人教版 高中 英语 选修 7 Unit 2 Robots全单元课件(共132张PPT)
文档属性
| 名称 | 人教版 高中 英语 选修 7 Unit 2 Robots全单元课件(共132张PPT) |  | |
| 格式 | zip | ||
| 文件大小 | 8.0MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 人教版(新课程标准) | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2020-03-21 21:12:21 | ||
图片预览





文档简介
(共136张PPT)
Unit 2 Robots
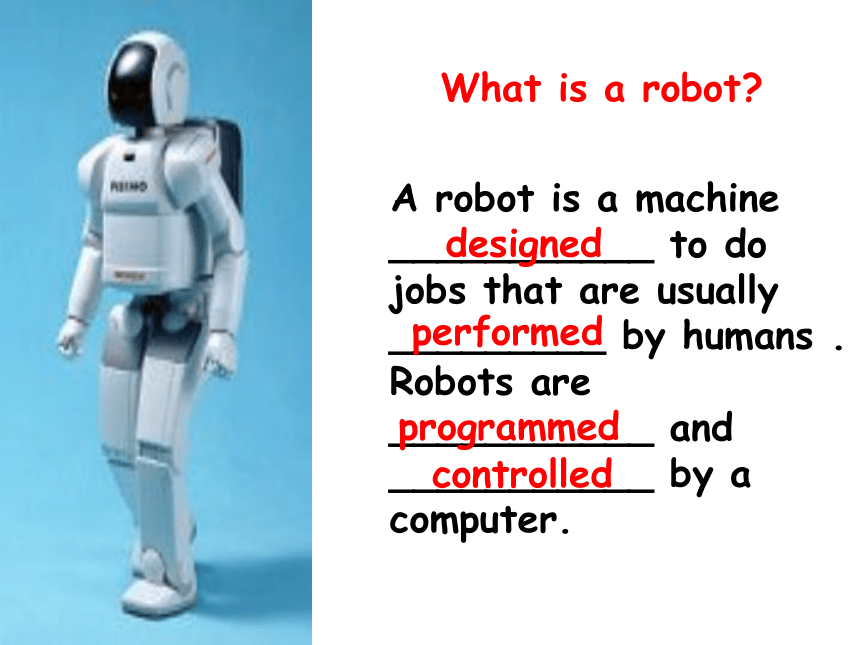
What is a robot?
A robot is a machine ___________ to do jobs that are usually _________ by humans . Robots are ___________ and ___________ by a computer.
designed
performed
programmed
controlled
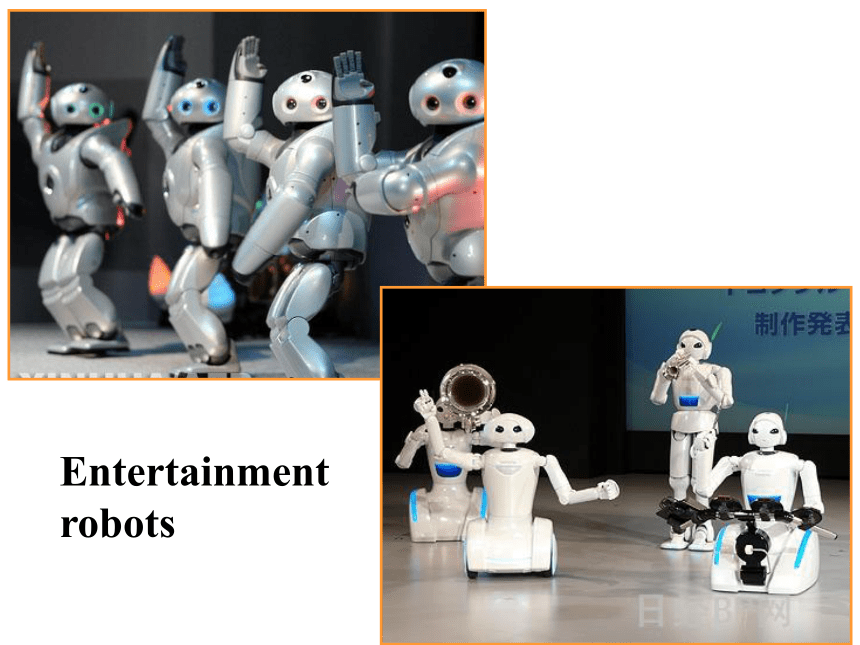
Entertainment
robots
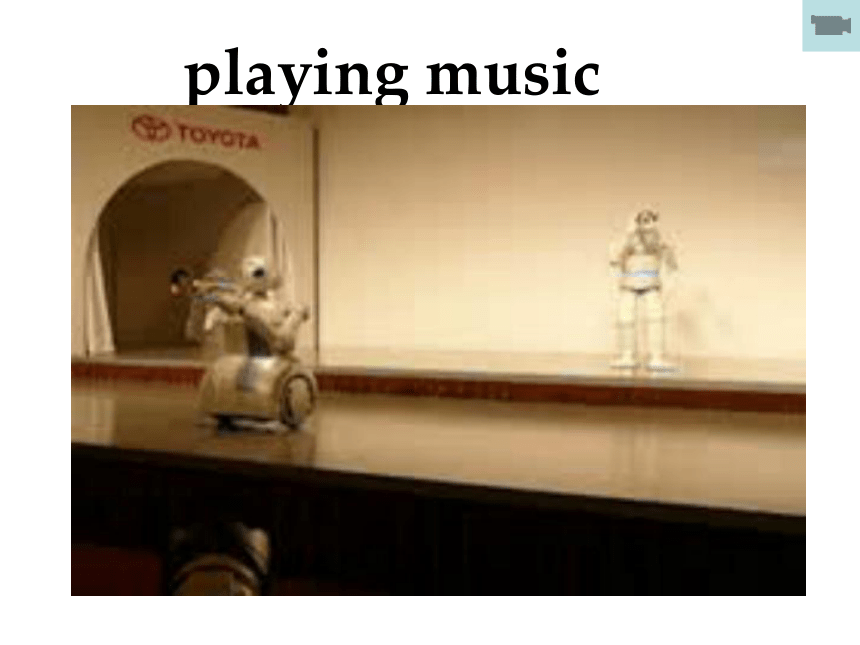
playing music
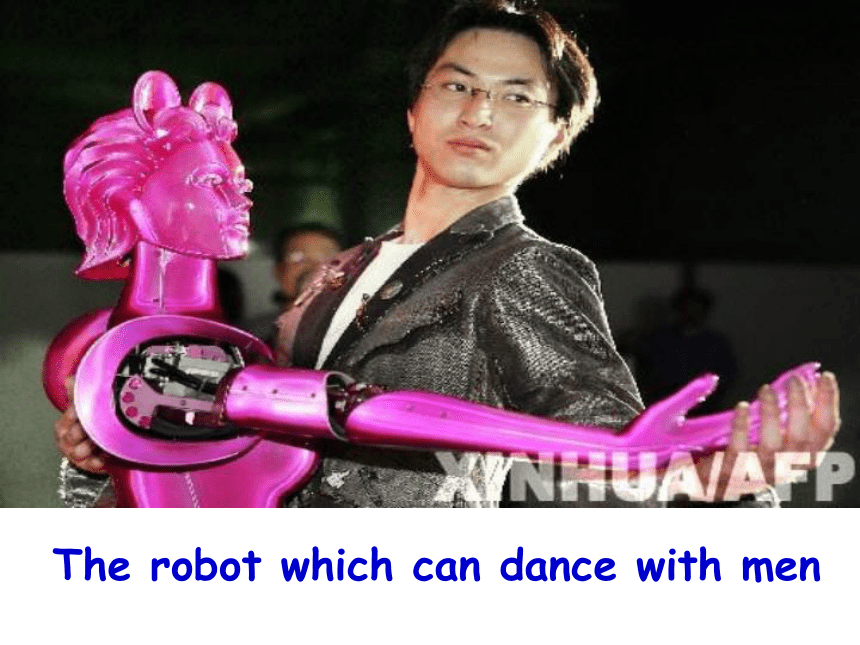
The robot which can dance with men
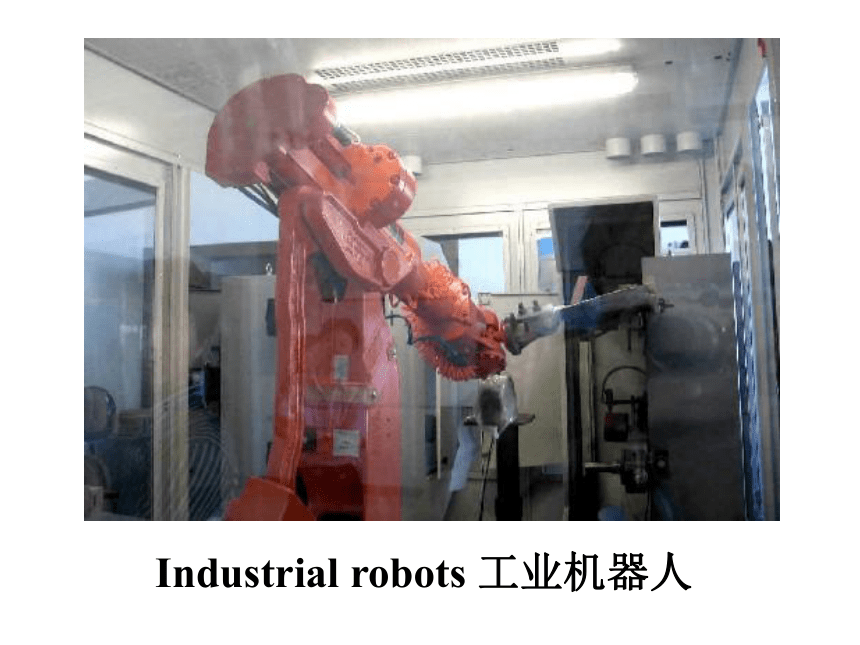
Industrial robots 工业机器人
explore dangerous places
clean the plane
Do the labour work
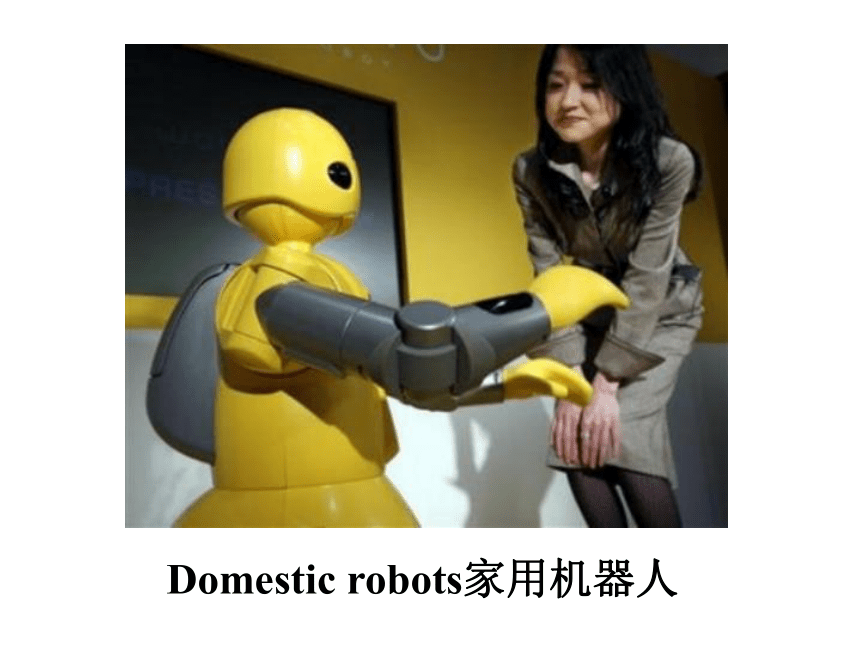
Domestic robots家用机器人
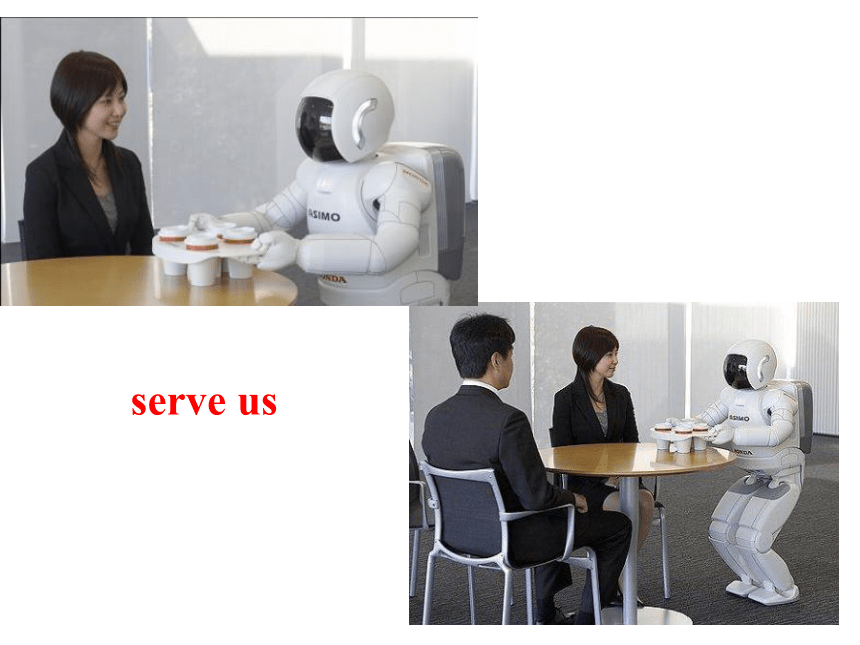
serve us
lead the way
The robot which can play with children.
The robot which can play football.
Nowadays robots can be made into all kinds of shapes for various uses.
Do you think it is possible for a robot to:
have feelings?
have its own needs and desires?
look and feel like a human being?
science fiction
Satisfaction Guaranteed
Let’s read a short story about a robot. It was originally written by Isaac Asimov, and published in 1951. Here the story has been retold by another writer.
Reading for main idea
1. What is the main idea of the story?
2. What are the main characters in the story?
Larry Belmont
Claire
Tony
Gladys Claffern
A robot
One of the richest
and most powerful
women around.
employed in a company
that makes robots
housewife
couple
was to be
tested out by Claire in their family
a woman that Claire envies
What is the text mainly about?
It is mainly about how a household _________ was _________ ________ in a family.
robot
tested
out
1. Why did Tony open the curtains?
He wanted Claire’s guests to see him and Claire together so that she would be envied by the women guests.
2. Why did Tony have to be rebuilt?
Tony had to be rebuilt because the company felt that they could not have women falling in love with a robot.
Claire had a sense of failure
She was
not
elegant
Her house
was not
elegant
The
salesman
was rude
to her
She wanted
to be
another
Gladys
She fell
off
a ladder
Claire had a sense of failure
She was
not
elegant
Her house
was not
elegant
The
salesman
was rude
to her
She wanted
to be
another
Gladys
She fell
off
a ladder
He gave
her a new
haircut and
changed the
make up she
wore
He
managed
to catch
her in
time from
the next
room
He
suggested
a party in
her house
He made
the
salesman
changed
his attitude
He
transformed
the house
completely
Was Claire satisfied with Tony?
Claire had a sense of failure
She was
not
elegant
Her house
was not
elegant
The
salesman
was rude
to her
She wanted
to be
another
Gladys
She fell
off
a ladder
Tony: Mr. Perfect !
What a sweet victory to be envied by those women! She might not be as beautiful as them, but none of them had such a handsome lover!
alarmed
tall
handsome
smooth
deep
Embarrassed
trust
fingernails
softness
warmth
Happy, surprised, shy
Reading for Details
Reading for details
sympathy
How did Claire feel? What happened?
____________ She saw Tony was ______ and ________. He had ______hair and his voice was _______.
____________ Tony asked whether she needed help dressing….she was offered__________
amazed By his _________ and the ________ and ________of his skin.
______________ Tony caught her in time, held her firmly in his arms .
surprised
happy
sad
declared
desire
How did Claire feel? What happened?
_____________ Tony folded his arms around her, bending his face close to hers and _______that he didn’t want to leave her and that he felt more than just the _____ to please her.
__________ She was envied by those women.
___________ She remembered Tony was just a machine.
How Claire’s emotion developed
Do you think it needs to rebuild Tony, why or why not?
Part 1:
Part 2:
Part 3:
Part 4
Para 1- Para 3
Para 4- Para 8
Para 9- Para 11
Para 12
Meet
Help
love
Leave
Reading for structure
1. desire v.
1) 渴望;希望(做某事):__________________
2) 要求某事__________________
3)要求(请求)某人做某事___________________
4)desire that…do/should do;
desire to do sth.
desire sth.
desire sb. to do sth.
我请您立即回信。
I desire ____________________ of yours.
我们希望有个好结果。
_____________________________
去请他进来。__________________________
Exercise
an immediate answer
We desire to have a good result.
Please desire him to come in.
他们要求你马上回来。
They desire ______________________________.
that you should come at once
desire n. (1) 愿望; 欲望 (2) 要求
(3) 食欲 (4) 向往的东西
他有强烈的求知欲。
He has ____________________________________.
a strong desire for knowledge / to learn
meet one’s desire
have\feel a great desire for
at one’s desire
满足某人的欲望
强烈渴望得到
照某人希望
2. satisfaction n. ( opp. dissatisfaction)
满意地_______________
令某人满意的是_________________________________
对……表示满意_________________________
获悉她身体康复非常欣慰。
It is a satisfaction to know she is well again.
with satisfaction
to sb’s satisfaction/ to the satisfaction of sb.
express one’s satisfaction at/ with
1) 满足; 满意; 舒服 (at; with) 2)令人满意的事物
satisfy vt.
satisfied adj.
satisfying adj.
satisfactory adj.
满足; 使满足
满意的; 满足的
令人满意的
令人满意的
1.It’s not easy to satisfy him.
2.I am satisfied with the result of the exam.
The result of the exam is satisfying.
3.It’s a satisfactory excuse for his absence.
3. experiment with
4. test out
5. alarm n. 警报; 惊慌; 恐慌
火灾引起很大恐慌。
____________________________
The fire caused much alarm.
alarm vt. 使警觉; 惊动; 使惊慌
不要惊慌 Don’t alarm yourself.
be alarmed at
6. sympathy n. 同情; 同感; 同情心
相关短语:
feel sympathy for, have sympathy for 同情
in sympathy with 赞成; 跟着; 和……一致
7. favour
n. 喜爱,恩惠 v.偏爱
Will you do me a favour?
She won her boss’s favour.
A teacher must not show too much favour
to one of his pupils.
A teacher must not favour to one of his pupils.
Which side do you favour?
I am in favour of his plan.
9. with wonder: 疑惑地
with + n 作状语
with surprise / embarrassment / fear
10. reach for / reach out one’s hand for
e.g.He reached out his hand for an apple.
n. reach
within one’s reach
out of one’s reach= beyond one’s reach
8. Or rather
He lives in London, or rather, he lives in a
suburb of London.
11. accompany v.
1) to go / stay with
I’d like you to accompany me to the
supermarket.
What accompanies him is always a dog.
2) to exist at the same time 和……一起发生
Lightning usually accompanies thunder.
She accompanied the singer on the piano.
I’ll keep you company while you are waiting.
12. affair n. 事情/ 暧昧关系/ 私通
pl 业务/ 事务/ 事态
Affairs at present in that country are unsettled.
那个国家当前的局势动荡不安.
current/foreign/world affairs 时事/外交事务/
世界事务
affairs of state 国事/ 国务/ 政务
She is having an affair with her boss.
13. Strike
The clock struck eight.
The ship struck against the rock.
A big earthquake struck that country.
He struck a match.
It struck me that she was accusing me.
They are striking for better working conditions.
14. declare vt. 宣布; 声明; 表明; 说明; 宣称
1) declare +n. 宣告
他们将很快宣布选举的结果。
_______________________________
_____________
2) declare+n.+(to be) n./ adj. 宣布……为……
裁判宣布他为比赛的冠军。
______________________________
_______________________
3. Do you have anything to declare?
They will declare the results of the
election soon.
The judge declared him (to be) the
winner of the competition.
15. more than + n _______________
+ adj._______________
+num.______________
不仅仅是, 不止
很 / 非常
超过
more + adj / adv / n / v + than
与其说……, ,不如说……
e.g.What he wants is more than money.
He is more than scared of cats.
He is more scared than ill.
他与其说是病了, 倒不如说他是受了惊吓。
16. envy vt. & n. 忌妒; 羡慕
I felt envy at his success.
She always envies me my curly hair.
17. leave…alone 不管; 不打扰; 让… …独自待着
不要动我的书.
_____________________
由我来做吧.
______________________
Leave my book alone.
Leave me alone to do it.
leave behind 留下; 忘带; 遗留
leave out 省去; 排除; 遗漏
leave off 停止
leave over 推迟某事; 剩下
18. have …doing = cause sb to do sth
1) 让……做
I won’t have him cleaning his bike in the kitchen.
She won’t have her children sitting down to
dinner with dirty hands.
2) 鼓励, 教会, 劝说
I’ll have them all talking in English in the
classroom.
As soon as I got there, I tried to have John
find me a house.
She had us all laughing at her jokes.
1.就我个人而言,我偏爱科幻小说。
2. 14岁以下的儿童必须有成年人陪伴。
3. 他声明他支持政府的决定。
4. 她一直嫉妒我的成功。
5. 听到一声巨响,这个男孩与其说害怕不如说惊讶。
6. 我突然意识到我不应该将Tom一个人留在山上,
因为那样很危险。
7. 她不容许孩子在公共场合无理顶撞。
8. 他是如此恐慌以致于让灯一晚上一直亮着,不敢睡觉。
9. 他并不仅仅是想取悦于她,更确切的说是爱上了她。
10. 这个小男孩有很强的求知欲让人很欣慰。
复习不定式
Revise the Infinitive
1. 作主语
2. 作宾语
3. 作宾语补足语
4. 作定语
5. 作状语
6. 作表语
7. 作独立成分
8. 与疑问词等连用
1. It’s an honour to be invited to the
ceremony.
2. She didn’t like to be treated as a child.
3. His dream was to be admitted to a good university.
4. There are a lot of things to be discussed.
5. She was sent there to be trained for the space flight.
作主语
作宾语
作表语
作定语
作状语
(6) 宾语补足语
He asked you to call him at ten o'clock.
I'd never allow my children to behave like that.
I will have the students write a passage about Internet.
It seemed so long before he heard the stone hit the water.
(7).独立结构
to be frank, to tell you the truth
to be honest, to begin with
to make the things worse
To tell the truth, I don’t agree with you.
类似的结构
(8)不定式与疑问词who,which, when, how, what等连用,在句中起名词作用,可充当主语、表语、宾语等。
He didn’t know what to say.他不知道说什么。(宾语)
How to solve the problem is very important.如何解决这个问题很重要。(主语) My question is when to start.我的问题是什么时候开始。(表语)
注意:
在与why连用时,只用于why或why not开头的简短疑问句中,后面紧跟的动词不定式不带to。
Why not have a rest?
语态
时态 主动语态 被动语态
一般式 to do to be done
完成式 to have
done to have
been done
进行式 to be doing /
(1).They pretended not to see us.
(2). He pretended to be sleeping.
(3).She pretended to have known it before.
(一般式表示与谓语的动作同时/几乎同时/发生在
它之后.)
(进行式表示在谓语动词发生的同时,不定式的动作
也正在进行)
(完成式表示动作发生在谓语动作之前)
(4).We’re happy to have been working with
you.
(完成进行式表示谓语动作发生之前,不定式的
动作一直在进行而且可能之后也继续)
二、不定式的主动形式表示被动
1.在there be结构中。
例如: There is a lot of homework to do.
(也可用to be done) There is no time to lose (to be lost).
2.在“n/pron + be + adj + to do”结构中。常用的形容词有easy,difficult,hard,impossible,nice,等。
例如: He is hard to convince.
He is an impossible person to work with.
3.在“too—to do; enough…to…”结构中。如:
The problem is too difficult to work out (to be worked out).
The house is big enough to live in.
4.在“with+n+to do”结构中。
例如: With nothing to do,he lay in bed. With so many exercises to do,I can’t go to the cinema.
Do you have anything to wash today?
Do you have anything to be washed?
5(to wash的主语为句子的主语you,其逻辑宾语为anything)
你今天要洗什么吗?
6(to be washed不是you做,而是由“我”或其他人来做)
你有什么要其他人洗的吗?
6.当不定式隐含在for sb to do结构中
时。
例如: This is the best book to read (=for us/you to read). The important thing to do is to lock the door when we leave the house.
7.一些作表语用的不定式的主动形式。
常见的这类动词有let(出租),blame等。
例如: The house is to let. I felt l was to blame.
解读动词不定式
误:We don’t allow to smoke in the lecture hall.
正:We don’t allow smoking in the lecture hall.
正:We don’t allow people to smoke in the lecture hall.
解析:在allow后跟动名词作宾语;当allow后有宾主时,则用不定式作补语,即allow sb to do sth。
2. 误:She was the first person thinking of the idea.
正:She was the first person to think of the idea.
解析:当序数词或由序数词所修饰的名词带定语时,此定语通常由不定式来充当。
3. 误:We need some paper to write.
正:We need some paper to write on.
解析:作定语的不定式如果是不及物动词,或者不定式所修饰的名词或代词是不定式动作的地点、工具等,不定式后面须跟相应的介词。但如果不定式所修饰的名词是time, place或way时,不定式后面的介词习惯上省去。如:
He had no money and no place to live (in). 他没有钱,也没有住的地方。
4. 误:The question being discussed at tomorrow’s meeting is a very important one.
正:The question to be discussed at
tomorrow’s meeting is a very important one.
5. 误:This boy was seen come late this morning.
正:This boy was seen to come late this morning.
解析:感官动词和使役动词转换为被动结构时,其后的不定式需要带to。
She tried to set aside some money every month.
Let’s set aside my personal feelings for now.
动词的时态
一般现在时:do/ does
一般过去时:did
现在进行时:am / is / are doing
过去进行时:was / were doing
现在完成时:have / has done
过去完成时:had done
一般将来时:shall / will done; be going to do
当句中含有情态动词时,句子结构为 can / must / have to…do
动词的被动语态也有时态
一般现在时:am / is / are done
一般过去时:was / were done
现在进行时:am / is / are being done
过去进行时:was / were being done
现在完成时:have / has been done
过去完成时:had been done
一般将来时:shall / will be done; be going to be done
当句中含有情态动词时,句子结构为 can / must / have to…be done
We are attached to he house and we hate
to move.
2. The institution is attached to the university.
3. Attach this card to your letter.
4. I attach great importance to fame and money.
I. 根据括号内的提示将下列句子补充完整。
1. He wanted the letter __________ (type) at once.
2. It is the first such project ______________ (design) by Chinese engineers.
to be typed
to be designed
6. She didn’t want her son ___________ (take) away.
7. Do let your mother know all the truth. She appears ________________ (tell) everything.
8. She is busy preparing for the exams __________ (hold) next month.
9. He hurried to the station only _________ (tell) that the train had left.
to be taken
to have been told
to be held
to be told
1. Having a trip abroad is certainly good for the old couple, but it remains ____ whether they will enjoy it.
A. to see B. to be seen
C. seeing D. seen
Exercise
B
2. I hurried to the meeting hall, only ____ that the meeting had been put off.
A. to tell B. to be told
C. telling D. told
B
3. Do let your mother know all the truth, she appears ____ everything.
A. to tell
B. to be told
C. to be telling
D. to have been told
D
4. Little Tom should love ____ to the theater this evening.
A. to be taken B. to take
C. being taken D. taking
A
5. It is said that plastics can be used to ____ many things. Now people are used to ____ plastics products.
A. make; using
B. making; using
C. making; use
D. make; use
A
6. With a lot of problems ____, the newly-elected president is having a hard time.
A. settled B. settling
C. to settle D. being settled
C
7. He ___ and was made to repeat it.
A. didn’t understand
B. didn’t be understood
C. wasn’t understand
D. wasn’t understood
D
8. The pupils here ____ all kinds of exercises every day in the past four weeks.
A. kept busy doing
B. keep on doing
C. have kept busy doing
D. have been kept busy doing
D
9. Visitors ____ not to touch the exhibits.
A. will request
B. request
C. are requesting
D. are requested
D
10. In some parts of the world, tea
____ with milk and sugar.
A. is serving
B. is served
C. serves
D. served
B
Reading task
Here and there are the mine signs.
In spite of so many warning signs, there are still many victims.
Pre-reading
1. What is the main topic of the article? Which part of the text tells you that?
2. Who wrote the article?
3. What do the three pictures show you?
4. Where is research being done on robots that can find landmines?
5. In which two countries might the robots be used?
Introduction: the damage landmines
26,000 people killed or badly injured each year
100 million buried in 60 countries
Most victims are innocent people
Suggested answers to Exercise 3:
Para graph Main idea Supporting details
1
The problem of landmines
Robots can help find traditional mines
Each year 100,00 removed
Each year 2,000,000 buried
Difficult and dangerous to remove
Much safer in the hunt for landmines
Faster at finding landmines
Research at Chiba University
2
3
Robots can find plastic mines
World opinion turned against landmines in the 19990s
Experimental robots in production
To use radar to locate mines
To identify types of mines
Agreement in Ottawa, Canada to stop the manufacture and use of landmines
Still a lot of work to be done
4
5
Careful reading
Answer key for Exercise 2:
1. How many people are killed or injured by landmines every year?
2. How often is someone killed or injured by a landmine?
3. For how long do landmines keep causing damage?
4. How many landmines are buried just beneath the surface of the ground?
5. In how many countries are landmines buried?
6. How many landmines are removed every year?
7. How many landmines are buried in the ground every year?
8. How big is the robot that can find landmines?
9. How much does it weigh?
10. How many legs has it got?
11. When was an agreement to stop the manufacture and use of landmines signed?
12. How many countries signed the agreement?
Unit 2
Using language-reading
1. Know something about Isaac Asimov.
2. Understand the details of the reading.
1. Understand the passage.
2. Develop the skills in reading.
1. Do you know who he is?
2. Have you ever seen the film from his works?
3. What do you know about him?
Isaac Asimov
( 1920-1992)
About Isaac Asimov
Isaac Asimov,American Jew, an American scientist and one of the most great science fiction writers.
He wrote so many works which are known as interesting, creative, imaginative.
In his works he described events and people that do not exist.
Isaac Asimov was an amazing writer who had finished more than 480 works since the beginning of1950’.
His most famous works
The
Foundation
Trilogy
I, Robot (我是机器人)
the foundation (1951)
the second foundation (1952)
the foundation and
Empire (1953)
Date
Event
Born in Russia
____________________________________
_____________________________________
Parents bought a candy store.
_____________________________________
Mother and her third child.
_____ Started to take himself seriously as a writer.
1939 ____________________________________
Sister born
Moved with family to New York
Started working in candy store
1931
Began having stories published in science fiction magazine
Post-reading
_______ Gained Master’s degree in chemistry
Finished working in the candy store
_______________________________
1942-1945
_______________________________
_______ Got PhD in chemistry
_______ Became a biochemistry teacher,…
Published his first novel.
-1953 Published “The Foundation Trilogy” and won an award for it
1941
Got married.
Worked as junior chemist, Philadelphia Navy Yard.
1948
1949
Date
Event
Event
Date
_______ Published first science book.
_______ Became a full-time writer.
Divorced his first wife.
____________________________
______ Had a blood transfusion. Because infected with HIV.
1992 ________________________________
1953
1958
Married for a second time.
1983
Died in New York.
Choose the best answer
1. Why could Isaac Asimov become a writer?
A. A friend of his made him a writer.
B. His parents wanted him to be a writer.
C. He had the talent for writing.
D. He had so many experiences in his life.
Reading & Discussing
Choose the best answer
2. How many years did Isaac Asimov work in his parents’ store?
A. 5 B. 9 C. 11 D. 13
Reading & Discussing
C. Isaac Asimov didn’t publish books until he became a full-time writer.
D. Isaac Asimov’ ideas about robots completely influenced scientists researching into artificial intelligence.
3. Which of the following statements is true according to the passage?
A. Isaac Asimov wrote some famous plays about Shakespeare.
B. Robots should protect human beings in “I ,Robot”
Reading & Discussing
Review Asimov’s laws for robots
first law : A robot must not injure human being or allow them to be injured.
Second law : A robot must obey the orders given to it by human beings (as long as human beings are not injured).
Third law : A robot must protect its own existence (as long as human being are not injured; and as long as the robot does not disobey the human beings).
Which law is the story “Satisfaction Guaranteed” based on?
Discuss in groups
1. an American scientist and writer (Page 16 Para 1)
一位科学家兼作家
The singer and dancer ________ (be) coming
for a visit.
The singer and the dancer __________ (be)
coming for a visit.
is / was
are/ were
2. He is also well known for his collection of short stories…
be known for … = be famous for …因……而著名
be known as… 作为……而著名
be known to… 为……所知
He is known ____ his honesty.
It’s known ____ the most dangerous part of the city.
He is known ____ everyone ____ a good actor.
for
介词填空:
(as, for, to)
as
to
as
Difficulties 难点
3.Asimov had both an extraordinary imagination that gave him the ability to explore future worlds and an amazing mind with which he searched for explanations of everything, in the present and the past.
阿西莫夫不仅有着超凡的想象力,使他能对未来世界进行探索,而且有着惊人的智力,使他能对现在的和过去的各种事物做出解释。
He seemed to look for words ________ he could
express what he was thinking about.
The novel ________ the film has been adapted
for children is written by a famous writer.
He is telling a story od a hero, ________ everyone
in the town is pround.
with which
from which
of whom
4. … which he searched for explanations of everything, …
search + 地方 / 人 表示在某地/某人身上寻找/搜寻。
search for :寻找某物
in search of:寻找,作状语,表示目的。例如:
The enemies _____________the Red Army man everywhere .
They have ____________ the whole city _____the missing boy .
The boy has been to many places ____________his lost cat .
searched
searched
in search of
for
5. The staff ________ very efficient.
All the staff _____ off today, so they can have
a good rest.
I’m ______ the staff of the college.
was
are
on
6. From 1942 to 1948 he worked as a junior chemist …
junior :younger , lower in rank:
较年轻的,职位稍低的
senior : older , higher in rank
较年长的,职位稍高的
He is the junior employee in the firm .
He is two years junior to me.
He is two years senior to me.
senior citizens 老人
have talent for... 对……有天赋
be of talent 有天赋的
talented adj.有才能的
7. talent n.天才;特殊的能力;才干(Page 16 Para 4.)
e.g. My brother showed a talent for music when he was
very young.
8. …he started to take himself seriously as a writer…
take …seriously :严肃对待/认真对待,例如: You can’t take her promises seriously, she never keeps her word.
He takes things too seriously.
反义短语: take …for granted:想当然
You should ________________________ (重视我的话) , it is good for you.
She ___________________ (想当然的认为) that her parents should give her everything.
take what I said seriously
takes it for granted
9. … Asimov received many awards, both for his science books and his science books.
award :奖,奖赏
He won the __________for the best student of year .
It 's an ___________to hear you speak so highly of me .
He won the Nobel _________for literature .
He got a ________of $ 100 for helping them.
award
填空:
(prize ,reward, honor)
honor
Prize
reward
10. Soon after his divorce in 1973, …
divorce:n. legal ending of a marriage:离婚,脱离
vt. put an end to a marriage by law
使离婚,与......脱离
ask for a divorce
get divorced
divorce … from
His wife asked for a divorce.
They got divorced last year. .
She divorced her husband two years ago.
We shouldn’t divorce theory from practice.
Isaac Asimov(1920-1992) was a Russian- born American writer. His family immigrated to the US when he was three years old and settled in New York. He gained a master’s degree in chemistry and later got his PhD. After he graduated, he became a biochemistry teacher at Boston University.
He was talented in writing. When he realized it, he gave up teaching and became a professional writer. In 1939, he had stories published and in 1950 he published his first novel, which made him famous and won many awards. The Foundation trilogy and I, Robot are very popular with the young and adults.
Isaac Asimov was such a productive writer that he wrote more than 480 books. The readers are impressed by his extraodinary iamgination and an amazing mind, which also influnced other writers and even scientists researching into artificial intellignce.
1. That book on the Holy Bible needs to be returned to the library by the end of the week.
2. That old armchair is to be replaced by a sofa next week.
3. Don’t worry. You still have plenty of time for that fax to be sent to your company.
4. Your decision to divorce your wife has to be made with her agreement.
5. There has been an accident but there is no need to be alarmed. Nobody has been hurt.
6. Although she had done well, she expected her parents to be disappionted by her exam results.
7. She was happy to be supported by the affection of her family when she had a serious operation in hospital.
8. He was so excited to be declared the winner of the talent competition.
9. He added the 2,000 yuan they had received to the 1,500 yuan to be offered, making 3,500 yuan in all.
10. Without their leading player, they are bound to be beaten in the coming competition.
动词的时态
一般现在时:do/ does
一般过去时:did
现在进行时:am / is / are doing
过去进行时:was / were doing
现在完成时:have / has done
过去完成时:had done
一般将来时:shall / will done; be going to do
当句中含有情态动词时,句子结构为 can / must / have to…do
动词的被动语态也有时态
一般现在时:am / is / are done
一般过去时:was / were done
现在进行时:am / is / are being done
过去进行时:was / were being done
现在完成时:have / has been done
过去完成时:had been done
一般将来时:shall / will be done; be going to be done
当句中含有情态动词时,句子结构为 can / must / have to…be done
Unit 2 Robots
What is a robot?
A robot is a machine ___________ to do jobs that are usually _________ by humans . Robots are ___________ and ___________ by a computer.
designed
performed
programmed
controlled
Entertainment
robots
playing music
The robot which can dance with men
Industrial robots 工业机器人
explore dangerous places
clean the plane
Do the labour work
Domestic robots家用机器人
serve us
lead the way
The robot which can play with children.
The robot which can play football.
Nowadays robots can be made into all kinds of shapes for various uses.
Do you think it is possible for a robot to:
have feelings?
have its own needs and desires?
look and feel like a human being?
science fiction
Satisfaction Guaranteed
Let’s read a short story about a robot. It was originally written by Isaac Asimov, and published in 1951. Here the story has been retold by another writer.
Reading for main idea
1. What is the main idea of the story?
2. What are the main characters in the story?
Larry Belmont
Claire
Tony
Gladys Claffern
A robot
One of the richest
and most powerful
women around.
employed in a company
that makes robots
housewife
couple
was to be
tested out by Claire in their family
a woman that Claire envies
What is the text mainly about?
It is mainly about how a household _________ was _________ ________ in a family.
robot
tested
out
1. Why did Tony open the curtains?
He wanted Claire’s guests to see him and Claire together so that she would be envied by the women guests.
2. Why did Tony have to be rebuilt?
Tony had to be rebuilt because the company felt that they could not have women falling in love with a robot.
Claire had a sense of failure
She was
not
elegant
Her house
was not
elegant
The
salesman
was rude
to her
She wanted
to be
another
Gladys
She fell
off
a ladder
Claire had a sense of failure
She was
not
elegant
Her house
was not
elegant
The
salesman
was rude
to her
She wanted
to be
another
Gladys
She fell
off
a ladder
He gave
her a new
haircut and
changed the
make up she
wore
He
managed
to catch
her in
time from
the next
room
He
suggested
a party in
her house
He made
the
salesman
changed
his attitude
He
transformed
the house
completely
Was Claire satisfied with Tony?
Claire had a sense of failure
She was
not
elegant
Her house
was not
elegant
The
salesman
was rude
to her
She wanted
to be
another
Gladys
She fell
off
a ladder
Tony: Mr. Perfect !
What a sweet victory to be envied by those women! She might not be as beautiful as them, but none of them had such a handsome lover!
alarmed
tall
handsome
smooth
deep
Embarrassed
trust
fingernails
softness
warmth
Happy, surprised, shy
Reading for Details
Reading for details
sympathy
How did Claire feel? What happened?
____________ She saw Tony was ______ and ________. He had ______hair and his voice was _______.
____________ Tony asked whether she needed help dressing….she was offered__________
amazed By his _________ and the ________ and ________of his skin.
______________ Tony caught her in time, held her firmly in his arms .
surprised
happy
sad
declared
desire
How did Claire feel? What happened?
_____________ Tony folded his arms around her, bending his face close to hers and _______that he didn’t want to leave her and that he felt more than just the _____ to please her.
__________ She was envied by those women.
___________ She remembered Tony was just a machine.
How Claire’s emotion developed
Do you think it needs to rebuild Tony, why or why not?
Part 1:
Part 2:
Part 3:
Part 4
Para 1- Para 3
Para 4- Para 8
Para 9- Para 11
Para 12
Meet
Help
love
Leave
Reading for structure
1. desire v.
1) 渴望;希望(做某事):__________________
2) 要求某事__________________
3)要求(请求)某人做某事___________________
4)desire that…do/should do;
desire to do sth.
desire sth.
desire sb. to do sth.
我请您立即回信。
I desire ____________________ of yours.
我们希望有个好结果。
_____________________________
去请他进来。__________________________
Exercise
an immediate answer
We desire to have a good result.
Please desire him to come in.
他们要求你马上回来。
They desire ______________________________.
that you should come at once
desire n. (1) 愿望; 欲望 (2) 要求
(3) 食欲 (4) 向往的东西
他有强烈的求知欲。
He has ____________________________________.
a strong desire for knowledge / to learn
meet one’s desire
have\feel a great desire for
at one’s desire
满足某人的欲望
强烈渴望得到
照某人希望
2. satisfaction n. ( opp. dissatisfaction)
满意地_______________
令某人满意的是_________________________________
对……表示满意_________________________
获悉她身体康复非常欣慰。
It is a satisfaction to know she is well again.
with satisfaction
to sb’s satisfaction/ to the satisfaction of sb.
express one’s satisfaction at/ with
1) 满足; 满意; 舒服 (at; with) 2)令人满意的事物
satisfy vt.
satisfied adj.
satisfying adj.
satisfactory adj.
满足; 使满足
满意的; 满足的
令人满意的
令人满意的
1.It’s not easy to satisfy him.
2.I am satisfied with the result of the exam.
The result of the exam is satisfying.
3.It’s a satisfactory excuse for his absence.
3. experiment with
4. test out
5. alarm n. 警报; 惊慌; 恐慌
火灾引起很大恐慌。
____________________________
The fire caused much alarm.
alarm vt. 使警觉; 惊动; 使惊慌
不要惊慌 Don’t alarm yourself.
be alarmed at
6. sympathy n. 同情; 同感; 同情心
相关短语:
feel sympathy for, have sympathy for 同情
in sympathy with 赞成; 跟着; 和……一致
7. favour
n. 喜爱,恩惠 v.偏爱
Will you do me a favour?
She won her boss’s favour.
A teacher must not show too much favour
to one of his pupils.
A teacher must not favour to one of his pupils.
Which side do you favour?
I am in favour of his plan.
9. with wonder: 疑惑地
with + n 作状语
with surprise / embarrassment / fear
10. reach for / reach out one’s hand for
e.g.He reached out his hand for an apple.
n. reach
within one’s reach
out of one’s reach= beyond one’s reach
8. Or rather
He lives in London, or rather, he lives in a
suburb of London.
11. accompany v.
1) to go / stay with
I’d like you to accompany me to the
supermarket.
What accompanies him is always a dog.
2) to exist at the same time 和……一起发生
Lightning usually accompanies thunder.
She accompanied the singer on the piano.
I’ll keep you company while you are waiting.
12. affair n. 事情/ 暧昧关系/ 私通
pl 业务/ 事务/ 事态
Affairs at present in that country are unsettled.
那个国家当前的局势动荡不安.
current/foreign/world affairs 时事/外交事务/
世界事务
affairs of state 国事/ 国务/ 政务
She is having an affair with her boss.
13. Strike
The clock struck eight.
The ship struck against the rock.
A big earthquake struck that country.
He struck a match.
It struck me that she was accusing me.
They are striking for better working conditions.
14. declare vt. 宣布; 声明; 表明; 说明; 宣称
1) declare +n. 宣告
他们将很快宣布选举的结果。
_______________________________
_____________
2) declare+n.+(to be) n./ adj. 宣布……为……
裁判宣布他为比赛的冠军。
______________________________
_______________________
3. Do you have anything to declare?
They will declare the results of the
election soon.
The judge declared him (to be) the
winner of the competition.
15. more than + n _______________
+ adj._______________
+num.______________
不仅仅是, 不止
很 / 非常
超过
more + adj / adv / n / v + than
与其说……, ,不如说……
e.g.What he wants is more than money.
He is more than scared of cats.
He is more scared than ill.
他与其说是病了, 倒不如说他是受了惊吓。
16. envy vt. & n. 忌妒; 羡慕
I felt envy at his success.
She always envies me my curly hair.
17. leave…alone 不管; 不打扰; 让… …独自待着
不要动我的书.
_____________________
由我来做吧.
______________________
Leave my book alone.
Leave me alone to do it.
leave behind 留下; 忘带; 遗留
leave out 省去; 排除; 遗漏
leave off 停止
leave over 推迟某事; 剩下
18. have …doing = cause sb to do sth
1) 让……做
I won’t have him cleaning his bike in the kitchen.
She won’t have her children sitting down to
dinner with dirty hands.
2) 鼓励, 教会, 劝说
I’ll have them all talking in English in the
classroom.
As soon as I got there, I tried to have John
find me a house.
She had us all laughing at her jokes.
1.就我个人而言,我偏爱科幻小说。
2. 14岁以下的儿童必须有成年人陪伴。
3. 他声明他支持政府的决定。
4. 她一直嫉妒我的成功。
5. 听到一声巨响,这个男孩与其说害怕不如说惊讶。
6. 我突然意识到我不应该将Tom一个人留在山上,
因为那样很危险。
7. 她不容许孩子在公共场合无理顶撞。
8. 他是如此恐慌以致于让灯一晚上一直亮着,不敢睡觉。
9. 他并不仅仅是想取悦于她,更确切的说是爱上了她。
10. 这个小男孩有很强的求知欲让人很欣慰。
复习不定式
Revise the Infinitive
1. 作主语
2. 作宾语
3. 作宾语补足语
4. 作定语
5. 作状语
6. 作表语
7. 作独立成分
8. 与疑问词等连用
1. It’s an honour to be invited to the
ceremony.
2. She didn’t like to be treated as a child.
3. His dream was to be admitted to a good university.
4. There are a lot of things to be discussed.
5. She was sent there to be trained for the space flight.
作主语
作宾语
作表语
作定语
作状语
(6) 宾语补足语
He asked you to call him at ten o'clock.
I'd never allow my children to behave like that.
I will have the students write a passage about Internet.
It seemed so long before he heard the stone hit the water.
(7).独立结构
to be frank, to tell you the truth
to be honest, to begin with
to make the things worse
To tell the truth, I don’t agree with you.
类似的结构
(8)不定式与疑问词who,which, when, how, what等连用,在句中起名词作用,可充当主语、表语、宾语等。
He didn’t know what to say.他不知道说什么。(宾语)
How to solve the problem is very important.如何解决这个问题很重要。(主语) My question is when to start.我的问题是什么时候开始。(表语)
注意:
在与why连用时,只用于why或why not开头的简短疑问句中,后面紧跟的动词不定式不带to。
Why not have a rest?
语态
时态 主动语态 被动语态
一般式 to do to be done
完成式 to have
done to have
been done
进行式 to be doing /
(1).They pretended not to see us.
(2). He pretended to be sleeping.
(3).She pretended to have known it before.
(一般式表示与谓语的动作同时/几乎同时/发生在
它之后.)
(进行式表示在谓语动词发生的同时,不定式的动作
也正在进行)
(完成式表示动作发生在谓语动作之前)
(4).We’re happy to have been working with
you.
(完成进行式表示谓语动作发生之前,不定式的
动作一直在进行而且可能之后也继续)
二、不定式的主动形式表示被动
1.在there be结构中。
例如: There is a lot of homework to do.
(也可用to be done) There is no time to lose (to be lost).
2.在“n/pron + be + adj + to do”结构中。常用的形容词有easy,difficult,hard,impossible,nice,等。
例如: He is hard to convince.
He is an impossible person to work with.
3.在“too—to do; enough…to…”结构中。如:
The problem is too difficult to work out (to be worked out).
The house is big enough to live in.
4.在“with+n+to do”结构中。
例如: With nothing to do,he lay in bed. With so many exercises to do,I can’t go to the cinema.
Do you have anything to wash today?
Do you have anything to be washed?
5(to wash的主语为句子的主语you,其逻辑宾语为anything)
你今天要洗什么吗?
6(to be washed不是you做,而是由“我”或其他人来做)
你有什么要其他人洗的吗?
6.当不定式隐含在for sb to do结构中
时。
例如: This is the best book to read (=for us/you to read). The important thing to do is to lock the door when we leave the house.
7.一些作表语用的不定式的主动形式。
常见的这类动词有let(出租),blame等。
例如: The house is to let. I felt l was to blame.
解读动词不定式
误:We don’t allow to smoke in the lecture hall.
正:We don’t allow smoking in the lecture hall.
正:We don’t allow people to smoke in the lecture hall.
解析:在allow后跟动名词作宾语;当allow后有宾主时,则用不定式作补语,即allow sb to do sth。
2. 误:She was the first person thinking of the idea.
正:She was the first person to think of the idea.
解析:当序数词或由序数词所修饰的名词带定语时,此定语通常由不定式来充当。
3. 误:We need some paper to write.
正:We need some paper to write on.
解析:作定语的不定式如果是不及物动词,或者不定式所修饰的名词或代词是不定式动作的地点、工具等,不定式后面须跟相应的介词。但如果不定式所修饰的名词是time, place或way时,不定式后面的介词习惯上省去。如:
He had no money and no place to live (in). 他没有钱,也没有住的地方。
4. 误:The question being discussed at tomorrow’s meeting is a very important one.
正:The question to be discussed at
tomorrow’s meeting is a very important one.
5. 误:This boy was seen come late this morning.
正:This boy was seen to come late this morning.
解析:感官动词和使役动词转换为被动结构时,其后的不定式需要带to。
She tried to set aside some money every month.
Let’s set aside my personal feelings for now.
动词的时态
一般现在时:do/ does
一般过去时:did
现在进行时:am / is / are doing
过去进行时:was / were doing
现在完成时:have / has done
过去完成时:had done
一般将来时:shall / will done; be going to do
当句中含有情态动词时,句子结构为 can / must / have to…do
动词的被动语态也有时态
一般现在时:am / is / are done
一般过去时:was / were done
现在进行时:am / is / are being done
过去进行时:was / were being done
现在完成时:have / has been done
过去完成时:had been done
一般将来时:shall / will be done; be going to be done
当句中含有情态动词时,句子结构为 can / must / have to…be done
We are attached to he house and we hate
to move.
2. The institution is attached to the university.
3. Attach this card to your letter.
4. I attach great importance to fame and money.
I. 根据括号内的提示将下列句子补充完整。
1. He wanted the letter __________ (type) at once.
2. It is the first such project ______________ (design) by Chinese engineers.
to be typed
to be designed
6. She didn’t want her son ___________ (take) away.
7. Do let your mother know all the truth. She appears ________________ (tell) everything.
8. She is busy preparing for the exams __________ (hold) next month.
9. He hurried to the station only _________ (tell) that the train had left.
to be taken
to have been told
to be held
to be told
1. Having a trip abroad is certainly good for the old couple, but it remains ____ whether they will enjoy it.
A. to see B. to be seen
C. seeing D. seen
Exercise
B
2. I hurried to the meeting hall, only ____ that the meeting had been put off.
A. to tell B. to be told
C. telling D. told
B
3. Do let your mother know all the truth, she appears ____ everything.
A. to tell
B. to be told
C. to be telling
D. to have been told
D
4. Little Tom should love ____ to the theater this evening.
A. to be taken B. to take
C. being taken D. taking
A
5. It is said that plastics can be used to ____ many things. Now people are used to ____ plastics products.
A. make; using
B. making; using
C. making; use
D. make; use
A
6. With a lot of problems ____, the newly-elected president is having a hard time.
A. settled B. settling
C. to settle D. being settled
C
7. He ___ and was made to repeat it.
A. didn’t understand
B. didn’t be understood
C. wasn’t understand
D. wasn’t understood
D
8. The pupils here ____ all kinds of exercises every day in the past four weeks.
A. kept busy doing
B. keep on doing
C. have kept busy doing
D. have been kept busy doing
D
9. Visitors ____ not to touch the exhibits.
A. will request
B. request
C. are requesting
D. are requested
D
10. In some parts of the world, tea
____ with milk and sugar.
A. is serving
B. is served
C. serves
D. served
B
Reading task
Here and there are the mine signs.
In spite of so many warning signs, there are still many victims.
Pre-reading
1. What is the main topic of the article? Which part of the text tells you that?
2. Who wrote the article?
3. What do the three pictures show you?
4. Where is research being done on robots that can find landmines?
5. In which two countries might the robots be used?
Introduction: the damage landmines
26,000 people killed or badly injured each year
100 million buried in 60 countries
Most victims are innocent people
Suggested answers to Exercise 3:
Para graph Main idea Supporting details
1
The problem of landmines
Robots can help find traditional mines
Each year 100,00 removed
Each year 2,000,000 buried
Difficult and dangerous to remove
Much safer in the hunt for landmines
Faster at finding landmines
Research at Chiba University
2
3
Robots can find plastic mines
World opinion turned against landmines in the 19990s
Experimental robots in production
To use radar to locate mines
To identify types of mines
Agreement in Ottawa, Canada to stop the manufacture and use of landmines
Still a lot of work to be done
4
5
Careful reading
Answer key for Exercise 2:
1. How many people are killed or injured by landmines every year?
2. How often is someone killed or injured by a landmine?
3. For how long do landmines keep causing damage?
4. How many landmines are buried just beneath the surface of the ground?
5. In how many countries are landmines buried?
6. How many landmines are removed every year?
7. How many landmines are buried in the ground every year?
8. How big is the robot that can find landmines?
9. How much does it weigh?
10. How many legs has it got?
11. When was an agreement to stop the manufacture and use of landmines signed?
12. How many countries signed the agreement?
Unit 2
Using language-reading
1. Know something about Isaac Asimov.
2. Understand the details of the reading.
1. Understand the passage.
2. Develop the skills in reading.
1. Do you know who he is?
2. Have you ever seen the film from his works?
3. What do you know about him?
Isaac Asimov
( 1920-1992)
About Isaac Asimov
Isaac Asimov,American Jew, an American scientist and one of the most great science fiction writers.
He wrote so many works which are known as interesting, creative, imaginative.
In his works he described events and people that do not exist.
Isaac Asimov was an amazing writer who had finished more than 480 works since the beginning of1950’.
His most famous works
The
Foundation
Trilogy
I, Robot (我是机器人)
the foundation (1951)
the second foundation (1952)
the foundation and
Empire (1953)
Date
Event
Born in Russia
____________________________________
_____________________________________
Parents bought a candy store.
_____________________________________
Mother and her third child.
_____ Started to take himself seriously as a writer.
1939 ____________________________________
Sister born
Moved with family to New York
Started working in candy store
1931
Began having stories published in science fiction magazine
Post-reading
_______ Gained Master’s degree in chemistry
Finished working in the candy store
_______________________________
1942-1945
_______________________________
_______ Got PhD in chemistry
_______ Became a biochemistry teacher,…
Published his first novel.
-1953 Published “The Foundation Trilogy” and won an award for it
1941
Got married.
Worked as junior chemist, Philadelphia Navy Yard.
1948
1949
Date
Event
Event
Date
_______ Published first science book.
_______ Became a full-time writer.
Divorced his first wife.
____________________________
______ Had a blood transfusion. Because infected with HIV.
1992 ________________________________
1953
1958
Married for a second time.
1983
Died in New York.
Choose the best answer
1. Why could Isaac Asimov become a writer?
A. A friend of his made him a writer.
B. His parents wanted him to be a writer.
C. He had the talent for writing.
D. He had so many experiences in his life.
Reading & Discussing
Choose the best answer
2. How many years did Isaac Asimov work in his parents’ store?
A. 5 B. 9 C. 11 D. 13
Reading & Discussing
C. Isaac Asimov didn’t publish books until he became a full-time writer.
D. Isaac Asimov’ ideas about robots completely influenced scientists researching into artificial intelligence.
3. Which of the following statements is true according to the passage?
A. Isaac Asimov wrote some famous plays about Shakespeare.
B. Robots should protect human beings in “I ,Robot”
Reading & Discussing
Review Asimov’s laws for robots
first law : A robot must not injure human being or allow them to be injured.
Second law : A robot must obey the orders given to it by human beings (as long as human beings are not injured).
Third law : A robot must protect its own existence (as long as human being are not injured; and as long as the robot does not disobey the human beings).
Which law is the story “Satisfaction Guaranteed” based on?
Discuss in groups
1. an American scientist and writer (Page 16 Para 1)
一位科学家兼作家
The singer and dancer ________ (be) coming
for a visit.
The singer and the dancer __________ (be)
coming for a visit.
is / was
are/ were
2. He is also well known for his collection of short stories…
be known for … = be famous for …因……而著名
be known as… 作为……而著名
be known to… 为……所知
He is known ____ his honesty.
It’s known ____ the most dangerous part of the city.
He is known ____ everyone ____ a good actor.
for
介词填空:
(as, for, to)
as
to
as
Difficulties 难点
3.Asimov had both an extraordinary imagination that gave him the ability to explore future worlds and an amazing mind with which he searched for explanations of everything, in the present and the past.
阿西莫夫不仅有着超凡的想象力,使他能对未来世界进行探索,而且有着惊人的智力,使他能对现在的和过去的各种事物做出解释。
He seemed to look for words ________ he could
express what he was thinking about.
The novel ________ the film has been adapted
for children is written by a famous writer.
He is telling a story od a hero, ________ everyone
in the town is pround.
with which
from which
of whom
4. … which he searched for explanations of everything, …
search + 地方 / 人 表示在某地/某人身上寻找/搜寻。
search for :寻找某物
in search of:寻找,作状语,表示目的。例如:
The enemies _____________the Red Army man everywhere .
They have ____________ the whole city _____the missing boy .
The boy has been to many places ____________his lost cat .
searched
searched
in search of
for
5. The staff ________ very efficient.
All the staff _____ off today, so they can have
a good rest.
I’m ______ the staff of the college.
was
are
on
6. From 1942 to 1948 he worked as a junior chemist …
junior :younger , lower in rank:
较年轻的,职位稍低的
senior : older , higher in rank
较年长的,职位稍高的
He is the junior employee in the firm .
He is two years junior to me.
He is two years senior to me.
senior citizens 老人
have talent for... 对……有天赋
be of talent 有天赋的
talented adj.有才能的
7. talent n.天才;特殊的能力;才干(Page 16 Para 4.)
e.g. My brother showed a talent for music when he was
very young.
8. …he started to take himself seriously as a writer…
take …seriously :严肃对待/认真对待,例如: You can’t take her promises seriously, she never keeps her word.
He takes things too seriously.
反义短语: take …for granted:想当然
You should ________________________ (重视我的话) , it is good for you.
She ___________________ (想当然的认为) that her parents should give her everything.
take what I said seriously
takes it for granted
9. … Asimov received many awards, both for his science books and his science books.
award :奖,奖赏
He won the __________for the best student of year .
It 's an ___________to hear you speak so highly of me .
He won the Nobel _________for literature .
He got a ________of $ 100 for helping them.
award
填空:
(prize ,reward, honor)
honor
Prize
reward
10. Soon after his divorce in 1973, …
divorce:n. legal ending of a marriage:离婚,脱离
vt. put an end to a marriage by law
使离婚,与......脱离
ask for a divorce
get divorced
divorce … from
His wife asked for a divorce.
They got divorced last year. .
She divorced her husband two years ago.
We shouldn’t divorce theory from practice.
Isaac Asimov(1920-1992) was a Russian- born American writer. His family immigrated to the US when he was three years old and settled in New York. He gained a master’s degree in chemistry and later got his PhD. After he graduated, he became a biochemistry teacher at Boston University.
He was talented in writing. When he realized it, he gave up teaching and became a professional writer. In 1939, he had stories published and in 1950 he published his first novel, which made him famous and won many awards. The Foundation trilogy and I, Robot are very popular with the young and adults.
Isaac Asimov was such a productive writer that he wrote more than 480 books. The readers are impressed by his extraodinary iamgination and an amazing mind, which also influnced other writers and even scientists researching into artificial intellignce.
1. That book on the Holy Bible needs to be returned to the library by the end of the week.
2. That old armchair is to be replaced by a sofa next week.
3. Don’t worry. You still have plenty of time for that fax to be sent to your company.
4. Your decision to divorce your wife has to be made with her agreement.
5. There has been an accident but there is no need to be alarmed. Nobody has been hurt.
6. Although she had done well, she expected her parents to be disappionted by her exam results.
7. She was happy to be supported by the affection of her family when she had a serious operation in hospital.
8. He was so excited to be declared the winner of the talent competition.
9. He added the 2,000 yuan they had received to the 1,500 yuan to be offered, making 3,500 yuan in all.
10. Without their leading player, they are bound to be beaten in the coming competition.
动词的时态
一般现在时:do/ does
一般过去时:did
现在进行时:am / is / are doing
过去进行时:was / were doing
现在完成时:have / has done
过去完成时:had done
一般将来时:shall / will done; be going to do
当句中含有情态动词时,句子结构为 can / must / have to…do
动词的被动语态也有时态
一般现在时:am / is / are done
一般过去时:was / were done
现在进行时:am / is / are being done
过去进行时:was / were being done
现在完成时:have / has been done
过去完成时:had been done
一般将来时:shall / will be done; be going to be done
当句中含有情态动词时,句子结构为 can / must / have to…be done
