高中英语人教版必修1 Unit 2 English around the world单元课件(96张ppt)
文档属性
| 名称 | 高中英语人教版必修1 Unit 2 English around the world单元课件(96张ppt) | 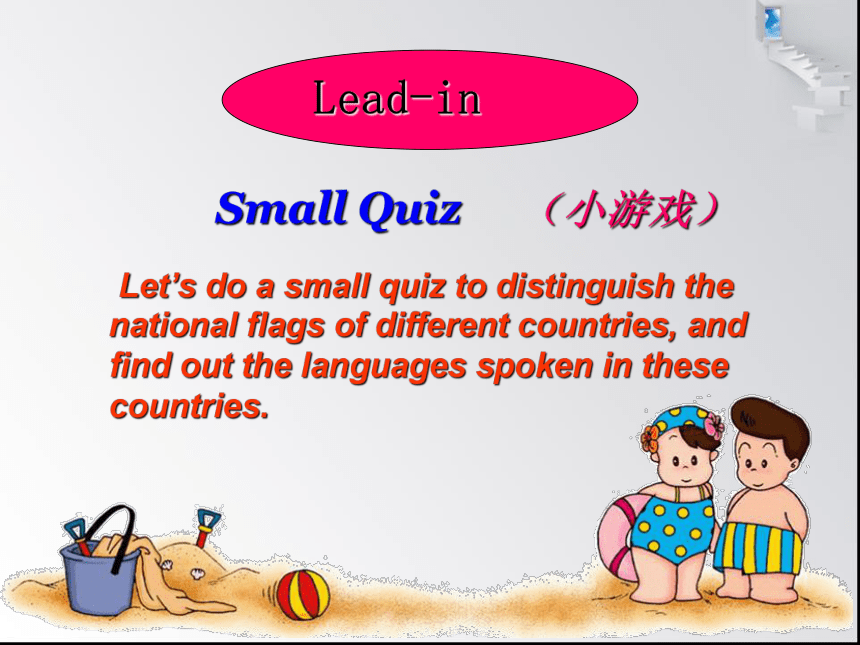 | |
| 格式 | zip | ||
| 文件大小 | 2.6MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 人教版(新课程标准) | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2020-01-30 20:50:41 | ||
图片预览









文档简介
(共93张PPT)
Small Quiz
(小游戏)
Lead-in
Let’s do a small quiz to distinguish the national flags of different countries, and find out the languages spoken in these countries.
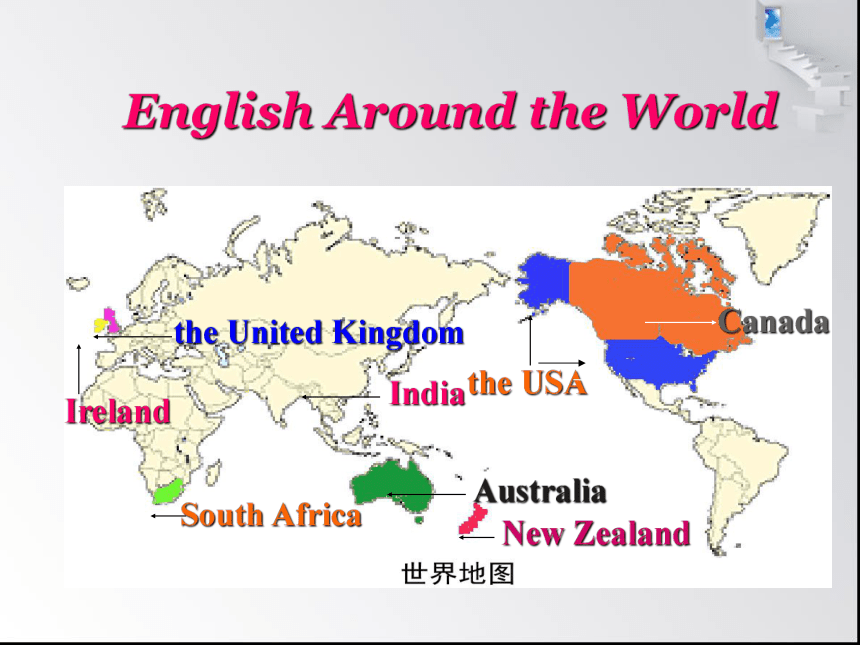
English Around the World
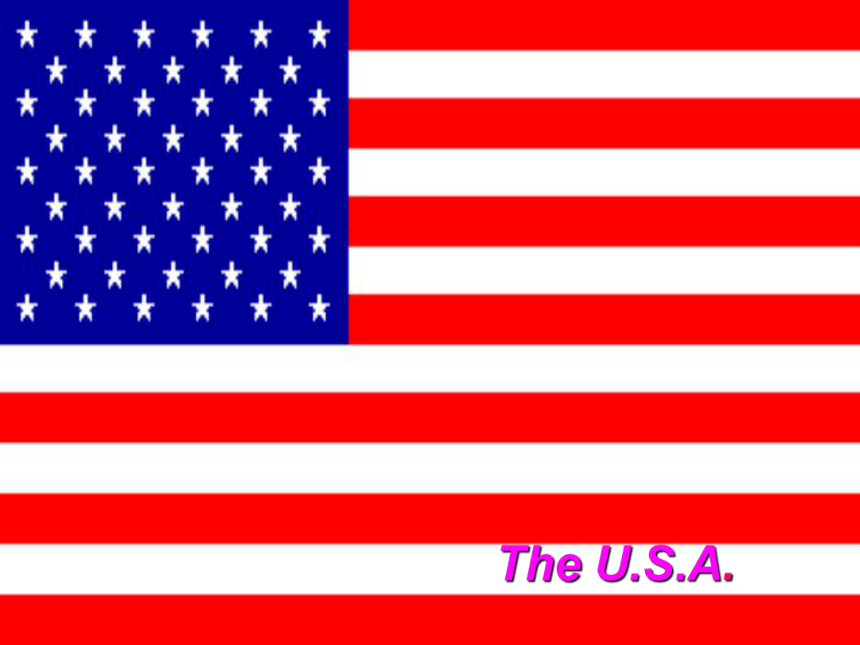
the USA
Canada
New Zealand
Australia
South Africa
the United Kingdom
Ireland
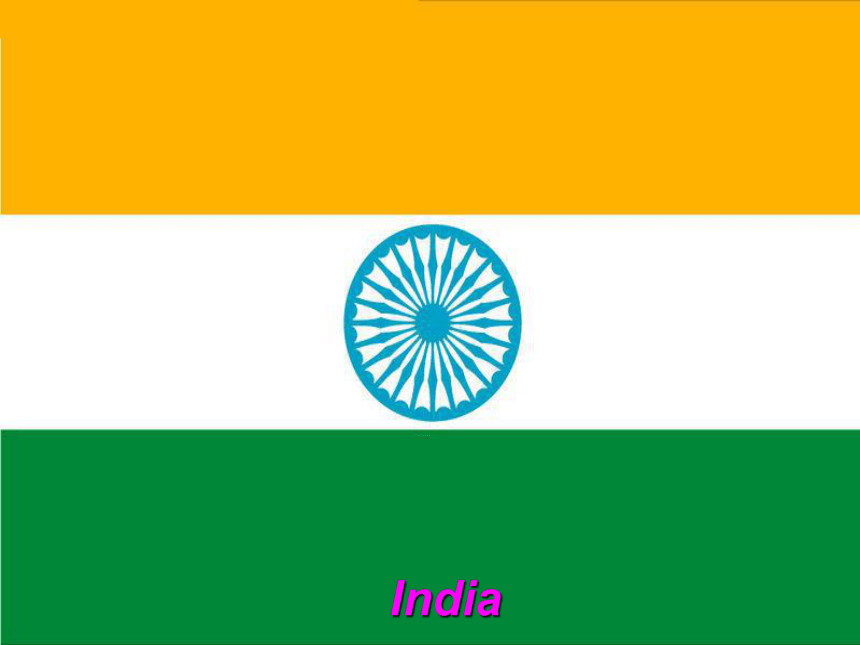
India
Australia
Canada
India
Ireland
New Zealand
South Africa
The U.S.A.
Singapore
Great Britain
English around the World
unit 2
English language and its development.
different kinds of English
Learning Goals
Knowledge Goals
Topic
Words and Expressions
Words:
elevator official voyage native apartment actually base gradual
identity fluent frequent command request expression Spanish eastern
recognize accent straight block
in…ways 在…方面??? such as 例如
believe it or not 信不信由你 come up with 提出
come up to a place 参观某地 ever before 从前
even if/ though 即使 at the end of 在…末期be based on 在...基础上 close to 距离…近
change…into 把…变成 in the early days 在早期
take…with…随身携带 the same…as 与…相同的
at present 目前
Expressions:
Difficulties in language communication
Direct and Indirect Speech
Requests and Demands
Functional Items
Grammar
Enable to know more about the differences between various English.
Develop the ability of learning English through different ways, such as reading newspapers, magazines and books, surfing the Internet, etc.
Have a positive attitude towards different culture.
Understand more phrasal and idioms of different English.
Ability Goals
Emotion Goals
Try to get more information about different English.
The usage of direct and indirect speech .
Try to use the sentences that can express requests and demands .
Important and Difficult Points
Important Points
Try to understand the differences between native English and foreign cultures, as well as the backgrounds of different development of their cultures.
Try to develop the ability of speaking English.
Difficult Points
What’s the difference between
A.E and B.E?
Do you know VOA?
Do you know BBC?
(Voice of America)
(British Broadcasting Corporation)
A. E: American English
B. E: British English
Warming Up
笑话一则
A: Do you like moving pictures?
B: Well. Yeah. Why not?
A: Ok, follow me .
B: what?
A: Let’s go downstairs to move the pictures.
B: Oh, oh…….
Moving pictures: movies:美国的旧时用法
Some different words in A. E. and BE.
Am. English Br. English
elevator lift
fall autumn
first floor ground floor
candy sweet
check bill
apartment flat
subway underground railway
1. With your partner, list the countries that use English as an official language.
2. Which country do you think has the most English learners?
3. Look at the title of the following passage and guess what it is about. Then read it quickly and see if you are right.
Pre-reading
1. Fast read the passage then try to answer :
How does the modern English develop?
Why there are so many kinds of English?
2. Listen to the tape
Reading
3. Do the exercise 1 on page 10, then give the reason that the sentence is wrong?
1. English had the most speakers in the 17th century.
2. English developed when new settlers and rulers came to Britain
3. Languages frequently change.
4. The language of the government is always the language of the country.
(F)
(T)
(F)
(F)
Answer
1. Because after the 17th century, more people began to speak English as a result of English conquering other parts of the world.
3. Because languages don’t change often but only when people come into close contact.
4. Because the government has to use the language of the country to rule it.
5. English is one of the official languages used in
India.
6. This reading passage describes the development of English language.
(T)
(T)
The list of development of English
During the 5th century AD
Based on more German
Between about AD800and 1150
Like more Danish and French
By the 1600s
Shakespeare used a wider vocabulary than ever before
1620
British settlers moved to American in the “Mayflower”
From the 18th century
British colonized
Australia
1765-1947
English spoken in India
By the 19th century
Dictionaries standardized the spelling of English
Read the text for the third time
While reading work with your partners and make a map of the English spoken countries you’ve learned in the passage, if necessary you may refer to the message on the internet. Then answer the question 3 on page 10.
Why do many people speak English?
Inferred answer from the text:
England was strong and made voyages to conquer other parts of the world.
Britain ruled some countries and taught them English.
What other factors affected the use of
language?
international role
economic development
development of democracy
the image in the world
cultural development
From the above aspects try to answer the second question by yourself.
——The development of English
When Julius Caesar, later to be Roman Emperor, invaded Britain in BC 54-5, the “Celtic” tribes lived in the British Isles. Their Celtic languages still survive as “Gaelic” in Scotland & Ireland, “Welsh”, in Wales, and “Manx” in the Isle of Man, as well as “Breton” in France.
The Romans brought Latin to Britain, which was part of the Roman Empire for over 400 years. But early English did not develop mainly from Latin.
Background
In AD 878, the Vikings invaded Britain from Scandinavia, bringing with them the Norse language, though this was similar to the old English or Anglo-Saxon language already used.
The dramatic arrival of the Norman army from France, led by King William the Conqueror in 1066, and the defeat of the English King Harold at the Battle of Hastings, brought very big changes to English life. The Normans brought with them the Old French language, which
Background
became the language of the Royal Court, and the ruling and business class. So it is unlike French, Spanish and Italian, which did come directly from Latin. “Early English” was the language of tribes who invaded from the East, from what is now Germany. They spoke different dialects of a “Germanic” language, from which modern German developed. This explains why German and English are often similar, as many of their words developed from the same original language.
Background
Differences in vocabulary usage
go to the pictures go to the movies
underground subway
lift elevator
in a team on a team
rubber eraser
flat apartment
lorry truck
petrol gas
B.E
A.E
…
James A.H. murray
Noah Webster
Noah Webster
Samuel Johnson
The Introduction of James A.H. Murray
James Augustus Henry Murray (7 February 1837 – 26 July 1915) was a Scottish lexicographer and philologist. He was the primary editor of the Oxford English Dictionary from 1879 until his death. As a young man Murray worked as a schoolmaster and a bank clerk, but always maintained a strong interest in other fields, particularly philology. In 1879 he was invited by Oxford University Press to edit the new English dictionary which had been proposed by the Philological Society.
The Introduction of Noah Webster
Noah Webster (16 October, 1758 – 28 May, 1843) was an American lexicographer, textbook author, spelling reformer, word enthusiast, and editor. He has been called the “Father of American Scholarship and Education.” His “Blue-Backed Speller” books were used to teach spelling and reading to five generations of American children. In the United States, his name has become synonymous with dictionaries, especially the modern Merriam-Webster dictionary that was first published in 1828 as An American Dictionary of the English Language.
The Introduction of Samuel Johnson
Samuel Johnson (18 September 1709 ?– 13 December 1784), often referred to as Dr. Johnson, was an English author who made lasting contributions to English literature as a poet, essayist, moralist, novelist, literary critic, biographer, editor and lexicographer. Johnson was a devout Anglican and political conservative, and has been described as "arguably the most distinguished man of letters in English history". He is also the subject of "the most famous single work of biographical art in the whole of literature": James Boswell's Life of Samuel Johnson.
The American Dictionary of the English Languages
explanations
Journey, voyage, trip, tour, travel的用法区别
1. journey指从一地到另一地,通常指陆地上的远距离“旅行”,有时也可以表示经常走的或长或短的“路程”。只作名词。例如:
E.g. How long is your journey to school?
—Only about 10 minutes.
2. voyage主要指远距离的水上旅行,也可以指空中旅行意思为“航海、航空、航行”等。只作名词。例如:
E.g. She usually gets seasick during the voyage.
They made a voyage across the Pacific by air.
3. trip 一般指时间短、距离近的“旅行、远足”,也可以指长途旅行。在非正式用语中可代替journey。只作名词。例如:
E.g. We made a boat trip to the island last week
and had a good time.
4. tour 着重指旅行线路比较曲折,常表示“(周游各地的)参观、访问、(巡回)旅游、视察、购物、演出”等意思。可作动词和名词。例如:
E.g. I will tour the world in the future.
My father has gone down-town on a shopping tour .
5. travel作“旅行、游历”解,一般表示从一地到另一地旅行这一总的概念。常指长时间、远距离的“旅行”。尤指出国旅行。可作动词和名词。其复数形式意思为“旅游笔记”、“游记”。例如:
E.g.
At present, many people are fond of travel in
their spare time.
I am reading a book about the travel to North Pole.
They came home after years of foreign travel.
Light travels faster than sound.
1. Because of that, English began to be spoken in many countries.
because & because of :因为,由于
(1)Because you are concerned about me, I find that life is full of hope.
(2)Because of your concern, I find that life is full of hope.
因为你的关心,我发现生活充满了希望。
language points
(1)Because it rained heavily, the boy went back home through the woods.
(2)Because of the heavy rain, the boy went back home through the woods.
因为雨下得很大,那个男孩穿过树林回家了。
2. Actually, it was based more on German than present day English.
(1) Actually: 事实上,实际上 adv
(2) be…..based on:以…..为基础
扩充:
It is + adj+ of /for sb to do sth
当句式中形容词修饰to do sth 时用for;
若形容词修饰sb,则用of。
E.g. It’s kind of you to help me carry the box.
3.?…there is more than one kind of English in the
world.
more than one+单数可数名词,作主语时,谓语用单数。
4.?It is not easy for a Chinese person to speak English as well as a native English speaker.
对于一个中国人来说把英语说得跟以英语为母语的人一样好是不容易的。
句型:It is + adj / n+ for sb to do sth 对于某人来说做某事是…
It is difficult for him to walk so long in the rain.
对他而言,在雨中走了这么久是很不容易的。
Learning about Language
Words
1. official
n. 行政官员
The President and the Secretary of State are government officials.
总统和国务卿是政府官员。
adj. 公务的, 公职的, 职权的
His official duties kept him busy.
公务使他繁忙不堪。
官方的, 正式的, 官方认可的
They have got some official figures about the population.
他们得到一些关于人口的官方数字。
2. native
adj. 出生地的, 故乡的, 本国的
At the end of the year some people will go back to their native homes.
年终时, 有些人要回故乡去。
当地(人)的; 原产于某地的
The panda is native to West China.
熊猫产于中国西部。
天生的, 有天赋的
The ability to swim is native to fish.
鱼生来就会游泳。
n. 当地人, 本地人
Are you a native, or just a visitor?
你是本地人还是外来人?
3. frequent
adj. 时常发生的, 常见的
Research is also advanced by frequent conference to exchange experience.
经常开会交流经验也促进了研究工作的发展。
Traffic accidents are alarmingly frequent of late.
近来交通事故频繁得吓人。
vt 常到, 光顾, 常与…交往
He frequents the local restaurants.
他经常光顾当地的餐馆。
4. command
n. 命令
The general issued a command that all of them should come at six o’clock.
将军颁布了一道命令, 所有的人都要在六点钟到。
指挥, 控制
The army is under the king’s direct command.
军队由国王直接统帅。
掌握; 运用力, 控制力
He has a good command of French.
他的法文很好。
部队, 兵团; 指挥部
Do you know where’s the United Nations Command?
你知道联合国部队司令部在什么地方吗?
vi. 指挥; 控制
You have no right to command.
你没有权利指挥。
vt. 命令
He commanded that man go at once.
他命令那个人马上走。
掌握,支配
The captain of a ship commands all the officers and men.
舰长统率舰上的全体官兵。
Morphology
Actual
Gradual
Fluent
Frequent
official
Actually
Gradually
Fluently
Frequently
officially
形容词
副 词
develop
move
improve
Arrange
manage
development
Movement
improvement
Arrangement
Management
动词
名词
Expressions
1. come up
上来; 走近
While we were talking, a man came up.
我们正在谈话时, 一个人走了过来。
发生
I expect something to come up soon.
我预料很快就要出事的。
升起; 长出来; 响起, 刮起
The sky was dark blue and clear when the moon came up.
月亮出来时, 天空是深蓝色的, 非常晴朗。
开庭
An important witness was absent when the case came up.
开庭时, 有个重要的证人没有出席。
显露光泽, 开始发光
The silver has come up beautifully.
那银器显露出美丽的光泽。
提到, 提及
The project came up in their conversation.
他们在谈话中提到了这项工程。
2. play a part in在…中起作用
Women play a very important part in socialist
construction.?
妇女在社会主义建设中起着很重要的作
用。
In a play singing and acting play an important
part.?
在戏剧中唱和表演起很重要的作用。
3. make use of 使用,利用
We should make use of the chance.?
我们应该利用机会。
Waste material must is make full use of.?
废弃材料必须充分利用。
4. at present目前, 现在
That firm is looking for a new accountant.
At present the salary they will offer has been
left open.
那家公司正在物色一位新的会计, 工
资多少尚未确定。
He is all right at present.
现在他没事了。
5. because of 因为, 由于
It was because of the job that he had taken
the flat.
他因为工作的原因租了那套公寓。
She is here because of me.
她是因为我而到这里来的。
1. in/on
2. at/on
3. past/after
4. in/on
5. From/than
6. in/on
B. E : in A. E: on
B. E: at A. E: on
B. E: past A. E: after
B. E: in A. E: on
B. E: from A. E: than
B. E: in A. E: on
Do the exercise 4 on page 11 try to make a difference between the B.E and A.E.
Some English proverbs
All good things come to an end.
天下没有不散的筵席。
All rivers run into sea.
海纳百川。
All roads lead to Rome.
条条大路通罗马。
All that ends well is well.
结果好,就一切都好。
All that glitters is not gold.
闪光的不一定都是金子。
Structures
一、 表达命令的句型
1. Don’t +动词原+宾语+其他:不要做某事
2.主语+had better +宾语+其他:最好不要做某事
3. Don’t let +宾语+动词原形+其他:不要让某人(某物)做某事
4. Never +动词原形+其他:不要再做某事
5. Don’t be +表语:不要……
6. ask sb not to do 叫某人不要做某事
二、请求的句型
1. would you please...?
could you please...?
你能…吗?/你可以…吗?
2. Would you mind +动词原形:
如果不介意的话…..
3. How about +动名词+其他:
…..怎么样可以么?
4. Please +动词原形:请……
5. Would you like +动词原形:…..可以么?
请求与命令的转述方式
一、注意所使用的动词
英语常用的表示命令、请求和建议的动词有advise, ask, invite, order, remind, request, tell, warn等。
advise vt. 劝告;建议
My mother advised me to wear my best clothes.
我妈妈建议我穿上最好的衣服。
2. ask vt. 请求;邀请
I asked them to come to my house for dinner.
我请他们来我家吃饭。
3. invite vt. 邀请
Lisa invited us to come to her party.
Lisa邀请我们参加她的聚会。
4. order vt. 命令;指挥
They ordered him not to stop.
他们命令他不要停下。
5. remind vt. 使想起;提醒
Remind me to write to Mother.
请提醒我给妈妈写信。
6. request vt. 要求;请求
We request the visitors not to pick the flowers.
我们要求参观者不要摘花。
7. tell v.t.告诉;告诫;命令;警告
I told you not to do it. 我叫你不要做这个。
8. warn v.t. 警告;告诫(常与of连用) 指对于确实
的危险所作的警告,具有命令的意思。
She was warned not to come in the room.
她被警告不得进入那间屋子
由此可见,上述动词作谓语时有一个共同的特点,即都可以使用如下句型:
advise / ask / invite / order / remind / request / tell / warn sb. to do sth. 建议/要求/邀请某人做某事。如果是否定句,则在to前加not。在这个句型中,不定式作宾语补足语。
三、注意由直接引语变为间接引语句子的方法。
要注意直接说的话(称为直接引语)与转述的话(称为间接引语)在表达上是不一样的。由于表示的是命令、请求和建议,所以直接说的话多用祈使句式。
1. 肯定句的变法
Please read English in the morning, Jim, said
Miss Liu.
→ Miss Liu asked Jim to read English in the
morning.
2. 否定句的变法
Don't talk in class, Mr. Green warned me.
→Mr Green warned me not to talk in class.
The expressions that can express commands:
Correct your spelling mistakes
Go and…! Do that now!
Say that again!
Hold that again!
Take the dog for a walk!
The expressions that can express requests:
How do you spell that please?
Would you do that more slowly?
Please… would you please…?
Could you repeat that sentence?
Would you please speak more slowly?
Can I sit here and wait for the doctor?
1. The children said to their teacher: “would you please sing a song for us?”
2. The mother said to her child: “turn off the radio.”
3. The dentist said to a patient: “open your mouth please, so I can see the bad tooth clearly.”
4. The secretary said to the woman on the phone: “ could you hold on for a minute?”
5. John said to his classmate: “ can I borrow you pen please?”
6. The teacher said to his student: “come up to my office!”
The exercises for retelling direct speech to indirect speech.
1. The children asked their teacher to sing a song for them. (request)
2. The mother told her child to turn off the radio. (command)
3. The dentist asked his/her patient to open his/her mouth so that he/she could see the bad tooth clearly. (request)
4. The secretary asked the woman on the phone to hold on for a minute or two. (request)
Suggested answers for the exercises:
5. John asked his classmate if he could borrow his pen (request)
6. The teacher told his /her student to come up to his/her office. (command)
Suggested answers for the exercises:
Fast read the passage then answer:
Is there a standard of English?
Does the NJ of the TV speak a standard English?
Why are there so many kinds of English in the world?
How many kinds of English do you know?
Using Language
中国的汉语方言地图
Listening
Listen to the conversation and
answer the questions.
1. What does Buford think of Texas? How do you
know?
2. How large was the Catfish?
3. Why did Lester get out of the water so quickly?
4. Why did Bufford and Big Billy Bob laugh?
The suggested answers to these questions:
He believes it’s almost a different country from the USA. The listening text tells us.
The boys thought that the catfish was almost the size of a house.
He thought the catfish would eat him.
They laughed because Laster believed the catfish would hurt him.
After answering the questions, can you retell the little story? Do the exercise 3 on page 14, then retell the story.
subway=underground: 地下铁
corner=block:转角
Could you please….. : 委婉的请求
round =around
介词on:表示某事物位于另一事物所朝的方向,这里的方向指相对。
E.g. China faces the Pacific on the east.
Reading and Speaking
Writing
Please think about the two situations. Use the expressions have been given and try to make a dialogue with your partner. Pay attention the tone you’ve chosen.
Summing-up
重点词汇:
official voyage native actually base gradual identity frequent command request expression Spanish recognize straight block
重点短语:
make a request 请求
request that …(should) +v原形
in one direction 朝一个方向
be different from 与…不同
in the 1600’s = in the 1600s
give commands 命令
as a rule 通常;照例
be native to 是…的土产动物/植物
as we know 正如我们所知
an international language 一门国际语言??
an international organization 一个国际组织
play a role/ part (in) 在…中担任角色;
在…中起作用;扮演一个角色;参与
play an important role/ part 在…中起重要作用??
because of 因为;由于
话题:
English around the world
功能:
命令(asking)
请求(request)
语法:
请求与命令的句型和其转述
Exercises
1. Mr. Huang will ________ in the movement.
A. play a leading part B. take parts
C. play leading part D. take a part
2. We discussed where to go for a whole morning, but we decided to stay at home_____.
A. at the end B. by the end C. in the end D. on end
3. _____ of the students who took part in the military training is 450.
A. A number B. A lot C. Lots D. The number
A
C
D
一、单项选择
4. Sometimes ________ English is quite different from _______ English in many ways.
A. speaking, writing B. spoken, written
C. speaking, written D. spoken, writing
5. Can you tell me if you have found the key ________ your car.
A. for B. to C. about D. by
B
B
Water costs money. In some places water is hard 16 . What 17 when a town has these problems? A small town in California found a happy 18 . Very 19 rain ever fell there. The town had no water 20 . The water it used was 21 from a river 300 miles away. As more people 22 live in the town, 23 water was needed. Now water 24 to be brought in from 600 miles away. All these cost 25 money.
二、完形填空
The town 26 a plan. It found 27 to clean its “dirty” water. Once the cleaned water was reused 28 many ways. Five 29 lakes were built. Here people could swim and fish and go 30 . They 31 have picnics in their new parks. Farmers had more water 32 their crops. New factories can be built, now that they have the promise of 33 . In most places, water is used and thrown 34 . The town that saved 35 water has saved the town!
16. A. supplying B. getting C. to get D. to supply
17. A. happens B. happening C. is happened D. happened
18. A. key B. answer C. answering D. way
19. A. little B. a little C. few D. a few
20. A. of itself B. of its own C. for its own D. for itself
21. A. fetch B. take C. brought in D. guided
22. A. come to B. came to C. coming to D. came for
23. A. many B. plenty of C. more D. many more
24. A. has B. had C. must D. needed
25. A. many B. a few C. a great many D. a lot of
26. A. put B. made C. supply D. noticed
27. A. a way B. ways C. an answer D. a key
28. A. for B. by C. at D. in
29. A. man-making B. man-make
C. man-made D. man made
30. A. boating B. to boat C. to boating
D. on boating
31. A. must B. could C. needed D. had to
32. A. as B. with C. for D. to
33. A. water enough B. enough water
C. crops enough D. enough crops
34. A. off B. of C. away D. out of
35. A. it’s B. its C. one’s D. his
Answer: 16—20 C A B A B 21—25 C B C A D
26—30 B A D C A 31—35 B C B C B
bye bye
Small Quiz
(小游戏)
Lead-in
Let’s do a small quiz to distinguish the national flags of different countries, and find out the languages spoken in these countries.
English Around the World
the USA
Canada
New Zealand
Australia
South Africa
the United Kingdom
Ireland
India
Australia
Canada
India
Ireland
New Zealand
South Africa
The U.S.A.
Singapore
Great Britain
English around the World
unit 2
English language and its development.
different kinds of English
Learning Goals
Knowledge Goals
Topic
Words and Expressions
Words:
elevator official voyage native apartment actually base gradual
identity fluent frequent command request expression Spanish eastern
recognize accent straight block
in…ways 在…方面??? such as 例如
believe it or not 信不信由你 come up with 提出
come up to a place 参观某地 ever before 从前
even if/ though 即使 at the end of 在…末期be based on 在...基础上 close to 距离…近
change…into 把…变成 in the early days 在早期
take…with…随身携带 the same…as 与…相同的
at present 目前
Expressions:
Difficulties in language communication
Direct and Indirect Speech
Requests and Demands
Functional Items
Grammar
Enable to know more about the differences between various English.
Develop the ability of learning English through different ways, such as reading newspapers, magazines and books, surfing the Internet, etc.
Have a positive attitude towards different culture.
Understand more phrasal and idioms of different English.
Ability Goals
Emotion Goals
Try to get more information about different English.
The usage of direct and indirect speech .
Try to use the sentences that can express requests and demands .
Important and Difficult Points
Important Points
Try to understand the differences between native English and foreign cultures, as well as the backgrounds of different development of their cultures.
Try to develop the ability of speaking English.
Difficult Points
What’s the difference between
A.E and B.E?
Do you know VOA?
Do you know BBC?
(Voice of America)
(British Broadcasting Corporation)
A. E: American English
B. E: British English
Warming Up
笑话一则
A: Do you like moving pictures?
B: Well. Yeah. Why not?
A: Ok, follow me .
B: what?
A: Let’s go downstairs to move the pictures.
B: Oh, oh…….
Moving pictures: movies:美国的旧时用法
Some different words in A. E. and BE.
Am. English Br. English
elevator lift
fall autumn
first floor ground floor
candy sweet
check bill
apartment flat
subway underground railway
1. With your partner, list the countries that use English as an official language.
2. Which country do you think has the most English learners?
3. Look at the title of the following passage and guess what it is about. Then read it quickly and see if you are right.
Pre-reading
1. Fast read the passage then try to answer :
How does the modern English develop?
Why there are so many kinds of English?
2. Listen to the tape
Reading
3. Do the exercise 1 on page 10, then give the reason that the sentence is wrong?
1. English had the most speakers in the 17th century.
2. English developed when new settlers and rulers came to Britain
3. Languages frequently change.
4. The language of the government is always the language of the country.
(F)
(T)
(F)
(F)
Answer
1. Because after the 17th century, more people began to speak English as a result of English conquering other parts of the world.
3. Because languages don’t change often but only when people come into close contact.
4. Because the government has to use the language of the country to rule it.
5. English is one of the official languages used in
India.
6. This reading passage describes the development of English language.
(T)
(T)
The list of development of English
During the 5th century AD
Based on more German
Between about AD800and 1150
Like more Danish and French
By the 1600s
Shakespeare used a wider vocabulary than ever before
1620
British settlers moved to American in the “Mayflower”
From the 18th century
British colonized
Australia
1765-1947
English spoken in India
By the 19th century
Dictionaries standardized the spelling of English
Read the text for the third time
While reading work with your partners and make a map of the English spoken countries you’ve learned in the passage, if necessary you may refer to the message on the internet. Then answer the question 3 on page 10.
Why do many people speak English?
Inferred answer from the text:
England was strong and made voyages to conquer other parts of the world.
Britain ruled some countries and taught them English.
What other factors affected the use of
language?
international role
economic development
development of democracy
the image in the world
cultural development
From the above aspects try to answer the second question by yourself.
——The development of English
When Julius Caesar, later to be Roman Emperor, invaded Britain in BC 54-5, the “Celtic” tribes lived in the British Isles. Their Celtic languages still survive as “Gaelic” in Scotland & Ireland, “Welsh”, in Wales, and “Manx” in the Isle of Man, as well as “Breton” in France.
The Romans brought Latin to Britain, which was part of the Roman Empire for over 400 years. But early English did not develop mainly from Latin.
Background
In AD 878, the Vikings invaded Britain from Scandinavia, bringing with them the Norse language, though this was similar to the old English or Anglo-Saxon language already used.
The dramatic arrival of the Norman army from France, led by King William the Conqueror in 1066, and the defeat of the English King Harold at the Battle of Hastings, brought very big changes to English life. The Normans brought with them the Old French language, which
Background
became the language of the Royal Court, and the ruling and business class. So it is unlike French, Spanish and Italian, which did come directly from Latin. “Early English” was the language of tribes who invaded from the East, from what is now Germany. They spoke different dialects of a “Germanic” language, from which modern German developed. This explains why German and English are often similar, as many of their words developed from the same original language.
Background
Differences in vocabulary usage
go to the pictures go to the movies
underground subway
lift elevator
in a team on a team
rubber eraser
flat apartment
lorry truck
petrol gas
B.E
A.E
…
James A.H. murray
Noah Webster
Noah Webster
Samuel Johnson
The Introduction of James A.H. Murray
James Augustus Henry Murray (7 February 1837 – 26 July 1915) was a Scottish lexicographer and philologist. He was the primary editor of the Oxford English Dictionary from 1879 until his death. As a young man Murray worked as a schoolmaster and a bank clerk, but always maintained a strong interest in other fields, particularly philology. In 1879 he was invited by Oxford University Press to edit the new English dictionary which had been proposed by the Philological Society.
The Introduction of Noah Webster
Noah Webster (16 October, 1758 – 28 May, 1843) was an American lexicographer, textbook author, spelling reformer, word enthusiast, and editor. He has been called the “Father of American Scholarship and Education.” His “Blue-Backed Speller” books were used to teach spelling and reading to five generations of American children. In the United States, his name has become synonymous with dictionaries, especially the modern Merriam-Webster dictionary that was first published in 1828 as An American Dictionary of the English Language.
The Introduction of Samuel Johnson
Samuel Johnson (18 September 1709 ?– 13 December 1784), often referred to as Dr. Johnson, was an English author who made lasting contributions to English literature as a poet, essayist, moralist, novelist, literary critic, biographer, editor and lexicographer. Johnson was a devout Anglican and political conservative, and has been described as "arguably the most distinguished man of letters in English history". He is also the subject of "the most famous single work of biographical art in the whole of literature": James Boswell's Life of Samuel Johnson.
The American Dictionary of the English Languages
explanations
Journey, voyage, trip, tour, travel的用法区别
1. journey指从一地到另一地,通常指陆地上的远距离“旅行”,有时也可以表示经常走的或长或短的“路程”。只作名词。例如:
E.g. How long is your journey to school?
—Only about 10 minutes.
2. voyage主要指远距离的水上旅行,也可以指空中旅行意思为“航海、航空、航行”等。只作名词。例如:
E.g. She usually gets seasick during the voyage.
They made a voyage across the Pacific by air.
3. trip 一般指时间短、距离近的“旅行、远足”,也可以指长途旅行。在非正式用语中可代替journey。只作名词。例如:
E.g. We made a boat trip to the island last week
and had a good time.
4. tour 着重指旅行线路比较曲折,常表示“(周游各地的)参观、访问、(巡回)旅游、视察、购物、演出”等意思。可作动词和名词。例如:
E.g. I will tour the world in the future.
My father has gone down-town on a shopping tour .
5. travel作“旅行、游历”解,一般表示从一地到另一地旅行这一总的概念。常指长时间、远距离的“旅行”。尤指出国旅行。可作动词和名词。其复数形式意思为“旅游笔记”、“游记”。例如:
E.g.
At present, many people are fond of travel in
their spare time.
I am reading a book about the travel to North Pole.
They came home after years of foreign travel.
Light travels faster than sound.
1. Because of that, English began to be spoken in many countries.
because & because of :因为,由于
(1)Because you are concerned about me, I find that life is full of hope.
(2)Because of your concern, I find that life is full of hope.
因为你的关心,我发现生活充满了希望。
language points
(1)Because it rained heavily, the boy went back home through the woods.
(2)Because of the heavy rain, the boy went back home through the woods.
因为雨下得很大,那个男孩穿过树林回家了。
2. Actually, it was based more on German than present day English.
(1) Actually: 事实上,实际上 adv
(2) be…..based on:以…..为基础
扩充:
It is + adj+ of /for sb to do sth
当句式中形容词修饰to do sth 时用for;
若形容词修饰sb,则用of。
E.g. It’s kind of you to help me carry the box.
3.?…there is more than one kind of English in the
world.
more than one+单数可数名词,作主语时,谓语用单数。
4.?It is not easy for a Chinese person to speak English as well as a native English speaker.
对于一个中国人来说把英语说得跟以英语为母语的人一样好是不容易的。
句型:It is + adj / n+ for sb to do sth 对于某人来说做某事是…
It is difficult for him to walk so long in the rain.
对他而言,在雨中走了这么久是很不容易的。
Learning about Language
Words
1. official
n. 行政官员
The President and the Secretary of State are government officials.
总统和国务卿是政府官员。
adj. 公务的, 公职的, 职权的
His official duties kept him busy.
公务使他繁忙不堪。
官方的, 正式的, 官方认可的
They have got some official figures about the population.
他们得到一些关于人口的官方数字。
2. native
adj. 出生地的, 故乡的, 本国的
At the end of the year some people will go back to their native homes.
年终时, 有些人要回故乡去。
当地(人)的; 原产于某地的
The panda is native to West China.
熊猫产于中国西部。
天生的, 有天赋的
The ability to swim is native to fish.
鱼生来就会游泳。
n. 当地人, 本地人
Are you a native, or just a visitor?
你是本地人还是外来人?
3. frequent
adj. 时常发生的, 常见的
Research is also advanced by frequent conference to exchange experience.
经常开会交流经验也促进了研究工作的发展。
Traffic accidents are alarmingly frequent of late.
近来交通事故频繁得吓人。
vt 常到, 光顾, 常与…交往
He frequents the local restaurants.
他经常光顾当地的餐馆。
4. command
n. 命令
The general issued a command that all of them should come at six o’clock.
将军颁布了一道命令, 所有的人都要在六点钟到。
指挥, 控制
The army is under the king’s direct command.
军队由国王直接统帅。
掌握; 运用力, 控制力
He has a good command of French.
他的法文很好。
部队, 兵团; 指挥部
Do you know where’s the United Nations Command?
你知道联合国部队司令部在什么地方吗?
vi. 指挥; 控制
You have no right to command.
你没有权利指挥。
vt. 命令
He commanded that man go at once.
他命令那个人马上走。
掌握,支配
The captain of a ship commands all the officers and men.
舰长统率舰上的全体官兵。
Morphology
Actual
Gradual
Fluent
Frequent
official
Actually
Gradually
Fluently
Frequently
officially
形容词
副 词
develop
move
improve
Arrange
manage
development
Movement
improvement
Arrangement
Management
动词
名词
Expressions
1. come up
上来; 走近
While we were talking, a man came up.
我们正在谈话时, 一个人走了过来。
发生
I expect something to come up soon.
我预料很快就要出事的。
升起; 长出来; 响起, 刮起
The sky was dark blue and clear when the moon came up.
月亮出来时, 天空是深蓝色的, 非常晴朗。
开庭
An important witness was absent when the case came up.
开庭时, 有个重要的证人没有出席。
显露光泽, 开始发光
The silver has come up beautifully.
那银器显露出美丽的光泽。
提到, 提及
The project came up in their conversation.
他们在谈话中提到了这项工程。
2. play a part in在…中起作用
Women play a very important part in socialist
construction.?
妇女在社会主义建设中起着很重要的作
用。
In a play singing and acting play an important
part.?
在戏剧中唱和表演起很重要的作用。
3. make use of 使用,利用
We should make use of the chance.?
我们应该利用机会。
Waste material must is make full use of.?
废弃材料必须充分利用。
4. at present目前, 现在
That firm is looking for a new accountant.
At present the salary they will offer has been
left open.
那家公司正在物色一位新的会计, 工
资多少尚未确定。
He is all right at present.
现在他没事了。
5. because of 因为, 由于
It was because of the job that he had taken
the flat.
他因为工作的原因租了那套公寓。
She is here because of me.
她是因为我而到这里来的。
1. in/on
2. at/on
3. past/after
4. in/on
5. From/than
6. in/on
B. E : in A. E: on
B. E: at A. E: on
B. E: past A. E: after
B. E: in A. E: on
B. E: from A. E: than
B. E: in A. E: on
Do the exercise 4 on page 11 try to make a difference between the B.E and A.E.
Some English proverbs
All good things come to an end.
天下没有不散的筵席。
All rivers run into sea.
海纳百川。
All roads lead to Rome.
条条大路通罗马。
All that ends well is well.
结果好,就一切都好。
All that glitters is not gold.
闪光的不一定都是金子。
Structures
一、 表达命令的句型
1. Don’t +动词原+宾语+其他:不要做某事
2.主语+had better +宾语+其他:最好不要做某事
3. Don’t let +宾语+动词原形+其他:不要让某人(某物)做某事
4. Never +动词原形+其他:不要再做某事
5. Don’t be +表语:不要……
6. ask sb not to do 叫某人不要做某事
二、请求的句型
1. would you please...?
could you please...?
你能…吗?/你可以…吗?
2. Would you mind +动词原形:
如果不介意的话…..
3. How about +动名词+其他:
…..怎么样可以么?
4. Please +动词原形:请……
5. Would you like +动词原形:…..可以么?
请求与命令的转述方式
一、注意所使用的动词
英语常用的表示命令、请求和建议的动词有advise, ask, invite, order, remind, request, tell, warn等。
advise vt. 劝告;建议
My mother advised me to wear my best clothes.
我妈妈建议我穿上最好的衣服。
2. ask vt. 请求;邀请
I asked them to come to my house for dinner.
我请他们来我家吃饭。
3. invite vt. 邀请
Lisa invited us to come to her party.
Lisa邀请我们参加她的聚会。
4. order vt. 命令;指挥
They ordered him not to stop.
他们命令他不要停下。
5. remind vt. 使想起;提醒
Remind me to write to Mother.
请提醒我给妈妈写信。
6. request vt. 要求;请求
We request the visitors not to pick the flowers.
我们要求参观者不要摘花。
7. tell v.t.告诉;告诫;命令;警告
I told you not to do it. 我叫你不要做这个。
8. warn v.t. 警告;告诫(常与of连用) 指对于确实
的危险所作的警告,具有命令的意思。
She was warned not to come in the room.
她被警告不得进入那间屋子
由此可见,上述动词作谓语时有一个共同的特点,即都可以使用如下句型:
advise / ask / invite / order / remind / request / tell / warn sb. to do sth. 建议/要求/邀请某人做某事。如果是否定句,则在to前加not。在这个句型中,不定式作宾语补足语。
三、注意由直接引语变为间接引语句子的方法。
要注意直接说的话(称为直接引语)与转述的话(称为间接引语)在表达上是不一样的。由于表示的是命令、请求和建议,所以直接说的话多用祈使句式。
1. 肯定句的变法
Please read English in the morning, Jim, said
Miss Liu.
→ Miss Liu asked Jim to read English in the
morning.
2. 否定句的变法
Don't talk in class, Mr. Green warned me.
→Mr Green warned me not to talk in class.
The expressions that can express commands:
Correct your spelling mistakes
Go and…! Do that now!
Say that again!
Hold that again!
Take the dog for a walk!
The expressions that can express requests:
How do you spell that please?
Would you do that more slowly?
Please… would you please…?
Could you repeat that sentence?
Would you please speak more slowly?
Can I sit here and wait for the doctor?
1. The children said to their teacher: “would you please sing a song for us?”
2. The mother said to her child: “turn off the radio.”
3. The dentist said to a patient: “open your mouth please, so I can see the bad tooth clearly.”
4. The secretary said to the woman on the phone: “ could you hold on for a minute?”
5. John said to his classmate: “ can I borrow you pen please?”
6. The teacher said to his student: “come up to my office!”
The exercises for retelling direct speech to indirect speech.
1. The children asked their teacher to sing a song for them. (request)
2. The mother told her child to turn off the radio. (command)
3. The dentist asked his/her patient to open his/her mouth so that he/she could see the bad tooth clearly. (request)
4. The secretary asked the woman on the phone to hold on for a minute or two. (request)
Suggested answers for the exercises:
5. John asked his classmate if he could borrow his pen (request)
6. The teacher told his /her student to come up to his/her office. (command)
Suggested answers for the exercises:
Fast read the passage then answer:
Is there a standard of English?
Does the NJ of the TV speak a standard English?
Why are there so many kinds of English in the world?
How many kinds of English do you know?
Using Language
中国的汉语方言地图
Listening
Listen to the conversation and
answer the questions.
1. What does Buford think of Texas? How do you
know?
2. How large was the Catfish?
3. Why did Lester get out of the water so quickly?
4. Why did Bufford and Big Billy Bob laugh?
The suggested answers to these questions:
He believes it’s almost a different country from the USA. The listening text tells us.
The boys thought that the catfish was almost the size of a house.
He thought the catfish would eat him.
They laughed because Laster believed the catfish would hurt him.
After answering the questions, can you retell the little story? Do the exercise 3 on page 14, then retell the story.
subway=underground: 地下铁
corner=block:转角
Could you please….. : 委婉的请求
round =around
介词on:表示某事物位于另一事物所朝的方向,这里的方向指相对。
E.g. China faces the Pacific on the east.
Reading and Speaking
Writing
Please think about the two situations. Use the expressions have been given and try to make a dialogue with your partner. Pay attention the tone you’ve chosen.
Summing-up
重点词汇:
official voyage native actually base gradual identity frequent command request expression Spanish recognize straight block
重点短语:
make a request 请求
request that …(should) +v原形
in one direction 朝一个方向
be different from 与…不同
in the 1600’s = in the 1600s
give commands 命令
as a rule 通常;照例
be native to 是…的土产动物/植物
as we know 正如我们所知
an international language 一门国际语言??
an international organization 一个国际组织
play a role/ part (in) 在…中担任角色;
在…中起作用;扮演一个角色;参与
play an important role/ part 在…中起重要作用??
because of 因为;由于
话题:
English around the world
功能:
命令(asking)
请求(request)
语法:
请求与命令的句型和其转述
Exercises
1. Mr. Huang will ________ in the movement.
A. play a leading part B. take parts
C. play leading part D. take a part
2. We discussed where to go for a whole morning, but we decided to stay at home_____.
A. at the end B. by the end C. in the end D. on end
3. _____ of the students who took part in the military training is 450.
A. A number B. A lot C. Lots D. The number
A
C
D
一、单项选择
4. Sometimes ________ English is quite different from _______ English in many ways.
A. speaking, writing B. spoken, written
C. speaking, written D. spoken, writing
5. Can you tell me if you have found the key ________ your car.
A. for B. to C. about D. by
B
B
Water costs money. In some places water is hard 16 . What 17 when a town has these problems? A small town in California found a happy 18 . Very 19 rain ever fell there. The town had no water 20 . The water it used was 21 from a river 300 miles away. As more people 22 live in the town, 23 water was needed. Now water 24 to be brought in from 600 miles away. All these cost 25 money.
二、完形填空
The town 26 a plan. It found 27 to clean its “dirty” water. Once the cleaned water was reused 28 many ways. Five 29 lakes were built. Here people could swim and fish and go 30 . They 31 have picnics in their new parks. Farmers had more water 32 their crops. New factories can be built, now that they have the promise of 33 . In most places, water is used and thrown 34 . The town that saved 35 water has saved the town!
16. A. supplying B. getting C. to get D. to supply
17. A. happens B. happening C. is happened D. happened
18. A. key B. answer C. answering D. way
19. A. little B. a little C. few D. a few
20. A. of itself B. of its own C. for its own D. for itself
21. A. fetch B. take C. brought in D. guided
22. A. come to B. came to C. coming to D. came for
23. A. many B. plenty of C. more D. many more
24. A. has B. had C. must D. needed
25. A. many B. a few C. a great many D. a lot of
26. A. put B. made C. supply D. noticed
27. A. a way B. ways C. an answer D. a key
28. A. for B. by C. at D. in
29. A. man-making B. man-make
C. man-made D. man made
30. A. boating B. to boat C. to boating
D. on boating
31. A. must B. could C. needed D. had to
32. A. as B. with C. for D. to
33. A. water enough B. enough water
C. crops enough D. enough crops
34. A. off B. of C. away D. out of
35. A. it’s B. its C. one’s D. his
Answer: 16—20 C A B A B 21—25 C B C A D
26—30 B A D C A 31—35 B C B C B
bye bye
