人教必修二 Unit 2 The Olympic Games reading课件(22页PPT)
文档属性
| 名称 | 人教必修二 Unit 2 The Olympic Games reading课件(22页PPT) |

|
|
| 格式 | ppt | ||
| 文件大小 | 925.2KB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 人教版(新课程标准) | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2021-02-02 00:00:00 | ||
图片预览








文档简介
Unit2
The
Olympic
Games
When
and
where
did
the
ancient
Olympic
Games
start?
A.
776
BC;
in
Greece
B.
776
AD;
in
Greece
Competition
2.
What
events
were
there
in
the
ancient
Olympic
Games?
A.
Running,
jumping,
shooting,
throwing,
wrestling.
B.
Table
tennis,
jumping,
volleyball,
petition
3.
When
and
where
did
the
modern
Olympics
start?
A.
In
1896;
in
Athens
B.
In
1896;
in
America
Competition
4.
How
many
gold
medals
did
China
get
in
the
2012
London
Olympics?
A.
36
B.
37
C.
38
D.
39
Competition
5.
Who
was
China’s
first
gold
medal
winner
and
for
what
event?
A.
Xu
Haifeng;
shooting
B.
Xu
Haifeng;
table
tennis
Competition
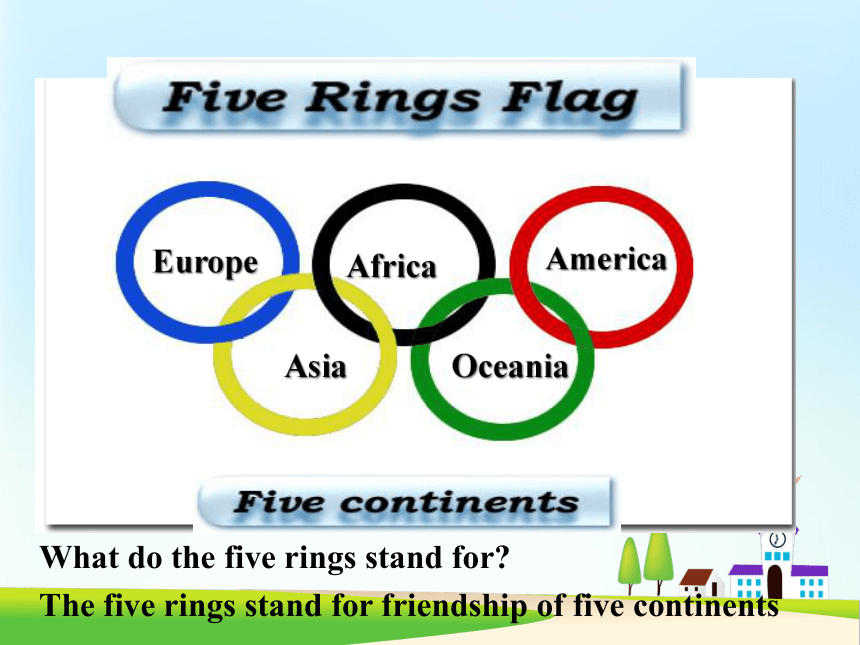
Asia
Europe
Africa
America
Oceania
The
five
rings
stand
for
friendship
of
five
continents
What
do
the
five
rings
stand
for?
Pausanias,
a
Greek
writer
2000
years
ago.
Li
Yan,
a
volunteer
for
the
2008
Olympics.
Step2:
Pre
-
reading
Characters
&
Identity
Interviewer
Interviewee
the
ancient
Olympic
Games
the
modern
Olympic
Games
the
difference
between
them
the
similarities
between
them
good
&
bad
effects
of
the
OG
Fast
reading
Listen
to
the
interview
quickly
to
check
what
it
is
about.
Step3:
Reading
How
many
questions
does
Pausanias
ask
about
the
modern
Olympics?
1.
How
often
are
the
Olympic
Games
held?
Every
four
years.
Athletes
who
are
good
enough,
including
men
and
women
from
all
over
the
world.
2.
Who
can
take
part
in
the
modern
Olympics?
3.
Where
can
competitors
stay?
4.
What
do
the
winners
get
as
a
prize?
5.
What
do
the
competitors
compete
for?
A
special
village
which
is
built
for
them.
They
get
medals
as
their
prize.
For
the
honor
---
“Swifter,
Higher
and
Stronger.”
And
answer
the
following:
Task
1
What
are
the
similarities
and
differences
about
the
ancient
and
modern
Olympics?
Group
work
Similarities
Both
are
held
every
four
years.
Both
are
held
not
for
money
but
for
honor.
Men
are
allowed
to
take
part
in
both
in
ancient
and
modern
Olympics.
The
motto
is
the
same.
(
Swifter,
Higher
and
Stronger.)
Some
events
remain
the
same,
such
as
running,
jumping,
shooting
and
throwing.
…
Item
The
ancient
Olympics
The
modern
Olympics
Place
In
Greece
?_____________________
Athletes
Only
men
from
________
cities.
From_______________
including___________________
Games
Only
the
summer
Olympics
?_____________________________________________________
Preparations
Not
exactly
mentioned
______________________________________________
are
built.
Events
Fewer
________
Prizes
?_______________
Olympic
medals
Differences
Any
country
Greek
all
over
the
world
men
and
women
Both
the
Summer
Olympics
and
the
Winter
Olympics
A
special
village
and
several
stadiums
More
The
olive
wreath
Task2
True
or
false
The
olive
wreath
has
been
replaced
by
money.(
)
At
first,
Pausanias
thinks
people
may
be
competing
for
money
in
the
modern
Olympic
Games.
(
)
3.
Pausanias
is
surprised
to
know
that
women
are
to
take
part
in
the
modern
Olympic
Games.
(
)
4.
Horse
riding
events
belong
to
the
Winter
Olympics.
(
)
5.
The
village
built
for
Olympic
athletes
is
made
up
of
a
main
reception
building,
several
stadiums
and
a
gymnasium.
(
)
6.
2012
Olympics
will
be
held
in
London.
(
)
F
T
T
F
T
T
Task3
Scanning
for
detailed
information
1.
Where
do
all
the
competitors
live?
A.
A
hotel
B.
A
special
village
C.A
restaurant.
D.A
place
hire
by
competitors
2.
Why
do
so
many
countries
want
to
host
the
Olympic
Games?
A.
To
run
faster,
jump
higher
and
throw
further
B.
To
get
a
great
honor.
C.
To
make
the
country
famous
.
D.
To
make
money.
3.
Which
of
the
following
is
included
in
the
Winter
Olympic
Games?
A.
Skiing
and
ice
skating.
B.
Running
races.
C.
Horse
riding.
D.
Swimming.
4.
Why
does
Pausanias
think
people
may
be
competing
for
money
in
the
modern
Olympic
Games?
A.
Because
the
winner
can
get
medals.
B.
Because
the
winner
can
be
awarded
lots
of
money
by
their
own
countries.
C.
Because
the
olive
wreaths
have
been
replaced
by
medals.
Knowledge
points
of
part
reading
1.I
used
to
write
about
the
Olympic
Games
a
long
time
ago.
used
to
do
过去常常做...
be/get
used
to
(doing)
sth. 习惯于
be
used
to
do
被用来做
过去我们常在一起玩.
We
used
to
play
together.
她习惯睡前喝一杯牛奶.
She
is
used
to
drinking
a
glass
of
milk
before
she
goes
to
bed.
2.
every
four
years
:
每四年或每隔三年
every
与数词连用表示
“
每…
每隔
…
every
基数词+复数名词
序数词+单数名词
每隔三米:
每两年,或每隔一年
every
four
meters,
every
fourth
meter
every
two
years:
every
second
year
every
other
year
every
few
years
每隔几年
3.It’s
in
the
Summer
Olympics
that
you
have
the
running
races,
together
with
swimming,
sailing
and
all
the
team
sports.跑步、游泳、划船和一些团体项目是在夏季奥运会上进行的。
强调句型:It
is/was+被强调部分+that/who+其他成分
(1)被强调部分可以是单词、短语,也可以是一个从句。被强调部分可以是主语、宾语、状语等,但不可以是定语和谓语。
e.g
It
is
I
who
am
right.
It
was
in
the
park
that
Tom
lost
his
watch.
(2)该结构的一般疑问句是把is或was提前。
e.g
Was
it
in
1939
that
the
WWII
broke
out?
(3)它的特殊疑问句需在一般疑问句前加特殊疑问词。
e.g
Who
was
it
that
broke
the
window?
4.
No
other
country
could
join
in,
nor
could
slaves
or
women.
其他国家都不能参加,奴隶和妇女也不行。
1)“nor+连系动词/助动词/情态动词+主语”,nor
用作连词,引起倒装句,表示前面的否定情况也适合于另一人或另一物,意为“也不…”。
e.g
I
don’t
know,
nor
do
I
care.
2)“nor+连系动词/助动词/情态动词+主语”,表示前面的肯定情况也适合于另一人或另一物,意为“也…”。
e.g
She
can
speak
French,so
can
I.
Thank
you.
The
Olympic
Games
When
and
where
did
the
ancient
Olympic
Games
start?
A.
776
BC;
in
Greece
B.
776
AD;
in
Greece
Competition
2.
What
events
were
there
in
the
ancient
Olympic
Games?
A.
Running,
jumping,
shooting,
throwing,
wrestling.
B.
Table
tennis,
jumping,
volleyball,
petition
3.
When
and
where
did
the
modern
Olympics
start?
A.
In
1896;
in
Athens
B.
In
1896;
in
America
Competition
4.
How
many
gold
medals
did
China
get
in
the
2012
London
Olympics?
A.
36
B.
37
C.
38
D.
39
Competition
5.
Who
was
China’s
first
gold
medal
winner
and
for
what
event?
A.
Xu
Haifeng;
shooting
B.
Xu
Haifeng;
table
tennis
Competition
Asia
Europe
Africa
America
Oceania
The
five
rings
stand
for
friendship
of
five
continents
What
do
the
five
rings
stand
for?
Pausanias,
a
Greek
writer
2000
years
ago.
Li
Yan,
a
volunteer
for
the
2008
Olympics.
Step2:
Pre
-
reading
Characters
&
Identity
Interviewer
Interviewee
the
ancient
Olympic
Games
the
modern
Olympic
Games
the
difference
between
them
the
similarities
between
them
good
&
bad
effects
of
the
OG
Fast
reading
Listen
to
the
interview
quickly
to
check
what
it
is
about.
Step3:
Reading
How
many
questions
does
Pausanias
ask
about
the
modern
Olympics?
1.
How
often
are
the
Olympic
Games
held?
Every
four
years.
Athletes
who
are
good
enough,
including
men
and
women
from
all
over
the
world.
2.
Who
can
take
part
in
the
modern
Olympics?
3.
Where
can
competitors
stay?
4.
What
do
the
winners
get
as
a
prize?
5.
What
do
the
competitors
compete
for?
A
special
village
which
is
built
for
them.
They
get
medals
as
their
prize.
For
the
honor
---
“Swifter,
Higher
and
Stronger.”
And
answer
the
following:
Task
1
What
are
the
similarities
and
differences
about
the
ancient
and
modern
Olympics?
Group
work
Similarities
Both
are
held
every
four
years.
Both
are
held
not
for
money
but
for
honor.
Men
are
allowed
to
take
part
in
both
in
ancient
and
modern
Olympics.
The
motto
is
the
same.
(
Swifter,
Higher
and
Stronger.)
Some
events
remain
the
same,
such
as
running,
jumping,
shooting
and
throwing.
…
Item
The
ancient
Olympics
The
modern
Olympics
Place
In
Greece
?_____________________
Athletes
Only
men
from
________
cities.
From_______________
including___________________
Games
Only
the
summer
Olympics
?_____________________________________________________
Preparations
Not
exactly
mentioned
______________________________________________
are
built.
Events
Fewer
________
Prizes
?_______________
Olympic
medals
Differences
Any
country
Greek
all
over
the
world
men
and
women
Both
the
Summer
Olympics
and
the
Winter
Olympics
A
special
village
and
several
stadiums
More
The
olive
wreath
Task2
True
or
false
The
olive
wreath
has
been
replaced
by
money.(
)
At
first,
Pausanias
thinks
people
may
be
competing
for
money
in
the
modern
Olympic
Games.
(
)
3.
Pausanias
is
surprised
to
know
that
women
are
to
take
part
in
the
modern
Olympic
Games.
(
)
4.
Horse
riding
events
belong
to
the
Winter
Olympics.
(
)
5.
The
village
built
for
Olympic
athletes
is
made
up
of
a
main
reception
building,
several
stadiums
and
a
gymnasium.
(
)
6.
2012
Olympics
will
be
held
in
London.
(
)
F
T
T
F
T
T
Task3
Scanning
for
detailed
information
1.
Where
do
all
the
competitors
live?
A.
A
hotel
B.
A
special
village
C.A
restaurant.
D.A
place
hire
by
competitors
2.
Why
do
so
many
countries
want
to
host
the
Olympic
Games?
A.
To
run
faster,
jump
higher
and
throw
further
B.
To
get
a
great
honor.
C.
To
make
the
country
famous
.
D.
To
make
money.
3.
Which
of
the
following
is
included
in
the
Winter
Olympic
Games?
A.
Skiing
and
ice
skating.
B.
Running
races.
C.
Horse
riding.
D.
Swimming.
4.
Why
does
Pausanias
think
people
may
be
competing
for
money
in
the
modern
Olympic
Games?
A.
Because
the
winner
can
get
medals.
B.
Because
the
winner
can
be
awarded
lots
of
money
by
their
own
countries.
C.
Because
the
olive
wreaths
have
been
replaced
by
medals.
Knowledge
points
of
part
reading
1.I
used
to
write
about
the
Olympic
Games
a
long
time
ago.
used
to
do
过去常常做...
be/get
used
to
(doing)
sth. 习惯于
be
used
to
do
被用来做
过去我们常在一起玩.
We
used
to
play
together.
她习惯睡前喝一杯牛奶.
She
is
used
to
drinking
a
glass
of
milk
before
she
goes
to
bed.
2.
every
four
years
:
每四年或每隔三年
every
与数词连用表示
“
每…
每隔
…
every
基数词+复数名词
序数词+单数名词
每隔三米:
每两年,或每隔一年
every
four
meters,
every
fourth
meter
every
two
years:
every
second
year
every
other
year
every
few
years
每隔几年
3.It’s
in
the
Summer
Olympics
that
you
have
the
running
races,
together
with
swimming,
sailing
and
all
the
team
sports.跑步、游泳、划船和一些团体项目是在夏季奥运会上进行的。
强调句型:It
is/was+被强调部分+that/who+其他成分
(1)被强调部分可以是单词、短语,也可以是一个从句。被强调部分可以是主语、宾语、状语等,但不可以是定语和谓语。
e.g
It
is
I
who
am
right.
It
was
in
the
park
that
Tom
lost
his
watch.
(2)该结构的一般疑问句是把is或was提前。
e.g
Was
it
in
1939
that
the
WWII
broke
out?
(3)它的特殊疑问句需在一般疑问句前加特殊疑问词。
e.g
Who
was
it
that
broke
the
window?
4.
No
other
country
could
join
in,
nor
could
slaves
or
women.
其他国家都不能参加,奴隶和妇女也不行。
1)“nor+连系动词/助动词/情态动词+主语”,nor
用作连词,引起倒装句,表示前面的否定情况也适合于另一人或另一物,意为“也不…”。
e.g
I
don’t
know,
nor
do
I
care.
2)“nor+连系动词/助动词/情态动词+主语”,表示前面的肯定情况也适合于另一人或另一物,意为“也…”。
e.g
She
can
speak
French,so
can
I.
Thank
you.
