Unit 4 Public transport Reading(1):The first underground in the world 课件(30张PPT)
文档属性
| 名称 | Unit 4 Public transport Reading(1):The first underground in the world 课件(30张PPT) |

|
|
| 格式 | zip | ||
| 文件大小 | 1.3MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 牛津译林版 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2020-02-28 00:00:00 | ||
图片预览











文档简介
(共30张PPT)
Reading (1 ):get the general idea of the passage
Can you explain the word “transport”?
Transport is a system built to carry people or goods to another place using vehicles, boats or airplanes.
Brainstorming
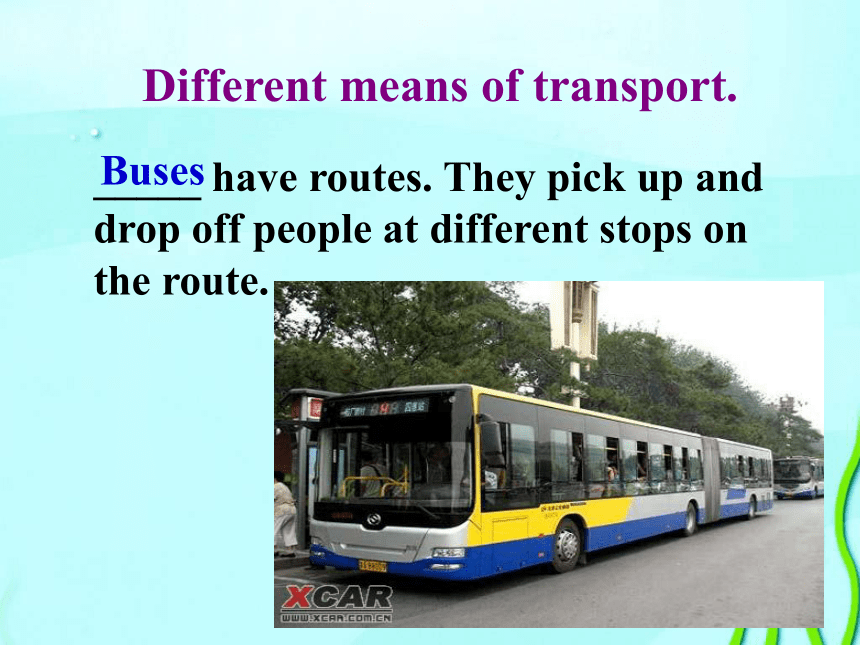
Different means of transport.
_____ have routes. They pick up and drop off people at different stops on the route.
Buses
_____ are a comfortable way to travel from place to place.
Ships
_______ are buses that carry people over long distances.
Coaches
__________ are used for rapid travel over long distances.
Airplanes
________________ run much faster than normal trains.
High-speed trains
________________ has become popular in crowded cities.
The underground
Reading 1
Preparation for reading
1. n. (常规) 路线
2. vt. 运送,输送;表达
3. prep. 经由,经过(某一地
方);通过,凭借
4. vt. 延迟,延期
5. n. 间隔,间隙
6. v. 承担,从事;承诺,答应
7. v. 扩大,扩展,增大
8. n. 少量的人或物;一把(的量)
convey
route
via
postpone
undertake
enlarge
handful
interval
(一) 基本单词
9. vi.& vt. 分割,(使)分开;撕开,
割破
10. adj. 每年的,一年一次的
11. n. 离开,出发;背离,违反
12. vi. 出现,产生
13. n.&v. 撞车;碰撞;倒闭;崩溃
14. vt. 处以罚金
15. adj. 喝醉的
n. 醉汉,酒鬼
16. n. 负荷,负载;大量,许多
vt. 装载,装上,装入
split
annual
departure
arise
load
crash
fine
drunk
1. 中途下客或卸货
2. 联合,连接
3. 每隔……距离或时间
4. 给某人接通(电话);
使经历
5. 决定,选定
6. 推迟,推延;使反感
7. 出现,到来;调高
(音量等)
drop off
link up
at (...) intervals
put through
decide on/upon
put off
turn up
8. 填写(表格);消磨(时间)
9. 少数的,少量的
10. 分组,分解;分离
11. (使)加速
12. 起因于,由……引起
13. 堵车,交通堵塞
fill in
a handful of
split up
speed up
arise from
traffic jam
Skimming
Skim the text and find the general idea of the passage.
This article is a tourist brochure about how the London Underground developed.
When was the first underground system opened?
Who first linked some of the different lines?
3. What did Charles Holden do?
In 1863.
Charles Yerkes.
He designed the most famous of the new stations constructed between 1918 and 1938.
What information did you get about the London Underground from the text?
reasons
development
unusual functions/uses
expansion & popularity
Structure analyzing
Paragraph 1
Paragraphs 2-3
Paragraphs 4
Paragraph 5-6
Part Paragraphs
Part 1
Part 2
Part 3
Part 4
The main ideas of the four parts
Part 1
Reasons why the first underground in the world was developed.
Part 2
Developments of the first underground.
Part 3
Some unusual uses of the first underground during World WarⅡ.
Part 4
Expansion and popularity of the first underground system.
Underline the time clues in the text quickly. Remember the details of each time clue as quickly as you can.
Scanning
An underground railway was approved to be built by the British government.
The first tunnels were opened.
The next section of the underground system was opened in the south of London.
Development of the LU system.
Date Event
1854
1863
1868
Two companies linked up to provide underground service in the middle of the city. The first railway tunnel under the River Thames was dug.
The first electric underground railway was opened.
The London Passenger Transport Board was created.
Many new stations were constructed.
The Jubilee Line was opened.
Date Event
1884
1890
1933
1918-1938
1979
1. Why was the underground system developed in London?
Most railway tracks did not go into the London city centre, so buses, trams, cabs, and carriages were used. The number of vehicles on the road caused traffic jams. So the underground system was developed in London.
Read again and answer the following questions.
2. What was the London Underground like in 1863?
The tunnels were just beneath the surface of the ground. The carriages did not have windows and were pulled by steam engines through the narrow tunnels .
3. What did Charles Yerkes do to improve the underground system?
He obtained ownership of the many different lines and set up the Underground Electric Railways Company of London.
4. What unusual uses did the tube have during World War II ?
During World War II, the tube was used as a bomb shelter, an airplane factory, a centre for directing the defence against air attacks and meeting rooms for the government administration.
5. What happened to the London Underground after World War II?
After World War II, the underground system was enlarged and more lines were added because more people travelled on the underground.
6. What does it mean when the brochure says that the underground system is user-friendly?
It means that it is very convenient for people to go to different places in the city from any station.
75. benefits/ advantages
76. advertise
77. sharing/having similar interests
78. a way of
79. Get assignments
80. apply for
81. It was impossible to fit all of them into her crowded room.
82. She wanted to persuade her to give up some of her old toys.
83. Her daughter got rid of many toys.
84. Split them into piles for donating, selling and saving.
Reading (1 ):get the general idea of the passage
Can you explain the word “transport”?
Transport is a system built to carry people or goods to another place using vehicles, boats or airplanes.
Brainstorming
Different means of transport.
_____ have routes. They pick up and drop off people at different stops on the route.
Buses
_____ are a comfortable way to travel from place to place.
Ships
_______ are buses that carry people over long distances.
Coaches
__________ are used for rapid travel over long distances.
Airplanes
________________ run much faster than normal trains.
High-speed trains
________________ has become popular in crowded cities.
The underground
Reading 1
Preparation for reading
1. n. (常规) 路线
2. vt. 运送,输送;表达
3. prep. 经由,经过(某一地
方);通过,凭借
4. vt. 延迟,延期
5. n. 间隔,间隙
6. v. 承担,从事;承诺,答应
7. v. 扩大,扩展,增大
8. n. 少量的人或物;一把(的量)
convey
route
via
postpone
undertake
enlarge
handful
interval
(一) 基本单词
9. vi.& vt. 分割,(使)分开;撕开,
割破
10. adj. 每年的,一年一次的
11. n. 离开,出发;背离,违反
12. vi. 出现,产生
13. n.&v. 撞车;碰撞;倒闭;崩溃
14. vt. 处以罚金
15. adj. 喝醉的
n. 醉汉,酒鬼
16. n. 负荷,负载;大量,许多
vt. 装载,装上,装入
split
annual
departure
arise
load
crash
fine
drunk
1. 中途下客或卸货
2. 联合,连接
3. 每隔……距离或时间
4. 给某人接通(电话);
使经历
5. 决定,选定
6. 推迟,推延;使反感
7. 出现,到来;调高
(音量等)
drop off
link up
at (...) intervals
put through
decide on/upon
put off
turn up
8. 填写(表格);消磨(时间)
9. 少数的,少量的
10. 分组,分解;分离
11. (使)加速
12. 起因于,由……引起
13. 堵车,交通堵塞
fill in
a handful of
split up
speed up
arise from
traffic jam
Skimming
Skim the text and find the general idea of the passage.
This article is a tourist brochure about how the London Underground developed.
When was the first underground system opened?
Who first linked some of the different lines?
3. What did Charles Holden do?
In 1863.
Charles Yerkes.
He designed the most famous of the new stations constructed between 1918 and 1938.
What information did you get about the London Underground from the text?
reasons
development
unusual functions/uses
expansion & popularity
Structure analyzing
Paragraph 1
Paragraphs 2-3
Paragraphs 4
Paragraph 5-6
Part Paragraphs
Part 1
Part 2
Part 3
Part 4
The main ideas of the four parts
Part 1
Reasons why the first underground in the world was developed.
Part 2
Developments of the first underground.
Part 3
Some unusual uses of the first underground during World WarⅡ.
Part 4
Expansion and popularity of the first underground system.
Underline the time clues in the text quickly. Remember the details of each time clue as quickly as you can.
Scanning
An underground railway was approved to be built by the British government.
The first tunnels were opened.
The next section of the underground system was opened in the south of London.
Development of the LU system.
Date Event
1854
1863
1868
Two companies linked up to provide underground service in the middle of the city. The first railway tunnel under the River Thames was dug.
The first electric underground railway was opened.
The London Passenger Transport Board was created.
Many new stations were constructed.
The Jubilee Line was opened.
Date Event
1884
1890
1933
1918-1938
1979
1. Why was the underground system developed in London?
Most railway tracks did not go into the London city centre, so buses, trams, cabs, and carriages were used. The number of vehicles on the road caused traffic jams. So the underground system was developed in London.
Read again and answer the following questions.
2. What was the London Underground like in 1863?
The tunnels were just beneath the surface of the ground. The carriages did not have windows and were pulled by steam engines through the narrow tunnels .
3. What did Charles Yerkes do to improve the underground system?
He obtained ownership of the many different lines and set up the Underground Electric Railways Company of London.
4. What unusual uses did the tube have during World War II ?
During World War II, the tube was used as a bomb shelter, an airplane factory, a centre for directing the defence against air attacks and meeting rooms for the government administration.
5. What happened to the London Underground after World War II?
After World War II, the underground system was enlarged and more lines were added because more people travelled on the underground.
6. What does it mean when the brochure says that the underground system is user-friendly?
It means that it is very convenient for people to go to different places in the city from any station.
75. benefits/ advantages
76. advertise
77. sharing/having similar interests
78. a way of
79. Get assignments
80. apply for
81. It was impossible to fit all of them into her crowded room.
82. She wanted to persuade her to give up some of her old toys.
83. Her daughter got rid of many toys.
84. Split them into piles for donating, selling and saving.
