外研版选修8 Module 1 Deep South Grammar 课件(37张PPT)
文档属性
| 名称 | 外研版选修8 Module 1 Deep South Grammar 课件(37张PPT) |

|
|
| 格式 | zip | ||
| 文件大小 | 739.9KB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 外研版 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2020-05-21 00:00:00 | ||
图片预览











文档简介
(共37张PPT)
Module 1 Deep South
Grammar
Yesterday Once More
When I was young
I'd listen to the radio
Waitin' for my favorite songs
When they played I'd sing along
It made me smile
Those were such happy times
And not so long ago
How I wondered where they'd gone
But they're back again
Just like a long lost friend
All the songs I loved so well
Every sha la la la
Every wo o wo o
Still shines
Every shing a ling a ling
That they're startin' to sing's
So fine
When they get to the part
Where he's breakin' her heart
It can really make me cry
Just like before
It's yesterday once more
Review of subjects.
Review of verbs.
Learning aims
Look at the sentences and find out the subjects in these sentences.
98% of the surface is covered permanently in the ice
cap.
2. Covering about 14 million square kilometres around
the South Pole, it is the fifth largest continent
in the world.
Grammar (1): 主语
Leading-in
3. A high mountain range, the Trans-Antarctic range, runs from east to west, cutting the continent in two.
4. It is difficult to imagine a more inhospitable place.
5. Antarctica is full of wildlife, which has adapted to its extreme conditions.
6. Only two types of flowering plants are found.
7. There are different types of penguins, flying birds, seals, and whales.
8. Protecting Antarctica from nuclear tests and radioactive waste is very important to this continent.
9. What the treaty aims to do is to prevent the commercial and military use of the continent.
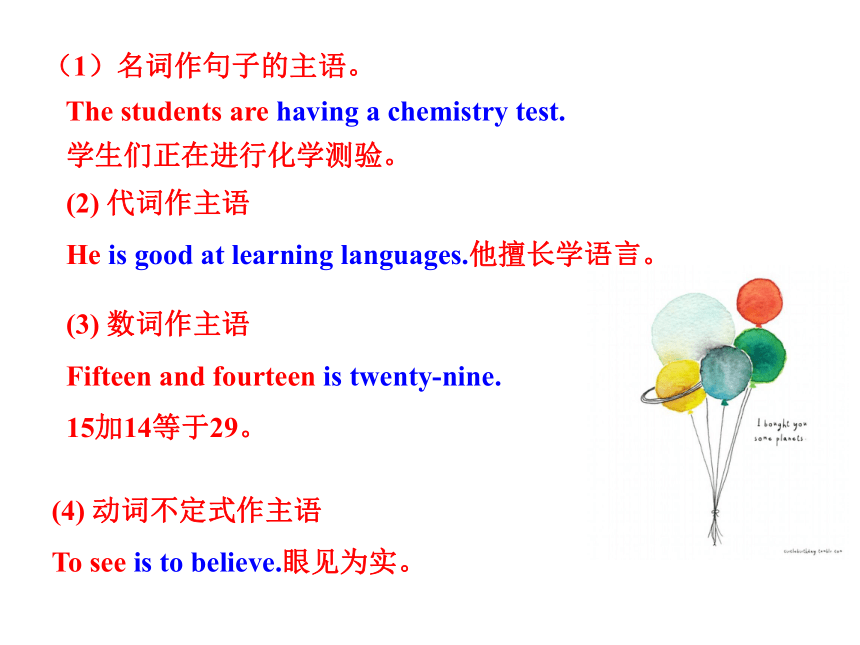
主语是句子动作的发出者,是句子叙述的主体,是句子所要说明的人或事物,表示句子描述的是谁或什么。主语通常由名词,代词,数词,名词化的形容词,动词不定式,动名词或从句等充当。通常位于谓语动词前。
(2) 代词作主语
He is good at learning languages.他擅长学语言。
(3) 数词作主语
Fifteen and fourteen is twenty-nine.
15加14等于29。
(4) 动词不定式作主语
To see is to believe.眼见为实。
(1)名词作句子的主语。
The students are having a chemistry test.
学生们正在进行化学测验。
(5) 动名词作主语
Reading in bed is a bad habit.
在床上阅读是个坏习惯。
(6) it作形式主语
It’s not easy to master a foreign language.
掌握一门外语不容易。
(7) 从句作主语
What he wanted best was knowledge.
他最想要的是知识。
注意下列的主语形式:
(1)v.-ing作主语时,可以有自己的逻辑主语及代词或名词所有格等。
Jack’s/ My winning the match is an inspiration to all of the team.
杰克/我赢得比赛对于所有的队员是个鼓舞。
(2)以there引导的句子,主语通常放在谓语的后面,
谓语动词的数根据后面的主语来定。
There stand/ are a large number of factories in the east of the city. 在城市的东部有许多工厂。
(3)在it作主语的句子中。
①人称代词:不明身份性别时用it
Someone is knocking at the door. Who can it be?
有人在敲门,它可能是谁?
②非人称代词:表示天气,时间等。
It’s raining. 天正在下雨。
③形式主语/宾语:
It’s important for us to learn English well.
学好英语对我们来说很重要。
④用于强调: it is... that /who...
It was because of the bad weather that we were late for school yesterday.
由于坏天气,昨天我们迟到了。
(4)名词化的其他词类。the + adj.表示一类,复数概念,谓语用复数。
The rich should help the poor.富人应该帮助穷人。
The wounded were treated in time.
伤员们得到了及时救治。
1. ___________________________describes a bright future for the company.
你在会议上所说的描述了公司的美好未来。
2. _________ basic first-aid techniques will help you
respond quickly to emergencies.
知道基本的急救技术将会帮助你对紧急情况快速作出
反应。
Class exercises
What you said at the meeting
Knowing
Ⅰ.完成句子。
3. (2014·陕西高考) ______________________________
depends much on the weather.
延时航班何时起飞主要取决于天气。
4. (2014·山东高考)It’s standard practice for a company
like this one __________a security officer.
像这样的公司常规做法是要雇用一位安全人员。
to employ
When the delayed flight will take off
Underline the verb structures in these sentences.
(1)The Endurance became trapped, and Shackleton
and his men watched it sink into the icy sea.
(2) He and five men would take one of the lifeboats,
and sail 800 miles to South Georgia, where there was a
permanent camp.
(3) He had to walk 36 hours over mountains to reach
the camp.
Grammar (2):动词
(4) The whale hunters at the camp couldn’t believe
their eyes when they saw the six men walking down
from the mountains.
(5) He returned to Elephant Island to rescue the crew
he had been forced to abandon.
谓语动词是对主语动作或状态的陈述或说明,指出做什么,是什么或是怎么样。谓语动词的位置一般在主语之后。在英语中,动词按作用和功能主要分为两大类,一类是谓语动词,另一类是非谓语动词。
行为动词: 表示动作或状态,能单独作谓语动词。谓
语动词可分及物和不及物两种。及物动词后带宾语,不
及物动词后不带宾语。
I thought hard and found the answer.
我努力思考,找到了答案。
动词的种类和基本形式
根据动词实际的意义可分为行为动词或实义动词;根据
动词能否带宾语,分为及物动词和不及物动词;
根据动词的作用可分为连系动词、情态动词和助动词。
2. 连系动词:连系动词本身有一定的词义,但不能独立作谓语,必须与表语一起构成谓语。系动词没有被动语态。表语通常由名词、形容词,或相当于名词或形容词的词或短语等充当,说明主语是什么或怎么样。
The mountain is very attractive.
这座山非常有吸引力。
Those oranges taste good.
那些橘子很好吃。
It’s already ten in the morning. The store remains closed.
已经上午十点了,商店仍然关着。
Put the fish in the fridge, or it will go bad.
把鱼放在冰箱里,否则会变坏。
He became a doctor after growing up.
长大后他成了一名医生。
3. 情态动词(may, might, can, could; must, have to; ought to; will, would, shall, should; need; dare; used to)是传达说话人说话的感彩的词。它们都不能单独作谓语。
The girl must be her daughter. They look exactly alike.
这个女孩一定是她的女儿。她们看起来很像。
It may rain this afternoon.今天下午有可能下雨。
(2017?北京高考)Samuel, the tallest boy in our class, can easily reach the books on the top shelf.
塞缪尔是我们班上个子最高的男生,能轻易地够到书架顶上的书。
4. 助动词:助动词本身没有词义,不能独立作谓语。只能与主要动词一起构成谓语。在表示否定、疑问、时态或其他语法关系时也要用到助动词。
A. “do, does” 用于构成否定句和疑问句
B. “will, shall, have, has” 作为助动词用时,可构成不同时态
C. “ be” 用于构成被动语态和进行时态
1. 玩电脑游戏对健康是有害的。
2. 今天早上我来晚了使我们的老师很生气。
3. 一直抱怨是没有益处的。
4.现在我们应该做的事是保护环境。
5. 下午我们是否要开会还不清楚。
6.苹果尝起来很甜。
7. 到目前为止,他们已经种了上千棵树。
8. 当我到学校的时候,我意识到了我把作业落在家了。
9.昨天晚上一定下雨了,因为地面是湿的。
10. 不仅我,还有我的姐妹们也喜欢读书。
Playing computer games is bad for health.
My coming late this morning made our teacher very angry.
It is no good complaining all the time.
What we should do now is to protect the environment.
Whether we will hold the meeting in the afternoon is not clear.
The apple tastes sweet.
So far, they have planted thousands of trees.
When I got to school, I realized I had left my homework at home.
It must have rained last night, for the ground is wet.
Not only I but also my sisters like reading.
3
2
1
非谓语动词因其蕴含形式多变、用法繁杂等特征,考生容易出现理解失误而造成失分
动词的时态和语态是考查谓语动词时的必考点,考生在答题时如果分析不到位或相关知识欠缺,则容易误填答案
考生因不能判定是填谓语动词还是非谓语动词而失分
易错点
分析
示例
两句的差别是连词and。分析句子结构可知,①中空格处为现在分词作伴随状语;②中空格处与volunteered并列作谓语。故①填donating;②填donated。
①He volunteered to help control traffic, ________ (donate) an hour of his time every week.
②He volunteered to help control traffic, and ______ (donate) an hour of his time every week.
分析
示例
两句的差别是连词and。分析句子结构可知,①句为句式“祈使句+and+陈述句”;②句为分词短语作条件状语。故①填Call;②填Calling。
①________ (call) me tomorrow and I'll let you know the lab result.
②________ (call) me tomorrow, I'll let you know the lab result.
分析
示例
两句的差别是连词so。分析句子结构可知,①句为独立主格结构作原因状语;②句so连接两个并列句,空格处所填词应与第二个并列分句的谓语动词一致。故①填leading;②填led。
①The guide ________ (lead) the way, we had no trouble getting out of the forest.
②The guide ________ (lead) the way, so we had no trouble getting out of the forest.
分析
示例
两句的差别是连词if。分析句子结构可知,①句为独立主格结构作条件状语;②句为if引导的条件状语从句。故①填permitting;②填permits。
①The party will be held in the garden, weather __________ (permit).
②The party will be held in the garden, if weather ________ (permit).
分析
示例
三句的差别是逗号后面的部分。分析句子结构可知,①句为and连接两个并列句,通过时态、语态的分析,应用一般过去时的被动语态;②句为独立主格结构(with复合结构);③句为现在分词短语作伴随状语。故①填was fixed;②填fixed;③填fixing。
①Jim was listening attentively to the lecture, and all his attention ________ (fix) on it.
②Jim was listening attentively to the lecture, (with) all his attention ________ (fix) on it.
③Jim was listening attentively to the lecture, ______ (fix) all his attention on it.
分析
示例
两句看似结构一致,但仔细分析却是大相径庭。①句为and连接三个并列谓语;②句为and连接两个伴随状语。故①填sat;②填talking。
①He went into the room, ________ (sit) at the table and began to read newspapers.
②They walked along the stream together, ________ (talk) and laughing.
Revise the “Subjects” and “Verbs”.
Finish the exercises in your workbook.
Homework
The drop of rain makes a hole in the stone, not by violence, but by of falling.
雨滴穿石,不是靠蛮力,而是靠持之以恒。
Module 1 Deep South
Grammar
Yesterday Once More
When I was young
I'd listen to the radio
Waitin' for my favorite songs
When they played I'd sing along
It made me smile
Those were such happy times
And not so long ago
How I wondered where they'd gone
But they're back again
Just like a long lost friend
All the songs I loved so well
Every sha la la la
Every wo o wo o
Still shines
Every shing a ling a ling
That they're startin' to sing's
So fine
When they get to the part
Where he's breakin' her heart
It can really make me cry
Just like before
It's yesterday once more
Review of subjects.
Review of verbs.
Learning aims
Look at the sentences and find out the subjects in these sentences.
98% of the surface is covered permanently in the ice
cap.
2. Covering about 14 million square kilometres around
the South Pole, it is the fifth largest continent
in the world.
Grammar (1): 主语
Leading-in
3. A high mountain range, the Trans-Antarctic range, runs from east to west, cutting the continent in two.
4. It is difficult to imagine a more inhospitable place.
5. Antarctica is full of wildlife, which has adapted to its extreme conditions.
6. Only two types of flowering plants are found.
7. There are different types of penguins, flying birds, seals, and whales.
8. Protecting Antarctica from nuclear tests and radioactive waste is very important to this continent.
9. What the treaty aims to do is to prevent the commercial and military use of the continent.
主语是句子动作的发出者,是句子叙述的主体,是句子所要说明的人或事物,表示句子描述的是谁或什么。主语通常由名词,代词,数词,名词化的形容词,动词不定式,动名词或从句等充当。通常位于谓语动词前。
(2) 代词作主语
He is good at learning languages.他擅长学语言。
(3) 数词作主语
Fifteen and fourteen is twenty-nine.
15加14等于29。
(4) 动词不定式作主语
To see is to believe.眼见为实。
(1)名词作句子的主语。
The students are having a chemistry test.
学生们正在进行化学测验。
(5) 动名词作主语
Reading in bed is a bad habit.
在床上阅读是个坏习惯。
(6) it作形式主语
It’s not easy to master a foreign language.
掌握一门外语不容易。
(7) 从句作主语
What he wanted best was knowledge.
他最想要的是知识。
注意下列的主语形式:
(1)v.-ing作主语时,可以有自己的逻辑主语及代词或名词所有格等。
Jack’s/ My winning the match is an inspiration to all of the team.
杰克/我赢得比赛对于所有的队员是个鼓舞。
(2)以there引导的句子,主语通常放在谓语的后面,
谓语动词的数根据后面的主语来定。
There stand/ are a large number of factories in the east of the city. 在城市的东部有许多工厂。
(3)在it作主语的句子中。
①人称代词:不明身份性别时用it
Someone is knocking at the door. Who can it be?
有人在敲门,它可能是谁?
②非人称代词:表示天气,时间等。
It’s raining. 天正在下雨。
③形式主语/宾语:
It’s important for us to learn English well.
学好英语对我们来说很重要。
④用于强调: it is... that /who...
It was because of the bad weather that we were late for school yesterday.
由于坏天气,昨天我们迟到了。
(4)名词化的其他词类。the + adj.表示一类,复数概念,谓语用复数。
The rich should help the poor.富人应该帮助穷人。
The wounded were treated in time.
伤员们得到了及时救治。
1. ___________________________describes a bright future for the company.
你在会议上所说的描述了公司的美好未来。
2. _________ basic first-aid techniques will help you
respond quickly to emergencies.
知道基本的急救技术将会帮助你对紧急情况快速作出
反应。
Class exercises
What you said at the meeting
Knowing
Ⅰ.完成句子。
3. (2014·陕西高考) ______________________________
depends much on the weather.
延时航班何时起飞主要取决于天气。
4. (2014·山东高考)It’s standard practice for a company
like this one __________a security officer.
像这样的公司常规做法是要雇用一位安全人员。
to employ
When the delayed flight will take off
Underline the verb structures in these sentences.
(1)The Endurance became trapped, and Shackleton
and his men watched it sink into the icy sea.
(2) He and five men would take one of the lifeboats,
and sail 800 miles to South Georgia, where there was a
permanent camp.
(3) He had to walk 36 hours over mountains to reach
the camp.
Grammar (2):动词
(4) The whale hunters at the camp couldn’t believe
their eyes when they saw the six men walking down
from the mountains.
(5) He returned to Elephant Island to rescue the crew
he had been forced to abandon.
谓语动词是对主语动作或状态的陈述或说明,指出做什么,是什么或是怎么样。谓语动词的位置一般在主语之后。在英语中,动词按作用和功能主要分为两大类,一类是谓语动词,另一类是非谓语动词。
行为动词: 表示动作或状态,能单独作谓语动词。谓
语动词可分及物和不及物两种。及物动词后带宾语,不
及物动词后不带宾语。
I thought hard and found the answer.
我努力思考,找到了答案。
动词的种类和基本形式
根据动词实际的意义可分为行为动词或实义动词;根据
动词能否带宾语,分为及物动词和不及物动词;
根据动词的作用可分为连系动词、情态动词和助动词。
2. 连系动词:连系动词本身有一定的词义,但不能独立作谓语,必须与表语一起构成谓语。系动词没有被动语态。表语通常由名词、形容词,或相当于名词或形容词的词或短语等充当,说明主语是什么或怎么样。
The mountain is very attractive.
这座山非常有吸引力。
Those oranges taste good.
那些橘子很好吃。
It’s already ten in the morning. The store remains closed.
已经上午十点了,商店仍然关着。
Put the fish in the fridge, or it will go bad.
把鱼放在冰箱里,否则会变坏。
He became a doctor after growing up.
长大后他成了一名医生。
3. 情态动词(may, might, can, could; must, have to; ought to; will, would, shall, should; need; dare; used to)是传达说话人说话的感彩的词。它们都不能单独作谓语。
The girl must be her daughter. They look exactly alike.
这个女孩一定是她的女儿。她们看起来很像。
It may rain this afternoon.今天下午有可能下雨。
(2017?北京高考)Samuel, the tallest boy in our class, can easily reach the books on the top shelf.
塞缪尔是我们班上个子最高的男生,能轻易地够到书架顶上的书。
4. 助动词:助动词本身没有词义,不能独立作谓语。只能与主要动词一起构成谓语。在表示否定、疑问、时态或其他语法关系时也要用到助动词。
A. “do, does” 用于构成否定句和疑问句
B. “will, shall, have, has” 作为助动词用时,可构成不同时态
C. “ be” 用于构成被动语态和进行时态
1. 玩电脑游戏对健康是有害的。
2. 今天早上我来晚了使我们的老师很生气。
3. 一直抱怨是没有益处的。
4.现在我们应该做的事是保护环境。
5. 下午我们是否要开会还不清楚。
6.苹果尝起来很甜。
7. 到目前为止,他们已经种了上千棵树。
8. 当我到学校的时候,我意识到了我把作业落在家了。
9.昨天晚上一定下雨了,因为地面是湿的。
10. 不仅我,还有我的姐妹们也喜欢读书。
Playing computer games is bad for health.
My coming late this morning made our teacher very angry.
It is no good complaining all the time.
What we should do now is to protect the environment.
Whether we will hold the meeting in the afternoon is not clear.
The apple tastes sweet.
So far, they have planted thousands of trees.
When I got to school, I realized I had left my homework at home.
It must have rained last night, for the ground is wet.
Not only I but also my sisters like reading.
3
2
1
非谓语动词因其蕴含形式多变、用法繁杂等特征,考生容易出现理解失误而造成失分
动词的时态和语态是考查谓语动词时的必考点,考生在答题时如果分析不到位或相关知识欠缺,则容易误填答案
考生因不能判定是填谓语动词还是非谓语动词而失分
易错点
分析
示例
两句的差别是连词and。分析句子结构可知,①中空格处为现在分词作伴随状语;②中空格处与volunteered并列作谓语。故①填donating;②填donated。
①He volunteered to help control traffic, ________ (donate) an hour of his time every week.
②He volunteered to help control traffic, and ______ (donate) an hour of his time every week.
分析
示例
两句的差别是连词and。分析句子结构可知,①句为句式“祈使句+and+陈述句”;②句为分词短语作条件状语。故①填Call;②填Calling。
①________ (call) me tomorrow and I'll let you know the lab result.
②________ (call) me tomorrow, I'll let you know the lab result.
分析
示例
两句的差别是连词so。分析句子结构可知,①句为独立主格结构作原因状语;②句so连接两个并列句,空格处所填词应与第二个并列分句的谓语动词一致。故①填leading;②填led。
①The guide ________ (lead) the way, we had no trouble getting out of the forest.
②The guide ________ (lead) the way, so we had no trouble getting out of the forest.
分析
示例
两句的差别是连词if。分析句子结构可知,①句为独立主格结构作条件状语;②句为if引导的条件状语从句。故①填permitting;②填permits。
①The party will be held in the garden, weather __________ (permit).
②The party will be held in the garden, if weather ________ (permit).
分析
示例
三句的差别是逗号后面的部分。分析句子结构可知,①句为and连接两个并列句,通过时态、语态的分析,应用一般过去时的被动语态;②句为独立主格结构(with复合结构);③句为现在分词短语作伴随状语。故①填was fixed;②填fixed;③填fixing。
①Jim was listening attentively to the lecture, and all his attention ________ (fix) on it.
②Jim was listening attentively to the lecture, (with) all his attention ________ (fix) on it.
③Jim was listening attentively to the lecture, ______ (fix) all his attention on it.
分析
示例
两句看似结构一致,但仔细分析却是大相径庭。①句为and连接三个并列谓语;②句为and连接两个伴随状语。故①填sat;②填talking。
①He went into the room, ________ (sit) at the table and began to read newspapers.
②They walked along the stream together, ________ (talk) and laughing.
Revise the “Subjects” and “Verbs”.
Finish the exercises in your workbook.
Homework
The drop of rain makes a hole in the stone, not by violence, but by of falling.
雨滴穿石,不是靠蛮力,而是靠持之以恒。
