人教高中英语必修五Unit5 First Aid 全单元课件(98张)
文档属性
| 名称 | 人教高中英语必修五Unit5 First Aid 全单元课件(98张) |

|
|
| 格式 | ppt | ||
| 文件大小 | 3.4MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 人教版(新课程标准) | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2020-11-24 00:00:00 | ||
图片预览










文档简介
Unit 5 First aid全单元课件
Students discuss the question in pairs and they are encouraged to think out as much information as possible.
Brainstorming-I----definition (2m)
What is first aid?
the fist kind of help given to someone who suddenly falls ill or gets injured before a doctor can be found.
the initial care of a suddenly sick or injured person.
the care administered by a person as soon as possible after an accident or illness.
…
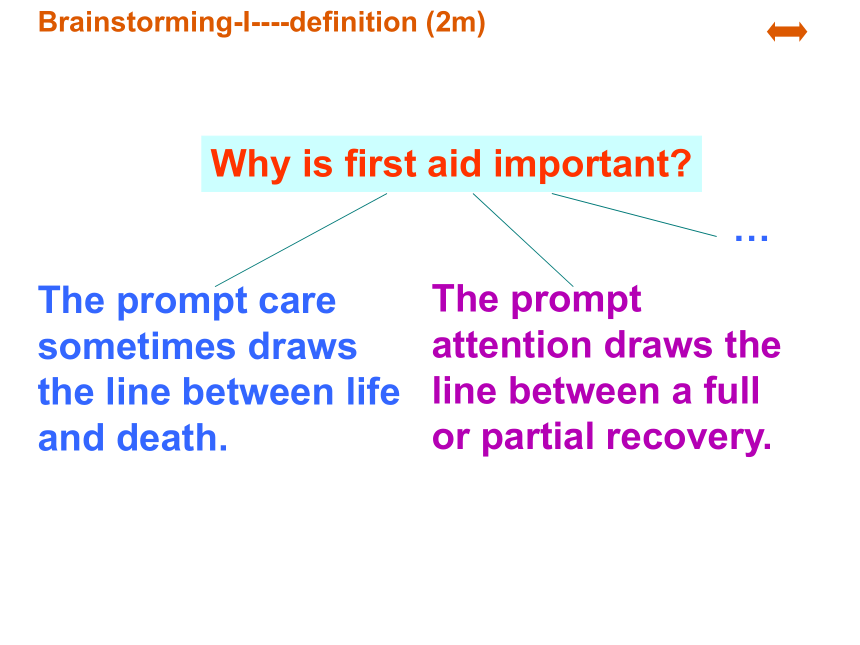
Why is first aid important?
Brainstorming-I----definition (2m)
The prompt care sometimes draws the line between life and death.
The prompt attention draws the line between a full or partial recovery.
…
Brainstorming-I----definition (2m)
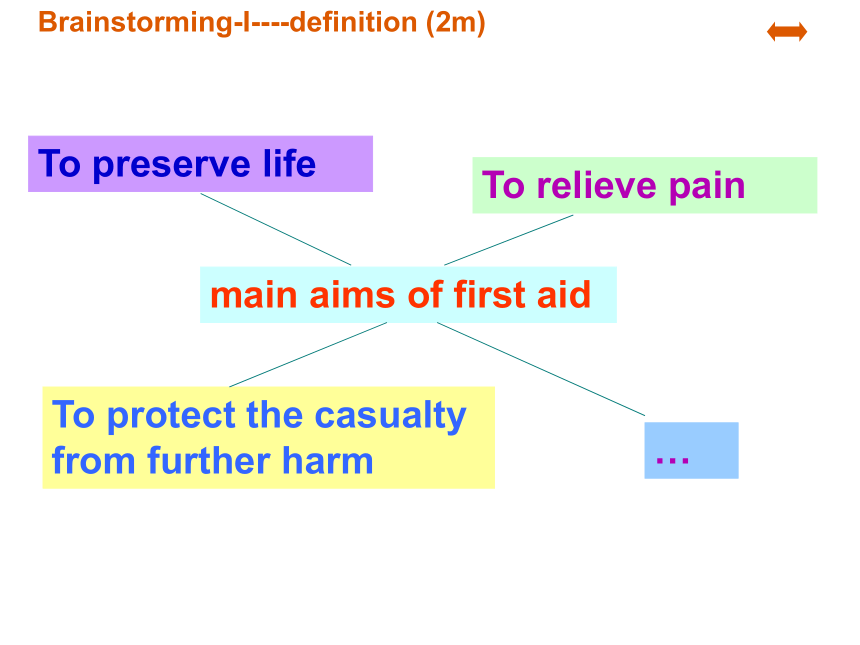
main aims of first aid
To preserve life
To protect the casualty from further harm
To relieve pain
…
Discuss in groups of four what has happened in each picture. Have you, or someone you know, been in any of these situations? Did you or someone else give help in any of them? If so, what kinds of help? What kinds of first aid you should give in the following situations.
Brainstorming-II----speaking (5m)
a snake bit
bleeding
a sprained ankle
choking
a broken arm
a bloody nose
What has happened?
What kind of first aid would you perform in this situation?
Pre-reading (3m)
What’s the topic of the text and how is the information organized?
Reading-I----skimming (1m)
It’s about first aid for burns and the information is organized according to cause, types, characteristic and first aid treatment for burns.
The reading passage is a text from a book called First Aid for the Family. It is a quite-reference book which is organized under headings in such a way that readers can quickly find the information they want. In this type of text, it is common for information to be in note form. It is also common that ellipsis is used in giving instruction. The article the is often omitted in the instructions under “First aid treatment”, for example, cover burnt area instead of cover the burnt area; hold bandage in place instead of hold the bandage in place.
How many parts can the text be divided into and what are they?
Reading-II----skimming (2m)
Part 1: the purpose of skin
Part 2: how we get burns
Part 3: the three types of burns
Part 4: the symptoms of burns
Part 5: how we get burns
1. What can skin do for our body?
2. How can we get burnt?
3. How many types of burns and what are they?
Reading-III----detailed reading (5m)
Detail Reading
What can skin do for our body?
Skin protects you against diseases, poisons and the sun’s harmful rays. It also keeps you warm or cool; it prevents your body from losing water; it is where you feel cold, heat or pain; and it gives you your sense of touch.
2. How can we get burnt?
3. How many types of burns and what are they?
You can get burnt by: hot liquids, steam, fire, radiation, the sun, electricity and chemicals.
There are three types of burns: first degree burns, second degree burns and third degree burns.
According to the text, label the following pictures with first degree burn, second degree burn and third degree burn.
Reading-IV----Practice (3m)
The second degree burn
The first degree burn
The third degree burn
Discuss in groups of four to see whether the following is right or wrong. If it’s wrong, explain why and give the correct statement.
1. Sam knocked over a kettle full of boiling water onto this legs. His legs became red, swollen and covered with blisters. Sam broke the blisters and poured icy water from the fridge onto the skin. ( )
2. While ironing clothes, Miss Good accidentally touched the iron. Her wrist blistered and became watery. It hurt a lot. She put her wrist under the cold water tap and then kept placing cool, clean, damp cloths on it until it was less painful. Then she went to see the doctor. ( )
Discussion-I (5m)
W
R
3. Mrs Casey’s sleeve caught fire while she was cooking. Her arm looked terrible but it didn’t hurt. The skin was charred. Her husband took off her blouse and picked off bits of the blouse stuck to the burn. He then placed butter on the burn and covered it with a wet bandage. ( )
4. After an hour in the sun, Lily noticed her arms were red and hurt a bit. She went home and put them under cool running water. ( )
W
R
Why should you put cold water on a burn?
Why doesn’t a third degree burn hurt?
Why do you think clothes and jewellery near burns should be removed?
If someone has a third degree burn, why might you see tissue?
Discussion-II (5m)
Students discuss the following questions in groups of four. After the discussion, the representatives from each group present their views.
Why should you put cold water on a burn?
Why doesn’t a third degree burn hurt?
Because the cold water stops the burning process, stops the pain and reduces the swelling.
Because in a third degree burn the nerves have been damaged. If there are no nerves, there is no pain.
Why do you think clothes and jewellery near burns should be removed?
4. If someone has a third degree burn, why might you see tissue?
Because bacteria from the clothes and jewellery could infect the burns.
Because all the layers of the skin have been burnt showing the tissue underneath.
Language points-1---- Phrases (3m)
first aid
fall ill
electric shock
squeeze out
Underline those you think are useful or difficult, then talk about them with your group members.
sense of touch
over and over again
in place
make … difference
Language points-2----Sentences (3m)
Take clothing off the burned area unless it is stuck to the burn.
First aid is the first kind of help given to someone who suddenly falls ill or gets injured before a doctor can be found.
You have three layers of skin that protect you against diseases, poisons and the sun’s harmful rays.
Burns are called first degree, second degree or third degree burns depending on which layers of the skin are burnt.
For second degree burns, keep cloths cool by putting them back in the cold water, squeeze them out and placing them on the burned area over and over again fro about an hour until pain is not so bad.
Unit 5 First aid
Discovering useful words and expressions:
Answer keys for Exercise 1:
Verb
Noun
Adjective
injure
injury
injured
poison
poison
poisonous
burn
burn
burnt
swell
swelling
swollen
damage
damage
damaged
treat
treatment
treatable
wound
wound
wounded
infect
infection
infected
Reading the words in the chart, students discuss with their partner and give there answers.
What do you notice about some of the verb/noun pairs?
What do you notice about many of the adjectives?
Discovery-I----discover the rules (2m)
In some of them the verb is the same as the noun.
Many end in –ed.
The past participle of a verb is often used as an adjective. For example, he showed the doctor his injured leg.
first aid
organ
causes
characteristics / symptoms
serious
process
Answer keys for Exercises 2:
Look at Ex.1 and discuss in groups of four. What the difference between sentences A and B. Which sentence is better and why it’s better. After the discussion, each group choose a student to present their views to the class.
Discovery-II (3m)
There are lots of repeated words and phrases in Sentence A. Sentence B is better than Sentence A because it doesn’t have unnecessary repetition in it, and it is easier to understand and it sounds much less awkward than Sentence A.
The burn she got from the iron was red and very painful.
A boy was in the left side of the sick woman, and a girl on the right.
She has a daughter in hospital.
He went to the doctor because he had to.
In Ex.2, sentences are all correct but they sound awkward because they have unnecessary words in them. Complete the exercise individually and then check with your partner.
5. Did she pass the first aid test she did yesterday or not?
6. She could not decide whether to send him to hospital or not.
7. When your nose is bleeding, bend forward so the blood runs out of your nose and not down your throat.
8. Only some of the students have done a first aid course but most haven’t.
Sentences in Ex. 3 are all correct, but some words have been left out. Rewrite the sentences to include the missing words and check them with your partner.
The cottage which is surrounded by a wall belongs to the local government.
The first book that I read this term was more interesting than the second book that I read this term.
To her teacher’s surprise, she did better in her first aid exam than she was expected to do.
4. I don’t think they have returned from the hospital, but they might have returned from the hospital.
5. He wanted to help the accident victim but his friend didn’t want to help the accident victim.
6. You can borrow my first aid notes if you want to borrow my first aid notes.
The sentences in the question sound natural whereas the sentences which include all the missing words do not sound natural; they sound awkward.
Sometimes sentences can be ambiguous because of ellipsis. Discuss the following sentences in groups of four and find out the two meanings in each sentence.
Jack loves nature more than his wife.
John understood himself better than Peter.
Max phoned his mother and Oscar did too.
I relied on you more than Roger.
Discussion (5m)
Jack loves nature more than his wife.
John understood himself better than Peter.
Jack loves nature more than he loves his wife.
Jack loves nature more than his wife loves nature.
John understood himself better than Peter understood John.
John understood himself better than Peter understood himself.
3. Max phoned his mother and Oscar did too.
4. I relied on you more than Roger.
Max phoned his mother and Oscar phoned Max’s mother too.
Max phoned Max’s mother and Oscar phoned Oscar’s mother.
I relied on you more than Roger relied on you.
I relied on you more than I relied on Roger.
The house rent is expensive, I’ve got about half the space I had at home and I’m paying _____ here.
A. as three times much B. as much three times
C. much as three times D. three times as much
高考链接
D
解析:答案D。修饰比较级的three times只能置于比较结构之前,不能置于其后或其中;本题中比较状语从句部分被省略。
2. What would have happened _______ , as far as the river bank?
A. Bob had walked farther
B. if Bob should walk farther
C. had Bob walked farther
D. if Bob walked farther
高考链接
C
解析:答案C。what would have happened暗示后面,使用虚拟语气,且与过去事实相反;当if省略时,可将were/had/should提前,构成部分倒装;用if从句表达则是if Bob had walked farther 题意:如果鲍勃走得更远些,走到河岸边会发生什么事呢?
3. Is this the reason ________ at the meeting for his carelessness in his work?
A. he explained B. what he explained
C. how he explained D. why he explained
高考链接
A
解析:答案A。explain作“解释”讲为及物动词,须接宾语;此处关系代词that或which被省略;why引导定语从句时,在句中作状语,相当于for which。
4. The disc, digitally _______ in the studio, sounded fantastic at the party that night.
A. recorded B. recording
C. to be recorded D. having recorded
高考链接
A
解析:答案A。因the disc与record之间存在逻辑的被动关系,且动作发生在过去,须用过去分词作定语,相当于which was digitally recorded in the studio。
5. ________ be sent to work there?
A. Who do you suggest
B. Who do you suggest that should
C. Do you suggest who should
D. Do you suggest whom should
高考链接
A
解析:答案A。本题结构为“疑问句+插入语+陈述句”do you suggest为插入语,suggest后宾语从句常用虚拟语气,谓语动词的形式“(should)+动词原形” should可省略。
Unit 5 First aid
Discuss the following situation in groups of four
Suppose you hear someone screaming and you find him sitting on the ground, bleeding heavily from deep knife wounds in his hands, what would you do? Will you help him? Will you call the police and ambulance, or whether you perform first aid?
Pre-reading-I----discussion (3m)
What do you think the article is about by reading this headline?
Pre-reading-II----prediction (3m)
The story is about a young man who sets us a good example because he could save one’s life using his knowledge of first aid.
When we read newspaper articles, we may only want to get a quick idea of a newspaper article and do not want to know all the details. For this reason, we might just read the headline and the first paragraph. This is because the headline gives readers a clue about the content and the first paragraph gives the most important information.
Reading-I----skimming (3m)
Skim the first paragraph and find out the answers to the five “W” Questions.
Who?
What?
When?
Where?
Why?
Reading-I----skimming (3m)
John Janson
was honoured at the Lifesaver Awards
last night
in Rivertown
for carrying out lifesaving first aid on his neighbour after a shocking knife attack
Read the newspaper article and then put these events in the order that they happened. Then in pairs, retell the story in your won words.
___ The attack ran away.
___ Anne was attacked and started to scream.
___ John performed first aid on Anne.
___ John was studying in his house.
___ The ambulance arrived.
___ John ran outside with his father.
___ John found Anne in her garden with terrible knife wounds.
Reading-II----scanning (4m)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
Read the article carefully and find out the answers to the following questions.
What did John do when he heard the screaming?
What happened to Anne?
What saved Ms Slade’s life?
What first aid did John perform on Anne?
What adjectives would you use to describe John’s actions? Give at least three.
Reading-III----detailed reading (4m)
What did John do when he heard the screaming?
What happened to Anne?
What saved Ms Slade’s life?
He was studying in his room.
She had been stabbed repeatedly with a knife. She was lying in her front garden bleeding very heavily.
It was John’s quick action and knowledge of the first aid that saved her life.
What first aid did John perform on Anne?
4. What adjectives would you use to describe John’s actions? Give at least three.
John dressed Ms Slade’s in juries with tea towels and applied pressure to the wounds to slow the bleeding.
Brave, heroic, courageous, quick-thinking, quick-minded, helpful, fearless, unselfish, confident
Discuss the following questions in groups of four. After the discussion, each group select a spokesperson to present their views.
Discussion (5m)
Do you think John was sill or brave to get involved in the situation? Give reasons.
Would you think it is worthwhile to take a course in first aid? Give reasons.
What if the attacker had still been at the scene of the stabbing?
What if the attacker had gone but had been returned to the woman?
What if the woman had AIDS?
What if John had performed first aid on the woman but she died anyway? How would he feel about having tried to help her?
Unit 5 First aid
Discuss in groups of four and give your own information.
Have you ever had to phone an emergency number?
Do you know what telephone number you would call in a medical emergency?
What telephone number you would call in a fire emergency?
What telephone number you would call in a police emergency?
Pre-listening----discussion (5m)
Listen to the tape and complete the table.
Listening-I (5m)
Name of caller
Sarah Grant
Telephone number
Address
What has happened
Number of people involved
61619486
12 Loft Street, East Horton
Mrs. Grant’s daughter fell from a table and maybe has broken her leg. She hit her head and is unconscious.
One (Mrs. Grant’s daughter)
Listen to the tape again and answer the following questions. You may discuss with your group members.
Do you think that Mrs. Grant should have rung the emergency number or should she have just taken her daughter to the doctor? Give reasons for your answer.
How do you think Mrs. Grant was feeling when she made the phone call?
Why do you think the operator was speaking so slowly and calmly?
What would have happened if Mrs. Grant had hung up the first time she said goodbye?
What would have been a safer way for Mrs. Grant’s daughter to reach the cupboard?
Listening-II (5m)
Do you think that Mrs. Grant should have rung the emergency number or should she have just taken her daughter to the doctor? Give reasons for your answer.
In this situation, the best thing to do was to ring the emergency number. The daughter’s leg would have been very painful and become worse if the mother had tried to move her. Also, the daughter was unconscious and you shouldn’t move an unconscious person.
2. How do you think Mrs. Grant was feeling when she made the phone call?
3. Why do you think the operator was speaking so slowly and calmly?
She must be very worried, concerned, nervous, anxious, in a panic, terrified, upset.
To try and calm Mrs. Grant down, if she also spoke quickly Mrs. Grant could become even more upset, to make herself clearly understood (a panicked person may not be thinking or understanding clearly).
What would have happened if Mrs. Grant had hung up the first time she said goodbye?
5. What would have been a safer way for Mrs. Grant’s daughter to reach the cupboard?
The ambulance would not have known where to go as she hadn’t given her address.
It would have been safer to use a ladder, especially if the mother had held onto it.
Read through Ex. 1 and make sure that you understand the meanings of the words in the list.
What first aid treatment you would give in the situations in the list. Write your suggestions on the board using the imperative.
Pre-listening----prediction (3m)
Listen to the tape for the first time. You don’t have to understand every detail in the listening text. Only circle the topics that the teacher asks questions about.
burning clothes broken bones
bleeding choking
snake bites nose bleeds
bruising sprained ankle
Listening-I (3m)
Listen to the tape and match each picture with a topic listed in question 1 above.
1. _____________ 2. ______________
Listening-II (3m)
sprained ankle
burning clothes
3. _______________ 4. _______________
a nose bleed
chocking
Listen to the first aid teacher giving instructions for rescue breathing. Number the boxes to show the correct order of the pictures. Write an instruction under each picture.
Listening (5m)
7
1
2
3
4
5
6
8
1
2
1 check if conscious
2 put into recovery position
4
3 clear airway
4 check if breathing
3
5 blow into mouth and watch for breating
6 check pulse
5
6
7
7 continue rescure
8 put into recovery position
8
Homework
Work in groups of four and make a dialogue. Suppose there is an accident, What could you offer the fist aid help? Make dialogue with your group members and act it out.
Unit 5 First aid
Period 6: 幻灯片84-96页
Read the title of the text and the headings within it.
What’s the topic of the text and how is the information organized?
Pre-reading----speaking (1m)
It’s about safety in the home and the information is organized according to particular rooms and also to one cause of accidents----fires.
Look at the pictures and answer the questions.
What do you think these pictures are telling us?
What do you think the purpose of the picture is?
What’s the purpose of the pamphlet?
Pre-reading----discussion (3m)
To turn saucepan handles towards the back of a stove; Not to use a hairdryer near water; To keep a fire extinguisher in the kitchen.
They emphasize some points in the pamphlet.
To tell us how to keep a safe home; how to prevent accidents in the home.
Read the text and finish the table.
Reading (5m)
Things we do
Things we shouldn’t do
In the kitchen
In the bedroom
In the bathroom
Read the text and finish the table.
Things we do
Things we shouldn’t do
In the kitchen
We always let the floor dry after it is washed before we use the kitchen again.
We keep a window open when we use gas fires.
I shouldn’t stand on chairs to reach things.
We shouldn’t leave matches anywhere.
Read the text and finish the table.
Things we do
Things we shouldn’t do
In the bedroom
I shouldn’t light candles in my room.
My father should never smoke in bed.
My mother keeps bottles of medicine on a high shelf out of the reach of children.
Read the text and finish the table.
Things we do
Things we shouldn’t do
In the bathroom
I always unplug the hairdryer after I’ve used it.
We shouldn’t take an electric heater into the bathroom.
Discuss the following questions in groups of four. After the discussion, one student from each group represent their ideas.
What things at home cat be dangerous?
How to prevent us from being injured at home?
Speaking-I (5m)
Students are encouraged to write down as many pieces of advice as possible.
Do the first aid quiz in groups. Give reasons for your answers. Check your answers with other classmates.
Speaking-II (5m)
Imagine that you want to provide first aid courses. In pairs, write a letter to your principle politely asking whether he or she could organize them. Use the outline and instructions to help you.
Writing (10m)
Dear ________,
Our class had been studying a unit on first aid____________ .
Even though the unit has been very interesting and useful,__________________.
We would like to request that_____________________.
We think that a first aid course at the school __________________.
Your sincerely,
____________
Write your principal’s name.
Say why the first aid unit has been useful.
Say why you would like a first aid course.
Say what you want the principal to do.
Say again why a first aid course would be a good thing to do.
Sing your names.
Language points for Reading I
Language points for Reading II
Video data
98-105
106-109
1. You skin also keeps you warm or cool; it prevents your body from losing water; it is where you feel cold, heat or pain; and it gives you your sense of touch.
keep you warm or cool 为keep复合结构,即keep+宾语+宾补。使处于某种状态……。宾补除由形容词充当之外,还可用名词,现在分词,过去分词,介词短语,副词来充当。
This coat will keep you warm.
This story will keep the children amused.
The illness kept her in hospital.
I’m sorry to keep you waiting.
prevent sb. from doing sth. 阻止某人做某事
What can we do to prevent this disease spreading?
She was prevented from taking the exam by illness.
sense of touch 触觉
sense of sight 视觉 sense of hearing 听觉
sense of taste 味觉 sense of smell 嗅觉
sense of humour 幽默感
sense of beauty 美感
sense of direction 方向感
sense of urgency 紧迫感
2. Burns are called first degree, second degree or third degree, depending on which layers of the skin are burned.
depending on which layers of the skin are burned 为现在分词短语作伴随状语。
Charles Darnay left France, preferring to give up his fortune.
depend on 相信,依赖,依靠
You can’t depend on John-he nearly always arrive late.
The country depends heavily on its tourist trade.
The amount you pay depends on where you live.
3. Examples include burns by electric shocks, burning clothes or severe petrol fires. 例如由电击引起的烧伤,因衣服起火引起的烧伤,或由汽油起火引起的烧伤。
electric
(1) 用电的,电动的
an electric clock 电钟 an electric fire 电炉
(2) 电的,发电的,带电的
electric power 电力
an electric storm 电闪雷鸣般的暴风雨
(3) 令人兴奋的
His speech had an electric effect on the crowd.
4. Take clothing off the burned are unless it is stuck to the burn. 除非衣服粘贴在烧伤面上,否则都要把它脱掉。
take off
(1) 脱下,脱掉
Take your coat off.
(2) 休假,歇……(天)假
Take a few days off, Michael.
(3) 开始有成就,开始成名
It was at this point that her acting career really took off.
(4) 升空,起飞
The plane took off so smoothly that the passengers could hardly feel it.
5. For second degree burns, keep cloths cool by putting them back in the cold water, squeezing them out and placing them on the burned area over and over again for about an hour until pain is not so bad. 对于二度烧伤,要保持湿布清凉,需把湿布放回冷水中,拧出水后放在烧伤面上,这样要反反复复地做一个小时左右,直到不太痛时为止。
squeeze
(1) vt. 压,挤,榨
He squeezed her arm sympathetically.
(2) vt. 压出,挤出,榨出,用于squeeze+n.+adv.&prep
She squeezed the water out of the sponge.
(3) vi. 挤入,塞,用于
squeeze+adv./prep.
squeeze+adj.+adv./prep.
Is the car full or can I squeeze in?
He was so fat that he could not just squeeze through the door.
Seventeen-year-old teenager, John Janson, was honoured at the Lifesaver Awards last night in Rivertown for carrying out lifesaving fist aid on his neighbour after a shocking knife attack.
honour
(1) vt. 尊敬;使感到荣幸
We are deeply honoured that you should agree to join us.
(2) n. 荣誉,尊敬
The Queen was welcomed at the airport by a guard of honour.
(3) n. 名声,名誉
It’s a point of honour with me to reply all my debts promptly.
(4) n. 增光的人(事),引以为荣的人(事),只用单数。
He’s an honour to the school.
2. John was presented with this reward at a ceremony which recognized the bravery of ten people who had saved the life of another.
present
(1) vt. 颁发,授予
present sth. to sb. 颁发……给某人
present sb. with sth. 授予某人……
When Mr Brown left the firm, the director presented a gold watch to him/ him with a gold watch.
(2) vt. 提出,呈递
When are the committees presenting their report?
3. It shows that a knowledge of first aid can make a real difference.
a knowledge of 知道,了解,具有……知识
He has a good knowledge of English.
make a/some/no difference 有一些/没有什么区别
It doesn’t make any difference to me whether you go or stay.
Students discuss the question in pairs and they are encouraged to think out as much information as possible.
Brainstorming-I----definition (2m)
What is first aid?
the fist kind of help given to someone who suddenly falls ill or gets injured before a doctor can be found.
the initial care of a suddenly sick or injured person.
the care administered by a person as soon as possible after an accident or illness.
…
Why is first aid important?
Brainstorming-I----definition (2m)
The prompt care sometimes draws the line between life and death.
The prompt attention draws the line between a full or partial recovery.
…
Brainstorming-I----definition (2m)
main aims of first aid
To preserve life
To protect the casualty from further harm
To relieve pain
…
Discuss in groups of four what has happened in each picture. Have you, or someone you know, been in any of these situations? Did you or someone else give help in any of them? If so, what kinds of help? What kinds of first aid you should give in the following situations.
Brainstorming-II----speaking (5m)
a snake bit
bleeding
a sprained ankle
choking
a broken arm
a bloody nose
What has happened?
What kind of first aid would you perform in this situation?
Pre-reading (3m)
What’s the topic of the text and how is the information organized?
Reading-I----skimming (1m)
It’s about first aid for burns and the information is organized according to cause, types, characteristic and first aid treatment for burns.
The reading passage is a text from a book called First Aid for the Family. It is a quite-reference book which is organized under headings in such a way that readers can quickly find the information they want. In this type of text, it is common for information to be in note form. It is also common that ellipsis is used in giving instruction. The article the is often omitted in the instructions under “First aid treatment”, for example, cover burnt area instead of cover the burnt area; hold bandage in place instead of hold the bandage in place.
How many parts can the text be divided into and what are they?
Reading-II----skimming (2m)
Part 1: the purpose of skin
Part 2: how we get burns
Part 3: the three types of burns
Part 4: the symptoms of burns
Part 5: how we get burns
1. What can skin do for our body?
2. How can we get burnt?
3. How many types of burns and what are they?
Reading-III----detailed reading (5m)
Detail Reading
What can skin do for our body?
Skin protects you against diseases, poisons and the sun’s harmful rays. It also keeps you warm or cool; it prevents your body from losing water; it is where you feel cold, heat or pain; and it gives you your sense of touch.
2. How can we get burnt?
3. How many types of burns and what are they?
You can get burnt by: hot liquids, steam, fire, radiation, the sun, electricity and chemicals.
There are three types of burns: first degree burns, second degree burns and third degree burns.
According to the text, label the following pictures with first degree burn, second degree burn and third degree burn.
Reading-IV----Practice (3m)
The second degree burn
The first degree burn
The third degree burn
Discuss in groups of four to see whether the following is right or wrong. If it’s wrong, explain why and give the correct statement.
1. Sam knocked over a kettle full of boiling water onto this legs. His legs became red, swollen and covered with blisters. Sam broke the blisters and poured icy water from the fridge onto the skin. ( )
2. While ironing clothes, Miss Good accidentally touched the iron. Her wrist blistered and became watery. It hurt a lot. She put her wrist under the cold water tap and then kept placing cool, clean, damp cloths on it until it was less painful. Then she went to see the doctor. ( )
Discussion-I (5m)
W
R
3. Mrs Casey’s sleeve caught fire while she was cooking. Her arm looked terrible but it didn’t hurt. The skin was charred. Her husband took off her blouse and picked off bits of the blouse stuck to the burn. He then placed butter on the burn and covered it with a wet bandage. ( )
4. After an hour in the sun, Lily noticed her arms were red and hurt a bit. She went home and put them under cool running water. ( )
W
R
Why should you put cold water on a burn?
Why doesn’t a third degree burn hurt?
Why do you think clothes and jewellery near burns should be removed?
If someone has a third degree burn, why might you see tissue?
Discussion-II (5m)
Students discuss the following questions in groups of four. After the discussion, the representatives from each group present their views.
Why should you put cold water on a burn?
Why doesn’t a third degree burn hurt?
Because the cold water stops the burning process, stops the pain and reduces the swelling.
Because in a third degree burn the nerves have been damaged. If there are no nerves, there is no pain.
Why do you think clothes and jewellery near burns should be removed?
4. If someone has a third degree burn, why might you see tissue?
Because bacteria from the clothes and jewellery could infect the burns.
Because all the layers of the skin have been burnt showing the tissue underneath.
Language points-1---- Phrases (3m)
first aid
fall ill
electric shock
squeeze out
Underline those you think are useful or difficult, then talk about them with your group members.
sense of touch
over and over again
in place
make … difference
Language points-2----Sentences (3m)
Take clothing off the burned area unless it is stuck to the burn.
First aid is the first kind of help given to someone who suddenly falls ill or gets injured before a doctor can be found.
You have three layers of skin that protect you against diseases, poisons and the sun’s harmful rays.
Burns are called first degree, second degree or third degree burns depending on which layers of the skin are burnt.
For second degree burns, keep cloths cool by putting them back in the cold water, squeeze them out and placing them on the burned area over and over again fro about an hour until pain is not so bad.
Unit 5 First aid
Discovering useful words and expressions:
Answer keys for Exercise 1:
Verb
Noun
Adjective
injure
injury
injured
poison
poison
poisonous
burn
burn
burnt
swell
swelling
swollen
damage
damage
damaged
treat
treatment
treatable
wound
wound
wounded
infect
infection
infected
Reading the words in the chart, students discuss with their partner and give there answers.
What do you notice about some of the verb/noun pairs?
What do you notice about many of the adjectives?
Discovery-I----discover the rules (2m)
In some of them the verb is the same as the noun.
Many end in –ed.
The past participle of a verb is often used as an adjective. For example, he showed the doctor his injured leg.
first aid
organ
causes
characteristics / symptoms
serious
process
Answer keys for Exercises 2:
Look at Ex.1 and discuss in groups of four. What the difference between sentences A and B. Which sentence is better and why it’s better. After the discussion, each group choose a student to present their views to the class.
Discovery-II (3m)
There are lots of repeated words and phrases in Sentence A. Sentence B is better than Sentence A because it doesn’t have unnecessary repetition in it, and it is easier to understand and it sounds much less awkward than Sentence A.
The burn she got from the iron was red and very painful.
A boy was in the left side of the sick woman, and a girl on the right.
She has a daughter in hospital.
He went to the doctor because he had to.
In Ex.2, sentences are all correct but they sound awkward because they have unnecessary words in them. Complete the exercise individually and then check with your partner.
5. Did she pass the first aid test she did yesterday or not?
6. She could not decide whether to send him to hospital or not.
7. When your nose is bleeding, bend forward so the blood runs out of your nose and not down your throat.
8. Only some of the students have done a first aid course but most haven’t.
Sentences in Ex. 3 are all correct, but some words have been left out. Rewrite the sentences to include the missing words and check them with your partner.
The cottage which is surrounded by a wall belongs to the local government.
The first book that I read this term was more interesting than the second book that I read this term.
To her teacher’s surprise, she did better in her first aid exam than she was expected to do.
4. I don’t think they have returned from the hospital, but they might have returned from the hospital.
5. He wanted to help the accident victim but his friend didn’t want to help the accident victim.
6. You can borrow my first aid notes if you want to borrow my first aid notes.
The sentences in the question sound natural whereas the sentences which include all the missing words do not sound natural; they sound awkward.
Sometimes sentences can be ambiguous because of ellipsis. Discuss the following sentences in groups of four and find out the two meanings in each sentence.
Jack loves nature more than his wife.
John understood himself better than Peter.
Max phoned his mother and Oscar did too.
I relied on you more than Roger.
Discussion (5m)
Jack loves nature more than his wife.
John understood himself better than Peter.
Jack loves nature more than he loves his wife.
Jack loves nature more than his wife loves nature.
John understood himself better than Peter understood John.
John understood himself better than Peter understood himself.
3. Max phoned his mother and Oscar did too.
4. I relied on you more than Roger.
Max phoned his mother and Oscar phoned Max’s mother too.
Max phoned Max’s mother and Oscar phoned Oscar’s mother.
I relied on you more than Roger relied on you.
I relied on you more than I relied on Roger.
The house rent is expensive, I’ve got about half the space I had at home and I’m paying _____ here.
A. as three times much B. as much three times
C. much as three times D. three times as much
高考链接
D
解析:答案D。修饰比较级的three times只能置于比较结构之前,不能置于其后或其中;本题中比较状语从句部分被省略。
2. What would have happened _______ , as far as the river bank?
A. Bob had walked farther
B. if Bob should walk farther
C. had Bob walked farther
D. if Bob walked farther
高考链接
C
解析:答案C。what would have happened暗示后面,使用虚拟语气,且与过去事实相反;当if省略时,可将were/had/should提前,构成部分倒装;用if从句表达则是if Bob had walked farther 题意:如果鲍勃走得更远些,走到河岸边会发生什么事呢?
3. Is this the reason ________ at the meeting for his carelessness in his work?
A. he explained B. what he explained
C. how he explained D. why he explained
高考链接
A
解析:答案A。explain作“解释”讲为及物动词,须接宾语;此处关系代词that或which被省略;why引导定语从句时,在句中作状语,相当于for which。
4. The disc, digitally _______ in the studio, sounded fantastic at the party that night.
A. recorded B. recording
C. to be recorded D. having recorded
高考链接
A
解析:答案A。因the disc与record之间存在逻辑的被动关系,且动作发生在过去,须用过去分词作定语,相当于which was digitally recorded in the studio。
5. ________ be sent to work there?
A. Who do you suggest
B. Who do you suggest that should
C. Do you suggest who should
D. Do you suggest whom should
高考链接
A
解析:答案A。本题结构为“疑问句+插入语+陈述句”do you suggest为插入语,suggest后宾语从句常用虚拟语气,谓语动词的形式“(should)+动词原形” should可省略。
Unit 5 First aid
Discuss the following situation in groups of four
Suppose you hear someone screaming and you find him sitting on the ground, bleeding heavily from deep knife wounds in his hands, what would you do? Will you help him? Will you call the police and ambulance, or whether you perform first aid?
Pre-reading-I----discussion (3m)
What do you think the article is about by reading this headline?
Pre-reading-II----prediction (3m)
The story is about a young man who sets us a good example because he could save one’s life using his knowledge of first aid.
When we read newspaper articles, we may only want to get a quick idea of a newspaper article and do not want to know all the details. For this reason, we might just read the headline and the first paragraph. This is because the headline gives readers a clue about the content and the first paragraph gives the most important information.
Reading-I----skimming (3m)
Skim the first paragraph and find out the answers to the five “W” Questions.
Who?
What?
When?
Where?
Why?
Reading-I----skimming (3m)
John Janson
was honoured at the Lifesaver Awards
last night
in Rivertown
for carrying out lifesaving first aid on his neighbour after a shocking knife attack
Read the newspaper article and then put these events in the order that they happened. Then in pairs, retell the story in your won words.
___ The attack ran away.
___ Anne was attacked and started to scream.
___ John performed first aid on Anne.
___ John was studying in his house.
___ The ambulance arrived.
___ John ran outside with his father.
___ John found Anne in her garden with terrible knife wounds.
Reading-II----scanning (4m)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
Read the article carefully and find out the answers to the following questions.
What did John do when he heard the screaming?
What happened to Anne?
What saved Ms Slade’s life?
What first aid did John perform on Anne?
What adjectives would you use to describe John’s actions? Give at least three.
Reading-III----detailed reading (4m)
What did John do when he heard the screaming?
What happened to Anne?
What saved Ms Slade’s life?
He was studying in his room.
She had been stabbed repeatedly with a knife. She was lying in her front garden bleeding very heavily.
It was John’s quick action and knowledge of the first aid that saved her life.
What first aid did John perform on Anne?
4. What adjectives would you use to describe John’s actions? Give at least three.
John dressed Ms Slade’s in juries with tea towels and applied pressure to the wounds to slow the bleeding.
Brave, heroic, courageous, quick-thinking, quick-minded, helpful, fearless, unselfish, confident
Discuss the following questions in groups of four. After the discussion, each group select a spokesperson to present their views.
Discussion (5m)
Do you think John was sill or brave to get involved in the situation? Give reasons.
Would you think it is worthwhile to take a course in first aid? Give reasons.
What if the attacker had still been at the scene of the stabbing?
What if the attacker had gone but had been returned to the woman?
What if the woman had AIDS?
What if John had performed first aid on the woman but she died anyway? How would he feel about having tried to help her?
Unit 5 First aid
Discuss in groups of four and give your own information.
Have you ever had to phone an emergency number?
Do you know what telephone number you would call in a medical emergency?
What telephone number you would call in a fire emergency?
What telephone number you would call in a police emergency?
Pre-listening----discussion (5m)
Listen to the tape and complete the table.
Listening-I (5m)
Name of caller
Sarah Grant
Telephone number
Address
What has happened
Number of people involved
61619486
12 Loft Street, East Horton
Mrs. Grant’s daughter fell from a table and maybe has broken her leg. She hit her head and is unconscious.
One (Mrs. Grant’s daughter)
Listen to the tape again and answer the following questions. You may discuss with your group members.
Do you think that Mrs. Grant should have rung the emergency number or should she have just taken her daughter to the doctor? Give reasons for your answer.
How do you think Mrs. Grant was feeling when she made the phone call?
Why do you think the operator was speaking so slowly and calmly?
What would have happened if Mrs. Grant had hung up the first time she said goodbye?
What would have been a safer way for Mrs. Grant’s daughter to reach the cupboard?
Listening-II (5m)
Do you think that Mrs. Grant should have rung the emergency number or should she have just taken her daughter to the doctor? Give reasons for your answer.
In this situation, the best thing to do was to ring the emergency number. The daughter’s leg would have been very painful and become worse if the mother had tried to move her. Also, the daughter was unconscious and you shouldn’t move an unconscious person.
2. How do you think Mrs. Grant was feeling when she made the phone call?
3. Why do you think the operator was speaking so slowly and calmly?
She must be very worried, concerned, nervous, anxious, in a panic, terrified, upset.
To try and calm Mrs. Grant down, if she also spoke quickly Mrs. Grant could become even more upset, to make herself clearly understood (a panicked person may not be thinking or understanding clearly).
What would have happened if Mrs. Grant had hung up the first time she said goodbye?
5. What would have been a safer way for Mrs. Grant’s daughter to reach the cupboard?
The ambulance would not have known where to go as she hadn’t given her address.
It would have been safer to use a ladder, especially if the mother had held onto it.
Read through Ex. 1 and make sure that you understand the meanings of the words in the list.
What first aid treatment you would give in the situations in the list. Write your suggestions on the board using the imperative.
Pre-listening----prediction (3m)
Listen to the tape for the first time. You don’t have to understand every detail in the listening text. Only circle the topics that the teacher asks questions about.
burning clothes broken bones
bleeding choking
snake bites nose bleeds
bruising sprained ankle
Listening-I (3m)
Listen to the tape and match each picture with a topic listed in question 1 above.
1. _____________ 2. ______________
Listening-II (3m)
sprained ankle
burning clothes
3. _______________ 4. _______________
a nose bleed
chocking
Listen to the first aid teacher giving instructions for rescue breathing. Number the boxes to show the correct order of the pictures. Write an instruction under each picture.
Listening (5m)
7
1
2
3
4
5
6
8
1
2
1 check if conscious
2 put into recovery position
4
3 clear airway
4 check if breathing
3
5 blow into mouth and watch for breating
6 check pulse
5
6
7
7 continue rescure
8 put into recovery position
8
Homework
Work in groups of four and make a dialogue. Suppose there is an accident, What could you offer the fist aid help? Make dialogue with your group members and act it out.
Unit 5 First aid
Period 6: 幻灯片84-96页
Read the title of the text and the headings within it.
What’s the topic of the text and how is the information organized?
Pre-reading----speaking (1m)
It’s about safety in the home and the information is organized according to particular rooms and also to one cause of accidents----fires.
Look at the pictures and answer the questions.
What do you think these pictures are telling us?
What do you think the purpose of the picture is?
What’s the purpose of the pamphlet?
Pre-reading----discussion (3m)
To turn saucepan handles towards the back of a stove; Not to use a hairdryer near water; To keep a fire extinguisher in the kitchen.
They emphasize some points in the pamphlet.
To tell us how to keep a safe home; how to prevent accidents in the home.
Read the text and finish the table.
Reading (5m)
Things we do
Things we shouldn’t do
In the kitchen
In the bedroom
In the bathroom
Read the text and finish the table.
Things we do
Things we shouldn’t do
In the kitchen
We always let the floor dry after it is washed before we use the kitchen again.
We keep a window open when we use gas fires.
I shouldn’t stand on chairs to reach things.
We shouldn’t leave matches anywhere.
Read the text and finish the table.
Things we do
Things we shouldn’t do
In the bedroom
I shouldn’t light candles in my room.
My father should never smoke in bed.
My mother keeps bottles of medicine on a high shelf out of the reach of children.
Read the text and finish the table.
Things we do
Things we shouldn’t do
In the bathroom
I always unplug the hairdryer after I’ve used it.
We shouldn’t take an electric heater into the bathroom.
Discuss the following questions in groups of four. After the discussion, one student from each group represent their ideas.
What things at home cat be dangerous?
How to prevent us from being injured at home?
Speaking-I (5m)
Students are encouraged to write down as many pieces of advice as possible.
Do the first aid quiz in groups. Give reasons for your answers. Check your answers with other classmates.
Speaking-II (5m)
Imagine that you want to provide first aid courses. In pairs, write a letter to your principle politely asking whether he or she could organize them. Use the outline and instructions to help you.
Writing (10m)
Dear ________,
Our class had been studying a unit on first aid____________ .
Even though the unit has been very interesting and useful,__________________.
We would like to request that_____________________.
We think that a first aid course at the school __________________.
Your sincerely,
____________
Write your principal’s name.
Say why the first aid unit has been useful.
Say why you would like a first aid course.
Say what you want the principal to do.
Say again why a first aid course would be a good thing to do.
Sing your names.
Language points for Reading I
Language points for Reading II
Video data
98-105
106-109
1. You skin also keeps you warm or cool; it prevents your body from losing water; it is where you feel cold, heat or pain; and it gives you your sense of touch.
keep you warm or cool 为keep复合结构,即keep+宾语+宾补。使处于某种状态……。宾补除由形容词充当之外,还可用名词,现在分词,过去分词,介词短语,副词来充当。
This coat will keep you warm.
This story will keep the children amused.
The illness kept her in hospital.
I’m sorry to keep you waiting.
prevent sb. from doing sth. 阻止某人做某事
What can we do to prevent this disease spreading?
She was prevented from taking the exam by illness.
sense of touch 触觉
sense of sight 视觉 sense of hearing 听觉
sense of taste 味觉 sense of smell 嗅觉
sense of humour 幽默感
sense of beauty 美感
sense of direction 方向感
sense of urgency 紧迫感
2. Burns are called first degree, second degree or third degree, depending on which layers of the skin are burned.
depending on which layers of the skin are burned 为现在分词短语作伴随状语。
Charles Darnay left France, preferring to give up his fortune.
depend on 相信,依赖,依靠
You can’t depend on John-he nearly always arrive late.
The country depends heavily on its tourist trade.
The amount you pay depends on where you live.
3. Examples include burns by electric shocks, burning clothes or severe petrol fires. 例如由电击引起的烧伤,因衣服起火引起的烧伤,或由汽油起火引起的烧伤。
electric
(1) 用电的,电动的
an electric clock 电钟 an electric fire 电炉
(2) 电的,发电的,带电的
electric power 电力
an electric storm 电闪雷鸣般的暴风雨
(3) 令人兴奋的
His speech had an electric effect on the crowd.
4. Take clothing off the burned are unless it is stuck to the burn. 除非衣服粘贴在烧伤面上,否则都要把它脱掉。
take off
(1) 脱下,脱掉
Take your coat off.
(2) 休假,歇……(天)假
Take a few days off, Michael.
(3) 开始有成就,开始成名
It was at this point that her acting career really took off.
(4) 升空,起飞
The plane took off so smoothly that the passengers could hardly feel it.
5. For second degree burns, keep cloths cool by putting them back in the cold water, squeezing them out and placing them on the burned area over and over again for about an hour until pain is not so bad. 对于二度烧伤,要保持湿布清凉,需把湿布放回冷水中,拧出水后放在烧伤面上,这样要反反复复地做一个小时左右,直到不太痛时为止。
squeeze
(1) vt. 压,挤,榨
He squeezed her arm sympathetically.
(2) vt. 压出,挤出,榨出,用于squeeze+n.+adv.&prep
She squeezed the water out of the sponge.
(3) vi. 挤入,塞,用于
squeeze+adv./prep.
squeeze+adj.+adv./prep.
Is the car full or can I squeeze in?
He was so fat that he could not just squeeze through the door.
Seventeen-year-old teenager, John Janson, was honoured at the Lifesaver Awards last night in Rivertown for carrying out lifesaving fist aid on his neighbour after a shocking knife attack.
honour
(1) vt. 尊敬;使感到荣幸
We are deeply honoured that you should agree to join us.
(2) n. 荣誉,尊敬
The Queen was welcomed at the airport by a guard of honour.
(3) n. 名声,名誉
It’s a point of honour with me to reply all my debts promptly.
(4) n. 增光的人(事),引以为荣的人(事),只用单数。
He’s an honour to the school.
2. John was presented with this reward at a ceremony which recognized the bravery of ten people who had saved the life of another.
present
(1) vt. 颁发,授予
present sth. to sb. 颁发……给某人
present sb. with sth. 授予某人……
When Mr Brown left the firm, the director presented a gold watch to him/ him with a gold watch.
(2) vt. 提出,呈递
When are the committees presenting their report?
3. It shows that a knowledge of first aid can make a real difference.
a knowledge of 知道,了解,具有……知识
He has a good knowledge of English.
make a/some/no difference 有一些/没有什么区别
It doesn’t make any difference to me whether you go or stay.
