2021-2022学年初升高英语衔接课动词和动词语态 课件(共24张PPT)
文档属性
| 名称 | 2021-2022学年初升高英语衔接课动词和动词语态 课件(共24张PPT) |

|
|
| 格式 | pptx | ||
| 文件大小 | 135.6KB | ||
| 资源类型 | 试卷 | ||
| 版本资源 | 通用版 | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2021-08-10 00:00:00 | ||
图片预览






文档简介
(共24张PPT)
相约“动词和动词时态”
动词
考 点 概 览 考 查 角 度 考 查 频 次
动词分类 动词的分类及用法; 常见动词短语的用法 ★★★★
动词的时态 一般现在时、一般过去时、一般将来时、现在进行时、过去进行时及现在完成时六种时态 ★★★★
分类 定 义 例 词 实 义 动 词 实义动词是指具有完整意义、可以单独作谓语的动词, 主要表示主语的动作、状态和品质。根据能否带宾语, 又分为及物动词和不及物动词 及物 动词 borrow, enjoy, put, forget, worry, love, guess, use
不及 物动 词 arrive, come, go, run, walk, cry, swim, fall, happen
连 系 动 词 连接主语和表示主语身份、性质、状态的动词称为连系动词 be, seem, look, become, get, grow, feel, appear, turn 分类 定 义 例 词
助 动 词 本身没有词义, 不能单独作谓语, 只能和别的动词一起构成谓语动词, 表示时态、语态、语气等特征。帮助构成否定、疑问、强调、省略等。有人称和数的变化 do (does, did, done), have (has, had), shall, will
情 态 动 词 情态动词表示能力、义务、必要、猜测等, 表示说话人的语气或情态。情态动词只能和动词原形一起构成谓语动词, 没有人称和数的变化 can, could, may, might, must, need, shall, should, will, would
动词的基本形式
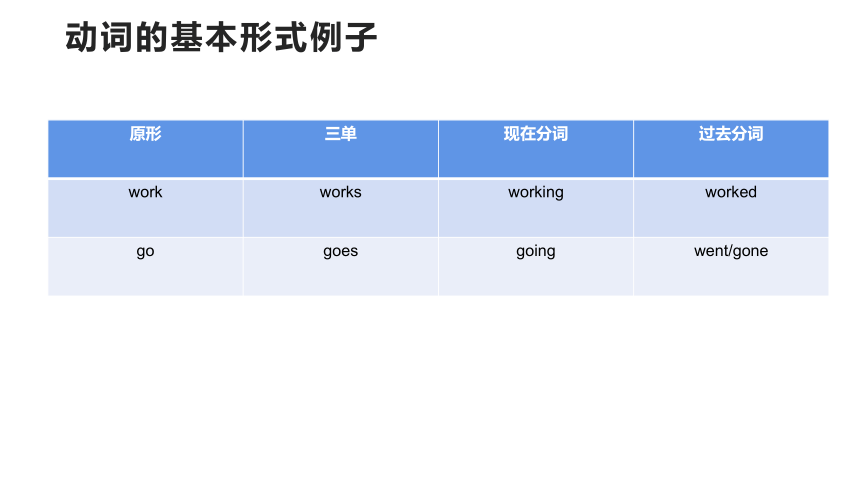
动词的基本形式例子
原形 三单 现在分词 过去分词
work works working worked
go goes going went/gone
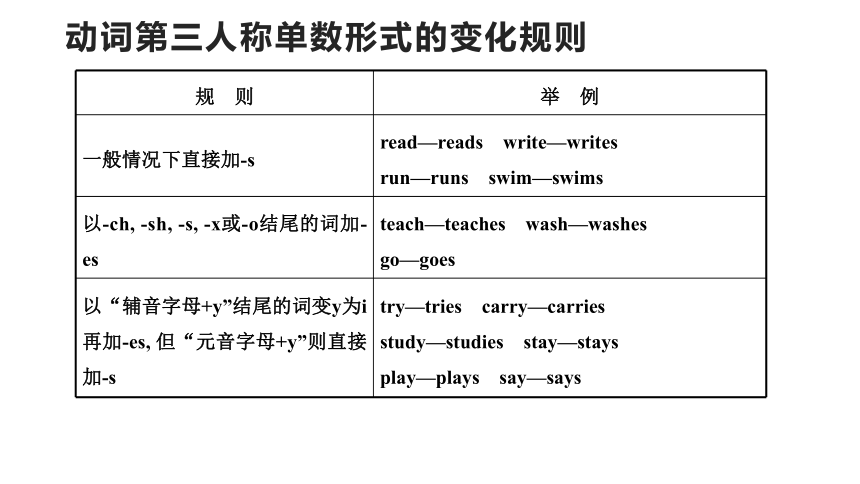
动词第三人称单数形式的变化规则
规 则 举 例
一般情况下直接加-s read—reads write—writes
run—runs swim—swims
以-ch, -sh, -s, -x或-o结尾的词加-es teach—teaches wash—washes
go—goes
以“辅音字母+y”结尾的词变y为i再加-es, 但“元音字母+y”则直接加-s try—tries carry—carries
study—studies stay—stays
play—plays say—says
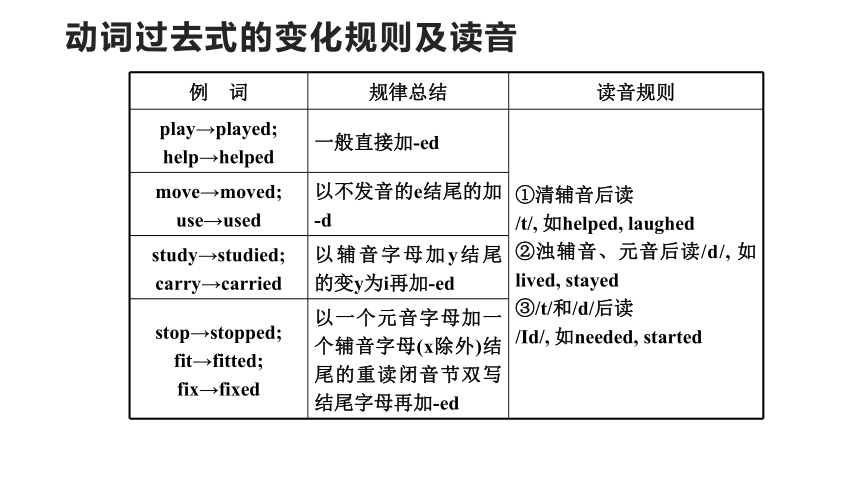
动词过去式的变化规则及读音
例 词 规律总结 读音规则
play→played; help→helped 一般直接加-ed ①清辅音后读
/t/, 如helped, laughed
②浊辅音、元音后读/d/, 如lived, stayed
③/t/和/d/后读
/Id/, 如needed, started
move→moved; use→used 以不发音的e结尾的加-d study→studied; carry→carried 以辅音字母加y结尾的变y为i再加-ed stop→stopped; fit→fitted; fix→fixed 以一个元音字母加一个辅音字母(x除外)结尾的重读闭音节双写结尾字母再加-ed 现在分词的变化规律
规律总结 例 词
以不发音的e结尾的动词去e再加-ing make→making
have→having
以一个单独发音的元音字母+一个辅音字母结尾的重读闭音节要双写最后一个辅音字母再加-ing swim→swimming
run→running
以-ie结尾的动词, 变ie为y, 再加-ing lie→lying
tie→tying
不符合上述情况的直接加-ing play→playing
sing→singing
动词的几种时态
1.一般现在时
定义:
1.表示经常性或习惯性的动作或者存在的状态,常与always, often, sometimes, every day等频率副词连用。
I am a teacher.
He usually gets up at five.
2.表示客观真理或自然规律。
The sun rises in the east. 太阳从东边升起。
1. He usually _____ TV on Sunday evening.
A. watch B. watches C. watching D. is watching
2. Nobody ______ how to run this machines.
A. know B. have known
C. knows D. is knowing
3. He _____ to do his lessons at eight every evening.
A. is beginning B. is beginning
C. begin D. begins
B
C
D
2.一般过去时
表示过去某一时间发生的动作或存在的状态。常见的时间状语:yesterday, last year, two days ago, in the past, the other day, this morning, just now, when I was young.
1. Paper _____ (be)first invented in China.
2. You know quite a lot about the show.
Well, Cathy (introduce)it to me during the lunch.
was
introduced
3.一般将来时
用 法 例 句
表示在将来某个时间将要发生的动作或存在的状态。常与tomorrow, soon, later, next time, in+一段时间等连用 I’ll start tomorrow.
我明天动身。
1.tomorrow ,the day after tomorrow,
2. next week/month/year/summer,
3. in the future, in + 时间段,( in two days/weeks)
4. some day(将来某一天)
时间标志词
一般将来时
结构 含义
1. will/ shall do 主观性的,意愿性的将来
2. be going to do 客观性的,计划性的未来
和“天气”相关的将来
3. be to do 1)表示正式的将来,一般用在会议发言等场合;
2)用在if 条件从句的从句部分表示“如果想要”
4. be about to be about to …when….
“……正要……这时……”
5. be doing 表示移动的瞬间动词用在进行时表将来
4.现在进行时:表示正在发生的动作
例 句
Listen! The bird is singing in the tree.
听! 鸟儿正在树上唱歌。
The students were reading .
学生们正在读书。
构成:is/am/are+doing
5.过去进行时:表示过去某一时刻或者某一时间段正在进行或发生的动作
构成:was/were+doing
例 句
The bird was singing in the tree when I saw it yesterday.
当我昨天看到这只鸟的时候,它正在树上唱歌。
The students were reading while the teacher was grading their homework.
学生们在看书, 而老师在批改他们的家庭作业。
5. 现在完成时
(1)现在完成时的构成
have/has+动词的过去分词
have/has为助动词, 无实际意义
(2)现在完成时的用法
用 法 例 句
表示说话之前已经完成了的动作, 而且这个动作对现在仍有影响, 常与already, yet, in the past few yea9rs等时间状语连用 (1)I have seen the film already. 我已经看过这部电影了。(已知电影内容)
(2) I have studied in the school since 2009.
自从2009年我就在这所学校学习。
(3)一般过去时与现在完成时的区别
区 别 例 句
用 法 一般过去时表示过去某时发生的动作或单纯的叙述过去发生的事情, 强调过去, 与具体的表示过去的时间的词连用 Tom lived in Beijing two years ago. 两年前汤姆住在北京。(不知道现在是否还住在北京)
现在完成时的动作虽然是发生在过去, 但是对现在有影响 Tom has lived in Beijing for two years. 汤姆住在北京两年了。(现在汤姆仍然还在北京)
7. 过去完成时
(1) 构成: 主语+had+过去分词
(2)过去完成时的用法:
表示过去某一时间或动作之前已经发生或完成了的动作(即“过去的过去”)。因此使用过去完成时必须以过去某一时间作为前提, 通常用by, before短语或when, before, after, until等引导的从句来表示。例如:
(1)After the sun had set, we decided to return home.
太阳落山以后, 我们决定回家。
(2) She wondered who had left the door open.
她想知道是谁让门开着的。
8. 过去将来时
(1)过去将来时的构成
①would +动词原形
②should +动词原形
③was/were + going to +动词原形
(2)过去将来时的用法
用 法 例 句
表示从过去某一时间看将要发生的动作或存在的状态; 常用的时间状语有two days later, the next week, the following day等 Tom said he would come.
汤姆说他要来的。
Linda said she was going to see her aunt.
琳达说她打算去看她的姑妈。
谓语动词的十大时态汇总
时 态 过去 过去将来 现在 将来
一般
进行
完成
完成进行
1. was, were
2.did
1. would be
2. would do
1. am, is are
2. do/ does
1. will be/ shall be
2. be going to do
3. be to do
4. be about to do
was/ were doing
am/ is/ are+ doing
had done
have/ has done
EXERCISE
1.What is he doing now
-He ______ a picture.
A. draws B. drew C. is drawing D. was drawing
2. Look! An elephant (come) this way.
3.It was Monday morning, and the writing class had just________(begin)
4.I (cook)a meal when you rang me.
5.It really ________ (annoy ) me when people don't behave themselves.
6.It was the first time that I (talk)to my parents face to face.
begun
C
is coming
was cooking
annoys
had talked
相约“动词和动词时态”
动词
考 点 概 览 考 查 角 度 考 查 频 次
动词分类 动词的分类及用法; 常见动词短语的用法 ★★★★
动词的时态 一般现在时、一般过去时、一般将来时、现在进行时、过去进行时及现在完成时六种时态 ★★★★
分类 定 义 例 词 实 义 动 词 实义动词是指具有完整意义、可以单独作谓语的动词, 主要表示主语的动作、状态和品质。根据能否带宾语, 又分为及物动词和不及物动词 及物 动词 borrow, enjoy, put, forget, worry, love, guess, use
不及 物动 词 arrive, come, go, run, walk, cry, swim, fall, happen
连 系 动 词 连接主语和表示主语身份、性质、状态的动词称为连系动词 be, seem, look, become, get, grow, feel, appear, turn 分类 定 义 例 词
助 动 词 本身没有词义, 不能单独作谓语, 只能和别的动词一起构成谓语动词, 表示时态、语态、语气等特征。帮助构成否定、疑问、强调、省略等。有人称和数的变化 do (does, did, done), have (has, had), shall, will
情 态 动 词 情态动词表示能力、义务、必要、猜测等, 表示说话人的语气或情态。情态动词只能和动词原形一起构成谓语动词, 没有人称和数的变化 can, could, may, might, must, need, shall, should, will, would
动词的基本形式
动词的基本形式例子
原形 三单 现在分词 过去分词
work works working worked
go goes going went/gone
动词第三人称单数形式的变化规则
规 则 举 例
一般情况下直接加-s read—reads write—writes
run—runs swim—swims
以-ch, -sh, -s, -x或-o结尾的词加-es teach—teaches wash—washes
go—goes
以“辅音字母+y”结尾的词变y为i再加-es, 但“元音字母+y”则直接加-s try—tries carry—carries
study—studies stay—stays
play—plays say—says
动词过去式的变化规则及读音
例 词 规律总结 读音规则
play→played; help→helped 一般直接加-ed ①清辅音后读
/t/, 如helped, laughed
②浊辅音、元音后读/d/, 如lived, stayed
③/t/和/d/后读
/Id/, 如needed, started
move→moved; use→used 以不发音的e结尾的加-d study→studied; carry→carried 以辅音字母加y结尾的变y为i再加-ed stop→stopped; fit→fitted; fix→fixed 以一个元音字母加一个辅音字母(x除外)结尾的重读闭音节双写结尾字母再加-ed 现在分词的变化规律
规律总结 例 词
以不发音的e结尾的动词去e再加-ing make→making
have→having
以一个单独发音的元音字母+一个辅音字母结尾的重读闭音节要双写最后一个辅音字母再加-ing swim→swimming
run→running
以-ie结尾的动词, 变ie为y, 再加-ing lie→lying
tie→tying
不符合上述情况的直接加-ing play→playing
sing→singing
动词的几种时态
1.一般现在时
定义:
1.表示经常性或习惯性的动作或者存在的状态,常与always, often, sometimes, every day等频率副词连用。
I am a teacher.
He usually gets up at five.
2.表示客观真理或自然规律。
The sun rises in the east. 太阳从东边升起。
1. He usually _____ TV on Sunday evening.
A. watch B. watches C. watching D. is watching
2. Nobody ______ how to run this machines.
A. know B. have known
C. knows D. is knowing
3. He _____ to do his lessons at eight every evening.
A. is beginning B. is beginning
C. begin D. begins
B
C
D
2.一般过去时
表示过去某一时间发生的动作或存在的状态。常见的时间状语:yesterday, last year, two days ago, in the past, the other day, this morning, just now, when I was young.
1. Paper _____ (be)first invented in China.
2. You know quite a lot about the show.
Well, Cathy (introduce)it to me during the lunch.
was
introduced
3.一般将来时
用 法 例 句
表示在将来某个时间将要发生的动作或存在的状态。常与tomorrow, soon, later, next time, in+一段时间等连用 I’ll start tomorrow.
我明天动身。
1.tomorrow ,the day after tomorrow,
2. next week/month/year/summer,
3. in the future, in + 时间段,( in two days/weeks)
4. some day(将来某一天)
时间标志词
一般将来时
结构 含义
1. will/ shall do 主观性的,意愿性的将来
2. be going to do 客观性的,计划性的未来
和“天气”相关的将来
3. be to do 1)表示正式的将来,一般用在会议发言等场合;
2)用在if 条件从句的从句部分表示“如果想要”
4. be about to be about to …when….
“……正要……这时……”
5. be doing 表示移动的瞬间动词用在进行时表将来
4.现在进行时:表示正在发生的动作
例 句
Listen! The bird is singing in the tree.
听! 鸟儿正在树上唱歌。
The students were reading .
学生们正在读书。
构成:is/am/are+doing
5.过去进行时:表示过去某一时刻或者某一时间段正在进行或发生的动作
构成:was/were+doing
例 句
The bird was singing in the tree when I saw it yesterday.
当我昨天看到这只鸟的时候,它正在树上唱歌。
The students were reading while the teacher was grading their homework.
学生们在看书, 而老师在批改他们的家庭作业。
5. 现在完成时
(1)现在完成时的构成
have/has+动词的过去分词
have/has为助动词, 无实际意义
(2)现在完成时的用法
用 法 例 句
表示说话之前已经完成了的动作, 而且这个动作对现在仍有影响, 常与already, yet, in the past few yea9rs等时间状语连用 (1)I have seen the film already. 我已经看过这部电影了。(已知电影内容)
(2) I have studied in the school since 2009.
自从2009年我就在这所学校学习。
(3)一般过去时与现在完成时的区别
区 别 例 句
用 法 一般过去时表示过去某时发生的动作或单纯的叙述过去发生的事情, 强调过去, 与具体的表示过去的时间的词连用 Tom lived in Beijing two years ago. 两年前汤姆住在北京。(不知道现在是否还住在北京)
现在完成时的动作虽然是发生在过去, 但是对现在有影响 Tom has lived in Beijing for two years. 汤姆住在北京两年了。(现在汤姆仍然还在北京)
7. 过去完成时
(1) 构成: 主语+had+过去分词
(2)过去完成时的用法:
表示过去某一时间或动作之前已经发生或完成了的动作(即“过去的过去”)。因此使用过去完成时必须以过去某一时间作为前提, 通常用by, before短语或when, before, after, until等引导的从句来表示。例如:
(1)After the sun had set, we decided to return home.
太阳落山以后, 我们决定回家。
(2) She wondered who had left the door open.
她想知道是谁让门开着的。
8. 过去将来时
(1)过去将来时的构成
①would +动词原形
②should +动词原形
③was/were + going to +动词原形
(2)过去将来时的用法
用 法 例 句
表示从过去某一时间看将要发生的动作或存在的状态; 常用的时间状语有two days later, the next week, the following day等 Tom said he would come.
汤姆说他要来的。
Linda said she was going to see her aunt.
琳达说她打算去看她的姑妈。
谓语动词的十大时态汇总
时 态 过去 过去将来 现在 将来
一般
进行
完成
完成进行
1. was, were
2.did
1. would be
2. would do
1. am, is are
2. do/ does
1. will be/ shall be
2. be going to do
3. be to do
4. be about to do
was/ were doing
am/ is/ are+ doing
had done
have/ has done
EXERCISE
1.What is he doing now
-He ______ a picture.
A. draws B. drew C. is drawing D. was drawing
2. Look! An elephant (come) this way.
3.It was Monday morning, and the writing class had just________(begin)
4.I (cook)a meal when you rang me.
5.It really ________ (annoy ) me when people don't behave themselves.
6.It was the first time that I (talk)to my parents face to face.
begun
C
is coming
was cooking
annoys
had talked
同课章节目录
