼貌
e.g. “ Would you like to see my flat?” She asked.
e.g. Would you please open the window?
命令(command)语气和请求(request)语气
