高中英语 人教版 必修1 Unit 4 Earthquakes Reading 课件(38张)
文档属性
| 名称 | 高中英语 人教版 必修1 Unit 4 Earthquakes Reading 课件(38张) |

|
|
| 格式 | zip | ||
| 文件大小 | 1.5MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 人教版(新课程标准) | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2020-02-02 17:36:38 | ||
图片预览










文档简介
课件38张PPT。Unit 4
EarthquakesPeriod 2-3
ReadingA NIGHT THE EARTH DIDN'T SLEEP
Strange things were happening in the countryside of northeast Hebei. For three days the water in the village wells rose and fell, rose and fell. Farmers noticed that the well walls had deep cracks in them. A smelly gas came out of the cracks. In the farmyards, the chickens and even the pigs were too nervous to eat. Mice ran out of the fields looking for places to hide. Fish jumped out of their bowls and ponds. At about 3:00 am on July 28, 1976, some people saw bright lights in the sky. The sound of planes could be heard outside the city of Tangshan even when no planes were in the sky. In the city, the water pipes in some buildings cracked and burst. But the one million people of the city, who thought little of these events, were asleep as usual that night.
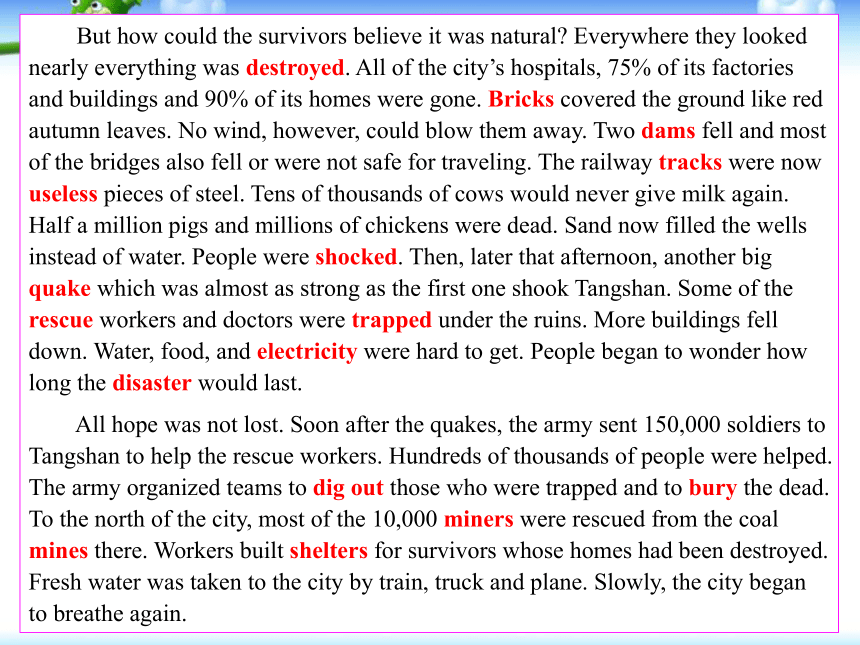
At 3:42 am everything began to shake. It seemed as if the world was at an end! Eleven kilometres directly below the city the greatest earthquake of the 20th century had begun. It was felt in Beijing, which is more than two hundred kilometres away. One-third of the nation felt it. A huge crack that was eight kilometres long and thirty metres wide cut across houses, roads and canals. Steam burst from holes in the ground. Hard hills of rock became rivers of dirt. In fifteen terrible seconds a large city lay in ruins. The suffering of the people was extreme. Two-thirds of them died or were left without parents. The number of people who were killed or injured reached more than 400,000. But how could the survivors believe it was natural? Everywhere they looked nearly everything was destroyed. All of the city’s hospitals, 75% of its factories and buildings and 90% of its homes were gone. Bricks covered the ground like red autumn leaves. No wind, however, could blow them away. Two dams fell and most of the bridges also fell or were not safe for traveling. The railway tracks were now useless pieces of steel. Tens of thousands of cows would never give milk again. Half a million pigs and millions of chickens were dead. Sand now filled the wells instead of water. People were shocked. Then, later that afternoon, another big quake which was almost as strong as the first one shook Tangshan. Some of the rescue workers and doctors were trapped under the ruins. More buildings fell down. Water, food, and electricity were hard to get. People began to wonder how long the disaster would last.
All hope was not lost. Soon after the quakes, the army sent 150,000 soldiers to Tangshan to help the rescue workers. Hundreds of thousands of people were helped. The army organized teams to dig out those who were trapped and to bury the dead. To the north of the city, most of the 10,000 miners were rescued from the coal mines there. Workers built shelters for survivors whose homes had been destroyed. Fresh water was taken to the city by train, truck and plane. Slowly, the city began to breathe again. 地球的一个不眠之夜
河北省东北部的农村不断有些怪事发生:三天来,村子里的井水升升降降,起起伏伏。农夫注意到,水井的井壁上有深深的裂缝,裂缝里冒出臭气。农家大院里的鸡, 甚至猪都紧张得不想吃食。老鼠从田地里跑出来找地方藏身。鱼缸和池塘里的鱼会往外跳。在1976年7月28日凌晨3点左右,有些人看到天上一道道明亮的光。即使天空没有飞机,在唐山城外也可以听到飞机声。在市内,有些建筑物里的水管爆裂开来。但是,唐山市的一百万居民几乎都没有把这些情况当一回事,当天晚上照常睡着了。
在凌晨3点42分,一切都开始摇晃起来。世界似乎到了末日!二十世纪最大的一次地震就在唐山市正下方11公里处发生了。200多公里以外的北京市都感到了地震,全国1 / 3的地方都有震感。一条8公里长30米宽的巨大裂缝横穿房舍、马路和渠道。地上一些洞穴冒出了蒸气。石头山变成了泥沙河,在可怕的15秒钟内,一座大城市就沉沦在一片废墟之中。人们遭受的灾难极为深重。2/3的人在地震中死去或受伤。成千上万个家庭遇难,许多孩子变成了孤儿。死伤的人数达到40多万。
幸存的人们又怎么能相信这是自然现象呢?人们无论朝哪里看,哪里的一切都几乎被毁了。所有的市内医院、75%的工厂和建筑物、90%的家园都消失了。残砖就像秋天的红叶覆盖着大地,然而它们是不可能被风刮走的。两座大坝垮了,多数桥梁不是塌了就是无法安全通行了。铁轨如今成了一条条废钢。好几万头牛再也挤不出奶来。50万头猪和几百万只鸡全都死了。井里满是沙子,而不是水。人们惊呆了。接着,在下午晚些时候,又一次和第一次一样的强烈的地震震撼着唐山。有些医生和救援人员被困在废墟下面。更多的房屋倒塌了。水、电和食物都很难弄到。人们开始纳闷,这场灾难还会持续多久。
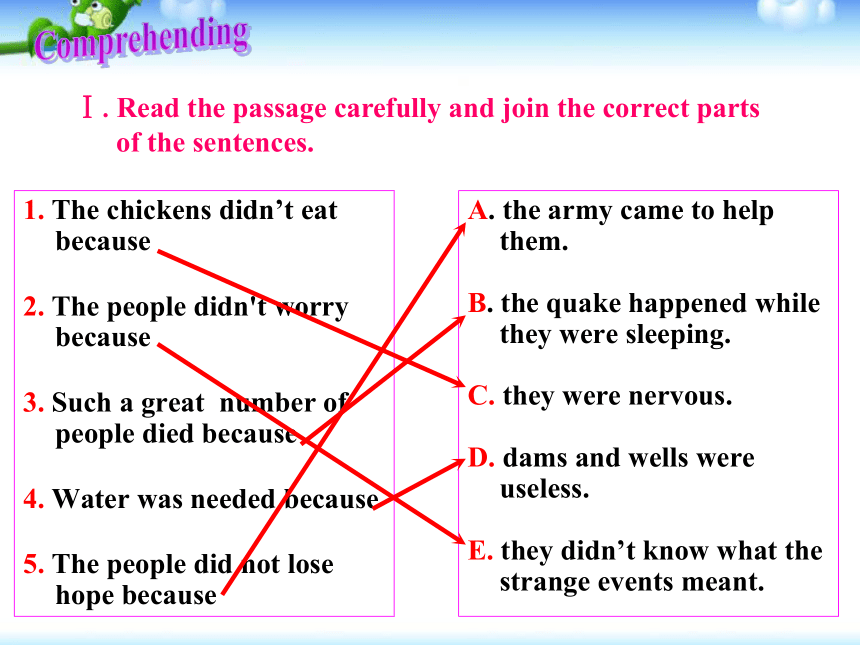
不是所有的希望都破灭了。地震后不久,部队派了15万名战士到唐山来协助救援人员,数十万的人得到了救助。部队人员组成小分队,将受困的人们挖出来,将死者掩埋。在唐山市的北边,有一个万名矿工的煤矿,其中多数人得救了。援救人员为那些家园被毁的幸存者盖起了避难所,用火车、卡车和飞机向市内运来了水。慢慢地,这座城市又开始出现了生机。Ⅰ.Read the passage carefully and join the correct parts
of the sentences.1. The chickens didn’t eat because
2. The people didn't worry because
3. Such a great number of people died because
4. Water was needed because
5. The people did not lose hope becauseA. the army came to help them.
B. the quake happened while they were sleeping.
C. they were nervous.
D. dams and wells were useless.
E. they didn’t know what the strange events meant.ComprehendingⅡ. Read the passage again and make a timetable.TIME
For three daysEVENTS
⒈ water in the village wells rose and fell
⒉ well walls developed deep cracks
⒊ a smelly gas came out of the cracks
⒋ mice ran out of the fields
⒌ fish jumped out of their bowls and pondsⅡ. Read the passage again and make a timetable.TIME
At about 3:00 am on July 28, 1976EVENTS
⒈ bright lights appeared in the sky
⒉ the sound of planes could be heard although there were no planes
⒊ some water pipes burstⅡ. Read the passage again and make a timetable.TIME
At 3:42 am on July 28, 1976EVENTS
⒈ everything began to shake
⒉ huge cracks appeared in the roads
⒊ steam burst from holes in the ground
⒋ rock turned into rivers of dirt
⒌ 75% of buildings and 90% of homes were gone
⒍ more than 400,000 people were killed or injuredⅡ. Read the passage again and make a timetable.TIME
Afternoon of July 28, 1976EVENTS
⒈ a second quake almost as strong as the first one
⒉ more damage to buildings and rescuersⅡ. Read the passage again and make a timetable.TIME
Soon after the quakeEVENTS
⒈ the army arrived
⒉ shelters built for survivors
⒊ water supplies brought inⅡ. Read the passage again and make a timetable.TIME
For three daysEVENTS
⒈ water in the village wells rose and fell
⒉ well walls developed deep cracks
⒊ a smelly gas come out of the cracks
⒋ mice ran out of the fields
⒌ fish jumped out of their bowls and ponds Ⅲ. Read the text quickly to find out which paragraph(s) the
following sentences are about.Para. 1
Para. 2
Para. 3
Para. 4A. The people were very shocked at the destruction.
B. The army came to help the survivors, bringing hope for a new life.
The earthquake destroyed the city of Tangshan.
Before the earthquake, strange things began to happen, but no one paid attention to them. Ⅳ. Sum up the main idea of each part of the passage. Part 1: Para 1
Part 2: Para 2&3
Part 3: Para 4Ⅴ. Choose the best answer according to the text.⒈ Before the earthquake people were asleep as usual because ___ .
A. they didn’t notice anything strange happening
B. they knew well about earthquakes
C. something strange happened in many places
D. they didn’t realize the arrival of an earthquake
⒉ When did the earthquake happen?
A. On the night of July 28th, 1976.
B. On the morning of July 28th, 1976.
C. On the afternoon of July 28th, 1976.
D. The writer didn’t tell us.
⒊ How many soldiers were sent to Tangshan to help the rescue workers?
A. 50,000. B. 10,000. C. 150,000. D. 200,000.⒋ Which is TRUE according to the passage?
A. People paid much attention to those strange things before the earthquake.
B. Before the earthquake animals became nervous.
C. After the earthquake water was needed because there was no water in dams
and wells.
D. After the earthquake the people in Tangshan lost all hope because they were
homeless.
⒌ What does the sentence “Slowly, the city began to breathe again.” mean?
A. The city will not die; it has hope and it can recover from the pain.
B. The army sent 150,000 soldiers to Tangshan to help people.
C. Hundreds of thousands of people were helped.
D. Most of the 10,000 miners were rescued.
⒍ What does the passage talk about?
A. It talks about an earthquake in Tangshan.
B. It talks about how to protect oneself when an earthquake happens.
C. It talks about how to rescue the injured people during the earthquake.
D. It talks about what to do when an earthquake happens.Details of each part What strange things happened before Tangshan Earthquake? rose and fell
deep cracks, smelly gas
too nervous to eat
ran out of, looking for places to hide
jumped out
bright lights
sound of planes heard even no planes
cracked and burstPart 1Data (数据) ____ of the nation felt the earthquake.
A huge crack that was __ kilometers long and metres wide
cut across houses.
In ___ terrible seconds a large city lay in ruins.
____ of the people died or were injured during the earthquake.
The number of people who were killed or injured reached
more than ________.
All of the city’s hospitals, _____ of its factories and buildings
and _____ of its homes were gone.1/3830152/3400,00075%90%Para. 2-3Part 2How did the army help the people in Tangshan?The army organized teams to dig out those who were trapped and to bury those who were dead.Miners were rescued from the coal mines.Shelters were built for survivors whose homes had been destroyed.Fresh water was taken to the city.☆☆☆☆Part 3After the earthquake An ___________ happened in Tangshan in 1976. For a few days, water in the wells ____________. Mice, chicken, pigs and even fish became ________. And the water pipes in the buildings cracked and ______. But the people in Tangshan _______________ these events.
At 3:42 am, everything began to ______. It seemed that the world was _________. A huge _____ cut across the houses and roads, then the city lay _______. Two-thirds of the people _____or were _______. Then later that afternoon, another big quake shook Tangshan. People began to wonder how long ___________________. But ________ was not lost. Soldiers came to help Tangshan people. Slowly, the city began to _______ again.rose and fellearthquakenervousburstthought little ofshakeat an endcrackin ruinsdiedinjuredthe disaster would lastall hopebreathe Retell the storyTangshan—in 1976Tangshan—nowTangshan’s new look★ Don’t be nervous and keep calm.
★ Don’t try to run out of the classroom.
★ Protect your head by putting your bag on your head.
★ Squat (蹲下)or sit down under your desk.
★ Leave the classroom after the earthquake.AttentionLife is so beautiful.
We must love our lives.
In an earthquake
SPEED IS LIFE.⒈ In the city, the water pipes in some buildings cracked and burst. 在市区里,有些楼房里的水管爆裂了。
① burst vi. (burst, burst) 爆裂;爆发 n. [C] 突然破裂;爆发
That balloon will burst if you blow it up any more. 你再给气球充气,它就会爆了。
a burst in the water pipe 水管爆裂
a sudden burst of anger 怒火的迸发
② burst into 突然发作
The sad story made the girl burst into tears. 那个悲惨的故事使那女孩突然放声大哭起来。Language Points⒉ In fifteen terrible seconds a large city lay in ruins. 在可怕的15秒钟内,一座大城市就沉沦在一片废墟之中。
① lie (lay, lain) vi. 躺;位于;处于……状态
I often lie there for reading. 我经常躺在那里看书。
China lies in the east of Asia. 中国位于亚洲的东部。
The farmland has lain waste for over two years. 那块耕地荒了两年多了。
② in ruins: badly destroyed or damaged 严重损坏,破败不堪
The city of Berlin was in ruins at the end of the war. 在战争结束时柏林变成了一片废墟。
Our plans lie in ruins. 我们的计划失败了。 ⒊ The number of people who were killed or injured reached more than 400,000.死伤的人数达到40多万。
① number n. 数量,数目,数字
The number of students is increasing. 学生的数量在增加。
The number of deaths has risen to fifty. 死亡的人数已上升到50人。
I need the exact number! 需要准确的数字!
注意:当the number of作主语时,相当于一个单数名词。
a number of : several 几个,一些
a great / large / good number of 许多,大量的(后接复数名词)
A number of people have left. 一些人已走了。
A large number of students have read the book. 许多学生读过这本书。
③ injure: vt. (尤指事故中)伤害
He fell off his bike and injured his left leg. 他从单车上摔下来,伤了左腿。
比较: harm / hurt / wound辨析:injure / harm / hurt / wound
① injure 一般指由于意外事故而受伤。
He had one leg injured in a car accident. 在一场车祸中他的一条腿受伤了。
② harm 多指精神上的伤害以及对健康、权利、事业等无形的伤害。
Don’t harm your eyes by reading in dim light. 不要在昏暗的灯光下看书,以免损害眼睛。
③ hurt 是一般用语,既可指肉体上的伤痛,也可指精神上的伤害,还可指对利益等造成损害或不良影响。如:
He hurt his back when he fell. 他跌倒时伤了后背。
I’m sorry I didn’t mean to hurt you. 对不起,我不是故意要伤害你的感情
④ wound 指外伤,多指枪伤、刀伤、剑伤等,尤指在战争或战斗中受伤。
The soldier was badly wounded in the head. 那位战士头部受了重伤。
运用用上面所提供的辨析词的适当形式填空:
① The man who ____________ his leg in a traffic accident is still in hospital.
② In the battle, hundreds of soldiers were ________ and some were even killed.
③ Reading in the sun will ______ your eyes.
④ How could you _____ her feeling?injured / hurt wounded harm hurt ⒋ Some of the rescue workers and doctors were trapped under the ruins. 有些医生和救援人员被困在废墟下面。
① rescue n.营救,救援 vt.营救,救援,使免遭损失
Rescue workers rushed to the site. 营救人员赶往雪崩地点。
Thanks for coming to my rescue. 谢谢你救了我。
They braved the storm to rescue their sheep. 他们冒著暴风雨抢救羊群。
② trap vt. 使陷入困境 n.困境,陷阱,圈套
20 miners were trapped underground. 20名矿工被困在矿井下。
I will not fall into his trap. 我不会落入他的圈套。⒌ People began to wonder how long the disaster would last. 人们开始纳闷,这场灾难还会持续多久。
① wonder vt.对……感到好奇;纳闷;感到诧异;想弄明白
I wonder why you were late again. 我想知道你为什么又迟到了。
I just wonder what that is. 我只是纳闷是怎么回事。
② last vi. 持续
The sports meet lasted three days. 运动会开了三天。
War of Resistance Against Japan lasted eight years. 抗日战争打了八年。
The rain lasted a week. 那场雨下了一个星期。⒍ The army organized teams to dig out those who were trapped and to bury the dead. 部队人员组成小分队,将受困的人们挖出来,将死者掩埋。
① dig out 发掘出,找出
We used to go to the fields to dig out eels and catch frogs in summer. 夏天我们经常去田野里掘出鳝鱼,捕捉青蛙。
We are expecting to dig out some important facts. 我们希望能找出一些重要的事实。
② bury vt. 埋葬,掩埋,隐蔽
They dug a pit to bury the rubbish. 他们挖了一个坑把垃圾埋掉.
She buried her face in the pillows. 她把脸埋进枕头里。⒈ But the one million people of the city, who thought little of these events, were asleep as usual that night. 但是,唐山市的一百万居民几乎都没有把这些情况当一回事,当天晚上照常睡着了。
① who thought little of these events 为非限制性定语从句,先行词是前面的“people”。非限制性定语从句与先行词的关系不够紧密,只起补充说明的作用,它的前后需要用逗号与主句分开。
It was felt in Beijing, which is more than two hundred kilometres away. 200多公里以外的北京都感到了地震。/北京离唐山有200多公里,也感到了地震。
② thought little of these events 没有把这些情况当一回事 / 对这些情况几乎没有考虑
类似的用法还有:
think nothing of it 认为没有什么
think much / a lot of … 对……印象很好
think highly of…对……评价很高
think badly of…对……评价很糟糕⒉ It seemed as if the world was at an end!仿佛到了世界末日!
点拨:本句是个复合句,含有一个 as if 引导的表语从句,其句型为“It looks / seems / sounds / feels as if...”。其中 it 本身无词义,常与 look, seem, feel, sound, smell 等连系动词连用。
① as if 常可以和 as though 互换,意为“仿佛;好像”。as if 引导的从句谓语动词常用虚拟语气,表示不真实或极少有可能发生或存在的情况:若表示与现在事实相反的主观设想,动词用过去式 (be 动词用 were,适用于各种人称);若表示与过去事实相反的主观设想,动词用“had+过去分词”形式。
He acts as if he were smoking. 他的举动好像在抽烟。(其实不是)
They talked as if they had been friends for years. 他们谈话的样子好像他们是多年的好朋友。(其实不是)
as if 引导的从句也可用陈述语气,表示说话者认为陈述的事情是真实的或极可能发生或存在的。
It sounds as if someone is coming. 听起来似乎有人来了。(很可能存在)
② at an end 结束,终止,终结
at the end of 在终点;在...的末了;在...的结尾;到...的尽头;到...的极限⒊ One-third of the nation felt it. 全国三分之一的地方都有震感。
点拨:句子的主语用了分数表示法。英语中的分数表示规则为:分子用基数词,分母用序数词,当分子大于 1 时,分母序数词词尾要加-s,分子和分母中间可以用连字符,也可不用。
三分之一——one third 或 one-third 或 a third
三分之二——two thirds 或 two-thirds
拓展:当分数作句子主语时,谓语的单复数由分数后面名词的单复数来决定。
One third of the apple has rotted. 这个苹果的三分之一烂了。
One third of the apples have rotted. 这些苹果中三分之一烂了。
Three fifths of the students in our class are from the countryside.
Three fifths of the work has been finished already.⒋ Everywhere they looked nearly everything was destroyed. 人们无论朝哪里看,哪里的一切都几乎被毁了。
点拨:everywhere 作从属连词,引导地点状语从句,相当于 wherever 或 no matter where。
Everywhere / Wherever / No matter where he goes, he gets warm welcome. 无论他走到哪里都受到热烈的欢迎。
拓展:every time, each time, the moment, anywhere 也可作连词引导状语从句。
Each time I saw him, I thought of his poor brother. 每次看见他,我就想起了他可怜的弟弟。⒌ All hope was not lost. 并非所有的希望都破灭了。
点拨:该句使用了部分否定的句子结构。部分否定是由表示 “ 全 体 ” 意 义 的 代 词 、 副 词 或 形 容 词 all, both, every, everybody, always 等和否定副词 not 连用构成的。
Everyone doesn’t like the story.=Not everyone likes the story. 非每个人都喜欢这个故事。
Both of the students don't like the story. 并非这两个学生都喜欢这个故事。
拓展:如要对上述的 all, both, every, always 等词作完全否定,那就分别要用与之相对应的全否定词,如 no, none, neither, no one, never, not (never)...at all 等。
All of them can do it. 他们每个人都能做这件事。
None of them can do it. 没有一个人能做这件事。
He is often late. 他经常迟到。
He is never late. 他从不迟到。Homework⒈ Find more news reports about earthquake.
⒉ Write a piece of news about Tangshan using the information in the passage.
⒊ Discover some useful expressions and structures.
ReadingA NIGHT THE EARTH DIDN'T SLEEP
Strange things were happening in the countryside of northeast Hebei. For three days the water in the village wells rose and fell, rose and fell. Farmers noticed that the well walls had deep cracks in them. A smelly gas came out of the cracks. In the farmyards, the chickens and even the pigs were too nervous to eat. Mice ran out of the fields looking for places to hide. Fish jumped out of their bowls and ponds. At about 3:00 am on July 28, 1976, some people saw bright lights in the sky. The sound of planes could be heard outside the city of Tangshan even when no planes were in the sky. In the city, the water pipes in some buildings cracked and burst. But the one million people of the city, who thought little of these events, were asleep as usual that night.
At 3:42 am everything began to shake. It seemed as if the world was at an end! Eleven kilometres directly below the city the greatest earthquake of the 20th century had begun. It was felt in Beijing, which is more than two hundred kilometres away. One-third of the nation felt it. A huge crack that was eight kilometres long and thirty metres wide cut across houses, roads and canals. Steam burst from holes in the ground. Hard hills of rock became rivers of dirt. In fifteen terrible seconds a large city lay in ruins. The suffering of the people was extreme. Two-thirds of them died or were left without parents. The number of people who were killed or injured reached more than 400,000. But how could the survivors believe it was natural? Everywhere they looked nearly everything was destroyed. All of the city’s hospitals, 75% of its factories and buildings and 90% of its homes were gone. Bricks covered the ground like red autumn leaves. No wind, however, could blow them away. Two dams fell and most of the bridges also fell or were not safe for traveling. The railway tracks were now useless pieces of steel. Tens of thousands of cows would never give milk again. Half a million pigs and millions of chickens were dead. Sand now filled the wells instead of water. People were shocked. Then, later that afternoon, another big quake which was almost as strong as the first one shook Tangshan. Some of the rescue workers and doctors were trapped under the ruins. More buildings fell down. Water, food, and electricity were hard to get. People began to wonder how long the disaster would last.
All hope was not lost. Soon after the quakes, the army sent 150,000 soldiers to Tangshan to help the rescue workers. Hundreds of thousands of people were helped. The army organized teams to dig out those who were trapped and to bury the dead. To the north of the city, most of the 10,000 miners were rescued from the coal mines there. Workers built shelters for survivors whose homes had been destroyed. Fresh water was taken to the city by train, truck and plane. Slowly, the city began to breathe again. 地球的一个不眠之夜
河北省东北部的农村不断有些怪事发生:三天来,村子里的井水升升降降,起起伏伏。农夫注意到,水井的井壁上有深深的裂缝,裂缝里冒出臭气。农家大院里的鸡, 甚至猪都紧张得不想吃食。老鼠从田地里跑出来找地方藏身。鱼缸和池塘里的鱼会往外跳。在1976年7月28日凌晨3点左右,有些人看到天上一道道明亮的光。即使天空没有飞机,在唐山城外也可以听到飞机声。在市内,有些建筑物里的水管爆裂开来。但是,唐山市的一百万居民几乎都没有把这些情况当一回事,当天晚上照常睡着了。
在凌晨3点42分,一切都开始摇晃起来。世界似乎到了末日!二十世纪最大的一次地震就在唐山市正下方11公里处发生了。200多公里以外的北京市都感到了地震,全国1 / 3的地方都有震感。一条8公里长30米宽的巨大裂缝横穿房舍、马路和渠道。地上一些洞穴冒出了蒸气。石头山变成了泥沙河,在可怕的15秒钟内,一座大城市就沉沦在一片废墟之中。人们遭受的灾难极为深重。2/3的人在地震中死去或受伤。成千上万个家庭遇难,许多孩子变成了孤儿。死伤的人数达到40多万。
幸存的人们又怎么能相信这是自然现象呢?人们无论朝哪里看,哪里的一切都几乎被毁了。所有的市内医院、75%的工厂和建筑物、90%的家园都消失了。残砖就像秋天的红叶覆盖着大地,然而它们是不可能被风刮走的。两座大坝垮了,多数桥梁不是塌了就是无法安全通行了。铁轨如今成了一条条废钢。好几万头牛再也挤不出奶来。50万头猪和几百万只鸡全都死了。井里满是沙子,而不是水。人们惊呆了。接着,在下午晚些时候,又一次和第一次一样的强烈的地震震撼着唐山。有些医生和救援人员被困在废墟下面。更多的房屋倒塌了。水、电和食物都很难弄到。人们开始纳闷,这场灾难还会持续多久。
不是所有的希望都破灭了。地震后不久,部队派了15万名战士到唐山来协助救援人员,数十万的人得到了救助。部队人员组成小分队,将受困的人们挖出来,将死者掩埋。在唐山市的北边,有一个万名矿工的煤矿,其中多数人得救了。援救人员为那些家园被毁的幸存者盖起了避难所,用火车、卡车和飞机向市内运来了水。慢慢地,这座城市又开始出现了生机。Ⅰ.Read the passage carefully and join the correct parts
of the sentences.1. The chickens didn’t eat because
2. The people didn't worry because
3. Such a great number of people died because
4. Water was needed because
5. The people did not lose hope becauseA. the army came to help them.
B. the quake happened while they were sleeping.
C. they were nervous.
D. dams and wells were useless.
E. they didn’t know what the strange events meant.ComprehendingⅡ. Read the passage again and make a timetable.TIME
For three daysEVENTS
⒈ water in the village wells rose and fell
⒉ well walls developed deep cracks
⒊ a smelly gas came out of the cracks
⒋ mice ran out of the fields
⒌ fish jumped out of their bowls and pondsⅡ. Read the passage again and make a timetable.TIME
At about 3:00 am on July 28, 1976EVENTS
⒈ bright lights appeared in the sky
⒉ the sound of planes could be heard although there were no planes
⒊ some water pipes burstⅡ. Read the passage again and make a timetable.TIME
At 3:42 am on July 28, 1976EVENTS
⒈ everything began to shake
⒉ huge cracks appeared in the roads
⒊ steam burst from holes in the ground
⒋ rock turned into rivers of dirt
⒌ 75% of buildings and 90% of homes were gone
⒍ more than 400,000 people were killed or injuredⅡ. Read the passage again and make a timetable.TIME
Afternoon of July 28, 1976EVENTS
⒈ a second quake almost as strong as the first one
⒉ more damage to buildings and rescuersⅡ. Read the passage again and make a timetable.TIME
Soon after the quakeEVENTS
⒈ the army arrived
⒉ shelters built for survivors
⒊ water supplies brought inⅡ. Read the passage again and make a timetable.TIME
For three daysEVENTS
⒈ water in the village wells rose and fell
⒉ well walls developed deep cracks
⒊ a smelly gas come out of the cracks
⒋ mice ran out of the fields
⒌ fish jumped out of their bowls and ponds Ⅲ. Read the text quickly to find out which paragraph(s) the
following sentences are about.Para. 1
Para. 2
Para. 3
Para. 4A. The people were very shocked at the destruction.
B. The army came to help the survivors, bringing hope for a new life.
The earthquake destroyed the city of Tangshan.
Before the earthquake, strange things began to happen, but no one paid attention to them. Ⅳ. Sum up the main idea of each part of the passage. Part 1: Para 1
Part 2: Para 2&3
Part 3: Para 4Ⅴ. Choose the best answer according to the text.⒈ Before the earthquake people were asleep as usual because ___ .
A. they didn’t notice anything strange happening
B. they knew well about earthquakes
C. something strange happened in many places
D. they didn’t realize the arrival of an earthquake
⒉ When did the earthquake happen?
A. On the night of July 28th, 1976.
B. On the morning of July 28th, 1976.
C. On the afternoon of July 28th, 1976.
D. The writer didn’t tell us.
⒊ How many soldiers were sent to Tangshan to help the rescue workers?
A. 50,000. B. 10,000. C. 150,000. D. 200,000.⒋ Which is TRUE according to the passage?
A. People paid much attention to those strange things before the earthquake.
B. Before the earthquake animals became nervous.
C. After the earthquake water was needed because there was no water in dams
and wells.
D. After the earthquake the people in Tangshan lost all hope because they were
homeless.
⒌ What does the sentence “Slowly, the city began to breathe again.” mean?
A. The city will not die; it has hope and it can recover from the pain.
B. The army sent 150,000 soldiers to Tangshan to help people.
C. Hundreds of thousands of people were helped.
D. Most of the 10,000 miners were rescued.
⒍ What does the passage talk about?
A. It talks about an earthquake in Tangshan.
B. It talks about how to protect oneself when an earthquake happens.
C. It talks about how to rescue the injured people during the earthquake.
D. It talks about what to do when an earthquake happens.Details of each part What strange things happened before Tangshan Earthquake? rose and fell
deep cracks, smelly gas
too nervous to eat
ran out of, looking for places to hide
jumped out
bright lights
sound of planes heard even no planes
cracked and burstPart 1Data (数据) ____ of the nation felt the earthquake.
A huge crack that was __ kilometers long and metres wide
cut across houses.
In ___ terrible seconds a large city lay in ruins.
____ of the people died or were injured during the earthquake.
The number of people who were killed or injured reached
more than ________.
All of the city’s hospitals, _____ of its factories and buildings
and _____ of its homes were gone.1/3830152/3400,00075%90%Para. 2-3Part 2How did the army help the people in Tangshan?The army organized teams to dig out those who were trapped and to bury those who were dead.Miners were rescued from the coal mines.Shelters were built for survivors whose homes had been destroyed.Fresh water was taken to the city.☆☆☆☆Part 3After the earthquake An ___________ happened in Tangshan in 1976. For a few days, water in the wells ____________. Mice, chicken, pigs and even fish became ________. And the water pipes in the buildings cracked and ______. But the people in Tangshan _______________ these events.
At 3:42 am, everything began to ______. It seemed that the world was _________. A huge _____ cut across the houses and roads, then the city lay _______. Two-thirds of the people _____or were _______. Then later that afternoon, another big quake shook Tangshan. People began to wonder how long ___________________. But ________ was not lost. Soldiers came to help Tangshan people. Slowly, the city began to _______ again.rose and fellearthquakenervousburstthought little ofshakeat an endcrackin ruinsdiedinjuredthe disaster would lastall hopebreathe Retell the storyTangshan—in 1976Tangshan—nowTangshan’s new look★ Don’t be nervous and keep calm.
★ Don’t try to run out of the classroom.
★ Protect your head by putting your bag on your head.
★ Squat (蹲下)or sit down under your desk.
★ Leave the classroom after the earthquake.AttentionLife is so beautiful.
We must love our lives.
In an earthquake
SPEED IS LIFE.⒈ In the city, the water pipes in some buildings cracked and burst. 在市区里,有些楼房里的水管爆裂了。
① burst vi. (burst, burst) 爆裂;爆发 n. [C] 突然破裂;爆发
That balloon will burst if you blow it up any more. 你再给气球充气,它就会爆了。
a burst in the water pipe 水管爆裂
a sudden burst of anger 怒火的迸发
② burst into 突然发作
The sad story made the girl burst into tears. 那个悲惨的故事使那女孩突然放声大哭起来。Language Points⒉ In fifteen terrible seconds a large city lay in ruins. 在可怕的15秒钟内,一座大城市就沉沦在一片废墟之中。
① lie (lay, lain) vi. 躺;位于;处于……状态
I often lie there for reading. 我经常躺在那里看书。
China lies in the east of Asia. 中国位于亚洲的东部。
The farmland has lain waste for over two years. 那块耕地荒了两年多了。
② in ruins: badly destroyed or damaged 严重损坏,破败不堪
The city of Berlin was in ruins at the end of the war. 在战争结束时柏林变成了一片废墟。
Our plans lie in ruins. 我们的计划失败了。 ⒊ The number of people who were killed or injured reached more than 400,000.死伤的人数达到40多万。
① number n. 数量,数目,数字
The number of students is increasing. 学生的数量在增加。
The number of deaths has risen to fifty. 死亡的人数已上升到50人。
I need the exact number! 需要准确的数字!
注意:当the number of作主语时,相当于一个单数名词。
a number of : several 几个,一些
a great / large / good number of 许多,大量的(后接复数名词)
A number of people have left. 一些人已走了。
A large number of students have read the book. 许多学生读过这本书。
③ injure: vt. (尤指事故中)伤害
He fell off his bike and injured his left leg. 他从单车上摔下来,伤了左腿。
比较: harm / hurt / wound辨析:injure / harm / hurt / wound
① injure 一般指由于意外事故而受伤。
He had one leg injured in a car accident. 在一场车祸中他的一条腿受伤了。
② harm 多指精神上的伤害以及对健康、权利、事业等无形的伤害。
Don’t harm your eyes by reading in dim light. 不要在昏暗的灯光下看书,以免损害眼睛。
③ hurt 是一般用语,既可指肉体上的伤痛,也可指精神上的伤害,还可指对利益等造成损害或不良影响。如:
He hurt his back when he fell. 他跌倒时伤了后背。
I’m sorry I didn’t mean to hurt you. 对不起,我不是故意要伤害你的感情
④ wound 指外伤,多指枪伤、刀伤、剑伤等,尤指在战争或战斗中受伤。
The soldier was badly wounded in the head. 那位战士头部受了重伤。
运用用上面所提供的辨析词的适当形式填空:
① The man who ____________ his leg in a traffic accident is still in hospital.
② In the battle, hundreds of soldiers were ________ and some were even killed.
③ Reading in the sun will ______ your eyes.
④ How could you _____ her feeling?injured / hurt wounded harm hurt ⒋ Some of the rescue workers and doctors were trapped under the ruins. 有些医生和救援人员被困在废墟下面。
① rescue n.营救,救援 vt.营救,救援,使免遭损失
Rescue workers rushed to the site. 营救人员赶往雪崩地点。
Thanks for coming to my rescue. 谢谢你救了我。
They braved the storm to rescue their sheep. 他们冒著暴风雨抢救羊群。
② trap vt. 使陷入困境 n.困境,陷阱,圈套
20 miners were trapped underground. 20名矿工被困在矿井下。
I will not fall into his trap. 我不会落入他的圈套。⒌ People began to wonder how long the disaster would last. 人们开始纳闷,这场灾难还会持续多久。
① wonder vt.对……感到好奇;纳闷;感到诧异;想弄明白
I wonder why you were late again. 我想知道你为什么又迟到了。
I just wonder what that is. 我只是纳闷是怎么回事。
② last vi. 持续
The sports meet lasted three days. 运动会开了三天。
War of Resistance Against Japan lasted eight years. 抗日战争打了八年。
The rain lasted a week. 那场雨下了一个星期。⒍ The army organized teams to dig out those who were trapped and to bury the dead. 部队人员组成小分队,将受困的人们挖出来,将死者掩埋。
① dig out 发掘出,找出
We used to go to the fields to dig out eels and catch frogs in summer. 夏天我们经常去田野里掘出鳝鱼,捕捉青蛙。
We are expecting to dig out some important facts. 我们希望能找出一些重要的事实。
② bury vt. 埋葬,掩埋,隐蔽
They dug a pit to bury the rubbish. 他们挖了一个坑把垃圾埋掉.
She buried her face in the pillows. 她把脸埋进枕头里。⒈ But the one million people of the city, who thought little of these events, were asleep as usual that night. 但是,唐山市的一百万居民几乎都没有把这些情况当一回事,当天晚上照常睡着了。
① who thought little of these events 为非限制性定语从句,先行词是前面的“people”。非限制性定语从句与先行词的关系不够紧密,只起补充说明的作用,它的前后需要用逗号与主句分开。
It was felt in Beijing, which is more than two hundred kilometres away. 200多公里以外的北京都感到了地震。/北京离唐山有200多公里,也感到了地震。
② thought little of these events 没有把这些情况当一回事 / 对这些情况几乎没有考虑
类似的用法还有:
think nothing of it 认为没有什么
think much / a lot of … 对……印象很好
think highly of…对……评价很高
think badly of…对……评价很糟糕⒉ It seemed as if the world was at an end!仿佛到了世界末日!
点拨:本句是个复合句,含有一个 as if 引导的表语从句,其句型为“It looks / seems / sounds / feels as if...”。其中 it 本身无词义,常与 look, seem, feel, sound, smell 等连系动词连用。
① as if 常可以和 as though 互换,意为“仿佛;好像”。as if 引导的从句谓语动词常用虚拟语气,表示不真实或极少有可能发生或存在的情况:若表示与现在事实相反的主观设想,动词用过去式 (be 动词用 were,适用于各种人称);若表示与过去事实相反的主观设想,动词用“had+过去分词”形式。
He acts as if he were smoking. 他的举动好像在抽烟。(其实不是)
They talked as if they had been friends for years. 他们谈话的样子好像他们是多年的好朋友。(其实不是)
as if 引导的从句也可用陈述语气,表示说话者认为陈述的事情是真实的或极可能发生或存在的。
It sounds as if someone is coming. 听起来似乎有人来了。(很可能存在)
② at an end 结束,终止,终结
at the end of 在终点;在...的末了;在...的结尾;到...的尽头;到...的极限⒊ One-third of the nation felt it. 全国三分之一的地方都有震感。
点拨:句子的主语用了分数表示法。英语中的分数表示规则为:分子用基数词,分母用序数词,当分子大于 1 时,分母序数词词尾要加-s,分子和分母中间可以用连字符,也可不用。
三分之一——one third 或 one-third 或 a third
三分之二——two thirds 或 two-thirds
拓展:当分数作句子主语时,谓语的单复数由分数后面名词的单复数来决定。
One third of the apple has rotted. 这个苹果的三分之一烂了。
One third of the apples have rotted. 这些苹果中三分之一烂了。
Three fifths of the students in our class are from the countryside.
Three fifths of the work has been finished already.⒋ Everywhere they looked nearly everything was destroyed. 人们无论朝哪里看,哪里的一切都几乎被毁了。
点拨:everywhere 作从属连词,引导地点状语从句,相当于 wherever 或 no matter where。
Everywhere / Wherever / No matter where he goes, he gets warm welcome. 无论他走到哪里都受到热烈的欢迎。
拓展:every time, each time, the moment, anywhere 也可作连词引导状语从句。
Each time I saw him, I thought of his poor brother. 每次看见他,我就想起了他可怜的弟弟。⒌ All hope was not lost. 并非所有的希望都破灭了。
点拨:该句使用了部分否定的句子结构。部分否定是由表示 “ 全 体 ” 意 义 的 代 词 、 副 词 或 形 容 词 all, both, every, everybody, always 等和否定副词 not 连用构成的。
Everyone doesn’t like the story.=Not everyone likes the story. 非每个人都喜欢这个故事。
Both of the students don't like the story. 并非这两个学生都喜欢这个故事。
拓展:如要对上述的 all, both, every, always 等词作完全否定,那就分别要用与之相对应的全否定词,如 no, none, neither, no one, never, not (never)...at all 等。
All of them can do it. 他们每个人都能做这件事。
None of them can do it. 没有一个人能做这件事。
He is often late. 他经常迟到。
He is never late. 他从不迟到。Homework⒈ Find more news reports about earthquake.
⒉ Write a piece of news about Tangshan using the information in the passage.
⒊ Discover some useful expressions and structures.
