2012年中考英语语法复习—动词的时态
文档属性
| 名称 | 2012年中考英语语法复习—动词的时态 |

|
|
| 格式 | zip | ||
| 文件大小 | 565.2KB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 通用版 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2012-03-22 00:00:00 | ||
图片预览



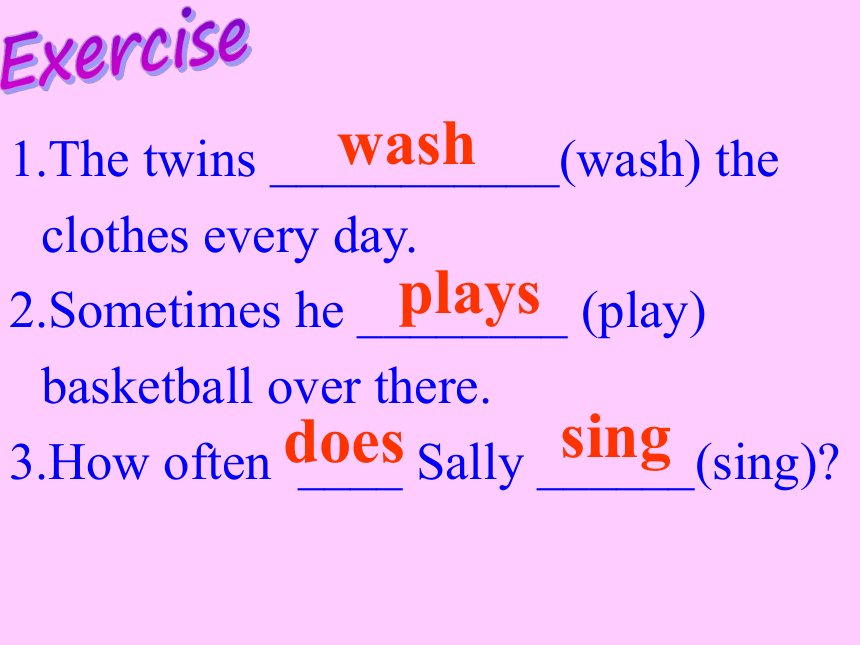

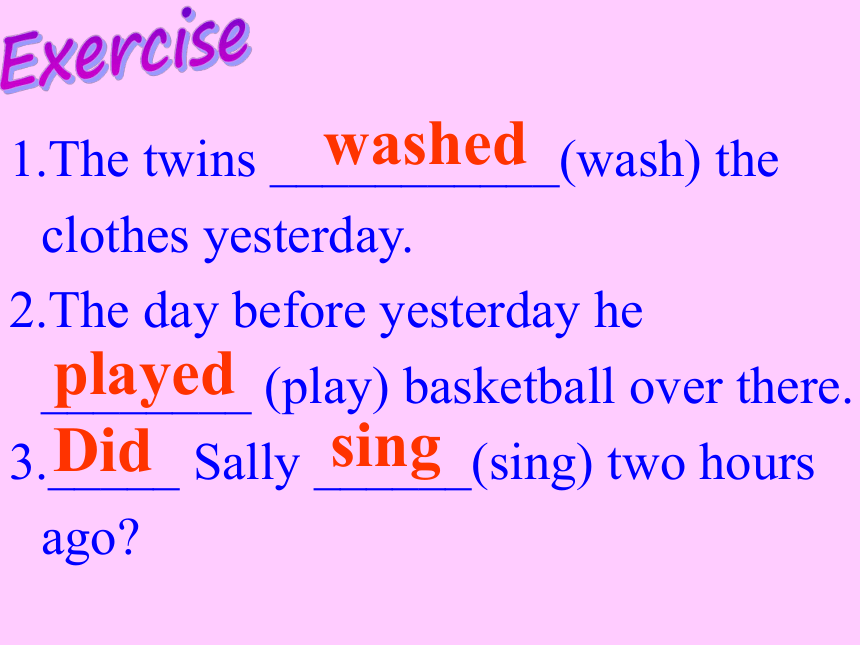




文档简介
(共44张PPT)
时态
中考语法专项复习
Tenses(时态)
1、The Present Simple Tense (一般现在时)
2、 The Past Simple Tense (一般过去时)
3、 The Future Tense (一般将来时)
5、 The Present Continuous Tense (现在进行时)
6、 The Past Continuous Tense (过去进行时)
7、The Present Perfect Tense (现在完成时)
8、The Past Perfect Tense (过去完成时)
4、 The Future in the Past (过去将来时)
八种时态的用法和构成
The Present Simple Tense(一般现在时)
用法:
1、现阶段经常性、习惯性动作;
2、目前的状态;
3、客观真理。
构成:
主语是第三人称单数时,作谓语的行为动词要加词尾
-s(-es),
其他人称和数用动词原形。
常用时间状语:
often,
always,
sometimes,
every day,
on Sunday…
例句:
Jack often goes to school by bike.
Guangzhou is 2313 kilometres away from Beijing.
We have five lessons in the morning.
The twins ___________(wash) the clothes every day.
Sometimes he ________ (play) basketball over there.
How often ____ Sally ______(sing)
wash
plays
does
sing
The Past Simple Tense(一般过去时)
用法:
1、过去发生的动作;
2、过去存在的状态。
构成:
用动词的过去式。
常用时间状语:
yesterday,
two days ago,
last week,
in 1990…
例句:
He went to work by bus yesterday.
Han Meimei was in the classroom a moment ago.
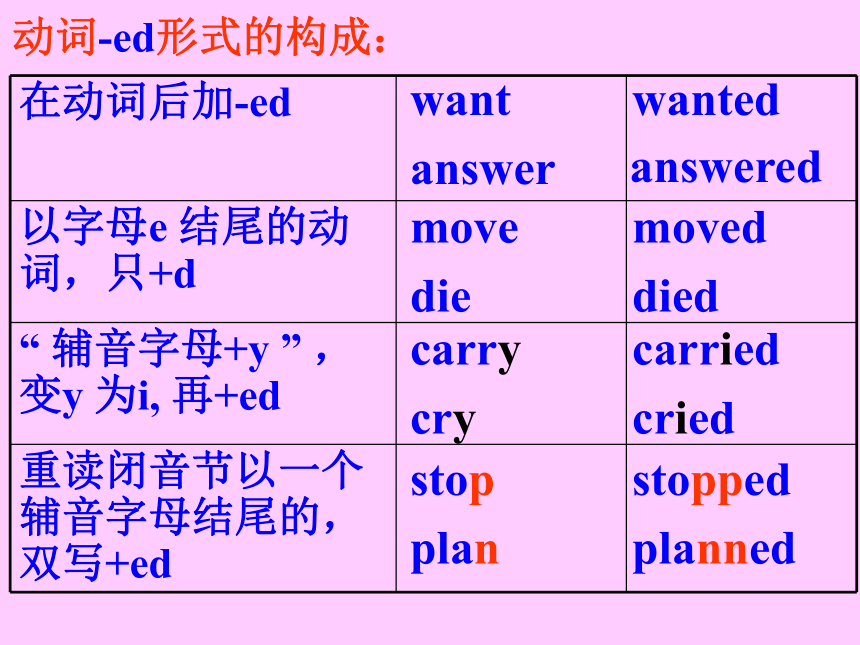
动词-ed形式的构成:
在动词后加-ed
以字母e 结尾的动词,只+d
“ 辅音字母+y ” ,变y 为i, 再+ed
重读闭音节以一个辅音字母结尾的,双写+ed
want
answer
move
die
carry
cry
stop
plan
wanted
moved
died
carried
cried
stopped
planned
answered
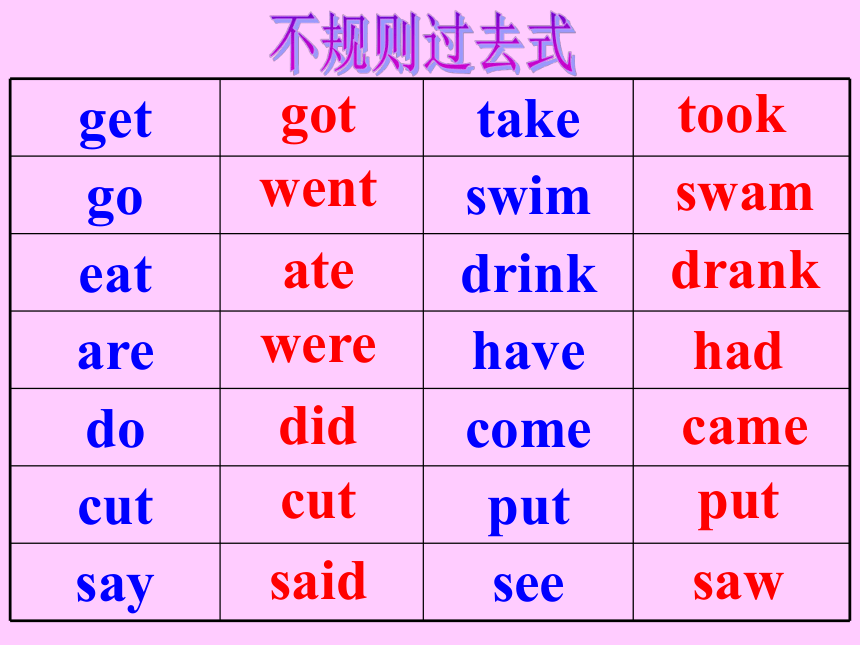
got
drank
took
went
swam
ate
cut
were
had
did
came
said
saw
put
get take
go swim
eat drink
are have
do come
cut put
say see
The twins ___________(wash) the clothes yesterday.
The day before yesterday he ________ (play) basketball over there.
_____ Sally ______(sing) two hours ago
washed
played
Did
sing
The Future Tense(一般将来时)
用法:
1、将来发生的动作;
2、将来存在的状态。
构成:
1、助动词
will(shall) +
动词原形;
2、am(is,are) + going to
常用时间状语:
tomorrow,
next week,
in two hours…
例句:
They will (are going to) meet outside the school gate tomorrow afternoon.
The people will not be pleased if you jump the queue.
备注:
一般现在时代替将来时。
在时间状语从句和条件状语从句中用
Future Simple
表示将要发生的动作
结构: will do、 shall do、
be (is、am、are) going to do
标志语:tomorrow、in..、next…
The Future in the Past(过去将来时)
用法:
从过去某一时间来看将来要发生的动作或存在的状态
构成:
1、助动词
would +
动词原形;
2、was,were + going to
常用时间状语:
(the) next day,
(the) next year,
that afternoon…
例句:
Linda said that she would (was going to) visit her uncle next Saturday.
He wanted to know if they would go to the mountain village that afternoon.
备注:
常用于宾语从句中
时间
现在
过去
那时所预见的情况
一般过去将来时
一、基本概念:
过去将来时表示从过去的某一时间看将要发生的动作或存在的状态。它是一个相对的时态,即立足于过去某时,从过去的某一时间看即将发生的事情就要用这一时态。
1) He said his mother would buy a bike for him
2) My brother told me he wouldn’t believe Jack any more.
3) Would it be all right if he knew his illness
二、基本形式:
would/should+动词原形
(其中 would 用于各种人称, should 常用于第一人称)。
例如:
They were sure they would win the final victory.
他们坚信会赢得最后胜利。
He didn't expect that we should(would)all be there.
他没想到我们都在那里。
上述两个例句中的宾语从句谓语 would win 和 should(would)be 分别与其主句谓语 were sure 和 didn't expect 相对应。
三、过去将来时的一些其它表达形式:
1.was/were+going to+动词原形
He said he was going to try.
他说他准备试试。
2.was/were+to+动词原形
They said the railway was to be opened to traffic on May Day.
他们说这条铁路将在五一节通车。
3.was/were about+动词原形
We were about to go out when it began to rain.
我们正要出去天(突然)下起雨来。
4.过去进行时(一般多为动作概念较强的动词,如 go,come, leave,start, open,begin 等)也可用于表示将来。
I didn't know when they were coming again.
我不知道他们什么时候再来。
四、用法注意点:
1.在时间和条件状语从句中,常用一般过去时来表示过去将来时。例如:
He said he would come to see you when he had time.
他说他有时间就来看望你。
2.“would+动词原形”可表示过去习惯性的动作。此时,不管什么人称,都可用would。
When he was a child he would get up early.
他年幼时,总是很早起床。
考例精练:
1.We were all surprised when he made it clear that he ____ office soon.
A.leaves B.would leave C.left D.had left
2.— Alice, why didn't you come yesterday?
— I ____ ,but I had an unexpected visitor.
A.had B.would C.was going to D.did
1. The old man _____ two days after he had been sent to hospital.
A. died B. would die C. had died D. has died
2. Old McDonald gave up smoking for a while, but soon ______ to his old ways.
A. returned B. returns C. was returning D. had returned
3. I _____ my son _____ a doctor, but he wasn’t good enough at science.
A. hoped; would become B. had hoped; would become
C. had hoped; will become D. hope; will become
4. I _____ to take a good holiday this year, but I wasn’t able to get away.
A. hope B. have hoped C. had hoped D. hoped
5. Helen _____ her key in the office so she had to wait until her husband _____ home.
A. has left; comes B. left; had come
C. had left; came D. had left; would come
The Present Continuous Tense(现在进行时)
用法:
说话时或现阶段正在进行的动作。
构成:
am(is,are) +
动词的现在分词
常用时间状语:
now
例句:
Kate’s parents are working in Canada now.
Look, the child is playing in the street.
备注:
将要发生的动作。
come,go等动词的现在进行时形式可表示
一般在动词原形后+ing
以不发音的e结尾的,去e,+ing
重读闭音节以一个辅音字母结尾的,双写这一字母+ing
动词-ing形式的构成:
writing
taking
getting
running
swimming
going
go
ask
write
take
get
run
swim
asking
The twins ___________(wash) the clothes now.
Look! He ________ (play) basketball over there.
Listen! ______ Sally _______(sing)
are washing
is playing
Is
singing
The Past Continuous Tense(过去进行时)
用法:
过去某一阶段或某一时刻正在进行的动作。
构成:
was(were) +
动词的现在分词
常用时间状语:
at four yesterday afternoon,
at this time yesterday,
表示过去时间的状语从句…
例句:
He was mending his bike at ten o’clock yesterday.
The twins were sweeping the floor when the teacher came
in.
Past Progressive
表示过去正在发生的动作
结构: be (was,were) + doing
标志语:at 8:00 yesterday 、
when、 while、…
1.现在完成时的构成:助动词have (has) + 动词的过去分词
注:has 用于第三人称单数,have 用于其他所有人称。
2.现在完成时的用法:
(1)现在完成时表示过去发生或已经完成的某一动作对现在造成的影响或结果。通常与表示包括现在在内的时间副词just,already, before, yet, never, ever等状语连用。例如:
① I have never heard of that before.
② Have you ever ridden a horse
③ She has already finished the work.
④ Have you milked the cow yet Yes, I have done that already.
⑤ I’ve just lost my science book.
有时没有时间状语;多是一般疑问句。
The Present Perfect Tense(现在完成时)
(2)现在完成时表示过去已经开始,持续到现在,也许还会持续下去的动作或状态。可以和表示从过去某一时刻延续到现在(包括现在在内)的一段时间的状语连用。 如:for和since,以及 so far, now, today, this week(month, year) 等。
① I haven’t seen her these days.
② She has learnt English for 3 years.
③ They have lived here since 1990.
④ What has happened to the USA in the last 350 years
注意:表示短暂时间动作的词,如come, go, die, marry, buy等的完成时不能与for, since等表示一段时间的短语连用。
(3)现在完成时还可以用在时间和条件状语从句中,表示将来某时完成的动作,例如:
I’ll go to your home when I have finished my homework.
If it has stopped snowing in the morning, we’ll go to the park.
(4) have been (to)和have gone (to)的区别:
★have / has been (to) 表示“曾经去过”某地,说话时此人很可能不在那里,已经回来。侧重指经历。
★have / has gone (to) 表示某人“已经去了”某地,说话时此人在那里,或可能在路上,反正不在这里。
试比较:
He has been to Beijing. 他曾去过北京。
(人已回来,可能在这儿)
He has gone to Beijing. 他已经去了北京。
(人已走,不在这儿)。
get
go
eat
are
do
cut
say
got gotten
went gone
ate eaten
cut cut
were been
did done
said said
take
swim
drink
have
come
put
see
took taken
swam swum
drank drunk
put put
had had
came come
saw seen
The twins ___________(wash) the clothes for an hour.
He ________ (play) basketball since three years ago.
How long _____ Sally ______(sing) yet
have washed
has played
has
sung
1、概念:表示过去的过去。
-----------|----------------|--------------------|---->
那时以前 那时 现在
其结构是:had + 过去分词
2、过去完成时的用法:
(1)过去完成时表示过去某一时刻或者某一动作之前完成的动作或状态;句中常用by, before, until, when等词引导的时间状语。
By the end of last year we had built five new houses.
I had learnt 5000 words before I entered the university.
(2)过去完成时的动词还可以表示过去某一时刻之前发生的动作或者状态持续到过去某个时间或者持续下去。
Before he slept, he had worked for 12 hours.
The Past Perfect Tense(过去完成时)
(3)在told, said, knew, heard, thought等动词后的宾语从句。
She said (that) she had never been to Paris.
(4)在过去不同时间发生的两个动作中,发生在先,用过去完成时;发生在后,用一般过去时。
When the police arrived, the thieves had run away.
(5)表示意向的动词,如hope, wish, expect, think, intend, mean, suppose等,用过去完成时表示"原本…,未能…"
We had hoped that you would come, but you didn't.
(6)过去完成时的时间状语before, by, until , when, after, once, as soon as。
He said that he had learned some English before.
By the time he was twelve, Edison had began to make a living by himself.
Tom was disappointed that most of the guests had left when he arrived at the party.
时态的区别
一般时态与进行时态的区别
We ________ (read) newspapers every day.
She ______ now ________ (read) the newspaper.
He _______ (sing) well.
He _________ (sing) a revolutionary song(革命歌曲).
read
is
reading
sings
is singing
1)一般时态通常表示经常的动作或状态,而进行时态则表示在某一时刻或某段时间正在进行着的动作;
2)一般时态表示主语的固有特征、能力等,而进行时态则表示主语在某一时刻或某段时间内所进行的具体动作。
一般过去时与过去进行时的区别
She ________ (write) a letter to her friend yesterday.
She __________ (write) a letter to her friend at nine o’clock yesterday evening.
She __________ (write) a letter to her friend when her mother ________ (come) home yesterday evening.
wrote
was writing
was writing
came
一般过去时通常表示过去发生的一个单纯的事实,而过去进行时则表示在过去某一时刻或某段时间正在进行的动作。
一般过去时与现在完成时之比较
1)过去时表示过去某时发生的动作或单纯叙述过去的事情,强调动作;现在完成时为过去发生的,强调过去的事情对现在的影响,强调的是影响。
2)过去时常与具体的时间状语连用,而现在完成时通常与模糊的时间状语连用,或无时间状语。
◎ 一般过去时的时间状语有:yesterday, last week,…ago, in1980, in October, just now, 具体的时间状语。
◎ 共同的时间状语有:this morning, tonight, this April, now, once,before, already, recently,lately等。
◎ 现在完成时的时间状语有:for, since, so far, ever, never, just, yet, till / until, up to now, in past years, always, 等不确定的时间状语。
现在完成时与一般过去时的区别
I __________ (lose) my pen. Can I borrow yours
She ______ (lose) her pen yesterday.
2) My sister _________ (see) the film twice.
She ______ (see) the film last week.
A: ______ you ______ (have) your lunch
B: Yes, I ________.
A: When _______ you ________ (have) it
B: I ______ (have) it an hour ago.
have lost
lost
has seen
saw
Have
had
have
did
have
had
现在完成时和一般过去时都表示在过去完成的动作,但现在完成时强调这一动作与现在的关系,如对现在的结果、影响等,而一般过去时则表示动作发生在过去,不一定表示和现在的关系。
过去完成时与一般过去时的区别
1) Deming _________(go) to bed at 9:00 last night. His mother ______(come) back at 10:00.
Deming _________(go) to bed before his mother ______(come) back.
2) Uncle Li _______(miss) the train yesterday, because the train _______(leave) when he _______(get) to the station.
过去完成时和一般过去时都表示在过去完成的动作,但过去完成时强调这一动作到过去某一时间或动作之前已经完成的动作(即强调过去的过去),对过去有影响。
went
came
had gone
came
missed
had left
got
用一般过去时代替完成时
1) 两个动作如按顺序发生,又不强调先后,或用then,and,but 等连词时,多用一般过去时。
When she saw the mouse,she screamed.
My aunt gave me a hat and I lost it.
2) 两个动作相继发生,可用一般过去时;如第一个动作需要若干时间完成,用过去完成时。
When I heard the news, I was very excited.
3) 叙述历史事实,可不用过去完成时,而只用一般过去时。
Our teacher told us that Columbus discovered America in 1492.
延续动词与瞬间动词
1) 用于完成时的区别:
延续动词表示经验、经历; 瞬间动词表示行为的结果,不能与表示段的时间状语连用。
He has completed the work.
他已完成了那项工作。 (表结果)
I've known him since then.
我从那时起就认识他了。(表经历)
2) 用于till / until 从句的差异:
延续动词用于肯定句,表示“做……直到……” ;瞬间动词用于否定句,表示“到……,才……”。
He didn't come back until ten o'clock.
他到10 点才回来。
He slept until ten o'clock.
他一直睡到10点。
典型例题:
1. You don't need to describe her. I ___ her several times.
A. had met B. have met C. met D. meet
答案B ;首先本题后句强调对现在的影响,我知道她的模样,你不用描述。再次,several times告知为反复发生的动作,因此用现在完成时。
2. --- I'm sorry to keep you waiting.
--- Oh, not at all. I ___ here only a few minutes.
A. have been B. had been C. was D. will be
答案A ; 等待的动作由过去开始,持续到现在,应用现在完成时。
Tom’s uncle ______ as a chemistry teacher in a school.
He ____________ there since Tom was born.
He ________ there more than thirty years ago.
He ____________ in the science lab when Tom called last night.
He said he ___________ in the lab for two hours.
Now he _______________ in the lab.
He said he ___________ there for three more years.
He ___________even harder in the coming three years.
works
has worked
worked
was working
had worked
is still working
would work
will work
_____________________
____________________________
__________________
__________
_____
______________
_____
_____
__________________
_____________________
______
Betty _____________ TV this time last night.
The Shutes usually ______ supper at 6:30.
Mrs Green __________ back in half an hour.
The boys ____________ football on the playground now.
Mr White ___________ to him several times already.
Lucy ______ the classroom twenty minutes ago.
The little girl ___________ 300 English words by the end of last month.
was watching
have
will come
are playing
has talked
left
had learned
_____________________
_________
_________________
_____
________
_____________________
___
_______________________
练习
1、Her father ______ (know) Beijing very well because he
________ (be) there many times. Now he ________ (tell) the boys something about the Great Wall.
2、Our maths teacher isn’t here now. She ________ (go) to the
library. She __________ (return) in fifteen minutes.
3、The students ___________ (pick) apples on the farm when it
suddenly _______ (begin) to rain yesterday.
4、Lin Tao often ________ (go) back to his home town. He _______
(be) there many times.
5、______ you ______ (go) for a picnic with us tomorrow I ______
(go) if it ______ not ______ (rain) tomorrow. If it ______ (rain), I ___________ (stay) at home instead.
knows
————
has been
——
is telling
has gone
———————
will return
——
were picking
————
began
____
goes
________
has been
————
Will
go
will go
does
rain
_
rains
will stay
练习
6、I can’t find my dictionary. ______ you ______(see) it anywhere
7、A: Look at my book. It ____ (be) very interesting.
B: Where ____ you _____ (buy) it
A: I ________ (buy) it at the bookshop near our school.
B: ____ you often _____ (buy) new books at the bookshop .
A: Not very often.I usually _______ (borrow) books from our
school library.
B: ______ you ______ (go) to the library tomorrow
A: Oh, I _______ not _____ (go) because I ______ just _______
(borrow) some books from the library.
8、I ___________ (listen) to the music when someone __________
(knock) at the door half an hour ago.
Have
seen
is
did
buy
bought
——
Do
buy
_____
borrow
—————
Will
go
will
go
have
__
borrowed
was listening
knocked
练习
9、The gate keeper doesn’t let him in because he ________ (lose)
his ticket.
10、_____ you ______ (like) science books
Yes, I _____ just _______ (buy) some. Look, they _____(be)
all interesting.
11、 ______ the foreign friends _______ (arrive) yet
Yes, they ______. They _______ (arrive) fifteen minutes ago.
has lost
DO
like
have
bought
——
are
——
Have
arrived
have
————————
arrived
Homework: 1) Go over the six tenses.
2) Finish P.5-8
练习
1、
2、
3、
4、
5、
6、
7、
8、
were、
doing
are、
staying、
am doing、
have、
finished、
didn’t do、
did、
didn’t、
did、
do、
was、
took、
got、
was、
was、
will、
take、
will finish
Have、
been、
haven’t、
will go
will buy、
has lost
Did、
see、
was playing、
saw、
Does、
play、
does、
plays、
goes
has turned
have waited、
hasn’t come
Have、
drawn、
have、
drew
时态
中考语法专项复习
Tenses(时态)
1、The Present Simple Tense (一般现在时)
2、 The Past Simple Tense (一般过去时)
3、 The Future Tense (一般将来时)
5、 The Present Continuous Tense (现在进行时)
6、 The Past Continuous Tense (过去进行时)
7、The Present Perfect Tense (现在完成时)
8、The Past Perfect Tense (过去完成时)
4、 The Future in the Past (过去将来时)
八种时态的用法和构成
The Present Simple Tense(一般现在时)
用法:
1、现阶段经常性、习惯性动作;
2、目前的状态;
3、客观真理。
构成:
主语是第三人称单数时,作谓语的行为动词要加词尾
-s(-es),
其他人称和数用动词原形。
常用时间状语:
often,
always,
sometimes,
every day,
on Sunday…
例句:
Jack often goes to school by bike.
Guangzhou is 2313 kilometres away from Beijing.
We have five lessons in the morning.
The twins ___________(wash) the clothes every day.
Sometimes he ________ (play) basketball over there.
How often ____ Sally ______(sing)
wash
plays
does
sing
The Past Simple Tense(一般过去时)
用法:
1、过去发生的动作;
2、过去存在的状态。
构成:
用动词的过去式。
常用时间状语:
yesterday,
two days ago,
last week,
in 1990…
例句:
He went to work by bus yesterday.
Han Meimei was in the classroom a moment ago.
动词-ed形式的构成:
在动词后加-ed
以字母e 结尾的动词,只+d
“ 辅音字母+y ” ,变y 为i, 再+ed
重读闭音节以一个辅音字母结尾的,双写+ed
want
answer
move
die
carry
cry
stop
plan
wanted
moved
died
carried
cried
stopped
planned
answered
got
drank
took
went
swam
ate
cut
were
had
did
came
said
saw
put
get take
go swim
eat drink
are have
do come
cut put
say see
The twins ___________(wash) the clothes yesterday.
The day before yesterday he ________ (play) basketball over there.
_____ Sally ______(sing) two hours ago
washed
played
Did
sing
The Future Tense(一般将来时)
用法:
1、将来发生的动作;
2、将来存在的状态。
构成:
1、助动词
will(shall) +
动词原形;
2、am(is,are) + going to
常用时间状语:
tomorrow,
next week,
in two hours…
例句:
They will (are going to) meet outside the school gate tomorrow afternoon.
The people will not be pleased if you jump the queue.
备注:
一般现在时代替将来时。
在时间状语从句和条件状语从句中用
Future Simple
表示将要发生的动作
结构: will do、 shall do、
be (is、am、are) going to do
标志语:tomorrow、in..、next…
The Future in the Past(过去将来时)
用法:
从过去某一时间来看将来要发生的动作或存在的状态
构成:
1、助动词
would +
动词原形;
2、was,were + going to
常用时间状语:
(the) next day,
(the) next year,
that afternoon…
例句:
Linda said that she would (was going to) visit her uncle next Saturday.
He wanted to know if they would go to the mountain village that afternoon.
备注:
常用于宾语从句中
时间
现在
过去
那时所预见的情况
一般过去将来时
一、基本概念:
过去将来时表示从过去的某一时间看将要发生的动作或存在的状态。它是一个相对的时态,即立足于过去某时,从过去的某一时间看即将发生的事情就要用这一时态。
1) He said his mother would buy a bike for him
2) My brother told me he wouldn’t believe Jack any more.
3) Would it be all right if he knew his illness
二、基本形式:
would/should+动词原形
(其中 would 用于各种人称, should 常用于第一人称)。
例如:
They were sure they would win the final victory.
他们坚信会赢得最后胜利。
He didn't expect that we should(would)all be there.
他没想到我们都在那里。
上述两个例句中的宾语从句谓语 would win 和 should(would)be 分别与其主句谓语 were sure 和 didn't expect 相对应。
三、过去将来时的一些其它表达形式:
1.was/were+going to+动词原形
He said he was going to try.
他说他准备试试。
2.was/were+to+动词原形
They said the railway was to be opened to traffic on May Day.
他们说这条铁路将在五一节通车。
3.was/were about+动词原形
We were about to go out when it began to rain.
我们正要出去天(突然)下起雨来。
4.过去进行时(一般多为动作概念较强的动词,如 go,come, leave,start, open,begin 等)也可用于表示将来。
I didn't know when they were coming again.
我不知道他们什么时候再来。
四、用法注意点:
1.在时间和条件状语从句中,常用一般过去时来表示过去将来时。例如:
He said he would come to see you when he had time.
他说他有时间就来看望你。
2.“would+动词原形”可表示过去习惯性的动作。此时,不管什么人称,都可用would。
When he was a child he would get up early.
他年幼时,总是很早起床。
考例精练:
1.We were all surprised when he made it clear that he ____ office soon.
A.leaves B.would leave C.left D.had left
2.— Alice, why didn't you come yesterday?
— I ____ ,but I had an unexpected visitor.
A.had B.would C.was going to D.did
1. The old man _____ two days after he had been sent to hospital.
A. died B. would die C. had died D. has died
2. Old McDonald gave up smoking for a while, but soon ______ to his old ways.
A. returned B. returns C. was returning D. had returned
3. I _____ my son _____ a doctor, but he wasn’t good enough at science.
A. hoped; would become B. had hoped; would become
C. had hoped; will become D. hope; will become
4. I _____ to take a good holiday this year, but I wasn’t able to get away.
A. hope B. have hoped C. had hoped D. hoped
5. Helen _____ her key in the office so she had to wait until her husband _____ home.
A. has left; comes B. left; had come
C. had left; came D. had left; would come
The Present Continuous Tense(现在进行时)
用法:
说话时或现阶段正在进行的动作。
构成:
am(is,are) +
动词的现在分词
常用时间状语:
now
例句:
Kate’s parents are working in Canada now.
Look, the child is playing in the street.
备注:
将要发生的动作。
come,go等动词的现在进行时形式可表示
一般在动词原形后+ing
以不发音的e结尾的,去e,+ing
重读闭音节以一个辅音字母结尾的,双写这一字母+ing
动词-ing形式的构成:
writing
taking
getting
running
swimming
going
go
ask
write
take
get
run
swim
asking
The twins ___________(wash) the clothes now.
Look! He ________ (play) basketball over there.
Listen! ______ Sally _______(sing)
are washing
is playing
Is
singing
The Past Continuous Tense(过去进行时)
用法:
过去某一阶段或某一时刻正在进行的动作。
构成:
was(were) +
动词的现在分词
常用时间状语:
at four yesterday afternoon,
at this time yesterday,
表示过去时间的状语从句…
例句:
He was mending his bike at ten o’clock yesterday.
The twins were sweeping the floor when the teacher came
in.
Past Progressive
表示过去正在发生的动作
结构: be (was,were) + doing
标志语:at 8:00 yesterday 、
when、 while、…
1.现在完成时的构成:助动词have (has) + 动词的过去分词
注:has 用于第三人称单数,have 用于其他所有人称。
2.现在完成时的用法:
(1)现在完成时表示过去发生或已经完成的某一动作对现在造成的影响或结果。通常与表示包括现在在内的时间副词just,already, before, yet, never, ever等状语连用。例如:
① I have never heard of that before.
② Have you ever ridden a horse
③ She has already finished the work.
④ Have you milked the cow yet Yes, I have done that already.
⑤ I’ve just lost my science book.
有时没有时间状语;多是一般疑问句。
The Present Perfect Tense(现在完成时)
(2)现在完成时表示过去已经开始,持续到现在,也许还会持续下去的动作或状态。可以和表示从过去某一时刻延续到现在(包括现在在内)的一段时间的状语连用。 如:for和since,以及 so far, now, today, this week(month, year) 等。
① I haven’t seen her these days.
② She has learnt English for 3 years.
③ They have lived here since 1990.
④ What has happened to the USA in the last 350 years
注意:表示短暂时间动作的词,如come, go, die, marry, buy等的完成时不能与for, since等表示一段时间的短语连用。
(3)现在完成时还可以用在时间和条件状语从句中,表示将来某时完成的动作,例如:
I’ll go to your home when I have finished my homework.
If it has stopped snowing in the morning, we’ll go to the park.
(4) have been (to)和have gone (to)的区别:
★have / has been (to) 表示“曾经去过”某地,说话时此人很可能不在那里,已经回来。侧重指经历。
★have / has gone (to) 表示某人“已经去了”某地,说话时此人在那里,或可能在路上,反正不在这里。
试比较:
He has been to Beijing. 他曾去过北京。
(人已回来,可能在这儿)
He has gone to Beijing. 他已经去了北京。
(人已走,不在这儿)。
get
go
eat
are
do
cut
say
got gotten
went gone
ate eaten
cut cut
were been
did done
said said
take
swim
drink
have
come
put
see
took taken
swam swum
drank drunk
put put
had had
came come
saw seen
The twins ___________(wash) the clothes for an hour.
He ________ (play) basketball since three years ago.
How long _____ Sally ______(sing) yet
have washed
has played
has
sung
1、概念:表示过去的过去。
-----------|----------------|--------------------|---->
那时以前 那时 现在
其结构是:had + 过去分词
2、过去完成时的用法:
(1)过去完成时表示过去某一时刻或者某一动作之前完成的动作或状态;句中常用by, before, until, when等词引导的时间状语。
By the end of last year we had built five new houses.
I had learnt 5000 words before I entered the university.
(2)过去完成时的动词还可以表示过去某一时刻之前发生的动作或者状态持续到过去某个时间或者持续下去。
Before he slept, he had worked for 12 hours.
The Past Perfect Tense(过去完成时)
(3)在told, said, knew, heard, thought等动词后的宾语从句。
She said (that) she had never been to Paris.
(4)在过去不同时间发生的两个动作中,发生在先,用过去完成时;发生在后,用一般过去时。
When the police arrived, the thieves had run away.
(5)表示意向的动词,如hope, wish, expect, think, intend, mean, suppose等,用过去完成时表示"原本…,未能…"
We had hoped that you would come, but you didn't.
(6)过去完成时的时间状语before, by, until , when, after, once, as soon as。
He said that he had learned some English before.
By the time he was twelve, Edison had began to make a living by himself.
Tom was disappointed that most of the guests had left when he arrived at the party.
时态的区别
一般时态与进行时态的区别
We ________ (read) newspapers every day.
She ______ now ________ (read) the newspaper.
He _______ (sing) well.
He _________ (sing) a revolutionary song(革命歌曲).
read
is
reading
sings
is singing
1)一般时态通常表示经常的动作或状态,而进行时态则表示在某一时刻或某段时间正在进行着的动作;
2)一般时态表示主语的固有特征、能力等,而进行时态则表示主语在某一时刻或某段时间内所进行的具体动作。
一般过去时与过去进行时的区别
She ________ (write) a letter to her friend yesterday.
She __________ (write) a letter to her friend at nine o’clock yesterday evening.
She __________ (write) a letter to her friend when her mother ________ (come) home yesterday evening.
wrote
was writing
was writing
came
一般过去时通常表示过去发生的一个单纯的事实,而过去进行时则表示在过去某一时刻或某段时间正在进行的动作。
一般过去时与现在完成时之比较
1)过去时表示过去某时发生的动作或单纯叙述过去的事情,强调动作;现在完成时为过去发生的,强调过去的事情对现在的影响,强调的是影响。
2)过去时常与具体的时间状语连用,而现在完成时通常与模糊的时间状语连用,或无时间状语。
◎ 一般过去时的时间状语有:yesterday, last week,…ago, in1980, in October, just now, 具体的时间状语。
◎ 共同的时间状语有:this morning, tonight, this April, now, once,before, already, recently,lately等。
◎ 现在完成时的时间状语有:for, since, so far, ever, never, just, yet, till / until, up to now, in past years, always, 等不确定的时间状语。
现在完成时与一般过去时的区别
I __________ (lose) my pen. Can I borrow yours
She ______ (lose) her pen yesterday.
2) My sister _________ (see) the film twice.
She ______ (see) the film last week.
A: ______ you ______ (have) your lunch
B: Yes, I ________.
A: When _______ you ________ (have) it
B: I ______ (have) it an hour ago.
have lost
lost
has seen
saw
Have
had
have
did
have
had
现在完成时和一般过去时都表示在过去完成的动作,但现在完成时强调这一动作与现在的关系,如对现在的结果、影响等,而一般过去时则表示动作发生在过去,不一定表示和现在的关系。
过去完成时与一般过去时的区别
1) Deming _________(go) to bed at 9:00 last night. His mother ______(come) back at 10:00.
Deming _________(go) to bed before his mother ______(come) back.
2) Uncle Li _______(miss) the train yesterday, because the train _______(leave) when he _______(get) to the station.
过去完成时和一般过去时都表示在过去完成的动作,但过去完成时强调这一动作到过去某一时间或动作之前已经完成的动作(即强调过去的过去),对过去有影响。
went
came
had gone
came
missed
had left
got
用一般过去时代替完成时
1) 两个动作如按顺序发生,又不强调先后,或用then,and,but 等连词时,多用一般过去时。
When she saw the mouse,she screamed.
My aunt gave me a hat and I lost it.
2) 两个动作相继发生,可用一般过去时;如第一个动作需要若干时间完成,用过去完成时。
When I heard the news, I was very excited.
3) 叙述历史事实,可不用过去完成时,而只用一般过去时。
Our teacher told us that Columbus discovered America in 1492.
延续动词与瞬间动词
1) 用于完成时的区别:
延续动词表示经验、经历; 瞬间动词表示行为的结果,不能与表示段的时间状语连用。
He has completed the work.
他已完成了那项工作。 (表结果)
I've known him since then.
我从那时起就认识他了。(表经历)
2) 用于till / until 从句的差异:
延续动词用于肯定句,表示“做……直到……” ;瞬间动词用于否定句,表示“到……,才……”。
He didn't come back until ten o'clock.
他到10 点才回来。
He slept until ten o'clock.
他一直睡到10点。
典型例题:
1. You don't need to describe her. I ___ her several times.
A. had met B. have met C. met D. meet
答案B ;首先本题后句强调对现在的影响,我知道她的模样,你不用描述。再次,several times告知为反复发生的动作,因此用现在完成时。
2. --- I'm sorry to keep you waiting.
--- Oh, not at all. I ___ here only a few minutes.
A. have been B. had been C. was D. will be
答案A ; 等待的动作由过去开始,持续到现在,应用现在完成时。
Tom’s uncle ______ as a chemistry teacher in a school.
He ____________ there since Tom was born.
He ________ there more than thirty years ago.
He ____________ in the science lab when Tom called last night.
He said he ___________ in the lab for two hours.
Now he _______________ in the lab.
He said he ___________ there for three more years.
He ___________even harder in the coming three years.
works
has worked
worked
was working
had worked
is still working
would work
will work
_____________________
____________________________
__________________
__________
_____
______________
_____
_____
__________________
_____________________
______
Betty _____________ TV this time last night.
The Shutes usually ______ supper at 6:30.
Mrs Green __________ back in half an hour.
The boys ____________ football on the playground now.
Mr White ___________ to him several times already.
Lucy ______ the classroom twenty minutes ago.
The little girl ___________ 300 English words by the end of last month.
was watching
have
will come
are playing
has talked
left
had learned
_____________________
_________
_________________
_____
________
_____________________
___
_______________________
练习
1、Her father ______ (know) Beijing very well because he
________ (be) there many times. Now he ________ (tell) the boys something about the Great Wall.
2、Our maths teacher isn’t here now. She ________ (go) to the
library. She __________ (return) in fifteen minutes.
3、The students ___________ (pick) apples on the farm when it
suddenly _______ (begin) to rain yesterday.
4、Lin Tao often ________ (go) back to his home town. He _______
(be) there many times.
5、______ you ______ (go) for a picnic with us tomorrow I ______
(go) if it ______ not ______ (rain) tomorrow. If it ______ (rain), I ___________ (stay) at home instead.
knows
————
has been
——
is telling
has gone
———————
will return
——
were picking
————
began
____
goes
________
has been
————
Will
go
will go
does
rain
_
rains
will stay
练习
6、I can’t find my dictionary. ______ you ______(see) it anywhere
7、A: Look at my book. It ____ (be) very interesting.
B: Where ____ you _____ (buy) it
A: I ________ (buy) it at the bookshop near our school.
B: ____ you often _____ (buy) new books at the bookshop .
A: Not very often.I usually _______ (borrow) books from our
school library.
B: ______ you ______ (go) to the library tomorrow
A: Oh, I _______ not _____ (go) because I ______ just _______
(borrow) some books from the library.
8、I ___________ (listen) to the music when someone __________
(knock) at the door half an hour ago.
Have
seen
is
did
buy
bought
——
Do
buy
_____
borrow
—————
Will
go
will
go
have
__
borrowed
was listening
knocked
练习
9、The gate keeper doesn’t let him in because he ________ (lose)
his ticket.
10、_____ you ______ (like) science books
Yes, I _____ just _______ (buy) some. Look, they _____(be)
all interesting.
11、 ______ the foreign friends _______ (arrive) yet
Yes, they ______. They _______ (arrive) fifteen minutes ago.
has lost
DO
like
have
bought
——
are
——
Have
arrived
have
————————
arrived
Homework: 1) Go over the six tenses.
2) Finish P.5-8
练习
1、
2、
3、
4、
5、
6、
7、
8、
were、
doing
are、
staying、
am doing、
have、
finished、
didn’t do、
did、
didn’t、
did、
do、
was、
took、
got、
was、
was、
will、
take、
will finish
Have、
been、
haven’t、
will go
will buy、
has lost
Did、
see、
was playing、
saw、
Does、
play、
does、
plays、
goes
has turned
have waited、
hasn’t come
Have、
drawn、
have、
drew
同课章节目录
- 词法
- 名词
- 动词和动词短语
- 动词语态
- 动词时态
- 助动词和情态动词
- 非谓语动词
- 冠词
- 代词
- 数词和量词
- 形容词副词及其比较等级
- 介词和介词短语
- 连词和感叹词
- 构词法
- 相似、相近词比较
- 句法
- 陈述句
- 一般疑问句和否定疑问句
- 特殊疑问句及选择疑问句
- 反意疑问句
- 存在句(There be句型)
- 宾语从句
- 定语从句
- 状语从句
- 主谓一致问题
- 简单句
- 并列句
- 复合句
- 主谓一致
- 主、表语从句
- 名词性从句
- 直接引语和间接引语
- 虚拟语气
- 感叹句
- 强调句
- 倒装句
- 祈使句
- 句子的成分
- 句子的分类
- 题型专区
- 单项选择部分
- 易错题
- 完形填空
- 阅读理解
- 词汇练习
- 听说训练
- 句型转换
- 补全对话
- 短文改错
- 翻译
- 书面表达
- 任务型阅读
- 语法填空
- 其他资料
