初中英语情态动词 (共51张PPT)
文档属性
| 名称 | 初中英语情态动词 (共51张PPT) |

|
|
| 格式 | zip | ||
| 文件大小 | 1.3MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 人教新目标(Go for it)版 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2020-05-05 22:19:25 | ||
图片预览









文档简介
(共51张PPT)
1. can与could的用法 ★★★
语法知识
情态动词 用法 例句
can/
could 表示"能力",can表示现在的能力,could表示过去的能力 Can you lift this heavy box? 你能举起这个重箱子吗?
表示推测,通常用于否定句中,can’t表示 "不可能",用于表示把握比较大的否定推测 That can’t be Mary, for she is in hospital. 那不可能是玛丽,因为她在住院。
典例1 (not) you keep the children quiet? I’m trying to concentrate.
解析 结合下句"I’m trying to concentrate."可知,空处所在句应表示"难道你不能让孩子们保持安静吗?",此处表示能力,用Can’t。
答案 Can’t
语法知识
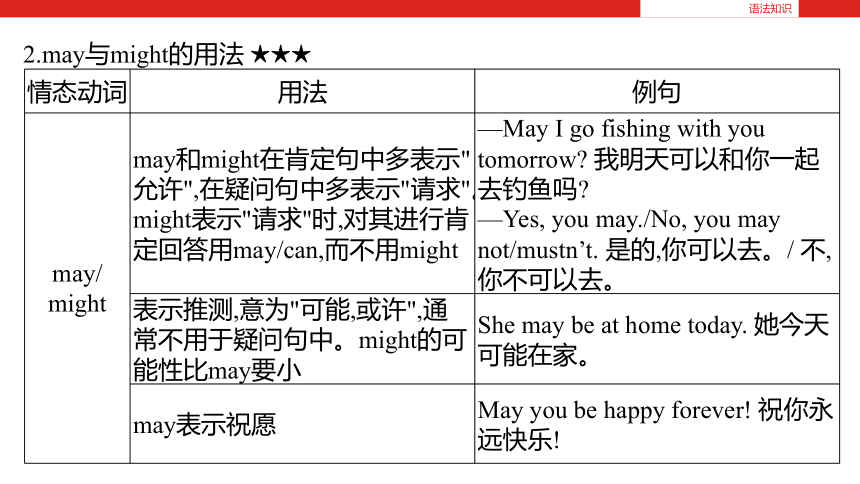
2.may与might的用法 ★★★
语法知识
情态动词 用法 例句
may/
might may和might在肯定句中多表示"允许",在疑问句中多表示"请求"。might表示"请求"时,对其进行肯定回答用may/can,而不用might —May I go fishing with you tomorrow? 我明天可以和你一起去钓鱼吗?
—Yes, you may./No, you may not/mustn’t. 是的,你可以去。/ 不,你不可以去。
表示推测,意为"可能,或许",通常不用于疑问句中。might的可能性比may要小 She may be at home today. 她今天可能在家。
may表示祝愿 May you be happy forever! 祝你永远快乐!
典例2 —You needn’t take an umbrella. It isn’t going to rain.
—Well, I don’t know. It do.
解析 句意:—你不必带伞。不会下雨的。—嗯,我不知道,可能会下吧。所填词表示把握不大的推测,意为"或许,可能",故本题填might"可能"。
答案 might
语法知识
3.must与have to的用法 ★☆☆
语法知识
情态动词 用法 例句
must 表示义务、必要性、命令等,意为"必须,应该",更强调主观态度。其否定形式为mustn’t,意为"不许,禁止" You must finish your
homeworkthis afternoon. 今天下午你必须完成你的家庭作业。
You mustn’t smoke here. 你不能在这儿吸烟。
表示推测,语气最为肯定,一般用于肯定句,意为"一定,准是" She must be tired after such a long walk. 走了这么长的路,她一定累了。
表示"偏偏,偏要",表示说话者对主语发出的动作是不满的,甚至是生气的 Must you make her cry?你偏要把她弄哭吗?
续表
语法知识
情态动词 用法 例句
have
to 表示客观需要,意为"必须,不得不",强调客观上的必要性 You have to be back before 10 o’clock becausethe train leaves at 10:05.你必须在10:00之前回来,因为火车10:05开。
典例3 Can’t you stay a little longer?
—It’s getting late. I really go now. My daughter is home alone.
解析 句意:—你就不能多待一会儿吗?—天越来越晚了。我现在真的必须走了。我女儿一个人在家里呢。根据答语中的"It’ getting late."以及"My daughter is home alone."可知,这里表示必须离开,故用must。
答案 must
语法知识
4.shall,should与ought to的用法 ★★★
语法知识
情态动词 用法 例句
shall 征求对方意见。用于主语是第一人称或第三人称的疑问句中 Henry is waiting outside. Shall he come in, sir?亨利正在门外等着,要他进来吗,先生?
表示说话者给出的命令、警告、许诺或威胁等。用于主语是第二人称或第三人称的陈述句中 You shall be punished for what you’ve done. 你将会为你所做的事情受到处罚。
Tell Jerry he shall get a gift if he is nice. 告诉杰里,如果表现好,他会得到一份礼物。
在条约、规定、法令等文件中表示规定或义务等 Those belonging to our club shall wear uniforms. 我们俱乐部的成员应该穿制服。
语法知识
情态动词 用法 例句
should 表示劝告、建议或命令 You should learn to respect your elders. 你应该学学尊敬长者。
表示义务和道义上的责任 You should help him because he is in trouble.你应该帮助他, 因为他有麻烦。
表示期待,用于表达合理的推断或明显的结果,且所期待的事几乎是事实 It is three o’clock now. The football match should begin soon. 现在3点了。足球赛应该很快就要开始了。
表示惊讶、忧虑、惋惜等情绪,意为"竟会,竟然" It’s a pity that you should be so careless. 很遗憾,你竟然如此粗心。
Why should anyone want to marry Tony?怎么竟然还有人想和托尼结婚?
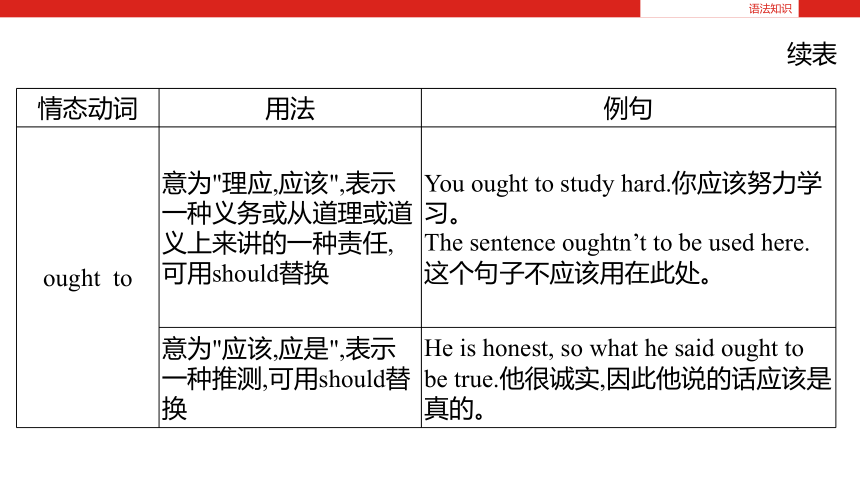
续表
语法知识
情态动词 用法 例句
ought to 意为"理应,应该",表示一种义务或从道理或道义上来讲的一种责任,可用should替换 You ought to study hard.你应该努力学习。
The sentence oughtn’t to be used here.这个句子不应该用在此处。
意为"应该,应是",表示一种推测,可用should替换 He is honest, so what he said ought to be true.他很诚实,因此他说的话应该是真的。
典例4 It was sad to me that they, so poor themselves, bring me food.
解析 句意:让我难过的是,如此贫穷的他们竟然给我带来了食物。should"竟然",符合句意。
答案 should
语法知识
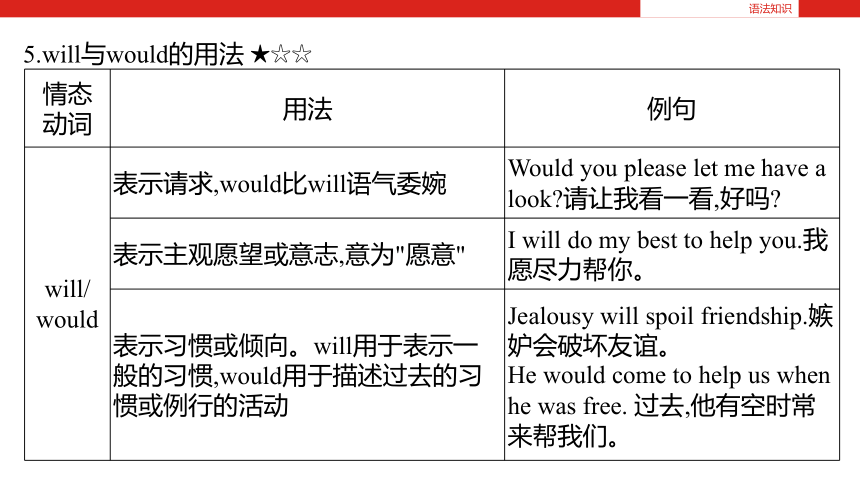
5.will与would的用法 ★☆☆
语法知识
情态
动词 用法 例句
will/
would 表示请求,would比will语气委婉 Would you please let me have a look?请让我看一看,好吗?
表示主观愿望或意志,意为"愿意" I will do my best to help you.我愿尽力帮你。
表示习惯或倾向。will用于表示一般的习惯,would用于描述过去的习惯或例行的活动 Jealousy will spoil friendship.嫉妒会破坏友谊。
He would come to help us when he was free. 过去,他有空时常来帮我们。
典例5 Days later, my brother called to say he was all right, but say where he was.
解析 句意:几天后,我的哥哥打电话说他一切都好,但是他不愿说他在哪儿。Wouldn’t "不愿意",符合语境。
答案 wouldn’t
语法知识
6.need与dare的用法 ★★☆
语法知识
情态动词 用法 例句
need 表示必要性,常用于疑问句和否定句中,needn’t 表示"不必";对need引出的一般疑问句作肯定回答时用must而不用need,作否定回答时用needn’t This is a free service; you needn’t pay for it.这是免费服务,你不必为此付款。
—Need I hand in the application now? 我需要现在交申请吗?
—Yes, you must./ No, you needn’t. 是的,你必须交。/ 不,你不必交。
续表
语法知识
情态动词 用法 例句
dare 意为"敢,胆敢",作情态动词时后跟动词原形,主要用于疑问句、否定句和条件句中 How dare she do things like that to me? 她怎么敢对我做那种事?
—Dare you catch the mouse? 你敢抓老鼠吗?
—No, I daren’t. 不,我不敢。
典例6 —I’ve prepared all kinds of food for the picnic.
—Do you mean we bring anything with us?
解析 句意:—我已经为野餐准备了各种食物。—你是说我们不必带任何东西了?needn’t"不必,不需要"。
答案 needn’t
语法知识
"情态动词+have done"既可表示对过去情况的推测,又可表示某种情绪、态度。情态动词不同,该结构所表示的含义也不同。
1. must have done ★★★
意为"一定已经做了……,想必……",用于肯定句中,表示对过去的肯定情况把握比较大的推测。
例 He must have been a doctor, for he knows medicines so well.他过去肯定是一位医生,因为他对药物非常了解。
考点2 "情态动词+have done"的用法
典例7 Harry is feeling uncomfortable. He have drunk too much at the party last night.
解析 句意:Harry觉得不舒服,他昨晚在聚会上肯定喝太多了。由last night及语境可知,此处表示对过去的肯定情况把握较大的推测。must have done sth."一定做了某事"。
答案 must
语法知识
2.could have done ★★☆
(1)意为"本能做某事(而实际上未做)",表示对过去未能实现的动作的一种责备或惋惜之情,此时could不能用 can替换。
例 We could have visited the museum but we spent too much time shopping.我们本来可以参观那个博物馆的,但我们购物花了太长时间。
(2) 意为"可能已经做了某事",表示对过去情况的推测。
例 He could have already arrived in Beijing.他可能已经到了北京。
特别提醒:
could have done的否定形式 couldn’t have done 只能表推测,相当于 can’t have done, 意为"(过去)不可能做了某事"。
语法知识
典例8 We have faced the difficulty together, but why didn’t you tell me?
解析 句意:我们本可以共同面对困难的,可你为什么不告诉我呢?but后的分句用的是一般过去时,由此可知but前的分句是对过去情况的推测,所以用"情态动词+have done"。could have done表示"本可以做某事(而实际上却没有做)",符合句意。
答案 could
语法知识
3.can’t have done/can have done ★☆☆
Can’t have done意为"不可能做了某事",表示对过去的否定情况把握较大的推测,相当于couldn’t have done;can have done表示"可能已经做了某事",用于疑问句中。需要特别注意的是can have done不用于肯定的陈述句中。
例 I think that he couldn’t/can’t have gone abroad. I saw him just now.我认为他不可能出国了。我刚才还看见他了。
例 Can he have arrived there?他可能已经到那儿了吗?
语法知识
典例9 —Why are your eyes so red? You have slept well last night.
—Yeah, I stayed up late writing a report.
解析 句意:—你的眼为什么这么红?你昨晚一定睡得不好。—是的,我熬夜写报告了。此处表示对过去的否定情况把握比较大的推测,故用can’t have done(不可能做了某事)这一结构。
答案 can’t
4. may/might have done ★★☆
(1)意为"可能已经做了某事",表示对过去情况的推测,might have done表示的可能性更小。
语法知识
例 You might have read about it in the newspaper.你可能已经在报上看过这个消息了。
典例10 —I left my handbag on the train, but luckily someone gave it to a railway official.
—How unbelievable to get it back! I mean, someone have stolen it.
解析 从对话情景可知他们在谈论过去的可能性:手提包当时有可能已被偷走, might have done在此意为"可能已经做了某事"。
答案 might
语法知识
(2)意为"本可以做某事(而实际上没做)",表示对过去某一未实现的动作的责备或惋惜之情。
例 He might have given you help, even though he was very busy. 即便很忙,他也本可以帮助你的。
5.should/ought to have done ★☆☆
可用于肯定句和否定句,should/ought to have done意为"本该做某事(而实际上未做)",表示责备或惋惜之情;shouldn’t/oughtn’t to have done意为"本不该做某事而实际上做了",表示责备或惋惜之情。
例 Yesterday was the deadline, and he should have completed his work.昨天是最后期限,他本该完成工作的。
语法知识
例 Tom oughtn’t to have told me your secret, but he meant no
harm.汤姆本不应该把你的秘密告诉我的,但他并无恶意。
6.needn’t have done ★☆☆
意为"本不必做某事(而实际上做了)"。
例 —Catherine, I have cleaned the room for you. 凯瑟琳,我已经替你把房间打扫了。
例 —Thanks. You needn’t have done it. I could manage it. 谢谢,你本不必做的,我能够应付。
语法知识
典例11 We have bought so much food now that Suzie won’t be with us for dinner.
解析 句意:既然Suzie不和我们一起吃晚饭了,我们本没有必要买这么多食物的。根据"now that Suzie won’t be with us for dinner"可知应填needn’t,needn’t have done表示"本没有必要做某事(而实际上做了)"。
答案 needn’t
通关秘籍:
表示推测时,"情态动词+have done"和"情态动词+do"的显著区别在于:前者表示过去的、有结果的事情,后者表示对现在或将来的推测。
语法知识
1.虚拟条件句 ★★★
(1)不同虚拟条件下,非真实条件句谓语的形式
考点3 虚拟语气
例 If I were 10 years younger, I would start all over again.如果我再年轻10岁,我会从头开始的。(虚拟现在)
例 If you succeeded/should succeed/were to succeed, everything would be all right.如果你成功的话,一切都会好起来的。(推测将来)
例 If you had warned him of the danger, he would not have been seriously injured.如果你警告他有危险,他就不会伤得这么严重。(虚拟过去)
典例12 We (be) back in the hotel now if you didn’t lose the map.
解析 句意:如果你没有把地图弄丢,那么我们现在就回到宾馆了。根据语境和now可知,此处表示的是对现在情况的虚拟,主句应用"情态动词+动词原形"。
答案 would be
语法知识
典例13 —Do you think George has passed the driving test?
—No. If so, he (drive) his car to our college yesterday.
解析 句意:—你认为乔治通过驾照考试了吗?—我想没有。如果通过了,他昨天就会开车去我们的大学了。结合答句句意可知,答句第二句所说的是非真实的情况,而且是对过去的情况进行虚拟,那么主句谓语形式应为should/would/could/might+have done。题干中的If so是If he had passed the driving test的省略形式。
答案 would have driven
语法知识
(2)虚拟条件句的倒装
例 Were I you, I would find a chance to make up with him.如果我是你,我就会找机会与他和好。
例 Had you had a deep communication with your mother, she would have supported you.如果你与你的妈妈深入地谈谈,她会支持你的。
例 Should I have time, I would go and watch the football game.要是我有时间,我会去看足球赛的。
语法知识
特别提醒:
如果条件从句的谓语为否定式,其中的否定词not应置于主语之后,而不能随were, should, had置于句首。如:
如果不是我警告你,你可能已经被杀了。
【正】 If I hadn’t warned you, you could have been killed.
【正】 Had I not warned you, you could have been killed.
【误】 Hadn’t I warned you, you could have been killed.
语法知识
典例14 (be) there no modern telecommunications, we would have to wait for weeks to get news from around the world.
解析 句意:如果没有现代化的电讯,要想收到来自世界各地的消息,我们就不得不等几个星期。本题是if条件句的虚拟语气,表示与现在事实相反,if从句中使用"一般过去时/were",即If there were no modern telecommunications,主句使用"情态动词+动词原形";当if省略的时候,要使用部分倒装,即Were there no modern telecommunications。
答案 Were
语法知识
2.错综时间条件句 ★☆☆
在错综时间条件句中,条件从句和结果主句的谓语动作发生的时间背景不同,因此,条件从句和结果主句的谓语要根据谓语动作各自的时间背景选用不同的形式。不同虚拟条件下,条件从句/结果主句谓语的形式:
条件从句
结果主句
语法知识
例 If I were you, I wouldn’t have missed the film last night. 如果我是你,我就不会错过昨天晚上的那部电影。(现在→过去)
例 If he had followed the doctor’s advice, he would recover now. 如果他听了医生的劝告,现在病就好了。(过去→现在)
例 If you hesitated this moment, you might suffer in future. 如果你此刻犹豫不决,你以后会吃苦头的。(现在→将来)
语法知识
特别提醒:
在错综时间条件句中,要特别注意主、从句中的时间状语,题干中有的明确给出了不同的时间状语,有的必须结合语境推测出时间。找准时间上的不同后,还要牢记主、从句谓语在不同虚拟条件下的不同形式,只有这样才能准确解题。
语法知识
典例15 If he had spent more time practising speaking English before, he
(be) able to speak it much better now.
解析 句意:如果他以前多花点儿时间练习说英语的话,现在他就能说得更好了。题干为错综时间条件句,从条件从句谓语的形式不难看出,从句表示对过去情况的虚拟;而从结果主句的时间状语可知,该主句表示对现在情况的虚拟,故该主句谓语动词的形式应为"would/should/could/might+动词原形"。
答案 would be
语法知识
3.含蓄条件句 ★☆☆
含蓄条件句中没有if引导的从句来表示虚拟条件,其虚拟条件通常由without,but for,otherwise等引出或表示,有些情况下,虚拟条件甚至要我们从上下文中来推断。without…,but for…,otherwise等可转化为if引导的条件从句。不同虚拟条件下,含蓄条件句谓语的形式:
例 But for your help, we couldn’t have succeeded. 要是没有你的帮助,我们是不会成功的。(虚拟过去)
语法知识
例 Without your help, I wouldn’t finish it.如果没有你的帮助,我将无法完成此事。(虚拟将来)
典例16 I (go) to my cousin’s birthday party last night, but I was not available.
解析 句意:要不是昨晚抽不出时间,我就去参加我堂弟的生日聚会了。结合句意和句中的"but I was not available"可知,题干前半句为含蓄条件句;由last night可知,该含蓄条件句表示对过去情况的虚拟,所以谓语形式为would/should/could/might+have done。
答案 would have gone
语法知识
4.虚拟语气在从句中的应用 ★★★
(1)在宾语从句中的应用
①command, demand,request, insist(坚持要求), require, order, suggest(建议)等表示命令、要求、建议的动词后的宾语从句用虚拟语气,从句谓语形式为"(should+)动词原形"。
例 She insisted that we (should) book some seats in advance.她坚持要求我们提前订些座位。
例 Mother suggested that I (should) go and apologize to my teacher.妈妈建议我去向老师道歉。
语法知识
特别提醒:
1.insist作"坚持要求"解,表示一种要求、请求时,其后的宾语从句用虚拟语气,即从句谓语形式为"(should+)do";而insist作"坚持认为,坚持说"解,用于陈述一种看法、实情的时候,其后的从句用陈述语气。如:
He insisted that he was innocent.他坚持认为他是无辜的。
2.suggest作"建议"解,表示一种意见的时候,其后的宾语从句用虚拟语气,即从句谓语形式为"(should+)do";而suggest作"表明,暗示"解,用于陈述一种实际情况的时候,从句谓语用陈述语气。如:
What he said suggested that he was a fraud. 他说的话表明他是个骗子。
语法知识
典例17 My mom suggests that we eat out for a change this weekend.
解析 句意:我的母亲建议我们这个周末出去吃饭,换换口味。suggest意为"建议",后接宾语从句时,从句要用虚拟语气,即从句谓语形式为"should+动词原形",should可以省略。
答案 should
通关秘籍:
表示"主张、要求、命令、建议"之类的动词后的宾语从句中,谓语动词要用"should+动词原形"的形式,should可省略。这样的动词有:一个"主张"→urge;两个"命令"→order,command;三个"建议"→suggest,advise,propose;四个"要求"→demand,request,require,ask。
语法知识
②wish后的宾语从句应用虚拟语气,不同虚拟条件下,从句谓语的形式:
例 I wish I hadn’t given him such a promise.我希望当初我没有向他许下那样的承诺。
例 I wish it were a sunny day today.我希望今天是个晴天。
例 I wish you could give me the book you borrowed from me last week tomorrow.我希望你明天把你上周从我这儿借的书还给我。
语法知识
典例18 wish I (be)at my sister’s wedding last Tuesday, but I was on a business trip in New York then.
解析 句意:我希望上周二参加了我姐姐的婚礼,但那时我在纽约出差。wish后的宾语从句应用虚拟语气,可用一般过去时表示与现在事实相反的虚拟语气,用过去完成时表示与过去事实相反的虚拟语气。由句中时间状语"last Tuesday"和"then"可知,空处表示与过去事实相反的虚拟语气,故用过去完成时。
答案 had been
语法知识
③would rather后的宾语从句用虚拟语气,不同虚拟条件下,从句谓语的形式:
例 I would rather you came to see me tomorrow.我宁愿你明天来看我。
例 I would rather you hadn’t told me the truth.我宁可你没有告诉我实情。
(2)在主语从句中的应用
语法知识
例 It is necessary that we (should) clean the room every day.我们每天打扫房间是有必要的。
例 It is required that middle school students (should) take exercise for at least one hour every day.中学生被要求每天至少进行一个小时的锻炼。
(3)在同位语从句中的应用
advice, suggestion, proposal, request, requirement, order, demand, desire等表示建议、要求、命令、愿望等的名词后的同位语从句通常用虚拟语气,即从句谓语形式为"(should+)动词原形"。
例 We agreed to his suggestion that we (should) go to Beijing for sightseeing.我们同意他提出的去北京观光的建议。
语法知识
例 He issued the order that the troops(should) withdraw at once.他命令部队马上撤退。
(4)在表语从句中的应用
advice, suggestion, proposal, request, requirement, order, demand, desire等表示建议、要求、命令、愿望等的名词后的表语从句通常用虚拟语气,即从句谓语形式为"(should+)动词原形"。
例 His suggestion is that we (should) persuade her to stay here first.他的建议是我们首先说服她待在这儿。
例 My desire is that we (should) not quarrel over such things again.我的希望是我们不要再为这样的事情争吵了。
语法知识
典例19 My suggestion was that necessary measures (take) to protect the children from dangerous classrooms.
解析 句意:我的建议是采取必要措施来保护孩子远离危险的教室。that在此引导表语从句,suggestion(建议)后的表语从句通常用虚拟语气,故从句谓语部分用"(should+)动词原形",又measures与take之间为动宾关系,故应填(should) be taken。
答案 (should)be taken
语法知识
(5)在其他句型中的应用
①as if/as though引导的方式状语从句/表语从句表示与事实相反的情况或推测将来时,从句用虚拟语气。不同虚拟条件下从句谓语的形式:
例 He speaks as if/as though he knew all about it.他说起话来就好像他完全知道这件事似的。
例 He talks about pyramids as if/as though he had seen them himself.他谈论起金字塔来就好像他曾经亲眼见过似的。
语法知识
典例20 Don’t handle the vase as if it (be) made of steel.
解析 as if表示"似乎,好像",在此引导方式状语从句。主句的时态是一般现在时,此处as if引导的方式状语从句表示对现在情况的虚拟,故从句谓语应该用一般过去时。
答案 were
通关秘籍:
as if/as though引导表语从句时,常位于look,seem,feel,taste,smell,sound等系动词之后;引导方式状语从句时,常位于behave,act,talk等行为动词之后。若从句叙述的情况是真实的或出现的可能性很大,从句用陈述语气;若从句叙述的情况是非真实的或出现的可能性很小,则从句用虚拟语气。
语法知识
②It’s (high/about)time (that)…句型中,that引导的从句通常用虚拟语气,此时从句中谓语动词用过去式或"should+动词原形",必须注意的是should不能省掉。
例 It is about time that we were off.我们该离开了。
例 It is high time that you should teach him a lesson.你该教训一下他了。
典例21 Jack is a great talker. It’s high time that he (do) something instead of just talking.
解析 句意:杰克总是夸夸其谈,他该做点事了,而不是仅仅空谈。题干第二句是“It’s high time that…"句型,其中从句中谓语动词用过去式或"should+动词原形",且should不能省略。
答案 did/should do
语法知识
③if only后的句子常用虚拟语气,句子谓语用一般过去时表示当前没有实现的愿望,用过去完成时表示过去没有实现的愿望。
例 If only she had known where to find you.当时她要是知道去哪儿找你就好了。
例 If only I could speak several foreign languages!我要是能说几门外语就好了!
典例22 If only he (lie) quietly as instructed, he would not suffer so much now.
解析 if only 后的句子通常用虚拟语气,且此处表示对过去情况的虚拟,故此处谓语形式为"had+过去分词"。
答案 had lain
语法知识
1. can与could的用法 ★★★
语法知识
情态动词 用法 例句
can/
could 表示"能力",can表示现在的能力,could表示过去的能力 Can you lift this heavy box? 你能举起这个重箱子吗?
表示推测,通常用于否定句中,can’t表示 "不可能",用于表示把握比较大的否定推测 That can’t be Mary, for she is in hospital. 那不可能是玛丽,因为她在住院。
典例1 (not) you keep the children quiet? I’m trying to concentrate.
解析 结合下句"I’m trying to concentrate."可知,空处所在句应表示"难道你不能让孩子们保持安静吗?",此处表示能力,用Can’t。
答案 Can’t
语法知识
2.may与might的用法 ★★★
语法知识
情态动词 用法 例句
may/
might may和might在肯定句中多表示"允许",在疑问句中多表示"请求"。might表示"请求"时,对其进行肯定回答用may/can,而不用might —May I go fishing with you tomorrow? 我明天可以和你一起去钓鱼吗?
—Yes, you may./No, you may not/mustn’t. 是的,你可以去。/ 不,你不可以去。
表示推测,意为"可能,或许",通常不用于疑问句中。might的可能性比may要小 She may be at home today. 她今天可能在家。
may表示祝愿 May you be happy forever! 祝你永远快乐!
典例2 —You needn’t take an umbrella. It isn’t going to rain.
—Well, I don’t know. It do.
解析 句意:—你不必带伞。不会下雨的。—嗯,我不知道,可能会下吧。所填词表示把握不大的推测,意为"或许,可能",故本题填might"可能"。
答案 might
语法知识
3.must与have to的用法 ★☆☆
语法知识
情态动词 用法 例句
must 表示义务、必要性、命令等,意为"必须,应该",更强调主观态度。其否定形式为mustn’t,意为"不许,禁止" You must finish your
homeworkthis afternoon. 今天下午你必须完成你的家庭作业。
You mustn’t smoke here. 你不能在这儿吸烟。
表示推测,语气最为肯定,一般用于肯定句,意为"一定,准是" She must be tired after such a long walk. 走了这么长的路,她一定累了。
表示"偏偏,偏要",表示说话者对主语发出的动作是不满的,甚至是生气的 Must you make her cry?你偏要把她弄哭吗?
续表
语法知识
情态动词 用法 例句
have
to 表示客观需要,意为"必须,不得不",强调客观上的必要性 You have to be back before 10 o’clock becausethe train leaves at 10:05.你必须在10:00之前回来,因为火车10:05开。
典例3 Can’t you stay a little longer?
—It’s getting late. I really go now. My daughter is home alone.
解析 句意:—你就不能多待一会儿吗?—天越来越晚了。我现在真的必须走了。我女儿一个人在家里呢。根据答语中的"It’ getting late."以及"My daughter is home alone."可知,这里表示必须离开,故用must。
答案 must
语法知识
4.shall,should与ought to的用法 ★★★
语法知识
情态动词 用法 例句
shall 征求对方意见。用于主语是第一人称或第三人称的疑问句中 Henry is waiting outside. Shall he come in, sir?亨利正在门外等着,要他进来吗,先生?
表示说话者给出的命令、警告、许诺或威胁等。用于主语是第二人称或第三人称的陈述句中 You shall be punished for what you’ve done. 你将会为你所做的事情受到处罚。
Tell Jerry he shall get a gift if he is nice. 告诉杰里,如果表现好,他会得到一份礼物。
在条约、规定、法令等文件中表示规定或义务等 Those belonging to our club shall wear uniforms. 我们俱乐部的成员应该穿制服。
语法知识
情态动词 用法 例句
should 表示劝告、建议或命令 You should learn to respect your elders. 你应该学学尊敬长者。
表示义务和道义上的责任 You should help him because he is in trouble.你应该帮助他, 因为他有麻烦。
表示期待,用于表达合理的推断或明显的结果,且所期待的事几乎是事实 It is three o’clock now. The football match should begin soon. 现在3点了。足球赛应该很快就要开始了。
表示惊讶、忧虑、惋惜等情绪,意为"竟会,竟然" It’s a pity that you should be so careless. 很遗憾,你竟然如此粗心。
Why should anyone want to marry Tony?怎么竟然还有人想和托尼结婚?
续表
语法知识
情态动词 用法 例句
ought to 意为"理应,应该",表示一种义务或从道理或道义上来讲的一种责任,可用should替换 You ought to study hard.你应该努力学习。
The sentence oughtn’t to be used here.这个句子不应该用在此处。
意为"应该,应是",表示一种推测,可用should替换 He is honest, so what he said ought to be true.他很诚实,因此他说的话应该是真的。
典例4 It was sad to me that they, so poor themselves, bring me food.
解析 句意:让我难过的是,如此贫穷的他们竟然给我带来了食物。should"竟然",符合句意。
答案 should
语法知识
5.will与would的用法 ★☆☆
语法知识
情态
动词 用法 例句
will/
would 表示请求,would比will语气委婉 Would you please let me have a look?请让我看一看,好吗?
表示主观愿望或意志,意为"愿意" I will do my best to help you.我愿尽力帮你。
表示习惯或倾向。will用于表示一般的习惯,would用于描述过去的习惯或例行的活动 Jealousy will spoil friendship.嫉妒会破坏友谊。
He would come to help us when he was free. 过去,他有空时常来帮我们。
典例5 Days later, my brother called to say he was all right, but say where he was.
解析 句意:几天后,我的哥哥打电话说他一切都好,但是他不愿说他在哪儿。Wouldn’t "不愿意",符合语境。
答案 wouldn’t
语法知识
6.need与dare的用法 ★★☆
语法知识
情态动词 用法 例句
need 表示必要性,常用于疑问句和否定句中,needn’t 表示"不必";对need引出的一般疑问句作肯定回答时用must而不用need,作否定回答时用needn’t This is a free service; you needn’t pay for it.这是免费服务,你不必为此付款。
—Need I hand in the application now? 我需要现在交申请吗?
—Yes, you must./ No, you needn’t. 是的,你必须交。/ 不,你不必交。
续表
语法知识
情态动词 用法 例句
dare 意为"敢,胆敢",作情态动词时后跟动词原形,主要用于疑问句、否定句和条件句中 How dare she do things like that to me? 她怎么敢对我做那种事?
—Dare you catch the mouse? 你敢抓老鼠吗?
—No, I daren’t. 不,我不敢。
典例6 —I’ve prepared all kinds of food for the picnic.
—Do you mean we bring anything with us?
解析 句意:—我已经为野餐准备了各种食物。—你是说我们不必带任何东西了?needn’t"不必,不需要"。
答案 needn’t
语法知识
"情态动词+have done"既可表示对过去情况的推测,又可表示某种情绪、态度。情态动词不同,该结构所表示的含义也不同。
1. must have done ★★★
意为"一定已经做了……,想必……",用于肯定句中,表示对过去的肯定情况把握比较大的推测。
例 He must have been a doctor, for he knows medicines so well.他过去肯定是一位医生,因为他对药物非常了解。
考点2 "情态动词+have done"的用法
典例7 Harry is feeling uncomfortable. He have drunk too much at the party last night.
解析 句意:Harry觉得不舒服,他昨晚在聚会上肯定喝太多了。由last night及语境可知,此处表示对过去的肯定情况把握较大的推测。must have done sth."一定做了某事"。
答案 must
语法知识
2.could have done ★★☆
(1)意为"本能做某事(而实际上未做)",表示对过去未能实现的动作的一种责备或惋惜之情,此时could不能用 can替换。
例 We could have visited the museum but we spent too much time shopping.我们本来可以参观那个博物馆的,但我们购物花了太长时间。
(2) 意为"可能已经做了某事",表示对过去情况的推测。
例 He could have already arrived in Beijing.他可能已经到了北京。
特别提醒:
could have done的否定形式 couldn’t have done 只能表推测,相当于 can’t have done, 意为"(过去)不可能做了某事"。
语法知识
典例8 We have faced the difficulty together, but why didn’t you tell me?
解析 句意:我们本可以共同面对困难的,可你为什么不告诉我呢?but后的分句用的是一般过去时,由此可知but前的分句是对过去情况的推测,所以用"情态动词+have done"。could have done表示"本可以做某事(而实际上却没有做)",符合句意。
答案 could
语法知识
3.can’t have done/can have done ★☆☆
Can’t have done意为"不可能做了某事",表示对过去的否定情况把握较大的推测,相当于couldn’t have done;can have done表示"可能已经做了某事",用于疑问句中。需要特别注意的是can have done不用于肯定的陈述句中。
例 I think that he couldn’t/can’t have gone abroad. I saw him just now.我认为他不可能出国了。我刚才还看见他了。
例 Can he have arrived there?他可能已经到那儿了吗?
语法知识
典例9 —Why are your eyes so red? You have slept well last night.
—Yeah, I stayed up late writing a report.
解析 句意:—你的眼为什么这么红?你昨晚一定睡得不好。—是的,我熬夜写报告了。此处表示对过去的否定情况把握比较大的推测,故用can’t have done(不可能做了某事)这一结构。
答案 can’t
4. may/might have done ★★☆
(1)意为"可能已经做了某事",表示对过去情况的推测,might have done表示的可能性更小。
语法知识
例 You might have read about it in the newspaper.你可能已经在报上看过这个消息了。
典例10 —I left my handbag on the train, but luckily someone gave it to a railway official.
—How unbelievable to get it back! I mean, someone have stolen it.
解析 从对话情景可知他们在谈论过去的可能性:手提包当时有可能已被偷走, might have done在此意为"可能已经做了某事"。
答案 might
语法知识
(2)意为"本可以做某事(而实际上没做)",表示对过去某一未实现的动作的责备或惋惜之情。
例 He might have given you help, even though he was very busy. 即便很忙,他也本可以帮助你的。
5.should/ought to have done ★☆☆
可用于肯定句和否定句,should/ought to have done意为"本该做某事(而实际上未做)",表示责备或惋惜之情;shouldn’t/oughtn’t to have done意为"本不该做某事而实际上做了",表示责备或惋惜之情。
例 Yesterday was the deadline, and he should have completed his work.昨天是最后期限,他本该完成工作的。
语法知识
例 Tom oughtn’t to have told me your secret, but he meant no
harm.汤姆本不应该把你的秘密告诉我的,但他并无恶意。
6.needn’t have done ★☆☆
意为"本不必做某事(而实际上做了)"。
例 —Catherine, I have cleaned the room for you. 凯瑟琳,我已经替你把房间打扫了。
例 —Thanks. You needn’t have done it. I could manage it. 谢谢,你本不必做的,我能够应付。
语法知识
典例11 We have bought so much food now that Suzie won’t be with us for dinner.
解析 句意:既然Suzie不和我们一起吃晚饭了,我们本没有必要买这么多食物的。根据"now that Suzie won’t be with us for dinner"可知应填needn’t,needn’t have done表示"本没有必要做某事(而实际上做了)"。
答案 needn’t
通关秘籍:
表示推测时,"情态动词+have done"和"情态动词+do"的显著区别在于:前者表示过去的、有结果的事情,后者表示对现在或将来的推测。
语法知识
1.虚拟条件句 ★★★
(1)不同虚拟条件下,非真实条件句谓语的形式
考点3 虚拟语气
例 If I were 10 years younger, I would start all over again.如果我再年轻10岁,我会从头开始的。(虚拟现在)
例 If you succeeded/should succeed/were to succeed, everything would be all right.如果你成功的话,一切都会好起来的。(推测将来)
例 If you had warned him of the danger, he would not have been seriously injured.如果你警告他有危险,他就不会伤得这么严重。(虚拟过去)
典例12 We (be) back in the hotel now if you didn’t lose the map.
解析 句意:如果你没有把地图弄丢,那么我们现在就回到宾馆了。根据语境和now可知,此处表示的是对现在情况的虚拟,主句应用"情态动词+动词原形"。
答案 would be
语法知识
典例13 —Do you think George has passed the driving test?
—No. If so, he (drive) his car to our college yesterday.
解析 句意:—你认为乔治通过驾照考试了吗?—我想没有。如果通过了,他昨天就会开车去我们的大学了。结合答句句意可知,答句第二句所说的是非真实的情况,而且是对过去的情况进行虚拟,那么主句谓语形式应为should/would/could/might+have done。题干中的If so是If he had passed the driving test的省略形式。
答案 would have driven
语法知识
(2)虚拟条件句的倒装
例 Were I you, I would find a chance to make up with him.如果我是你,我就会找机会与他和好。
例 Had you had a deep communication with your mother, she would have supported you.如果你与你的妈妈深入地谈谈,她会支持你的。
例 Should I have time, I would go and watch the football game.要是我有时间,我会去看足球赛的。
语法知识
特别提醒:
如果条件从句的谓语为否定式,其中的否定词not应置于主语之后,而不能随were, should, had置于句首。如:
如果不是我警告你,你可能已经被杀了。
【正】 If I hadn’t warned you, you could have been killed.
【正】 Had I not warned you, you could have been killed.
【误】 Hadn’t I warned you, you could have been killed.
语法知识
典例14 (be) there no modern telecommunications, we would have to wait for weeks to get news from around the world.
解析 句意:如果没有现代化的电讯,要想收到来自世界各地的消息,我们就不得不等几个星期。本题是if条件句的虚拟语气,表示与现在事实相反,if从句中使用"一般过去时/were",即If there were no modern telecommunications,主句使用"情态动词+动词原形";当if省略的时候,要使用部分倒装,即Were there no modern telecommunications。
答案 Were
语法知识
2.错综时间条件句 ★☆☆
在错综时间条件句中,条件从句和结果主句的谓语动作发生的时间背景不同,因此,条件从句和结果主句的谓语要根据谓语动作各自的时间背景选用不同的形式。不同虚拟条件下,条件从句/结果主句谓语的形式:
条件从句
结果主句
语法知识
例 If I were you, I wouldn’t have missed the film last night. 如果我是你,我就不会错过昨天晚上的那部电影。(现在→过去)
例 If he had followed the doctor’s advice, he would recover now. 如果他听了医生的劝告,现在病就好了。(过去→现在)
例 If you hesitated this moment, you might suffer in future. 如果你此刻犹豫不决,你以后会吃苦头的。(现在→将来)
语法知识
特别提醒:
在错综时间条件句中,要特别注意主、从句中的时间状语,题干中有的明确给出了不同的时间状语,有的必须结合语境推测出时间。找准时间上的不同后,还要牢记主、从句谓语在不同虚拟条件下的不同形式,只有这样才能准确解题。
语法知识
典例15 If he had spent more time practising speaking English before, he
(be) able to speak it much better now.
解析 句意:如果他以前多花点儿时间练习说英语的话,现在他就能说得更好了。题干为错综时间条件句,从条件从句谓语的形式不难看出,从句表示对过去情况的虚拟;而从结果主句的时间状语可知,该主句表示对现在情况的虚拟,故该主句谓语动词的形式应为"would/should/could/might+动词原形"。
答案 would be
语法知识
3.含蓄条件句 ★☆☆
含蓄条件句中没有if引导的从句来表示虚拟条件,其虚拟条件通常由without,but for,otherwise等引出或表示,有些情况下,虚拟条件甚至要我们从上下文中来推断。without…,but for…,otherwise等可转化为if引导的条件从句。不同虚拟条件下,含蓄条件句谓语的形式:
例 But for your help, we couldn’t have succeeded. 要是没有你的帮助,我们是不会成功的。(虚拟过去)
语法知识
例 Without your help, I wouldn’t finish it.如果没有你的帮助,我将无法完成此事。(虚拟将来)
典例16 I (go) to my cousin’s birthday party last night, but I was not available.
解析 句意:要不是昨晚抽不出时间,我就去参加我堂弟的生日聚会了。结合句意和句中的"but I was not available"可知,题干前半句为含蓄条件句;由last night可知,该含蓄条件句表示对过去情况的虚拟,所以谓语形式为would/should/could/might+have done。
答案 would have gone
语法知识
4.虚拟语气在从句中的应用 ★★★
(1)在宾语从句中的应用
①command, demand,request, insist(坚持要求), require, order, suggest(建议)等表示命令、要求、建议的动词后的宾语从句用虚拟语气,从句谓语形式为"(should+)动词原形"。
例 She insisted that we (should) book some seats in advance.她坚持要求我们提前订些座位。
例 Mother suggested that I (should) go and apologize to my teacher.妈妈建议我去向老师道歉。
语法知识
特别提醒:
1.insist作"坚持要求"解,表示一种要求、请求时,其后的宾语从句用虚拟语气,即从句谓语形式为"(should+)do";而insist作"坚持认为,坚持说"解,用于陈述一种看法、实情的时候,其后的从句用陈述语气。如:
He insisted that he was innocent.他坚持认为他是无辜的。
2.suggest作"建议"解,表示一种意见的时候,其后的宾语从句用虚拟语气,即从句谓语形式为"(should+)do";而suggest作"表明,暗示"解,用于陈述一种实际情况的时候,从句谓语用陈述语气。如:
What he said suggested that he was a fraud. 他说的话表明他是个骗子。
语法知识
典例17 My mom suggests that we eat out for a change this weekend.
解析 句意:我的母亲建议我们这个周末出去吃饭,换换口味。suggest意为"建议",后接宾语从句时,从句要用虚拟语气,即从句谓语形式为"should+动词原形",should可以省略。
答案 should
通关秘籍:
表示"主张、要求、命令、建议"之类的动词后的宾语从句中,谓语动词要用"should+动词原形"的形式,should可省略。这样的动词有:一个"主张"→urge;两个"命令"→order,command;三个"建议"→suggest,advise,propose;四个"要求"→demand,request,require,ask。
语法知识
②wish后的宾语从句应用虚拟语气,不同虚拟条件下,从句谓语的形式:
例 I wish I hadn’t given him such a promise.我希望当初我没有向他许下那样的承诺。
例 I wish it were a sunny day today.我希望今天是个晴天。
例 I wish you could give me the book you borrowed from me last week tomorrow.我希望你明天把你上周从我这儿借的书还给我。
语法知识
典例18 wish I (be)at my sister’s wedding last Tuesday, but I was on a business trip in New York then.
解析 句意:我希望上周二参加了我姐姐的婚礼,但那时我在纽约出差。wish后的宾语从句应用虚拟语气,可用一般过去时表示与现在事实相反的虚拟语气,用过去完成时表示与过去事实相反的虚拟语气。由句中时间状语"last Tuesday"和"then"可知,空处表示与过去事实相反的虚拟语气,故用过去完成时。
答案 had been
语法知识
③would rather后的宾语从句用虚拟语气,不同虚拟条件下,从句谓语的形式:
例 I would rather you came to see me tomorrow.我宁愿你明天来看我。
例 I would rather you hadn’t told me the truth.我宁可你没有告诉我实情。
(2)在主语从句中的应用
语法知识
例 It is necessary that we (should) clean the room every day.我们每天打扫房间是有必要的。
例 It is required that middle school students (should) take exercise for at least one hour every day.中学生被要求每天至少进行一个小时的锻炼。
(3)在同位语从句中的应用
advice, suggestion, proposal, request, requirement, order, demand, desire等表示建议、要求、命令、愿望等的名词后的同位语从句通常用虚拟语气,即从句谓语形式为"(should+)动词原形"。
例 We agreed to his suggestion that we (should) go to Beijing for sightseeing.我们同意他提出的去北京观光的建议。
语法知识
例 He issued the order that the troops(should) withdraw at once.他命令部队马上撤退。
(4)在表语从句中的应用
advice, suggestion, proposal, request, requirement, order, demand, desire等表示建议、要求、命令、愿望等的名词后的表语从句通常用虚拟语气,即从句谓语形式为"(should+)动词原形"。
例 His suggestion is that we (should) persuade her to stay here first.他的建议是我们首先说服她待在这儿。
例 My desire is that we (should) not quarrel over such things again.我的希望是我们不要再为这样的事情争吵了。
语法知识
典例19 My suggestion was that necessary measures (take) to protect the children from dangerous classrooms.
解析 句意:我的建议是采取必要措施来保护孩子远离危险的教室。that在此引导表语从句,suggestion(建议)后的表语从句通常用虚拟语气,故从句谓语部分用"(should+)动词原形",又measures与take之间为动宾关系,故应填(should) be taken。
答案 (should)be taken
语法知识
(5)在其他句型中的应用
①as if/as though引导的方式状语从句/表语从句表示与事实相反的情况或推测将来时,从句用虚拟语气。不同虚拟条件下从句谓语的形式:
例 He speaks as if/as though he knew all about it.他说起话来就好像他完全知道这件事似的。
例 He talks about pyramids as if/as though he had seen them himself.他谈论起金字塔来就好像他曾经亲眼见过似的。
语法知识
典例20 Don’t handle the vase as if it (be) made of steel.
解析 as if表示"似乎,好像",在此引导方式状语从句。主句的时态是一般现在时,此处as if引导的方式状语从句表示对现在情况的虚拟,故从句谓语应该用一般过去时。
答案 were
通关秘籍:
as if/as though引导表语从句时,常位于look,seem,feel,taste,smell,sound等系动词之后;引导方式状语从句时,常位于behave,act,talk等行为动词之后。若从句叙述的情况是真实的或出现的可能性很大,从句用陈述语气;若从句叙述的情况是非真实的或出现的可能性很小,则从句用虚拟语气。
语法知识
②It’s (high/about)time (that)…句型中,that引导的从句通常用虚拟语气,此时从句中谓语动词用过去式或"should+动词原形",必须注意的是should不能省掉。
例 It is about time that we were off.我们该离开了。
例 It is high time that you should teach him a lesson.你该教训一下他了。
典例21 Jack is a great talker. It’s high time that he (do) something instead of just talking.
解析 句意:杰克总是夸夸其谈,他该做点事了,而不是仅仅空谈。题干第二句是“It’s high time that…"句型,其中从句中谓语动词用过去式或"should+动词原形",且should不能省略。
答案 did/should do
语法知识
③if only后的句子常用虚拟语气,句子谓语用一般过去时表示当前没有实现的愿望,用过去完成时表示过去没有实现的愿望。
例 If only she had known where to find you.当时她要是知道去哪儿找你就好了。
例 If only I could speak several foreign languages!我要是能说几门外语就好了!
典例22 If only he (lie) quietly as instructed, he would not suffer so much now.
解析 if only 后的句子通常用虚拟语气,且此处表示对过去情况的虚拟,故此处谓语形式为"had+过去分词"。
答案 had lain
语法知识
同课章节目录
- 词法
- 名词
- 动词和动词短语
- 动词语态
- 动词时态
- 助动词和情态动词
- 非谓语动词
- 冠词
- 代词
- 数词和量词
- 形容词副词及其比较等级
- 介词和介词短语
- 连词和感叹词
- 构词法
- 相似、相近词比较
- 句法
- 陈述句
- 一般疑问句和否定疑问句
- 特殊疑问句及选择疑问句
- 反意疑问句
- 存在句(There be句型)
- 宾语从句
- 定语从句
- 状语从句
- 主谓一致问题
- 简单句
- 并列句
- 复合句
- 主谓一致
- 主、表语从句
- 名词性从句
- 直接引语和间接引语
- 虚拟语气
- 感叹句
- 强调句
- 倒装句
- 祈使句
- 句子的成分
- 句子的分类
- 题型专区
- 单项选择部分
- 易错题
- 完形填空
- 阅读理解
- 词汇练习
- 听说训练
- 句型转换
- 补全对话
- 短文改错
- 翻译
- 书面表达
- 任务型阅读
- 语法填空
- 其他资料
