Unit 4 A good read Grammar 课件(37张PPT)
文档属性
| 名称 | Unit 4 A good read Grammar 课件(37张PPT) |

|
|
| 格式 | ppt | ||
| 文件大小 | 1.7MB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 牛津译林版 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2021-03-18 21:13:24 | ||
图片预览









文档简介
8B
Unit
4
A
good
read
Grammar
hand
hand
in
v.
交;递,给
上交,递交
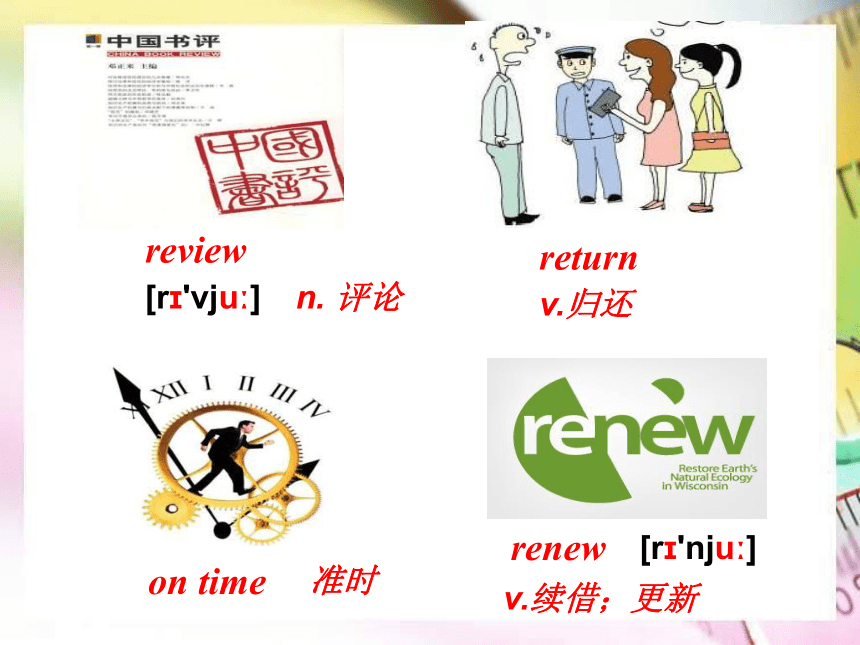
review
return
renew
on
time
n.
评论
[r?'vju?]
v.归还
准时
v.续借;更新
[r?'nju?]
动词不定式
To
do
that
kind
of
thing
is
foolish。
I
want
to
see
you
this
evening.
All
you
have
to
do
is
to
finish
it
quickly.
We
found
a
house
to
live
in.
She
came
here
to
study
English.
He
asked
the
patient
not
to
eat
cold
water
after
the
operation.
主语
宾语
表语
定语
状语
宾补
Using
question
words
+
to
infinitives
Andy
doesn't
know
____________.
(穿什么)
what
to
wear
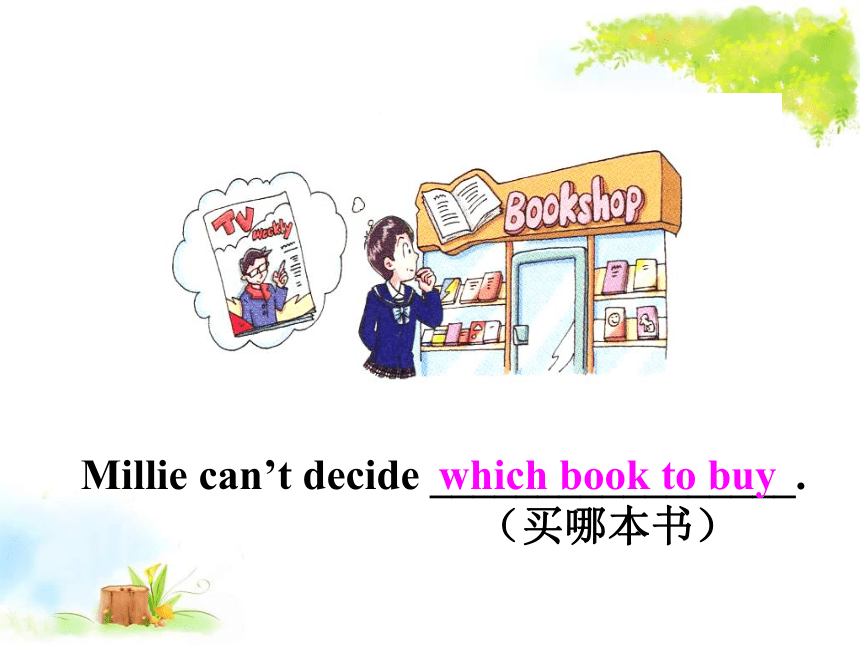
Millie
can’t
decide
_________________.
(买哪本书)
which
book
to
buy
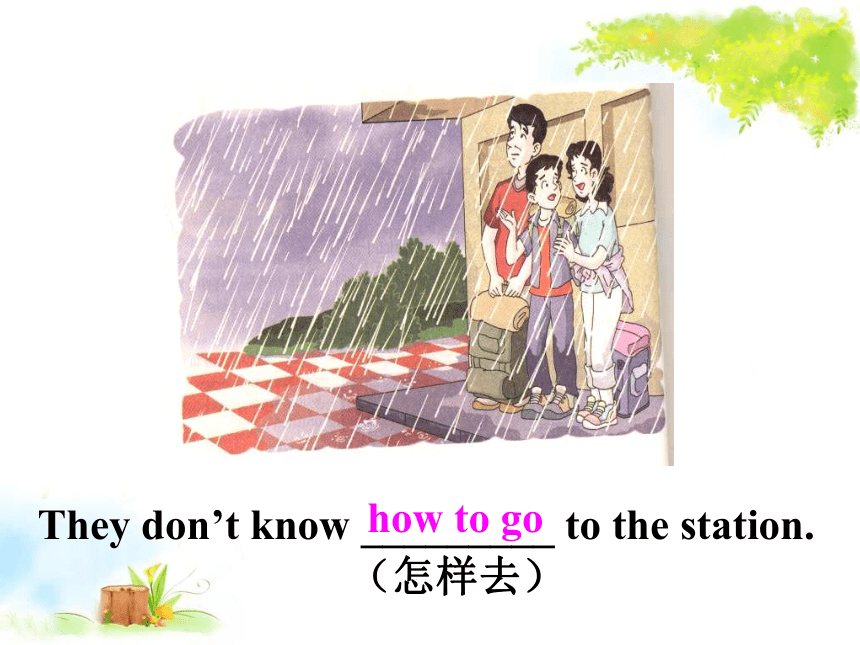
They
don’t
know
_________
to
the
station.
(怎样去)
how
to
go
We
can
use
a
question
word
with
a
to-
infinitive
after
a
verb.
e.g.
1.
Millie
has
decided________________(读什么).
2.
Daniel
did
not
say
_____________(和谁交谈)about
this
book.
3.
Simon
forgot
______________(什么时候见)his
friends.
4.
Kitty
cannot
decide
________________(选哪一个)first.
5.
Sandy
is
wondering
______________(去哪儿请求)for
help.
6.
Amy
does
not
know
_____________(怎样写)the
report.
what
to
read
who
to
talk
to
when
to
meet
which
to
choose
where
to
ask
how
to
write
我们可以用疑问词加动词不定式放在动词后做宾语。
All
question
words
can
be
used
in
this
way,
except
why.
Suzy
will
explain
why
to
recommend
this
book.
Suzy
will
explain
why
she
recommend
this
book.
√
×
所有疑问词中,只有why不可以与动词不定式连用
We
can
use
a
verb
+
object
before
a
question
word
with
a
to-infinitive.
advise,
ask,
decide,
discuss,
find
out,
forget,
know,
learn
remember,
say,
show,
teach,
think,
understand,
wonder
e.g.
1.
Mr
Wu
advised
us
________________
(选择哪一个)
as
after-school
activities.
2.
The
students
asked
their
teacher
______________
(什么时候上交)their
work.
3.
Millie
showed
us________________(下一步做什么).
4.
Daniel
taught
himself__________(怎样用)a
computer
to
draw.
5.
Don’t
forget
to
tell
your
mum
_______________you.
which
to
choose
when
to
hand
in
what
to
do
next
how
to
use
where
to
meet
(在哪儿接)
我们可以在疑问词+动词不定式前使用动词+宾语
We
can
use
a
noun
after
what,
which,
whose,
how
many
and
how
much.
(我们可以在what,
which,
whose,
how
many和how
much后加上一个名词)
e.g.
1.
They
are
discussing
____________________
(涂哪一个颜色)
the
walls.
2.
You
can
ask
your
parents
_____________________
(带多少钱)with
you.
which
color
to
paint
how
much
money
to
take
e.g.
Suzy
was
not
sure
______________(向谁请求)help.
Are
you
clear
___________
(什么时候见面)
at
the
gate
tomorrow?
who
to
ask
for
when
to
meet
We
can
also
use
an
adjective
like
sure
or
clear
before
a
question
word.
(
我们还可以在疑问词钱用像sure
或clear这样的形容词。)
四种结构
1)
动词+
疑问词
+
to
do
sth.
2)
动词+
宾语+
疑问词+to
do
sth.
3)
动词+
疑问词+
名词+
to
do
sth.
4)
adj.
(sure/clear)+
疑问词+to
do
sth.
I
don’t
know
what
to
say
next.
我不知道接下来该说什么。
I
can’t
decide
which
to
take.
我不能决定该拿哪一个。
Please
tell
me
how
to
get
there.
请告诉我怎样到那儿。
e.g.
2.“疑问词+动词不定式”
结构在句子中还可以做主语和表语。
1)
_________________
(如何处理
)
the
waste
is
still
a
hard
problem.
2)
The
problem
is
______________
(何时离开)the
place.
3.
“疑问词+动词不定式”
结构可以改写成由该疑问词引
导的从句。
e.g.
I
don’t
know
what
to
do.(该做什么)
=
I
do
not
know
what
I
should
do.
注意:所有疑问句中,只有why不可以
与动词不定式连用。
What
to
do
with
when
to
leave
(1)
He
did
not
know
where
he
could
find
other
people.
=
_______________.
(2)He
wondered
who
he
could
ask
for
help.
=
_____________________.
(3He
did
not
know
how
he
could
break
the
ropes.
=
______________.
(4)
He
found
out
what
he
could
do
with
the
tiny
man.
=
______________.
(5)
He
decided
when
he
should
leave
Lilliput.
=
_____________.
(6)
I
don’t
know______________________________.
(怎么办)
=_________________________
where
to
find
4.
同义句转换
who
to
ask
for
how
to
break
what
to
do
when
to
leave
what
to
do
/
how
to
do
it
what
I
should
do
/how
I
should
do
it
Amy
and
Daniel
are
talking
about
their
Reading
plete
their
conversation.
Use
the
correct
question
words
and
to-infinitives.
Amy:
Mr
Wu
has
recommended
so
many
interesting
books.
Have
you
decided
(1)
____________
first,
Daniel?
Daniel:
Yes.
I
want
to
read
Black
Beauty
first.
But
I
don’t
know
(2)
___________
the
book.
how,
what,
ask
for,
find,
when,
where,
hand
in,
read,
which,
who,
speak,
travel,
write
about
which
to
read
where
to
find
Amy:
You
can
try
our
school
library
or
Sunshine
Library.
Oh,
did
you
know
Peter
is
reading
Around
the
World
in
Eighty
Days?
He
wants
to
find
out
(3)
___________
around
the
world
in
such
a
short
time.
Daniel:
Wow,
that’s
amazing!
By
the
way,
can
you
tell
me
(4)______________
our
book
report?
how
to
travel
when
to
hand
in
Amy:
Before
next
Friday.
I’m
still
not
sure
(5)
_________________
in
the
report.
Daniel:
You
can
write
anything
about
your
book
–
what
the
book
is
about,
what
you
think
of
it
and
so
on.
You
should
read
some
reviews
about
the
book
before
writing.
what
to
write
about
Amy:
Thank
you.
Anyway,
I
know
(6)
______________
help
with
writing.
Mr
Wu
is
always
there
to
help
us.
who
to
ask
for
Using
must
and
have
to
We
must
obey
school
rules
when
we're
at
school.
What
school
rules
do
we
have?
What
must
we
do?
What
mustn’t
we
do?
We
must
wear
school
uniforms.
We
must
get
to
school
on
time.
We
must
keep
quiet
in
the
school
library.
We
mustn’t
throw
rubbish
on
the
ground.
We
mustn’t
pick
the
flowers
in
the
garden.
We
use
must
when
the
speaker
feels
that
something
is
necessary.
We
use
must
not
to
say
that
something
is
not
allowed.
If
you’re
ill
and
the
doctor
asks
you
to
stay
at
home,
what’ll
you
have
to
do?
Do
you
have
to
go
to
school
at
weekends?
No,
we
don’t
have
to.
We
use
have
to
when
the
situation
makes
something
necessary.
We
use
do
not
have
to
to
say
that
it’s
not
necessary
to
do
something.
Different
forms:has
to,
had
to,
will
have
to
and
have/has
got
to.
We
use
must
and
have
to
to
say
that
it
is
necessary
to
do
something.
We
use
must
when
the
speaker
feels
that
something
is
necessary.
e.g.
“I
must
run
away
from
them,”
Gulliver
thought.
We
use
have
to
when
the
situation
makes
something
necessary.
e.g.
I
have
to
use
them
to
reach
the
box
on
the
fridge.
She
has
to
take
her
daughter
from
school
in
the
afternoon.
We
use
must
not
to
say
that
something
is
not
allowed.
e.g.
You
must
not
smoke
in
the
library.
We
use
do
not
have
to
to
say
that
it
is
not
necessary
to
do
something.
e.g.
We
do
not
have
to
go
to
school
at
weekends.
We
use
must
and
have
to
to
say
that
it
is
necessary
to
do
something
Have
to
has
different
forms,
has
to
had
to
will
have
to
have/has
got
to
Tip1
must
not
=
mustn't
do
not
have
to
=
don’t
have
to
Tip2
表示义务、命令或必要,主要用于肯定句和疑问句,“必须,得,要”。
must用在一般疑问句中,肯定回答用must,否定回答用needn’t
或don’t
have
to
you
needn’t.
/
don’t
have
to
you
must
--Must
I
hand
it
in
before
five?
--
No,
you
_________________________.
--
Yes,
______________.
You
must
finish
your
homework
today.
We
must
keep
our
word.
You
must
not
park
your
car
here.
You
mustn’t
smoke
in
the
office.
2.
must
用在否定句结构中表示“不允许、禁止,
不能,不行”。”
1.
have
to
表一种客观的需要,“不得不”。have
to
有
人称和数的变化。
e.g.
It
is
getting
dark.
He
has
to
go
home
now.得
Mum
is
out,
so
I
have
to
look
after
the
shop.
2.
have
to
的否定形式do
not
have
to,
相当于need
not
。
e.g.
They
do
not
have
to
buy
a
computer
at
the
moment.
He
does
not
have
to
go.不必
含义不同:
must
表示说话人的主观思想,强调个人意志和主观的心。
have
to
侧重于客观上的必要,强调客观条件
作用的结果。
You
must
do
it
now.
I
have
to
go
now.
2.
适用时态不同
must
只能用于一般现在时和一般过去时(在间接引语中),
have
to
可用于更多的场合。
She
said
she
must
do
well
in
her
English.
3.
否定含义不同
在否定句中,
have
to表示不需要,must则
表示不允许。
You
don’t
have
to
go
there.
You
mustn’t
go
there.
4.
注意:must
还可以表示肯定猜测,意思是
“一定”
。否定的猜测是can’t。
e.g.
You
must
be
hungry
after
all
that
walking.
走了那么远的路,你一定饿了吧。
That
can’t
be
Lucy.
She
has
gone
to
America.
那肯定不是Lucy,她已经去了美国。
Amy
is
telling
her
cousin
Shirley
some
library
plete
what
she
says
with
must,
must
not,
have
to
or
don’t
have
to.
You
(1)
_____
keep
quiet
in
the
library.
You
(2)
_____
keep
the
books
clean
and
tidy.
You
(3)
_______
draw
or
write
on
the
books
.
must
must
mustn’t
You
(4)
_______
eat
or
drink
in
the
library.
You
(5)
_____
return
the
books
on
time.
If
you
want
to
keep
them
longer,
you
(6)
______
renew
them.
You
(7)
____________
bring
your
student
card
every
time
you
go
to
the
library,
but
remember
to
bring
your
library
card.
mustn’t
must
have
to
do
not
have
to
Millie
已经决定读
什么了。
2.
Daniel没有说和谁谈
论这本书。
3.Simon忘记什么时候
接他的朋友。
4.
Kitty不能决定先选哪
一个。
5.
Sandy想知道去哪儿
寻求帮助。
6.
Amy不知道怎样写报告。
7.
上交
Millie
has
decided
what
to
read.
Daniel
did
not
say
who
to
talk
to
about
this
book.
Simon
forgot
when
to
meet
his
friends.
Kitty
cannot
decide
which
to
choose
first.
Sandy
is
wondering
where
to
ask
for
help.
Amy
does
not
know
how
to
write
the
report.
hand
in
8.
写有关…
9.
在这么短的时间
10.
等等
11.
读一些有关…评论
12.在写作上请求帮助
13.
吴老师总是会给
我们帮助
14.你不可以在图书馆抽烟
15.
我们周末不需要上课。
16.
按时还书
17.
想要再借久点
18.
续借他们
19.
带上你的学生证
20.
记住带上你的借书证
write
about
in
such
a
short
time
and
so
on
read
some
reviews
about
ask
for
help
with
writing
Mr
Wu
is
always
there
to
help
us.
You
must
not
smoke
in
the
library.
We
don’t
have
to
go
to
school
at
weekends.
return
books
on
time
want
to
keep
them
longer
renew
them
bring
your
student
card
remember
to
bring
your
library
card
一、完成下列句子。
1.
I
don’t
know
______________________
(在会上说什么).
2.
Can
you
tell
me
___________________
(在哪里能买到这本书)?
3.
_________________________________
(在何时何地召开这会议)
hasn’t
been
decided
yet.
what
to
say
at
the
meeting
where
to
buy
this
book
When
and
where
to
hold
the
meeting
翻译句子
1.我不知道如何解决这个问题.
I
_____________________________.
2.汤姆不知道该和谁玩.
Tom______________________________.
3.我忘了下一步该做什么.
I
forgot
___________________________.
4.我们还没决定在哪儿见面.
We
haven’t
________________________.
5.请告诉我何时开班会.
Please
tell
me
____________________________.
when
to
begin
the
class
meeting
doesn’t
know
who
to
play
with
what
to
do
next
decided
where
to
meet
don’t
know
how
to
solve
this
problem
1.
When
I
go
into
the
clothes
shop,
I
always
can’t
decide
_____
one
to
buy.
2.
My
grandfather
doesn’t
know
____
to
use
a
computer.
3.
---
Will
you
please
show
me
____
to
drive
a
car?
---
Yes,
of
course.
Now
let
me
tell
you
____
to
do
first.
4.
I
will
tell
Lucy
_____
and
_____
to
meet.
which
how
how
what
when
where
二、用how,
which,
what,
when,
where填空。
Don’t
be
late
again.
You
____
be
here
on
time.
A.
may
B.
can
C.
must
D.
needn’t
You
___
do
it
even
if
you
don’t
want
to.
A.
can’t
B.
mustn’t
C.
needn’t
D.
have
to
3.
——
Must
I
take
a
bus?
——
No,
you
___.
You
can
walk
from
here.
A.
mustn’t
B.
don’t
C.
don’t
have
to
D.
had
better
not
to
Remember
the
grammar
in
this
lesson.
Unit
4
A
good
read
Grammar
hand
hand
in
v.
交;递,给
上交,递交
review
return
renew
on
time
n.
评论
[r?'vju?]
v.归还
准时
v.续借;更新
[r?'nju?]
动词不定式
To
do
that
kind
of
thing
is
foolish。
I
want
to
see
you
this
evening.
All
you
have
to
do
is
to
finish
it
quickly.
We
found
a
house
to
live
in.
She
came
here
to
study
English.
He
asked
the
patient
not
to
eat
cold
water
after
the
operation.
主语
宾语
表语
定语
状语
宾补
Using
question
words
+
to
infinitives
Andy
doesn't
know
____________.
(穿什么)
what
to
wear
Millie
can’t
decide
_________________.
(买哪本书)
which
book
to
buy
They
don’t
know
_________
to
the
station.
(怎样去)
how
to
go
We
can
use
a
question
word
with
a
to-
infinitive
after
a
verb.
e.g.
1.
Millie
has
decided________________(读什么).
2.
Daniel
did
not
say
_____________(和谁交谈)about
this
book.
3.
Simon
forgot
______________(什么时候见)his
friends.
4.
Kitty
cannot
decide
________________(选哪一个)first.
5.
Sandy
is
wondering
______________(去哪儿请求)for
help.
6.
Amy
does
not
know
_____________(怎样写)the
report.
what
to
read
who
to
talk
to
when
to
meet
which
to
choose
where
to
ask
how
to
write
我们可以用疑问词加动词不定式放在动词后做宾语。
All
question
words
can
be
used
in
this
way,
except
why.
Suzy
will
explain
why
to
recommend
this
book.
Suzy
will
explain
why
she
recommend
this
book.
√
×
所有疑问词中,只有why不可以与动词不定式连用
We
can
use
a
verb
+
object
before
a
question
word
with
a
to-infinitive.
advise,
ask,
decide,
discuss,
find
out,
forget,
know,
learn
remember,
say,
show,
teach,
think,
understand,
wonder
e.g.
1.
Mr
Wu
advised
us
________________
(选择哪一个)
as
after-school
activities.
2.
The
students
asked
their
teacher
______________
(什么时候上交)their
work.
3.
Millie
showed
us________________(下一步做什么).
4.
Daniel
taught
himself__________(怎样用)a
computer
to
draw.
5.
Don’t
forget
to
tell
your
mum
_______________you.
which
to
choose
when
to
hand
in
what
to
do
next
how
to
use
where
to
meet
(在哪儿接)
我们可以在疑问词+动词不定式前使用动词+宾语
We
can
use
a
noun
after
what,
which,
whose,
how
many
and
how
much.
(我们可以在what,
which,
whose,
how
many和how
much后加上一个名词)
e.g.
1.
They
are
discussing
____________________
(涂哪一个颜色)
the
walls.
2.
You
can
ask
your
parents
_____________________
(带多少钱)with
you.
which
color
to
paint
how
much
money
to
take
e.g.
Suzy
was
not
sure
______________(向谁请求)help.
Are
you
clear
___________
(什么时候见面)
at
the
gate
tomorrow?
who
to
ask
for
when
to
meet
We
can
also
use
an
adjective
like
sure
or
clear
before
a
question
word.
(
我们还可以在疑问词钱用像sure
或clear这样的形容词。)
四种结构
1)
动词+
疑问词
+
to
do
sth.
2)
动词+
宾语+
疑问词+to
do
sth.
3)
动词+
疑问词+
名词+
to
do
sth.
4)
adj.
(sure/clear)+
疑问词+to
do
sth.
I
don’t
know
what
to
say
next.
我不知道接下来该说什么。
I
can’t
decide
which
to
take.
我不能决定该拿哪一个。
Please
tell
me
how
to
get
there.
请告诉我怎样到那儿。
e.g.
2.“疑问词+动词不定式”
结构在句子中还可以做主语和表语。
1)
_________________
(如何处理
)
the
waste
is
still
a
hard
problem.
2)
The
problem
is
______________
(何时离开)the
place.
3.
“疑问词+动词不定式”
结构可以改写成由该疑问词引
导的从句。
e.g.
I
don’t
know
what
to
do.(该做什么)
=
I
do
not
know
what
I
should
do.
注意:所有疑问句中,只有why不可以
与动词不定式连用。
What
to
do
with
when
to
leave
(1)
He
did
not
know
where
he
could
find
other
people.
=
_______________.
(2)He
wondered
who
he
could
ask
for
help.
=
_____________________.
(3He
did
not
know
how
he
could
break
the
ropes.
=
______________.
(4)
He
found
out
what
he
could
do
with
the
tiny
man.
=
______________.
(5)
He
decided
when
he
should
leave
Lilliput.
=
_____________.
(6)
I
don’t
know______________________________.
(怎么办)
=_________________________
where
to
find
4.
同义句转换
who
to
ask
for
how
to
break
what
to
do
when
to
leave
what
to
do
/
how
to
do
it
what
I
should
do
/how
I
should
do
it
Amy
and
Daniel
are
talking
about
their
Reading
plete
their
conversation.
Use
the
correct
question
words
and
to-infinitives.
Amy:
Mr
Wu
has
recommended
so
many
interesting
books.
Have
you
decided
(1)
____________
first,
Daniel?
Daniel:
Yes.
I
want
to
read
Black
Beauty
first.
But
I
don’t
know
(2)
___________
the
book.
how,
what,
ask
for,
find,
when,
where,
hand
in,
read,
which,
who,
speak,
travel,
write
about
which
to
read
where
to
find
Amy:
You
can
try
our
school
library
or
Sunshine
Library.
Oh,
did
you
know
Peter
is
reading
Around
the
World
in
Eighty
Days?
He
wants
to
find
out
(3)
___________
around
the
world
in
such
a
short
time.
Daniel:
Wow,
that’s
amazing!
By
the
way,
can
you
tell
me
(4)______________
our
book
report?
how
to
travel
when
to
hand
in
Amy:
Before
next
Friday.
I’m
still
not
sure
(5)
_________________
in
the
report.
Daniel:
You
can
write
anything
about
your
book
–
what
the
book
is
about,
what
you
think
of
it
and
so
on.
You
should
read
some
reviews
about
the
book
before
writing.
what
to
write
about
Amy:
Thank
you.
Anyway,
I
know
(6)
______________
help
with
writing.
Mr
Wu
is
always
there
to
help
us.
who
to
ask
for
Using
must
and
have
to
We
must
obey
school
rules
when
we're
at
school.
What
school
rules
do
we
have?
What
must
we
do?
What
mustn’t
we
do?
We
must
wear
school
uniforms.
We
must
get
to
school
on
time.
We
must
keep
quiet
in
the
school
library.
We
mustn’t
throw
rubbish
on
the
ground.
We
mustn’t
pick
the
flowers
in
the
garden.
We
use
must
when
the
speaker
feels
that
something
is
necessary.
We
use
must
not
to
say
that
something
is
not
allowed.
If
you’re
ill
and
the
doctor
asks
you
to
stay
at
home,
what’ll
you
have
to
do?
Do
you
have
to
go
to
school
at
weekends?
No,
we
don’t
have
to.
We
use
have
to
when
the
situation
makes
something
necessary.
We
use
do
not
have
to
to
say
that
it’s
not
necessary
to
do
something.
Different
forms:has
to,
had
to,
will
have
to
and
have/has
got
to.
We
use
must
and
have
to
to
say
that
it
is
necessary
to
do
something.
We
use
must
when
the
speaker
feels
that
something
is
necessary.
e.g.
“I
must
run
away
from
them,”
Gulliver
thought.
We
use
have
to
when
the
situation
makes
something
necessary.
e.g.
I
have
to
use
them
to
reach
the
box
on
the
fridge.
She
has
to
take
her
daughter
from
school
in
the
afternoon.
We
use
must
not
to
say
that
something
is
not
allowed.
e.g.
You
must
not
smoke
in
the
library.
We
use
do
not
have
to
to
say
that
it
is
not
necessary
to
do
something.
e.g.
We
do
not
have
to
go
to
school
at
weekends.
We
use
must
and
have
to
to
say
that
it
is
necessary
to
do
something
Have
to
has
different
forms,
has
to
had
to
will
have
to
have/has
got
to
Tip1
must
not
=
mustn't
do
not
have
to
=
don’t
have
to
Tip2
表示义务、命令或必要,主要用于肯定句和疑问句,“必须,得,要”。
must用在一般疑问句中,肯定回答用must,否定回答用needn’t
或don’t
have
to
you
needn’t.
/
don’t
have
to
you
must
--Must
I
hand
it
in
before
five?
--
No,
you
_________________________.
--
Yes,
______________.
You
must
finish
your
homework
today.
We
must
keep
our
word.
You
must
not
park
your
car
here.
You
mustn’t
smoke
in
the
office.
2.
must
用在否定句结构中表示“不允许、禁止,
不能,不行”。”
1.
have
to
表一种客观的需要,“不得不”。have
to
有
人称和数的变化。
e.g.
It
is
getting
dark.
He
has
to
go
home
now.得
Mum
is
out,
so
I
have
to
look
after
the
shop.
2.
have
to
的否定形式do
not
have
to,
相当于need
not
。
e.g.
They
do
not
have
to
buy
a
computer
at
the
moment.
He
does
not
have
to
go.不必
含义不同:
must
表示说话人的主观思想,强调个人意志和主观的心。
have
to
侧重于客观上的必要,强调客观条件
作用的结果。
You
must
do
it
now.
I
have
to
go
now.
2.
适用时态不同
must
只能用于一般现在时和一般过去时(在间接引语中),
have
to
可用于更多的场合。
She
said
she
must
do
well
in
her
English.
3.
否定含义不同
在否定句中,
have
to表示不需要,must则
表示不允许。
You
don’t
have
to
go
there.
You
mustn’t
go
there.
4.
注意:must
还可以表示肯定猜测,意思是
“一定”
。否定的猜测是can’t。
e.g.
You
must
be
hungry
after
all
that
walking.
走了那么远的路,你一定饿了吧。
That
can’t
be
Lucy.
She
has
gone
to
America.
那肯定不是Lucy,她已经去了美国。
Amy
is
telling
her
cousin
Shirley
some
library
plete
what
she
says
with
must,
must
not,
have
to
or
don’t
have
to.
You
(1)
_____
keep
quiet
in
the
library.
You
(2)
_____
keep
the
books
clean
and
tidy.
You
(3)
_______
draw
or
write
on
the
books
.
must
must
mustn’t
You
(4)
_______
eat
or
drink
in
the
library.
You
(5)
_____
return
the
books
on
time.
If
you
want
to
keep
them
longer,
you
(6)
______
renew
them.
You
(7)
____________
bring
your
student
card
every
time
you
go
to
the
library,
but
remember
to
bring
your
library
card.
mustn’t
must
have
to
do
not
have
to
Millie
已经决定读
什么了。
2.
Daniel没有说和谁谈
论这本书。
3.Simon忘记什么时候
接他的朋友。
4.
Kitty不能决定先选哪
一个。
5.
Sandy想知道去哪儿
寻求帮助。
6.
Amy不知道怎样写报告。
7.
上交
Millie
has
decided
what
to
read.
Daniel
did
not
say
who
to
talk
to
about
this
book.
Simon
forgot
when
to
meet
his
friends.
Kitty
cannot
decide
which
to
choose
first.
Sandy
is
wondering
where
to
ask
for
help.
Amy
does
not
know
how
to
write
the
report.
hand
in
8.
写有关…
9.
在这么短的时间
10.
等等
11.
读一些有关…评论
12.在写作上请求帮助
13.
吴老师总是会给
我们帮助
14.你不可以在图书馆抽烟
15.
我们周末不需要上课。
16.
按时还书
17.
想要再借久点
18.
续借他们
19.
带上你的学生证
20.
记住带上你的借书证
write
about
in
such
a
short
time
and
so
on
read
some
reviews
about
ask
for
help
with
writing
Mr
Wu
is
always
there
to
help
us.
You
must
not
smoke
in
the
library.
We
don’t
have
to
go
to
school
at
weekends.
return
books
on
time
want
to
keep
them
longer
renew
them
bring
your
student
card
remember
to
bring
your
library
card
一、完成下列句子。
1.
I
don’t
know
______________________
(在会上说什么).
2.
Can
you
tell
me
___________________
(在哪里能买到这本书)?
3.
_________________________________
(在何时何地召开这会议)
hasn’t
been
decided
yet.
what
to
say
at
the
meeting
where
to
buy
this
book
When
and
where
to
hold
the
meeting
翻译句子
1.我不知道如何解决这个问题.
I
_____________________________.
2.汤姆不知道该和谁玩.
Tom______________________________.
3.我忘了下一步该做什么.
I
forgot
___________________________.
4.我们还没决定在哪儿见面.
We
haven’t
________________________.
5.请告诉我何时开班会.
Please
tell
me
____________________________.
when
to
begin
the
class
meeting
doesn’t
know
who
to
play
with
what
to
do
next
decided
where
to
meet
don’t
know
how
to
solve
this
problem
1.
When
I
go
into
the
clothes
shop,
I
always
can’t
decide
_____
one
to
buy.
2.
My
grandfather
doesn’t
know
____
to
use
a
computer.
3.
---
Will
you
please
show
me
____
to
drive
a
car?
---
Yes,
of
course.
Now
let
me
tell
you
____
to
do
first.
4.
I
will
tell
Lucy
_____
and
_____
to
meet.
which
how
how
what
when
where
二、用how,
which,
what,
when,
where填空。
Don’t
be
late
again.
You
____
be
here
on
time.
A.
may
B.
can
C.
must
D.
needn’t
You
___
do
it
even
if
you
don’t
want
to.
A.
can’t
B.
mustn’t
C.
needn’t
D.
have
to
3.
——
Must
I
take
a
bus?
——
No,
you
___.
You
can
walk
from
here.
A.
mustn’t
B.
don’t
C.
don’t
have
to
D.
had
better
not
to
Remember
the
grammar
in
this
lesson.
