外研版高一英语必修三 Module 6 Old and New 全单元教案
文档属性
| 名称 | 外研版高一英语必修三 Module 6 Old and New 全单元教案 |
|
|
| 格式 | zip | ||
| 文件大小 | 17.3KB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 外研版 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2019-10-17 00:00:00 | ||
图片预览




文档简介
Module 6 Old and New
一、教学内容、目的和要求 (from the teacher’s book )
题材内容
与学习目的
主要介绍了我国著名的三峡大坝工程。通过大型建筑工程的介绍,帮助学生了解它们给社会环境、经济所带来的日新月异的变化。
语
音知识目标
语音
学习定语从句的语调。
词汇
见MODULE FILE
语法
非限制性定语从句(non-defining relative clauses)
定语从句的缩略形式(contraction of relative clauses)
功能
学习一些能表达强烈感情的形容词(adjectives expressing strong feelings)
话题
谈论三峡大坝、香港机场和万里长城。
语音技能目标
听
在听的过程中能够用关键词记下主要信息,能正确理解定语从句中关系代词的省略;正确理解具有强烈感彩的形容词在表达中的强调作用。
说
运用本模块所学词汇和短语介绍一些著名的建筑工程;在表达中使用限制性和非限制性定语从句,并且做到语调正确;学会使用含有强烈感彩的形容词。
读
阅读中能识别新学词汇、短语并推断出意思;正确理解介绍长城、香港机场及三峡大坝工程的短文;能汲取表格所包含的有用信息;能正确理解限制性定语从句和非限制性定语从句的不同功能;阅读工程中能快速把握每一段落的主旨大意。
写
运用本模块所学词汇和短语,完成所有书面练习;掌握撰写电子邮件的要点;能够正确写出省略形式的定语从句。
表达与展示
说出与著名建筑工程有关的词汇、短语(越多越好);口头介绍长城、三峡大坝、世界著名摩天大楼等;制作新闻简报,介绍家乡的巨大变化。
学习策略
学习从自然(natural)和人造角度(man-made)类比归纳一些常见的名词;学会从形式和功能两个识别限制性和非限制性定语从句;学会以著名建筑工程为话题与外国友人进行口头交际。
文化意识
了解当今世界的发展与变化,开阔眼界,增强世界意识和时代责任感。
情感态度
增进对我国著名工程的了解,增强民族自豪感。
任务
用新闻的形式写出所在地区发生的变化。
Period 1Introduction + Listening + Pronunciation
Part 1. Introduction
Task: Practice oral expression by learning man-made projects.
Teaching procedures:
1. 1) Discuss the four questions in pairs.
2) Ask the students to read out their answers.
2. 1) Read through the words in the box and ask the students to look up the
words they don’t know.
2) Play a game. The teacher says some explanations of the words and let the
students say this word out.
3. 1) Before reading the passage, ask: How much do you know about the Great Wall of China /Hongkong International Airport /The Three Gorges Dam?
2) Let the students read through the passage and write down the key words.
3) Work in groups to introduce the one of the three man-made projects
4) Find the answers to the three questions on the student’s book.
4. Explain some new words, phrases.
Part 2. Listening
Task: Train the students to make notes while listening and pay attention to the language phenomena to make preparations for Function and Everyday English.
Teaching procedures:
1. 1) Ask the students to read the subjects
2) Listen to the tape and tick the subjects that they hear
3) Check the answers with them
2. 1) Read through the questions.
2) Listen to the tape again and answer the questions.
3) Check their answers.
3. 1) Have the students do the activity individually, then check with a partner.
2) Listen to the tape once more to check their answers.
Part 3. Pronunciation
Task: Practise the intonation of the students with non-defining attributive clauses.
Teaching procedures:
1. Read the sentences and underline the attributive clauses.
2. Check their answers.
3. Play the type for a couple of times.
4. Let the students follow the tape to read.
5. Pair them to practice.
Homework: Write about a famous man-made project..
Period 2 Reading and Vocabulary
Task: Learn about the Three Gorges Dam.
Teaching procedures:
1. Revision Ask the students to introduce another man-made project
2. 1) Deal with the new words and phrases in the text by reading for them.
2) Make sure the students know about their meanings.
3. Ask the students to do “T” or “F” questions and check the answers.
4. 1) Have the students read the questions and then read the text.
2) Ask the students to answer the questions one by one and correct them.
5.1) Ask the students to read the passage again.
2) Write questions for the answers.
6. Give the students some other questions to answer.
7. 1) Read the text again and write down the key words.
2) Try to say something about the Three Gorges Dam without referring to the book.
8.1) Work in groups to discuss the questions on the student’s book.
2) Call back their ideas.
Home work: Retell the passage about the Three Gorges Dam.
Period 3 Language points of Reading +Task +speaking
Part 1. Language points of Reading
Teaching procedures:
1. Revision Let students retell the text.
2. Key words, phrases
1) dream vt. +n./prep./that clause
eg. He dreamt that he was flying around the earth .
I dreamt a sweet dream last night.
dream of 梦见,向往,渴望
eg. Tom often dreams of having his own car.
2) hold back
阻止,阻碍
eg. Nothing can hold back the wheel of history.
……忍住,抑制
eg. Hearing the exciting news. She couldn’t hold back her tears.
隐瞒,保留
eg. He held something back from me.
3) provide something for sb./sb. with sth. 为某人提供某物
eg. Our school provided books for us.
= Our school provided us with books.
4) 建议suggest sth./sth. to sb. /doing sth. /that-clause
eg. The teacher suggested a rest to us.
He suggested starting at once.
The doctor suggested the patient ( should ) be operated on immediately.
表明,暗示。有……迹象
eg. Dark clouds suggest it will rain.
live a…life 过……生活
dream /die /sleep/breathe /smile /laugh
eg. We are living a happy life.
Guo Jingjing breathed a deep breath and jumped into the water.
5) flood n.
eg. A lot of houses were washed away by the floods.
The heart-broken mother was in floods of tears.
The river was in flood.
vi. after the storm, the rivers flooded.
Many days of heavy rain flooded the whole city.
6) remove vt
eg. The doctor did what he could to remove their doubts.
He removed the mud from his clothes.
The teachers and students all came to remove the bricks.
7) be being done
eg. More and more forests are being destroyed, causing many animals to die out.
Part 2. Task
Task: Prepare a news bulletin about changes that have taken pace in the students’ region.
Teaching procedures:
1. Work in small groups. List the changes.
2. Imagine that the students are preparing the news item for a foreign audience who need extra information. Let the students add extra information.
3. Act out the news item for the rest of the class.
Period 4 Grammar I + Grammar II
Part 1. Grammar I
Task: Learn about Non-defining attributive clauses
Teaching procedures:
1. 1) Have the students read the text and find out all the attributive clauses in it.
* Mao Zedong wrote a poem in which he dreamed of “walls of stone to hold back clouds and rain”.
* The Three Gorges Dam, which is the biggest construction project in China since the building of the Great wall and the Grand Canal, has been built to control flooding.
* SunYat-sen, who was the tender of the 1911 Revolution, first suggested the idea in 1919.
* More than a million people who lived in the region have moved from their homes.
2) Ask the students to answer the questions on the student’s book.
2. 1) Read the sentences on the student’s book and add commas if necessary.
2) Check the answers with them.
3. Compare the following sentences.
1) The college students who know the truth left the small town.
The college students, who know the truth , left the small town.
2) He was a son who works in a hospital.
He has a son, who works in a hospital.
4. Let students fill in the table.
类别
意义
功能
形式
关系代、副词
限制性定语从句
起限定作用。若省略,原句意义不完整。
修饰先行词
通常紧接先行词后,无逗号。
关系词可由that代替,也可省略
非限制性定语从句
起补充说明作用。
既可修饰先行词。也可修饰整个句子。
有逗号与主句隔开。
关系词不可由that代替,也不能省略
Part 2. Grammar 2
Task:Learn about contraction of attributive clauses.
Teaching procedures:
1. Have the students read out the sentences on the student’s book and answer the questions.
2. Tell the students if the relative pronouns are objects, we call cross them out.
3. Give students some examples.
4. Do the exercises on the student’s book.
2.1) Show the students another kind of omittance.
eg. The valley is now part of the reservoir (which was) created by the Three Gorges Dam.
The people (who were) living in the village have moved to the other places.
2) Give the students some other sentences to practise.
* The building (which was) built last year is our library.
* The student (who is ) standing there is my deskmate.
* When ( I am) in trouble, I always turn to our head teacher for help.
* If (it is) necessary, I’ll go there at once.
3) Explain how to omit.
When the subject of the principle clause is “the same with the one of the subordinate clause, and there is a “be”, we can omit “the subject and be” of the subordinate clause.
3.1) Finish the exercises on the student’s book and make each pair of sentences into one sentence.
2) Check their answers.
Homework: Make as many sentences as possible and use contraction of attributive clauses.
Period 5 Writing + Function and Every day English + Cultural corner
Part 1. Writing
Task: Practise writing an email.
Teaching procedures:
1. 1) Ask the students to go through the questions before they read the text.
2) Have them answer the questions and correct them.
2. 1) Let the students write an email to a friend about a visit to a place which has changed since their last visit.
2) Exchange their writing with a partner to correct the mistakes.
3) Ask a few of them to read email to the whole class.
Part 2. Function and Everyday English
Task: Experience the fun_ction of strong adjectives.
Teaching procedures:
1. 1) Read down the two lists of adjectives and do the matching individually.
2) Have one student read the adjective and another the strong adjective.
2. Ask the students to complete these conversations and check the answers
with them.
3. 1) Ask the students to complete these conversation with other adjectives
from the list in activity 1 and check the answers.
2) Pair the students to practice the dialogue.
4. 1) Work in pairs to write a short conversation which ends with another of the
strong adjectives in the list in activity1.
2) Have pairs first practice and then perform their dialogue.
Part 3. Cultural corner
Task: Get some information about the Empire State Building, New York and
other famous buildings in the world.
Teaching procedures:
1. Go through the questions before they read the passage.
2. Read the passage and then answer the questions.
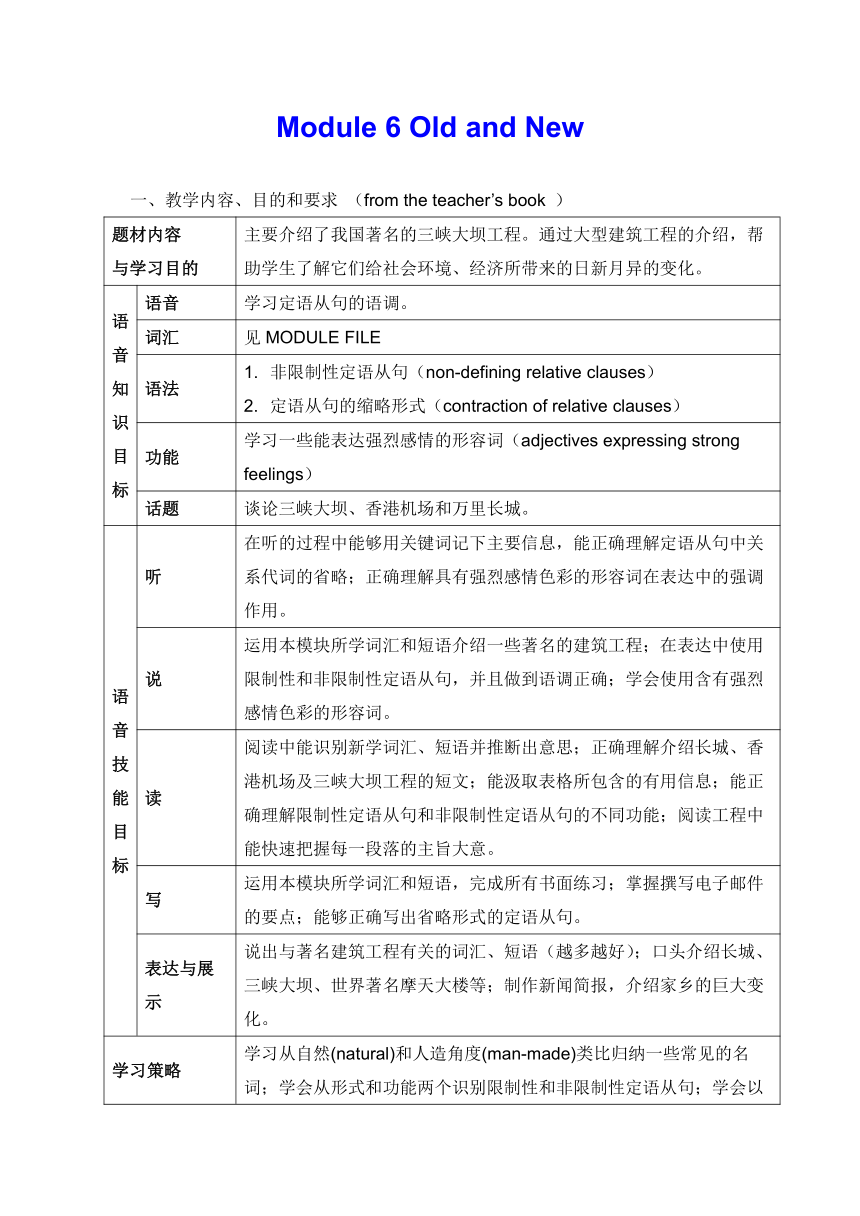
一、教学内容、目的和要求 (from the teacher’s book )
题材内容
与学习目的
主要介绍了我国著名的三峡大坝工程。通过大型建筑工程的介绍,帮助学生了解它们给社会环境、经济所带来的日新月异的变化。
语
音知识目标
语音
学习定语从句的语调。
词汇
见MODULE FILE
语法
非限制性定语从句(non-defining relative clauses)
定语从句的缩略形式(contraction of relative clauses)
功能
学习一些能表达强烈感情的形容词(adjectives expressing strong feelings)
话题
谈论三峡大坝、香港机场和万里长城。
语音技能目标
听
在听的过程中能够用关键词记下主要信息,能正确理解定语从句中关系代词的省略;正确理解具有强烈感彩的形容词在表达中的强调作用。
说
运用本模块所学词汇和短语介绍一些著名的建筑工程;在表达中使用限制性和非限制性定语从句,并且做到语调正确;学会使用含有强烈感彩的形容词。
读
阅读中能识别新学词汇、短语并推断出意思;正确理解介绍长城、香港机场及三峡大坝工程的短文;能汲取表格所包含的有用信息;能正确理解限制性定语从句和非限制性定语从句的不同功能;阅读工程中能快速把握每一段落的主旨大意。
写
运用本模块所学词汇和短语,完成所有书面练习;掌握撰写电子邮件的要点;能够正确写出省略形式的定语从句。
表达与展示
说出与著名建筑工程有关的词汇、短语(越多越好);口头介绍长城、三峡大坝、世界著名摩天大楼等;制作新闻简报,介绍家乡的巨大变化。
学习策略
学习从自然(natural)和人造角度(man-made)类比归纳一些常见的名词;学会从形式和功能两个识别限制性和非限制性定语从句;学会以著名建筑工程为话题与外国友人进行口头交际。
文化意识
了解当今世界的发展与变化,开阔眼界,增强世界意识和时代责任感。
情感态度
增进对我国著名工程的了解,增强民族自豪感。
任务
用新闻的形式写出所在地区发生的变化。
Period 1Introduction + Listening + Pronunciation
Part 1. Introduction
Task: Practice oral expression by learning man-made projects.
Teaching procedures:
1. 1) Discuss the four questions in pairs.
2) Ask the students to read out their answers.
2. 1) Read through the words in the box and ask the students to look up the
words they don’t know.
2) Play a game. The teacher says some explanations of the words and let the
students say this word out.
3. 1) Before reading the passage, ask: How much do you know about the Great Wall of China /Hongkong International Airport /The Three Gorges Dam?
2) Let the students read through the passage and write down the key words.
3) Work in groups to introduce the one of the three man-made projects
4) Find the answers to the three questions on the student’s book.
4. Explain some new words, phrases.
Part 2. Listening
Task: Train the students to make notes while listening and pay attention to the language phenomena to make preparations for Function and Everyday English.
Teaching procedures:
1. 1) Ask the students to read the subjects
2) Listen to the tape and tick the subjects that they hear
3) Check the answers with them
2. 1) Read through the questions.
2) Listen to the tape again and answer the questions.
3) Check their answers.
3. 1) Have the students do the activity individually, then check with a partner.
2) Listen to the tape once more to check their answers.
Part 3. Pronunciation
Task: Practise the intonation of the students with non-defining attributive clauses.
Teaching procedures:
1. Read the sentences and underline the attributive clauses.
2. Check their answers.
3. Play the type for a couple of times.
4. Let the students follow the tape to read.
5. Pair them to practice.
Homework: Write about a famous man-made project..
Period 2 Reading and Vocabulary
Task: Learn about the Three Gorges Dam.
Teaching procedures:
1. Revision Ask the students to introduce another man-made project
2. 1) Deal with the new words and phrases in the text by reading for them.
2) Make sure the students know about their meanings.
3. Ask the students to do “T” or “F” questions and check the answers.
4. 1) Have the students read the questions and then read the text.
2) Ask the students to answer the questions one by one and correct them.
5.1) Ask the students to read the passage again.
2) Write questions for the answers.
6. Give the students some other questions to answer.
7. 1) Read the text again and write down the key words.
2) Try to say something about the Three Gorges Dam without referring to the book.
8.1) Work in groups to discuss the questions on the student’s book.
2) Call back their ideas.
Home work: Retell the passage about the Three Gorges Dam.
Period 3 Language points of Reading +Task +speaking
Part 1. Language points of Reading
Teaching procedures:
1. Revision Let students retell the text.
2. Key words, phrases
1) dream vt. +n./prep./that clause
eg. He dreamt that he was flying around the earth .
I dreamt a sweet dream last night.
dream of 梦见,向往,渴望
eg. Tom often dreams of having his own car.
2) hold back
阻止,阻碍
eg. Nothing can hold back the wheel of history.
……忍住,抑制
eg. Hearing the exciting news. She couldn’t hold back her tears.
隐瞒,保留
eg. He held something back from me.
3) provide something for sb./sb. with sth. 为某人提供某物
eg. Our school provided books for us.
= Our school provided us with books.
4) 建议suggest sth./sth. to sb. /doing sth. /that-clause
eg. The teacher suggested a rest to us.
He suggested starting at once.
The doctor suggested the patient ( should ) be operated on immediately.
表明,暗示。有……迹象
eg. Dark clouds suggest it will rain.
live a…life 过……生活
dream /die /sleep/breathe /smile /laugh
eg. We are living a happy life.
Guo Jingjing breathed a deep breath and jumped into the water.
5) flood n.
eg. A lot of houses were washed away by the floods.
The heart-broken mother was in floods of tears.
The river was in flood.
vi. after the storm, the rivers flooded.
Many days of heavy rain flooded the whole city.
6) remove vt
eg. The doctor did what he could to remove their doubts.
He removed the mud from his clothes.
The teachers and students all came to remove the bricks.
7) be being done
eg. More and more forests are being destroyed, causing many animals to die out.
Part 2. Task
Task: Prepare a news bulletin about changes that have taken pace in the students’ region.
Teaching procedures:
1. Work in small groups. List the changes.
2. Imagine that the students are preparing the news item for a foreign audience who need extra information. Let the students add extra information.
3. Act out the news item for the rest of the class.
Period 4 Grammar I + Grammar II
Part 1. Grammar I
Task: Learn about Non-defining attributive clauses
Teaching procedures:
1. 1) Have the students read the text and find out all the attributive clauses in it.
* Mao Zedong wrote a poem in which he dreamed of “walls of stone to hold back clouds and rain”.
* The Three Gorges Dam, which is the biggest construction project in China since the building of the Great wall and the Grand Canal, has been built to control flooding.
* SunYat-sen, who was the tender of the 1911 Revolution, first suggested the idea in 1919.
* More than a million people who lived in the region have moved from their homes.
2) Ask the students to answer the questions on the student’s book.
2. 1) Read the sentences on the student’s book and add commas if necessary.
2) Check the answers with them.
3. Compare the following sentences.
1) The college students who know the truth left the small town.
The college students, who know the truth , left the small town.
2) He was a son who works in a hospital.
He has a son, who works in a hospital.
4. Let students fill in the table.
类别
意义
功能
形式
关系代、副词
限制性定语从句
起限定作用。若省略,原句意义不完整。
修饰先行词
通常紧接先行词后,无逗号。
关系词可由that代替,也可省略
非限制性定语从句
起补充说明作用。
既可修饰先行词。也可修饰整个句子。
有逗号与主句隔开。
关系词不可由that代替,也不能省略
Part 2. Grammar 2
Task:Learn about contraction of attributive clauses.
Teaching procedures:
1. Have the students read out the sentences on the student’s book and answer the questions.
2. Tell the students if the relative pronouns are objects, we call cross them out.
3. Give students some examples.
4. Do the exercises on the student’s book.
2.1) Show the students another kind of omittance.
eg. The valley is now part of the reservoir (which was) created by the Three Gorges Dam.
The people (who were) living in the village have moved to the other places.
2) Give the students some other sentences to practise.
* The building (which was) built last year is our library.
* The student (who is ) standing there is my deskmate.
* When ( I am) in trouble, I always turn to our head teacher for help.
* If (it is) necessary, I’ll go there at once.
3) Explain how to omit.
When the subject of the principle clause is “the same with the one of the subordinate clause, and there is a “be”, we can omit “the subject and be” of the subordinate clause.
3.1) Finish the exercises on the student’s book and make each pair of sentences into one sentence.
2) Check their answers.
Homework: Make as many sentences as possible and use contraction of attributive clauses.
Period 5 Writing + Function and Every day English + Cultural corner
Part 1. Writing
Task: Practise writing an email.
Teaching procedures:
1. 1) Ask the students to go through the questions before they read the text.
2) Have them answer the questions and correct them.
2. 1) Let the students write an email to a friend about a visit to a place which has changed since their last visit.
2) Exchange their writing with a partner to correct the mistakes.
3) Ask a few of them to read email to the whole class.
Part 2. Function and Everyday English
Task: Experience the fun_ction of strong adjectives.
Teaching procedures:
1. 1) Read down the two lists of adjectives and do the matching individually.
2) Have one student read the adjective and another the strong adjective.
2. Ask the students to complete these conversations and check the answers
with them.
3. 1) Ask the students to complete these conversation with other adjectives
from the list in activity 1 and check the answers.
2) Pair the students to practice the dialogue.
4. 1) Work in pairs to write a short conversation which ends with another of the
strong adjectives in the list in activity1.
2) Have pairs first practice and then perform their dialogue.
Part 3. Cultural corner
Task: Get some information about the Empire State Building, New York and
other famous buildings in the world.
Teaching procedures:
1. Go through the questions before they read the passage.
2. Read the passage and then answer the questions.
