选修九Unit 2 Sailing the oceans Reading 课件(26张PPT)
文档属性
| 名称 | 选修九Unit 2 Sailing the oceans Reading 课件(26张PPT) |

|
|
| 格式 | zip | ||
| 文件大小 | 660.5KB | ||
| 资源类型 | 教案 | ||
| 版本资源 | 人教版(新课程标准) | ||
| 科目 | 英语 | ||
| 更新时间 | 2021-08-09 00:00:00 | ||
图片预览





文档简介
(共26张PPT)
Reading
A
compass
consists
of
a
small
magnet
balanced
on
a
point
so
that
it
can
move
round
in
a
circle.
The
magnet
is
generally
called
a
needle
because
it
is
shaped
like
a
needle.
One
end
of
the
needle
is
often
marked
“N”
for
north,
or
coloured
in
some
way
to
indicate
that
it
points
toward
north.
astrolabe
The
astrolabe
measures
the
height
and
position
of
the
sun.
If
you
can
measure
this
accurately,
a
sailor
can
tell
how
many
degrees
the
boat
is
from
the
North
Pole.
From
this
he
can
tell
where
the
boat
is
in
the
ocean.
sextant
The
sextant
is
a
navigational
instrument
for
measuring
the
angle
between
the
horizon
and
some
object
in
the
sky.
First
a
sailor
looks
at
the
horizon
through
an
eyepiece.
At
the
same
time
he
can
see
light
from
the
sun
or
a
star
reflected
off
a
small
mirror
on
top
of
the
instrument,
onto
a
second
mirror
and
into
the
eyepiece.
The
navigator
can
then
see
two
images,
the
horizon
and
the
sun
side
by
side.
He
can
then
measure
the
angle
between
them
on
a
scale
at
the
bottom
of
the
instrument.
The
scale
goes
from
0
to
120
degrees.
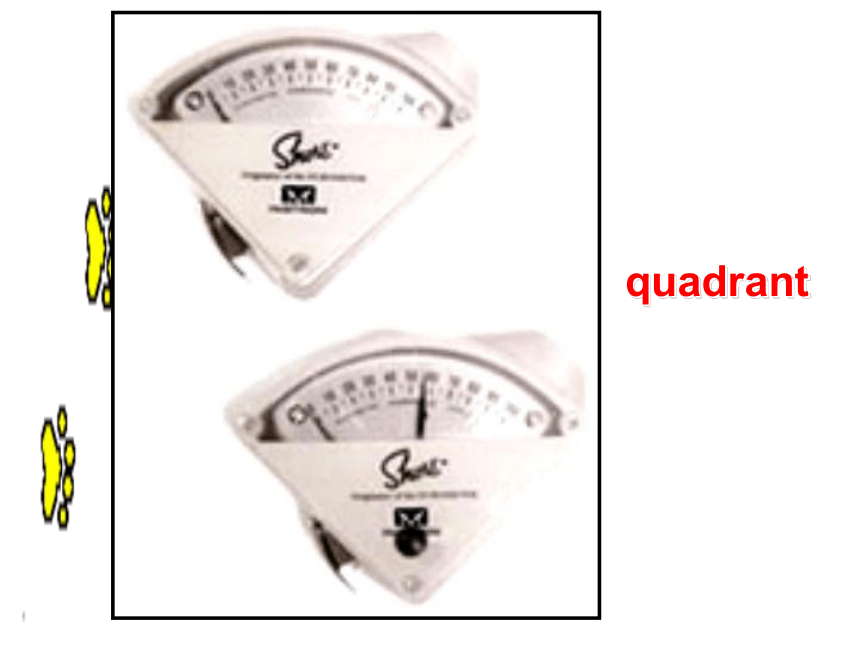
An
earlier
instrument,
called
a
quadrant,
measured
in
angle
in
the
same
way
but
it
could
only
measure
angles
from
0
to
90
degrees.
quadrant
nautical
chart
Zheng
He’s
Voyage
Zheng
He’s
Voyage
Nautical
charts
are
maps
of
the
depth
of
the
sea
and
the
currents
of
the
oceans.
They
provide
modern
sailors
with
routes
through
the
seas,
rather
like
roads
through
the
countryside.
The
information
began
to
be
collected
in
the
nineteenth
century
and
has
continued
to
be
updated
ever
since.
These
charts
were
not
available
to
Captain
Bligh
or
Zheng
He.
Discuss
1.
How
do
you
think
seamen
found
their
way
before
modern
accurate
methods
of
navigation
were
invented?
Kept
close
to
the
shore,
used
nature
such
as
the
sun,
wind,
birds,
tide,
etc,
to
help
them,
and
used
some
of
the
instruments
including
a
compass,
astrolabe,
etc.
2.
Which
do
you
think
was
easier
to
work
out:
latitude
or
longitude?
Latitude,
because
it
was
used
to
measure
how
far
you
had
traveled
from
land
on
a
straight
line.
It
was
discovered
a
long
time
before
longitude.
3.
Can
you
identify
these
early
navigational
instruments
seamen
used
and
explain
how
they
are
used?
1)
compass
(
in
ancient
China)
2)
astrolabe
3)
sextant
4)
sea
/
nautical
/
marine
chart
4.
Which
ones
do
you
think
are
still
used
today?
Sea
charts
are
still
used
today.
Language
points
on
P14
1.
course
n.
过程,
经过,
进程,
方针,
路线,
跑道,
课程,
一道菜
Tom
made
much
noise
in
the
course
of
discussion.
在讨论期间汤姆弄出了很大的响声。
The
ship
was
blown
off
course.
那船被吹离了航向。
We
made
three
courses:
soup,
meat
and
vegetables,
and
fruit.
我们有三道菜:
汤,
肉和蔬菜,
还有水果。
Phrases
with
“course”
in
course
of
正在……过程中,
在……期间
in
due
course
=
at
the
proper
or
right
time
在合适或正好的时间
of
course
①
in
the
natural
or
expected
order
of
things;
naturally.
按事物自然的或预期的顺序;自然地
2.
aim
n.目标,
目的,
瞄准
v.
对...瞄准,
打算
He
aimed
the
gun
at
the
enemy
officer.
他用枪瞄准了敌军官。
The
hunter
took
aim
at
a
wolf.
猎手瞄准了一匹狼。
②without
any
doubt;
certainly.
无疑地;当然地
3.
be
prepared
to
do
准备做某事(思想上准备好了)
prepare
to
do
准备做某事(强调动作)
They
are
prepared
to
do
it.
(准备好或愿意)
They
are
preparing
to
do
it.
(正在准备)
prepare
sth.
准备……
prepare
for
sth.
为……做准备
The
teacher
is
preparing
the
reviewing
exercises,
and
the
students
are
preparing
for
the
final
examination.
老师正在准备复习用的练习,
而学生们正在为期末考试做准备。
4.
justify
v.
证明……是正当的;为……辩护
The
course
of
events
fully
justifies
our
views.
事情的发展完全证明我们的意见是正确的。
How
can
you
justify
your
rude
and
foolish
behavior?
你怎样为你粗鲁而愚蠢的行为辩护?
Goodbye
Reading
A
compass
consists
of
a
small
magnet
balanced
on
a
point
so
that
it
can
move
round
in
a
circle.
The
magnet
is
generally
called
a
needle
because
it
is
shaped
like
a
needle.
One
end
of
the
needle
is
often
marked
“N”
for
north,
or
coloured
in
some
way
to
indicate
that
it
points
toward
north.
astrolabe
The
astrolabe
measures
the
height
and
position
of
the
sun.
If
you
can
measure
this
accurately,
a
sailor
can
tell
how
many
degrees
the
boat
is
from
the
North
Pole.
From
this
he
can
tell
where
the
boat
is
in
the
ocean.
sextant
The
sextant
is
a
navigational
instrument
for
measuring
the
angle
between
the
horizon
and
some
object
in
the
sky.
First
a
sailor
looks
at
the
horizon
through
an
eyepiece.
At
the
same
time
he
can
see
light
from
the
sun
or
a
star
reflected
off
a
small
mirror
on
top
of
the
instrument,
onto
a
second
mirror
and
into
the
eyepiece.
The
navigator
can
then
see
two
images,
the
horizon
and
the
sun
side
by
side.
He
can
then
measure
the
angle
between
them
on
a
scale
at
the
bottom
of
the
instrument.
The
scale
goes
from
0
to
120
degrees.
An
earlier
instrument,
called
a
quadrant,
measured
in
angle
in
the
same
way
but
it
could
only
measure
angles
from
0
to
90
degrees.
quadrant
nautical
chart
Zheng
He’s
Voyage
Zheng
He’s
Voyage
Nautical
charts
are
maps
of
the
depth
of
the
sea
and
the
currents
of
the
oceans.
They
provide
modern
sailors
with
routes
through
the
seas,
rather
like
roads
through
the
countryside.
The
information
began
to
be
collected
in
the
nineteenth
century
and
has
continued
to
be
updated
ever
since.
These
charts
were
not
available
to
Captain
Bligh
or
Zheng
He.
Discuss
1.
How
do
you
think
seamen
found
their
way
before
modern
accurate
methods
of
navigation
were
invented?
Kept
close
to
the
shore,
used
nature
such
as
the
sun,
wind,
birds,
tide,
etc,
to
help
them,
and
used
some
of
the
instruments
including
a
compass,
astrolabe,
etc.
2.
Which
do
you
think
was
easier
to
work
out:
latitude
or
longitude?
Latitude,
because
it
was
used
to
measure
how
far
you
had
traveled
from
land
on
a
straight
line.
It
was
discovered
a
long
time
before
longitude.
3.
Can
you
identify
these
early
navigational
instruments
seamen
used
and
explain
how
they
are
used?
1)
compass
(
in
ancient
China)
2)
astrolabe
3)
sextant
4)
sea
/
nautical
/
marine
chart
4.
Which
ones
do
you
think
are
still
used
today?
Sea
charts
are
still
used
today.
Language
points
on
P14
1.
course
n.
过程,
经过,
进程,
方针,
路线,
跑道,
课程,
一道菜
Tom
made
much
noise
in
the
course
of
discussion.
在讨论期间汤姆弄出了很大的响声。
The
ship
was
blown
off
course.
那船被吹离了航向。
We
made
three
courses:
soup,
meat
and
vegetables,
and
fruit.
我们有三道菜:
汤,
肉和蔬菜,
还有水果。
Phrases
with
“course”
in
course
of
正在……过程中,
在……期间
in
due
course
=
at
the
proper
or
right
time
在合适或正好的时间
of
course
①
in
the
natural
or
expected
order
of
things;
naturally.
按事物自然的或预期的顺序;自然地
2.
aim
n.目标,
目的,
瞄准
v.
对...瞄准,
打算
He
aimed
the
gun
at
the
enemy
officer.
他用枪瞄准了敌军官。
The
hunter
took
aim
at
a
wolf.
猎手瞄准了一匹狼。
②without
any
doubt;
certainly.
无疑地;当然地
3.
be
prepared
to
do
准备做某事(思想上准备好了)
prepare
to
do
准备做某事(强调动作)
They
are
prepared
to
do
it.
(准备好或愿意)
They
are
preparing
to
do
it.
(正在准备)
prepare
sth.
准备……
prepare
for
sth.
为……做准备
The
teacher
is
preparing
the
reviewing
exercises,
and
the
students
are
preparing
for
the
final
examination.
老师正在准备复习用的练习,
而学生们正在为期末考试做准备。
4.
justify
v.
证明……是正当的;为……辩护
The
course
of
events
fully
justifies
our
views.
事情的发展完全证明我们的意见是正确的。
How
can
you
justify
your
rude
and
foolish
behavior?
你怎样为你粗鲁而愚蠢的行为辩护?
Goodbye
