Unit 2 Sailing the oceans Warming up & Reading课件(39张PPT)
文档属性
| 名称 | Unit 2 Sailing the oceans Warming up & Reading课件(39张PPT) |

|
|
| 格式 | zip | ||
| 文件大小 | 2.9MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 人教版(新课程标准) | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2019-10-26 00:00:00 | ||
图片预览










文档简介
(共39张PPT)
新人教版 高三 英语选修 9
课题:Unit 2 Sailing the Oceans
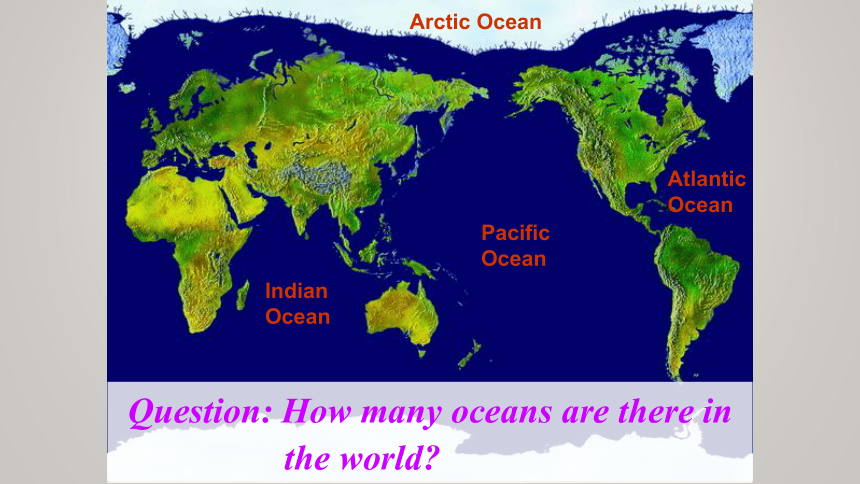
Indian Ocean
Pacific Ocean
Atlantic Ocean
Arctic Ocean
Question: How many oceans are there in
the world?
Have you ever dreamed of sailing on the sea?
Zheng He
Marco Polo
Exploring oceans was always a dream for ancient people.
Look at these famous people.
What do you know about them?
Zheng He
1371-1433
He led a large fleet to explore
Southeast Asia, India and the Middle East in the Ming Dynasty. Altogether he made 7 voyages in the 15th century. He travelled more than 50,000 km and visited 30 countries new to China and developed many trade links. He is considered one of the earliest naval explorers in Chinese history.
海军探险家
舰队
Marco Polo
1254--1324
He is the most famous westerner to travel the Silk Road and the only person to provide information about China to the outside world. In 1271 he set out to reach the Mongol Empire and then China. In 1295, he arrived back in Europe. Three years later he was imprisoned by the Genoese. While in prison, he told the story of his travel to a fellow prisoner who wrote his adventures down. When his book was published it became a best-seller.
热那亚人
How do you think seamen like them found their way before modern accurate methods of navigation were invented?
*Kept close to the shore, used nature such as the sun, wind, birds, tide, etc, to help them;
*used some of the instruments including a compass, astrolabe, etc
compass
astrolabe
星盘
sextant
陀螺六分仪
nautical chart
四分仪,象限仪
quadrant
How did seamen explore the oceans before latitude and longitude made it possible to plot a ship’s position?
Using nature
Keeping alongside the coastline
Using celestial bodies
Using wildlife
Using the weather
Using the sea
Using celestial bodies
to plot the positions
to work out the latitude
a special cloud formation which indicates there is land close by
Using wildlife
If seaweed was fresh and smelled strongly, the ship was close to land.
Seabirds could be used to show the way to land when it was nowhere to be seen.
Using the weather
To help identify the position of a stream or river when …
To direct their sailing
Use the information to analyze the navigational skills and write the answers in your own words.
To find the ship’s position at sea a sailor used _______________________.
A sailor knew that land was nearby if he saw ______________________________ _________________________________.
Sailors used ______________________ ______ to increase their speed.
the North Star and the sun
sea currents or tides and
winds
Using nature
clouds, fresh seaweed, nesting birds returning home in the evening or fog
What skills did sailors use to explore the seas and discover new lands?
Using navigational instruments
1. Finding longitude
2. Finding latitude
the compass
the bearing circle (方位圆)
the astrolabe (星盘)
the quadrant (象限仪, 四分仪)
the sextant (六分仪)
Read again and fill in the blanks.
There were two methods to find longitude: 1. __________________________
2. __________________________
______________________
measuring time and speed
compass and complicated
mathematical tables
Using instruments
Write down the working principles of the following instruments.
Bearing circle:
Astrolabe:
to compare the height of the sun now with the position of the sun at midday.
to compare the position of the ship in relation to some stars or the sun.
Quadrant:
a more precise form of the astrolabe, to measure how high stars are above the horizon, and compare that measurement with previous measurements (using the ship as one of the fixed points to find its position)
Sextant:
an updated version of the quadrant and so it was more accurate, to measure the angle between two fixed points outside the ship (using two mirrors to find the ship’s position).
Read the passage and answer the following questions.
What is the use of a bearing circle, astrolabe, quadrant or sextant? ( )
What is the use of a compass? ( )
A. to set the course of the ship
B. to measure the position of the ship
C. to measure the speed of the ship
D. to tell the time
B
A
Using instruments
Skim the text and fill in the blanks.
plot
latitude
Wildlife
way
Nature Celestial bodies were used to _____ the positions of navigators and to work out their _______.
_______ was used to tell where the ship was close to land or to show the ____ to land.
identify
tides and currents
compass
sextant
The weather could help ________ the position of a stream or river and to direct the sailing.
Certain ________________ on the sea were used to carry ships to the destination.
Navigational instruments The ________ was used to help find longitude.
The Bearing Circle, the Astrolabe, the Quadrant and the ________ were used to find latitude.
.
We may want to know (1)____seamen explored the oceans(2)_______ latitude appeared. (3)_______they didn’t have the modern navigational help, seamen could still control the sea by using some skills to explore seas and discover the new lands. (4)______ (use) nature is the first and most useful form of (5)_________(explore), such as using celestial bodies, using wildlife, using the weather, and using the sea. Because of these skill, sailors increased the ability(6)__ navigate new seas when they used instruments,(7)______ (include) longitude and latitude.
how
before
Though
Using
exploration
to
including
Task1. Summary
Task 2: Read the chart below and fill in your plans of action
to deal with them.
What would you do if: Plan of action
You were far from land and a storm arose.
What would you do if : Plan of action
You were blown off course.
Task 2: Read the chart below and fill in your plans of action
to deal with them.
What would you do if: Plan of action
You were far from land and a storm arose.
What would you do if: Plan of action
You were lost with no land in sight.
follow nesting birds to shore;
look for special cloud formations or fog over streams to find land
What would you do if : Plan of action
You were offshore but you needed more food and water.
use the compass and the astrolabe, quadrant or sextant to find out your position, return to your former course
What would you do if : Plan of action
You were blown off course.
follow nesting birds to shore;
look for special cloud formations or fog over streams to find land
What would you do if : Plan of action
You were offshore but you needed more food and water.
measure your position using the sun or stars; look for sea birds, cloud formations, fog or seaweed to show that land is nearby
What would you do if: Plan of action
You were lost with no land in sight.
Writing:
Imagine you are on a boat with 29 other people. You have a small box for your personal things but it can only hole ten items. What would you need for a week’s journey across the North Sea to England and why?
新人教版 高三 英语选修 9
课题:Unit 2 Sailing the Oceans
Indian Ocean
Pacific Ocean
Atlantic Ocean
Arctic Ocean
Question: How many oceans are there in
the world?
Have you ever dreamed of sailing on the sea?
Zheng He
Marco Polo
Exploring oceans was always a dream for ancient people.
Look at these famous people.
What do you know about them?
Zheng He
1371-1433
He led a large fleet to explore
Southeast Asia, India and the Middle East in the Ming Dynasty. Altogether he made 7 voyages in the 15th century. He travelled more than 50,000 km and visited 30 countries new to China and developed many trade links. He is considered one of the earliest naval explorers in Chinese history.
海军探险家
舰队
Marco Polo
1254--1324
He is the most famous westerner to travel the Silk Road and the only person to provide information about China to the outside world. In 1271 he set out to reach the Mongol Empire and then China. In 1295, he arrived back in Europe. Three years later he was imprisoned by the Genoese. While in prison, he told the story of his travel to a fellow prisoner who wrote his adventures down. When his book was published it became a best-seller.
热那亚人
How do you think seamen like them found their way before modern accurate methods of navigation were invented?
*Kept close to the shore, used nature such as the sun, wind, birds, tide, etc, to help them;
*used some of the instruments including a compass, astrolabe, etc
compass
astrolabe
星盘
sextant
陀螺六分仪
nautical chart
四分仪,象限仪
quadrant
How did seamen explore the oceans before latitude and longitude made it possible to plot a ship’s position?
Using nature
Keeping alongside the coastline
Using celestial bodies
Using wildlife
Using the weather
Using the sea
Using celestial bodies
to plot the positions
to work out the latitude
a special cloud formation which indicates there is land close by
Using wildlife
If seaweed was fresh and smelled strongly, the ship was close to land.
Seabirds could be used to show the way to land when it was nowhere to be seen.
Using the weather
To help identify the position of a stream or river when …
To direct their sailing
Use the information to analyze the navigational skills and write the answers in your own words.
To find the ship’s position at sea a sailor used _______________________.
A sailor knew that land was nearby if he saw ______________________________ _________________________________.
Sailors used ______________________ ______ to increase their speed.
the North Star and the sun
sea currents or tides and
winds
Using nature
clouds, fresh seaweed, nesting birds returning home in the evening or fog
What skills did sailors use to explore the seas and discover new lands?
Using navigational instruments
1. Finding longitude
2. Finding latitude
the compass
the bearing circle (方位圆)
the astrolabe (星盘)
the quadrant (象限仪, 四分仪)
the sextant (六分仪)
Read again and fill in the blanks.
There were two methods to find longitude: 1. __________________________
2. __________________________
______________________
measuring time and speed
compass and complicated
mathematical tables
Using instruments
Write down the working principles of the following instruments.
Bearing circle:
Astrolabe:
to compare the height of the sun now with the position of the sun at midday.
to compare the position of the ship in relation to some stars or the sun.
Quadrant:
a more precise form of the astrolabe, to measure how high stars are above the horizon, and compare that measurement with previous measurements (using the ship as one of the fixed points to find its position)
Sextant:
an updated version of the quadrant and so it was more accurate, to measure the angle between two fixed points outside the ship (using two mirrors to find the ship’s position).
Read the passage and answer the following questions.
What is the use of a bearing circle, astrolabe, quadrant or sextant? ( )
What is the use of a compass? ( )
A. to set the course of the ship
B. to measure the position of the ship
C. to measure the speed of the ship
D. to tell the time
B
A
Using instruments
Skim the text and fill in the blanks.
plot
latitude
Wildlife
way
Nature Celestial bodies were used to _____ the positions of navigators and to work out their _______.
_______ was used to tell where the ship was close to land or to show the ____ to land.
identify
tides and currents
compass
sextant
The weather could help ________ the position of a stream or river and to direct the sailing.
Certain ________________ on the sea were used to carry ships to the destination.
Navigational instruments The ________ was used to help find longitude.
The Bearing Circle, the Astrolabe, the Quadrant and the ________ were used to find latitude.
.
We may want to know (1)____seamen explored the oceans(2)_______ latitude appeared. (3)_______they didn’t have the modern navigational help, seamen could still control the sea by using some skills to explore seas and discover the new lands. (4)______ (use) nature is the first and most useful form of (5)_________(explore), such as using celestial bodies, using wildlife, using the weather, and using the sea. Because of these skill, sailors increased the ability(6)__ navigate new seas when they used instruments,(7)______ (include) longitude and latitude.
how
before
Though
Using
exploration
to
including
Task1. Summary
Task 2: Read the chart below and fill in your plans of action
to deal with them.
What would you do if: Plan of action
You were far from land and a storm arose.
What would you do if : Plan of action
You were blown off course.
Task 2: Read the chart below and fill in your plans of action
to deal with them.
What would you do if: Plan of action
You were far from land and a storm arose.
What would you do if: Plan of action
You were lost with no land in sight.
follow nesting birds to shore;
look for special cloud formations or fog over streams to find land
What would you do if : Plan of action
You were offshore but you needed more food and water.
use the compass and the astrolabe, quadrant or sextant to find out your position, return to your former course
What would you do if : Plan of action
You were blown off course.
follow nesting birds to shore;
look for special cloud formations or fog over streams to find land
What would you do if : Plan of action
You were offshore but you needed more food and water.
measure your position using the sun or stars; look for sea birds, cloud formations, fog or seaweed to show that land is nearby
What would you do if: Plan of action
You were lost with no land in sight.
Writing:
Imagine you are on a boat with 29 other people. You have a small box for your personal things but it can only hole ten items. What would you need for a week’s journey across the North Sea to England and why?
